Eating Frequency in European Children from 1 to 96 Months of Age: Results of the Childhood Obesity Project Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Eating Frequency (EF)
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Strength and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. Scientific Report of the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee: Advisory Report to the Secretary of Agriculture and the Secretary of Health and Human Services. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Leidy, H.J.; Campbell, W.W. The effect of eating frequency on appetite control and food intake: Brief synopsis of controlled feeding studies. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiva, M. Cultural aspects of meals and meal frequency. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 77 (Suppl. 1), S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition Novel Foods Food Allergens. Appropriate age range for introduction of complementary feeding into an infant’s diet. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan American Health Organization; World Health Organization. Guiding Principles for Complementary Feeding of the Breastfed Child; Pan American Health Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, J.; Lumeng, J.; Miller, L.; Smethers, A.; Lott, M. Evidence-Based Recommendations and Best Practices for Promoting Healthy Eating Behaviors in Children 2 to 8 Years; Healthy Eating Research: Durham, NC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vatanparast, H.; Islam, N.; Patil, R.P.; Shafiee, M.; Smith, J.; Whiting, S. Snack Consumption Patterns among Canadians. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Maguire, R.L.; Liu, J.; Kollins, S.H.; Murphy, S.K.; Hoyo, C.; Fuemmeler, B.F. Snacking frequency and dietary intake in toddlers and preschool children. Appetite 2019, 142, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayet-Moore, F.; Peters, V.; McConnell, A.; Petocz, P.; Eldridge, A.L. Weekday snacking prevalence, frequency, and energy contribution have increased while foods consumed during snacking have shifted among Australian children and adolescents: 1995, 2007 and 2011–12 National Nutrition Surveys. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, S.; Correia, D.; Severo, M.; Oliveira, A.; Torres, D.; Lopes, C. Eating frequency and weight status in Portuguese children aged 3–9 years: Results from the cross-sectional National Food, Nutrition and Physical Activity Survey 2015–2016. