Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
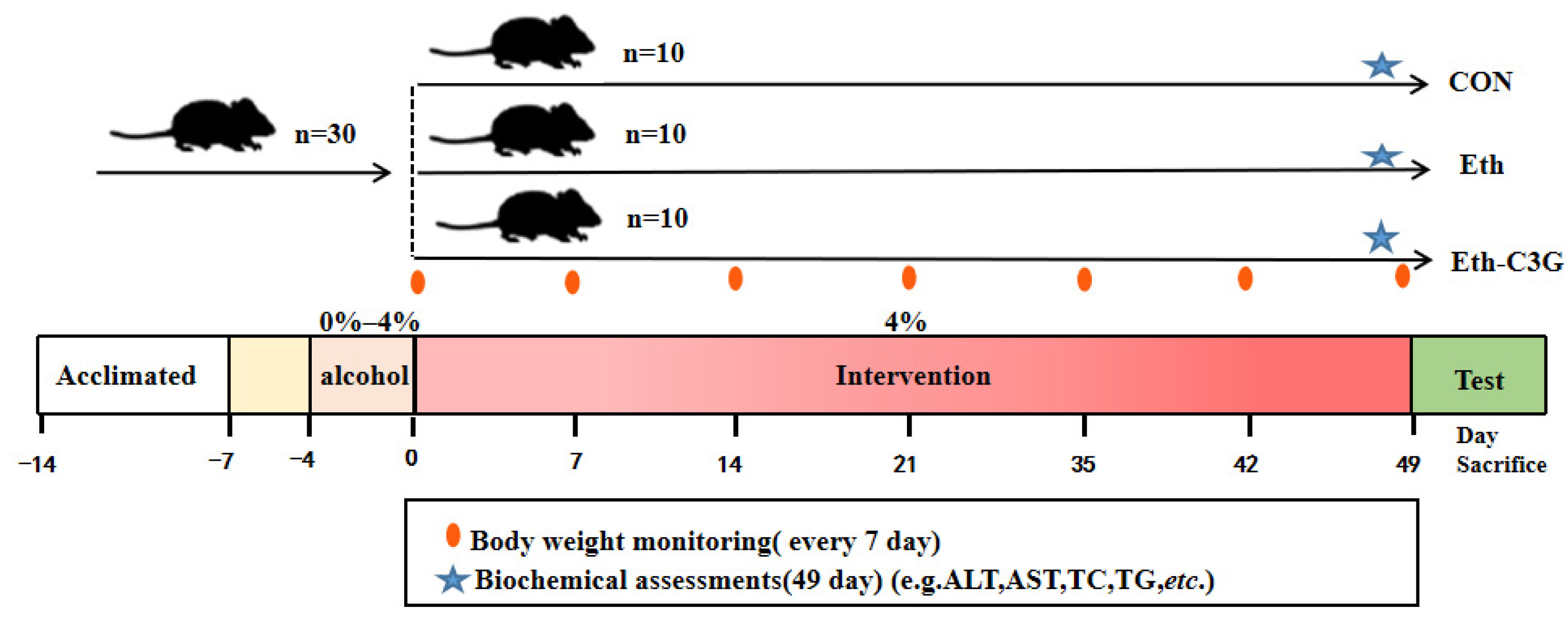
2.1. Animal and Experimental Design
2.2. Biochemical Assays
2.3. Histological Evaluation
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assessment
2.5. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Metabolomic Analysis of Cecal Contents
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of C3G Administration on Body Weight and Liver Index
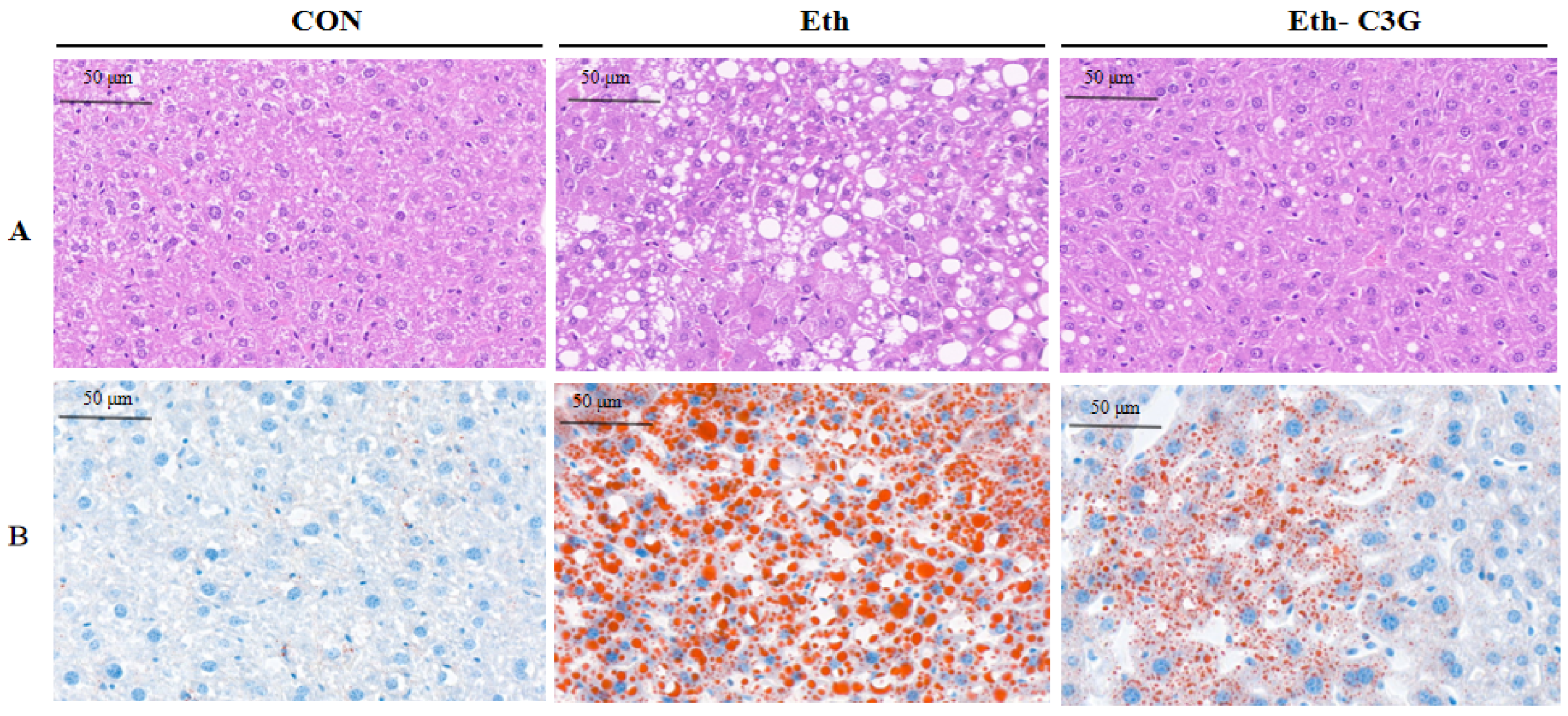
3.2. Effects of C3G on the Hepatic Histopathological Changes
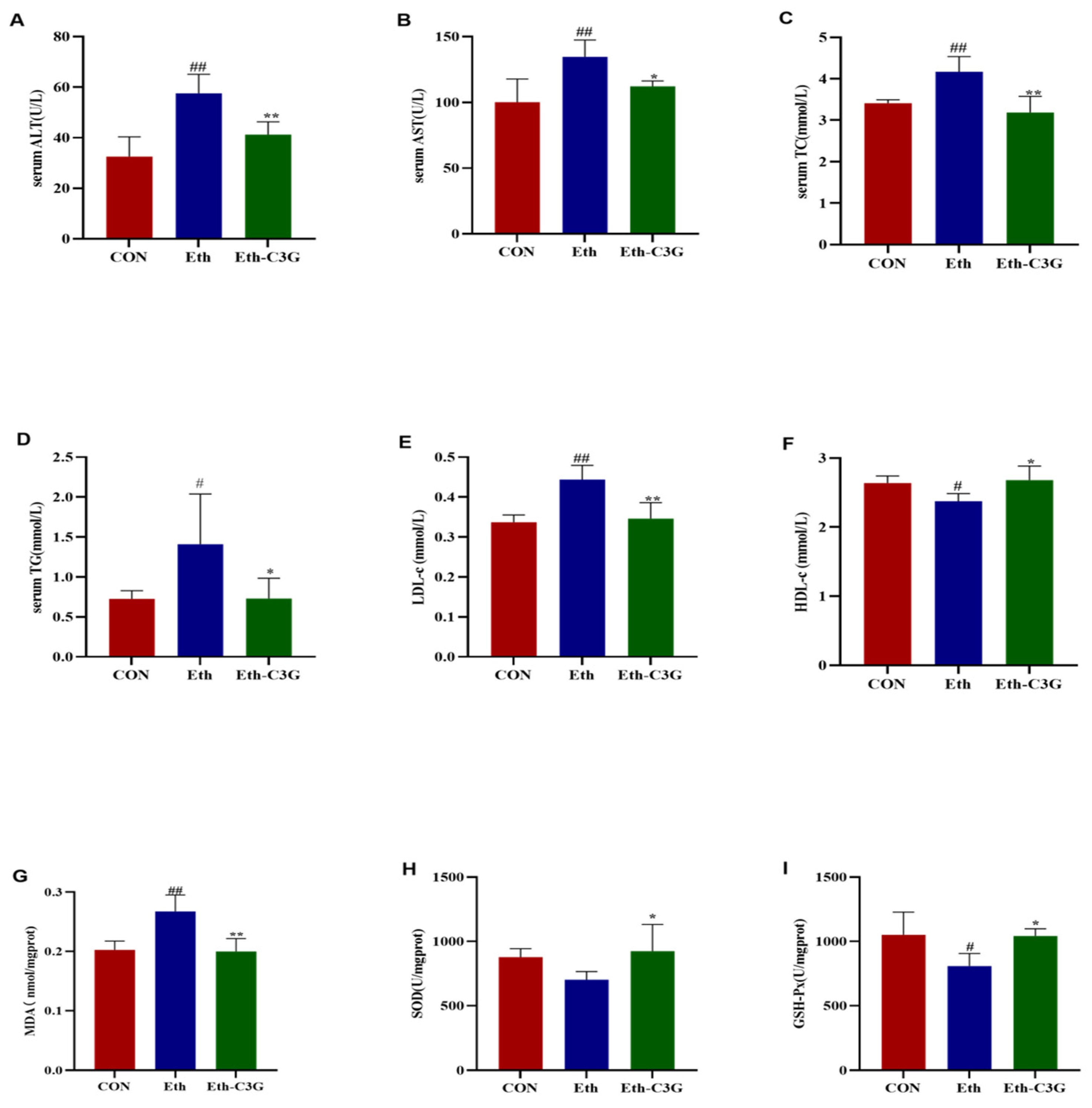
3.3. Effects of C3G on Biochemical Metabolic-Related Parameters
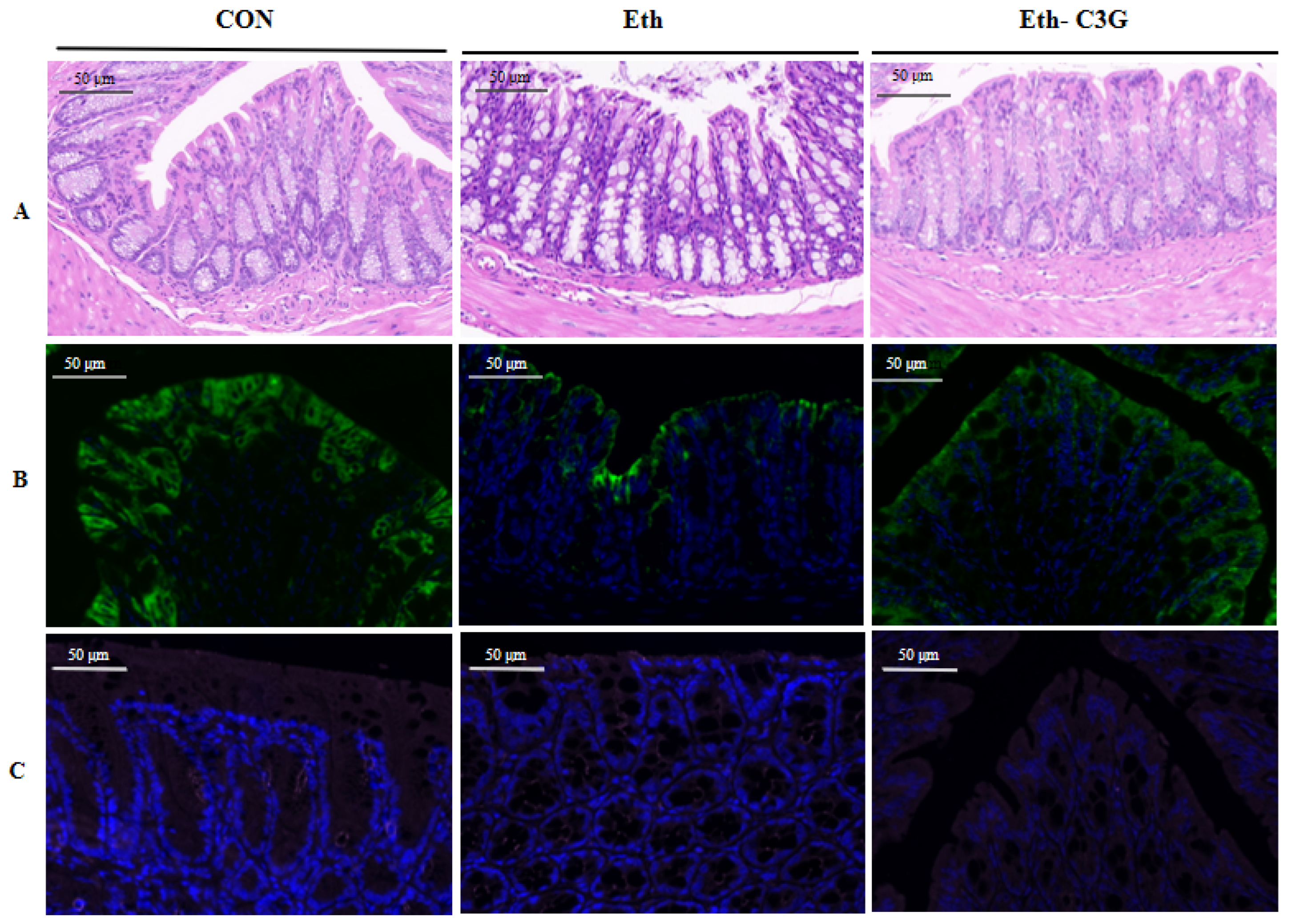
3.4. Effects of C3G on Intestinal Histopathological Feature
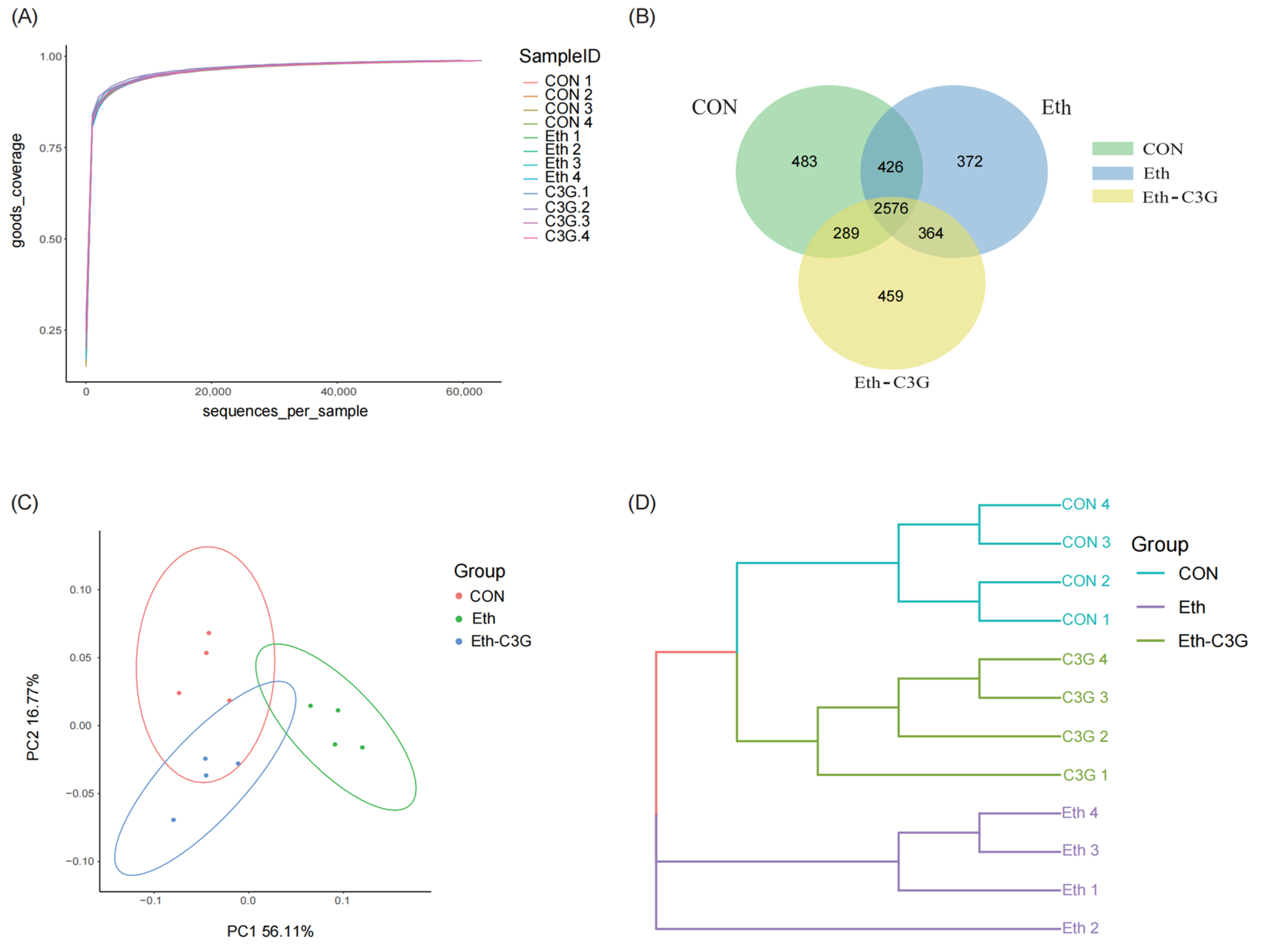
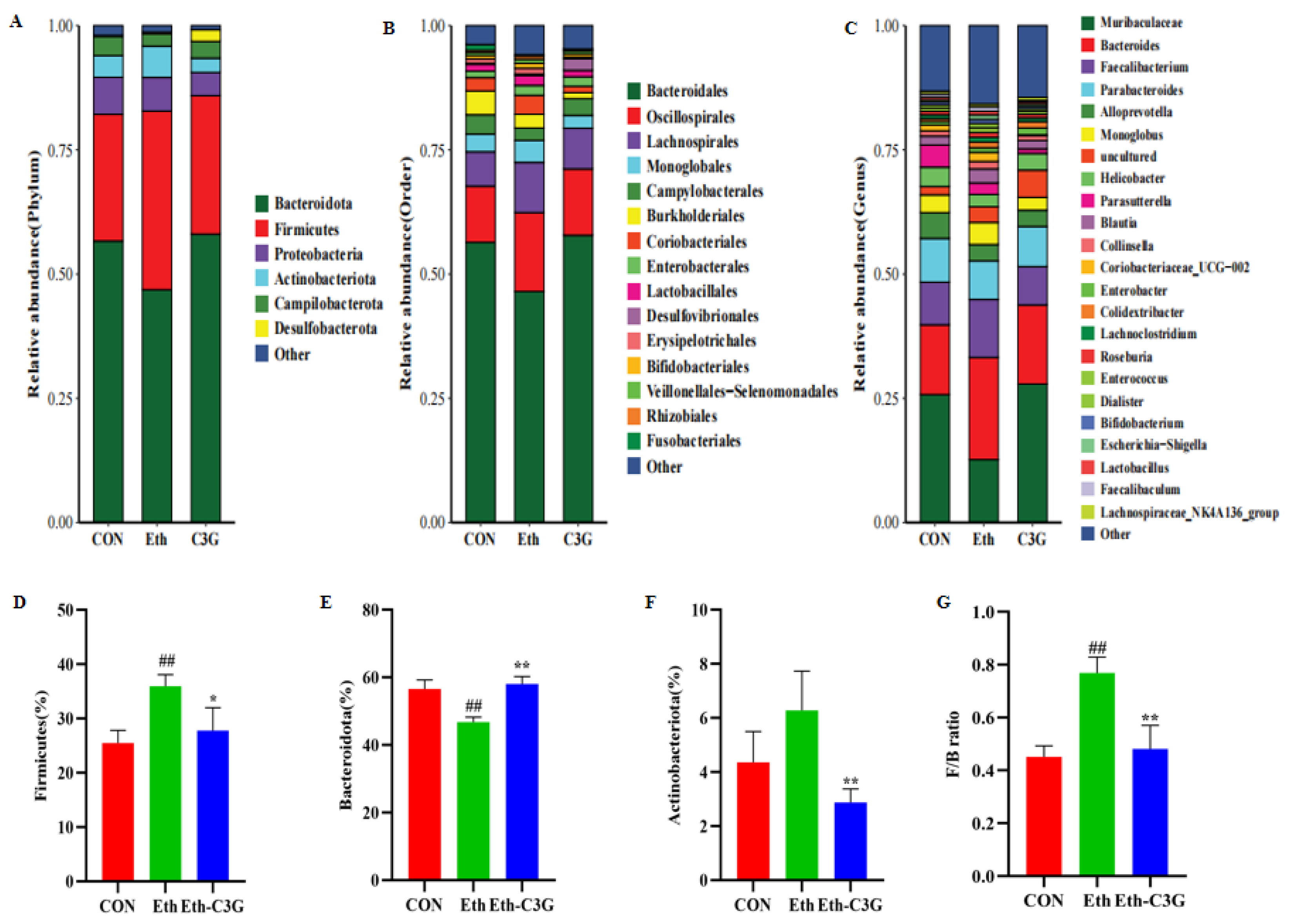
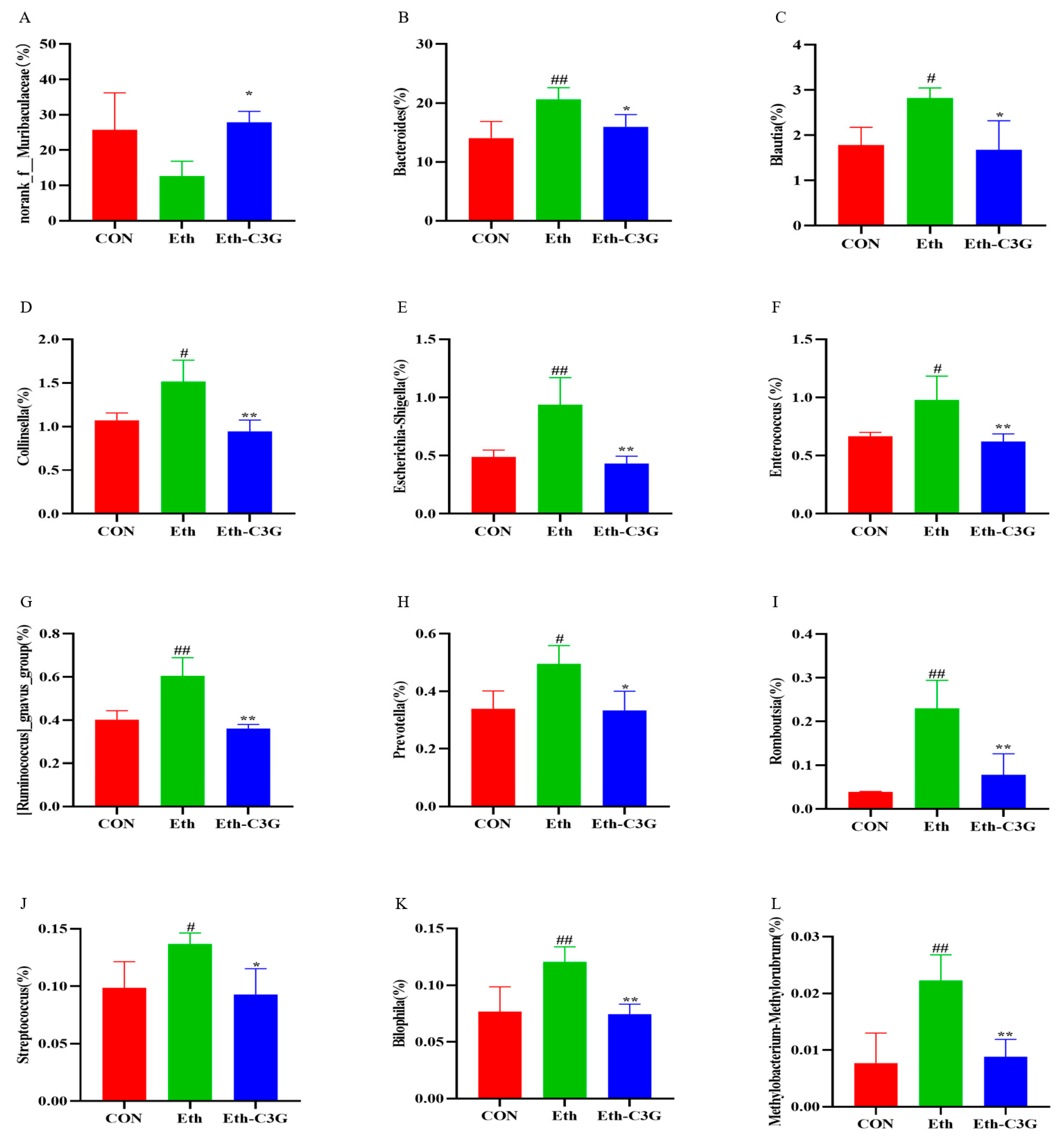
3.5. Effects of C3G on Gut Microbiota in Mice
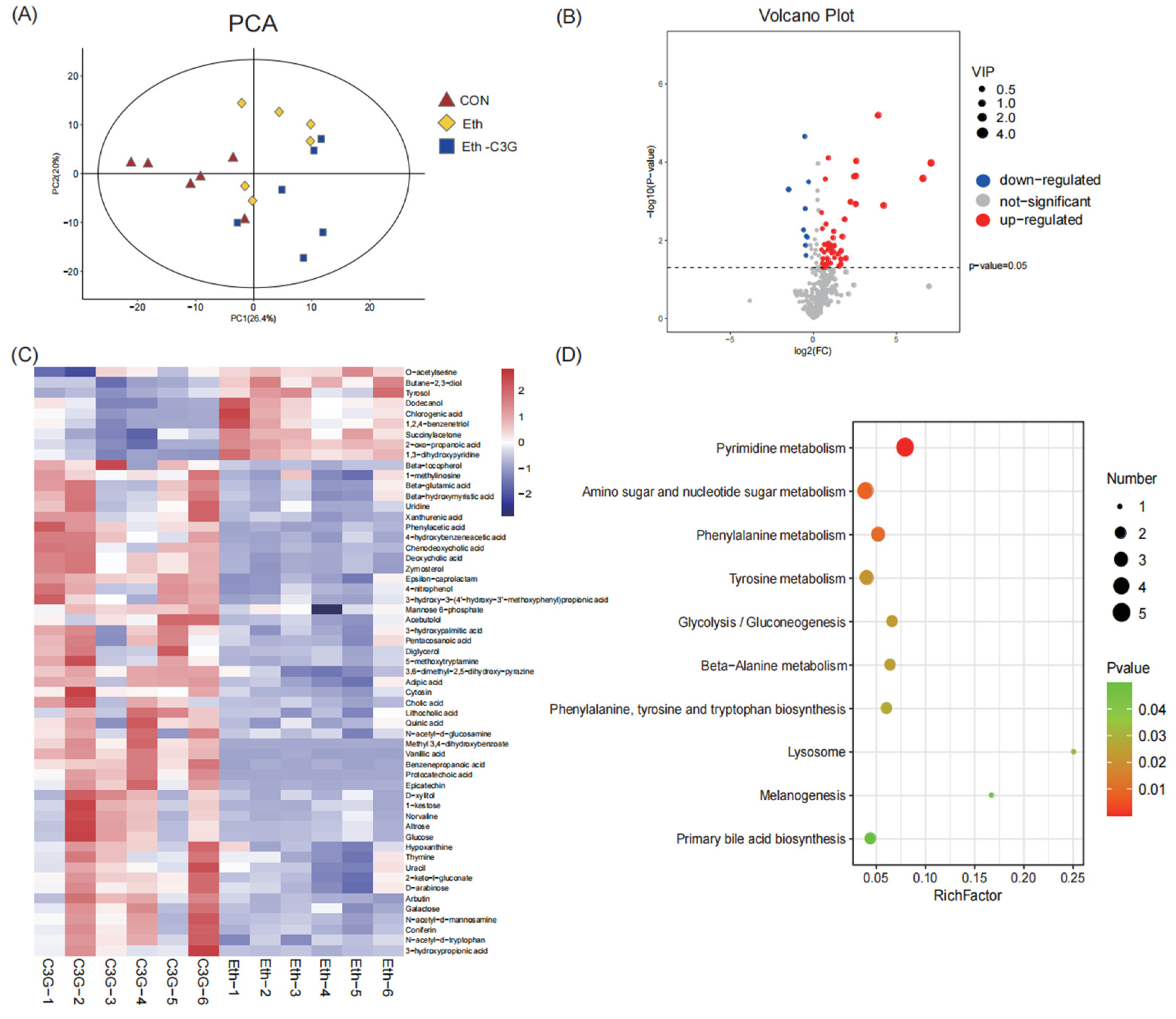
3.6. Effects of C3G on Profiles of Metabolites in Cecal Contents
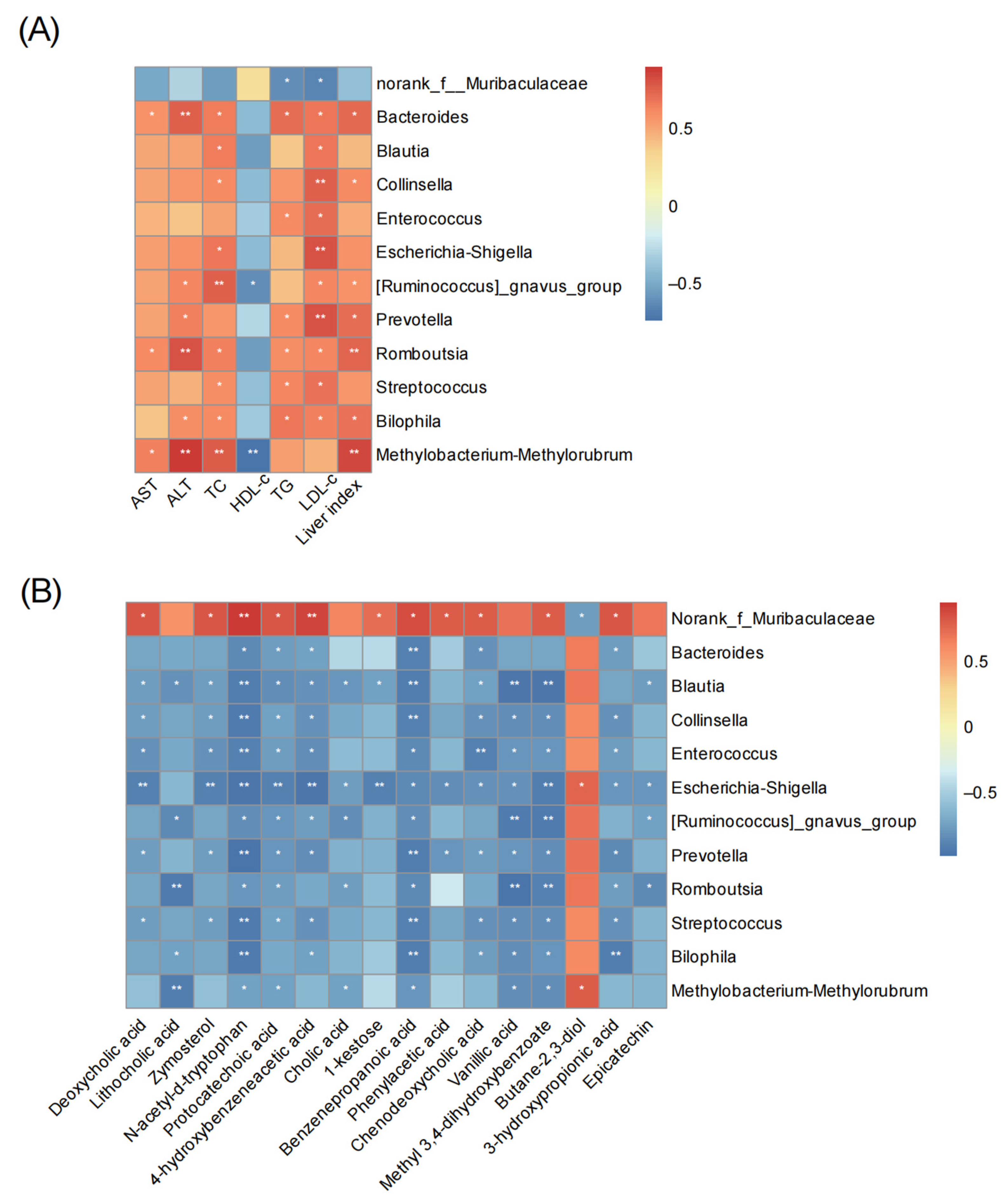
3.7. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thursz, M.; Kamath, P.; Mathurin, P.; Szabo, G.; Shah, V. Alcohol-related liver disease: Areas of consensus, unmet needs and opportunities for further study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, K.R.; Reinus, J. Spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznyak, V.; Rekve, D. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-92-4-156563-9. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565639 (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H. Identification and quantification of anthocyanins from the grains of black rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Nagao, N.; Itani, T.; Irifune, K. Anti-oxidative analysis, and identification and quantification of anthocyanin pigments in different coloured rice. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2783–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wu, T.; Hao, L. Ameliorative effect of black rice anthocyanin on senescent mice induced by D-galactose. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, J.; Tanabe, S.; Bergeron, C.; Gafner, S.; Grenier, D. Anthocyanin-rich black currant extract and cyanidin-3-O-glucoside have cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, M.Y.; Ahn, J.; Ha, T.Y. Hypolipidaemic effects of cyanidin 3-glucoside rich extract from black rice through regulating hepatic lipogenic enzyme activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3126–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamuangmorn, S.; Prom-U-Thai, C. The potential of high-anthocyanin purple rice as a functional ingredient in human health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtrakul, P.; Yodkeeree, S.; Pitchakarn, P.; Punfa, W. Suppression of inflammatory responses by black rice extract in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells via downregulation of NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.W.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.W.; Shen, T.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Shui, G.H.; Loor, J.; Fang, Z.Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.H.; et al. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3591–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.O.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, M.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.; et al. A dietary anthocyanin cyanidin-3-O-glucoside binds to PPARs to regulate glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Song, R.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wei, J.; et al. Dietary ursolic acid prevents alcohol-induced liver injury via gut-liver axis homeostasis modulation: The key role of microbiome manipulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7074–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Z.; Shen, X.C.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.D. Black rice anthocyanins alleviate hyperlipidemia, liver steatosis and insulin resistance by regulating lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in obese mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10160–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.Y.; Zhu, L.F.; Zhou, Y.P.; Han, S.; Cao, Y.Y.; Hu, Z.M.; Luo, Y.; Bao, L.Y.; Wu, X.X.; Qin, D.D.; et al. Laminarin ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage and its molecular mechanism in mice. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Jones, D.; Day, C.P. Alcoholic liver disease: New insights into mechanisms and preventative strategies. Trends Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.D.; Cao, Y.N.; Peng, L.X.; Yan, Z.Y.; Zhao, G. Coarse cereals and legume grains exert beneficial effects through their interaction with gut microbiota: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, G.M.