Kinetics of Cellular Cobalamin Uptake and Conversion: Comparison of Aquo/Hydroxocobalamin to Cyanocobalamin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Accumulation of Radioactive 57Cbl in HeLa Cells
2.3. Extraction of Cbls from Cells
2.4. Measurements of Radioactivity
2.5. HPLC Separation of Cbls
2.6. Computer Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Exploratory Tests of Cbl Uptake by HeLa Cells (24 h)
3.2. Time-Dependent Accumulation of Cbl in HeLa Cells
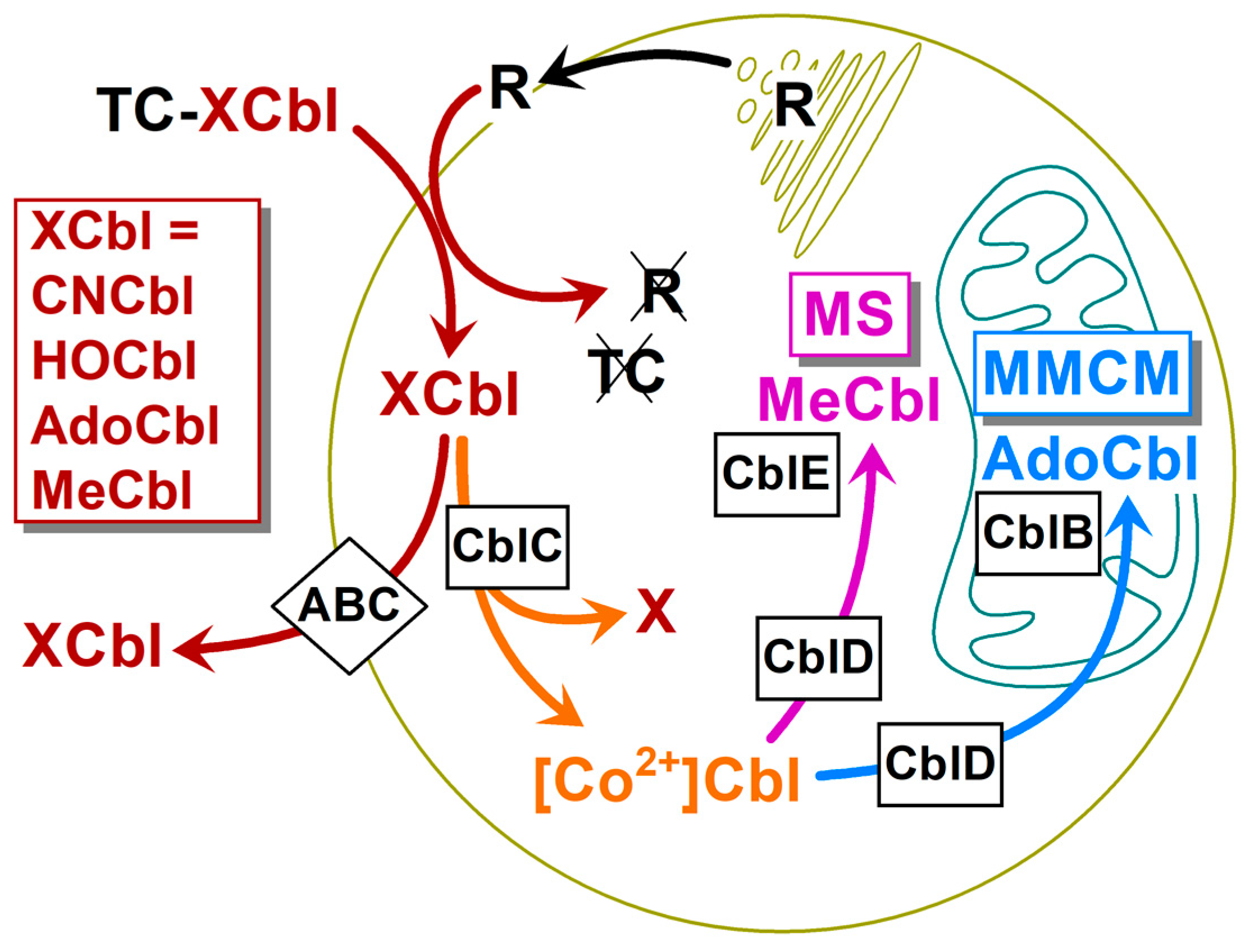
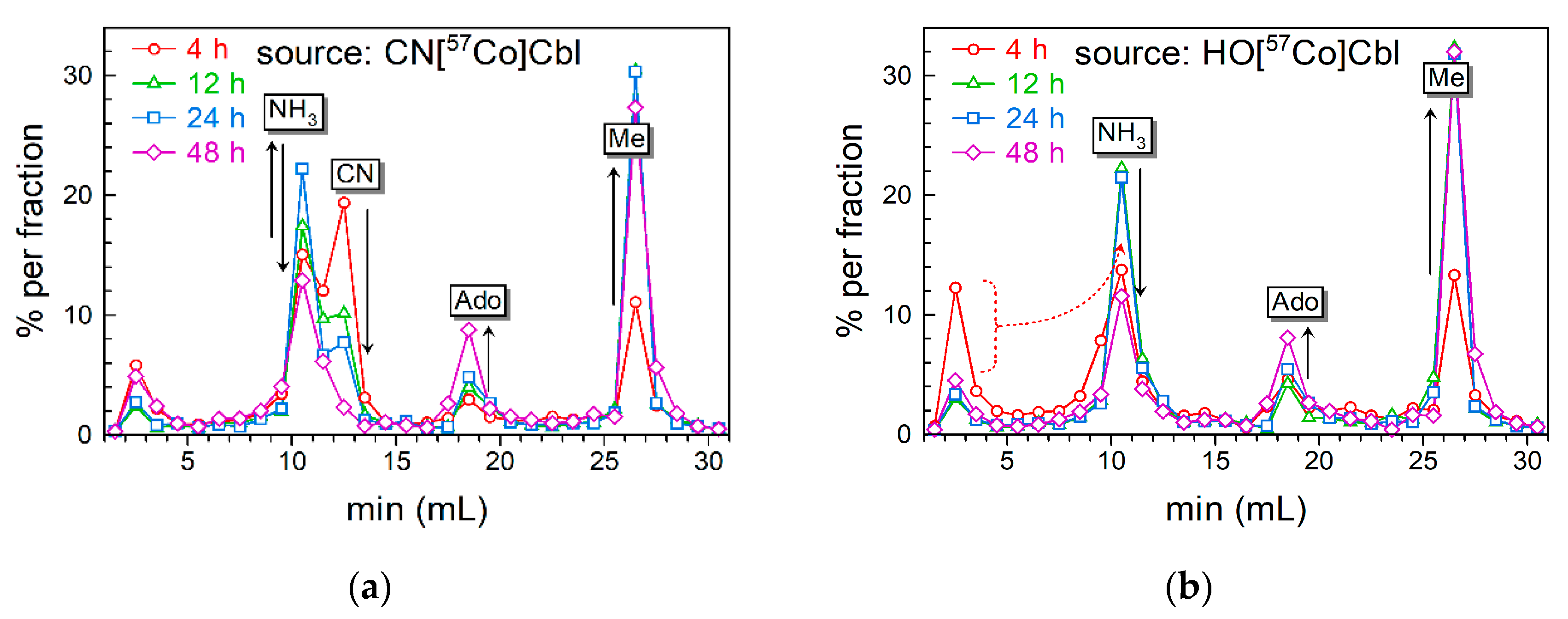
3.3. Intracellular Cbls and The Extraction and Analysis of Cbl Forms by HPLC
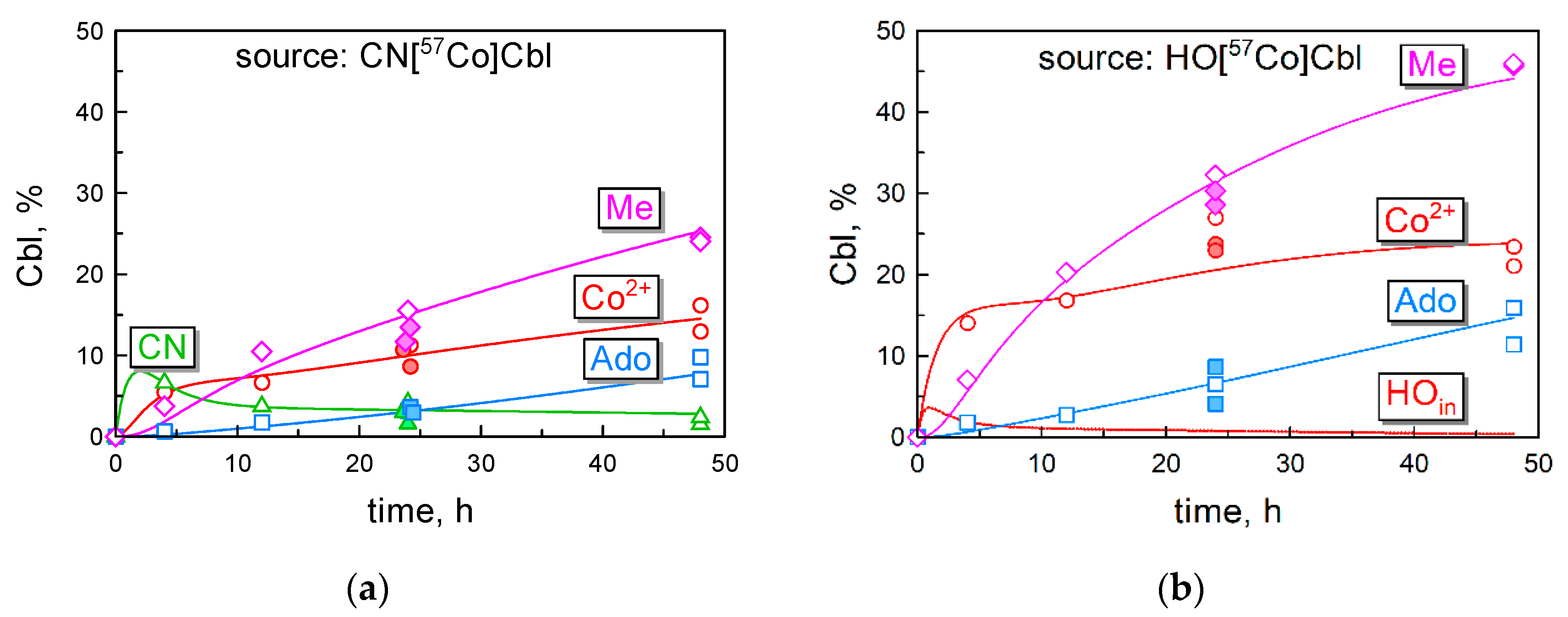
3.4. Transformations of the Intracellular Cbls over Time
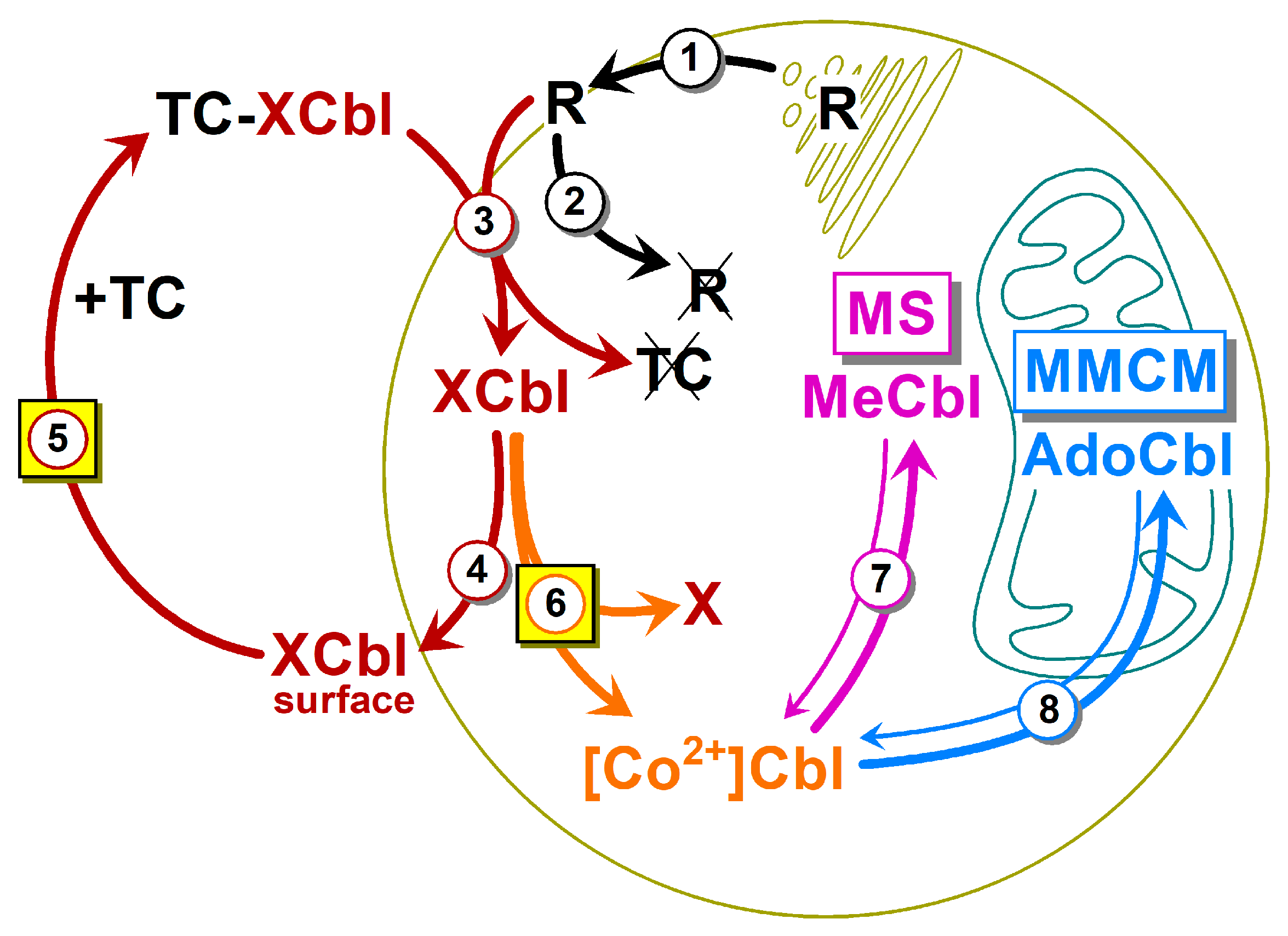
3.5. Kinetic Model of Cbl Uptake and Its Intracellular Transformations
| Step | Parameter | Value | Step | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | v1 (R synthesis) | 4% h−1 | 6CN | k6 (reduction to Co2+) | 0.27 h−1 |
| 2 | k2 (futile R-clearance) | 0.1 h−1 | 6OH | k6(reduction to Co2+) | 1.8 h−1 |
| 3 | k3 (R+TC-Cbl uptake) | 0.003% h−1 | 7+ | k+7 (MeCbl synthesis) | 0.2 h−1 |
| 4 | k4 (Cbl cell → surface) | 0.5 h−1 | 7− | k−7 (MeCbl→ [Co2+]) | 0.1 h−1 |
| 5CN | k5 (Cbl→ medium + TC) | 0.16 h−1 | 8+ | k+8 (AdoCbl synthesis) | 0.02 h−1 |
| 5OH | k5 (Cbl→ medium + TC) | 0.04 h−1 | 8− | k−8 (AdoCbl→ [Co2+]) | 0.01 h−1 |
4. Discussion
4.1. General Observations
4.2. Kinetic Model: Fusion of Several Metabolic Steps into One
4.3. Kinetic Model: Steps 1–3, the Circulation of the Surface Receptor R, and the Internalization of Cbl
4.4. Kinetic Model: Steps 4 and 5, the Recirculation of the Unprocessed Cbl
4.5. Kinetic Model: Step 6, the Reduction of the Internalized Cbl
4.6. Kinetic Model: Steps 7 and 8, the Synthesis of MeCbl and AdoCbl
4.7. Study Limitations
4.8. Potential Inferences Relevant to B12 Treatment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, Z.; Stroinski, A. Comprehensive B12. Chemistry, Biochemistry, Nutrition, Ecology, Medicine; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Allen, L.H.