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B. Associations of eating frequency with adiposity measures, blood lipid profiles and blood pressure in British children and adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrad, H.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Johnson, L.; Boniface, D.; Jebb, S.A.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.; Wardle, J. Meal size is a critical driver of weight gain in early childhood. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, V.; Escribano, J.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Zaragoza-Jordana, M.; Ferré, N.; Grote, V.; Koletzko, B.; Totzauer, M.; Verduci, E.; ReDionigi, A.; et al. Unhealthy Dietary Patterns Established in Infancy Track to Mid-Childhood: The EU Childhood Obesity Project. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisari, P.; Yannakoulia, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Eating frequency and overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, E.; Oldigs, H.-D.; Santer, R.; Schaub, J. Feeding Patterns in Breast-Fed and Formula-Fed Infants. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2002, 46, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; von Kries, R.; Closa, R.; Escribano, J.; Scaglioni, S.; Giovannini, M.; Beyer, J.; Demmelmair, H.; Gruszfeld, D.; Dobrzanska, A.; et al. Lower protein in infant formula is associated with lower weight up to age 2 y: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.; Grote, V.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; Langhendries, J.-P.; Dain, E.; Giovannini, M.; Verduci, E.; Gruszfeld, D.; Socha, P.; et al. Lower protein content in infant formula reduces BMI and obesity risk at school age: Follow-up of a randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawellek, I.; Grote, V.; Theurich, M.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Stolarczyk, A.; Verduci, E.; Xhonneux, A.; Koletzko, B. Factors associated with sugar intake and sugar sources in European children from 1 to 8 years of age. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, V.; Escribano, J.; Mendez-Riera, G.; Schiess, S.; Koletzko, B.; Verduci, E.; Stolarczyk, A.; Martin, F.; Closa-Monasterolo, R. Methodological approaches for dietary intake assessment in formula-fed infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwied-Jorky, S.; Schiess, S.; Luque, V.; Grote, V.; Scaglioni, S.; Vecchi, F.; Martin, F.; Stolarczyk, A.; Koletzko, B.; European Childhood Obesity, P. Methodology for longitudinal assessment of nutrient intake and dietary habits in early childhood in a transnational multicenter study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.; Luque, V.; Xhonneux, A.; Verduci, E.; Socha, P.; Koletzko, B.; Berger, U.; Grote, V. A simple method for identification of misreporting of energy intake from infancy to school age: Results from a longitudinal study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Guidance on the EU Menu methodology. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, B.M.; Bleil, M.E.; Waring, M.E.; Schneider, K.L.; Nackers, L.M.; Busch, A.M.; Whited, M.C.; Pagoto, S.L. Beverages contribute extra calories to meals and daily energy intake in overweight and obese women. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 122, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, V.; Koletzko, B.; Luque, V.; Ferré, N.; Gruszfeld, D.; Gradowska, K.; Verduci, E.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Xhonneux, A.; Poncelet, P.; et al. Distribution of energy and macronutrient intakes across eating occasions in European children from 3 to 8 years of age: The EU Childhood Obesity Project Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 62, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Advances in Cross-National Comparison: A European Working Book for Demographic and Socio-Economic Variables; International standard classification of education, ISCED 1997; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, D.G.; Royston, P. The cost of dichotomising continuous variables. BMJ 2006, 332, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding Recommendations. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding#tab=tab_2 (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Entwistle, F.M. The Evidence and Rationale for the UNICEF UK Baby Friendly Initiative Standards; UNICEF UK: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hörnell, A.; Aarts, C.; Kylberg, E.; Hofvander, Y.; Gebre-Medhin, M. Breastfeeding patterns in exclusively breastfed infants: A longitudinal prospective study in Uppsala, Sweden. Acta Paediatr. 