Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional and Sensory Profiles of Commercial Processed Meat Products Made from Beef and Plant-Based Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Proximate Composition and Total Calories
2.3. Mineral Contents Determination
2.4. Cholesterol Content
2.5. Sugar Content Determination
2.6. Fatty Acid Composition
2.7. Amino Acid Composition
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Composition, Total Calories, and Cholesterol Content
3.2. Mineral Contents
3.3. Sugar Content
3.4. Change of Fatty Acid Composition
3.5. Change of Amino Acid Composition
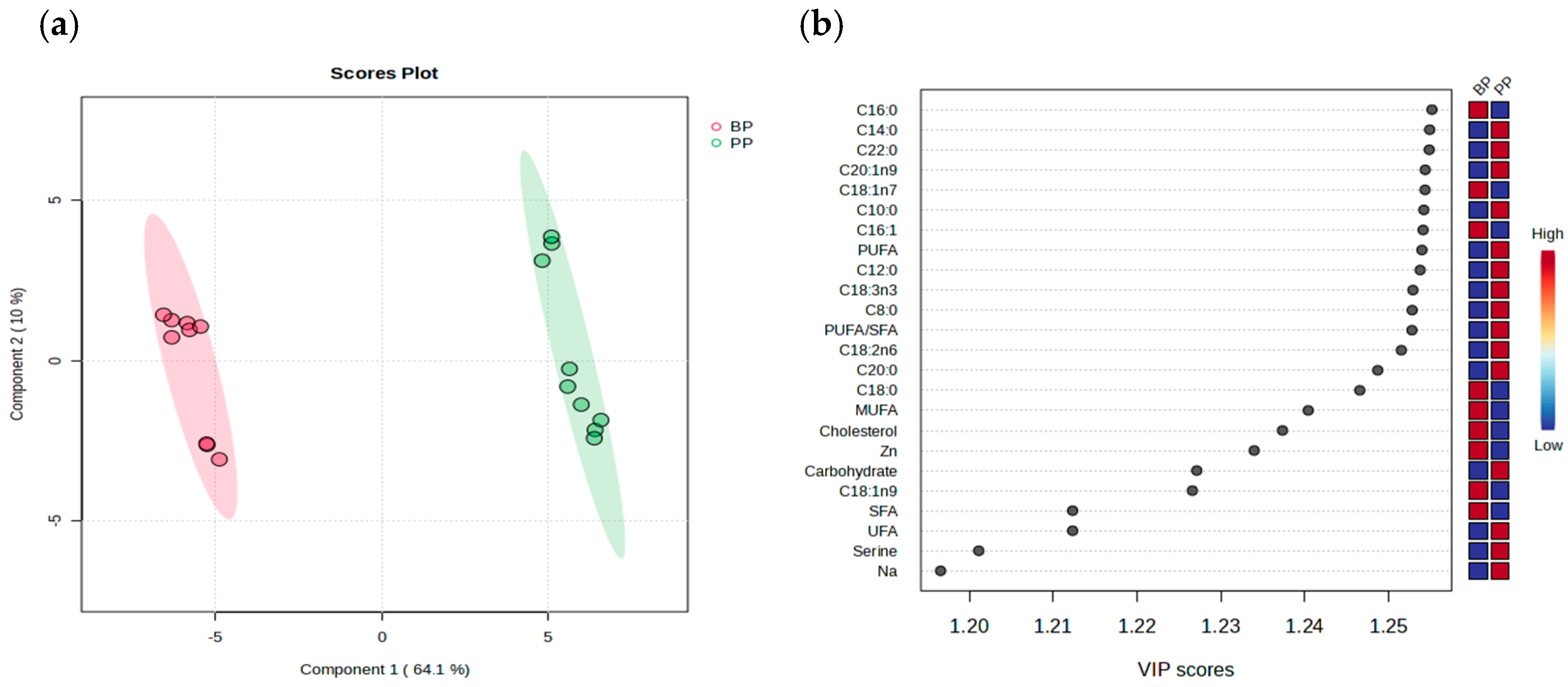
3.6. Multivariate Analysis of Nutritional Profiles
3.7. Sensory Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jang, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-K. Effects of Doneness on the Microbial, Nutritional, and Quality Properties of Pork Steak of Different Thicknesses. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2019, 39, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, L.; Huang, Z.; Shan, K.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Plant-Based Meat Analogues Weaken Gastrointestinal Digestive Function and Show Less Digestibility Than Real Meat in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12442–12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Ansorena, D.; Van Hecke, T.; Astiasarán, I.; De Smet, S.; Estévez, M. Meat Lipids, NaCl and Carnitine: Do They Unveil the Conundrum of the Association between Red and Processed Meat Intake and Cardiovascular Diseases? Invited Review. Meat Sci. 2021, 171, 108278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, M.A.; Riley, M.; Stockmann, R.; Bennett, L.; Kahl, A.; Lockett, T.; Osmond, M.; Sanguansri, P.; Stonehouse, W.; Zajac, I.; et al. Role of Food Processing in Food and Nutrition Security. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.S.; Choi, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Min, J.H.; Choi, Y.I. Comparison of Quality Characteristics between Hanwoo Added Tteokgalbi and Market Tteokgalbi Products. Bull. Anim. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, G.-W.; Jeong, H.-G. Development of Tteokgalbi Added with Red Pepper Seed Powder. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 45, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tuccillo, F.; Lampi, A.M.; Knaapila, A.; Pulkkinen, M.; Kariluoto, S.; Coda, R.; Edelmann, M.; Jouppila, K.; Sandell, M.; et al. Flavor Challenges in Extruded Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2898–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Fang, Y. Meat and Plant-Based Meat Analogs: Nutritional Profile and in Vitro Digestion Comparison. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.Y.; Hwang, Y.H.; Joo, S.T. Evaluation of Rheological and Sensory Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analog with Comparison to Beef and Pork. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Sabikun, N.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. A Novel Approach for Tuning the Physicochemical, Textural, and Sensory Characteristics of Plant-Based Meat Analogs with Different Levels of Methylcellulose Concentration. Foods 2021, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, C. Real Meat and Plant-Based Meat Analogues Have Different In Vitro Protein Digestibility Properties. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.; Li, Y.; Alavi, S. Chemical and Physicochemical Features of Common Plant Proteins and Their Extrudates for Use in Plant-Based Meat. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 131, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [MFDS]. Labeling Standards of Food. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/ (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [MFDS]. The Rules for Labeling and Advertising of Food and Other Products. Available online: https://www.law.go.kr/ (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [MFDS]. Food Code. Available online: https://various.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/ (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Lee, D.Y.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Mariano, E., Jr.; Joo, S.; Choi, I.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, G.; Lee, J.; et al. Analysis of Commercial Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) and Its Substitutes in the Development of Cultured Meat. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.-T.; Choi, J.-S.; Hur, S.-J.; Kim, G.-D.; Kim, C.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Bakhsh, A.; Hwang, Y.-H. A Comparative Study on the Taste Characteristics of Satellite Cell Cultured Meat Derived from Chicken and Cattle Muscles. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, B.; Wea, A.; Andriati, N. Physicochemical, Sensory Attributes and Protein Profile by SDS-PAGE of Beef Sausage Substituted with Texturized Vegetable Protein. Food Res. 2017, 2, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, D.; Kalaikannan, A.; Sureshkumar, S. Factors Influencing Meat Emulsion Properties and Product Texture: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Ansah, P.; Besiwah, E.K.; Bonah, E.; Amagloh, F.K. Non-Meat Ingredients in Meat Products: A Scoping Review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, D.S.; Shey, L.; Eaton, R.P. Cholesterol Review: A Metabolically Important Molecule. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. Review: Nutrient Density and Nutritional Value of Meat Products and Non-Meat Foods High in Protein. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, V.A.; Busso, D.; Maiz, A.; Arteaga, A.; Nervi, F.; Rigotti, A. Physiological and Pathological Implications of Cholesterol. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falowo, A.B. A Comprehensive Review of Nutritional Benefits of Minerals in Meat and Meat Products. Sci. Lett. 2021, 9, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Jang, A. Correlations between the Levels of the Bioactive Compounds and Quality Traits in Beef Loin and Round during Cold Storage. Food Control 2021, 120, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.C.; Saadoun, A. An Overview of the Nutritional Value of Beef and Lamb Meat from South America. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swing, C.J.; Thompson, T.W.; Guimaraes, O.; Geornaras, I.; Engle, T.E.; Belk, K.E.; Gifford, C.L.; Nair, M.M. Nutritional Composition of Novel Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Traditional Animal-Based Meats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.T.Y.; Bi, X.; Henry, C.J. Are Plant-Based Meat Analogues Richer in Minerals than Their Meat Counterparts? Food Humanit. 