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Brito, A.; Guéant, J.L.; Miller, J.W.; Molloy, A.M.; Nexo, E.; Stabler, S.; Toh, B.H.; et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyńska-Malefora, A.; Delvin, E.; McCaddon, A.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Harrington, D.J. Vitamin B12 status in health and disease: A critical review. Diagnosis of deficiency and insufficiency—Clinical and laboratory pitfalls. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 399–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, J.-H.; Barg, H.; Warren, M.; Jahn, D. Microbial production of vitamin B12. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 58, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, C.L.; Santschi, D.E.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H. Apparent ruminal synthesis and intestinal disappearance of vitamin B12 and its analogs in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadros, E.V. Advances in the Understanding of Cobalamin Assimilation and Metabolism. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedosov, S.N. Physiological and molecular aspects of cobalamin transport. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 56, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gick, G.G.; Arora, K.; Sequeira, J.M.; Nakayama, Y.; Lai, S.C.; Quadros, E.V. Cellular uptake of vitamin B12: Role and fate of TCblR/CD320, the transcobalamin receptor. Exp. Cell. Res. 2020, 396, 112256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, J.M. Inorganic Chemistry of Vitamin B12; Academic Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1972; ISBN 0125640501. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, H.M. The inorganic chemistry of the cobalt corrinoids—An update. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2023, 242, 112154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, L.; Kim, J.; Brasch, N.E.; Wang, S.; Rosenblatt, D.S.; Banerjee, R.; Jacobsen, D.W. Processing of alkylcobalamins in mammalian cells: A role for the MMACHC (cblC) gene product. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 97, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Gouda, H.; Pillay, S. Redox-Linked Coordination Chemistry Directs Vitamin B12 Trafficking. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2003–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gherasim, C.; Lesniak, N.A.; Banerjee, R. Glutathione-dependent one-electron transfer reactions catalyzed by a B12 trafficking protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16487–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräutler, B. Antivitamins B12—Same inaugural milestones. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 15438–15445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beedholm-Ebsen, R.; van de Wetering, K.; Hardlei, T.; Nexø, E.; Borst, P.; Moestrup, S.K. Identification of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) as a molecular gate for cellular export of cobalamin. Blood 2010, 115, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, L.; Bolisetty, K.; Axhemi, A.; DiBello, P.M.; Quadros, E.V.; Fedosov, S.; Jacobsen, D.W. Transcellular transport of cobalamin in aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5506–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, C.; Hannibal, L.; Rajagopalan, D.; Jacobsen, D.W.; Banerjee, R. The C-terminal domain of CblD interacts with CblC and influences intracellular cobalamin partitioning. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kräutler, B.; Puffer, B. Vitamin B12–derivatives: Organometallic catalysts, cofactors and ligands of bio–macromolecules. In Handbook of Porphyrin Science; Kadish, K.M., Smith, K.M., Guilard, R., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore; London, UK, 2012; Volume 21–25, pp. 133–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Willard, H.F.; Youngdahl-Turner, P.; Rosenberg, L.E. Cobalamin coenzyme synthesis in normal and mutant human fibroblasts. Evidence for a processing enzyme activity deficient in cblC cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 11847–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.A.; Begley, J.A.; Green-Colligan, P.D. The availability of therapeutic hydroxocobalamin to cells. Blood 1984, 63, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, R.C.; Begley, J.A.; Colligan, P.D.; Hall, C.A. The methylcobalamin metabolism of cultured human fibroblasts. Metabolism 1993, 42, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutti, E.; Ruetz, M.; Birn, H.; Kräutler, B.; Nexo, E. 4-ethylphenyl-cobalamin impairs tissue uptake of vitamin B12 and causes vitamin B12 deficiency in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suormala, T.