The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Literature Search
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Data Analysis and Quality Appraisal
3. Results
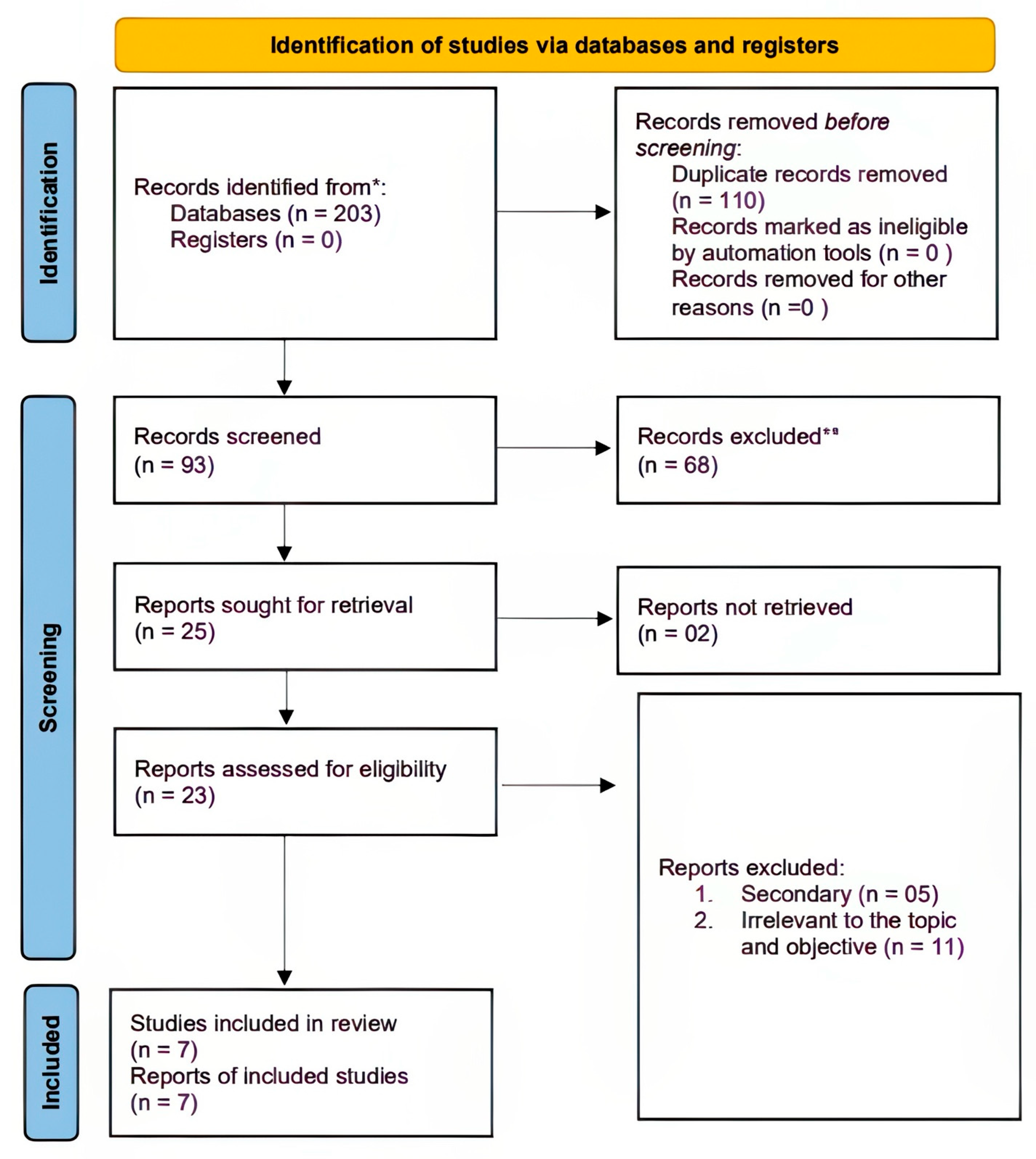
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.2.1. Summary of the Study Characteristics
3.2.2. Quality Assessment
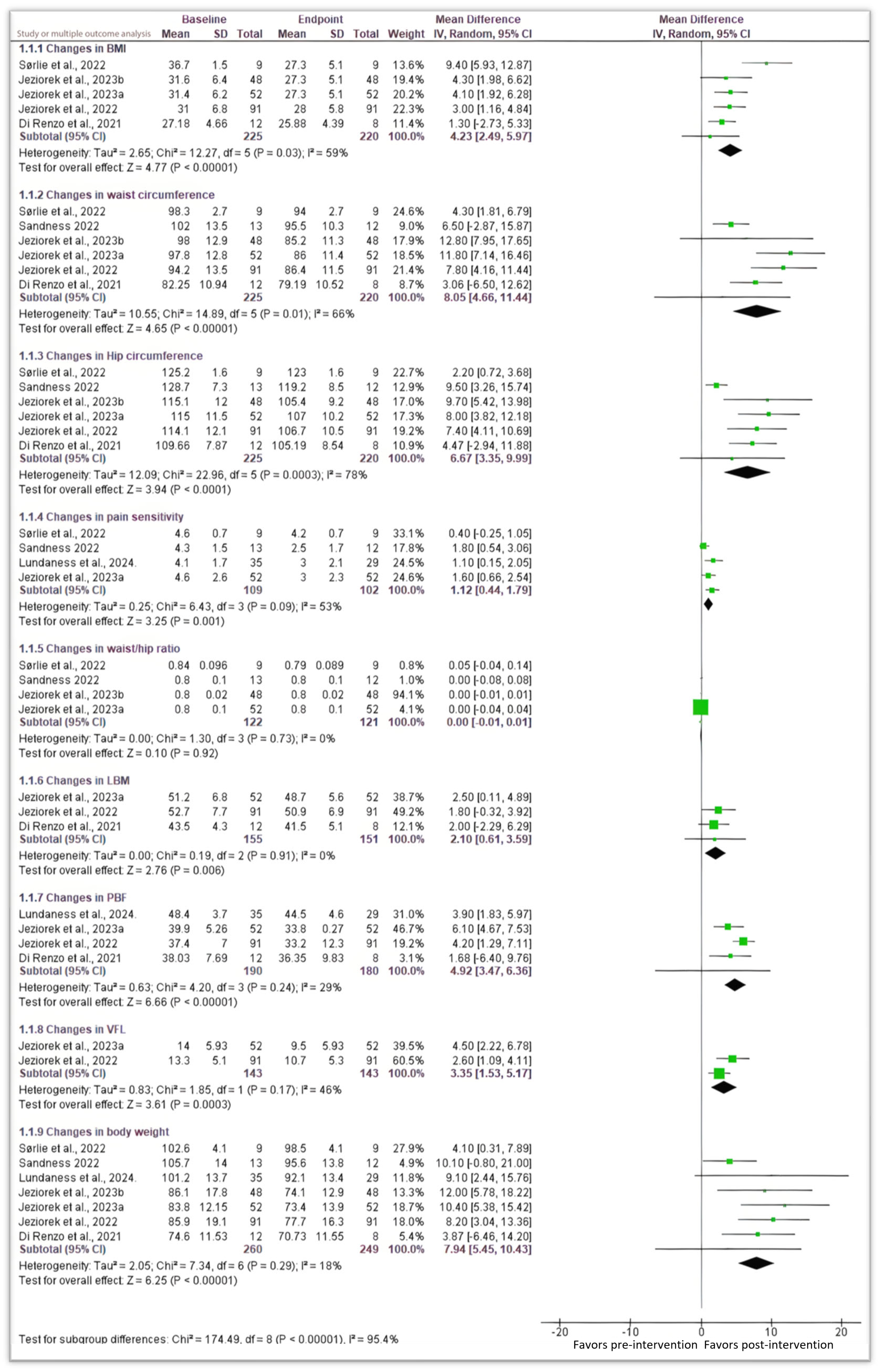
3.3. Anthropometric and Body Composition Analysis
3.3.1. Body Mass Index (BMI) and Body Weight
3.3.2. Changes in Waist and Hip Circumferences, and Waist/Hip Ratio
3.3.3. Changes in LBM, PBF, and VFL
3.4. Pain Sensitivity
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Child, A.H.; Gordon, K.D.; Sharpe, P.; Brice, G.; Ostergaard, P.; Jeffery, S.; Mortimer, P.S. Lipedema: An Inherited Condition. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, A.C.; Amato, L.L.; Benitti, D.; Amato, J.L. Assessing the Prevalence of HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 in Lipedema Patients and the Potential Benefits of a Gluten-Free Diet. Cureus 2023, 15, e41594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolacci, S.; Precone, V.; Acquaviva, F.; Chiurazzi, P.; Fulcheri, E.; Pinelli, M.; Buffelli, F.; Michelini, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Unfer, V.; et al. Genetics of Lipedema: New Perspectives on Genetic Research and Molecular Diagnoses. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5581–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szél, E.; Kemény, L.; Groma, G.; Szolnoky, G. Pathophysiological Dilemmas of Lipedema. Med. Hypotheses 2014, 83, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruglikov, I.L.; Scherer, P.E. Is the Endotoxin–Complement Cascade the Major Driver in Lipedema? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.C.M. The Essential Guide to Living with Lipedema: Discovering the Truth and Transforming Treatment of a Misunderstood Condition, 1st ed.; Amato-Instituto de Medicina Avançada: SãoPaulo, Brazil, 2024; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Katzer, K.; Hill, J.L.; McIver, K.B.; Foster, M.T. Lipedema and the Potential Role of Estrogen in Excessive Adipose Tissue Accumulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-G.; Hsu, S.-D.; Chen, T.-M.; Wang, H.-J. Painful Fat Syndrome in a Male Patient. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2004, 57, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Camajani, E.; Annunziata, G.; Sojat, A.; Marina, L.V.; Colao, A.; Caprio, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L. Ketogenic Diet: A Nutritional Therapeutic Tool for Lipedema? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, Y.S.D.; Wadeea, R.; Rosas, V.