1999, 88, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.C.; Hepworth, A.R.; Sherriff, J.L.; Cox, D.B.; Mitoulas, L.R.; Hartmann, P.E. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Feeding Infants and Children from Birth to 24 Months: Summarizing Existing Guidance; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guiding Principles for Feeding Non-Breastfed Children 6–24 Months of Age; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lutter, C.K.; Grummer-Strawn, L.; Rogers, L. Complementary feeding of infants and young children 6 to 23 months of age. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 825–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redsell, S.A.; Edmonds, B.; Swift, J.A.; Siriwardena, A.N.; Weng, S.; Nathan, D.; Glazebrook, C. Systematic review of randomised controlled trials of interventions that aim to reduce the risk, either directly or indirectly, of overweight and obesity in infancy and early childhood. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 12, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.D.; Ziegler, P.; Pac, S.; Barvara, D. Meal and Snack Patterns of Infants and Toddlers. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.W.; Iosua, E.; Heath, A.M.; Gray, A.R.; Taylor, B.J.; Lawrence, J.A.; Hanna, M.; Cameron, S.L.; Sayers, R.; Galland, B. Eating frequency in relation to BMI in very young children: A longitudinal analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition and Allergies. Scientific Opinion on nutrient requirements and dietary intakes of infants and young children in the European Union. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. High ratio of resting energy expenditure to body mass in childhood and adolescence: A mechanistic model. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2012, 24, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, T.K.; Geoghegan, J.G.; Baird, A.W.; Winter, D.C. Implications of altered gastrointestinal motility in obesity. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, P.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Verschueren, S.; Lehmann, A.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Review article: The role of gastric motility in the control of food intake. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, G.; van Eijnatten, E.J.M.; van Lieshout, G.A.A.; Lambers, T.T.; Smeets, P.A.M. Gastric Emptying and Intragastric Behavior of Breast Milk and Infant Formula in Lactating Mothers. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3718–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Driessche, M.; Peeters, K.; Marien, P.; Ghoos, Y.; Devlieger, H.; Veereman-Wauters, G. Gastric emptying in formula-fed and breast-fed infants measured with the 13C-octanoic acid breath test. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 29, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsum, E.; Lonnerdal, B. Variation in the contents of nutrients of breast milk during one feeding. Nutr. Rep. Int. 1979, 19, 815–820. [Google Scholar]

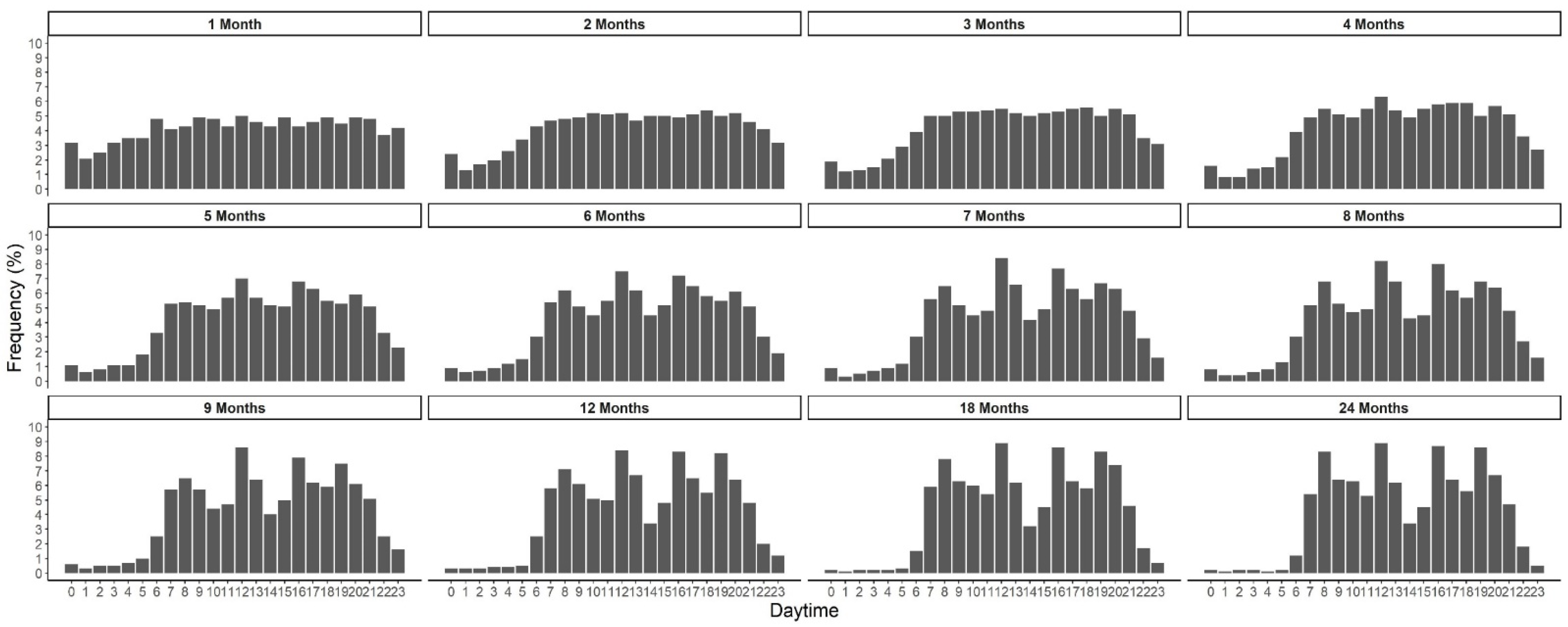
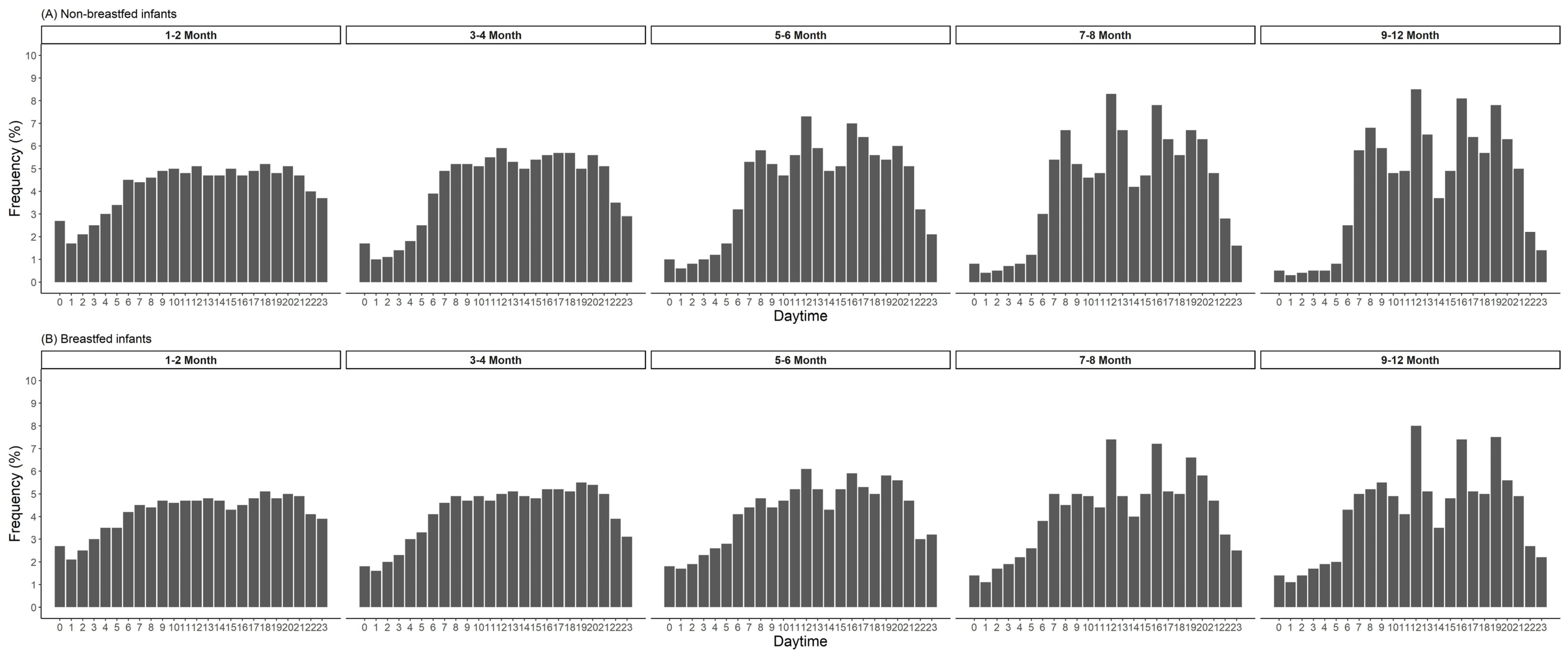
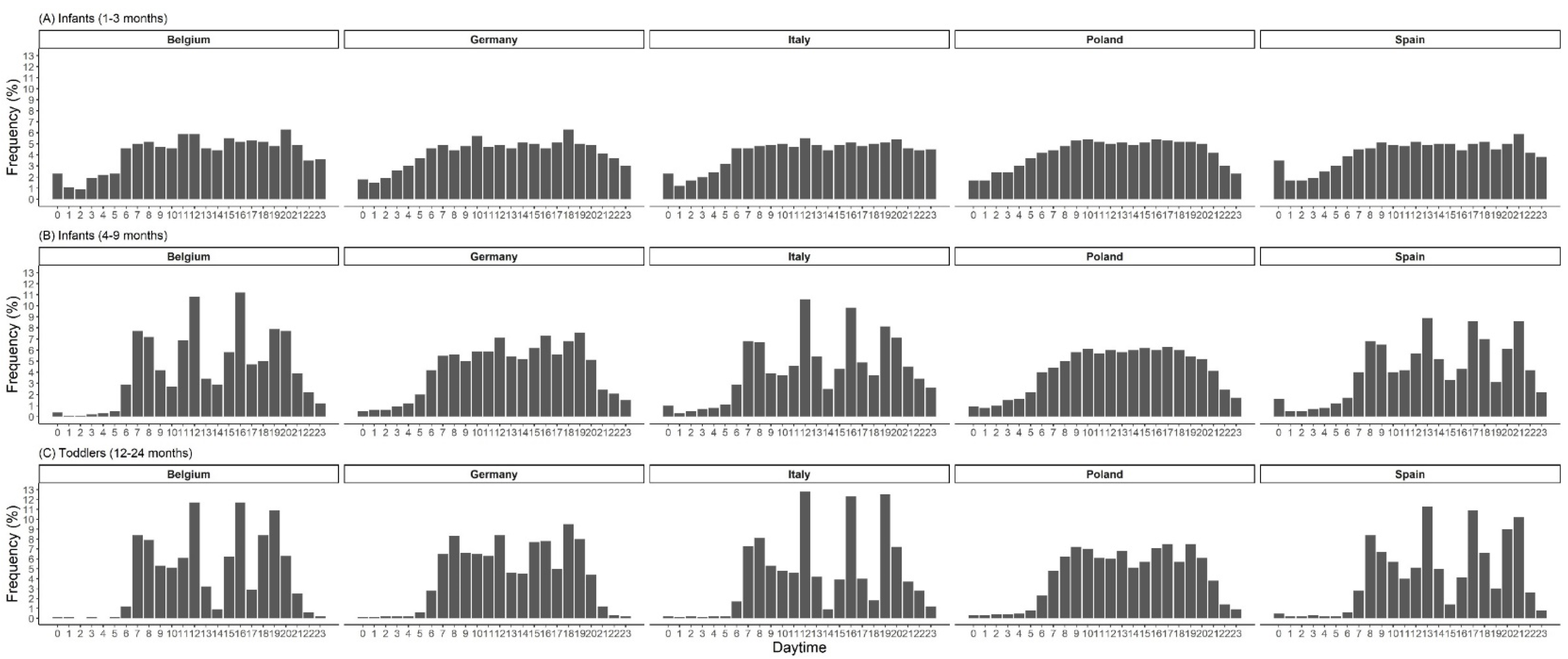
| Age in Months | n | Eating Frequency | Energy | Carbohydrates | Protein | Fat | Misreporting ** | Energy Density | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kcal/day | Kcal/kg/day * | %E | g/day | %E | g/day | %E | g/day | Under- Report * | Over- Report * | ||||
| 1 | 616 | 7.3 ± 1.9 | 526 ± 117 | 154 ± 42 | 44 ± 2 | 57 ± 12 | 9 ± 2 | 12 ± 4 | 47 ± 3 | 27 ± 6 | --- | --- | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 2 | 833 | 7.1 ± 2.2 | 571 ± 125 | --- | 44 ± 2 | 62 ± 13 | 9 ± 2 | 13 ± 4 | 47 ± 3 | 29 ± 6 | --- | --- | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 3 | 839 | 6.6 ± 2.1 | 600 ± 136 | 99 ± 22 | 44 ± 2 | 65 ± 15 | 9 ± 2 | 14 ± 4 | 47 ± 3 | 31 ± 6 | 104 (12) | 86 (10) | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | 808 | 6.4 ± 2.1 | 640 ± 136 | --- | 46 ± 4 | 72 ± 17 | 9 ± 2 | 15 ± 5 | 45 ± 5 | 31 ± 6 | --- | --- | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 5 | 815 | 6.4 ± 2.2 | 685 ± 147 | --- | 49 ± 6 | 83 ± 21 | 10 ± 3 | 18 ± 6 | 40 ± 6 | 30 ± 7 | --- | --- | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 6 | 812 | 6.3 ± 2.3 | 731 ± 176 | 93 ± 21 | 52 ± 6 | 94 ± 24 | 11 ± 3 | 20 ± 7 | 36 ± 6 | 29 ± 8 | 39 (5) | 205 (25) | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| 7 | 784 | 6.1 ± 2.1 | 772 ± 172 | --- | 53 ± 6 | 101 ± 24 | 13 ± 3 | 24 ± 8 | 34 ± 6 | 29 ± 8 | --- | --- | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| 8 | 778 | 6.1 ± 2.1 | 812 ± 183 | --- | 53 ± 6 | 106 ± 24 | 13 ± 3 | 26 ± 8 | 33 ± 6 | 30 ± 8 | --- | --- | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| 9 | 783 | 6.2 ± 2.2 | 838 ± 200 | --- | 53 ± 6 | 109 ± 26 | 13 ± 3 | 28 ± 9 | 33 ± 6 | 30 ± 9 | --- | --- | 0.8 ± 0.5 |