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Coelho, D.; Zavadakova, P.; Kozich, V.; Koch, H.G.; Berghaüser, M.; Wraith, J.E.; Burlina, A.; Sewell, A.; et al. The cblD defect causes either isolated or combined deficiency of methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42742–42749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannibal, L.; Axhemi, A.; Glushchenko, A.V.; Moreira, E.S.; Brasch, N.E.; Jacobsen, D.W. Accurate assessment and identification of naturally occurring cellular cobalamins. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnell, J.C.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Hussein, H.A.; Wise, I.J.; Matthews, D.M. Tissue Distribution of Coenzyme and other Forms of Vitamin B12 in Control Subjects and Patients with Pernicious Anaemia. Clin. Sci. Mol. Med. 1974, 46, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, E.V.; Matthews, D.M.; Wise, I.J.; Linnell, J.C. Tissue distribution of endogenous cobalamins and other corrins in the rat, cat and guinea pig. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 421, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.J.; Gruner, T.M.; Sykes, A.R. Development of a method for the separation of corrinoids in ovine tissues by HPLC. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedosov, S.N.; Nexo, E.; Heegaard, C.W. Low methylcobalamin in liver tissues is an artifact as shown by a revised extraction procedure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2023, 1867, 130315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornerup, L.S.; Juul, C.B.; Fedosov, S.N.; Heegaard, C.W.; Greibe, E.; Nexo, E. Absorption and retention of free and milk protein-bound cyano- and hydroxocobalamins. An experimental study in rats. Biochimie 2016, 126, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Recent advances in the chemistry of vitamin B 12 and vitamin B 12 model compounds: Reductive cobalt-carbon bond cleavage reactions. Pure Appl. Chem. 1973, 33, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Kroenke, C.D.; Song, J.