Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: From the Old Paradigm to the New Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Acute Pancreatitis
4. Clinical Nutrition
5. Nutrition in Mild Acute Pancreatitis
6. Nutrition in Severe Acute Pancreatitis
7. Timing of Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis
8. Focus on Enteral Nutrition
8.1. Route of Administration
8.2. Composition of Enteral Formulas
9. The Role of Immunonutrition in AP
10. The Immunonutrients
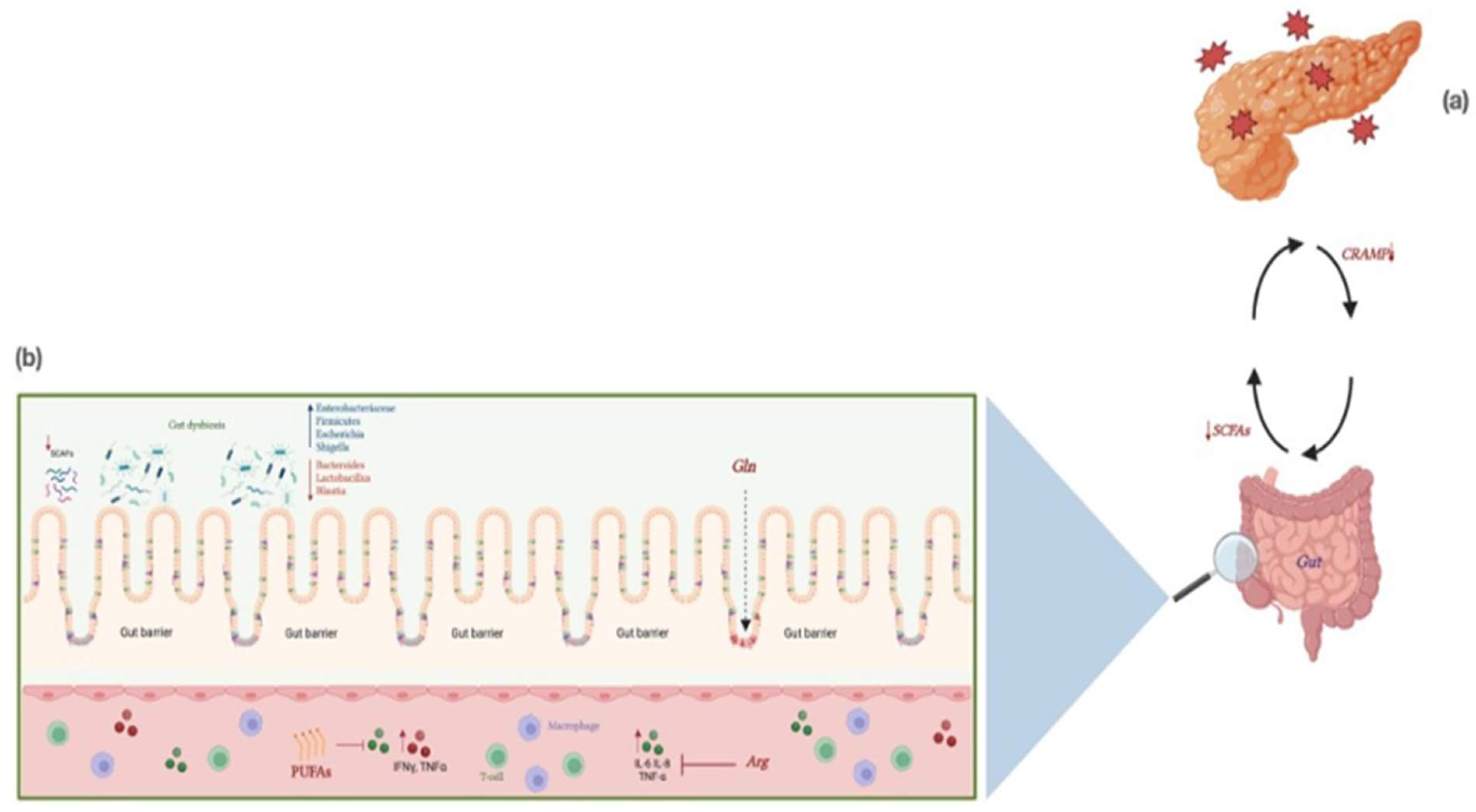
11. The Role of Gut Microbiota in AP
12. Modulation of Microbiota in AP
13. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frost, J.C.; Baldwin, A.J. “Food for Thought”: The Importance of Nutrition to Patient Care and the Role of the Junior Doctor. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, E272–E274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitakis, M.; Ockenga, J.; Bezmarevic, M.; Gianotti, L.; Krznarić, Ž.; Lobo, D.N.; Löser, C.; Madl, C.; Meier, R.; Phillips, M.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 612–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.H.; Brown, R.A.; Toussaint, G.P.M.L.; Thompson, A.G. Changing Methods in the Treatment of Severe Pancreatitis. Am. J. Surg. 1974, 127, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. Nutritional Support in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Current Standards. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.F.; Beglinger, C. Nutrition in Pancreatic Diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 20, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliari, D.; Brizi, M.G.; Saviano, A.; Mancarella, F.A.; Dal Lago, A.A.; Serricchio, M.L.; Newton, E.E.; Attili, F.; Manfredi, R.; Gasbarrini, A. Clinical Assessment and Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Multi-Disciplinary Approach in the XXI Century. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankisch, P.G.; Apte, M.; Banks, P.A. Acute Pancreatitis. Lancet 2015, 386, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, J.P.; King, J.A.; Leong, J.H.; Quan, J.; Windsor, J.W.; Tanyingoh, D.; Coward, S.; Forbes, N.; Heitman, S.J.; Shaheen, A.A.; et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.Y.; Tan, M.L.Y.; Wu, L.M.; Asrani, V.M.; Windsor, J.A.; Yadav, D.; Petrov, M.S. Global Incidence and Mortality of Pancreatic Diseases: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression of Population-Based Cohort Studies. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.E.; Morrison-Rees, S.; John, A.; Williams, J.G.; Brown, T.H.; Samuel, D.G. The Incidence and Aetiology of Acute Pancreatitis across Europe. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, C.; Deshpande, A.; Olyaee, M.; Anderson, M.P.; Bitar, A.; Steele, M.I.; Bass, P.F.; Sferra, T.J. Epidemiology of Acute Pancreatitis in Hospitalized Children in the United States from 2000–2009. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxhoorn, L.; Voermans, R.P.; Bouwense, S.A.; Bruno, M.J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G. Acute Pancreatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Geenen, E.J.M.; van der Peet, D.L.; Bhagirath, P.; Mulder, C.J.J.; Bruno, M.J. Etiology and Diagnosis of Acute Biliary Pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bálint, E.R.; Fűr, G.; Kiss, L.; Németh, D.I.; Soós, A.; Hegyi, P.; Szakács, Z.; Tinusz, B.; Varjú, P.; Vincze, Á.; et al. Assessment of the Course of Acute Pancreatitis in the Light of Aetiology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toouli, J.; Brooke-Smith, M.; Bassi, C.; Carr-Locke, D.; Telford, J.; Freeny, P.; Imrie, C.; Tandon, R. Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17 (Suppl. 1), S15–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Windsor, J.A.; Horvath, K.D.; et al. Classification of Acute Pancreatitis--2012: Revision of the Atlanta Classification and Definitions by International Consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Shanbhag, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Windsor, J.A. Organ Failure and Infection of Pancreatic Necrosis as Determinants of Mortality in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D.; et al. 2019 WSES Guidelines for the Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.X.; Ma, C.E. The Value of BISAP Score for Predicting Mortality and Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Definitions and Terminology of Clinical Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Martinez-Urbistondo, D.; Vargas-Nuñez, J.A.; Martinez, J.A. The Role of Nutrition on Meta-inflammation: Insights and Potential Targets in Communicable and Chronic Disease Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Who, J.; FAO Expert Consultation. Diet, Nutrition and the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2003, 916, 1–149. [Google Scholar]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Health Effects of Dietary Risks in 195 Countries, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downer, S.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Harlan, T.S.; Olstad, D.L.; Mozaffarian, D. Food Is Medicine: Actions to Integrate Food and Nutrition into Healthcare. BMJ 2020, 369, m2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, J.; Smith, T. Malnutrition: Causes and Consequences. Clin. Med. 2010, 10, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo Martín, C.A.; Aportela Vázquez, V.A.; Becerril Hernández, F.; Aguilar Medina, C.R.; Ayala Carrillo, S.L.; Chávez Flores, A.; Gabriel Almanza, E.; Guizar Agredano, M.I.; Montoya Vilchis, J.D. The GLIM criteria for adult malnutrition and its relation with adverse outcomes, a prospective observational study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 38, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Bosaeus, I.; Barazzoni, R.; Bauer, J.; van Gossum, A.; Klek, S.; Muscaritoli, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Ockenga, J.