The Human Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
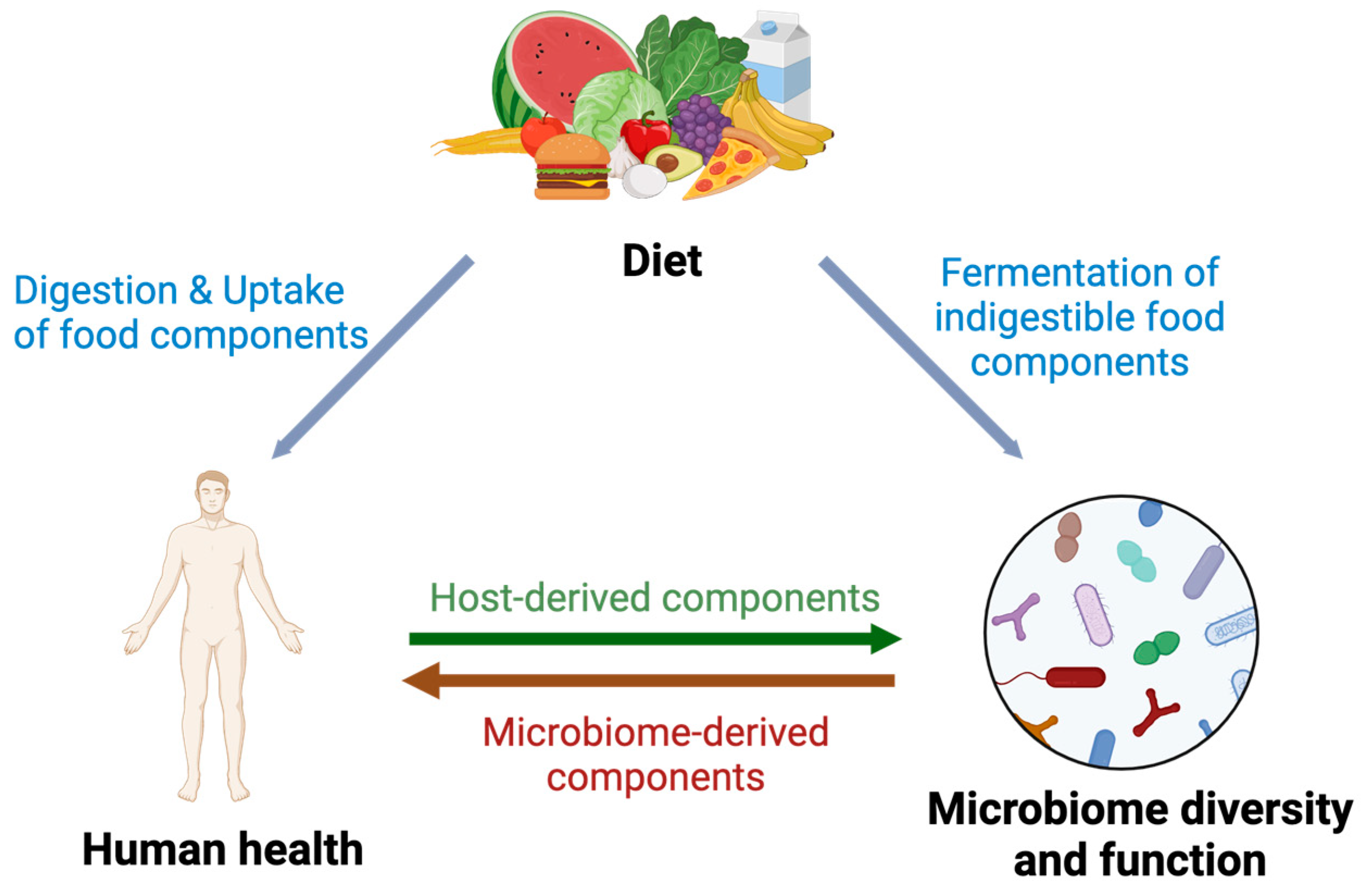
2. Interplay between the Human Microbiota, Diet and Health Determines Metabolic Outcome
3. Altered Microbiota in Metabolic Syndrome
4. The Human Microbiome as Therapeutic Target to Improve Metabolic Health
5. Potential Therapeutic Bacteria for Metabolic Health
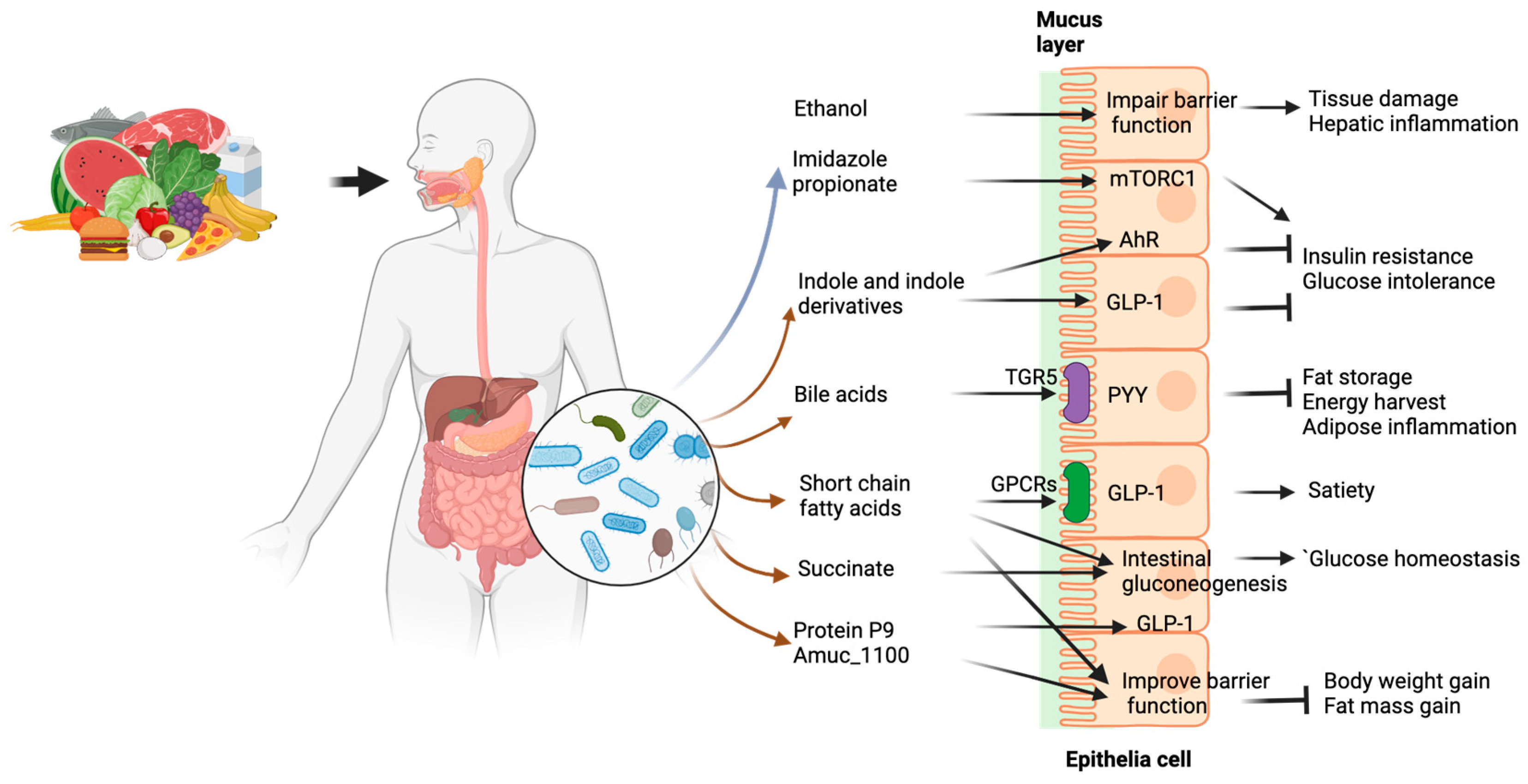
6. Microbial Components Affect Host Metabolism
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMT | fecal microbiota transplantation |
| SCFA | short chain fatty acid |
| BMI | body mass index |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| MASLD | metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| FFAR3 | free fatty acid receptor 3 |
| GPCR | G protein coupled receptors |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AhR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| TGR5 | takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor FXR |
| mTORC1 | mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 |
References
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; de Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 996–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, B.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Havulinna, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Jousilahti, P.; Ritchie, S.C.; Tokolyi, A.; Sanders, J.G.; Valsta, L.; Brożyńska, M.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Combined effects of host genetics and diet on human gut microbiota and incident disease in a single population cohort. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.-R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, N.W.S.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Kong, G.; Lin, C.; Chin, Y.H.; Lim, W.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Quek, J.; Fu, C.E.; et al. The global burden of metabolic disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 414–428.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Vandevijvere, S.; Pan, A.; McGowan, C.J.; Wallace, C.; Imamura, F.; Mozaffarian, D.; Swinburn, B.; Ezzati, M. The obesity transition: Stages of the global epidemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila in overweight and obese human volunteers: A proof-of-concept exploratory study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayappan, S.; Manneras-Holm, L.; Chaplin-Scott, A.; Belzer, C.; Herrema, H.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Duncan, S.H.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Groen, A.K.; Flint, H.J.; et al. Oral treatment with Eubacterium hallii improves insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2016, 2, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, A.; Van Nood, E.; Holleman, F.; Salojärvi, J.; Kootte, R.S.; Bartelsman, J.F.W.M.; Dallinga–Thie, G.M.; Ackermans, M.T.; Serlie, M.J.; Oozeer, R.; et al. Transfer of Intestinal Microbiota from Lean Donors Increases Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals With Metabolic Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 913–916.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Berry, S.E.; Valdes, A.M.; Nguyen, L.H.; Piccinno, G.; Drew, D.A.; Leeming, E.; Gibson, R.; Le Roy, C.; Khatib, H.A.; et al. Microbiome connections with host metabolism and habitual diet from 1,098 deeply phenotyped individuals. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. The Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cotillard, A.; Kennedy, S.P.; Kong, L.C.