Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz against Human Gastric Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Network Pharmacological Analysis of AMK
2.1.1. Identification and Screening of Active Compounds of AMK
2.1.2. Analysis of Targets
2.2. In Vivo and In Vitro Experiments
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. HPLC Analysis
2.2.3. Cell Culture and Cell Viability Assay
2.2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.2.5. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Levels
2.2.6. Mitochondrial Depolarization Assay
2.2.7. Caspase Assay
2.2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.2.9. Wound Healing Assay
2.2.10. Spheroid Formation Assay
2.2.11. Preparation of AGS-iRFP Cells
2.2.12. Animal Experiment
2.2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Network-Based Pharmacological Analysis
3.1.1. Eighteen Active Compounds Meet the ADME Parameter Criteria
3.1.2. Identification of 37 Compounds Related to Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancer in AMK
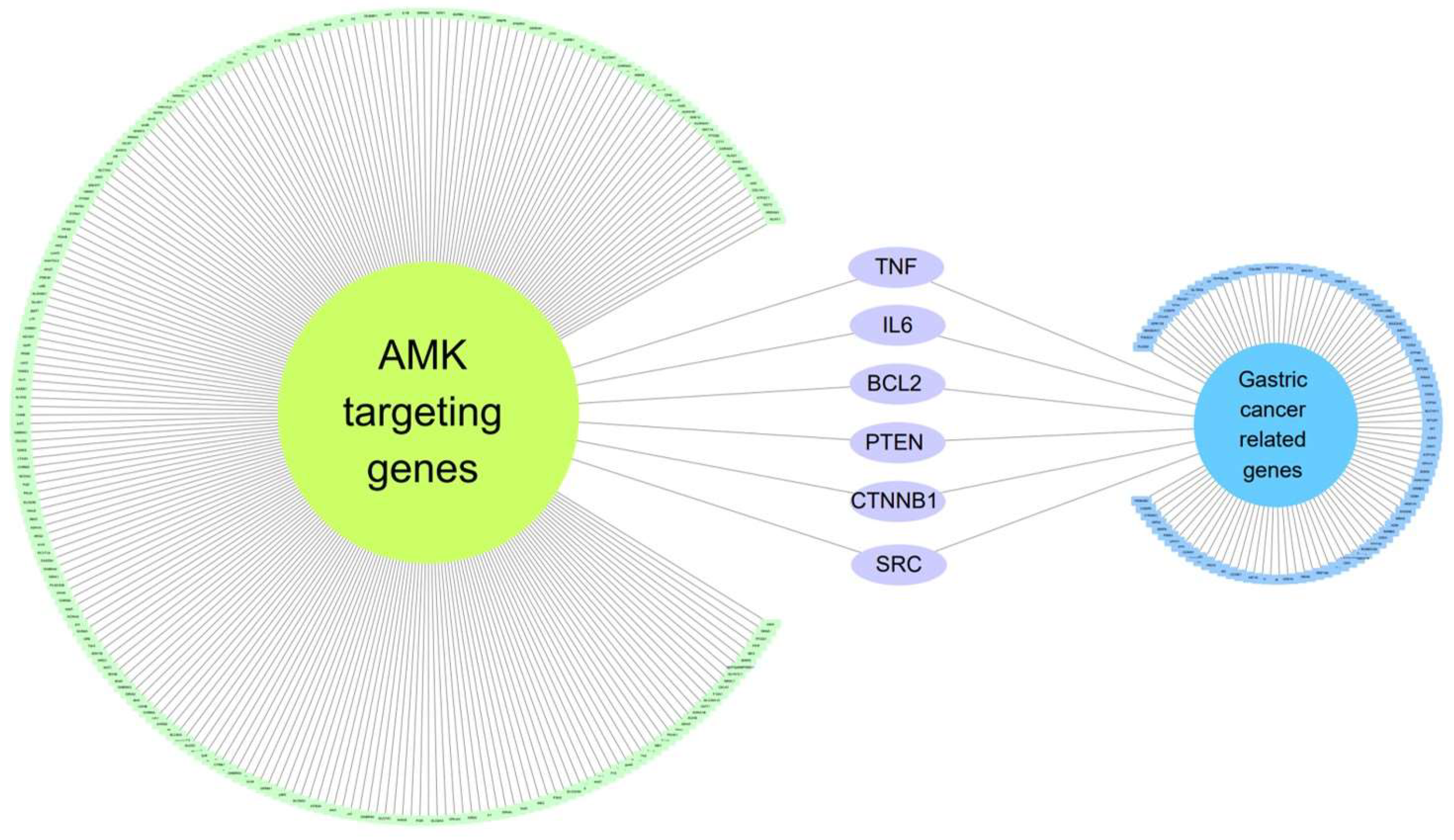
3.1.3. Six Genes Are Included in Both Gastric-Cancer-Related Genes and AMK Target Genes
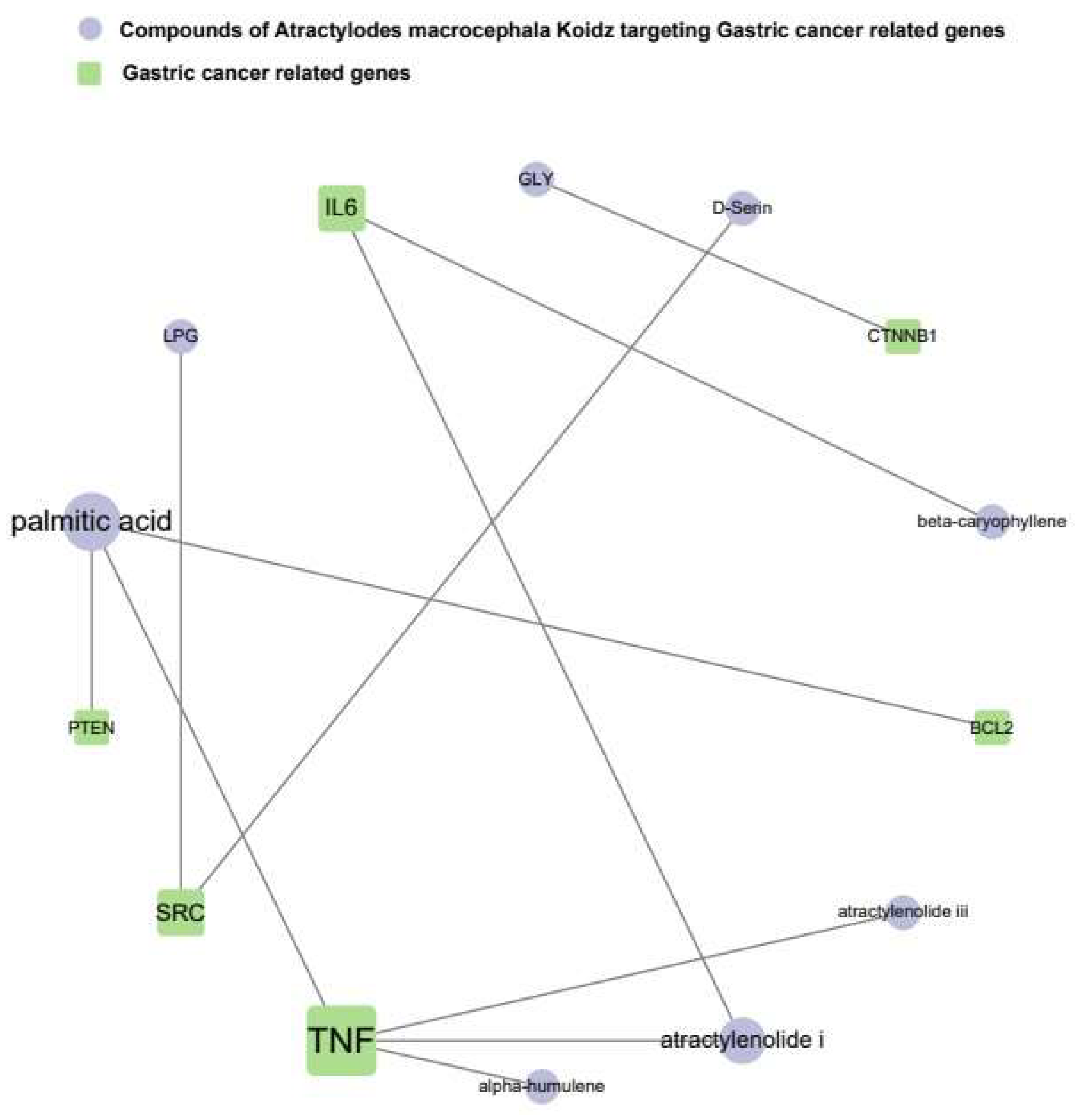
3.1.4. The Network of AMK Compounds and Gastric-Cancer-Related Genes
3.2. In Vitro Experiments
3.2.1. Quantification of Major Components in AMK by HPLC-UV
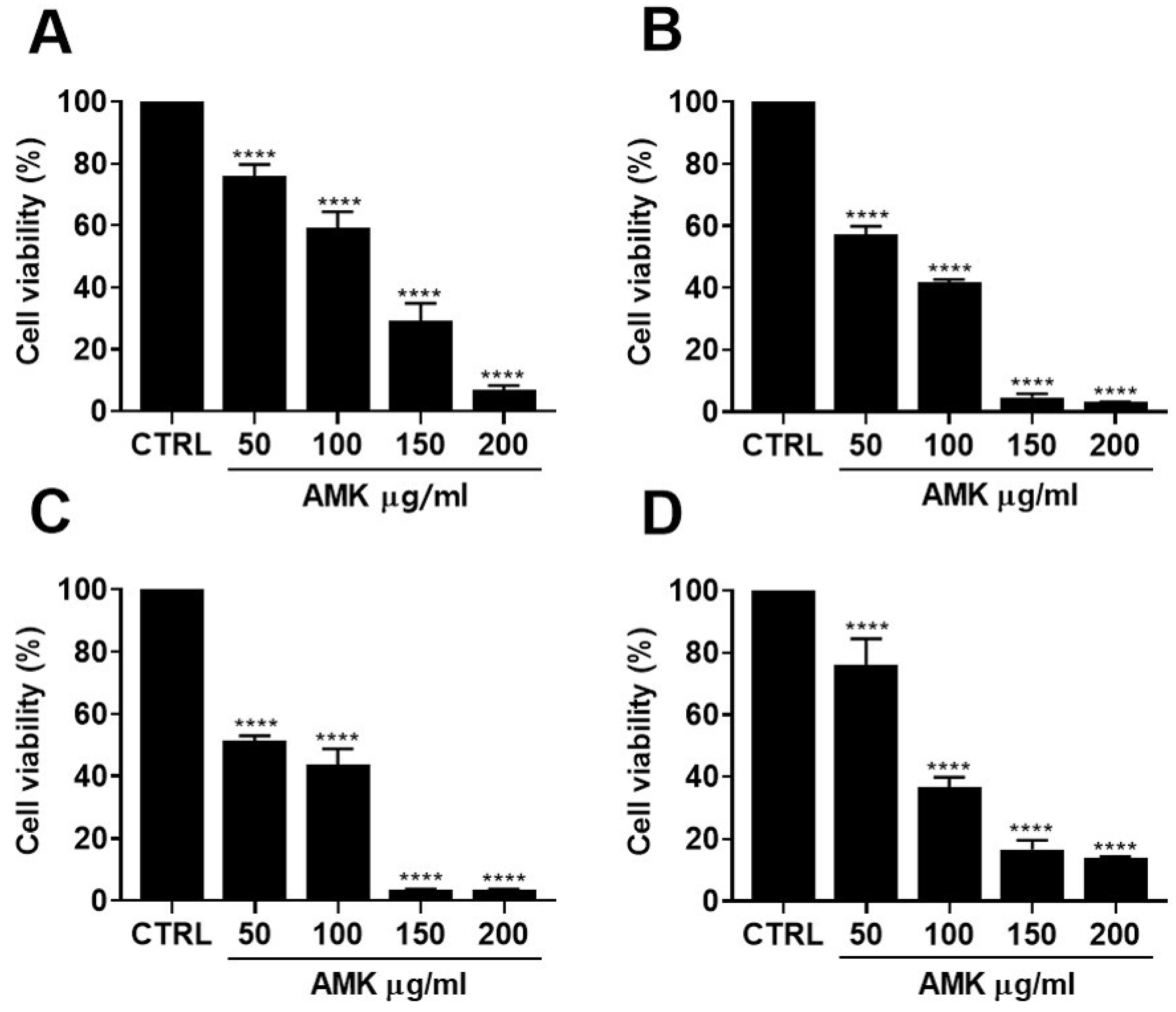
3.2.2. Effects of AMK Extract on Cytotoxicity in AGS Cells
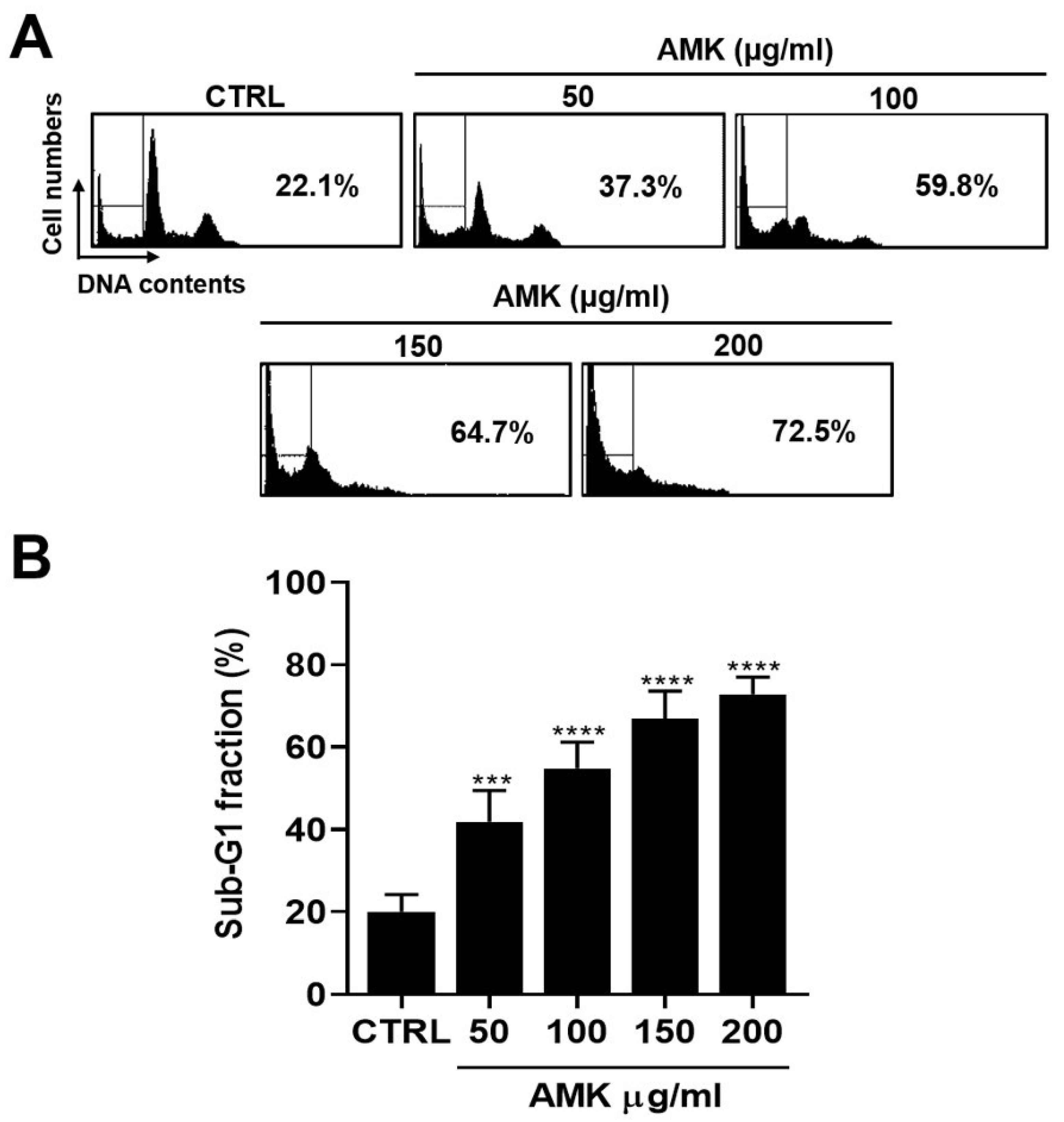
3.2.3. AMK Extract Induces Cell Cycle G1 Arrest in AGS Cells
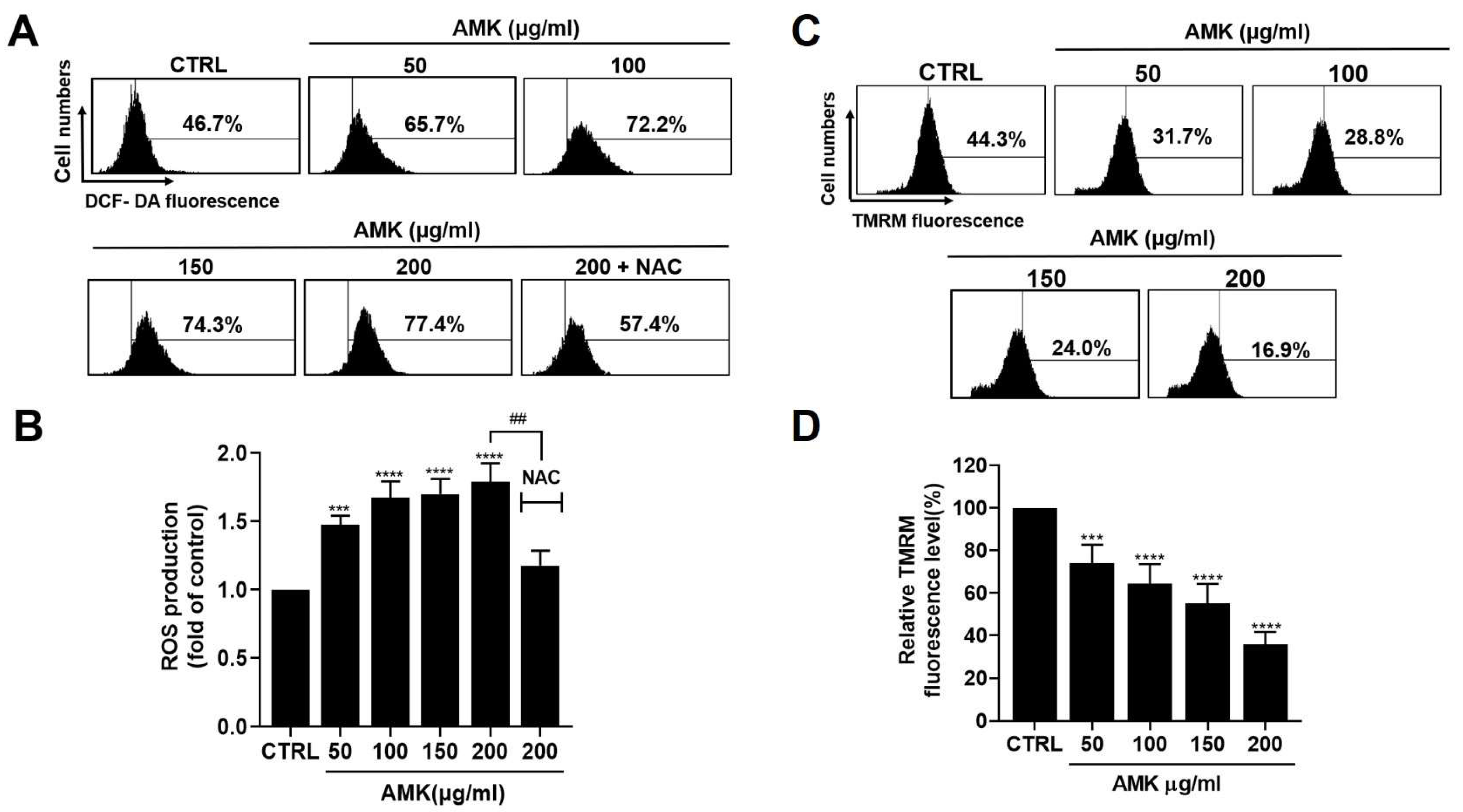
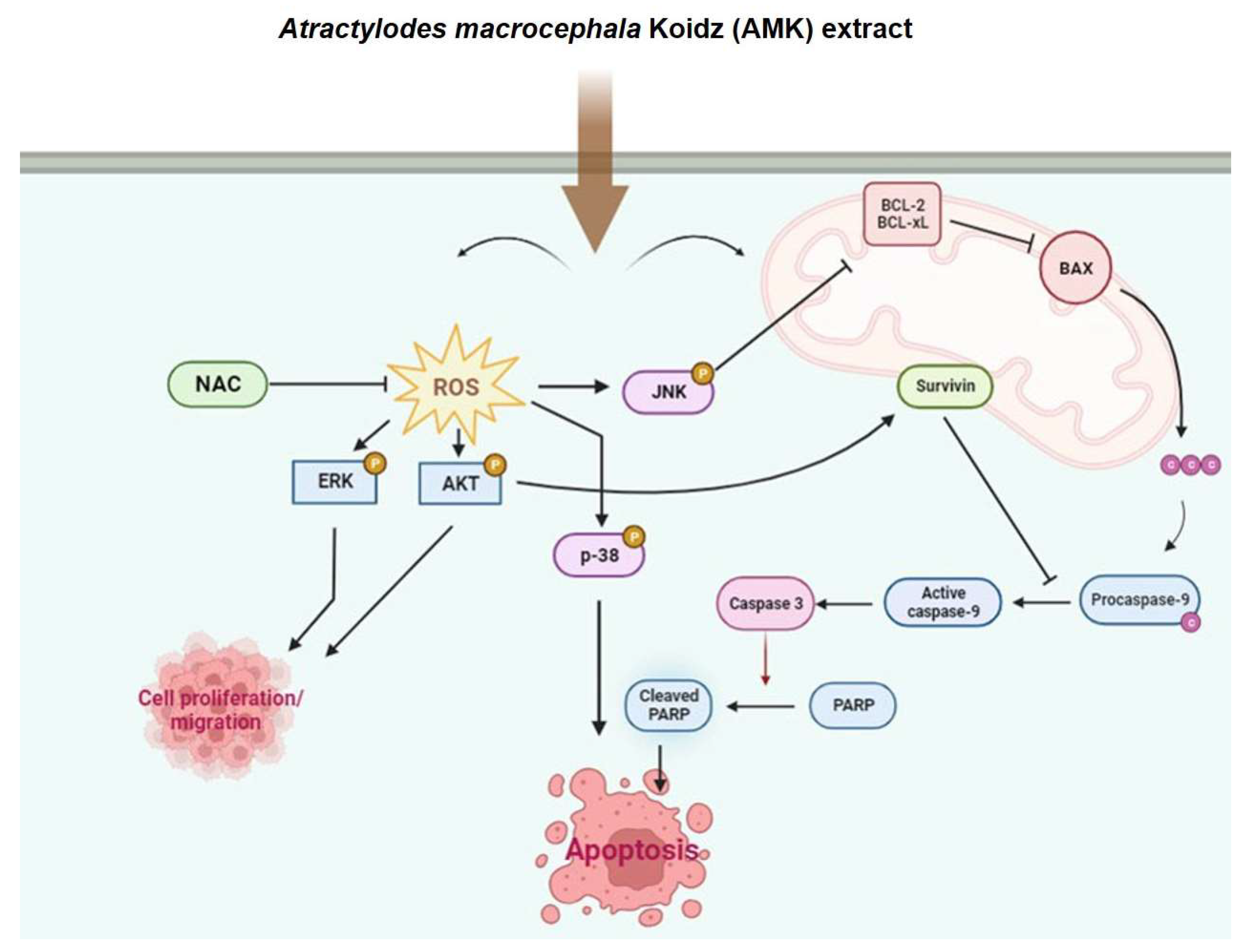
3.2.4. AMK Extract Induces Apoptosis through ROS Generation in AGS Cells
3.2.5. Alterations in the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in AGS Cells
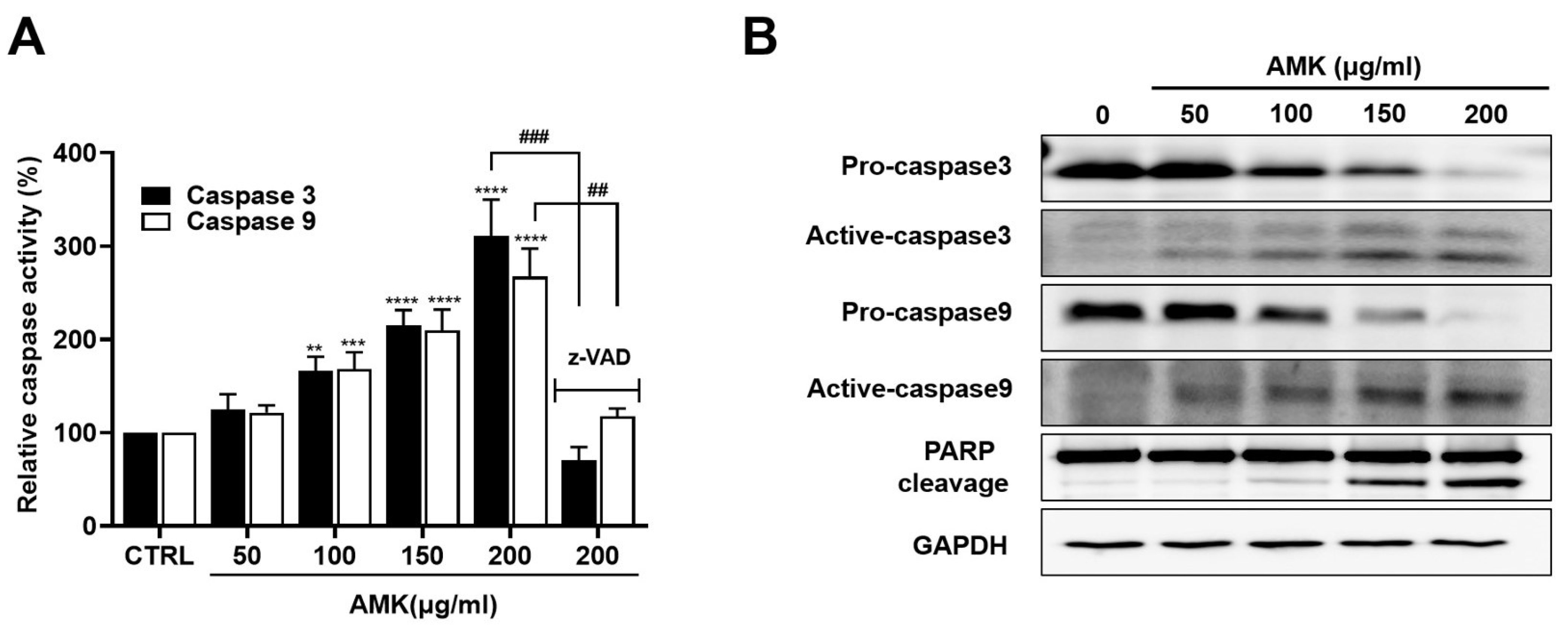
3.2.6. AMK Extract Induces the Activation of Caspases in AGS Cells
3.2.7. Relationship between AMK-Extract-Induced Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Pathway in AGS Cells
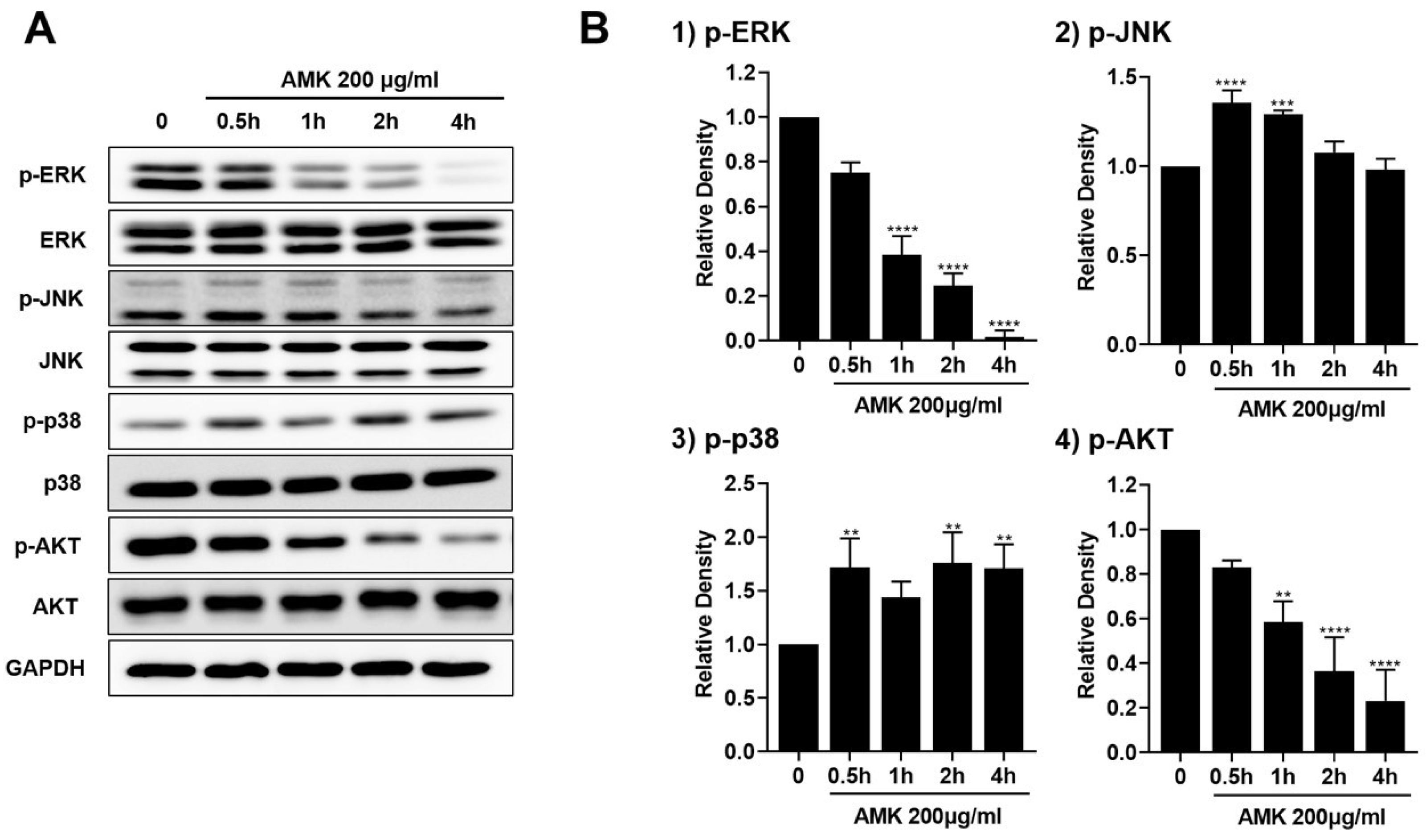
3.2.8. AMK Extract-Mediated Regulation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) in AGS Cells
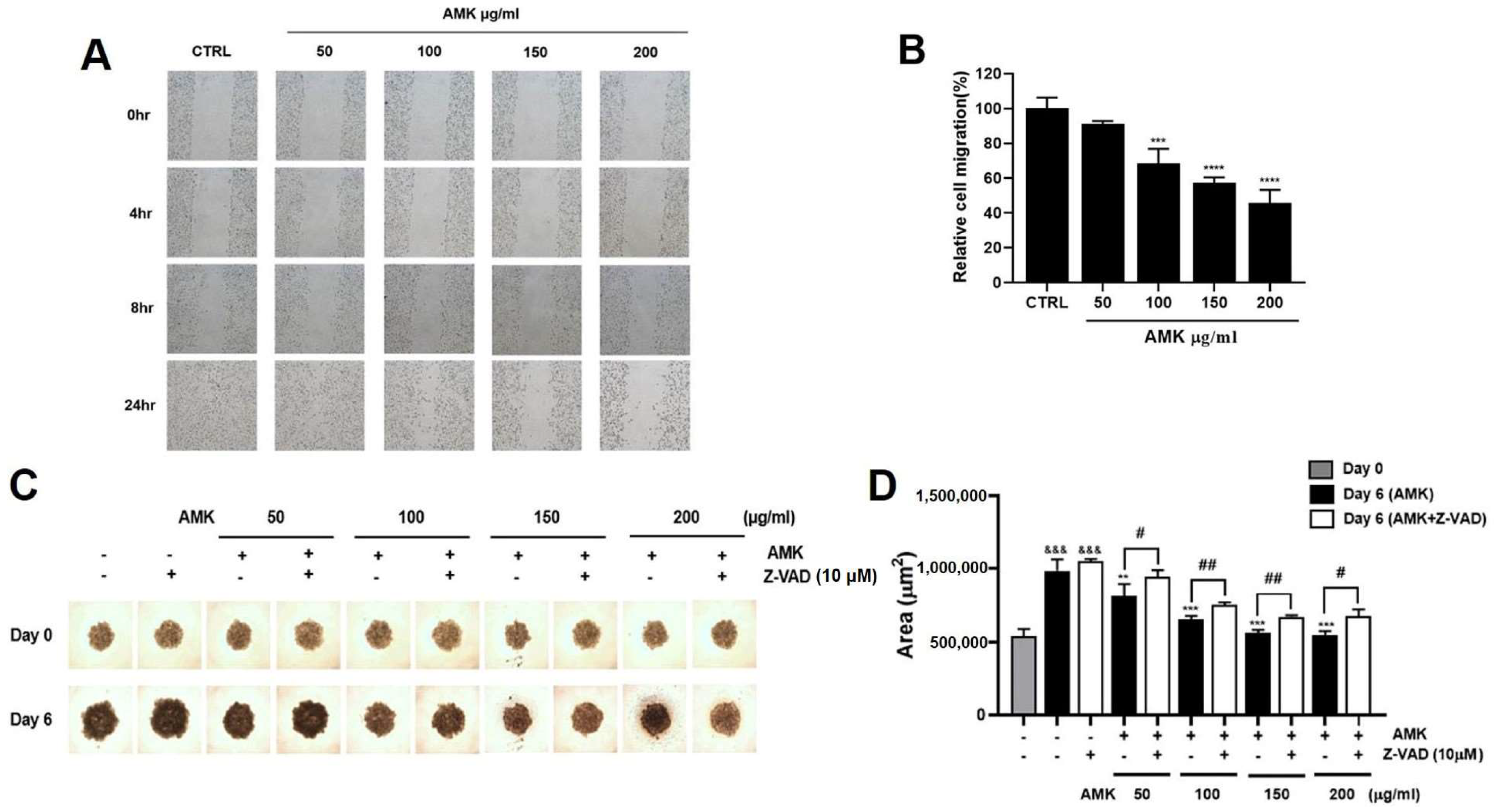
3.2.9. Effects of AMK Extract on Migration Ability in AGS Cells
3.2.10. AMK Extract Suppresses the Growth of AGS Cells in the Spheroid Formation Assay
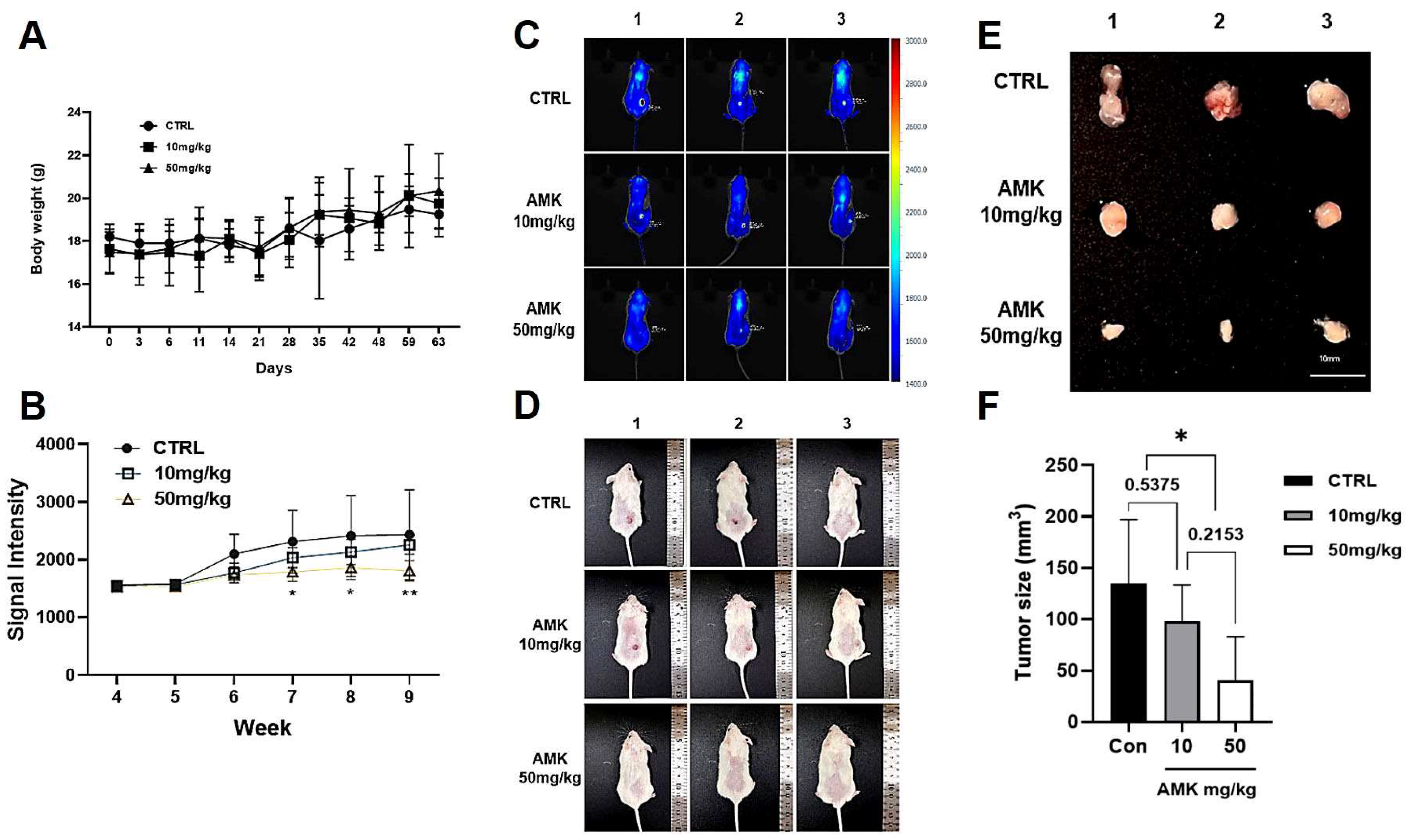
3.3. In Vivo Experiments
AMK Extract Inhibits Tumor Growth in the Xenograft Mouse Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mather, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, V.; Labianca, R.; Beretta, G.D.; Gatta, G.; De, B.F.; Van, C.E. Gastric cancer. Oncol. Hematol. 2009, 71, 127–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Islami, F.; Anandasabapathy, S.; Freedman, N.D.; Kamangar, F. Gastric cancer: Descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.G.; George, A.; Vidyasagar, M.S.; Mathew, S.; Nayak, S.; Nayak, B.S.; Shashidhara, Y.N.; Kamath, A. Quality of Life among Cancer Patients. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2017, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, Q.L.; Hua, J.W.; Cheng, W.L.; Qin, L.P. The traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 226, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Chaudhry, G.E.S. Understanding Apoptosis and Apoptotic Pathways Targeted Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.M.; Chan, W.Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, C.H. Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.D.; Kim, U.; Suh, J.H.; Eom, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, Y.S.; Han, S.B. Classification of the medicinal plants of the genus Atractylodes using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array and tandem mass spectrometry detection combined with multivariate statistical analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, K.; Berneman, Z.N.; Van Bockstaele, D.R. Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2003, 36, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondrak, G.T. Redox-directed cancer therapeutics: Molecular mechanisms and opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 2009, 11, 3013–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Jin, T.R.; Tzen, J.T.; Li, T.M.; Tang, C.H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cell apoptosis of human chondrosarcoma cells through apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1 pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.C.; Hsiao, C.D.; Chen, W.M.; Wen, Y.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, T.W.; Yao, F.Y.; Hung, S.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Chiu, J.H.; et al. Cytotoxic effects of 15d-PGJ2 against osteosarcoma through ROS-mediated AKT and cell cycle inhibition. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.J.; Bai, H.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.W.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, J.X.; Mai, S.J.; Zeng, M.S.; Sun, H.D.; et al. Longikaurin A, a natural ent-kaurane, induces G2/M phase arrest via downregulation of Skp2 and apoptosis induction through ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulares, A.H.; Zoltoski, A.J.; Contreras, F.J.; Yakovlev, A.G.; Yoshihara, K.; Smulson, M.E. Regulation of DNAS1L3 endonuclease activity by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation during etoposide-induced apoptosis. Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage in endonuclease activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibowitz, B.; Yu, J. Mitochondrial signaling in cell death via the Bcl-2 family. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T. Antitumor, antiviral, and anti Inflammatory efficacy of essential oils from atractylodes macrocephala koidz. produced with different processing methods. Molecules 2019, 24, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșu, M.C.; Mihnea, P.D.; Ardelean, A.; Moldovan, S.D.; Popețiu, R.O.; Totolici, B.D. Clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and carcinoembryonic antigen in gastric cancer. J. Med. Life 2022, 15, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoshida, G.J.; Naoi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Naka, K.; Ju, X.; Yamada, Y.; Minamoto, T.; Mukaida, N.; et al. TNF-α/TNFR1 signaling promotes gastric tumorigenesis through induction of Noxo1 and Gna14 in tumor cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3820–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Xue, L. The diagnostic value of interleukin 6 as a biomarker for gastric cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Medicine 2021, 100, e27945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Yasui, W.; Kuniyasu, H.; Yokozaki, H.; Tahara, E. Expression of interleukin-6 and its effect on the cell growth of gastric carcinoma cell lines. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1997, 88, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryko, M.; Pryczynicz, A.; Zareba, K.; Kędra, B.; Kemona, A.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K. The expression of Bcl-2 and BID in gastric cancer cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 953203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.T.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N.H. Roles of PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog) in gastric cancer development and progression. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, D.; Heo, Y.J.; Kim, K.M. PTEN Protein Loss and Loss-of-Function Mutations in Gastric Cancers: The Relationship with Microsatellite Instability, EBV, HER2, and PD-L1 Expression. Cancers 2020, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Kawabata, T.; Aoyagi, K.; Yokozaki, H.; Sasaki, H. Gene expression and pathway analysis of CTNNB1 in cancer and stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2016, 8, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fátima Ferreira Borges Da Costa, J.; De Castro Sant’ Anna, C.; Muniz, J.A.P.C.; Da Rocha, C.A.M.; Lamarão, L.M.; De Fátima Aquino Moreira Nunes, C.; De Assumpção, P.P.; Burbano, R.R. Deregulation of the SRC Family Tyrosine Kinases in Gastric Carcinogenesis in Non-human Primates. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6317–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, T.J. A renaissance for SRC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.J.; Im, S.A.; Oh, D.Y.; Elvin, P.; Kim, H.P.; Yoon, Y.K.; Min, A.; Song, S.H.; Han, S.W.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Antitumor activity of saracatinib (AZD0530), a c-Src/Abl kinase inhibitor, alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic agents in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.P.; Yu, F.M.; Zhang, G.M.; Yang, Z.S.; Huang, F.F.; Ding, G.F. A purified serine protease from Nereis virens and its impaction of apoptosis on human lung cancer cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Liang, Y.N.