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: Friend and Foe. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, J.E.; Białaszek, W.; Ostaszewski, P. Quality of Life in Women with Lipoedema: A Contextual Behavioral Approach. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, H.; Karadag, A.S.; Wollina, U. Cause and Management of Lipedema-Associated Pain. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 34, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keast, D.H.; Moffatt, C.; Janmohammad, A. Lymphedema Impact and Prevalence International Study: The Canadian Data. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2019, 17, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, T.; Erbacher, G. Lipoedema-Myths and Facts Part 1. Phlebologie 2018, 47, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Shavit, E.; Wollina, U.; Alavi, A. Lipoedema Is Not Lymphoedema: A Review of Current Literature. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojari, A.; Dev, K.; Rabiee, A. Lipedema: Insights into Morphology, Pathophysiology, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, K.L.; Kahn, L.A.; Iker, E.; Ehrlich, C.; Wright, T.; McHutchison, L.; Schwartz, J.; Sleigh, M.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Lisson, K.H.; et al. Standard of Care for Lipedema in the United States. Phlebology 2021, 36, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Verde, L.; Sulu, C.; Katsiki, N.; Hassapidou, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cucalón, G.; Pazderska, A.; Yumuk, V.D.; Colao, A.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Obesity-Related Disorders: What Is the Evidence? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumuk, V.; Tsigos, C.; Fried, M.; Schindler, K.; Busetto, L.; Micic, D.; Toplak, H. European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults. Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, S.; Minty, R.; O’Driscoll, T.; Willms, H.; Poirier, D.; Madden, S.; Kelly, L. Intermittent Fasting and Weight Loss. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, D.; Williams, A. Best Practice Guidelines for the Management of Lipoedema. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2017, 22, S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Cinelli, G.; Romano, L.; Zomparelli, S.; Lou De Santis, G.; Nocerino, P.; Bigioni, G.; Arsini, L.; Cenname, G.; Pujia, A.; et al. Potential Effects of a Modified Mediterranean Diet on Body Composition in Lipoedema. Nutrients 2021, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, L.; Seo, C.A.; Rowsemitt, C.; Pfeffer, M.; Wahi, M.; Staggs, M.; Dudek, J.; Gower, B.; Carmody, M. Ketogenic Diet as a Potential Intervention for Lipedema. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 146, 110435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, D.W.; Herbst, K.L. Lipedema: A Relatively Common Disease with Extremely Common Misconceptions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2016, 4, e1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, C.E.; Phinney, S.D.; Fernandez, M.L.; Quann, E.E.; Wood, R.J.; Bibus, D.M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Feinman, R.D.; Volek, J.S. Comparison of Low Fat and Low Carbohydrate Diets on Circulating Fatty Acid Composition and Markers of Inflammation. Lipids 2008, 43, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.C.M. Ketogenic Therapy for Lipedema: Transforming Fat into Energy, 1st ed.; 2024; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jeziorek, M.; Szuba, A.; Kujawa, K.; Regulska-Ilow, B. The Effect of a Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet versus Moderate-Carbohydrate and Fat Diet on Body Composition in Patients with Lipedema. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 2545–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeziorek, M.; Chachaj, A.; Sowicz, M.; Adaszyńska, A.; Truszyński, A.; Putek, J.; Kujawa, K.; Szuba, A. The Benefits of Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat (LCHF) Diet on Body Composition, Leg Volume, and Pain in Women with Lipedema. J. Obes. 2023, 2023, 5826630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørlie, V.; De Soysa, A.K.; Hyldmo, Å.A.; Retterstøl, K.; Martins, C.; Nymo, S. Effect of a Ketogenic Diet on Pain and Quality of Life in Patients with Lipedema: The LIPODIET Pilot Study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2022, 8, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeziorek, M.; Szuba, A.; Sowicz, M.; Adaszyńska, A.; Kujawa, K.; Chachaj, A. The Effect of a Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet on Laboratory Parameters in Women with Lipedema in Comparison to Overweight/Obese Women. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundanes, J.; Sandnes, F.; Gjeilo, K.H.; Hansson, P.; Salater, S.; Martins, C.; Nymo, S. Effect of a Low-carbohydrate Diet on Pain and Quality of Life in Female Patients with Lipedema: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesity 2024, 32, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandnes, F.H. Effect of Ketosis on Pain and Quality of Life in Women with Lipedema. Master’s Thesis, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Zomparelli, S.; De Santis, G.L.; Seraceno, S.; Zuena, C.; Frank, G.; Cianci, R.; Centofanti, D.; De Lorenzo, A. Modified Mediterranean-Ketogenic Diet and Carboxytherapy as Personalized