| 12 | 829 | 5.9 ± 1.9 | 896 ± 208 | 91 ± 22 | 52 ± 7 | 115 ± 28 | 15 ± 3 | 33 ± 10 | 33 ± 6 | 32 ± 9 | 47 (6) | 273 (33) | 1.0 ± 0.7 |
| 18 | 742 | 5.8 ± 1.7 | 1042 ± 246 | --- | 50 ± 7 | 128 ± 32 | 17 ± 3 | 42 ± 12 | 33 ± 6 | 38 ± 10 | --- | --- | 1.2 ± 0.9 |
| 24 | 778 | 5.9 ± 1.7 | 1120 ± 283 | 90 ± 24 | 49 ± 7 | 136 ± 33 | 16 ± 3 | 45 ± 13 | 34 ± 6 | 42 ± 12 | 61 (8) | 171 (22) | 1.2 ± 0.9 |
| 36 | 556 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 1234 ± 303 | 83 ± 22 | 50 ± 7 | 150 ± 37 | 16 ± 3 | 47 ± 12 | 34 ± 6 | 46 ± 13 | 36 (6) | 95 (17) | 1.3 ± 1.0 |
| 48 | 528 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 1329 ± 304 | 78 ± 20 | 50 ± 7 | 162 ± 35 | 15 ± 3 | 50 ± 13 | 35 ± 6 | 51 ± 14 | 29 (5) | 73 (14) | 1.4 ± 1.1 |
| 60 | 483 | 5.3 ± 1.4 | 1404 ± 325 | 72 ± 19 | 50 ± 7 | 172 ± 40 | 15 ± 3 | 52 ± 13 | 35 ± 6 | 54 ± 14 | 48 (10) | 57 (12) | 1.4 ± 1.0 |
| 72 | 520 | 5.2 ± 1.2 | 1481 ± 325 | 68 ± 17 | 50 ± 6 | 183 ± 39 | 15 ± 3 | 55 ± 13 | 35 ± 6 | 57 ± 14 | 60 (12) | 43 (8) | 1.4 ± 1.0 |
| 96 | 444 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | 1596 ± 364 | 57 ± 16 | 49 ± 7 | 191 ± 42 | 15 ± 3 | 60 ± 15 | 36 ± 6 | 63 ± 18 | 109 (25) | 14 (3) | 1.5 ± 1.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaeger, V.; Koletzko, B.; Luque, V.; Gruszfeld, D.; Verduci, E.; Xhonneux, A.; Grote, V. Eating Frequency in European Children from 1 to 96 Months of Age: Results of the Childhood Obesity Project Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040984
Jaeger V, Koletzko B, Luque V, Gruszfeld D, Verduci E, Xhonneux A, Grote V. Eating Frequency in European Children from 1 to 96 Months of Age: Results of the Childhood Obesity Project Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040984
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaeger, Vanessa, Berthold Koletzko, Veronica Luque, Dariusz Gruszfeld, Elvira Verduci, Annick Xhonneux, and Veit Grote. 2023. "Eating Frequency in European Children from 1 to 96 Months of Age: Results of the Childhood Obesity Project Study" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040984
APA StyleJaeger, V., Koletzko, B., Luque, V., Gruszfeld, D., Verduci, E., Xhonneux, A., & Grote, V. (2023). Eating Frequency in European Children from 1 to 96 Months of Age: Results of the Childhood Obesity Project Study. Nutrients, 15(4), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040984