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Diversity of the autochthonous colonic microbiota. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.L.; Deng, J.C.; Pan, Y.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Hong, J.L.; Shi, F.F.; Liu, G.L.; Qian, M.; Bai, W.D.; Zhang, W. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides and their relationships with the modulation of intestinal microflora in diabetic mice induced by high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Guo, W.L.; Li, Q.Y.; Xu, J.X.; Cao, Y.J.; Liu, B.; Yu, X.D.; Rao, P.F.; Ni, L.; Lv, X.C. The protective mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum FZU3013 against non-alcoholic fatty liver associated with hyperlipidemia in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3316–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Zhao, F.F.; Wang, T.R.; Xu, Y.Y.; Qiu, J.; Qian, Y.Z. Host metabolic disorders induced by alterations in intestinal flora under dietary pesticide exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6303–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Iftikhar, A.; Iftikhar, M.; Aboelenin, S.M.; Wang, C.T. Protective effects of ellagic acid against alcoholic liver disease in mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 744520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, H.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, W.F.; Guo, W.L.; Lv, X.C.; Rao, P.F.; Ni, L.; Liu, P.H. Auricularia auricula melanin protects against alcoholic liver injury and modulates intestinal microbiota composition in mice exposed to alcohol intake. Foods 2021, 10, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Q.Y.; Deng, H.T.; Wang, S.X.; EI-Seedi, H.; Cao, H.; Chen, L.; Teng, H. Dietary supplementation with casein/cyanidin-3-O-glucoside nanoparticles alters the gut microbiota in high-fat fed C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Chen, W.P.; Tu, C.; Jia, R.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, X.D.; Chu, Q. Food-derived cyanidin-3-O-glucoside alleviates oxidative stress: Evidence from the islet cell line and diabetic db/db mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11599–11610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.F.