Magnesium Administration in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
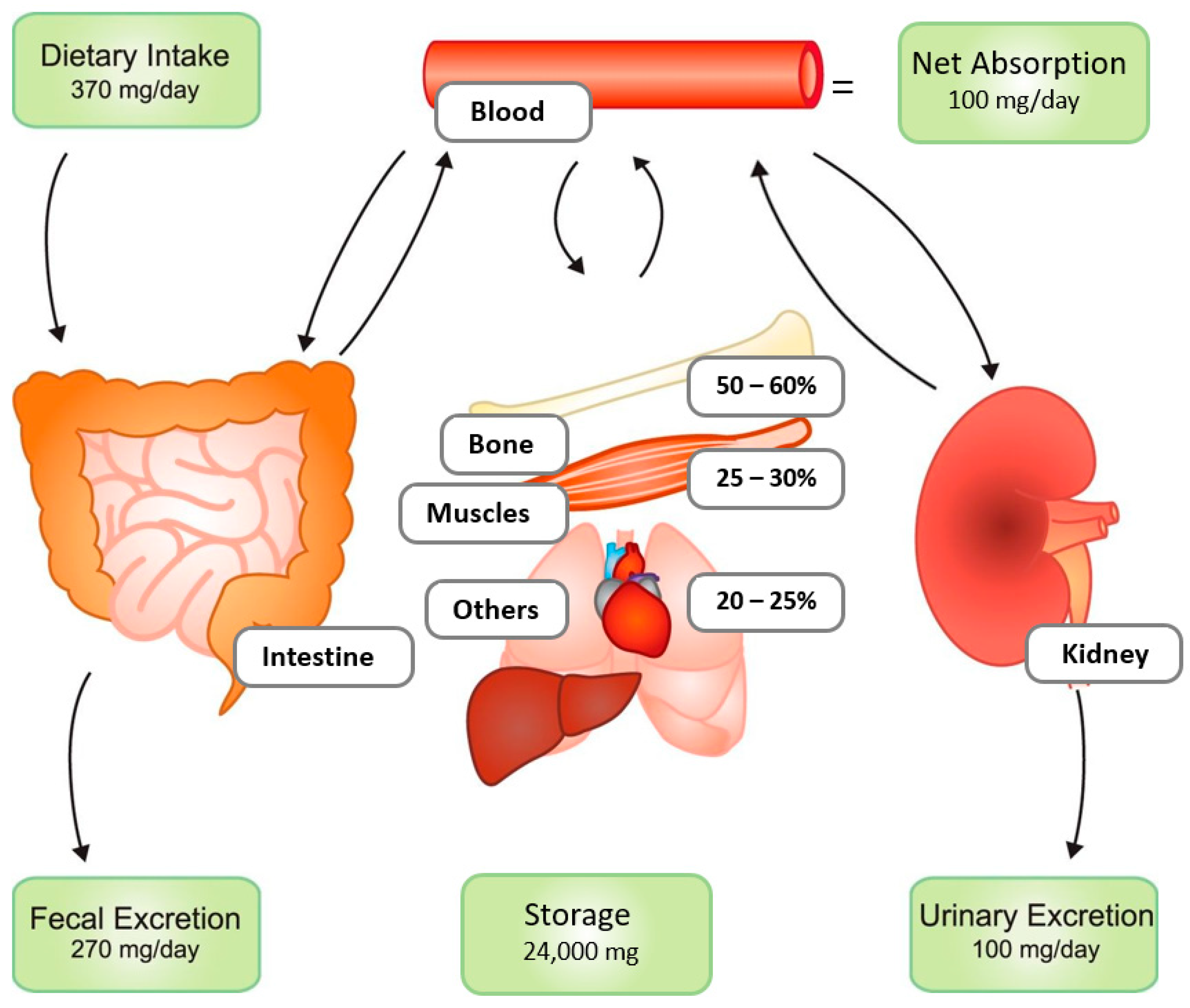
1. Introduction
2. Modes to Administer Magnesium
3. Magnesium Administration to Improve Health
3.1. Impact of Magnesium Administration on Cardiac Function
3.2. Impact of Magnesium Administration on Vascular Disease
3.3. Impact of Magnesium Administration on Calcification Propensity
3.4. Impact of Magnesium Administration on Markers of CKD-MBD
3.5. Magnesium Administration and Other Clinically Relevant Outcomes
4. Risks of Magnesium Administration
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quamme, G.A. Recent developments in intestinal magnesium absorption. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, L.A.; Caesar, J.J.; Burgen, A.S. Gastrointestinal absorption and excretion of Mg 28 in man. Metabolism 1960, 9, 646–659. [Google Scholar]
- Schmulen, A.C.; Lerman, M.; Pak, C.Y.; Zerwekh, J.; Morawski, S.; Fordtran, J.S.; Vergne-Marini, P. Effect of 1,25-(OH)2D3 on jejunal absorption of magnesium in patients with chronic renal disease. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1980, 238, G349–G352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elin, R.J. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Disease-A-Month 1988, 34, 166–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quamme, G.A.; Dirks, J.H. The Physiology of Renal Magnesium Handling. Ren Physiol. 1986, 9, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-González, J.F.; Mora-Fernández, C.; García-Pérez, J. Clinical Implications of Disordered Magnesium Homeostasis in Chronic Renal Failure and Dialysis. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovtzer, M.M.; Schainuck, L.I.; Massry, S.G.; Kleeman, C.R. Divalent Ion Excretion in Chronic Kidney Disease: Relation to Degree of Renal Insufficiency. Clin. Sci. 1970, 38, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, J.W.; Popovtzer, M.M.; Massry, S.G.; Kleeman, C.R. The Physicochemical State and Renal Handling of Divalent Ions in Chronic Renal Failure. Arch. Intern. Med. 1969, 124, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, T.; Vallon, V.; Van Der Kemp, A.W.; Loffing, J.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Enhanced passive Ca2+ reabsorption and reduced Mg2+ channel abundance explains thiazide-induced hypocalciuria and hypomagnesemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quamme, G.A. Effect of furosemide on calcium and magnesium transport in the rat nephron. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1981, 241, F340–F347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lameris, A.L.L.; Hess, M.W.; Van Kruijsbergen, I.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Omeprazole enhances the colonic expression of the Mg2+ transporter TRPM6. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2013, 465, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cundy, T.; Dissanayake, A. Severe hypomagnesaemia in long-term users of proton-pump inhibitors. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feeney, K.A.; Hansen, L.L.; Putker, M.; Olivares-Yañez, C.; Day, J.; Eades, L.J.; Larrondo, L.F.; Hoyle, N.P.; O’Neill, J.S.; Van Ooijen, G. Daily magnesium fluxes regulate cellular timekeeping and energy balance. Nature 2016, 532, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workinger, J.L.; Doyle, R.P.; Bortz, J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutten, J.C.; Post, A.; van der Meer, M.; Ijmker, J.; Goorman, F.; Danel, R.M.; Vervloet, M.G.; de Borst, M.H.; Touw, D.J.; Bakker, S.J. Comparison of two methods for the assessment of intra-erythrocyte magnesium and its determinants: Results from the LifeLines cohort study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Ryan, M.F.; Counihan, T.B. The Effect of Diuretics on Lymphocyte Magnesium and Potassium. Acta Med. Scand. 