An Evaluation of the Effects of Pineapple-Extract and Bromelain-Based Treatment after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Three-Arm Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
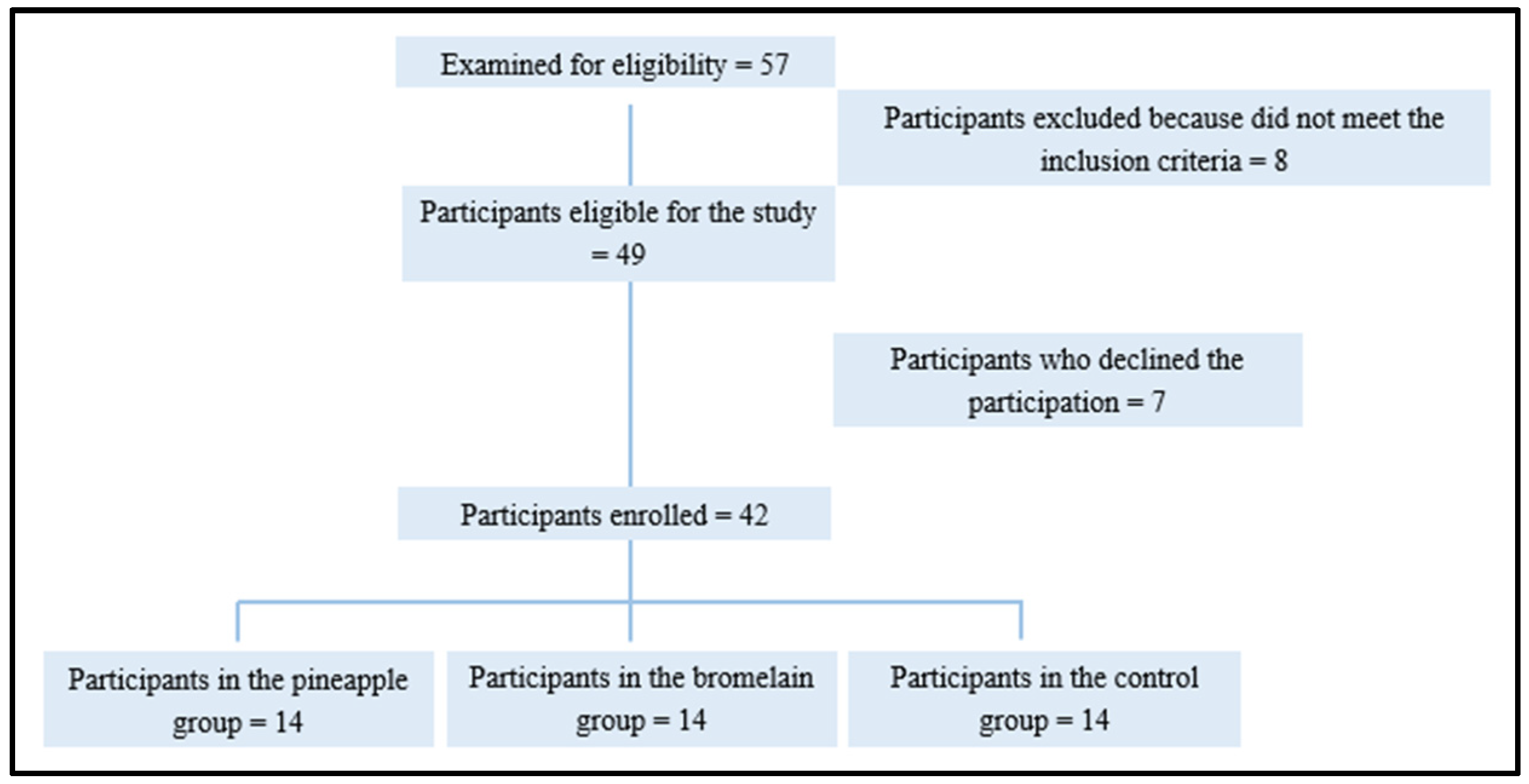
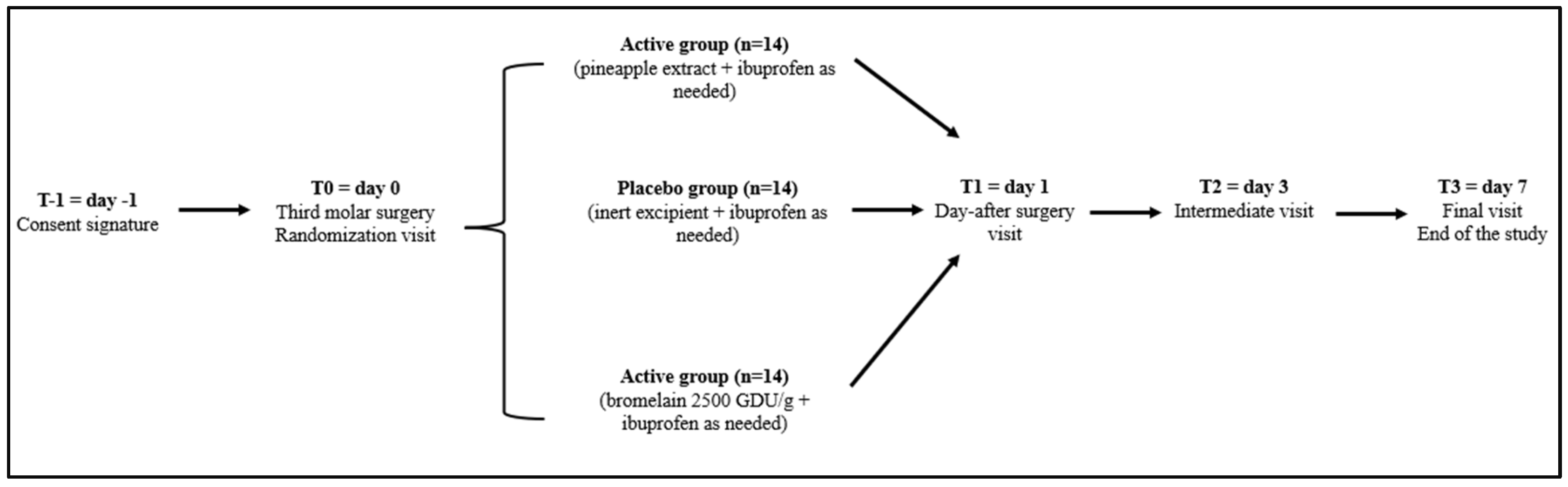
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Treatment
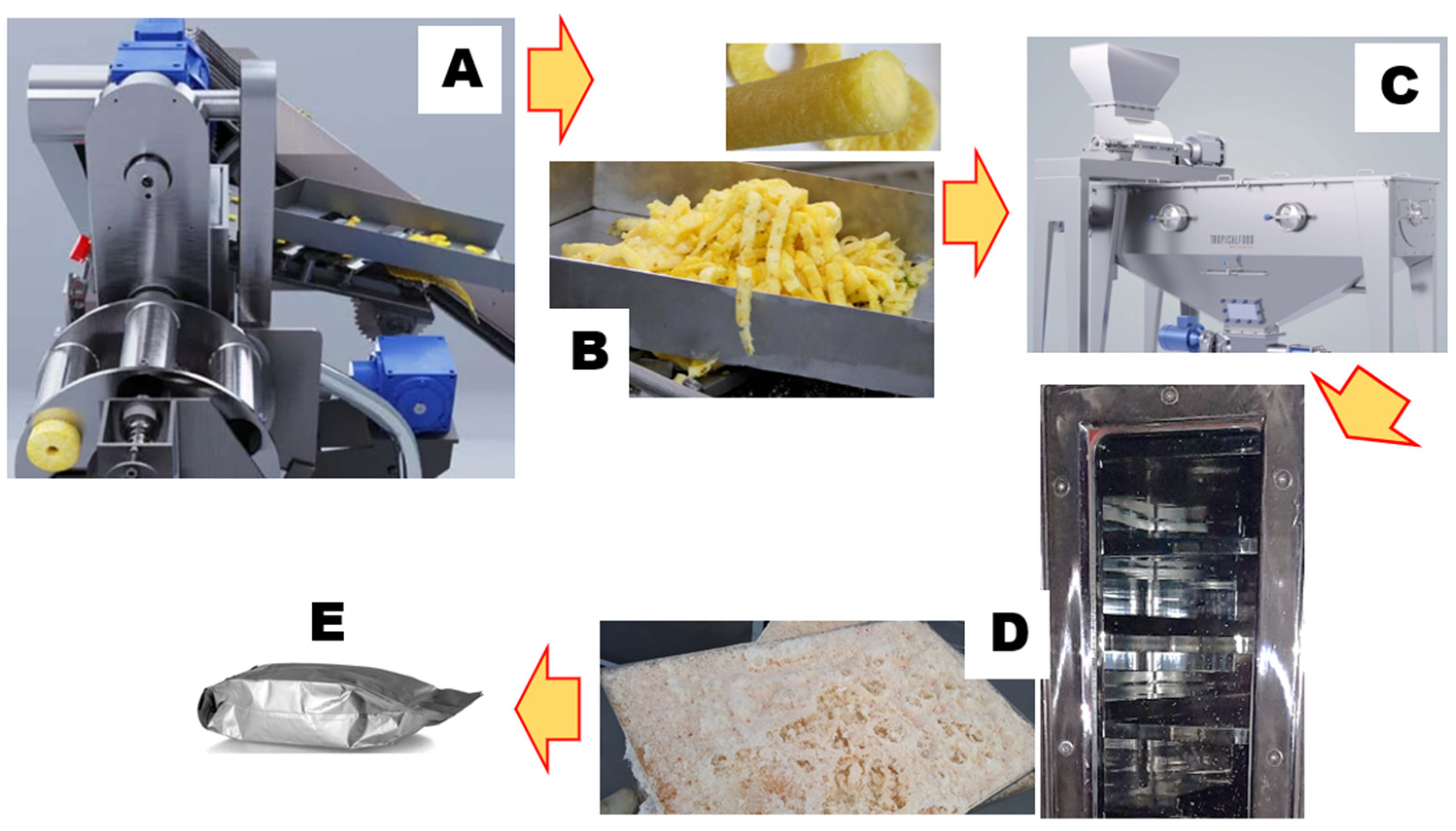
2.3. Product Preparation
2.4. Efficacy Assessment
2.5. Assessment of Safety and Tolerability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Lencastre Novaes, L.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Lopes, A.M.; de Carvalho Santos-Ebinuma, V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Pessoa Junior, A. Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rábade, N.; Badillo-Corona, J.A.; Aranda-Barradas, J.S.; del Carmen Oliver-Salvador, M. Production of plant proteases in vivo and in vitro—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, A.; Li, S.; Marengo, M.; Adinolfi, S.; Cravotto, G. Recent Advances and Insights into Bromelain Processing, Pharmacokinetics and Therapeutic Uses. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, R.; Jain, S.; Shraddha; Kumar, A. Properties and Therapeutic Application of Bromelain: A Review. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 976203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, C. Oral Bromelain for the Control of Facial Swelling, Trismus, and Pain after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.; Nascimento-Junior, E.D.; Reinheimer, D.; Martins-Filho, P. Efficacy of proteolytic enzyme bromelain on health outcomes after third molar surgery. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, e61–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.D.A.; Lima, F.D.S.; Vasconcelos, B.D.E. Is bromelain an effective drug for the control of pain and inflammation associated with impacted third molar surgery? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, G.M.; Fernandes, I.A.; Dos Santos, C.R.R.; Falci, S.G.M. Is bromelain effective in controlling the inflammatory parameters of pain, edema, and trismus after lower third molar surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, R.J.; Johnson, M.P. Review of Top 10 Prescribed Drugs and Their Interaction with Dental Treatment. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 60, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martino, M.; Chiarugi, A.; Boner, A.; Montini, G.; De’ Angelis, G.L. Working Towards an Appropriate Use of Ibuprofen in Children: An Evidence-Based Appraisal. Drugs 2017, 77, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.C.; Langman, M.J.; Laporte, J.R.; Matthews, J.N.; Rawlins, M.D.; Wiholm, B.E. Dose-response relationships between individual nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NANSAIDs) and serious upper gastrointestinal bleeding: A meta-analysis based on individual patient data. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Schinnar, R.; Bilker, W.B.; Feldman, H.; Farrar, J.T.; Carson, J.L. Gastrointestinal tract bleeding associated with naproxen sodium vs ibuprofen. Arch. Intern. Med. 1997, 157, 2626–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.M.; Lichtenstein, D.R.; Singh, G. Gastrointestinal toxicity of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1888–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchina, V.; Stabile, S.; Cenna, R.; Mannozzi, F.; Federici, I.; Testoni, S.; Sinno, V.; Cagnazzo, C. ISO 9001: 2015 standard implementation in clinical trial centers: An exploratory analysis of benefits and barriers in Italy. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2023, 33, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fissore, A.; Marengo, M.; Santoro, V.; Grillo, G.; Oliaro-Bosso, S.; Cravotto, G.; Dal Piaz, F.; Adinolfi, S. Extraction and Characterization of Bromelain from Pineapple Core: A Strategy for Pineapple Waste Valorization. Processes 2023, 11, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, O.W. Submucosal dexamethasone injection improves quality of life measures after third molar surgery: A comparative study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R. Dietary supplements and nutraceuticals market growth during the coronavirus pandemic—Implications for consumers and regulatory oversight. PharmaNutrition 2021, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomas-Barber, F.A. Nutraceuticals: Facts and fiction. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2986–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S. Global $275 Billion Nutraceuticals 2017–2021: New Applications for Probiotics, Genetic Modification and Diet as Products Make Gains in Rx Territory—ResearchAndMarkets.com. 2018. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180118005641/en/Global-275-Billion-Nutraceuticals-2017–2021-New-Applications-for-Probiotics-Genetic-Modification-and-Diet-as-Products-Make-Gains-in-Rx-Territory (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Faramarzi, M.; Sadighi, M.; Shirmohamadi, A.; Kazemi, R.; Zohdi, M. Effectiveness of Bromelain in the control of