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Le Chatelier, E.; Almeida, M.; Quinquis, B.; Levenez, F.; Galleron, N.; et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature 2013, 500, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Soto, M.; Kostic, A.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Pan, H.; Ussar, S.; Altindis, E.; Li, N.; Bry, L.; et al. Diet, Genetics, and the Gut Microbiome Drive Dynamic Changes in Plasma Metabolites. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 3072–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wastyk, H.C.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Perelman, D.; Dahan, D.; Merrill, B.D.; Yu, F.B.; Topf, M.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Van Treuren, W.; Han, S.; et al. Gut-microbiota-targeted diets modulate human immune status. Cell 2021, 184, 4137–4153.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.; Miller, P.E.; Verbeke, K. Effects of cereal fiber on bowel function: A systematic review of intervention trials. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8952–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roager, H.M.; Hansen, L.B.S.; Bahl, M.I.; Frandsen, H.L.; Carvalho, V.; Gøbel, R.J.; Dalgaard, M.D.; Plichta, D.R.; Sparholt, M.H.; Vestergaard, H.; et al. Colonic transit time is related to bacterial metabolism and mucosal turnover in the gut. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xia, K.; Dai, M.; Han, X.; Yuan, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Jia, F.; Chen, J.; Jiang, F.; et al. Intermittent fasting modulates the intestinal microbiota and improves obesity and host energy metabolism. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordova, R.; Viallon, V.; Fontvieille, E.; Peruchet-Noray, L.; Jansana, A.; Wagner, K.-H.; Kyrø, C.; Tjønneland, A.; Katzke, V.; Bajracharya, R.; et al. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and risk of multimorbidity of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases: A multinational cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2023, 35, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Courten, B.; de Courten, M.P.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Walker, K.Z.; Forbes, J. Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products Consumption as a Direct Modulator of Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Humans: A Study Protocol for a Double-Blind, Randomized, Two Period Cross-Over Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2015, 4, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, K.; Ferreira, G.; Reis, F.; Viana, S. Impact of Dietary Sugars on Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health. Diabetology 2022, 3, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijnikman, A.S.; Davids, M.; Herrema, H.; Aydin, O.; Tremaroli, V.; Rios-Morales, M.; Levels, H.; Bruin, S.; de Brauw, M.; Verheij, J.; et al. Microbiome-derived ethanol in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Thaiss, C.A.; Maza, O.; Israeli, D.; Zmora, N.; Gilad, S.; Weinberger, A.; et al. Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota. Nature 2014, 514, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.; Peterson, D.; Gordon, J. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Isolauri, E.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S. Distinct composition of gut microbiota during pregnancy in overweight and normal-weight women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, S.H.; Lobley, G.E.; Holtrop, G.; Ince, J.; Johnstone, A.M.; Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Human colonic microbiota associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1720–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tims, S.; Derom, C.; Jonkers, D.M.; Vlietinck, R.; Saris, W.H.