2023, 1, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Sweeteners as Food Additives in the XXI Century: A Review of What Is Known, and What Is to Come. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, D.; Mastanjević, K. Cryoprotective Effect of Trehalose and Maltose on Washed and Frozen Stored Beef Meat. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Park, B.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, I.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.M. Fatty Acid Profiles and Sensory Properties of Longissimus Dorsi, Triceps Brachii, and Semimembranosus Muscles from Korean Hanwoo and Australian Angus Beef. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, K.-H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Youm, K.E.; Lee, M. Effect of Storage Condition on Sensory Properties and Fatty Acid Composition of Pre-Packed Hanwoo Loin. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 42, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiker, N.R.W.; Bertram, H.C.; Mejborn, H.; Dragsted, L.O.; Kristensen, L.; Carrascal, J.R.; Bügel, S.; Astrup, A. Meat and Human Health—Current Knowledge and Research Gaps. Foods 2021, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashek, D.; Wu, C. MUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 6, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, K.M.; Ruggio, D.M.; Howe, J.C.; Leheska, J.M.; Smith, S.B.; Engle, T.; Rasor, A.S.; Conley, N.A. Preparation and Characterization of Control Materials for the Analysis of Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Trans-Vaccenic Acid in Beef. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samard, S.; Ryu, G. A Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics, Texture, and Structure of Meat Analogue and Meats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, D.; Choo, H.-J.; Shin, D.-J.; Jang, A. Effect of Rosemary and Clove Essential Oils on Quality and Flavor Compounds of Fried Korean Native Chicken Thigh Meat. Korean J. Poult. Sci. 2023, 50, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.S.; Woerner, D.R.; Brooks, J.C.; Legako, J.F. Descriptive Sensory Attributes and Volatile Flavor Compounds of Plant-Based Meat Alternatives and Ground Beef. Molecules 2023, 28, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Lv, Y.; Guo, S. Effects of Heat Treatment and β-Cyclodextrin Addition on Soymilk Flavor. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Bak, K.H.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Insights into Formation, Detection and Removal of the Beany Flavor in Soybean Protein. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | The Listed Ingredients of the Products | Nutritional Facts (per 100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| BP-1 | Hanwoo beef, dry bread crumbs, onions, sugar, pear juice, carrots, minced garlic, large green onions, potato starch, sesame oil, water, soju, salt, L-glutamate, black pepper, sesame seeds | Not shown |
| BP-2 | Hanwoo beef, Hanwoo fat, rice cakes, moist bread crumbs, bulgogi sauce [soy sauce {amino acid liquid, brewed soy sauce extract, salt, garlic, green onions, fructose, pear puree (pear, vitamin C), onions, apple puree, seasoning sauce extract, black, pepper, citric acid, xanthan gum, caramel colorant}] | Not shown |