postoperative pain after periodontal surgery: A crossover randomized clinical trial. J. Adv. Periodontol. Implant. Dent. 2023, 15, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasemsuk, T.; Saengpetch, N.; Sibmooh, N.; Unchern, S. Improved WOMAC score following 16-week treatment with bromelain for knee osteoarthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevali, A.; Vaccaro, S.; Borselli, M.; Bousyf, S.; Lamonica, L.; Randazzo, G.; Giannaccare, G.; Scorcia, V. Anatomical and Functional Effects of an Oral Supplementation of Bromelain and Curcugreen in Patients with Focal Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, L.; Sengar, A.S.; Neog, R.; Sunil, C.K. Pineapple processing waste (PPW): Bioactive compounds, their extraction, and utilisation: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4152–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, O.W.; Al-Mashhadani, B.A. Perioperative bromelain reduces pain and swelling and improves quality of life measures after mandibular third molar surgery: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzhugh, D.J.; Shan, S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Hale, L.P. Bromelain treatment decreases neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 128, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochi, B.N.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.-Y.; Zhang, W. Therapeutic Application of Pineapple Protease (Bromelain): A Review. Pak. J. Nutr. 2008, 7, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, C.H.; Seldin, E.B.; Dodson, T.B. Types, frequencies, and risk factors for complications after third molar extraction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, G.R.; Bissias, E.; Ruta, D.A.; Ogston, S. Quality of life following third molar removal: A patient versus professional perspective. Br. Dent. J. 1998, 185, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, H. Bromelain: Biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Bromelain (n = 14) | Brome-Inf® (n = 14) | Placebo (n = 14) | Total | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 22.4 ± 4.9 | 22.9 ± 4.5 | 23.1 ± 4.1 | 22.8 ± 4.5 | n.s. |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 5 | 6 | 8 | 19 | n.a. |
| Female | 8 | 7 | 8 | 23 | n.a. |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 24.4 ± 0.2 *** | 24.6 ± 0.2 | 24.8 ± 0.3 | 24.6 ± 0.2 | Placebo vs. Bromelain p = 0.0002 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.0963 n.s. Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.0963 n.s. |