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Vos, W.M.; Zoetendal, E.G. Microbiota conservation and BMI signatures in adult monozygotic twins. ISME J. 2013, 7, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Wolin, M.; de Macario, E.; Macario, A. Isolation of Methanobrevibacter smithii from human feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Godneva, A.; Bar, N.; Kurilshikov, A.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Zhernakova, A.; et al. Structural variation in the gut microbiome associates with host health. Nature 2019, 568, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaye, I.; Witjes, J.J.; Koopen, A.M.; van der Vossen, E.W.J.; Zwirs, D.; Wortelboer, K.; Collard, D.; Kemper, E.M.; Winkelmeijer, M.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Oral Anaerobutyricum soehngenii augments glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. iScience, 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilijamse, P.W.; Hartstra, A.V.; Levin, E.; Wortelboer, K.; Serlie, M.J.; Ackermans, M.T.; Herrema, H.; Nederveen, A.J.; Imangaliyev, S.; Aalvink, S.; et al. Treatment with Anaerobutyricum soehngenii: A pilot study of safety and dose–response effects on glucose metabolism in human subjects with metabolic syndrome. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Esteve, E.; Tremaroli, V.; Khan, M.T.; Caesar, R.; Mannerås-Holm, L.; Ståhlman, M.; Olsson, L.M.; Serino, M.; Planas-Fèlix, M.; et al. Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, R.; Norvaisas, P.; Marinos, G.; Best, L.; Thingholm, L.B.; Quintaneiro, L.M.; De Haes, W.; Esser, D.; Waschina, S.; Lujan, C.; et al. Host-Microbe-Drug-Nutrient Screen Identifies Bacterial Effectors of Metformin Therapy. Cell 2019, 178, 1299–1312.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Belda, E.; Nielsen, T.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Chakaroun, R.; Forslund, S.K.; Assmann, K.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Nguyen, T.T.D.; et al. Statin therapy is associated with lower prevalence of gut microbiota dysbiosis. Nature 2020, 581, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwenger, K.J.; Clermont-Dejean, N.; Allard, J.P. The role of the gut microbiome in chronic liver disease: The clinical evidence revised. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Seth, A.; Sheth, P. Recent Advances in Alcoholic Liver Disease I. Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G881–G884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros, I.C.; de Lima, J.G. Is nonalcoholic fatty liver disease an endogenous alcoholic fatty liver disease?—A mechanistic hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 2015, 85, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Madsen, K.; Spiller, R.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Verne, G. Intestinal barrier function in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Grosheva, I.; Zheng, D.; Soffer, E.; Blacher, E.; Braverman, S.; Tengeler, A.C.; Barak, O.; Elazar, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia drives intestinal barrier dysfunction and risk for enteric infection. Science 2018, 359, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedé-Ubieto, R.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Breaking the barriers: The role of gut homeostasis in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2331460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, D.A.; Luck, H.; Tsai, S.; Winer, S. The Intestinal Immune System in Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segers, A.; de Vos, W.M. Mode of action of Akkermansia muciniphila in the intestinal dialogue: Role of extracellular proteins, metabolites and cell envelope components. Microbiome Res. Rep. 2023, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kootte, R.S.; Levin, E.; Salojärvi, J.; Smits, L.P.; Hartstra, A.V.; Udayappan, S.D.; Hermes, G.; Bouter, K.E.; Koopen, A.M.