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Malnutrition—An ESPEN Consensus Statement. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.V.; Guenter, P.; Jensen, G.; Malone, A.; Schofield, M. Consensus Statement: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: Characteristics Recommended for the Identification and Documentation of Adult Malnutrition (Undernutrition). J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2012, 36, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Haß, U.; Pirlich, M. Malnutrition in Older Adults-Recent Advances and Remaining Challenges. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, C.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Clavé, P.; Costa, A.; Assegehegn, G. Nutritional Aspects of Dysphagia Management. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 271–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, M. Changing Concepts of Nutrient Requirements in Disease: Implications for Artificial Nutritional Support. Lancet 1995, 345, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawood, A.; Holmes, E.; Holdoway, A.; Parsons, E.; Anderson, L.; Milligan, W.; Relph, W.-L.; Ashworth, A.; Collery, R. Survey of Malnutrition and Nutritional Care in Adults; BAPEN: Worcestershire, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Besora-Moreno, M.; Llauradó, E.; Tarro, L.; Solà, R. Social and Economic Factors and Malnutrition or the Risk of Malnutrition in the Elderly: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungqvist, O.; Man, F. Under nutrition: A major health problem in Europe. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russel, C.A.; Elia, M. Nutrition Screening Survey in the UK and Republic of Ireland; BAPEN: Worcestershire, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-899467-81-5. [Google Scholar]
- Elia, M.; Russell, C.A. Nutrition Screening Survey in the UK in 2008. Hospitals, Care Homes and Mental Health Units; BAPEN: Worcestershire, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-1-899467-41-9. [Google Scholar]
- Imoberdorf, R.; Meier, R.; Krebs, P.; Hangartner, P.J.; Hess, B.; Stäubli, M.; Wegmann, D.; Rühlin, M.; Ballmer, P.E. Prevalence of Undernutrition on Admission to Swiss Hospitals. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarya, S.; Singh, K.; Sabharwal, M. Changes during Aging and Their Association with Malnutrition. J. Clin. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borum, P.R. Disease-Related Malnutrition: An Evidence-Based Approach to Treatmentedited by Rebecca J Stratton, Ceri J Green, and Marinos Elia, 2003, 824 Pages, Hardcover, $175. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, United Kingdom. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 1128–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Seres, D.; Lobo, D.N.; Gomes, F.; Kaegi-Braun, N.; Stanga, Z. Management of Disease-Related Malnutrition for Patients Being Treated in Hospital. Lancet 2021, 398, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, J.; Kondrup, J.; Prokopowicz, J.; Schiesser, M.; Krähenbühl, L.; Meier, R.; Liberda, M. EuroOOPS: An International, Multicentre Study to Implement Nutritional Risk Screening and Evaluate Clinical Outcome. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.M.; Veyres, P.; Pivot, X.; Soummer, A.-M.; Jambou, P.; Filippi, J.; van Obberghen, E.; Hébuterne, X. Malnutrition Is an Independent Factor Associated with Nosocomial Infections. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, M.; Russell, C.A. (Eds.) Combating Malnutrition: Recommendations for Action. Report from the Advisory Group on Malnutrition; BAPEN: Worcestershire, UK, 2009; ISBN 9781899467365. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, S.; Woods, R.T. Malnutrition and Quality of Life in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalatbari-Soltani, S.; Marques-Vidal, P. The Economic Cost of Hospital Malnutrition in Europe; a Narrative Review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2015, 10, e89–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, M. The Cost of Malnutrition in England and Potential Cost Savings from Nutritional Interventions (Short Version) A Report on the Cost of Disease-Related Malnutrition in England and a Budget Impact Analysis of Implementing the NICE Clinical Guidelines/Quality Standard on Nutritional Support in Adults; BAPEN: Worcestershire, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-899467-03-3. [Google Scholar]
- van Bokhorst-de van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Guaitoli, P.R.; Jansma, E.P.; de Vet, H.C.W. Nutrition Screening Tools: Does One Size Fit All? A Systematic Review of Screening Tools for the Hospital Setting. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis Bresson, J.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Ildico Hirsch-Ernst, K.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.; Naska, A.; Neuhäuser-Berthold, M.; et al. Scientific and Technical Guidance on Foods for Special Medical Purposes in the Context of Article 3 of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, M.L.; Brown, P.M.; Escuro, A.; Grenda, B.; Johnston, T.; Kozeniecki, M.; Limketkai, B.N.; Nelson, K.K.; Powers, J.; Ronan, A.; et al. ASPEN Enteral Nutrition Committee. When is enteral nutrition indicated? JPEN J. Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2022, 46, 1470–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.T. Medication Administration through Enteral Feeding Tubes. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makola, D. Elemental and Semi-Elemental Formulas: Are They Superior to Polymeric Formulas? Pract. Gastroenterol. 2005, 29, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Limketkai, B.N.; Shah, N.D.; Sheikh, G.N.; Allen, K. Classifying Enteral Nutrition: Tailored for Clinical Practice. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.; Puckett, Y. Total Parenteral Nutrition; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lappas, B.M.; Patel, D.; Kumpf, V.; Adams, D.W.; Seidner, D.L. Parenteral Nutrition: Indications, Access, and Complications. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Maldonado, E.; Gordo, S.L.Ó.P.; Pueyo, E.M.; Sánchez-García, A.; Mayol, S.; González, S.; Elvira, J.; Memba, R.; Fondevila, C.; Jorba, R. Immediate Oral Refeeding in Patients With Mild and Moderate Acute Pancreatitis: A Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial (PADI Trial). Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.M.; Nahikian-Nelms, M.; Ukleja, A.; Lara, L.F. Nutritional Aspects of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.M.M.; Felga, G.E.G.; Chebli, L.A.; Franco, M.B.; Gomes, C.A.; Gaburri, P.D.; Zanini, A.; Chebli, J.M.F. A Full Solid Diet as the Initial Meal in Mild Acute Pancreatitis Is Safe and Result in a Shorter Length of Hospitalization: Results from a Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, Double.e-Blind Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, L.; Sun, W. Efficacy Comparisons of Enteral Nutrition and Parenteral Nutrition in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis from Randomized Controlled Trials. BioSci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.M.; Ji, K.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, G.F.; Zang, B.; Chen, W.M. Total Enteral Nutrition in Prevention of Pancreatic Necrotic Infection in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2010, 39, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fostier, R.; Arvanitakis, M.; Gkolfakis, P. Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: When, What and How. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, L.; Zang, K.; Wang, M.; Shang, F.; Zhang, G. Comparison of the Preference of Nutritional Support for Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2019, 42, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.; Hackert, T.; Hartwig, W.; Rossmanith, F.; Strobel, O.; Schneider, L.; Will-Schweiger, K.; Kommerell, M.; Büchler, M.W.; Werner, J. Bacterial Translocation and Infected Pancreatic Necrosis in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Derives from Small Bowel Rather than from Colon. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 200, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClave, S.A.; Heyland, D.K. The Physiologic Response and Associated Clinical Benefits from Provision of Early Enteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2009, 24, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, P.; Peng, S.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y. Effects of Immediate or Early Oral Feeding on Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition on the Prognosis of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 10779–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klek, S.; Sierzega, M.; Turczynowski, L.; Szybinski, P.; Szczepanek, K.; Kulig, J. Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition in the Conservative Treatment of Pancreatic Fistula: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besselink, M.; van Santvoort, H.; Freeman, M.; Gardner, T.; Mayerle, J.; Vege, S.S.; Zyromski, N. IAP/APA Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2013, 13 (Suppl. 2), E1–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, S.D.; Wani, S.; Gardner, T.B.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Barkun, A.N.; Crockett, S.; Feuerstein, J.; Flamm, S.; Gellad, Z.; Gerson, L.; et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.H.; Tian, X.Y.; Qin, Y.L.; Han, X.T.; Wang, W. Immediate Enteral Nutrition Can Accelerate Recovery and Be Safe in Mild Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, O.J.; van Brunschot, S.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G.; Bollen, T.L.; Boermeester, M.A.; Dejong, C.H.; van Goor, H.; Bosscha, K.; Ali, U.A.; et al. Early versus On-Demand Nasoenteric Tube Feeding in Acute Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, I.; Horibe, M.; Sanui, M.; Sasaki, M.; Sawano, H.; Goto, T.; Ikeura, T.; Takeda, T.; Oda, T.; Yasuda, H.; et al. Impact of Enteral Nutrition Within 24 Hours Versus Between 24 and 48 Hours in Patients With Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Pancreas 2021, 50, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhong, Y.; Lu, X.; Kang, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Pei, L. Enteral Nutrition Provided within 48 Hours after Admission in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, G.C.; Yuan, Y.H.; Zhong, W.; Zhao, L.N.; Chen, Q.K. Enteral Nutrition within 48 Hours of Admission Improves Clinical Outcomes of Acute Pancreatitis by Reducing Complications: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nally, D.M.; Kelly, E.G.; Clarke, M.; Ridgway, P. Nasogastric Nutrition Is Efficacious in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.J.D. Physiological Response of the Human Pancreas to Enteral and Parenteral Feeding. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2006, 9, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.M.; Dobb, G.J.; Webb, S.A.R. A Comparison of Early Gastric and Post-Pyloric Feeding in Critically Ill Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, N.; Prakash, S.; Saraya, A.; Joshi, Y.K. Early Enteral Nutrition in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Nasojejunal and Nasogastric Routes. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, M.S.; Td Correia, I.; Windsor, J.A. Nasogastric Tube Feeding in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis. A Systematic Review of the Literature to Determine Safety and Tolerance. JOP 2008, 9, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, B.; Sharma, M.; Sachdev, V.; Bhardwaj, P.; Mani, K.; Joshi, Y.K.; Saraya, A. Evaluation of Early Enteral Feeding through Nasogastric and Nasojejunal Tube in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Noninferiority Randomized Controlled Trial. Pancreas 2012, 41, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.F.; Pisani, J.C.; Macedo, E.D.; Campos, A.C. The Nasogastric Feeding Tube as a Risk Factor for Aspiration and Aspiration Pneumonia. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Pietraszewski, M.; Holst, J.J.; O’Keefe, S.J.D. Enteral Feeding without Pancreatic Stimulation. Pancreas 2005, 31, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Fu, H.-Q.; Xiao, Y.-M.; Liu, J.-C. Nasogastric or Nasojejunal Feeding in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Ye, X.; Wei, J. Nasogastric Nutrition versus Nasojejunal Nutrition in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 6430632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendharkar, S.A.; Plank, L.D.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Quality of Life in a Randomized Trial of Nasogastric Tube Feeding in Acute Pancreatitis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerwall, G.E.; Axelsson, J.B.; Andersson, R.G. Early Nasogastric Feeding in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Clinical, Randomized Study. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatock, F.C.; Chong, P.; Menezes, N.; Murray, L.; McKay, C.J.; Carter, C.R.; Imrie, C.W. A Randomized Study of Early Nasogastric versus Nasojejunal Feeding in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, T.B.; Fu, K.Y.; Hipwell, R.C.; Baraghoshi, G.; Mone, M.C.; Nirula, R.; Kimball, E.J.; Barton, R.G. Safe, Timely, Convenient, and Cost-Effective: A Single-Center Experience with Bedside Placement of Enteral Feeding Tubes by Midlevel Providers Using Fluoroscopic Guidance. Am. J. Surg. 2012, 204, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Lv, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Ke, L.; Li, G.; Tong, Z.; Tu, J.; Li, W. Incidence and Risk Factors of Nasogastric Feeding Intolerance in Moderately-Severe to Severe Acute Pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClave, S.A.; Taylor, B.E.; Martindale, R.G.; Warren, M.M.; Johnson, D.R.; Braunschweig, C.; McCarthy, M.S.; Davanos, E.; Rice, T.W.; Cresci, G.A.; et al. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Adult Critically Ill Patient. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 159–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Brunschot, S.; van Grinsven, J.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Bakker, O.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Bosscha, K.; Bouwense, S.A.; Bruno, M.J.; et al. Endoscopic or Surgical Step-up Approach for Infected Necrotising Pancreatitis: A Multicentre Randomised Trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, K.; Freeny, P.; Escallon, J.; Heagerty, P.; Comstock, B.; Glickerman, D.J.; Bulger, E.; Sinanan, M.; Langdale, L.; Kolokythas, O.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Video-Assisted Retroperitoneal Debridement for Infected Pancreatic Collections: A Multicenter, Prospective, Single-Arm Phase 2 Study. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, A.R.; Malbrain, M.L.N.G.; Regli, A. Abdominal Pressure and Gastrointestinal Function: An Inseparable Couple? Anaesthesiol. Intensive 2017, 49, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D. UK Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 2005, 54 (Suppl. 3), iii1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatock, F.C.; Brombacher, G.D.; Steven, A.; Imrie, C.W.; McKay, C.J.; Carter, R. Nasogastric Feeding in Severe Acute Pancreatitis May Be Practical and Safe. Int. J. Pancreatol. 2000, 28, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Goel, A.; Kirubakaran, R.; Chacko, A.; Tharyan, P. Nasogastric versus Nasojejunal Tube Feeding for Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 3, CD010582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, M.; Aadam, A.A. Nutrition Management in Acute Pancreatitis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34 (Suppl. 1), S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A. Nutritional Support in Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Clin Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, M.S.; McIlroy, K.; Grayson, L.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Windsor, J.A. Early Nasogastric Tube Feeding versus Nil per Os in Mild to Moderate Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jing, X.; Tian, Z. Comparison of Nasogastric Feeding versus Nasojejunal Feeding for Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 22814–22823. [Google Scholar]