Therapeutic Strategies in Lipedema: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Pereson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. Tugwell The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Amato, A.C.; Amato, J.L.; Benitti, D. Efficacy of Liposuction in the Treatment of Lipedema: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e55260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellana, M.; Conte, E.; Cignarelli, A.; Perrini, S.; Giustina, A.; Giovanella, L.; Giorgino, F.; Trimboli, P. Efficacy and Safety of Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) in Patients with Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghadban, S.; Herbst, K.L.; Bunnell, B.A. Lipedema: A Painful Adipose Tissue Disorder. In Adipose Tissue-An Update; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, C.; Iker, E.; Herbst, K. Lymphedema and Lipedema Nutrition Guide: Foods, Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements; Lymph Notes: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Nourollahi, S.; Mondry, T.E.; Herbst, K.L. Bucher’s Broom and Selenium Improve Lipedema: A Retrospective Case Study. Altern. Integr. Med. 2013, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halk, A.B.; Damstra, R.J. First Dutch Guidelines on Lipedema Using the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Phlebology 2017, 32, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, M.; Liang, J.; He, G.; Chen, N. Ketogenic Diet Benefits to Weight Loss, Glycemic Control, and Lipid Profiles in Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowis, K.; Banga, S. The Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author(s) | PMID/Study ID | Study Design | Country | Population (N) | Gender | Age (Years) (Mean) | Treatment Interventions | Treatment Duration (Weeks) | Outcomes (Overall Change) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight (Kg) | BMI [Kg/m2] | LBM | PBF [%] | VFL | Pain | Waist (cm) | Hip (cm) | Waist/Hip Ratio | |||||||||
| Jeziorek et al., 2022 [30] | 36035515 | Prospective case-controlled trial | Poland | 91 | Female | 43.2 ± 12.8 | LCHF and MCMF | 16 | −8.21 ± 4.1 | −3.0 ± 1.5 | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 4.2 ± 2.1 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | N/A | 7.8 ± 3.9 | 7.4 ± 3.7 | - |
| Jeziorek et al., 2023 [31] | 5826630 | Case–control | Poland | 52 | Female | 39.0 (33.0–62.0) | LCHF with anti-inflammatory properties | 28 | −11.9 (−13.8, −10.5) | −4.1 ± 2.5 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 6.0 (3.4, 8.3) | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 11.7 ± 6.6 | 8.5 (6.3, 11.8) | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Sørlie et al., 2022 [32] | 35949278 | Prospective clinical trial | Norway | 9 | Female | 49.9 ± 9.0 | Eucaloric LCHF diet | 13 | −4.1 ± 0.0 | −1.4 (−1.9, −1.0) | - | - | - | 0.4 (−1.5, 2.2) | 2.3 (1.2, 4.4) | 2.2 (1.0, 3.6) | −0.01 (−0.01, 0.03) |