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity after Lean Donor Feces in Metabolic Syndrome Is Driven by Baseline Intestinal Microbiota Composition. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 611–619.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Interplay between gut microbiome, host genetic and epigenetic modifications in MASLD and MASLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrick, B.; Allen, L.; Masirah, M.Z.N.; Forbes, B.; Shawcross, D.L.; Goldenberg, S.D. Regulation, risk and safety of Faecal Microbiota Transplant. Infect Prev. Pract. 2020, 2, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.T.; Brul, S.; Zhang, J.; Wortel, M.T. Synthetic microbial communities (SynComs) of the human gut: Design, assembly, and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douchant, K.; He, S.-M.; Noordhof, C.; Greenlaw, J.; Vancuren, S.; Schroeter, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Sjaarda, C.; Vanner, S.J.; Petrof, E.O.; et al. Defined microbial communities and their soluble products protect mice from Clostridioides difficile infection. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Auchtung, J.M. Control of Clostridium difficile Infection by Defined Microbial Communities. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Collado, M.C.; Ben-Amor, K.; Salminen, S.; de Vos, W.M. The mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila is an abundant resident of the human intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, N.; Nigro, E.; Punčochář, M.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Ciciani, M.; Manghi, P.; Zolfo, M.; Cumbo, F.; Manara, S.; Golzato, D.; et al. Genomic diversity and ecology of human-associated Akkermansia species in the gut microbiome revealed by extensive metagenomic assembly. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzer, C.; Chia, L.W.; Aalvink, S.; Chamlagain, B.; Piironen, V.; Knol, J.; de Vos, W.M. Microbial Metabolic Networks at the Mucus Layer Lead to Diet-Independent Butyrate and Vitamin B(12) Production by Intestinal Symbionts. mBio 2017, 8, e00770-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.-h.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cuesta-Zuluaga, J.; Mueller, N.T.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Carmona, J.A.; Abad, J.M.; Escobar, J.S. Metformin Is Associated with Higher Relative Abundance of Mucin-Degrading Akkermansia muciniphila and Several Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Microbiota in the Gut. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Tsagarakis, S. Microbiome and diabetes: Where are we now? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 146, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Schmidt, C.; Lundqvist, A.; Olsson, L.M.; Krämer, M.; Gummesson, A.; Perkins, R.; Bergström, G.; Bäckhed, F. The Gut Microbiota in Prediabetes and Diabetes: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 379–390.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Nielsen, T.; Falony, G.; Le Chatelier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; Prifti, E.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Krogh Pedersen, H.; et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopen, A.; Witjes, J.; Wortelboer, K.; Majait, S.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Herrema, H.; Winkelmeijer, M.; Aalvink, S.