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, F.; Deng, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.X.; Wei, Z.C.; Tang, X.J.; Zhang, M.W. Lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) pulp phenolic extract provides protection against alcoholic liver injury in mice by alleviating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and liver inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9675–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Cimino, F.; Fratantonio, D.; Molonia, M.S.; Bashllari, R.; Busà, R.; Saija, A.; Speciale, A. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside modulates the in vitro inflammatory crosstalk between intestinal epithelial and endothelial cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 3454023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.Q.; Wu, T.; Zhang, L.; Wan, J.; Ruan, Z. Chlorogenic acid improves the intestinal barrier by relieving endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibiting ROCK/MLCK signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4562–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Etxeberria, U.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Hul, M.V.; Everard, A.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Rhubarb extract prevents hepatic inflammation induced by acute alcohol intake, an effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Wieser, V.; Lowe, P.; Wrzosek, L.; Gyongyosi, B.; Ward, D.V.; Grabherr, F.; Gerner, R.R.; Pfister, A.; et al. Recovery of ethanol-induced Akkermansia muciniphila depletion ameliorates alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2018, 67, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinkina, V.B.; Tyakht, A.V.; Odintsova, V.Y.; Yarygin, K.S.; Kovarsky, B.; Pavlenko, A.V.; Ischenko, D.S.; Popenko, A.S.; Alexeev, D.G.; Taraskina, A.Y.; et al. Links of gut microbiota composition with alcohol dependence syndrome and alcoholic liver disease. Microbiome 2017, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Gao, R.Y.; Yan, X.B.; Huang, L.S.; Qin, H.L. Probiotics improve gut microbiota dysbiosis in obese mice fed a high-fat or high-sucrose diet. Nutrition 2019, 60, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.J.; Zheng, X.J.; Ma, X.H.; Jiang, R.Q.; Zhou, W.Y.; Zhou, S.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lei, S.; Wang, S.L.; Kuang, J.L.; et al. Theabrownin from Pu-erh tea attenuates hypercholesterolemia via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.W.; Fouts, D.E.; Brandl, J.; Stärkel, P.; Torralba, M.; Schott, E.