Antioxidant and Antiaging Activity of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction and Fractionation
2.2. Evaluation of Polyphenol and Flavonoid Contents
2.3. Measurement of DPPH and ABTS Radical Scavenging Activities
2.4. Assessment of Superoxide Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5. Caenorhabditis Elegans Culture
2.6. Measurement of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in C. elegans
2.7. Evaluation of Ros Accumulation in C. elegans
2.8. Stress Tolerance Assessment
2.9. Fluorescent Expression of sod-3, daf-16, and hsp16.2 in C. elegans
2.10. Evaluating the Longevity Effects and Analyzing Protein Expression
2.11. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Measurement of Polyphenol and Flavonoid Contents
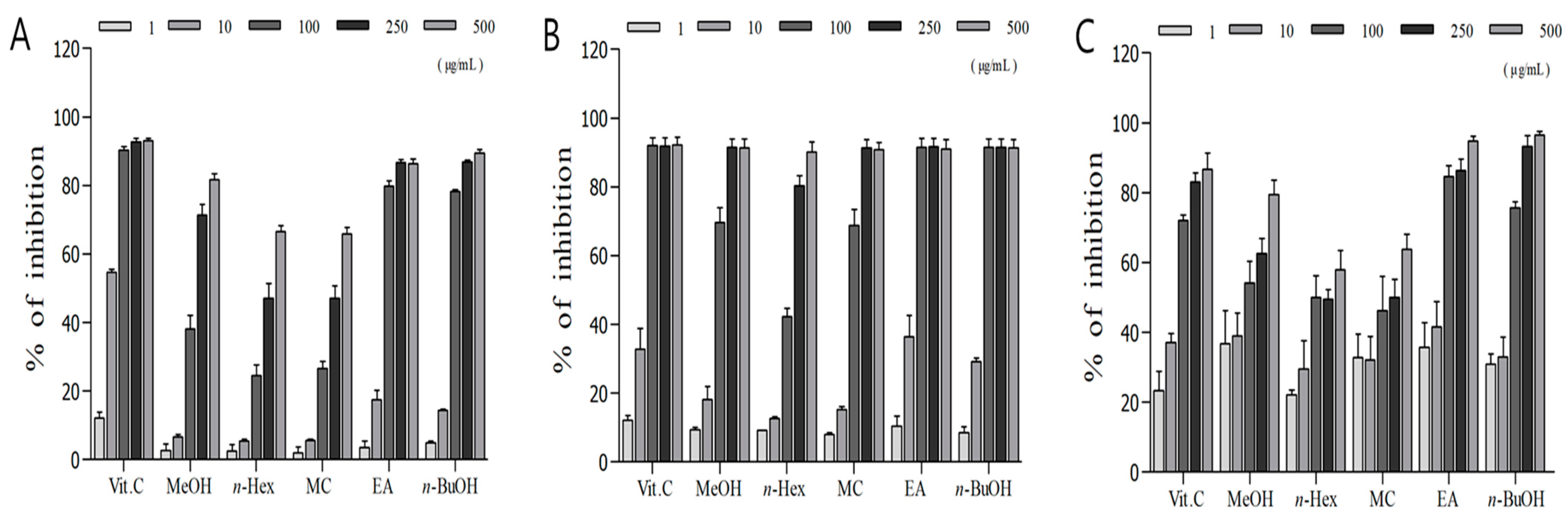
3.2. Measurement of DPPH and ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
3.3. Measurement of Superoxide Radical Scavenging Activity
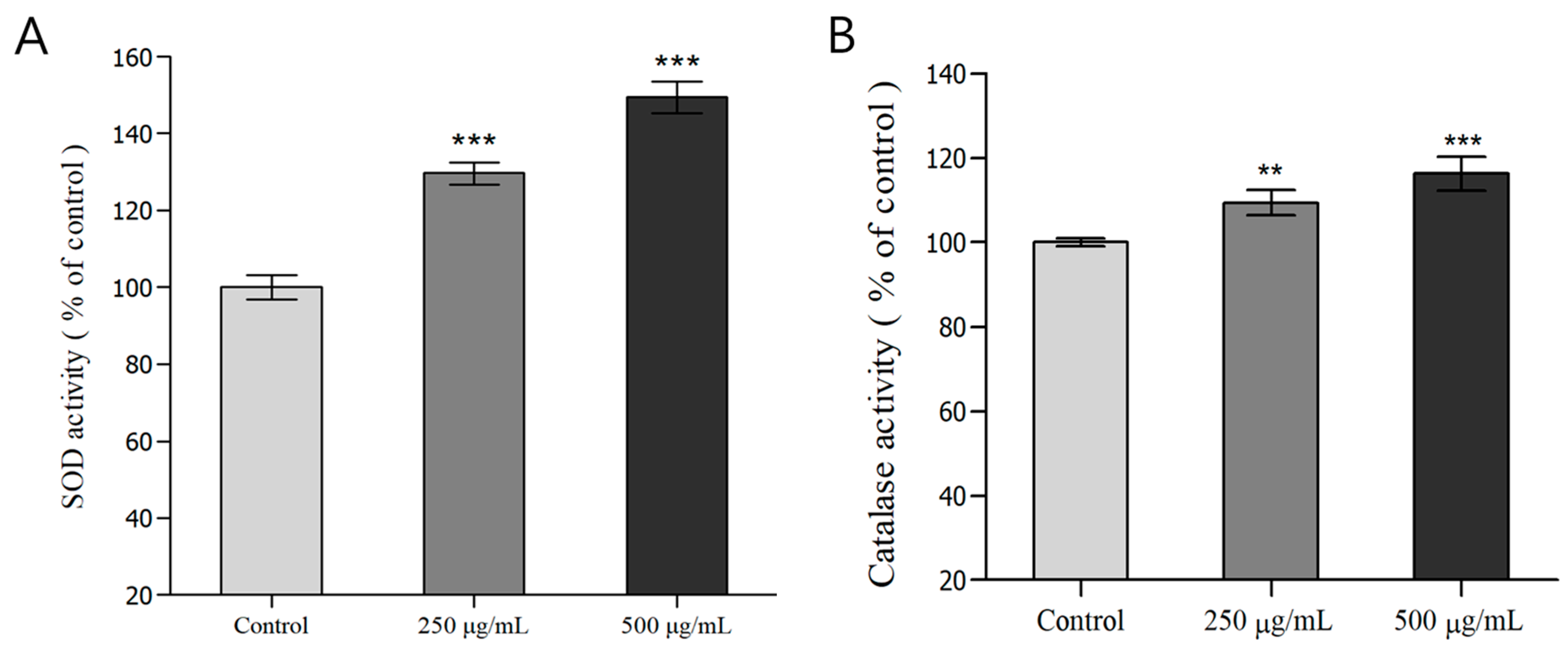
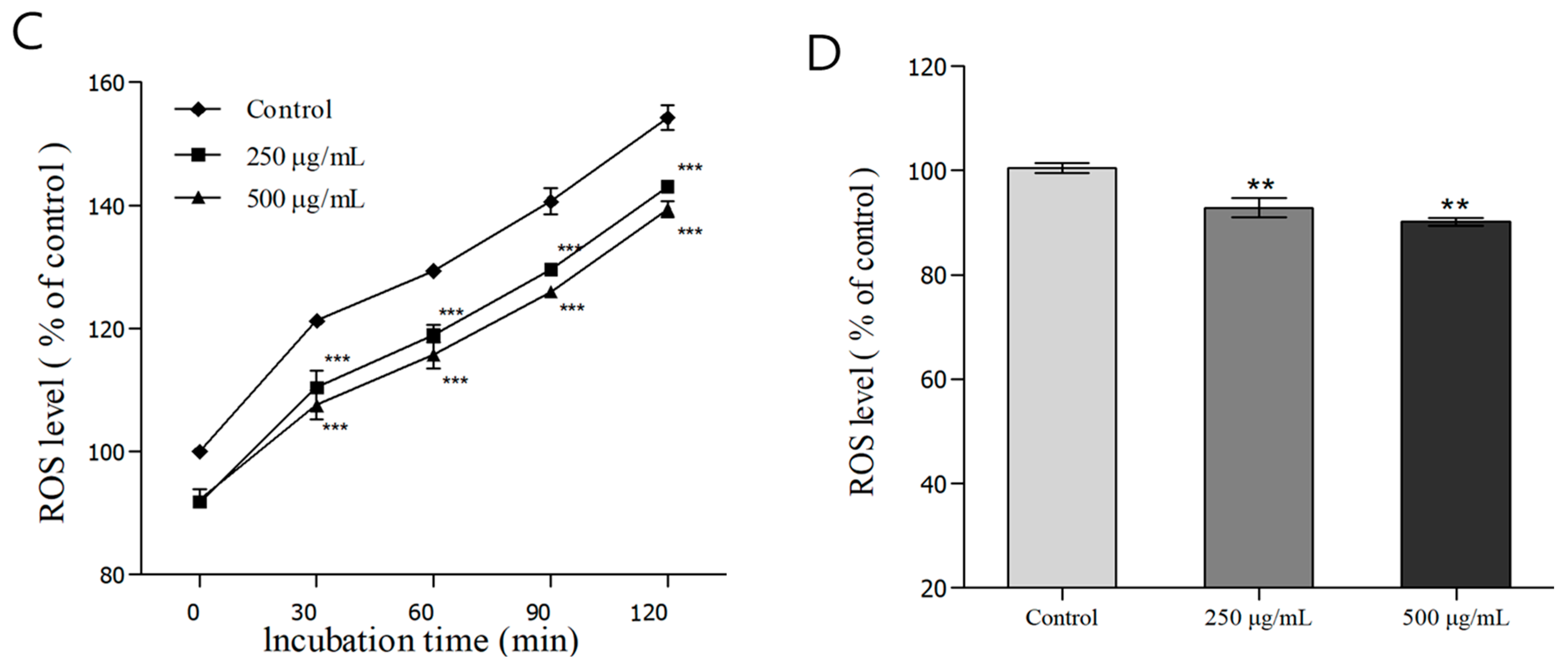
3.4. Measurement of Antioxidant Enzyme (SOD, Catalase) Activity in C. elegans
3.5. Analysis of ROS in C. elegans
3.6. Evaluating Oxidative and Heat Stress Resistance
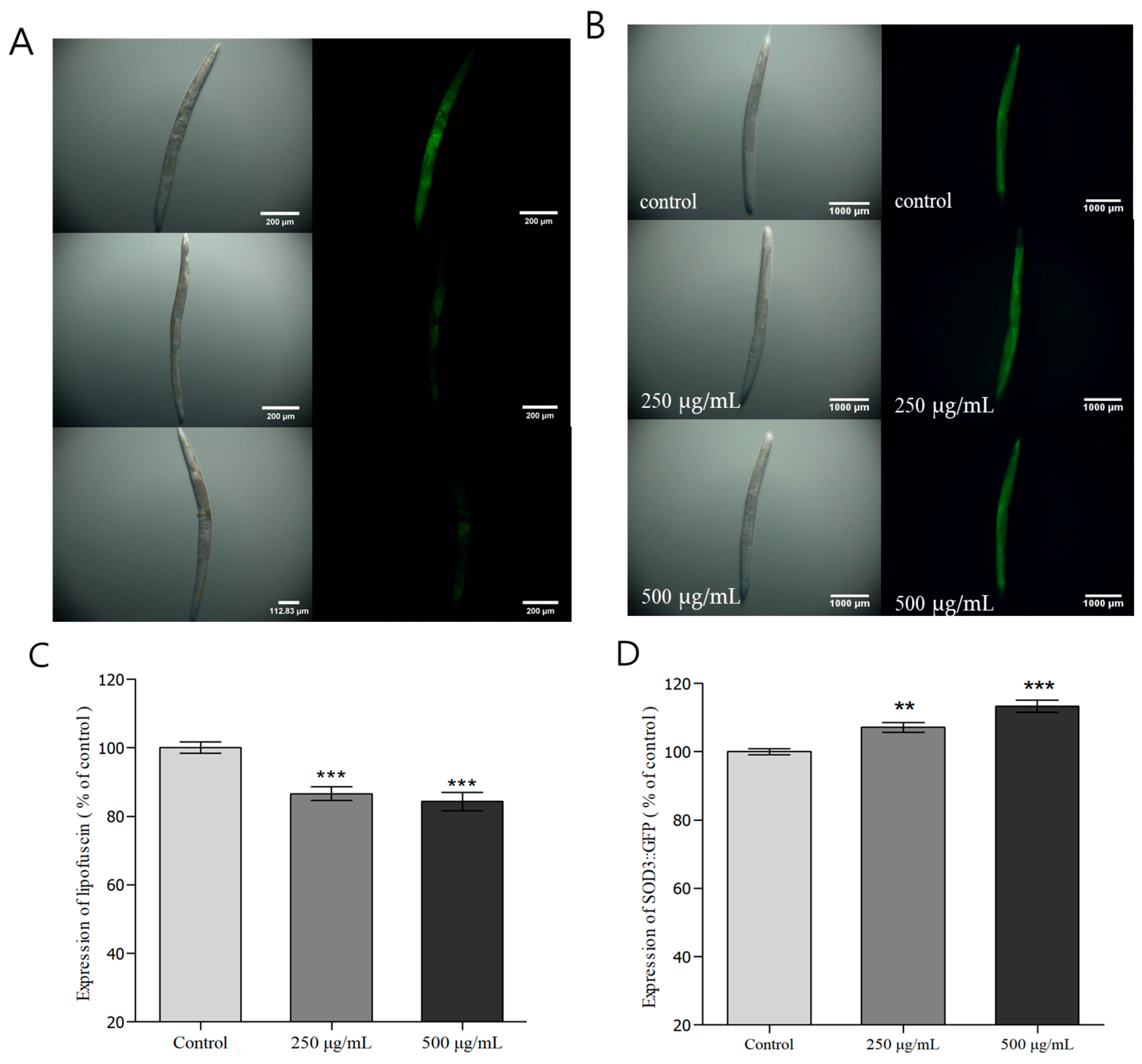
3.7. Evaluation of Fluorescence Expression and Accumulation in C. elegans
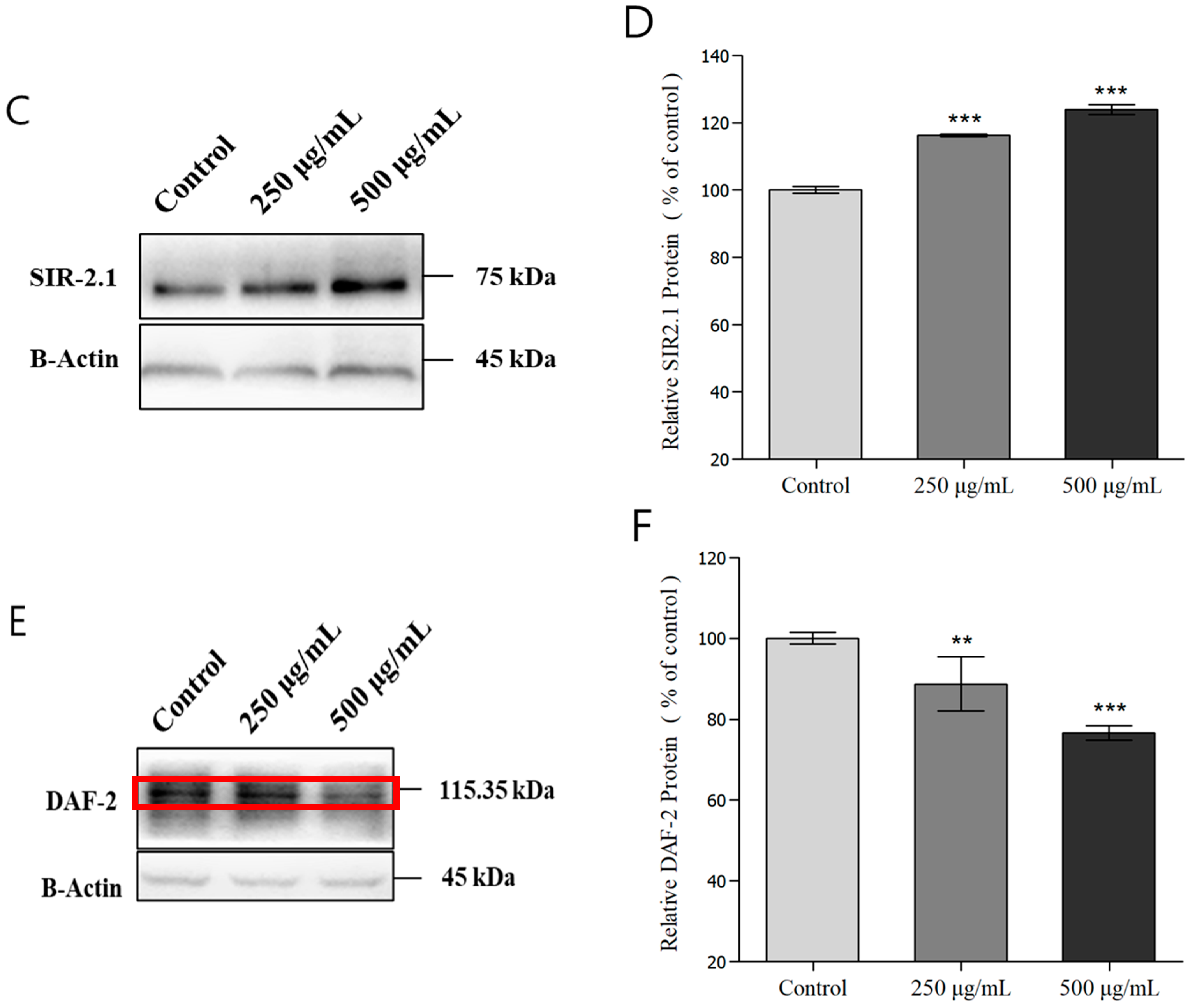
3.8. Evaluation of Lifespan Extension and Protein Expression
3.9. LC/MS-MS and TLC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, H.J.; Traa, A.; Van Raamsdonk, J.M. Beneficial and detrimental effects of reactive oxygen species on lifespan: A comprehensive review of comparative and experimental studies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.J.P.O.; de Oliveira, J.C.P.L.; da Silva Pontes, L.V.; de Souza Júnior, J.F.; Gonçalves, T.A.F.; Dantas, S.H.; Feitosa, M.S.d.A.; Silva, A.O.; de Medeiros, I.A. ROS: Basic concepts, sources, cellular signaling, and its implications in aging pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1225578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Yu, M.R.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, B.H. Total polyphenols, total flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of Korean natural and medicinal plants. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 44, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, S.C.; Moldão-Martins, M.; Alves, V.D. Antioxidants of natural plant origins: From sources to food industry applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant phenolics: Extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Park, S.N.; Yoon, M.S.; Choi, O.B. Effects of Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract inhibits on the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2011, 42, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, M.H. Comparison of Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Korean Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Extracts. J. Korean Appl. Sci. Technol. 2021, 38, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shingnaisui, K.; Dey, T.; Manna, P.; Kalita, J. Therapeutic potentials of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. against inflammation and oxidative stress: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, Y.M.; Park, S.N. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cellular protective effects of Houttuynia cordata extract and fraction. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2018, 29, 452–460. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, M.H.; Sohn, H.Y. Antithrombosis, Antidiabetes, and Antioxidant Activities of Houttuynia cordata. J. Life Sci. 2023, 33, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.G.; Kim, Y.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.E.; Im, D.S.; Kim, H.S. Anti-allergic activity of the extracts from houttuynia cordata thunb fermented by lactic acid bacteria. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2017, 26, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.; Hao, H.; Ijaz, M.; Raza, A. Pharmacological effects of Houttuynia cordata Thunb (H. cordata): A comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.S.; Li, Z.G. Modern Practical Chinese Traditional Medicine Quality Control Technology; People’s Hygiene Press: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Kaşıkcı, M.B.; Bağdatlıoğlu, N. Bioavailability of quercetin. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2016, 4, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Caenorhabditis elegans as a useful model for studying aging mutations. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 554994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.Y.; Sim, S.J.; Yi, J.; Park, K.; Chung, K.H.; Ryu, D.Y.; Choi, J. Ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using functional ecotoxicogenomics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Folin–Ciocalteu method for the measurement of total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity. In Measurement of Antioxidant Activity & Capacity: Recent Trends and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.Y.; Yoo, M.S.; Whang, Y.J.; Jin, Y.J.; Hong, M.H.; Pyo, Y.H. Vitamin C, total polyphenol, flavonoid contents and antioxidant capacity of several fruit peels. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 44, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovič, H.; Grobin, B.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Cigić, B. Relevance and standardization of in vitro antioxidant assays: ABTS, DPPH, and Folin–Ciocalteu. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4608405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Franus, W.; Panek, R.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Flieger, W.; Flieger, M.; Kołodziej, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using natural extracts with proven antioxidant activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuong, P.T.; Kang, H.J.; Na, M.; Jin, W.; Youn, U.J.; Seong, Y.H.; Bae, K. Anti-oxidant constituents from Sedum takesimense. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Mun, J.S.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, J.H. Antioxidant and Longevity Properties Activity of the Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Angelica gigas in Caenorhabditis elegans. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 53, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Seo, H.W.; Kim, B.S.; Lim, H.J.; Lee, H.N.