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M.; et al. Duodenal Anaerobutyricum soehngenii infusion stimulates GLP-1 production, ameliorates glycaemic control and beneficially shapes the duodenal transcriptome in metabolic syndrome subjects: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study. Gut 2022, 71, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.P.N.; Mannerås-Holm, L.; Puschmann, R.; Wu, H.; Troise, A.D.; Nijsse, B.; Boeren, S.; Bäckhed, F.; Fiedler, D.; deVos, W.M. Conversion of dietary inositol into propionate and acetate by commensal Anaerostipes associates with host health. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, T.; Moens de Hase, E.; Van Hul, M.; Paquot, A.; Pelicaen, R.; Régnier, M.; Depommier, C.; Druart, C.; Everard, A.; Maiter, D. Dysosmobacter welbionis is a newly isolated human commensal bacterium preventing diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Gut 2021, 71, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, W.M.; Nguyen Trung, M.; Davids, M.; Liu, G.; Rios-Morales, M.; Jessen, H.; Fiedler, D.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Bui, T.P.N. Phytate metabolism is mediated by microbial cross-feeding in the gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1812–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T. Human Genetics Shape the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; You, H.J.; Yoon, H.S.; Kwon, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Song, Y.M.; Lee, K.; Sung, J.; Ko, G. The effect of heritability and host genetics on the gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. Gut 2017, 66, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.L.; Ley, R.E. The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Bonder, M.J.; Cenit, M.C.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Maatman, A.; Dekens, J.A.; Brandsma, E.; Marczynska, J.; Imhann, F.; Weersma, R.K.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Contributes to a Substantial Proportion of the Variation in Blood Lipids. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.P.N.; Ritari, J.; Boeren, S.; de Waard, P.; Plugge, C.M.; de Vos, W.M. Production of butyrate from lysine and the Amadori product fructoselysine by a human gut commensal. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luévano-Contreras, C.; Gómez-Ojeda, A.; Macías-Cervantes, M.H.; Garay-Sevilla, M.E. Dietary Advanced Glycation End Products and Cardiometabolic Risk. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampanelli, E.; Romp, N.; Troise, A.D.; Ananthasabesan, J.; Wu, H.; Gül, I.S.; Pascale, S.D.; Scaloni, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Fogliano, V.; et al. Gut bacterium Intestinimonas butyriciproducens improves host metabolic health: Evidence from cohort and animal intervention studies. Research Square, 2024; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Liao, M.; Zhou, N.; Bao, L.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Parabacteroides distasonis Alleviates Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunctions via Production of Succinate and Secondary Bile Acids. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 222–235.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Ruano, I.; Calvo, E.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Rodríguez-Peña, M.M.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Cedó, L.; Núñez-Roa, C.; Miro-Blanch, J.; Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Balvay, A.; et al. Orally administered Odoribacter laneus improves glucose control and inflammatory profile in obese mice by depleting circulating succinate. Microbiome 2022, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.F.; Liu, J.H.; March, J.C. Engineered commensal bacteria reprogram intestinal cells into glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.R.