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.J.; Wang, Y.S.; You, Y.; Ai, Z.Y.; Dai, W.C.; Piao, C.H.; Liu, J.M.; Wang, Y.H. Fermented ginseng improved alcohol liver injury in association with changes in the gut microbiota of mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5566–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhao, R.Z.; Xia, M.; Shen, G.X. Impact of cyanidin-3-glucoside on gut microbiota and relationship with metabolism and inflammation in high fat-high sucrose diet-induced insulin resistant mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, Y.K.; Wang, X.H.; Luo, L.Y.; Sun, K.; Zeng, L. Gut microbiome and metabolome response of Pu-erh tea on metabolism disorder induced by chronic alcohol consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6615–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, R.G.; Pan, J.L.; Qi, D.F.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.Y. The protective effects of walnut green husk polysaccharide on liver injury, vascular endothelial dysfunction and disorder of gut microbiota in high fructose-induced mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.M.; Li, M.X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.X.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Z.G.; Zhao, Y.S.; Du, F.K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.G.; et al. Excessive intake of longan arillus alters gut homeostasis and aggravates colitis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 640417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caricilli, A.M.; Castoldi, A.; Câmara, N.O.S. Intestinal barrier: Agentlemen’s agreement between microbiota and immunity. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Manasson, J.; Scher, J.U. The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease. BMJ 2018, 360, j5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addolorato, G.; Ponziani, F.R.; Dionisi, T.; Mosoni, C.; Vassallo, G.A.; Sestito, L.; Petito, V.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E.; Tarli, C.; et al. Gut microbiota compositional and functional fingerprint in patients with alcohol use disorder and alcohol associated liver disease. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.D.; Sun, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Fan, J.G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajo-Pescado, S.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Juarez-Fernández, M.; Cuevas, M.J.; Mauriz, J.L.