| BP-3 | Hanwoo beef, sesame oil, corn syrup, brown sugar, garlic, onions, salt, soy sauce, potato starch, L-glutamate, caramel colorant, ginger, black pepper | Not shown |
| PP-1 | Water, soy protein concentrates, rapeseed oil, sugar, coconut oil, onion, garlic extract, large green onions, methylcellulose, grill sauce, Cookmate NF, sesame oil, isolated soy protein, soy sauce powder, salt, gellan gum, isolated soy protein, yeast extract, rice flour, black pepper, food additive 1 [brown rice oil, refined processed oil, sunflower oil, flavoring 1, flavoring 2, d-alpha-tocopherol, propylene glycol], cocoa colorant, beet red, oat dietary fiber, cysteine hydrochloride, citric acid, food additive 2 [smoke oil, soybean oil], food additive 3 [tomato colorant, glycerin, caramel colorant] | Calories (255 kcal), sodium (530 mg), total carbohydrate (16 g), total sugar (5 g), lipid (15 g), trans fatty acids (0 g), saturated fatty acids (5 g), cholesterol (0 mg), protein (14 g) |
| PP-2 | Processed bean products [vital wheat gluten, isolated soy protein, defatted soybean powder, starch, other processed ingredients], coconut oil, sauce [sugar, onion, hydrolyzed soy sauce, apple puree, brewed soy sauce], onion, large green onions, sugar, garlic, grain products, methylcellulose, seasoning, salt, sesame oil, yeast extract, food additive (dextrin, vegetable oil, modified starch, synthetic flavoring), processed sugar product, black pepper | Calories (255 kcal), sodium (510 mg), total carbohydrate (21 g), total sugar (12 g), lipid (15 g), trans fatty acids (0 g), saturated fatty acids (12 g), cholesterol (0 mg), protein (9 g) |
| PP-3 | Sunflower oil, processed bean products, wheat gluten, seasoning, isolated soy protein, sauce (paste for tteokgalbi), soy sauce, onion, rice cakes, garlic, sugar, alcoholic beverages, cocoa colorant, pepper | Calories (205 kcal), sodium (680 mg), total carbohydrate (13 g), total sugar (1 g), lipid (10 g), trans fatty acids (0 g), saturated fatty acids (1.1 g), cholesterol (0 mg), protein (15 g) |
| Traits | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 54.22 | 54.29 | 0.758 |
| Crude protein (%) | 13.04 | 13.65 | 0.885 |
| Crude lipids (%) | 22.26 a | 11.14 b | 1.337 |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 9.13 b | 18.74 a | 0.371 |
| Crude ash (%) | 1.34 b | 2.18 a | 0.149 |
| Total calories (kcal/100 g) | 289.05 a | 229.85 b | 9.056 |
| Cholesterol (mg/100 g) | 51.33 | N.D. | - |
| Minerals (mg/100 g) | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | 25.54 b | 75.63 a | 8.338 |
| Fe | 1.20 b | 1.56 a | 0.117 |
| K | 199.47 | 210.67 | 24.047 |
| Mg | 19.31 b | 39.12 a | 3.646 |
| Na | 271.63 b | 543.05 a | 15.322 |
| Zn | 3.08 a | 1.11 b | 0.067 |
| P | 184.62 | 213.69 | 18.911 |
| Cu | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.077 |
| Al | 0.17 | 1.16 | 0.338 |
| Sugar (g/100 g) | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fructose | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.053 |
| Glucose | 0.23 b | 1.30 a | 0.280 |
| Sucrose | 2.15 b | 6.83 a | 0.807 |
| Maltose | 0.52 | N.D. | - |
| Lactose | N.D. | N.D. | - |
| Total | 3.01 b | 8.37 a | 0.594 |
| Fatty Acid Composition (%) | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| C8:0 (Caprylic acid) | 0.20 b | 5.18 a | 0.064 |