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.-U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinken, A.; Ravcheev, D.A.; Baldini, F.; Heirendt, L.; Fleming, R.M.T.; Thiele, I. Systematic assessment of secondary bile acid metabolism in gut microbes reveals distinct metabolic capabilities in inflammatory bowel disease. Microbiome 2019, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Xu, M.; Dong, W.; Deng, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, S.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Secondary bile acid-induced dysbiosis promotes intestinal carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Gioiello, A.; Noriega, L.; Strehle, A.; Oury, J.; Rizzo, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Mataki, C.; Pruzanski, M.; et al. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorucci, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Palladino, G.; Cipriani, S. Bile-acid-activated receptors: Targeting TGR5 and farnesoid-X-receptor in lipid and glucose disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Vrbanac, A.; Fu, T.; Patras, K.A.; Christy, M.P.; Bodai, Z.; Belda-Ferre, P.; Tripathi, A.; Chung, L.K.; et al. Global chemical effects of the microbiome include new bile-acid conjugations. Nature 2020, 579, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzior, D.V.; Okros, M.; Shivel, M.; Armwald, B.; Bridges, C.; Fu, Y.; Martin, C.; Schilmiller, A.L.; Miller, W.M.; Ziegler, K.M.; et al. Bile salt hydrolase acyltransferase activity expands bile acid diversity. Nature 2024, 626, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Plichta, D.R.; Arai, Y.; Sasajima, S.; Kearney, S.M.; Suda, W.; Takeshita, K.; Sasaki, T.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Novel bile acid biosynthetic pathways are enriched in the microbiome of centenarians. Nature 2021, 599, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, S.; Ma, N.; Johnston, L.J.; Wu, C.; Ma, X. Metabolites of microbiota response to tryptophan and intestinal mucosal immunity: A therapeutic target to control intestinal inflammation. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1061–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, D.; Spitzer, M.H.; Van Treuren, W.; Merrill, B.D.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature 2017, 551, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.B.; Van Benschoten, A.H.; Cimermancic, P.; Donia, M.S.; Zimmermann, M.; Taketani, M.; Ishihara, A.; Kashyap, P.C.; Fraser, J.S.; Fischbach, M.A. Discovery and Characterization of Gut Microbiota Decarboxylases that Can Produce the Neurotransmitter Tryptamine. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, V.D.; Paananen, J.; Lindström, J.; Lankinen, M.A.; Shi, L.; Kuusisto, J.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Auriola, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Rolandsson, O.; et al. Indolepropionic acid and novel lipid metabolites are associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Sun, K.; Benechet, A.P.; Qiu, Z.; Maher, L.; Redinbo, M.R.; Phillips, R.S.; et al. Symbiotic Bacterial Metabolites Regulate Gastrointestinal Barrier Function via the Xenobiotic Sensor PXR and Toll-like Receptor 4. Immunity 2014, 41, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abildgaard, A.; Elfving, B.; Hokland, M.; Wegener, G.; Lund, S. The microbial metabolite indole-3-propionic acid improves glucose metabolism in rats, but does not affect behaviour. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimerel, C.; Emery, E.; Summers, D.K.; Keyser, U.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Bacterial Metabolite Indole Modulates Incretin Secretion from Intestinal Enteroendocrine L Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.N.; Swimm, A.; Sonowal, R.; Bretin, A.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Jones, R.M.; Kalman, D. Indoles from the commensal microbiota act via the AHR and IL-10 to tune the cellular composition of the colonic epithelium during aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21519–21526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Xiao, H.; Lin, C.; Wong, H.L.X.; Lam, Y.Y.; Gong, M.; Wu, G.; Ning, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived tryptamine and phenethylamine impair insulin sensitivity in metabolic syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P.; Nikolic, T.; Pellegrini, S.; Sordi, V.; Imangaliyev, S.; Rampanelli, E.; Hanssen, N.; Attaye, I.; Bakker, G.; Duinkerken, G.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation halts progression of human new-onset type 1 diabetes in a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2021, 70, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.; de Souza, R.; Kendall, C.W.; Emam, A.; Jenkins, D.J. Colonic health: Fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Pomare, E.W.; Branch, W.J.; Naylor, C.P.; Macfarlane, G.T. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; Bleeker, A.; Gerding, A.; van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; van Dijk, T.H.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Protect Against High-Fat Diet–Induced Obesity via a PPARγ-Dependent Switch from Lipogenesis to Fat Oxidation. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psichas, A.; Sleeth, M.L.; Murphy, K.G.; Brooks, L.; Bewick, G.A.; Hanyaloglu, A.C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Frost, G. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holz, G.G.T.; Kühtreiber, W.M.; Habener, J.F. Pancreatic beta-cells are rendered glucose-competent by the insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-1(7-37). Nature 1993, 361, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Goncalves, D.; Vinera, J.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-Generated Metabolites Promote Metabolic Benefits via Gut-Brain Neural Circuits. Cell 2014, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariadason, J.M.; Barkla, D.H.; Gibson, P.R. Effect of short-chain fatty acids on paracellular permeability in Caco-2 intestinal epithelium model. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272 Pt 1, G705–G712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Reytor, D.; Puebla, C.; Karahanian, E.; García, K. Use of Short-Chain Fatty Acids for the Recovery of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Affected by Bacterial Toxins. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 650313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, S.; Hara, H. Physiological concentrations of short-chain fatty acids immediately suppress colonic epithelial permeability. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.N.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; Anderson, P.D.; Hinkle, C.C.; Shah, R.; Pruscino, L.; Tabita-Martinez, J.; Sellers, K.F.; Rickels, M.R.; Reilly, M.P. Experimental endotoxemia induces adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Masujima, Y.; Ushiroda, C.; Mizushima, R.; Taira, S.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Kimura, I. Dietary short-chain fatty acid intake improves the hepatic metabolic condition via FFAR3. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Chang, X.; Qi, K. Short Chain Fatty Acids Prevent High-fat-diet-induced Obesity in Mice by Regulating G Protein-coupled Receptors and Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Fillier, T.; Pham, T.H.; Thomas, R.; Cheema, S.K. Intraperitoneal Administration of Short-Chain Fatty Acids Improves Lipid Metabolism of Long-Evans Rats in a Sex-Specific Manner. Nutrients 2021, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinolo, M.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Festuccia, W.T.; Crisma, A.R.; Alves, V.S.; Martins, A.R.; Amaral, C.L.; Fiamoncini, J.; Hirabara, S.M.; Sato, F.T.; et al. Tributyrin attenuates obesity-associated inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E272–E282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollica, M.P.; Mattace Raso, G.; Cavaliere, G.; Trinchese, G.; De Filippo, C.; Aceto, S.; Prisco, M.; Pirozzi, C.; Di Guida, F.; Lama, A.; et al. Butyrate Regulates Liver Mitochondrial Function, Efficiency, and Dynamics in Insulin-Resistant Obese Mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouter, K.E.; Bakker, G.J.; Levin, E.; Hartstra, A.V.; Kootte, R.S.; Udayappan, S.D.; Katiraei, S.; Bahler, L.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Tremaroli, V.; et al. Differential metabolic effects of oral butyrate treatment in lean versus metabolic syndrome subjects. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.S.; Byrne, C.S.; Aspey, K.; Chen, Y.; Khan, S.; Morrison, D.J.; Frost, G. Acute oral sodium propionate supplementation raises resting energy expenditure and lipid oxidation in fasted humans. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Murata, Y.; Harada, N.; Yamane, S.; Hamasaki, A.; Shibue, K.; Joo, E.; Sankoda, A.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. Distribution and hormonal characterization of primary murine L cells throughout the gastrointestinal tract. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; Molinaro, A.; Ståhlman, M.; Khan, M.T.; Schmidt, C.; Mannerås-Holm, L.; Wu, H.; Carreras, A.; Jeong, H.; Olofsson, L.E.; et al. Microbially Produced Imidazole Propionate Impairs Insulin Signaling through mTORC1. Cell 2018, 175, 947–961.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; Mannerås-Holm, L.; Yunn, N.-O.; Nilsson, P.M.; Ryu, S.H.; Molinaro, A.; Perkins, R.; Smith, J.G.; Bäckhed, F. Microbial Imidazole Propionate Affects Responses to Metformin through p38γ-Dependent Inhibitory AMPK Phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 643–653.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Lu, J.; Yan, C.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Xue, G.; et al. Fatty Liver Disease Caused by High-Alcohol-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 675–688.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-Produced Succinate Improves Glucose Homeostasis via Intestinal Gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruigrok, R.; Weersma, R.K.; Vila, A.V. The emerging role of the small intestinal microbiota in human health and disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2201155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bui, T.P.N. The Human Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142322
Bui TPN. The Human Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142322
Chicago/Turabian StyleBui, Thi Phuong Nam. 2024. "The Human Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142322
APA StyleBui, T. P. N. (2024). The Human Microbiome as a Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients, 16(14), 2322. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142322