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, Y.J.; Oh, J.W.; Oh, M.J.; Kwon, J.; et al. Lindera obtusilobaextends lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2015, 21, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, K.M.; Yang, J.H.; Ki, B.; Kim, D.K. Antioxidative-activity of Phellinus baumii Pilat in Caenorhabditis elegans. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2019, 50, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Z.; Shen, S.; Yuan, M.; Liu, J.; Ding, C. Thermal stress resistance and aging effects of Panax notoginseng polysaccharides on Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kwon, G.; Lim, Y.H. Elucidating the mechanism of Weissella-dependent lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.G.; Lee, S.B.; Deji-Oloruntoba, O.; Choi, S.I.; Jang, M.R. Inhibitory effect of Undaria pinnatifida Sporophyll extract on high glucose diet-induced lipid accumulation and ROS generation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 55, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.W.; Cheon, S.M.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, H.; Cha, D.S. Catalpol modulates lifespan via DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/Nrf2 activation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 524878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Ji, H.; Le, M.; Li, H.; Wieland, A.; Bauer, S.; Herr, I. Sulforaphane promotes C. elegans longevity and healthspan via DAF-16/DAF-2 insulin/IGF-1 signaling. Aging 2021, 13, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrit, F.R.G.; Ratnappan, R.; Keith, S.A.; Ghazi, A. The C. elegans lifespan assay toolkit. Methods 2014, 68, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, Y.T.; Cha, D.S. Neuroprotective effect of damaurone D in a C. elegans model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 747, 135623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H. The roles of dietary polyphenols in brain neuromodulation. J. Life Sci. 2018, 28, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, P.B.; Ha, S.E.; Vetrivel, P.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, G.S. Functions of polyphenols and its anticancer properties in biomedical research: A narrative review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, I.H.; Kwon, H.D. Antimicrobial activity of fractional extracts from Houttuynia cordata root. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 32, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, K.; Kim, S.U.; Um, I.S.; Bae, Y.D.; Rho, I.R. Analysis of antioxidant activity from medicinal crops cultivated in small area. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2017, 51, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirivibulkovit, K.; Nouanthavong, S.; Sameenoi, Y. Based DPPH assay for antioxidant activity analysis. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Kwon, O.J. Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 50, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A.; Terekhov, R.P. ABTS/PP decolorization assay ofantioxidant capacity reaction pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Sohn, H.Y.; Lee, C.I.; Hwang, H.Y.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.S. Functional chemical components and their biological activities of Houttuynia cordata and Lespedeza cuneata. J. Life Sci. 2020, 30, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, L. Reactive oxygen species: Key regulators in vascular health and diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Son, R.H.; Lee, Y.H. The inhibitory effects of Pogostemon cablin Bentham extract on melanogenesis. J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea 2009, 35, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.-J.; Bu, H.J.; Lee, S.-J. Screening for Antioxidative Activity of Jeju Native Plants. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2015, 28, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younus, H. Therapeutic potentials of superoxide dismutase. Int. J. Health Sci. 2018, 12, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, A.; Yan, L.J.; Jana, C.K.; Das, N. Role of catalase in oxidative stress-and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9613090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, H.S.; Roos, D.; Tabarelli, G.; Rodrigues, O.E.; Avila, D.; Quines, C.B. Activation of SOD-3 is involved in the antioxidant effect of a new class of β-aryl-chalcogenium azide compounds in Caenorhabditis elegans. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2020, 92, e20181147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, R.H.; Na, B.J.; Park, S.J.; Woo, W.H.; Lee, M.S.; Mun, Y.J. Effect of Houttuynia cordata Thunb and herbs mixture extract on the antioxidation in the LPS-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Physiol. Pathol. Korean Med. 2007, 21, 1520–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, B.-J. Effects of Houttuynia Cordata thunb on Antioxidative Activity against TCDD Damage. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2003, 12, 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhu, D.; Pei, T.; He, Z.; Xiao, W. Chemical profiling of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and analysis of its antioxidant activity in C2C12 cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 204, 114271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.I.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, B.J.; Yeo, J.; Lee, O.H. Antioxidant and anti-aging effects of extracts from leaves of Castanea crenata Siebold & Zucc. in human dermal fibroblast. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2017, 32, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Moloney, J.N.; Cotter, T.G. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 80, pp. 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Aithal, B.K.; Kumar, M.S.; Rao, B.N.; Udupa, N.; Rao, B.S. Juglone, a naphthoquinone from walnut, exerts cytotoxic and genotoxic effects against cultured melanoma tumor cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2009, 33, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Suzuki, Y.J. Juglone in oxidative stress and cell signaling. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithgow, G.J.; White, T.M.; Melov, S.; Johnson, T.E. Thermotolerance and extended life-span conferred by single-gene mutations and induced by thermal stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7540–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanase, S.; Yasuda, K.; Ishii, N. Interaction between the ins/IGF-1 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in molecular compensation of sod genes and modulation related to intracellular ROS levels in C. elegans. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 23, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, F.; Wang, T.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; You, Y.; Liu, X. Jujubae Fructus extract prolongs lifespan and improves stress tolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans dependent on DAF-16/SOD-3. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13713. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakou, E.; Taouktsi, E.; Syntichaki, P. The thermal stress coping network of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, E.P.M.; Dixon, D.K.; Graham, R.W.; Russnak, R.H.; Kay, R.J. Structure, organization, and expression of the 16-kDa heat shock gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome 1989, 31, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Rea, S.L.; Yashin, A.I.; Johnson, T.E. Visualizing hidden heterogeneity in isogenic populations of C. elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2006, 41, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, Z.; Mazer, T.C.; Slack, F.J. Autofluorescence as a measure of senescence in C. elegans: Look to red, not blue or green. Aging 2016, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Nishida, E. Lifespan-regulating genes in C. elegans. NPJ Aging 2016, 2, 16010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.; Zhou, X.; Chernobrovkin, A.; Puerta-Cavanzo, N.; Kanno, T.; Salignon, J.; Stoehr, A.; Lin, X.-X.; Baskaner, B.; Brandenburg, S.; et al. DAF-16/FOXO requires Protein Phosphatase 4 to initiate transcription of stress resistance and longevity promoting genes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.; Lithgow, G.J.; Link, W. Long live FOXO: Unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Extract and Fraction | Total Polyphenol (μg TAE/mg) (1) | Total Flavonoid (μg QE/mg) (2) |
|---|---|---|
| Methanol extract | 161.9 | 346.4 |
| n-Hexane fraction | 171.0 | 286.2 |
| Methylene chloride fraction | 140.5 | 226.7 |
| Ethyl acetate fraction | 881.3 | 1941.1 |
| n-Butanol fraction | 249.1 | 670.6 |
