Rising Rates of Obesity Amongst Children on the Autism Spectrum During the COVID-19 Pandemic †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panchal, U.; de Pablo, G.S.; Franco, M.; Moreno, C.; Parellada, M.; Arango, C.; Fusar-Poli, P. The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on child and adolescent mental health: Systematic review. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 32, 1151–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomiyama, A.J. Stress and Obesity. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2019, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, R.P.; Patel, S.R. The epidemiology of sleep and obesity. Sleep Health 2017, 3, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fauci, G.; Montalti, M.; Di Valerio, Z.; Gori, D.; Salomoni, M.G.; Salussolia, A.; Soldà, G.; Guaraldi, F. Obesity and COVID-19 in Children and Adolescents: Reciprocal Detrimental Influence-Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, B.P.; Kelly, M.K.; Powell, M.; Bouchelle, Z.; Mayne, S.L.; Fiks, A.G. COVID-19 and Changes in Child Obesity. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2021050123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-H.; Gu, T.-M.; Zhu, B.-Q.; Shen, Y.; He, X.-Y.; Bai, G.-N.; Shao, J. Comparison of anthropometric parameters and laboratory test results before and after the COVID-19 outbreak among Chinese children aged 3–18 years. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1048087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, K.K.; Cai, S.; Law, E.; Cheon, B.; Tan, G.; Loo, E.; Lee, Y.S.; Yap, F.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Daniel, M.; et al. COVID-19-Related Life Experiences, Outdoor Play, and Long-term Adiposity Changes Among Preschool- and School-Aged Children in Singapore 1 Year After Lockdown. JAMA Pediatr. 2022, 176, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahathuduwa, C.N.; West, B.D.; Blume, J.; Dharavath, N.; Moustaid-Moussa, N.; Mastergeorge, A. The risk of overweight and obesity in children with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolford, S.J.; Sidell, M.; Li, X.; Else, V.; Young, D.R.; Resnicow, K.; Koebnick, C. Changes in Body Mass Index Among Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA 2021, 326, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity, 1 April 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/ (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Lee, L. Dorscon Status to Lower from Yellow to Green on Feb 13, COVID-19 Task Force to Stand Down: MOH. TODAY. Published 9 February 2023. Available online: https://www.todayonline.com/singapore/singapore-dorscon-green-mtf-2103946 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Department of Statistics, Ministry of Trade and Industry, Singapore. Singapore Census of Population 2020, Statistical Release 1: Demographic Characteristics, Education, Language and Religion—Key Findings. Published June 2021. Available online: https://www.singstat.gov.sg/-/media/files/publications/cop2020/sr1/findings.ashx (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Khan, M.A.; Moverley Smith, J.E. “Covibesity”, a new pandemic. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.J.; Kompaniyets, L.; Freedman, D.S.; Kraus, E.M.; Porter, R.; Blanck, H.M.; Goodman, A.B. Longitudinal Trends in Body Mass Index Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among Persons Aged 2–19 Years—United States, 2018–2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Singapore. News Highlights—Annual Prevalence of Obesity for Children Aged Below 18 over Past Five Years, Their Profiles and Assessed Effectiveness of Preventive Measures. Published 14 February 2022. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg/news-highlights/details/annual-prevalence-of-obesity-for-children-aged-below-18-over-past-five-years-their-profile-and-assessed-effectiveness-of-preventive-measures/ (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Sammels, O.; Karjalainen, L.; Dahlgren, J.; Wentz, E. Autism Spectrum Disorder and Obesity in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Facts. 2022, 15, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundle, A.G.; Park, Y.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kinsey, E.W.; Wang, Y.C. COVID-19-Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain Among Children. Obesity 2020, 28, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.; Buckingham, A.; Schena, D., 2nd. Physical Activity Among Adults with Autism: Participation, Attitudes, and Barriers. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2020, 127, 874–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjwani, A.A.; Bailey, R.L.; Kelleher, B.L. COVID-19 and behaviors in children with autism spectrum disorder: Disparities by income and food security status. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2021, 115, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epidemiology & Disease Control Division and Policy, Research & Surveillance Group, Ministry of Health and Health Promotion Board, Singapore. National Population Health Survey 2020 (Household Interview and Health Examination). Published November 2021. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/default-document-library/nphs-2020-survey-report.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Brownlee, I.A.; Low, J.; Duriraju, N.; Chun, M.; Ong, J.X.Y.; Tay, M.E.; Hendrie, G.A.; Santos-Merx, L. Evaluation of the Proximity of Singaporean Children’s Dietary Habits to Food-Based Dietary Guidelines. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Statistics, Ministry of Trade & Industry, Republic of Singapore. Census of Population 2020 Statistical Release 1: Demographic Characteristics, Education, Language and Religion. Published June 2021. Available online: https://www.singstat.gov.sg/-/media/files/publications/cop2020/sr1/cop2020sr1.ashx (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Department of Statistics, Ministry of Trade and Industry, Singapore. Singapore Census of Population 2020, Statistical Release 2: Households, Geographic Distribution, Transport and Difficulty in Basic Activities. Published June 2021. Available online: https://www.singstat.gov.sg/-/media/files/publications/cop2020/sr2/findings2.ashx (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Yeung, J.; Chen, X.; Lee, J. “COVID-19 Learning Gap Effect” for Young Children in Singapore. Published April 2022. Available online: https://fass.nus.edu.sg/cfpr/sgleads/ (accessed on 18 August 2024).