1981, 209, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, N.H.J.; Vervloet, M.G. Magnesium: A Magic Bullet for Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease? Nutrients 2019, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrii, M.; Covic, A.; Massy, Z.A. Magnesium supplementation: A consideration in dialysis patients. Semin. Dial. 2017, 31, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.F.; Marakis, G.; Christie, S.; Byng, M. Mg citrate found more bioavailable than other Mg preparations in a randomised, double-blind study. Magnes. Res. 2003, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, D.M.; Farmer, B. Long-term effects of magnesium carbonate on coronary artery calcification and bone mineral density in hemodialysis patients: A pilot study. Hemodial. Int. 2009, 13, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanakis, I.P.; Papadaki, A.N.; Wei, M.; Kagia, S.; Spadidakis, V.V.; Kallivretakis, N.E.; Oreopoulos, D.G. Magnesium carbonate for phosphate control in patients on hemodialysis. A randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2008, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, D.M.; Farmer, B.; Smits, G.; Chonchol, M. Magnesium Carbonate Is an Effective Phosphate Binder for Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Hamano, T.; Obi, Y.; Monden, C.; Oka, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Matsui, I.; Hashimoto, N.; Matsumoto, A.; Shimada, K.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Magnesium Oxide and Oral Carbon Adsorbent for Coronary Artery Calcification in Predialysis CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, M.; Moeinzadeh, F.; Saadatnia, M.; Shahidi, S.; McGee, J.C.; Minagar, A. Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Flow-Mediated Dilatation among Hemodialysis Patients: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. Neurol. 2013, 69, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, O.; Kurt, H.; Sarı, Y.; Şarkış, C.; Us, H.; Kırık, A. Magnesium Replacement Improves the Metabolic Profile in Obese and Pre-Diabetic Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease: A 3-Month, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, M.; Azadbakht, L.; Khalili, N.; Mortazavi, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Improved Lipid Profile but Increased Insulin Resistance in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 193, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, H.R.; Zakizade, M.; Soleimani, A.; Bahmani, F.; Ghaderi, A.; Mirhosseini, N.; Eslahi, M.; Babadi, M.; Mansournia, M.A.; Asemi, Z. Effects of magnesium supplementation on carotid intima–media thickness and metabolic profiles in diabetic haemodialysis patients: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, F.; Kanbay, M.; Metin, M.R.; Uz, E.; Akcay, A.; Covic, A. Magnesium supplementation helps to improve carotid intima media thickness in patients on hemodialysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2008, 40, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, E.A.; Eelderink, C.; Hoekstra, T.; van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Raijmakers, P.; Beulens, J.W.; de Borst, M.H.; Vervloet, M.G. Reversal of Arterial Disease by modulating Magnesium and Phosphate (ROADMAP-study): Rationale and design of a randomized controlled trial assessing the effects of magnesium citrate supplementation and phosphate-binding therapy on arterial stiffness in moderate chronic kidney disease. Trials 2022, 23, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressendorff, I.; Hansen, D.; Schou, M.; Silver, B.; Pasch, A.; Bouchelouche, P.; Pedersen, L.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Brandi, L. Oral Magnesium Supplementation in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4: Efficacy, Safety, and Effect on Serum Calcification Propensity—A Prospective Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Dietary Reference Values for Nutrients; European Food Safety Authority: Parma, Italy, 2019.
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary reference intakes. In Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; Report No.: 0309063507; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wodschow, K.; Hansen, B.; Schullehner, J.; Ersbøll, A.K. Stability of Major Geogenic Cations in Drinking Water—An Issue of Public Health Importance: A Danish Study, 1980–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodschow, K.; Villanueva, C.M.; Larsen, M.L.; Gislason, G.; Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B.; Ersbøll, A.K. Association between magnesium in drinking water and atrial fibrillation incidence: A nationwide population-based cohort study, 2002–2015. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Qin, G.; Tan, N. Magnesium Levels in Drinking Water and Coronary Heart Disease Mortality Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braake, A.D.; Smit, A.E.; Bos, C.; van Herwaarden, A.E.; Alkema, W.; van Essen, H.W.; Bravenboer, N.; Vervloet, M.G.; Hoenderop, J.G.; de Baaij, J.H. Magnesium prevents vascular calcification in Klotho deficiency. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, N.H.J.; Bos, C.; Hoekstra, T.; Schurgers, L.J.; Vervloet, M.G.; Hoenderop, J.G.J. Dietary magnesium supplementation inhibits abdominal vascular calcification in an experimental animal model of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Tocados, J.M.; Peralta-Ramirez, A.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Raya, A.I.; Lopez, I.; Pineda, C.; Herencia, C.; de Oca, A.M.; Vergara, N.; Steppan, S.; et al. Dietary magnesium supplementation prevents and reverses vascular and soft tissue calcifications in uremic rats. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Ma, W.; Sun, X.Y.; Jia, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C. Magnesium Citrate Protects Against Vascular Calcification in an Adenine-induced Chronic Renal Failure Rat Model. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 72, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelt, J.G.E.; McCabe, K.M.; Svajger, B.; Barron, H.; Laverty, K.; Holden, R.M.; Adams, M.A. Magnesium Modifies the Impact of Calcitriol Treatment on Vascular Calcification in Experimental Chronic Kidney Disease. Experiment 2015, 355, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenders, N.H.J.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Hoekstra, T.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Vervloet, M.G. Routine hemodialysis induces a decline in plasma magnesium concentration in most patients: A prospective observational cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressendorff, I.; Hansen, D.; Schou, M.; Pasch, A.; Brandi, L. The Effect of Increasing Dialysate Magnesium on Serum Calcification Propensity in Subjects with End Stage Kidney Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressendorff, I.; Hansen, D.; Pasch, A.; Holt, S.G.; Schou, M.; Brandi, L.; Smith, E.R. The effect of increasing dialysate magnesium on calciprotein particles, inflammation and bone markers: Post hoc analysis from a randomized controlled clinical trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giorno, R.; Hadjeres, S.L.; Stefanelli, K.; Allegra, G.; Zapparoli, C.; Predrag, L.; Berwert, L.; Gabutti, L. Consequences of Supraphysiological Dialysate Magnesium on Arterial Stiffness, Hemodynamic Profile, and Endothelial Function in Hemodialysis: A Randomized Crossover Study Followed by a Non-Controlled Follow-Up Phase. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 4848–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, E.; Vervloet, M.G.; Lubach, C.H.; Nurmohamed, S.A.; Penne, E.L. Feasibility of long-term continuous subcutaneous magnesium supplementation in a patient with irreversible magnesium wasting due to cisplatin. Neth. J. Med. 2017, 75, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, S.K.; Baker, M.; Nightingale, J.M. High-output stoma after small-bowel resections for Crohn’s disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 2, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Martínez, J.J.; Romero, F.B.; Oliveira, C.L.; López, A.H. Severe hypocalcemia secondary to hypomagnesaemia, successfully treated by self-administered subcutaneous magnesium. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 354–356. [Google Scholar]
- Leenders, N.H.; Vermeulen, E.A.; van Ballegooijen, A.J.; Hoekstra, T.; de Vries, R.; Beulens, J.W.; Vervloet, M.G. The association between circulating magnesium and clinically relevant outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 3133–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misialek, J.R.; Lopez, F.L.; Lutsey, P.L.; Huxley, R.R.; Peacock, J.M.; Chen, L.Y.; Soliman, E.Z.; Agarwal, S.K.; Alonso, A. Serum and Dietary Magnesium and Incidence of Atrial Fibrillation in Whites and in African Americans—Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reffelmann, T.; Dörr, M.; Ittermann, T.; Schwahn, C.; Völzke, H.; Ruppert, J.; Robinson, D.; Felix, S.B. Low serum magnesium concentrations predict increase in left ventricular mass over 5 years independently of common cardiovascular risk factors. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Papacosta, O.; Lennon, L.; Whincup, P.H. Serum magnesium and risk of incident heart failure in older men: The British Regional Heart Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Alonso, A.; Michos, E.D.; Loehr, L.; Astor, B.C.; Coresh, J.; Folsom, A.R. Serum magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium are associated with risk of incident heart failure: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieboom, B.C.T.; Niemeijer, M.N.; Leening, M.J.G.; Berg, M.E.V.D.; Franco, O.H.; Deckers, J.W.; Hofman, A.; Zietse, R.; Stricker, B.H.; Hoorn, E.J. Serum Magnesium and the Risk of Death from Coronary Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac Death. J. Am. Hearth Assoc. 2016, 5, e002707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Lubitz, S.A.; Sullivan, L.; Sun, J.X.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.; Benjamin, E.J.; Wang, T. Low Serum Magnesium and the Development of Atrial Fibrillation in the Community. Circulation 2013, 127, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuijdewijn, C.L.M.D.R.V.; Grooteman, M.P.C.; Bots, M.L.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Steppan, S.; Büchel, J.; Groenwold, R.H.H.; Brandenburg, V.; Dorpel, M.A.V.D.; ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Serum Magnesium and Sudden Death in European Hemodialysis Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Venditti, F.J., Jr.; Evans, J.C.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D. The associations of levels of serum potassium and magnesium with ventricular premature complexes: The Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rob, P.M.; Niederstadt, C.; Finck, C.; Kreft, B.; Dibbelt, L.; Steinhoff, J. Dialysate magnesium, magnesium handling and clinical considerations in chronic hemodialysis patients. Trace. Elem. Electroly. 1999, 16, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Aggarwal, N.; Zurakowski, D.; Jonas, R.A.; Berul, C.I.; Hanumanthaiah, S.; Moak, J.P. Lower risk of postoperative arrhythmias in congenital heart surgery following intraoperative administration of magnesium. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorman, B.; Sade, R.M.; Burnette, J.S.; Wiles, H.B.; Pinosky, M.L.; Reeves, S.T.; Bond, B.R.; Spinale, F.G. Magnesium supplementation in the prevention of arrhythmias in pediatric patients undergoing surgery for congenital heart defects. Am. Hearth J. 2000, 139, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiset, C.; Kargacin, M.E.; Kondo, C.S.; Lester, W.M.; Duff, H.J. Hypomagnesemia: Characterization of a model of sudden cardiac death. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1996, 27, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircelli, F.; Peter, M.E.; Ok, E.S.; Celenk, F.G.; Yilmaz, M.; Steppan, S.; Asci, G.; Passlick-Deetjen, J. Magnesium reduces calcification in bovine vascular smooth muscle cells in a dose-dependent manner. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 27, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louvet, L.; Büchel, J.; Steppan, S.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Massy, Z.A. Magnesium prevents phosphate-induced calcification in human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 28, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Braake, A.D.; Eelderink, C.; Zeper, L.W.; Pasch, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; De Borst, M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Calciprotein particle inhibition explains magnesium-mediated protection against vascular calcification. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, A.O.; Biyani, M.; Hammond, I.; Harmon, J.P.; Lavoie, S.; McCormick, B.; Sood, M.M.; Wagner, J.; Pena, E.; Zimmerman, D.L. Lower serum magnesium is associated with vascular calcification in peritoneal dialysis patients: A cross sectional study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Katsuno, T.; Nobata, H.; Iwagaitsu, S.; Sugiyama, H.; Kinashi, H.; Banno, S.; Ando, M.; Kubo, Y.; et al. Association between serum magnesium levels and abdominal aorta calcification in patients with pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease stage 5. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, A.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Jacques, P.F.; Meigs, J.B.; Hoffmann, U.; McKeown, N.M. Magnesium Intake Is Inversely Associated with Coronary Artery Calcification: The Framingham Heart Study. JACC: Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhou, J.; Xu, T.; Sheng, Z.; Huang, A.; Sun, L.; Yao, L. Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder in Hemodialysis Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Mensink, R.P. Long-term magnesium supplementation improves arterial stiffness in overweight and obese adults: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutten, J.C.; Joris, P.J.; Groendijk, I.; Eelderink, C.; Groothof, D.; van der Veen, Y.; Westerhuis, R.; Goorman, F.; Danel, R.M.; de Borst, M.H.; et al. Effects of Magnesium Citrate, Magnesium Oxide, and Magnesium Sulfate Supplementation on Arterial Stiffness: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Intervention Trial. J. Am. Hearth Assoc. 2022, 11, e021783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.R.; D’El-Rei, J.; Medeiros, F.; Umbelino, B.; Oigman, W.; Touyz, R.M.; Neves, M.F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves endothelial function and attenuates subclinical atherosclerosis in thiazide-treated hypertensive women. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, A.; Block, G.A.; Bachtler, M.; Smith, E.R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Arampatzis, S.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.; Ma, X.; Floege, J. Blood Calcification Propensity, Cardiovascular Events, and Survival in Patients Receiving Hemodialysis in the EVOLVE Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasch, A.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Smith, E.R. Phosphate, Calcification in Blood, and Mineral Stress: The Physiologic Blood Mineral Buffering System and Its Association with Cardiovascular Risk. Int. J. Nephrol. 2018, 2018, 9182078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.R.; Ford, M.L.; Tomlinson, L.; Bodenham, E.; McMahon, L.P.; Farese, S.; Rajkumar, C.; Holt, S.; Pasch, A. Serum Calcification Propensity Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Predialysis CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 25, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyzer, C.A.; De Borst, M.; Berg, E.V.D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Arampatzis, S.; Farese, S.; Bergmann, I.P.; Floege, J.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.; et al. Calcification Propensity and Survival among Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 27, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, G.; Steubl, D.; Kemmner, S.; Pasch, A.; Koch-Sembdner, W.; Pham, D.; Haller, B.; Bachmann, Q.; Mayer, C.C.; Wassertheurer, S.; et al. Worsening calcification propensity precedes all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in haemodialyzed patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundy, J.D.; Cai, X.; Scialla, J.; Dobre, M.A.; Chen, J.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Leonard, M.B.; Go, A.S.; Rao, P.S.; Lash, J.P.; et al. Serum Calcification Propensity and Coronary Artery Calcification Among Patients With CKD: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braake, A.D.; Tinnemans, P.T.; Shanahan, C.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Magnesium prevents vascular calcification in vitro by inhibition of hydroxyapatite crystal formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Mora, C.; Jiménez, A.; Torres, A.; Macía, M.; García, J. Relationship between serum magnesium and parathyroid hormone levels in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 34, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Canalejo, A.; Herencia, C.; Martínez-Moreno, J.M.; Peralta-Ramírez, A.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Navarro-González, J.F.; Rodríguez, M.; Peter, M.; Gundlach, K.; et al. Magnesium modulates parathyroid hormone secretion and upregulates parathyroid receptor expression at moderately low calcium concentration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rude, R.K.; Oldham, S.B.; Sharp, C.F.; Singer, F.R. Parathyroid Hormone Secretion in Magnesium Deficiency*. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1978, 47, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, T.; Lohse, M. Magnesium and the parathyroid. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Francisco, A.L.; Leidig, M.; Covic, A.C.; Ketteler, M.; Benedyk-Lorens, E.; Mircescu, G.M.; Scholz, C.; Ponce, P.; Passlick-Deetjen, J. Evaluation of calcium acetate/magnesium carbonate as a phosphate binder compared with sevelamer hydrochloride in haemodialysis patients: A controlled randomized study (CALMAG study) assessing efficacy and tolerability. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonella, M.; Ballanti, P.; DELLA Rocca, C.; Calabrese, G.; Pratesi, G.; Vagelli, G.; Mazzotta, A.; Bonucci, E. Improved bone morphology by normalizing serum magnesium in chronically hemodialyzed patients. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1988, 14, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pletka, P.; Bernstein, D.; Hampers, C.; Merrill, J.; Sherwood, L. Effects of magnesium on parathyroid hormone secretion during chronic hæmodialysis. Lancet 1971, 298, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.-Q. Magnesium Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Folsom, A.R.; Melnick, S.L.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Sharrett, A.; Nabulsi, A.A.; Hutchinson, R.G.; Metcalf, P.A. Associations of serum and dietary magnesium with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, insulin, and carotid arterial wall thickness: The aric study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1995, 48, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Meigs, J.B.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Jacques, P.F.; McKeown, N.M. Higher Magnesium Intake Reduces Risk of Impaired Glucose and Insulin Metabolism and Progression from Prediabetes to Diabetes in Middle-Aged Americans. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Jing, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, W. Role of Magnesium in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 196, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieboom, B.C.T.; Ligthart, S.; Dehghan, A.; Kurstjens, S.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Zietse, R.; Stricker, B.H.; Hoorn, E.J. Serum magnesium and the risk of prediabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Simental-Mendía, L.; Hernández-Ronquillo, G.; Rodriguez-Morán, M. Oral magnesium supplementation improves glycaemic status in subjects with prediabetes and hypomagnesaemia: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes Metab. 2015, 41, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanakis, I.P.; Stamataki, E.E.; Papadaki, A.N.; Giannakis, N.; Damianakis, N.E.; Oreopoulos, D.G. Magnesium retards the progress of the arterial calcifications in hemodialysis patients: A pilot study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Moradi, S.; Nezamoleslami, S.; Moosavian, S.P.; Kermani, M.A.H.; Lazaridi, A.V.; Miraghajani, M. The Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Lipid Profile Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2021, 199, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazidi, M.; Rezaie, P.; Banach, M. Effect of magnesium supplements on serum C-reactive protein: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Med Sci. 2018, 14, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Qi, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhuang, S. Correlation of serum magnesium with cardiovascular risk factors in maintenance hemodialysis patients—A cross-sectional study. Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, J.; Kalogeropoulou, K.; Bilirakis, L.; Smirnioudis, N.; Pikounis, V.; Stamatiadis, D.; Liolia, E. Dialysate magnesium level and blood pressure. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, H.J.; Lemoine, S.; McIntyre, C.W. High magnesium dialysate does not improve intradialytic hemodynamics or abrogate myocardial stunning. Hemodial. Int. 2020, 24, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, S.R.; Korownyk, C.S.; Kolber, M.R.; Allan, G.M.; Musini, V.M.; Sekhon, R.K.; Dugré, N. Magnesium for skeletal muscle cramps. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, CD009402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Qi, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dual Function of Magnesium in Bone Biomineralization. Adv. Health Mater. 