| Operation time (min) | 31.2 ± 14.1 | 32.7 ± 18.2 | 31.5 ± 17.4 | 31.8 ± 16.5 | n.s. |
| Variable | Placebo (n = 14) | Bromelain (n = 14) | Brome-Inf® (n = 14) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS-10 | ||||
| Day-1 | 3.857 ± 0.462 | 2.286 ± 0.529 **** | 2.121 ± 0.387 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Day-3 | 2.836 ± 0.325 | 1.514 ± 0.419 **** | 1.457 ± 0.238 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Day-7 | 1.629 ± 0.190 | 0.407 ± 0.144 **** | 0.450 ± 0.129 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§) | (D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§) | (D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§) | ||
| Swelling | ||||
| Day-1 | 8.193 ± 0.329 | 7.7779 ± 0.345 ** | 7.929 ± 0.264 | Placebo vs. Bromelain p = 0.0037 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.0969, n.s. Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.6440, n.s. |
| Day-3 | 4.236 ± 0.448 | 3.093 ± 0.329 **** | 3.257 ± 0.253 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.6775, n.s. |
| Day-7 | 1.843 ± 0.214 | 1.207 ± 0.219 **** | 1.243 ± 0.320 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | D1 vs. D3; D3 vs. D7; D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | ||
| Trismus | ||||
| Day-1 | 13.1 ± 3.7 | 13.4 ± 3.9 | 13.1 ± 3.7 | Placebo vs. Bromelain p > 0.9999, n.s. Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Day-3 | 8.9 ± 2.1 | 7.5 ± 2.3 | 7.8 ± 2.5 | Placebo vs. Bromelain p = 0.3488, n.s. Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.6431, n.s. Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Day-7 | 5.4 ± 1.5 | 4.3 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 1.2 | Placebo vs. Bromelain p = 0.0850, n.s. Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p = 0.3171 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| D1 vs. D3: p = 0.0004 §§§ D3 vs. D7: p = 0.0030 §§ D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | D1 vs. D3: p < 0.0001 §§§§ D3 vs. D7: p = 0.0095 §§ D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | D1 vs. D3: p < 0.0001 §§§§ D3 vs. D7: p = 0.0089 §§ D1 vs. D7: p < 0.0001 §§§§ | ||
| Rescue tablets of ibuprofen | 6.4 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 1.2 **** | 3.2 ± 1.4 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf® p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf® p > 0.9999 n.s. |
| Variable | Placebo (n = 14) | Bromelain (n = 14) | Brome-Inf® (n = 14) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.2 **** | 0.3 ± 0.2 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p = 0.8196 n.s. |