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.X.; Liu, J.L.; Tang, Z.S. Cordycepin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of human lung cancer cell line H1975 via Inhibiting the Phosphorylation of EGFR. Molecules 2016, 21, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igney, F.H.; Krammer, P.H. Death and anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Mak, T.W. Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; El-Deiry, W.S. Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroemer, G.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Ranganathan, V.; Farnsworth, M.L.; Kavallaris, M.; Lock, R.B. Bcl-2 inhibits Bax translocation from cytosol to mitochondria during drug-induced apoptosis of human tumor cells. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.G. Multiparametric analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1678, 167–202. [Google Scholar]
- Long, F.Y.; Wang, T.; Jia, P.; Wang, H.F.; Qing, Y.; Xiong, T.T.; He, M.J.; Wang, X.L. Anti-tumor effects of Atractylenolide-I on human ovarian cancer cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, S.P.; Cai, D.W.; Kong, G.Q. Induction of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in T24 cells by a selenium (Se)-containing polysaccharide from Ginkgo Biloba L. leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.J.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.G. A polysaccharide from Pinellia ternata inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in human cholangiocarcinoma cells by targeting of Cdc42 and 67 kDa Laminin Receptor (LR). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobahat, M.; Narendran, A.; Riabowol, K. Survivin as a preferential target for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2494–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Duan, N.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Survivin and tumorigenesis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Lu, Y.H.; Xie, J.H.; Wang, F.; Zou, J.N.; Yang, J.S.; Xing, Y.Y.; Xi, T. Downregulation of survivin and activation of caspase-3through the PI3K/Akt pathway in ursolic acid-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Anticancer Drugs 2009, 20, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Yu, B.X.; Chen, J.F.; Lv, X.Y.; Yan, Z.J.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Q. Anti-tumor effects of Atractylenolide I on bladder cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Jiang, Y.N.; Fu, T.T.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, X.F.; Lu, Y. Naringin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced damage in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via attenuation of inflammation, apoptosis and MAPK pathways. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1473–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Qian, C.J. Sporamin induce apoptosis in human tongue carcinoma cells by down-regulating Akt/GSK-3 signaling. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 25, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.Z.; Chen, L.; Wei, X.B.; Xiang, Y.X.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, X.M. The Akt/GSK-3β pathway mediates flurbiprofen-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Molecule Name | Gene Name | Disease Name |
|---|---|---|
| (+/−)-Isoborneol | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| (1R)-2-methyl-1-phenylprop-2-en-1-ol | DPP4 | Malignancies |
| (1S,2R,4R)-Neoiso-dihydrocarveol | REN | Cancer, unspecific |
| (3S)-3-[(1R)-1,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl]-6-methylenecyclohexene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| (5E,9Z)-3,6,10-trimethyl-4,7,8,11-tetrahydrocyclodeca[b]furan | NOS3 | Colon cancer |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| 14-acetyl-12-senecioyl-2E,8Z,10E-atractylentriol | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| 3β-acetoxyatractylone | DPP4 | Malignancies |
| NOS3 | Colon cancer | |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| 8β-ethoxy atractylenolide III | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| Akridin | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| alpha-Curcumene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| alpha-humulene | TNF | * gastric cancer |
| Solid Tumor | ||
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| REN | Cancer, unspecific | |
| ASI | ALOX5 | Gastrointestinal Cancers |
| Pancreatic Cancer | ||
| Gastrointestinal Cancers | ||
| Pancreatic Cancer | ||
| CDC25B | Cancer, unspecific | |
| PTPN1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| atractylenolide i | IL6 | * gastric cancer |
| TNF | * gastric cancer | |
| Solid Tumor | ||
| VEGFA | Colorectal Neoplasms | |
| atractylenolide iii | TNF | * gastric cancer |
| Solid Tumor | ||
| atractylone | NOS3 | Colon cancer |
| beta-caryophyllene | IL6 | * gastric cancer |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| beta-Humulene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| beta-Selinene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| D-Camphene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| TOP2A | Cancer, unspecific | |
| D-Serin | SRC | * gastric cancer |
| Cancer, unspecific | ||
| DTY | DPP4 | Malignancies |
| NOS3 | Colon cancer | |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| PTPN1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| GLY | CTNNB1 | * gastric cancer |
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| ALDH1A1 | Neoplasms | |
| CDC25B | Cancer, unspecific | |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| Solid tumors | ||
| MMP8 | Tumors | |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| PTPN1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| REN | Cancer, unspecific | |