- Rinninella, E.; Annetta, M.; Serricchio, M.; Dal Lago, A.; Miggiano, G.; Mele, M. Nutritional Support in Acute Pancreatitis: From Physiopathology to Practice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClave, S.A.; Ritchie, C.S. Artificial nutrition in pancreatic disease: What lessons have we learned from the literature? Clin. Nutr. 2000, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiengou, L.E.; Gloro, R.; Pouzoulet, J.; Bouhier, K.; Read, M.H.; Arnaud-Battandier, F.; Plaze, J.M.; Blaizot, X.; Dao, T.; Piquet, M.A. Semi-Elemental Formula or Polymeric Formula: Is There a Better Choice for Enteral Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis? Randomized Comparative Study. JPEN J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2006, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidon, N.; Hecketsweiler, P.; Butel, J.; Bernier, J.J. Effect of Continuous Jejunal Perfusion of Elemental and Complex Nutritional Solutions on Pancreatic Enzyme Secretion in Human Subjects. Gut 1978, 19, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.R. Nutritional Support in Acute Pancreatitis: An Update on Management Issues. Semin Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 22, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Loveday, B.P.T.; Pylypchuk, R.D.; McIlroy, K.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Windsor, J.A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Enteral Nutrition Formulations in Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2009, 96, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, A.C.J.; Kanwar, S.; Li, A.G.K.; Barnes, E.; Guthrie, J.A.; Spark, J.I.; Welsh, F.; Guillou, P.J.; Reynolds, J.V. Compared with Parenteral Nutrition, Enteral Feeding Attenuates the Acute Phase Response and Improves Disease Severity in Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 1998, 42, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Patel, K.; Calder, P.C.; Yaqoob, P.; Primrose, J.N.; Johnson, C.D. A Randomised Clinical Trial to Assess the Effect of Total Enteral and Total Parenteral Nutritional Support on Metabolic, Inflammatory and Oxidative Markers in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis (APACHE II > or =6). Pancreatology 2003, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.J.; Murchison, J.T.; Fearon, K.C.H.; Ross, J.A.; Siriwardena, A.K. Randomized Controlled Trial of the Effect of Early Enteral Nutrition on Markers of the Inflammatory Response in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupelis, G.; Selga, G.; Austrums, E.; Kaminski, A. Jejunal Feeding, Even When Instituted Late, Improves Outcomes in Patients with Severe Pancreatitis and Peritonitis. Nutrition 2001, 17, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makola, D.; Krenitsky, J.; Parrish, C.; Dunston, E.; Shaffer, H.A.; Yeaton, P.; Kahaleh, M. Efficacy of Enteral Nutrition for the Treatment of Pancreatitis Using Standard Enteral Formula. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, A.; Shiraishi, A.; Fushimi, K.; Murata, K.; Otomo, Y. Comparative Effectiveness of Elemental Formula in the Early Enteral Nutrition Management of Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenner, S.; Baillie, J.; Dewitt, J.; Vege, S.S. American College of Gastroenterology Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, M.; Takada, T.; Mayumi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Isaji, S.; Wada, K.; Itoi, T.; Sata, N.; Gabata, T.; Igarashi, H.; et al. Japanese Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis: Japanese Guidelines 2015. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015, 22, 405–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, A.; Franklin, G.A.; Cheadle, W.G. Systemic Inflammation after Trauma. Injury 2007, 38, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.; Swrd, A.; Tingstedt, B.; Kerberg, D. Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis: Focus on Medical Care. Drugs 2009, 69, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyanarayan, G.; Garg, P.K.; Prasad, H.K.; Tandon, R.K. Elevated Level of Interleukin-6 Predicts Organ Failure and Severe Disease in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, A.R.; Leese, T.; Holliday, M.P.; Swann, R.A.; Cohen, J. Endotoxaemia and Serum Tumour Necrosis Factor as Prognostic Markers in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 1992, 33, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paajanens, H.; Laato, M.; Jaakkola, M.; Pulkki, K.; Niinikoski, J.; Nordback, I. Serum Tumour Necrosis Factor Compared with C-Reactive Protein in the Early Assessment of Severity of Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1995, 82, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.K.; Tong, Z.H.; Li, W.Q. The Effect of Immunonutrition in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2021, 34, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Romics, L. Enteral Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: A Review of the Current Evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16123–16131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrani, V.; Chang, W.K.; Dong, Z.; Hardy, G.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Glutamine Supplementation in Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pancreatology 2013, 13, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasztity, N.; Hamvas, J.; Biró, L.; Németh, É.