| Stress Condition | Mean Lifespan (Hours) | Maximum Lifespan (Hours) | Change in Mean Lifespan(%) | Log-Rank Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mM Juglone | Control | 13.5 ± 1.0 | 27 | - | - |
| 250 μg/mL | 23.3 ± 1.1 | 35 | 43.1 | *** p < 0.001 | |
| 500 μg/mL | 26.8 ± 1.2 | 40 | 57.0 | *** p < 0.001 | |
| 36 °C thermal tolerance | Control | 14.3 ± 0.4 | 20 | - | |
| 250 μg/mL | 17.2 ± 0.5 | 24 | 20.0 | *** p < 0.001 | |
| 500 μg/mL | 18.9 ± 0.5 | 27 | 32.5 | *** p < 0.001 |
| Fraction | Mean Lifespan (Day) | Maximum Lifespan (Day) | Change in Mean Lifespan | Log-Rank Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8.9 ± 0.2 | 16 | - | - |
| Methanol | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 17 | 7.3 | * p < 0.05 |
| n-Hexane | 9.1 ± 0.2 | 17 | - | - |
| Methylene chloride | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 17 | 7.2 | * p < 0.05 |
| Ethyl acetate | 10.9 ± 0.3 | 19 | 22.1 | *** p < 0.001 |
| n-Butanol | 9.9 ± 0.3 | 19 | 11.2 | ** p < 0.01 |
| Type | Concentration | Trace | RT | Response | ppb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercitrin | standard | 1000 ppm | 446.83 > 300.77 | 2.39 | 204,925.9 | 995.5 |
| Methanol | sample | 2.29 | 6503.775 | 31.5 | ||
| Ethyl acetate | sample | 2.30 | 95,119.67 | 462 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Mun, J.-S.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Antioxidant and Antiaging Activity of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234168
Kim H-J, Mun J-S, Oh S-H, Kim J-H. Antioxidant and Antiaging Activity of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients. 2024; 16(23):4168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234168
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeon-Ji, Ji-Su Mun, Suk-Heung Oh, and Jun-Hyung Kim. 2024. "Antioxidant and Antiaging Activity of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Caenorhabditis elegans" Nutrients 16, no. 23: 4168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234168
APA StyleKim, H.-J., Mun, J.-S., Oh, S.-H., & Kim, J.-H. (2024). Antioxidant and Antiaging Activity of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients, 16(23), 4168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234168