| RRM1 | Pancreatic Neoplasms | |
| SHMT2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| SRC | Cancer, unspecific | |
| TXNRD1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Malignancies | ||
| Gulutamine | LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer |
| Solid tumors | ||
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| PTPN1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Hemo-sol | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| Istidina | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| juniper camphor | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| L-Arginin | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| L-Ile | REN | Cancer, unspecific |
| LPG | SRC | * gastric cancer |
| Cancer, unspecific | ||
| CDC25B | Cancer, unspecific | |
| MMP8 | Tumors | |
| RRM1 | Pancreatic Neoplasms | |
| L-Valin | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| PTPN1 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| palmitic acid | BCL2 | * gastric cancer |
| PTEN | * gastric cancer | |
| TNF | * gastric cancer | |
| Solid Tumor | ||
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| PHA | DPP4 | Malignancies |
| NOS3 | Colon cancer | |
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| Prolinum | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| Scopoletol | CA1 | Pancreatic Cancer |
| LTA4H | Oesophageal cancer | |
| Solid tumors | ||
| NQO2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Tumors | ||
| PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific | |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| selina-4(14),7(11)-dien-8-one | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| α-Longipinene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma | ||
| γ-elemene | PTGS2 | Cancer, unspecific |
| Carcinoma in situ, unspecified | ||
| Colorectal cancer | ||
| Oropharyngeal squamous cell | ||
| Carcinoma |
| Gene Name | Protein Name |
|---|---|
| AFP | Alpha-1-fetoprotein |
| AKR7A3 | Aldo-keto reductase family 7, member A3 (aflatoxin aldehyde reductase) |
| AKT1 | V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1 |
| ALB | Serum albumin |
| ANXA5 | Placental anticoagulant protein 4 |
| ARID1A | SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily F member 1 |
| ATP12A | ATPase, H+/K+ transporting, nongastric, alpha polypeptide |
| ATP4A | ATPase, H+/K+ exchanging, alpha polypeptide |
| ATP4B | ATPase, H+/K+ exchanging, beta polypeptide |
| BCL2 | Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 |
| BRCA1 | Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein |
| BRCA2 | Breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein |
| C3orf36 | Chromosome 3 open reading frame 36 |
| CAGE1 | Cancer-associated gene 1 protein |
| CASP3 | Caspase 3, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| CASP9 | Caspase 9, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
| CCND1 | B-cell lymphoma 1 protein |