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Beneficial effects of exercise on gut microbiota functionality and barrier integrity, and gut-liver crosstalk in an in vivo model of early obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.C.; Cao, F.W.; Lai, S.L.; Zhuge, H.; Chang, K.X.; Valencak, T.G.; Liu, J.X.; Li, S.T.; Ren, D.X. Lactobacillus plantarum ZY08 relieves chronic alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and liver injury in mice via restoring intestinal flora homeostasis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astbury, S.; Atallah, E.; Vijay, A.; Aithal, P.G.; Grove, J.; Valdes, M.A. Lower gut microbiome diversity and higher abundance of proinflammatory genus Collinsella are associated with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Astbury, S.; Roy, C.L.; Spector, T.D.; Valdes, A.M. The prebiotic effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation: A six-week randomised intervention trial. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1863133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Y.; Song, H.; Zhang, X.J.; Song, G.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Ding, X.F.; Duan, X.G.; Li, L.F.; Sun, T.W.; Kan, Q.C. Metformin attenuated sepsis-related liver injury by modulating gut microbiota. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Llorente, C.; Lang, S.; Brandl, K.; Chu, H.K.; Jiang, L.; White, R.C.; Clarke, T.H.; Nguyen, K.; Torralba, M.; et al. Bacteriophage targeting of gut bacterium attenuates alcoholic liver disease. Nature 2019, 575, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, C.J.; Yao, W.C.; Zhu, D.F.; Lu, H.F.; Li, L.; Ma, B.; Sun, B.; Xue, D.B.; Zhang, W.H. Intestinal flora imbalance affects bile acid metabolism and is associated with gallstone formation. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierico, F.D.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; Stefanis, C.D.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cao, S.J.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Liu, C.; Qiu, F.; Kang, N. Berberrubine, a main metabolite of berberine, alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating glucose and lipid metabolism and restoring gut microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 913378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.D.; Cui, P.; Jiang, J.J.; Ning, C.Y.; Liang, B.Y.; Zhou, J.