Genetic Risk, BMI Status, BMI Change Patterns, and the Risk of Steatotic Liver Disease and Liver Enzyme Elevation in Chinese Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Genotyping and PRS Calculation
2.3. Measurement of Exposure: BMI and BMI Change Pattern
2.4. Measurement of Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Enzymes
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Participants
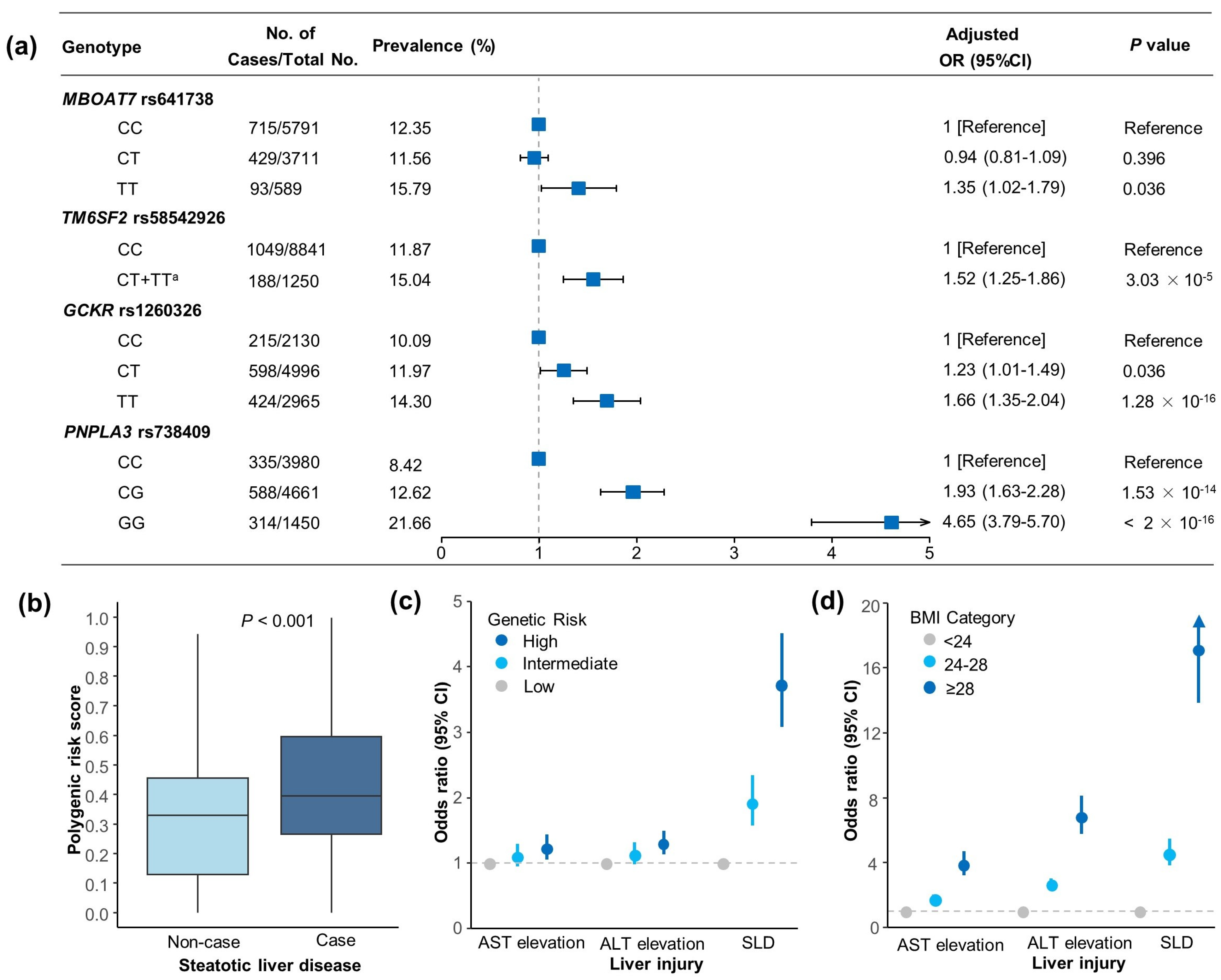
3.2. Genetic Associations with SLD and Liver Enzyme Elevation Risk
3.3. Associations of BMI with SLD and Liver Enzyme Elevation Risk
3.4. Joint Association and Interaction of BMI and PRS in SLD and Liver Enzyme Elevation Risk
3.5. Relations of BMI Change Pattern and SLD and Aminotransferase Elevation
3.6. Joint Effect and Interaction of BMI Change Pattern and PRS in Incident SLD and Aminotransferase Elevation Risk
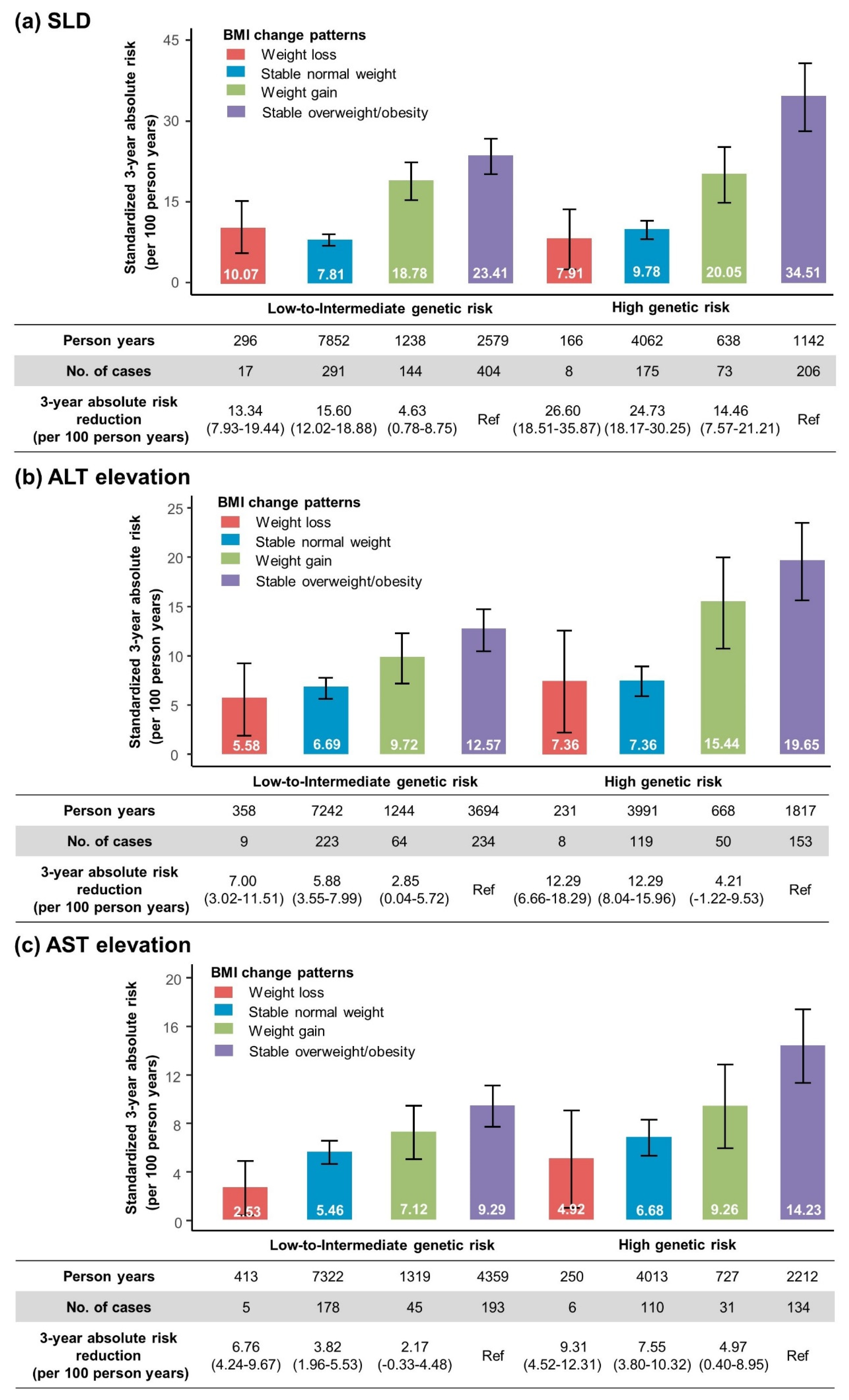
3.7. Standardized Three-Year Absolute Risk of SLD and Aminotransferase Elevation According to Genetic Risk and BMI Change Patterns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.; Rinella, M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, A.L.; Tavaglione, F.; Romeo, S.; Charlton, M. Endocrine aspects of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Beyond insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1524–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.W.; Yan, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhao, S.H.; Wang, B. Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanWagner, L.B.; Khan, S.S.; Ning, H.; Siddique, J.; Lewis, C.E.; Carr, J.J.; Vos, M.B.; Speliotes, E.; Terrault, N.A.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. Body mass index trajectories in young adulthood predict non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in middle age: The CARDIA cohort study. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Martinez-Perez, Y.; Calzadilla-Bertot, L.; Torres-Gonzalez, A.; Gra-Oramas, B.; Gonzalez-Fabian, L.; Friedman, S.L.; Diago, M.; Romero-Gomez, M. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 367–378.e5, quiz e14–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.Y.; Chang, Y.; Sung, E.; Kang, J.H.; Shin, H.; Wild, S.H.; Byrne, C.D.; Ryu, S. Weight Change and the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Metabolically Healthy Overweight Individuals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e583–e599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, G.; Hagiwara, Y.; Kimura, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Oba, K.; Masuda, K.; Matsuyama, Y. Impact of Body Weight Gain on the Incidence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Nonobese Japanese Individuals. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, M.C.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.; Cantor, R.M. Heritability of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Du, X.; Kuppa, A.; Feitosa, M.F.; Bielak, L.F.; O’Connell, J.R.; Musani, S.K.; Guo, X.; Kahali, B.; Chen, V.L.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies 17 loci associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincentis, A.; Tavaglione, F.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Picardi, A.; Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Valenti, L.; Romeo, S.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U. A Polygenic Risk Score to Refine Risk Stratification and Prediction for Severe Liver Disease by Clinical Fibrosis Scores. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Stinson, S.E.; Juel, H.B.; Lund, M.A.V.; Holm, L.A.; Fonvig, C.E.; Nielsen, T.; Grarup, N.; Pedersen, O.; Christiansen, M.; et al. An adult-based genetic risk score for liver fat associates with liver and plasma lipid traits in children and adolescents. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viitasalo, A.; Eloranta, A.M.; Atalay, M.; Romeo, S.; Pihlajamaki, J.; Lakka, T.A. Association of MBOAT7 gene variant with plasma ALT levels in children: The PANIC study. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stender, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Adiposity amplifies the genetic risk of fatty liver disease conferred by multiple loci. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, F.C.; Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, PR China. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, I.; Li, D.; Nasir, K.; Katz, R.; Larijani, V.N.; Budoff, M.J. Computed tomography scans in the evaluation of fatty liver disease in a population based study: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Acad. Radiol. 2012, 19, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwo, P.Y.; Cohen, S.M.; Lim, J.K. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unalp-Arida, A.; Ruhl, C.E. Noninvasive fatty liver markers predict liver disease mortality in the U.S. population. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, R.S.; Shu, S.S.; Cheung, B.H.; Li, L.