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Decsi, T.; Pap, Á.; Antal, M. Effect of Enterally Administered N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Acute Pancreatitis--a Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, C.B.; Sadek, S.A.; Walters, A.M.; Goggin, P.M.; Somers, S.S.; Toh, S.K.; Johns, T.; Duncan, H.D. A double-blind, randomised, controlled trial to study the effects of an enteral feed supplemented with glutamine, arginine, and omega-3 fatty acid in predicted acute severe pancreatitis. JOP 2006, 7, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.X.; Wang, X.P.; Ma, J.J.; Jing, D.D.; Wang, P.W.; Wu, K. Effects of enteral nutrition supplemented with glutamine and arginine on gut barrier in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008, 88, 2407–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, T.; Feizi, A.; Askari, G.; Fallah, A.A. Parenteral Immunonutrition in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poropat, G.; Giljaca, V.; Hauser, G.; Štimac, D. Enteral Nutrition Formulations for Acute Pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, M.S.; Atduev, V.A.; Zagainov, V.E. Advanced Enteral Therapy in Acute Pancreatitis: Is There a Room for Immunonutrition? A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2008, 6, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. The Role of Immunonutrition in Patients Undergoing Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klek, S.; Kulig, J.; Sierzega, M.; Szczepanek, K.; Szybiński, P.; Scislo, L.; Walewska, E.; Kubisz, A.; Szczepanik, A.M. Standard and Immunomodulating Enteral Nutrition in Patients after Extended Gastrointestinal Surgery--a Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, L.I.; Lu, Q.P.; Liu, S.H.; Fan, H. Efficacy of Glutamine-Enriched Nutrition Support for Patients With Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. JPEN J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, H.; MercanlIgil, S.M.; Inanç, N.; Ok, E. Effects of Glutamine-Enriched Total Parenteral Nutrition on Acute Pancreatitis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.H.; Yang, Y.; He, H.L.; Xie, J.F.; Cai, S.X.; Liu, A.R.; Wang, H.L.; Qiu, H.B. The Effect of Glutamine Therapy on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Elke, G.; Cook, D.; Berger, M.M.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Albert, M.; Muscedere, J.; Jones, G.; Day, A.G. Glutamine and Antioxidants in the Critically Ill Patient: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Large-Scale Randomized Trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.; Muscedere, J.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Cook, D.; Jones, G.; Albert, M.; Elke, G.; Berger, M.M.; Day, A.G. A Randomized Trial of Glutamine and Antioxidants in Critically Ill Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Jing, D.; Wu, Z. Preoperative Enteral Immunonutrition Improves Postoperative Outcome in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.Z.; Abumrad, N.; Barbul, A. Effect of a Specialized Amino Acid Mixture on Human Collagen Deposition. Ann. Surg. 2002, 236, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, S.; Franchello, A.; Deiro, G.; Galletti, R.; Cassine, D.; Campra, D.; Bonfanti, D.; de Carli, L.; Fop, F.; Fronda, G.R. Preoperative Oral Immunonutrition versus Standard Preoperative Oral Diet in Well Nourished Patients Undergoing Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 31, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.L.; Yeh, S.L.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, W.J. Effects of Arginine-Enriched Total Parenteral Nutrition on Inflammatory-Related Mediator and T-Cell Population in Septic Rats. Nutrition 2002, 18, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Li, J. Omega-3 Fatty Acids-Supplemented Parenteral Nutrition Decreases Hyperinflammatory Response and Attenuates Systemic Disease Sequelae in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized and Controlled Study. JPEN J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2008, 32, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.C.; Wang, X.Y.; Xia, X.F.; Zheng, H.Z.; Bi, J.C.; Tian, F.; Li, N. The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, F.C.F.; Brenner, T.; Uhle, F.; Loesch, S.; Hackert, T.; Ulrich, A.; Hofer, S.; Dalpke, A.H.; Weigand, M.A.; Boutin, S. Gut Microbiome Patterns Correlate with Higher Postoperative Complication Rates after Pancreatic Surgery. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M. Recent Research on Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Garach, A.; Diaz-Perdigones, C.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Intestinal Microbiota and Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Sandhu, K.; Peterson, V.; Dinan, T.G. The Gut Microbiome in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepis, T.; de Lucia, S.S.; Nista, E.C.; Manilla, V.; Pignataro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Piccioni, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; Candelli, M. Microbiota in Pancreatic Diseases: A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiola, F.; Ianiro, G.; Franceschi, F.; Fagiuoli, S.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Gut Microbiota in Autism and Mood Disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; You, L.; Yang, J.; Feng, M.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zheng, L.; et al. Role of the Microbiome in Occurrence, Development and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvanitakis, M.; Gkolfakis, P.; Fernandez, Y.; Viesca, M. Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2021, 24, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.K.; Patel, K.H.; Bhatia, M.; Iyer, S.G.; Madhavan, K.; Moochhala, S.M. Gut Microbiome in Acute Pancreatitis: A Review Based on Current Literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5019–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Sankaran, S.J.; Plank, L.D.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Meta-Analysis of Gut Barrier Dysfunction in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.D. Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1996, 83, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Ling, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cai, T.; Yuan, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, K. Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota Associated With Inflammation Involved in the Progression of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas 2015, 44, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werge, M.; Novovic, S.; Schmidt, P.N.; Gluud, L.L. Infection Increases Mortality in Necrotizing Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pancreatology 2016, 16, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, N.; Kozarek, R.A.; Kanji, Z.S.; Chihara, S.; Gan, S.I.; Irani, S.; Larsen, M.; Ross, A.S.; Gluck, M. The Microbiology of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis in the Era of Minimally.y Invasive Therapy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshintala, V.S.; Talukdar, R.; Singh, V.K.; Goggins, M. The Gut Microbiome in Pancreatic Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Lu, Y.; Lou, L.; Zheng, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Cao, Z.; et al. Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota and Decrease in Paneth Cell Antimicrobial Peptide Level during Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis in Rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, M.; Schwartz, D.M.; Tandon, M.; Son, A.; Zeng, M.; Swaim, W.; Eckhaus, M.; Hoffman, V.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, B.; et al. Orai1-Mediated Antimicrobial Secretion from Pancreatic Acini Shapes the Gut Microbiome and Regulates Gut Innate Immunity. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.M.; Jobin, C. Microbiota in Pancreatic Health and Disease: The next Frontier in Microbiome Research. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; He, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.H. Role of Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Barrier Function in Acute Pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Furio, L.; Mecheri, R.; van der Does, A.M.; Lundeberg, E.; Saveanu, L.; Chen, Y.; van Endert, P.; Agerberth, B.; Diana, J. Pancreatic β-Cells Limit Autoimmune Diabetes via an Immunoregulatory Antimicrobial Peptide Expressed under the Influence of the Gut Microbiota. Immunity 2015, 43, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gao, G.; Sakandar, H.A.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z. Gut Dysbiosis in Pancreatic Diseases: A Causative Factor and a Novel Therapeutic Target. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Hu, J.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xia, L.; He, W.; Liu, L.; et al. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Worsens the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis in Patients and Mice. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, C. Use of Probiotics in the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oláh, A.; Belágyi, T.; Issekutz, Á.; Gamal, M.E.; Bengmark, S. Randomized Clinical Trial of Specific Lactobacillus and Fibre Supplement to Early Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besselink, M.G.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Buskens, E.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Goor, H.; Timmerman, H.M.; Nieuwenhuijs, V.B.; Bollen, T.L.; van Ramshorst, B.; Witteman, B.J.; et al. Probiotic Prophylaxis in Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.H.; Wang, X.H.; Peng, L.H.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y.S. The Effects of Early Enteral Nutrition with Addition of Probiotics on the Prognosis of Patients Suffering from Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2013, 25, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, N.S.; Mahid, S.S.; Idstein, S.R.; Hornung, C.A.; Galandiuk, S. Antibiotic Prophylaxis Is Not Protective in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Surg. 2009, 197, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villatoro, E.; Mulla, M.; Larvin, M. Antibiotic Therapy for Prophylaxis against Infection of Pancreatic Necrosis in Acute Pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD002941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Dai, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, K.; Guo, L. Assessment of Prophylactic Carbapenem Antibiotics Administration for Severe Acute Pancreatitis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Digestion 2022, 103, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J.A.; Hsu, J.; Bawazeer, M.; Marshall, J.; Friedrich, J.O.; Nathens, A.; Coburn, N.; May, G.R.; Pearsall, E.; McLeod, R.S. Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Can. J. Surg. 2016, 59, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Tian, J.; Ma, B.; Jiang, L. Probiotics in Patients with Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2009, 394, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Reid, G. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, A.; Belágyi, T.; Pótó, L.; Romics, L., Jr.; Bengmark, S. Synbiotic control of inflammation and infection in severe acute pancreatitis: A prospective, randomized, double blind study. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2007, 54, 590–594. [Google Scholar]