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, T.; Zuo, T.P.; et al. Streptococcus, the predominant bacterium to predict the severity of liver injury in alcoholic liver disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 649060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.C.; Xu, J.X.; Zeng, C.F.; Zhao, X.H.; Li, L.Q.; Qi, L.N. Gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after extended hepatectomy liver failure. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.Y.; Wu, Q.L.; Leung, K.S.; Kundi, Z.M.; Savidge, T.C.; EI-Nezami, H. Yeast β-glucan reduces obesity-associated Bilophila abundance and modulates bile acid metabolism in healthy and high-fat diet mouse models. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G639–G655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: Metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharat, D.; Cavalcanti, R.R.M.; Petersen, C.; Begaye, N.; Cutler, B.R.; Costa, M.M.A.; Ramos, R.K.L.G.; Ferreira, M.R.; Li, Y.Y.; Bharath, L.P.; et al. Blueberry metabolites attenuate lipotoxicity-induced endothelial dysfunction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ferrars, R.M.; Czank, C.; Zhang, Q.; Botting, N.P.; Kroon, P.A.; Cassidy, A.; Kay, C.D. The pharmacokinetic of anthocyanins and their metabolites in humans. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3268–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.Y.; Huang, R.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Han, S.S.; Qin, X.C.; Li, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.Q.; Wang, T.; Xia, B.; et al. Protocatechuic acid ameliorates high fat diet-Induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.J.; Hu, R.Z.; Gong, J.T.; Fang, C.K.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, M.; He, Z.Y.; Hou, D.X.; Zhang, H.F.; He, J.H.; et al. Protection against metabolic associated fatty liver disease by protocatechuic acid. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2238959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.X.; Tian, R.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Xue, H.M.; Zhang, R.Z.; Han, S.P.; Ji, L.; Huang, W.D.; Zhan, J.C.; You, Y.L. Research progress on intervention effect and mechanism of protocatechuic acid on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 9053–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, M.X.; Sun, H.X.