- Tester, J.M.; Rosas, L.G.; Leung, C.W. Food Insecurity and Pediatric Obesity: A Double Whammy in the Era of COVID-19. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Statistics, Ministry of Trade and Industry, Singapore. General Household Survey 2005 Statistical Release 1: Socio-Demographic and Economic Characteristics. Published June 2006. Available online: https://www.singstat.gov.sg/-/media/files/publications/ghs/general_household_survey_release1/chap3.ashx (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Iacopetta, D.; Catalano, A.; Ceramella, J.; Pellegrino, M.; Marra, M.; Scali, E.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S. The Ongoing Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Obesity. Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straughan, P.; Xu, C. Parents’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices of childhood obesity in Singapore. SAGE Open 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irschik, S.; Brandt, J.B.; Eisenkölbl, J. COVID-19 pandemic-related weight gain in the pediatric population declined after restrictions ended, except among obese patients. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1260269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrecht, J.; Arayess, L.; Reijnders, D.; Hesselink, M.L.; Velde, G.T.; Janse, A.; von Rosenstiel, I.; van Mil, E.G.; Verweij, M.; Vreugdenhil, A.C. Weight Gain in Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic and the Protective Effect of Lifestyle Intervention in Children with Obesity. Obes. Facts. 2022, 15, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, M.; Carretero-Bravo, J.; Pérez-Muñoz, C.; Deudero-Sánchez, M. Lockdown due to COVID-19 in Spanish Children Up to 6 Years: Consequences on Diet, Lifestyle, Screen Viewing, and Sleep. Int. J. Public Health 2022, 67, 1604088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.J.; King, G.K.C.; Duerden, E.G. Screen time in children and youth during the pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob. Pediatr. 2023, 6, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Y.; Jia, F.Y.; Shan, L.; Miao, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L. The challenges of screen time in children with typical development and children with developmental disorders during COVID-19 pandemic. Transl. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardy, R.E.; Dupuis, A.; Anagnostou, E.; Ziolkowski, J.; Biddiss, E.A.; Monga, S.; Brian, J.; Penner, M.; Kushki, A. Characterizing Changes in Screen Time During the COVID-19 Pandemic School Closures in Canada and Its Perceived Impact on Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 702774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderson, M.M.; Bekelman, T.A.; Li, M.; Knapp, E.A.; Palmore, M.; Dong, Y.; Elliott, A.J.; Friedman, C.; Galarce, M.; Gilbert-Diamond, D.; et al. Trends in Screen Time Use Among Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic, July 2019 Through August 2021. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2256157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.; Werbeloff, N.; Fruchter, E.; Portuguese, S.; Davidson, M.; Weiser, M. IQ and obesity in adolescence: A population-based, cross-sectional study. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, W.H. Critical periods in childhood for the development of obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 59, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalitin, S.; Phillip, M.; Yackobovitch-Gavan, M. Changes in body mass index in children and adolescents in Israel during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fäldt, A.; Nejat, S.; Edvinsson Sollander, S.; Durbeej, N.; Holmgren, A. Increased incidence of overweight and obesity among preschool Swedish children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. J. Public Health 2023, 33, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Ahmad Hatib, N.A.; Chew, C.S.E. Preventing obesity from early childhood. Singapore Med. J. 2021, 62, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Dargue, N.; Paynter, J. Longitudinal studies of challenging behaviours in autistic children and adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2023, 104, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Social and Family Development (MSF), Singapore. Data of Children Aged Four Year-Old Currently Enrolled in Preschool and Plans to Expand Kindergarten Intake to 4 Year-Old Children. Published 4 July 2022. Available online: https://www.msf.gov.sg/media-room/article/Data-of-children-aged-four-year-old-currently-enrolled-in-preschool-and-plans-to-expand-kindergarten-intake-to-4-year-old-children (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- HealthHub, Singapore. Healthy Meals in Pre-schools Programme. Published 8 August 2023. Available online: https://www.healthhub.sg/live-healthy/healthy-meals-in-pre-schools-programme (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Chung, A.; Tully, L.; Czernin, S.; Thompson, R.; Mansoor, A.; Gortmaker, S.L. Reducing risk of childhood obesity in the wake of covid-19. BMJ. 2021, 374, n1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, W.G.; Berry, R.C.; McCracken, C.; Nuhu, N.N.; Marvel, E.; Saulnier, C.A.; Klin, A.; Jones, W.; Jaquess, D.L. Feeding problems and nutrient intake in children with autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis and comprehensive review of the literature. J. Autism. Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 2159–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peverill, S.; Smith, I.M.; Duku, E.; Szatmari, P.; Mirenda, P.; Vaillancourt, T.; Volden, J.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Bennett, T.; Elsabbagh, M.; et al. Developmental Trajectories of Feeding Problems in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2019, 44, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
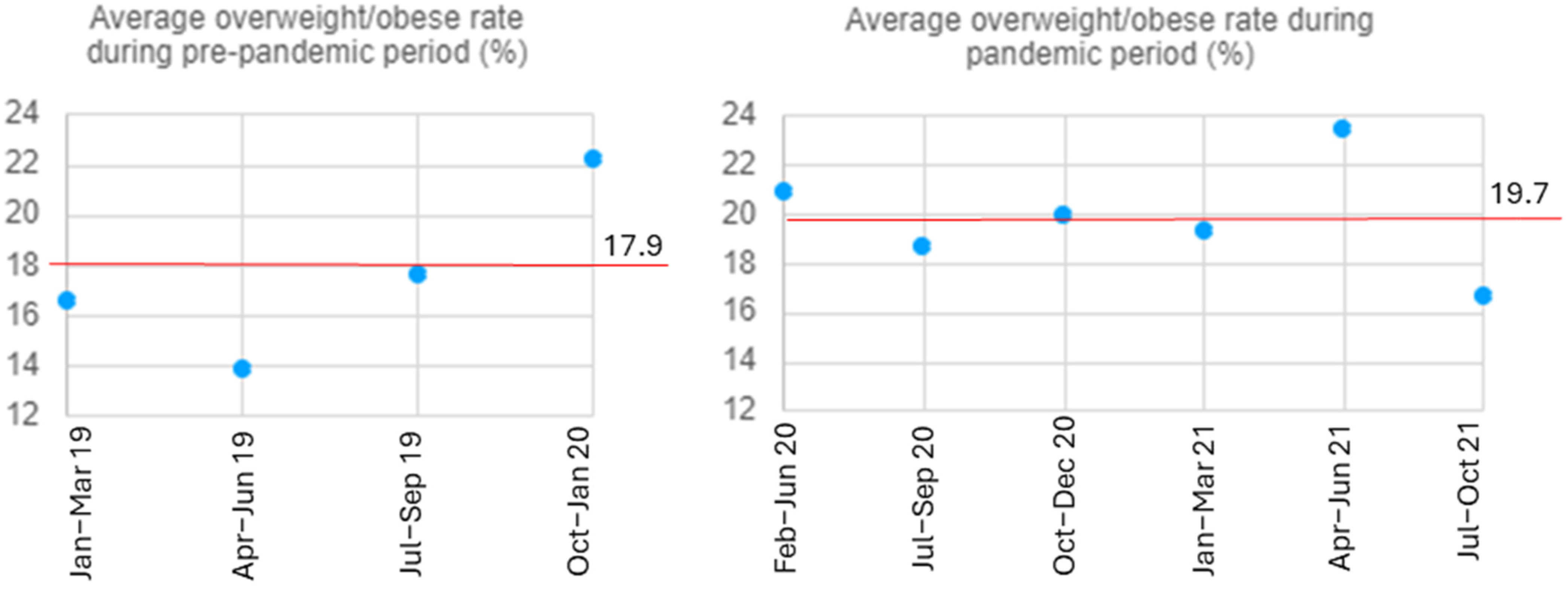
| Pre-Pandemic † Rate, % | Pandemic § rate, % | Difference in Rate, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n = 1330) | 17.9 | 19.7 | 1.8 |
| Child’s age | |||
| ≤4 years | 17.3 | 21.7 | 4.5 |
| >4 years | 21.5 | 18.0 | −3.5 |
| Ethnicity | |||
| Chinese | 14.5 | 15.3 | 0.8 |
| Non-Chinese | 21.3 | 26.0 | 4.6 |
| Parent’s highest education level | |||
| Diploma and below | 16.9 | 22.0 | 5.0 |
| Degree and above | 18.1 | 19.4 | 1.3 |
| Screen time | |||
| >2 h | 15.3 | 21.0 | 5.7 |
| ≤2 h | 22.5 | 24.1 | 1.6 |
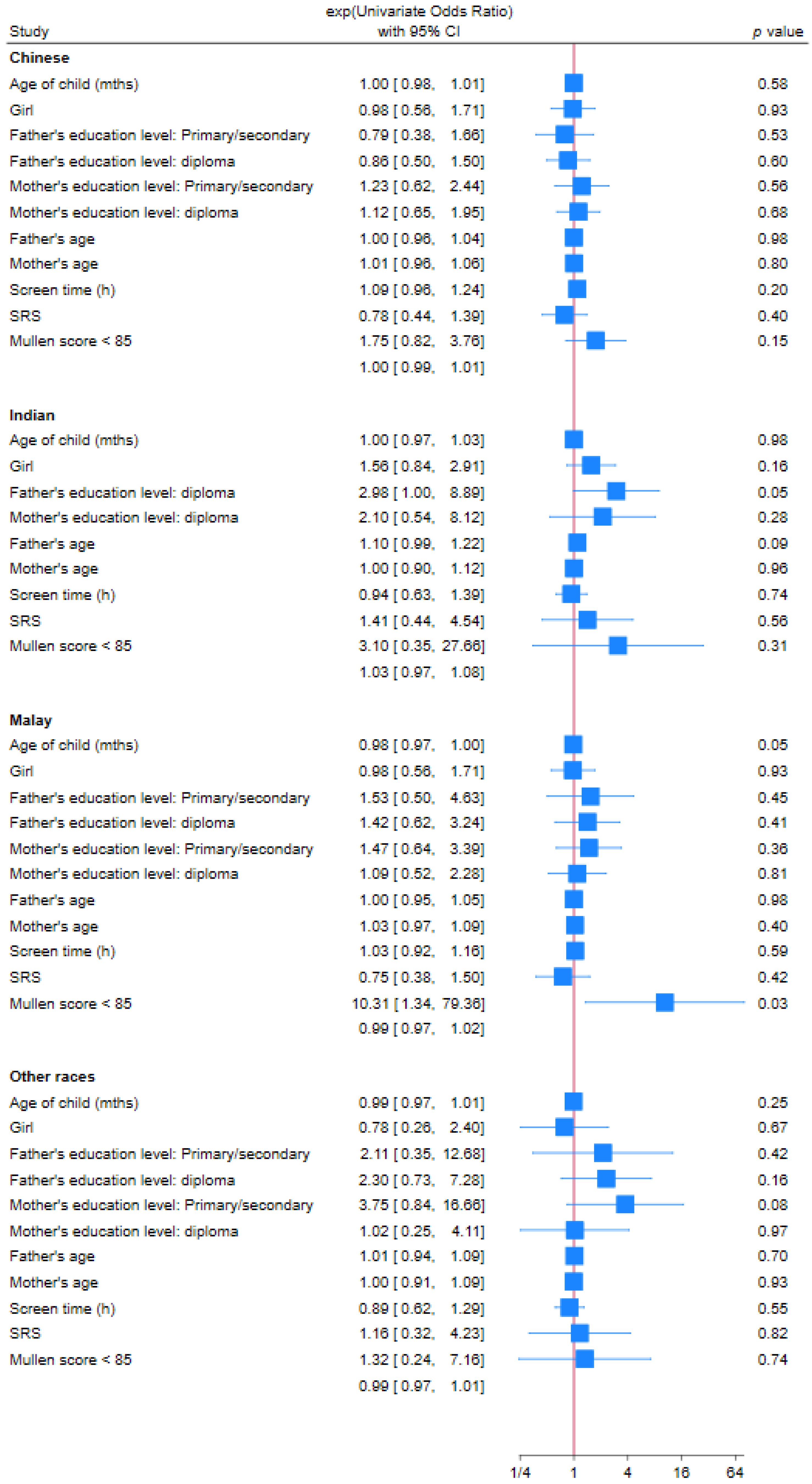
| Univariate OR (95% CI) | p Value | Multivariate OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of child | 0.99 (0.981–0.998) | 0.02 | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.54 |
| Gender (Female) | 1.07 (0.74–1.53) | 0.73 | 1.14 (0.50–2.61) | 0.76 |
| Race | ||||
| Chinese | Reference | |||
| Malay | 2.32 (1.64–3.28) | <0.01 | 3.29 (1.37–7.74) | 0.01 |
| Indian | 1.20 (0.70–2.09) | 0.5 | 2.90 (0.90–9.32) | 0.07 |
| Others | 1.43 (0.90–2.26) | 0.13 | 0.26 (0.03–2.07) | 0.2 |
| Father’s education level | ||||
| Degree and above | Reference | |||
| Post-Secondary or Diploma | 1.56 (1.10–2.20) | 0.01 | 1.71 (0.51–5.71) | 0.38 |
| Primary or Secondary | 1.07 (0.62–1.82) | 0.81 | 0.82 (0.34–1.98) | 0.66 |
| Mother’s education level | ||||
| Degree and above | Reference | |||
| Post-Secondary or Diploma | 1.35 (0.94–1.94) | 0.1 | 0.44 (0.13–1.48) | 0.19 |
| Primary or Secondary | 1.63 (1.05–2.55) | 0.03 | 0.97 (0.42–2.26) | 0.95 |
| Father’s age (years) | 1.00 (0.97–1.02) | 0.68 | 1.01 (0.94–1.08) | 0.78 |
| Mother’s age (years) | 1.00 (0.96–1.02) | 0.61 | 0.98 (0.90–1.08) | 0.73 |
| Screen time > 2 h/day | 1.07 (0.99–1.16) | 0.1 | 1.05 (0.93–1.18) | 0.45 |
| SRS T-score ≥ 60 | 0.82 (0.56–1.21) | 0.32 | 0.79 (0.38–1.67) | 0.55 |