- Bongaerts, G.P.A.; Severijnen, R.S.V.M. A Reassessment of the PROPATRIA Study and Its Implications for Probiotic Therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.D.; Zhu, R.X.; Bian, Z.Z.; Sun, T.W. Effect of Probiotics on Length of Hospitalization in Mild Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohith, G.; Sureshkumar, S.; Anandhi, A.; Kate, V.; Rajesh, B.S.; Abdulbasith, K.M.; Nanda, N.; Palanivel, C.; Vijayakumar, C. Effect of Synbiotics in Reducing the Systemic Inflammatory Response and Septic Complications in Moderately Severe and Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Prospective Parallel-Arm Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 68, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.W.; Yu, E.Z.; Feng, Q. Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Sun, C.; Xu, H.; Zhu, J. Soluble Dietary Fiber Reduces Feeding Intolerance in Severe Acute Pancreatitis: A Randomized Study. JPEN J. Parenter Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| First Author | Year | Study Design | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kwok M. Ho [76] | 2006 | RCT | In critically ill adults with a good gastric emptying function, the use of NJ feeding instead of NG feeding was not associated with significant clinical advantages. |
| Kumar A. [77] | 2006 | RCT | EN by both NK and NG is well tolerated in patients with SAP without leading to recurrence or worsening of pain. |
| Petrov MS. [78] | 2008 | SR | NG route is safe and well tolerated in patients with predicted SAP. |
| Petrov MS. [98] | 2013 | RCT | Comparing NG feeding with NPO, the former significantly reduces the intensity and span of abdominal pain, need for analgesic, and risk of oral food intolerance. |
| Sing N. [79] | 2012 | RCT | Early NG feeding was not inferior to NJ in patients with SAP. |
| Chang Ys. [82] | 2013 | MA | No significant differences were found between NG and NJ tube regarding tracheal aspiration, energy balance, diarrhea, and mortality rate. |
| Nally D. [74] | 2014 | SR and MA | NG feeding is fruitful in patients with severe AP. |
| Zhu Y. [83] | 2016 | MA | Comparing NG or NJ nutrition in patients with SAP, no significant dissimilarities were found in the mortality rate, infectious and/or digestive complications, achieving energy balance, or length of hospital stay. |
| Guo Y. [99] | 2016 | SR and MA | NG may be the feeding solution choice in patients with SAP. |
| Pendharkar SA. [84] | 2014 | SR and MA | Nasogastric tube feeding was found to have no influence on the patient’s quality of life. |
| Eatock FC. [86] | 2005 | RT | The simpler, inexpensive, and more manageable used NG feeding is as good as NJ feeding in SAP. |
| Hauschild TB. [87] | 2012 | CS | NG tube feeding constitutes an economically preferable solution. |
| First Author | Year | Study Design | Type of Nutrition and Formula | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windsor Ac. [106] | 1998 | CT | Standard formula vs. total parenteral nutrition. | Proving that enteral feeding modulates the inflammatory response with a consequent better clinical outcome, Windsor, for the first time, suggested the potential use of standard formulations in patients suffering from AP. |
| Gupta R. [107] | 2003 | RCT | Standard formula vs. parenteral nutrition | Early use of nutritional support in the form of TEN is safe in predicted SAP. |
| Powell JJ. [108] | 2000 | RCT | Standard formula vs. no nutritional interventions | Early enteral nutrition was found to have no effect on inflammatory response markers or on organ dysfunction. |
| Tiengou LE. [102] | 2006 | RCT | Standard formula vs. polymeric formula by NJ tube feeding. | Despite both formulations being well tolerated, within the semi-elemental group the infection rate and the median LOS were found to be shorter. |
| Pupelis G. [109] | 2001 | RCT | Standard formula by NJ tube feeding, | Standard formula by jejunal feeding, even when started late, improves outcomes in patients with SAP. |
| Makola D. [110] | 2006 | CT | Standard formula by NJ tube feeding. | Standard enteral formula is effective in the management of patients with complicated AP. |
| Eckerwal GE. [85] | 2006 | RCT | Standard formula by NG tube feeding vs. total parenteral nutrition | Standard formula can also be administered by NG route. |
| Petrov MS. [105] | 2009 | SR and MA | Standard formula vs. semi-elemental formula. | The use of polymeric formulation is not associated with a significantly higher risk of feeding intolerance, infectious complications, or mortality rate. |
| Endo A. [111] | 2008 | RCS | Elemental formula vs. semi-elemental formula and standard formula. | No clinical advantages of the elemental formula in comparison with other formulae in terms of risk of sepsis, hospital-free days, total healthcare costs, and in-hospital mortality. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Lucia, S.S.; Candelli, M.; Polito, G.; Maresca, R.; Mezza, T.; Schepis, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Zileri Dal Verme, L.; Nicoletti, A.; Franceschi, F.; et al. Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: From the Old Paradigm to the New Evidence. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081939
De Lucia SS, Candelli M, Polito G, Maresca R, Mezza T, Schepis T, Pellegrino A, Zileri Dal Verme L, Nicoletti A, Franceschi F, et al. Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: From the Old Paradigm to the New Evidence. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081939
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Lucia, Sara Sofia, Marcello Candelli, Giorgia Polito, Rossella Maresca, Teresa Mezza, Tommaso Schepis, Antonio Pellegrino, Lorenzo Zileri Dal Verme, Alberto Nicoletti, Francesco Franceschi, and et al. 2023. "Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: From the Old Paradigm to the New Evidence" Nutrients 15, no. 8: 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081939
APA StyleDe Lucia, S. S., Candelli, M., Polito, G., Maresca, R., Mezza, T., Schepis, T., Pellegrino, A., Zileri Dal Verme, L., Nicoletti, A., Franceschi, F., Gasbarrini, A., & Nista, E. C. (2023). Nutrition in Acute Pancreatitis: From the Old Paradigm to the New Evidence. Nutrients, 15(8), 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081939