| C10:0 (Capric acid) | 0.12 b | 3.35 a | 0.031 |
| C12:0 (Lauric acid) | 1.74 b | 10.22 a | 0.092 |
| C14:0 (Myristic acid) | 2.22 b | 6.94 a | 0.037 |
| C16:0 (Palmitic acid) | 25.54 a | 8.19 b | 0.119 |
| C16:1 (Palmitoleic acid) | 2.54 a | 0.32 b | 0.022 |
| C18:0 (Stearic acid) | 17.00 a | 6.26 b | 0.235 |
| C18:1n9 (Oleic acid) | 39.00 a | 30.84 b | 0.318 |
| C18:1n7 (Vaccenic Acid) | 1.37 | N.D. | - |
| C18:2n6 (Linoleic acid) | 6.15 b | 17.11 a | 0.166 |
| C18:3n3 (α-Linolenic acid) | 3.00 b | 8.19 a | 0.066 |
| C20:0 (Arachidic acid) | 0.34 b | 1.00 a | 0.013 |
| C20:1n9 (Eicosenoic acid) | 0.66 b | 1.77 a | 0.010 |
| C20:3n3 (Eicosatrienoic acid) | 0.06 | N.D. | - |
| C20:4n6 (Arachidonic acid) | 0.04 | N.D. | - |
| C22:0 (Behenic acid) | N.D. | 0.60 | - |
| SFA | 47.17 a | 41.76 b | 0.260 |
| UFA | 52.83 b | 58.24 a | 0.260 |
| MUFA | 43.58 a | 32.93 b | 0.300 |
| PUFA | 9.25 b | 25.31 a | 0.166 |
| MUFA/SFA | 0.92 a | 0.79 b | 0.011 |
| PUFA/SFA | 0.20 b | 0.61 a | 0.005 |
| Amino Acid (% in Protein) | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 9.16 | 10.18 | 0.067 |
| Threonine | 3.22 a | 2.73 b | 0.023 |
| Serine | 2.52 b | 3.58 a | 0.024 |
| Glutamic acid | 17.93 b | 23.96 a | 0.210 |
| Proline | 6.28 | 6.83 | 0.098 |
| Glycine | 8.84 a | 4.37 b | 0.122 |
| Alanine | 7.33 a | 4.69 b | 0.050 |
| Valine | 5.53 | 5.64 | 0.035 |
| Isoleucine | 4.67 b | 5.16 a | 0.033 |
| Leucine | 7.89 | 8.35 | 0.052 |
| Tyrosine | 1.51 | 1.42 | 0.013 |
| Phenylalanine | 4.80 b | 5.78 a | 0.036 |
| Histidine | 4.87 | 4.79 | 0.034 |
| Lysine | 8.57 a | 5.69 b | 0.048 |
| Arginine | 6.80 | 6.83 | 0.045 |
| Traits | BP | PP | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | 7.42 a | 6.59 b | 0.073 |
| Color | 7.37 a | 6.62 b | 0.076 |
| Off-flavor | 2.80 b | 4.08 a | 0.105 |
| Taste | 7.14 a | 4.81 b | 0.094 |
| Flavor | 6.90 a | 4.72 b | 0.096 |
| Juiciness | 5.82 a | 4.89 b | 0.091 |
| Tenderness | 6.09 | 6.17 | 0.083 |
| Overall acceptability | 7.13 a | 4.93 b | 0.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, D.; Jung, Y.; Hur, S.J.; Jang, A. Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional and Sensory Profiles of Commercial Processed Meat Products Made from Beef and Plant-Based Protein. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111771
Oh S, Lee DY, Kim D, Jung Y, Hur SJ, Jang A. Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional and Sensory Profiles of Commercial Processed Meat Products Made from Beef and Plant-Based Protein. Nutrients. 2025; 17(11):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111771
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Soomin, Da Young Lee, Dongwook Kim, Yousung Jung, Sun Jin Hur, and Aera Jang. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional and Sensory Profiles of Commercial Processed Meat Products Made from Beef and Plant-Based Protein" Nutrients 17, no. 11: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111771
APA StyleOh, S., Lee, D. Y., Kim, D., Jung, Y., Hur, S. J., & Jang, A. (2025). Comparative Analysis of the Nutritional and Sensory Profiles of Commercial Processed Meat Products Made from Beef and Plant-Based Protein. Nutrients, 17(11), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17111771