2019, 8, e1901030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Fujii, N.; Shoji, T.; Hayashi, T.; Rakugi, H.; Isaka, Y. Hypomagnesemia is a significant predictor of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azem, R.; Daou, R.; Bassil, E.; Anvari, E.M.; Taliercio, J.J.; Arrigain, S.; Schold, J.D.; Vachharajani, T.; Nally, J.; Na Khoul, G.N. Serum magnesium, mortality and disease progression in chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Hamano, T.; Wada, A.; Hoshino, J.; Masakane, I. Magnesium and Risk of Hip Fracture among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenders, N.H.; Douma, C.E.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Vervloet, M.G. Magnesium in chronic hemodialysis (MAGIC-HD): A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial to determine feasibility and safety of using increased dialysate magnesium concentrations to increase plasma magnesium concentrations in people treated with hemodialysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e063524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Vaqar, S. Hypermagnesemia; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo, H.; Nakamura, K.; Nishida, A.; Kubo, K.; Nakagawa, R.; Sumida, Y. A Case of Hypermagnesemia Accompanied by Hypercalcemia Induced by a Magnesium Laxative in a Hemodialysis Patient. Nephron 1995, 71, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.H.; Soffer, E.E. Adverse effects of laxatives. Dis. Colon Rectum 2001, 44, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairi, T.; Amer, S.; Spitalewitz, S.; Alasadi, L. Severe Symptomatic Hypermagnesemia Associated with Over-the-Counter Laxatives in a Patient with Renal Failure and Sigmoid Volvulus. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 560746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Shimada, H.; Yoshita, K.; Tsubata, Y.; Ikarashi, K.; Morioka, T.; Saito, N.; Sakai, S.; Narita, I. Severe hypermagnesemia induced by magnesium oxide ingestion: A case series. CEN Case Rep. 2019, 8, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, N.; Mori, M. An analysis of hypermagnesemia and hypomagnesemia. Jpn. J. Med. 1990, 29, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressendorff, I.; Hansen, D.; Schou, M.; Kragelund, C.; Brandi, L. The effect of magnesium supplementation on vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease—A randomised clinical trial (MAGiCAL-CKD): Essential study design and rationale. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Formulation | Form | Elemental Mg, milligram/day | Elemental Mg, millimol/day | Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg carbonate | Tablets | 700 mg a | 29 mmol | [22,23,24] |
| Mg oxide | Capsules | 71 mg b–365 mg | 3–15 mmol | [25,26,27,28,29] |
| Mg citrate | Capsules, pastilles | 50 mg c–350 mg | 3–15 mmol | [30,31] |
| Mg hydroxide | Slow release tablets | 360–720 d mg | 15–30 mmol | [32] |
| In Vitro | Animal Exp. | In Human Observational (Authors, Ref, Type of Study, Population, Outcome) | In Human Intervention Studies (Authors, Ref, Type of Study, Population, Intervention, Outcome) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac health | ||||
| n.a. |
|
| |
| n.a. | |||
| n.a. | |||
| Calcification | ||||
|
|
| ||
| n.a. | n.a. |
| |
| n.a. | n.a. | ||
|
| |||
| Markers of CKD-MBD | ||||
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| Other clinically relevant outcomes | ||||
| n.a. |
|
| |
| n.a. | |||
|
|
| ||
| n.a. | n.a. |
| |
| Mortality | ||||
| Cardiovascular Mortality | n.a. |
| ||
| All-cause mortality | n.a. |
| ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vermeulen, E.A.; Vervloet, M.G. Magnesium Administration in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030547
Vermeulen EA, Vervloet MG. Magnesium Administration in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030547
Chicago/Turabian StyleVermeulen, Emma A., and Marc G. Vervloet. 2023. "Magnesium Administration in Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030547
APA StyleVermeulen, E. A., & Vervloet, M. G. (2023). Magnesium Administration in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 15(3), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030547