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, C.K.; Leung, J.K.; Chu, W.C.; et al. Beneficial effects of lifestyle intervention in non-obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Jebb, S.A.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Cobbold, J.F.; Aveyard, P. Association of Weight Changes With Changes in Histological Features and Blood Markers in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e538–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Costanzo, A.; Belardinilli, F.; Bailetti, D.; Sponziello, M.; D’Erasmo, L.; Polimeni, L.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Ceci, F.; Montali, A.; et al. Evaluation of Polygenic Determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) By a Candidate Genes Resequencing Strategy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, C.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Pelusi, S.; Baselli, G.; Dongiovanni, P.; Zanoni, I.; Santoro, L.; Maier, S.; Liguori, A.; Meroni, M.; et al. Non-invasive stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver using polygenic risk scores. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.E.; Diergaarde, B.; Kuipers, A.L.; Adibi, J.J.; Luu, H.N.; Chang, X.; Dorajoo, R.; Heng, C.K.; Khor, C.C.; Wang, R.; et al. NAFLD polygenic risk score and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in an East Asian population. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Hennein, R.; Liu, C.; Long, M.T.; Hoffmann, U.; Jacques, P.F.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Hu, F.B.; Levy, D. Improved Diet Quality Associates With Reduction in Liver Fat, Particularly in Individuals With High Genetic Risk Scores for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellert-Kristensen, H.; Richardson, T.G.; Davey Smith, G.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Stender, S. Combined Effect of PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and HSD17B13 Variants on Risk of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the General Population. Hepatology 2020, 72, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurr, T.M.; Katz, S.F.; Justesen, J.M.; O’Sullivan, J.W.; Saliba-Gustafsson, P.; Assimes, T.L.; Carcamo-Orive, I.; Ahmed, A.; Ashley, E.A.; Hansen, T.; et al. Interactions of physical activity, muscular fitness, adiposity, and genetic risk for NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, C.A.; Haas, M.; Ajmera, V.; Simon, T.G.; Homburger, J.; Neben, C.; Jiang, L.; Wei, W.Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, A.; et al. Association of Genetic Variation With Cirrhosis: A Multi-Trait Genome-Wide Association and Gene-Environment Interaction Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1620–1633.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Wang, M.; Klarqvist, M.D.R.; Smith, K.; Shin, J.; Dashti, H.; Diamant, N.; Choi, S.H.; Jurgens, S.J.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Inherited basis of visceral, abdominal subcutaneous and gluteofemoral fat depots. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Total (N = 10,091) | Non-Steatotic Liver Disease (N = 8854) | Steatotic Liver Disease (N = 1237) | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, N(%) | ||||
| Male | 4923 (48.79) | 3952 (44.64) | 971 (78.50) | <0.001 |
| Female | 5168 (51.21) | 4902 (55.36) | 266 (21.50) | |
| Age (years), Mean ± SD | 38.29 ± 10.39 | 38.22 ± 10.40 | 38.81 ± 10.30 | 0.058 |
| Education level, N(%) | ||||
| High school or below | 609 (6.04) | 529 (5.97) | 80 (6.47) | 0.537 |
| College degree or above | 9482 (93.96) | 8325 (94.03) | 1157 (93.53) | |
| Smoking status, N(%) | ||||
| Never | 8457 (83.81) | 7565 (85.44) | 892 (72.11) | <0.001 |
| Ever | 1634 (16.19) | 1289 (14.56) | 345 (27.89) | |
| Drinking status, N(%) | ||||
| Never | 8460 (83.84) | 7537 (85.13) | 923 (74.62) | <0.001 |
| Ever | 1631 (16.16) | 1317 (14.87) | 314 (25.38) | |
| Regular physical activity, N(%) | ||||
| No | 6808 (67.47) | 5886 (66.48) | 922 (74.54) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 3283 (32.53) | 2968 (33.52) | 315 (25.46) | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2), Mean ± SD | 23.38 ± 3.34 | 22.85 ± 2.95 | 27.22 ± 3.45 | <0.001 |
| BMI category, N(%) | ||||
| <24 | 6166 (61.10) | 5961 (67.33) | 205 (16.57) | <0.001 |
| 24–28 | 3021 (29.94) | 2449 (27.66) | 572 (46.24) | |
| ≥28 | 904 (8.96) | 444 (5.01) | 460 (37.19) | |
| ALT (IU/L), Median (IQR) | 16.80 (11.80–25.90) | 15.50 (11.30–22.60) | 38.80 (26.40–57.50) | <0.001 |
| AST (IU/L), Median (IQR) | 19.70 (16.80–23.90) | 19.20 (16.50–22.80) | 27.00 (21.70–35.00) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, N(%) | ||||
| No | 8602 (85.24) | 7787 (87.95) | 815 (65.89) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1489 (14.76) | 1067 (12.05) | 422 (34.11) | |
| Diabetes, N(%) | ||||