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Ackerman, J.J.; Neil, J.J. Intracellular water-specific MR of microbead-adherent cells: The HeLa cell intracellular water exchange lifetime. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Accarino, E.; Herrera-Montávez, C.; Ramón, Y.; Cajal, S.; Aasen, T. Spontaneous cell detachment and reattachment in cancer cell lines: An in vitro model of metastasis and malignancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacser, H.; Acerenza, L. A universal method for achieving increases in metabolite production. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 216, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legent, G.; Thellier, M.; Norris, V.; Ripoll, C. Steady-state kinetic behaviour of two- or n-enzyme systems made of free sequential enzymes involved in a metabolic pathway. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2006, 329, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, E.V.; Sequeira, J.M. Cellular uptake of cobalamin: Transcobalamin and the TCblR/CD320 receptor. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.S.D.; Treston, A.M.; Bowman, E.P.W.; Owens, J.A.; Cooksley, W.G.E. The regulatory roles of liver and kidney in cobalamin (vitamin B12) metabolism in the rat: The uptake and intracellular binding of cobalamin and the activity of the cobalamin-dependent enzymes in response to varying cobalamin supply. Clin. Sci. 1984, 67, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Pasanna, R.M.; Shamshuddin, Z.; Bhat, K.; Sivadas, A.; Mandal, A.K.; Kurpad, A.V. Measuring vitamin B-12 bioavailability with [13C]-cyanocobalamin in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yamada, S.; Tobimatsu, T.; Toraya, T. Heterologous high level expression, purification, and enzymological properties of recombinant rat cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35571–35576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolovskaya, O.M.; Plessl, T.; Bailey, H.; Mackinnon, S.