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Chen, G.L.; Yu, Q.H.; Deng, C.S.; Zhu, W.; Song, J.P. Vanillic acid attenuates H2O2-induced injury in H9c2 cells by regulating mitophagy via the PINK1/Parkin/Mfn2 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 976156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekari, S.; Khonsha, F.; Rahmati-Yamchi, M.; Nejabati, H.R.; Mota, A. Vanillic acid and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A focus on AMPK in adipose and liver tissues. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4686–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.Z.; He, Z.Y.; Liu, M.; Tan, J.J.; Zhang, H.F.; Hou, D.X.; He, J.H.; Wu, S.S. Dietary protocatechuic acid ameliorates inflammation and up-regulates intestinal tight junction proteins by modulating gut microbiota in LPS-challenged piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.J.; Li, Y.L.; Hou, D.X.; Wu, S.S. The effects and mechanisms of cyanidin-3-glucoside and its phenolic metabolites in maintaining intestinal integrity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Guo, S.; Lu, Y.Y.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Shang, E.X.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhang, W.H.; Duan, J.A. Lycium barbarum L. leaves ameliorate type 2 diabetes in rats by modulating metabolic profiles and gut microbiota composition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthiah, M.D.; Smirnova, E.; Puri, P.; Chalasani, N.; Shah, V.H.; Kiani, C.; Taylor, S.; Mirshahi, F.; Sanyal, A.J. Development of alcohol-associated hepatitis is associated with specific changes in gut-modified bile acids. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1073–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Cao, F.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, T.; Yan, S.; Xie, Q.; Xia, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, G.; et al. Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050694
Zhu L, Cao F, Hu Z, Zhou Y, Guo T, Yan S, Xie Q, Xia X, Yuan H, Li G, et al. Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050694
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lingfeng, Fuliang Cao, Zuomin Hu, Yaping Zhou, Tianyi Guo, Sisi Yan, Qiutao Xie, Xinxin Xia, Hongyan Yuan, Gaoyang Li, and et al. 2024. "Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050694
APA StyleZhu, L., Cao, F., Hu, Z., Zhou, Y., Guo, T., Yan, S., Xie, Q., Xia, X., Yuan, H., Li, G., Luo, F., & Lin, Q. (2024). Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Injury via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Nutrients, 16(5), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050694