| No | 9833 (97.44) | 8706 (98.33) | 1127 (91.11) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 258 (2.56) | 148 (1.67) | 110 (8.89) | |
| Hyperlipidemia, N(%) | ||||
| No | 7779 (77.09) | 7204 (81.36) | 575 (46.48) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 2312 (22.91) | 1650 (18.64) | 662 (53.52) | |
| Genetic risk category, N (%) | ||||
| Low | 3063 (30.35) | 2834 (32.01) | 229 (18.51) | <0.001 |
| Intermediate | 3406 (33.75) | 3026 (34.18) | 380 (30.72) | |
| High | 3622 (35.89) | 2994 (33.82) | 628 (50.77) |
| Outcome | Risk Reduction: Weight Loss Versus Stable Overweight/Obesity † | Risk Raise: Weight Gain Versus Stable Normal Weight ‡ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. (Cases) | HR (95%CI) § | p Value | Total No. (Cases) | HR (95%CI) § | p Value | |
| Steatotic liver disease | 1441 (635) | 0.29 (0.20–0.44) | 3.37 × 10−9 | 4683 (683) | 2.14 (1.81–2.53) | <2 × 10−16 |
| ALT elevation | 2072 (404) | 0.40 (0.25–0.66) | 2.94 × 10−4 | 4478 (456) | 1.62 (1.30–2.01) | 1.77 × 10−5 |
| AST elevation | 2460 (338) | 0.33 (0.18–0.60) | 2.77 × 10−4 | 4529 (364) | 1.27 (0.98–1.64) | 0.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Liu, M.; Guo, H.; Lin, F.; Ding, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Yu, C.; et al. Genetic Risk, BMI Status, BMI Change Patterns, and the Risk of Steatotic Liver Disease and Liver Enzyme Elevation in Chinese Adults. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234212
Yang J, Tian C, Liu M, Guo H, Lin F, Ding Y, Yao W, Zhang J, Fan J, Yu C, et al. Genetic Risk, BMI Status, BMI Change Patterns, and the Risk of Steatotic Liver Disease and Liver Enzyme Elevation in Chinese Adults. Nutrients. 2024; 16(23):4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234212
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Juan, Chan Tian, Maojie Liu, Haiyan Guo, Fei Lin, Yang Ding, Wentao Yao, Jiahao Zhang, Jingyi Fan, Chengxiao Yu, and et al. 2024. "Genetic Risk, BMI Status, BMI Change Patterns, and the Risk of Steatotic Liver Disease and Liver Enzyme Elevation in Chinese Adults" Nutrients 16, no. 23: 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234212
APA StyleYang, J., Tian, C., Liu, M., Guo, H., Lin, F., Ding, Y., Yao, W., Zhang, J., Fan, J., Yu, C., Lu, J., & Zhang, Q. (2024). Genetic Risk, BMI Status, BMI Change Patterns, and the Risk of Steatotic Liver Disease and Liver Enzyme Elevation in Chinese Adults. Nutrients, 16(23), 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234212