| Jeziorek et al., 2023b [33] | 37299581 | Case–control | Poland | 48 | Female | 39.0 and 49.0 (median) | Personalized caloric-restricted, low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet | 28 | −11.1 (−15.9, −6.4) | −3.9 (−6,2, −2.5) | - | - | - | - | 12.8 ± 6.4 | 8.8 (6.3, 13.0) | 0.04 (0.0, 0.07) |
| Lundanes et al., 2024 [34] | 38627016 | Prospective clinical trial | Norway | 70 | Female | 47.3 ± 10.9 years | Low-energy, low-carbohydrate diet | 8 | −10.2 (−11.1, −9.3) | - | - | −3.90 (−1.83, 5.97) | - | −1.3 (−1.9, −0.7) | - | - | - |
| Sandnes et al., 2022 [35] | - | Prospective clinical trial | Norway | 29 | Female | 47.0 ± 11.2 years | Low-energy, ketogenic diet | 8 | −10.1 (0.8, −21) | −3.60 (0.01, −7.21) | - | - | - | −1.80 (−0.54, −3.06) | −6.50 (2.87, −15.87) | −9.5 (−3.26, −15.74) | 0 (0.08, −0.08) |
| Di Renzo et al., 2023 [36] | 37630844 | Prospective clinical trial | Italy | 30 | Female | 46 + 7.4 | Modified Mediterranean ketogenic diet | 10 | −3.87, (6.46, −14.20) | −1.30 (2.73, −5.33) | −2 (2.29, −6.29) | −1.68, (6.40, −9.76) | - | - | −3.06 (6.5, −12.62) | −4.47, (2.94, −11.88) | - |
| Study ID | Selection (/4) | Comparability (/2) | Outcome (/3) | Methodological Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeziorek et al., 2022 [30] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Jeziorek et al., 2023 [31] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Jeziorek et al., 2023b [33] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Sørlie et al., 2022 [32] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Lundanes et al., 2024 [34] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Sandnes et al., 2022. [35] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
| Di Renzo et al., 2023 [36] | 2 | 1 | 2 | Fair |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amato, A.C.M.; Amato, J.L.S.; Benitti, D.A. The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193276
Amato ACM, Amato JLS, Benitti DA. The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193276
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmato, Alexandre Campos Moraes, Juliana Lelis Spirandeli Amato, and Daniel Augusto Benitti. 2024. "The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193276
APA StyleAmato, A. C. M., Amato, J. L. S., & Benitti, D. A. (2024). The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16(19), 3276. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193276