| CCNE1 | G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 |
| CD274 | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 |
| CD4 | T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3 |
| CD44 | GP90 lymphocyte homing/adhesion receptor |
| CD8A | T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen T8/Leu-2 |
| CDH1 | Cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) |
| CDH2 | Cadherin 2, type 1, N-cadherin (neuronal) |
| CDX2 | Caudal-type homeobox protein 2 |
| CEACAM5 | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 |
| CGB | Chorionic gonadotropin, beta polypeptide |
| CLDN18 | Claudin 18 |
| COL5A2 | Collagen alpha-2(V) chain |
| CT83 | Kita-kyushu lung cancer antigen 1 |
| CTLA4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 |
| CTNNA1 | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1, 102kDa |
| CTNNB1 | Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa |
| DIRC1 | Disrupted in renal carcinoma 1 |
| EGFR | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1 |
| ENSP00000464218 | Zinc finger protein 286A |
| ERBB2 | V-erb-b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2 |
| ERBB3 | V-erb-b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 3 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit |
| FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 |
| FNDC1 | Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 1 |
| FNDC7 | Fibronectin type III domain-containing 7 |
| FNDC8 | Fibronectin type III domain containing 8 |
| FTO | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO |
| GAST | Gastrin |
| GLT8D2 | Glycosyltransferase 8 domain containing 2 |
| GPR176 | G protein-coupled receptor 176 |
| GPX4 | Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase, mitochondrial |
| HAVCR2 | T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 |
| HIF1A | Hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor) |
| HRAS | Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| IL6 | B-cell stimulatory factor 2 |
| KDR | Kinase insert domain receptor (a type III receptor tyrosine kinase) |
| KIAA1524 | Cancerous inhibitor of PP2A |
| KIT | V-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| KRT7 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 7 |
| LAG3 | Lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein |
| LGR5 | Leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 |
| LIPT1 | Lipoyltransferase 1, mitochondrial |
| LRP1B | Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-deleted in tumor |
| LRRD1 | Leucine rich repeats and death domain containing 1 |
| MAGEA11 | Melanoma-associated antigen 11 |
| MAP6 | Microtubule-associated protein 6 |
| METTL3 | N6-adenosine-methyltransferase catalytic subunit |
| MLH1 | DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 |
| MMP2 | Matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72 kDa gelatinase, 72 kDa type IV collagenase) |