| MSEL ELC score < 85 | 2.80 (1.53–5.15) | <0.01 | 0.99 (0.41–2.44) | 0.99 |
| Significant Variables on Univariate Analysis | Ethnic Distribution (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | Malay | Indian | Others | |
| Age of child (p = 0.006) | ||||
| 4 years and below | 50% | 26.6% | 10.2% | 12.4% |
| Above 4 years | 54.1% | 18.7% | 11.0% | 16.1% |
| Father’s education level (p < 0.001) | ||||
| Degree and above | 59.5% | 8.0% | 14.5% | 18.1% |
| Post-Secondary or Diploma | 43.8% | 43.8% | 6.9% | 5.4% |
| Primary or Secondary | 62.0% | 27.5% | 4.2% | 6.3% |
| Mother’s education level (p < 0.001) | ||||
| Degree and above | 56.8% | 10.1% | 15.6% | 17.6% |
| Post-Secondary or Diploma | 50.3% | 39.5% | 4.8% | 5.4% |
| Primary or Secondary | 51.2% | 37.8% | 5.2% | 5.8% |
| MSEL ELC Score (p < 0.001) | ||||
| <85 | 50.9% | 29.6% | 9.2% | 10.3% |
| ≥85 | 70.1% | 15.3% | 8.3% | 6.3% |
| Reference: whole study cohort | 52.1% | 23.4% | 10.5% | 13.9% |
| Study/Report | Weight Category | Pre-Pandemic Rate, % | Pandemic Rate, % | Difference in Rate, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Study | Overweight or obese | 17.9 | 19.7 | 1.8 |
| Ministry of Health, Singapore [16] | Overweight | 13 | 16 | 3 |
| Dong et al. [6] | Overweight Obese | 9.2 8.6 | 10.5 10.6 | 1.3 2.0 |
| Jenssen et al. [5] | Obese | 13.7 | 15.4 | 1.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuen, W.Y.; Lim, T.S.H.; Karthik, S.V.; Lim, Y.Y.; Teo, E.M.; Chan, Y.H.; Shen, L.; Mulay, K.V. Rising Rates of Obesity Amongst Children on the Autism Spectrum During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101683
Yuen WY, Lim TSH, Karthik SV, Lim YY, Teo EM, Chan YH, Shen L, Mulay KV. Rising Rates of Obesity Amongst Children on the Autism Spectrum During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients. 2025; 17(10):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101683
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuen, Wing Yan, Tammy S. H. Lim, S. V. Karthik, Yijuan Yvonne Lim, Elizabeth M. Teo, Yiong Huak Chan, Liang Shen, and Kalyani V. Mulay. 2025. "Rising Rates of Obesity Amongst Children on the Autism Spectrum During the COVID-19 Pandemic" Nutrients 17, no. 10: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101683
APA StyleYuen, W. Y., Lim, T. S. H., Karthik, S. V., Lim, Y. Y., Teo, E. M., Chan, Y. H., Shen, L., & Mulay, K. V. (2025). Rising Rates of Obesity Amongst Children on the Autism Spectrum During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients, 17(10), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17101683