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Yue, W.W.; Froese, D.S.; Taga, M.E. Naturally occurring cobalamin (B12) analogs can function as cofactors for human methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Biochimie 2021, 183, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greibe, E.; Nymark, O.; Fedosov, S.N.; Heegaard, C.W.; Nexo, E. Differences in tissue distribution of cyano–B12 and hydroxo–B12 one week after oral intake: An experimental study in male Wistar rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, C.B.; Fedosov, S.N.; Nexo, E.; Heegaard, C.W. Kinetic analysis of transcellular passage of the cobalamin–transcobalamin complex in Caco-2 monolayers. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, S.; Mahalle, N.; Greibe, E.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Heegaard, C.W.; Nexo, E.; Fedosov, S.N. Cyano-B12 or whey powder with endogenous hydroxo-B12 for supplementation in B12 deficient lactovegetarians. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | CN[57Co]Cbl, % | HO[57Co]Cbl, % | p of Equal Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular content | 28.5 ± 3.6 | 57.6 ± 4.2 | 0.0008 |
| Cell-free medium | 47.4 ± 4.4 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | 0.002 |
| Cell surface | 7.9 ± 2.2 | 6.9 ± 1.5 | 0.98 |
| Unaccounted loss | 14.6 ± 2.1 | 19.8 ± 4.2 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fedosov, S.N.; Nexo, E.; Heegaard, C.W. Kinetics of Cellular Cobalamin Uptake and Conversion: Comparison of Aquo/Hydroxocobalamin to Cyanocobalamin. Nutrients 2024, 16, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030378
Fedosov SN, Nexo E, Heegaard CW. Kinetics of Cellular Cobalamin Uptake and Conversion: Comparison of Aquo/Hydroxocobalamin to Cyanocobalamin. Nutrients. 2024; 16(3):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030378
Chicago/Turabian StyleFedosov, Sergey N., Ebba Nexo, and Christian W. Heegaard. 2024. "Kinetics of Cellular Cobalamin Uptake and Conversion: Comparison of Aquo/Hydroxocobalamin to Cyanocobalamin" Nutrients 16, no. 3: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030378
APA StyleFedosov, S. N., Nexo, E., & Heegaard, C. W. (2024). Kinetics of Cellular Cobalamin Uptake and Conversion: Comparison of Aquo/Hydroxocobalamin to Cyanocobalamin. Nutrients, 16(3), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030378