| MMP9 | Matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92 kDa gelatinase, 92 kDa type IV collagenase) |
| MSH2 | DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 |
| MSH6 | DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 |
| MTUS1 | Angiotensin-II type 2 receptor-interacting protein |
| MTUS2 | Microtubule associated tumor suppressor candidate 2 |
| MUC5AC | Mucin 5AC, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming |
| MUC6 | Mucin 6, oligomeric mucus/gel-forming |
| MYC | V-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog |
| NOTCH1 | Translocation-associated notch protein TAN-1 |
| OLFML2B | Olfactomedin-like protein 2B |
| PDCD1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase 110 kDa catalytic subunit alpha |
| PLOD2 | Procollagen-lysine, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2 |
| PMS2 | PMS2 postmeiotic segregation increased 2 (S. cerevisiae) |
| PSCA | Prostate stem cell antigen |
| PTEN | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1 |
| RNF180 | RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase RNF180 |
| RUNDC3A | RUN domain-containing protein 3A |
| S100A8 | Migration inhibitory factor-related protein 8 |
| SALL4 | Spalt-like transcription factor 4 |
| SLC7A11 | Solute carrier family 7 (anionic amino acid transporter light chain, xc-system), member 11 |
| SNAI1 | Snail family zinc finger 1 |
| SOX2 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 |
| SRC | SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) |
| TFF2 | Spasmolytic polypeptide |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 2 |
| TP53 | Cellular tumor antigen p53 |
| TRIM49C | Tripartite motif-containing protein 49-like protein 2 |
| VSIG1 | V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 |
| YAP1 | Yes-associated protein YAP65 homolog |
| YTHDF1 | Dermatomyositis associated with cancer putative autoantigen 1 |
| ZNF705A | Zinc finger protein 705A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, N.-R.; Choi, W.-G.; Zhu, A.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.-T.; Hong, J.; Kim, B.-J. Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz against Human Gastric Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070965
Choi N-R, Choi W-G, Zhu A, Park J, Kim Y-T, Hong J, Kim B-J. Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz against Human Gastric Cancer. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070965
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Na-Ri, Woo-Gyun Choi, Anlin Zhu, Joon Park, Yun-Tai Kim, Jaewoo Hong, and Byung-Joo Kim. 2024. "Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz against Human Gastric Cancer" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070965
APA StyleChoi, N.-R., Choi, W.-G., Zhu, A., Park, J., Kim, Y.-T., Hong, J., & Kim, B.-J. (2024). Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz against Human Gastric Cancer. Nutrients, 16(7), 965. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070965








