Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and Its By-Products: Healthy Effects in Internal Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Methods
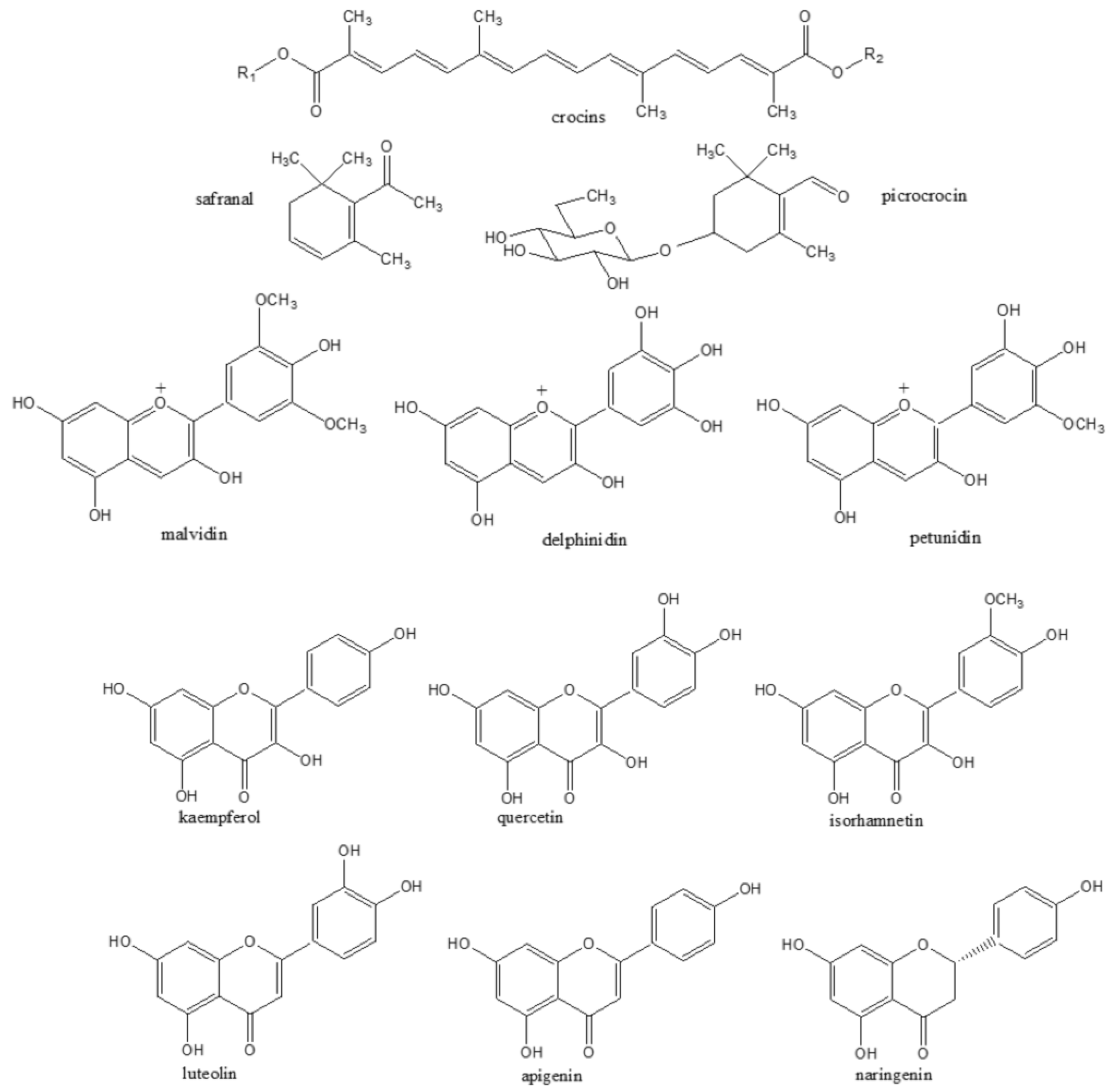
3. Saffron Natural Bioactive Compounds
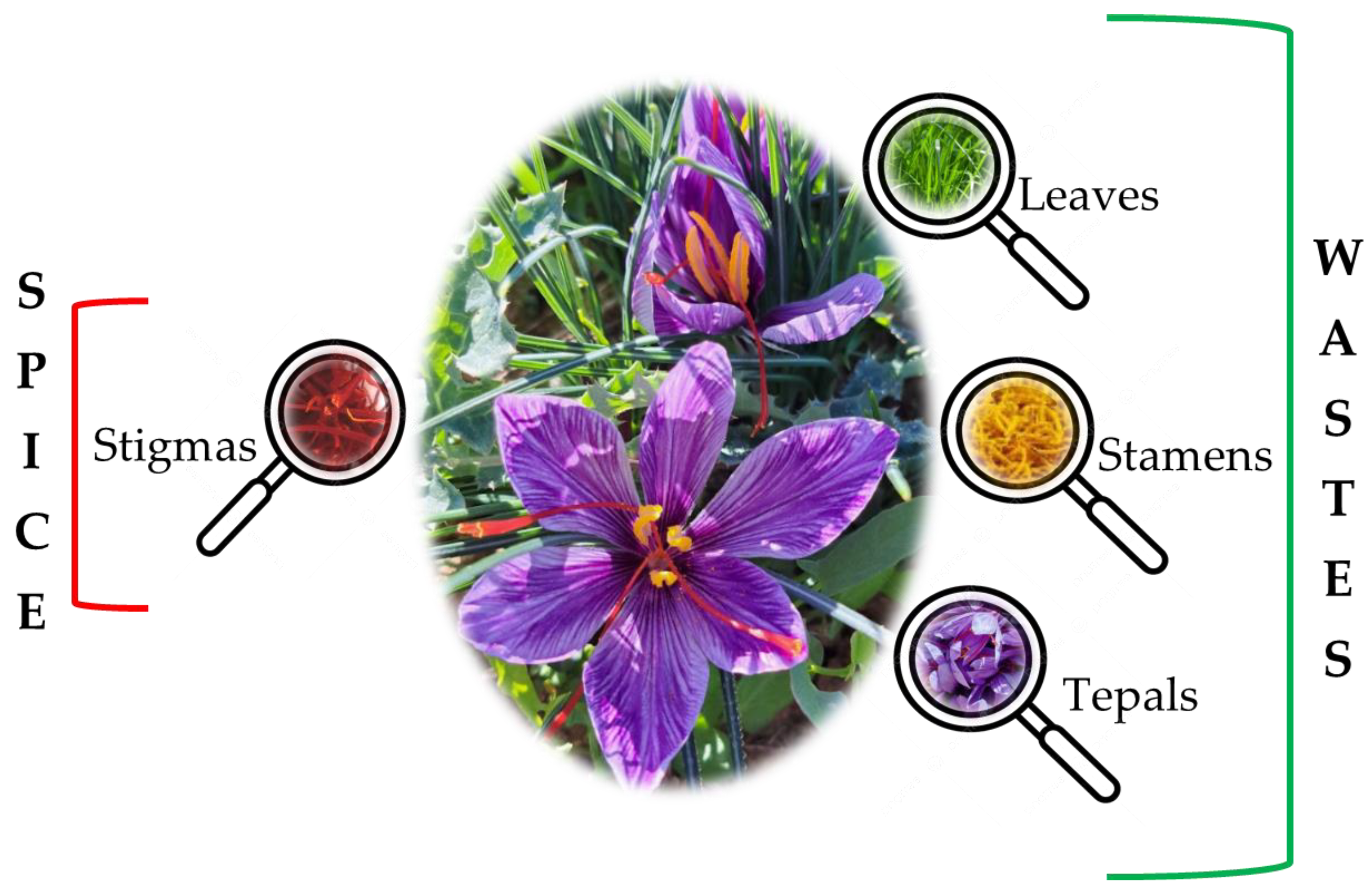
3.1. Saffron Stigmas
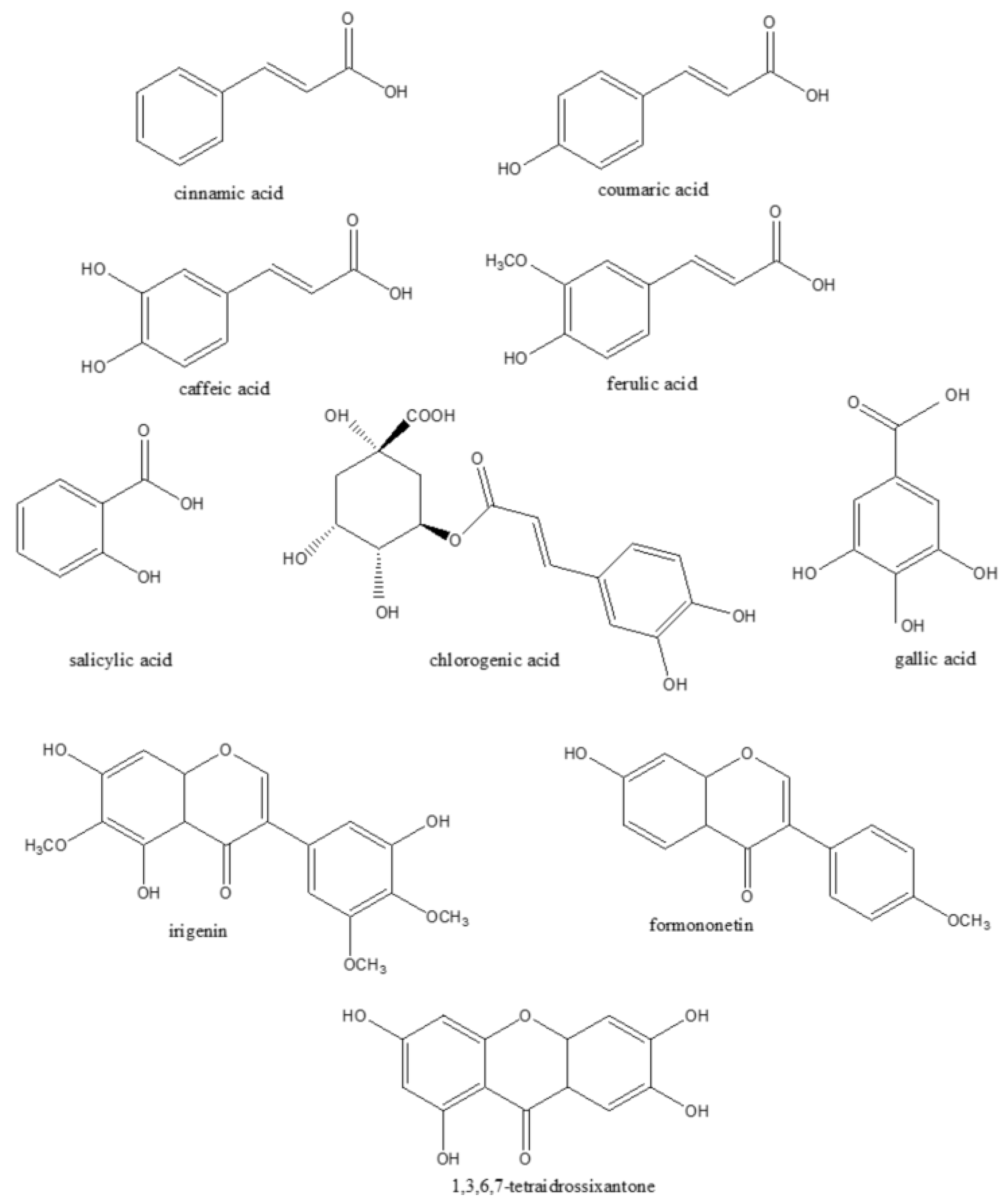
3.2. Saffron By-Products
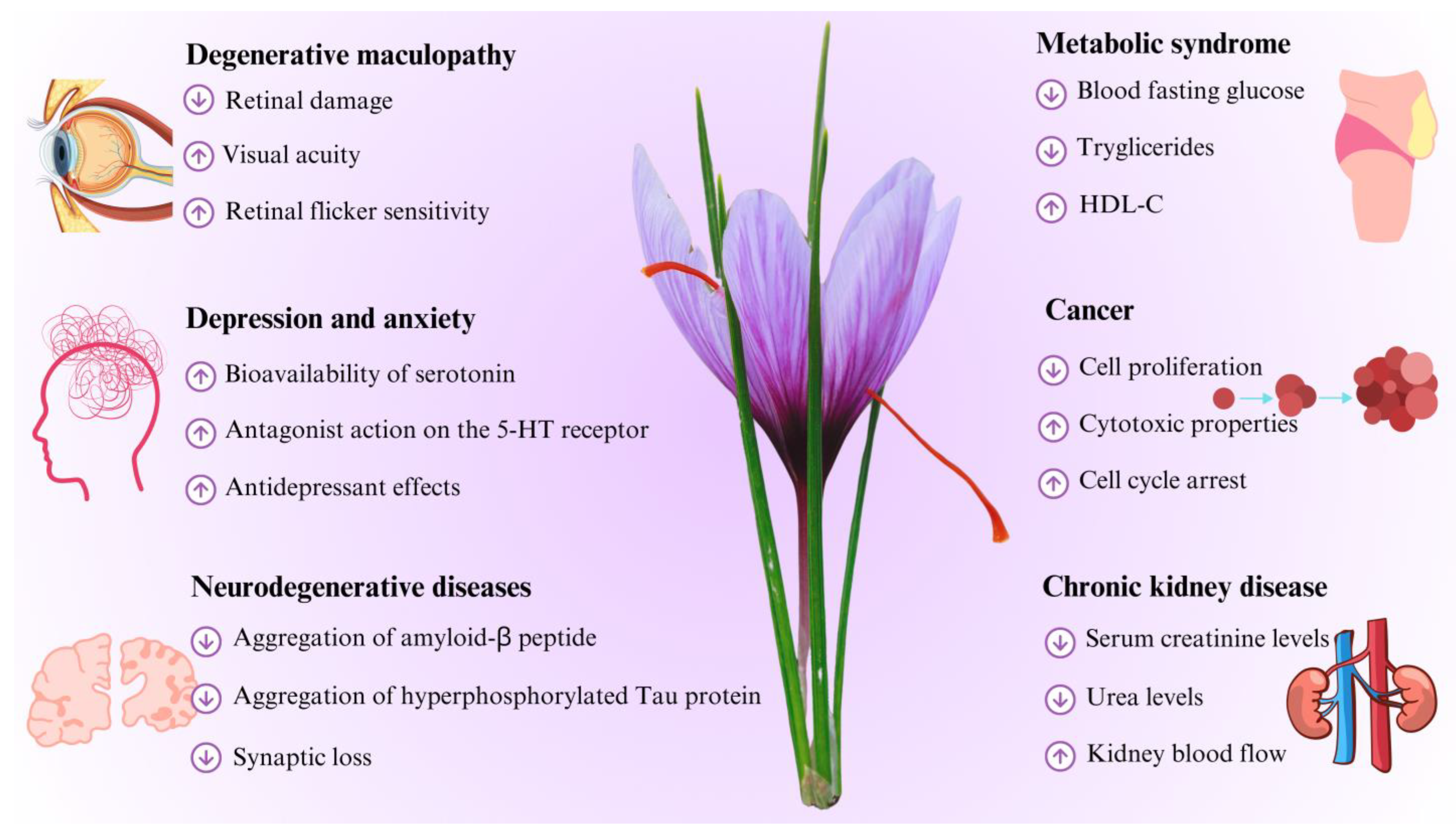
4. Beneficial Effects of Saffron in Internal Medicine
4.1. Degenerative Maculopathy
4.2. Depression and Anxiety
4.3. Neurodegenerative Diseases
4.4. Metabolic Syndrome
4.5. Cancer
4.6. Chronic Kidney Disease
5. Potential Toxic Effects of Saffron on Health
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Devi, M.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S. Introduction of high-value Crocus sativus (saffron) cultivation in non-traditional regions of India through ecological modelling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggieri, F.; Maggi, M.A.; Rossi, M.; Consonni, R. Comprehensive Extraction and Chemical Characterization of Bioactive Compounds in Tepals of Crocus sativus L. Molecules 2023, 28, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, D. Chapter 14—Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): Phytochemistry, therapeutic significance and omics-based biology. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants; Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 325–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, A.R.; Saeidnia, S.; Mahmoodabadi, M.K. An overview on saffron, phytochemicals, and medicinal properties. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/saffron-market (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Sut, S.; Gherardi, G.; Ruzza, F.; Caudullo, G.; Shrestha, S.S.; Sorrenti, V.; Dall’Acqua, S. Saffron the “Red Gold” and Its CNS Activity: A Challenge for Future Applications in Nutraceuticals. J. Food Biochem. 2024, 2024, 6672608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 3632-1; Spices—Saffron (Crocus sativus L.)—Part 1: Specification. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- García-Rodríguez, M.V.; López-Córcoles, H.; Alonso, G.L.; Pappas, C.S.; Polissiou, M.G.; Tarantilis, P.A. Comparative evaluation of an ISO 3632 method and an HPLC-DAD method for safranal quantity determination in saffron. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadfy, Z.; Atifi, H.; Mamouni, R.; Jadouali, S.M.; Chartier, A.; Nehmé, R.; Karra, Y.; Tahiri, A. Nutraceutical and cosmetic applications of bioactive compounds of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) stigmas and its by-products. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 163, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, M.; Christaki, S.; Gkatzionis, K.; Mourtzinos, I.; Tsouko, E. Residual biomass from major aromatic and medicinal flora of the Mediterranean: Challenges towards sustainable integration into food systems within the circular bioeconomy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Izneid, T.; Rauf, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Olatunde, A.; Khalid, A.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Sahab Uddin, M.; Heydari, M.; Khayrullin, M.; et al. Nutritional and health beneficial properties of saffron (Crocus sativus L.): A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 2683–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelluti, S.; Caser, M.; Demasi, S.; Scariot, V. Sustainable Processing of Floral Bio-Residues of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) for Valuable Biorefinery Products. Plants 2021, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakka, A.; Grigorakis, S.; Karageorgou, I.; Batra, G.; Kaltsa, O.