| Work | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.4 ** | 0.4 ± 0.3 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p = 0.0028 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p = 0.4809, n.s. |
| Eating | 8.1 ± 1.7 | 5.7 ± 1.0 **** | 5.8 ± 0.9 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Speech | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 0.7 **** | 1.2 ± 0.6 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Sleep | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 0.5 **** | 0.9 ± 0.4 **** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p < 0.0001 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Appearance | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 0.7 **** | 1.5 ± 0.8 *** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p < 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p = 0.0008 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p > 0.9999, n.s. |
| Total | 17.2 ±5.6 | 9.7 ± 3.5 *** | 10.1 ± 3.2 *** | Placebo vs. Bromelain: p = 0.0001 Placebo vs. Brome-Inf®: p = 0.0002 Bromelain vs. Brome-Inf®: p > 0.9999, n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colletti, A.; Procchio, C.; Pisano, M.; Martelli, A.; Pellizzato, M.; Cravotto, G. An Evaluation of the Effects of Pineapple-Extract and Bromelain-Based Treatment after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Three-Arm Clinical Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060784
Colletti A, Procchio C, Pisano M, Martelli A, Pellizzato M, Cravotto G. An Evaluation of the Effects of Pineapple-Extract and Bromelain-Based Treatment after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Three-Arm Clinical Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(6):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060784
Chicago/Turabian StyleColletti, Alessandro, Chiara Procchio, Mariaelena Pisano, Alma Martelli, Marzia Pellizzato, and Giancarlo Cravotto. 2024. "An Evaluation of the Effects of Pineapple-Extract and Bromelain-Based Treatment after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Three-Arm Clinical Study" Nutrients 16, no. 6: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060784
APA StyleColletti, A., Procchio, C., Pisano, M., Martelli, A., Pellizzato, M., & Cravotto, G. (2024). An Evaluation of the Effects of Pineapple-Extract and Bromelain-Based Treatment after Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized Three-Arm Clinical Study. Nutrients, 16(6), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16060784