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.; Makris, D.P. Saffron Processing Wastes as a Bioresource of High-Value Added Compounds: Development of a Green Extraction Process for Polyphenol Recovery Using a Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Diaz, J.; Sanchez, A.M.; Martinez-Tome, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Alonso, G.L. Flavonoid Determination in the Quality Control of Floral Bioresidues from Crocus sativus L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3125–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia, L.; Perez-Vidal, C.; Gracia-López, C. Automated cutting system to obtain the stigmas of the saffron flower. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignolini, P.; Heimler, D.; Pinelli, P.; Ieri, F.; Sciullo, A.; Romani, A. Characterization of By-products of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Production. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1959–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Ahmed, H.; Dixit, R.K.; Dharamveer; Saraf, S.A. Crocus sativus L.: A comprehensive review. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhassani, A.; Khavari, A.; Bathaie, S.Z. Saffron and natural carotenoids: Biochemical activities and anti-tumor effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, L.; Castronuovo, D.; Perniola, M.; Cicco, N.; Candido, V. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.), the king of spices: An overview. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, J.P.; Wang, S.; Marcone, M.F. Chemical and biological properties of the world’s most expensive spice: Saffron. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.A. Recent research developments in plant science. In Biology, Biotechnology and Biomedicine of Saffron; Research Signpost: Thiruvananthapuram, India, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 127–159. [Google Scholar]
- Olha, M.; Desenko, V.; Ivanauskas, L.; Georgiyants, V. Standard operating procedure of Ukrainian Saffron Cultivation According with Good Agricultural and Collection Practices to assure quality and traceability. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastani, S.; Vahedian, V.; Rashidi, M.; Mir, A.; Mirzaei, S.; Alipourfard, I.; Pouremamali, F.; Nejabati, H.; Kadkhoda, J.; Maroufi, N.F.; et al. An evaluation on potential anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Crocin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, R.A.; Sodhi, N.; Wani, I.; Khan, Z.; Dhillon, B.; Gani, A. Bioactive constituents of saffron plant: Extraction, Encapsulation and their Food and pharmaceutical applications. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Sánchez, A.M.; Ferreres, F.; Zalacain, A.; Tomás-Barberán, F.; Alonso, G.L. Identification of the flavonoid fraction in saffron spice by LC/DAD/MS/MS: Comparative study of samples from different geographical origins. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, M.; Zalacain, A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Novella, J.L.; Alonso, G.L. Crocetin esters, picrocrocin and its related compounds present in Crocus sativus stigmas and Gardenia jasminoides fruits. Tentative identification of seven new compounds by LC-ESI-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiri, M.; Rezadoost, H.; Ghassempour, A. A comparative quality study of saffron constituents through HPLC and HPTLC methods followed by isolation of crocins and picrocrocin. LWT 2017, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Perez, T.S.; Nevarez-Moorillon, G.V.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R.; Hernandez-Carranza, P.; Avila-Sosa, R. The Relation between Drying Conditions and the Development of Volatile Compounds in Saffron (Crocus sativus). Molecules 2021, 26, 6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghini, L.; Leporini, L.; Vecchiotti, G.; Locatelli, M.; Carradori, S.; Ferrante, C.; Zengin, G.; Recinella, L.; Chiavaroli, A.; Leone, S.; et al. Crocus sativus L. stigmas and byproducts: Qualitative fingerprint, antioxidant potentials and enzyme inhibitory activities. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goupy, P.; Vian, M.A.; Chemat, F.; Caris-Veyrat, C. Identification and quantification of flavonols, anthocyanins and lutein diesters in tepals of Crocus sativus by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to diode array and ion trap mass spectrometry detections. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshfegh, F.; Balanejad, S.Z.; Shahrokhabady, K.; Attaranzadeh, A. Crocus sativus (saffron) petals extract and its active ingredient, anthocyanin improves ovarian dysfunction, regulation of inflammatory genes and antioxidant factors in testosterone-induced PCOS mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigliobianco, M.R.; Cortese, M.; Peregrina, D.V.; Villa, C.; Lupidi, G.; Pruccoli, L.; Angeloni, C.; Tarozzi, A.; Censi, R.; Di Martino, P. Development of New Extracts of Crocus sativus L. By-Product from Two Different Italian Regions as New Potential Active Ingredient in Cosmetic Formulations. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Gahruie, H.; Parastouei, K.; Mokhtarian, M.; Rostami, H.; Niakousari, M.; Mohsenpour, Z. Application of innovative processing methods for the extraction of bioactive compounds from saffron (Crocus sativus) petals. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2020, 19, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, P.; Maldini, M.; Luciani, L.; Tuberoso, C.I.G.; Congiu, F.; Pizza, C. Radical Scavenging Activity and LC-MS Metabolic Profiling of Petals, Stamens, and Flowers of Crocus sativus L. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C893–C900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolskaite, L.; Talou, T.; Fabre, N.; Venskutonis, P.R. Valorization of saffron industry by-products: Bioactive compounds from leaves. In Innovations for Food Science and Production, Proceedings of the 6th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology FOODBALT-2011, Jelgava, Latvia, 5–6 May 2011; Faculty of Food Technology: Riga, Latvia; pp. 67–72.
- Baba, S.A.; Malik, A.H.; Wani, Z.A.; Mohiuddin, T.; Shah, Z.; Abbas, N.; Ashraf, N. Phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of different tissue types of Crocus sativus and oxidative stress alleviating potential of saffron extract in plants, bacteria, and yeast. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 99, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmass, I.; Lamkami, T.; Delporte, C.; Sikdar, S.; Van Antwerpen, P.; Saalaoui, E.; Megalizzi, V. The waste of saffron crop, a cheap source of bioactive compounds. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Zarinkamar, F.; Soltani, B.M.; Nazari, M. Induction of phenolic and flavonoid compounds in leaves of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by salicylic acid. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailenko, O.; Ivanauskas, L.; Bezruk, I.; Sidorenko, L.; Lesyk, R.; Georgiyants, V. Characterization of Phytochemical Components of Crocus sativus Leaves: A New Attractive By-Product. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.K.; Dong, A.; Hackett, S.F.; Bell, W.R.; Green, W.R.; Campochiaro, P.A. Oxidative damage in age-related macular degeneration. Histol. Histopathol. 2007, 22, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, M.F. Oxidatively modified proteins in aging and disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, A.R.; Chew, E.Y.; Clemons, T.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Danis, R.; Domalpally, A.; McBee, W.; Sperduto, R.; Ferris, F.L. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2): Study design and baseline characteristics (AREDS2 report number 1). Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsini, B.; Piccardi, M.; Minnella, A.; Savastano, C.; Capoluongo, E.; Fadda, A.; Balestrazzi, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S. Influence of saffron supplementation on retinal flicker sensitivity in early age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6118–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, K.; Moxley, R.T., 3rd. Autosomal dominant cramping disease. Arch. Neurol. 1990, 47, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Umigai, N.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Oral administration of crocetin prevents inner retinal damage induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 690, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M.; Marangoni, D.; Minnella, A.M.; Savastano, M.C.; Valentini, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Maccarone, R.; Bisti, S.; Falsini, B. A longitudinal follow-up study of saffron supplementation in early age-related macular degeneration: Sustained benefits to central retinal function. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 429124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamalan, O.A.; Moore, M.J.; Al Khalili, Y. Physiology, Serotonin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Lee, S.M. Neuroprotective Potency of Saffron Against Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Other Brain Disorders: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 579052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, B.; Hegyi, P.; Lantos, T.; Szakacs, Z.; Keremi, B.; Varga, G.; Tenk, J.; Petervari, E.; Balasko, M.; Rumbus, Z.; et al. The Efficacy of Saffron in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Depression: A Meta-analysis. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Lane, M.; Rocks, T.; Ruusunen, A.; Loughman, A.; Lopresti, A.; Marshall, S.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F.; Dean, O.M. Effect of saffron supplementation on symptoms of depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Drummond, P.D. Saffron (Crocus sativus) for depression: A systematic review of clinical studies and examination of underlying antidepressant mechanisms of action. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 29, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Sadeghi, O.; Rigi, S.; Tan, S.C.; Shokri, A.; Mousavi, S.M. Effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matraszek-Gawron, R.; Chwil, M.; Terlecki, K.; Skoczylas, M.M. Current Knowledge of the Antidepressant Activity of Chemical Compounds from Crocus sativus L. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsikas, N. Constituents of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders and Schizophrenia. Molecules 2016, 21, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Motamedshariaty, V.; Hadizadeh, F. Antidepressant effect of keamperol, a constituent of saffron (Crocus sativus) petal, in mice and rats. Pharmacologyonline 2007, 2, 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Mazidi, M.; Shemshian, M.; Mousavi, S.H.; Norouzy, A.; Kermani, T.; Moghiman, T.; Sadeghi, A.; Mokhber, N.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferns, G.A. A double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in the treatment of anxiety and depression. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2016, 13, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerda-Bernad, D.; Costa, L.; Serra, A.T.; Bronze, M.R.; Valero-Cases, E.; Perez-Llamas, F.; Candela, M.E.; Arnao, M.B.; Barberan, F.T.; Villalba, R.G.; et al. Saffron against Neuro-Cognitive Disorders: An Overview of Its Main Bioactive Compounds, Their Metabolic Fate and Potential Mechanisms of Neurological Protection. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamedani, S.G.; Pourmasoumi, M.; Zarifi, S.H.; Askari, G.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Bagherniya, M.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic effects of saffron and its components on neurodegenerative diseases. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gu, X. Crocetin Alleviates Inflammation in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models through Improving Mitochondrial Functions. Park. Dis. 2020, 2020, 9864370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, F.; Asadpour, E.; Hosseinzadeh, H.; Boroushaki, M.T.; Adab, A.; Dastpeiman, S.H.; Sadeghnia, H.R. Safranal protects against ischemia-induced PC12 cell injury through inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.K.; Qiao, L.Y.; Wen, X.N. Safranal prevents rotenone-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease through regulating Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sidhu, J.; Lui, F.; Tsao, J.W. Alzheimer Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, F.; Jamshidi, A.H.; Khodagholi, F.; Yans, A.; Azimi, L.; Faizi, M.; Vali, L.; Abdollahi, M.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Sharifzadeh, M. Reversal effects of crocin on amyloid beta-induced memory deficit: Modification of autophagy or apoptosis markers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2015, 139, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandreou, M.A.; Kanakis, C.D.; Polissiou, M.G.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Cordopatis, P.; Margarity, M.; Lamari, F.N. Inhibitory activity on amyloid-beta aggregation and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus stigmas extract and its crocin constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8762–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.S.; Dharamsi, A.; Priya, M.; Jain, S.; Mandal, V.; Girme, A.; Modi, S.J.; Hingorani, L. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) extract attenuates chronic scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment, amyloid beta, and neurofibrillary tangles accumulation in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, N.; Pazoki, B.; Momeni Roudsari, N.; Lashgari, N.A.; Jamshidi, V.; Momtaz, S.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Akhondzadeh, S. Prospects of Saffron and its Derivatives in Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Iran. Med. 2021, 24, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, Z.; Yang, G.; Ayati, M.H.; Emami, S.A.; Chang, D. Saffron for mild cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodriguez-Moran, M. Concordance between the 2005 International Diabetes Federation definition for diagnosing metabolic syndrome with the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III and the World Health Organization definitions. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2588–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javandoost, A.; Afshari, A.; Nikbakht-Jam, I.; Khademi, M.; Eslami, S.; Nosrati, M.; Foroutan-Tanha, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Tavalaie, S.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; et al. Effect of crocin, a carotenoid from saffron, on plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein and lipid profile in subjects with metabolic syndrome: A double blind randomized clinical trial. ARYA Atheroscler. 2017, 13, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noce, A.; Di Lauro, M.; Di Daniele, F.; Pietroboni Zaitseva, A.; Marrone, G.; Borboni, P.; Di Daniele, N. Natural Bioactive Compounds Useful in Clinical Management of Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronsisvalle, S.; Panico, A.; Santonocito, D.; Siciliano, E.A.; Sipala, F.; Montenegro, L.; Puglia, C. Evaluation of Crocin Content and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Glycation Activity of Different Saffron Extracts. Plants 2023, 12, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Diaz, J.; Sanchez, A.M.; Maggi, L.; Martinez-Tome, M.; Garcia-Diz, L.; Murcia, M.A.; Alonso, G.L. Increasing the applications of Crocus sativus flowers as natural antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C1162–C1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshanravan, B.; Samarghandian, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Amirabadizadeh, A.; Saeedi, F.; Farkhondeh, T. Metabolic impact of saffron and crocin: An updated systematic and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Rezaei Farimani, A.; Beydokhti, H.; Riahi, S.M. Comparison of the effect of saffron, crocin, and safranal on serum levels of oxidants and antioxidants in diabetic rats: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2429–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, A.; Aliyev, A.; Khamnei, S.; Delazar, A.; Mesgari Abbasi, M.; Mehmannavaz, Y. Effects of hydromethanolic extract of saffron (Crocus sativus) on serum glucose, insulin and cholesterol levels in healthy male rats. J. Med. Plants 2010, 4, 397–402. [Google Scholar]
- Mohajeri, D.; Mousavi, G.; Doustar, Y. Antihyperglycemic and Pancreas-Protective Effects of Crocus sativus L. (Saffron) Stigma Ethanolic Extract on Rats with Alloxan-Induced Diabetes. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 9, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Lee, H.; Jung, E.-S.; Seyedian, R.; Jo, M.; Kim, J.; Seyedian, R. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) increases glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity in muscle cells via multipathway mechanisms. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L.; Qian, Z.; Xu, G.; Zheng, S.; Sun, S.; Wen, N.; Sheng, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Beneficial impact of crocetin, a carotenoid from saffron, on insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. A radical explanation for glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1788–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, T.; Mousavi, S.H.; Shemshian, M.; Norouzy, A.; Mazidi, M.; Moezzi, A.; Moghiman, T.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferms, G.A. Saffron supplements modulate serum pro-oxidant-antioxidant balance in patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2015, 5, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Mojtahedi, S.; Hooshmand-Moghadam, B.; Rosenkranz, S.; Shourideh, Z.; Amirshaghaghi, F.; Shabkhiz, F. Improvement of inflammatory status following saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and resistance training in elderly hypertensive men: A randomized controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 162, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, T.; Mollaei, H.; Takhviji, V.; Bijari, B.; Zarban, A.; Rostami, Z.; Hoshyar, R. The anti-dyslipidemia property of saffron petal hydroalcoholicextract in cardiovascular patients: A double-blinded randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 55, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Spices for Prevention and Treatment of Cancers. Nutrients 2016, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, G.; Urciuoli, S.; Candi, E.; Bernini, R.; Vanni, G.; Masci, C.; Guerriero, C.; Mancini, M.; De Lorenzo, A.; Vignolini, P.; et al. Biological Activities of Molecules Derived from Olea europaea L. Tested In Vitro. Life 2023, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.M.; Mancini, A.; Lizzi, A.R.; De Simone, A.; Marroccella, C.E.; Gravina, G.L.; Tatone, C.; Festuccia, C. Crocus sativus stigma extract and its major constituent crocin possess significant antiproliferative properties against human prostate cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia, H.; Tavakkol Afshari, J.; Tabeshpour, J.; Younesi Rostami, M.; Mansourian, E.; Akhavan Rezayat, A.; Brook, A. Cytotoxic Effect of Saffron Stigma Aqueous Extract on Human Prostate Cancer and Mouse Fibroblast Cell Lines. Urol. J. 2020, 18, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezici, S. Comparative anticancer activity analysis of saffron extracts and a principle component, crocetin for prevention and treatment of human malignancies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5435–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Boskabady, M.H.; Davoodi, S. Use of in vitro assays to assess the potential antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in human lung cancer cell line. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2010, 6, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, E.; Gu, Y.; Shangguan, A.J.; Zhao, H.; Lv, T.; Yu, Z. Crocin inhibits cell proliferation and enhances cisplatin and pemetrexed chemosensitivity in lung cancer cells. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozon, L.; Saleh, E.; Menon, V.; Ramadan, W.S.; Amin, A.; El-Awady, R. Effect of safranal on the response of cancer cells to topoisomerase I inhibitors: Does sequence matter? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 938471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Q.; Fan, B.; Diao, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Inhibitory Effect of Crocin against Gastric Carcinoma via Regulating TPM4 Gene. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailenko, O.; Petrikaite, V.; Korinek, M.; Chang, F.R.; El-Shazly, M.; Yen, C.H.; Bezruk, I.; Chen, B.H.; Hsieh, C.F.; Lytkin, D.; et al. Pharmacological Potential and Chemical Composition of Crocus sativus Leaf Extracts. Molecules 2021, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, H. Anti-tumor effect of Crocus sativus petals polysaccharides by reconstructing tumor microenvironment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Gupta, M.; Nabi, G.; Biswas, S.; Ali, S.; Sarwat, M. Variation in the anti-oxidant, anti-obesity, and anti-cancer potential of different polarity extracts of saffron petals. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, R.; Trevisani, F.; Vignolini, P.; Vita, C.; Fiorio, F.; Campo, M.; Ieri, F.; Di Marco, F.; Salonia, A.; Romani, A.; et al. Evaluation of anti-cancer potential of saffron extracts against kidney and bladder cancer cells. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noce, A.; Marchetti, M.; Marrone, G.; Di Renzo, L.; Di Lauro, M.; Di Daniele, F.; Albanese, M.; Di Daniele, N.; De Lorenzo, A. Link between gut microbiota dysbiosis and chronic kidney disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 2057–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Singh, P.; Khurana, S.; Ganguly, N.K.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Rana, D.S.; Taneja, V.; Bhargava, V. Implications of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease: A review on current concepts and therapies. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooman, J.P.; Dekker, M.J.; Usvyat, L.A.; Kotanko, P.; van der Sande, F.M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and premature aging in advanced chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F938–F950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessi, M.; Noce, A.; Bertucci, P.; Noce, G.; Rizza, S.; De Stefano, A.; Manca di Villahermosa, S.; Bernardini, S.; De Lorenzo, A.; Di Daniele, N. Plasma and erythrocyte membrane phospholipids and fatty acids in Italian general population and hemodialysis patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2014, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Aryaeian, N.; Pahlavani, N.; Abbasi, D.; Hosseini, A.F.; Fallah, S.; Moradi, N.; Heydari, I. The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) supplementation on blood pressure, and renal and liver function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blinded, randomized clinical trial. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2019, 9, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, A.; Gu, Y.; Lin, S.Y. Herbal Treatment for Renal Diseases. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2005, 34, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Asadi-Samani, M.; Farkhondeh, T.; Bahmani, M. Assessment the effect of saffron ethanolic extract (Crocus sativus L.) on oxidative damages in aged male rat liver. Der Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, E.; Shahdadian, F.; Hadi, A.; Tarrahi, M.A.; Tarrahi, M.J. The Effect of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Supplementation on Renal Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 9622546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, G.R. The pecking order of free radicals and antioxidants: Lipid peroxidation, alpha-tocopherol, and ascorbate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 300, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Hendra, R.; Jaafar, H.Z. Evaluation of Crocus sativus L. stigma phenolic and flavonoid compounds and its antioxidant activity. Molecules 2010, 15, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, B.; Elyasi, S. Saffron nephroprotective effects against medications and toxins: A review of preclinical data. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariatifar, N.; Shoeibi, S.; Sani, M.J.; Jamshidi, A.H.; Zarei, A.; Mehdizade, A.; Dadgarnejad, M. Study on diuretic activity of saffron (stigma of Crocus sativus L.) Aqueous extract in rat. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2014, 5, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Ke, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, T.; Mentis, A.F.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Polissiou, M.G.; Tang, L.; et al. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and health outcomes: A meta-research review of meta-analyses and an evidence mapping study. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Betti, G.; Hensel, A. Saffron in phytotherapy: Pharmacology and clinical uses. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2007, 157, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modaghegh, M.H.; Shahabian, M.; Esmaeili, H.A.; Rajbai, O.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Safety evaluation of saffron (Crocus sativus) tablets in healthy volunteers. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.D.; Hallagan, J.B.; Taylor, S.L. The role of natural color additives in food allergy. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2001, 43, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Malik, K.; Moore, J.M.; Kamboj, B.R.; Malik, S.; Malik, V.K.; Arya, S.; Singh, K.; Mahanta, S.; Bishnoi, D.K. Valorisation of Agri-Food Waste for Bioactive Compounds: Recent Trends and Future Sustainable Challenges. Molecules 2024, 29, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marrone, G.; Urciuoli, S.; Di Lauro, M.; Cornali, K.; Montalto, G.; Masci, C.; Vanni, G.; Tesauro, M.; Vignolini, P.; Noce, A. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and Its By-Products: Healthy Effects in Internal Medicine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142319
Marrone G, Urciuoli S, Di Lauro M, Cornali K, Montalto G, Masci C, Vanni G, Tesauro M, Vignolini P, Noce A. Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and Its By-Products: Healthy Effects in Internal Medicine. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142319
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarrone, Giulia, Silvia Urciuoli, Manuela Di Lauro, Kevin Cornali, Giulia Montalto, Claudia Masci, Gianluca Vanni, Manfredi Tesauro, Pamela Vignolini, and Annalisa Noce. 2024. "Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and Its By-Products: Healthy Effects in Internal Medicine" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142319
APA StyleMarrone, G., Urciuoli, S., Di Lauro, M., Cornali, K., Montalto, G., Masci, C., Vanni, G., Tesauro, M., Vignolini, P., & Noce, A. (2024). Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and Its By-Products: Healthy Effects in Internal Medicine. Nutrients, 16(14), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142319






