Nutritional Assessment and Support in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Benefits of Working with a Registered Dietitian
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Nutritional Assessment
2.3. Nutritional Education
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Dietary Intake
3.2.1. Nutrients
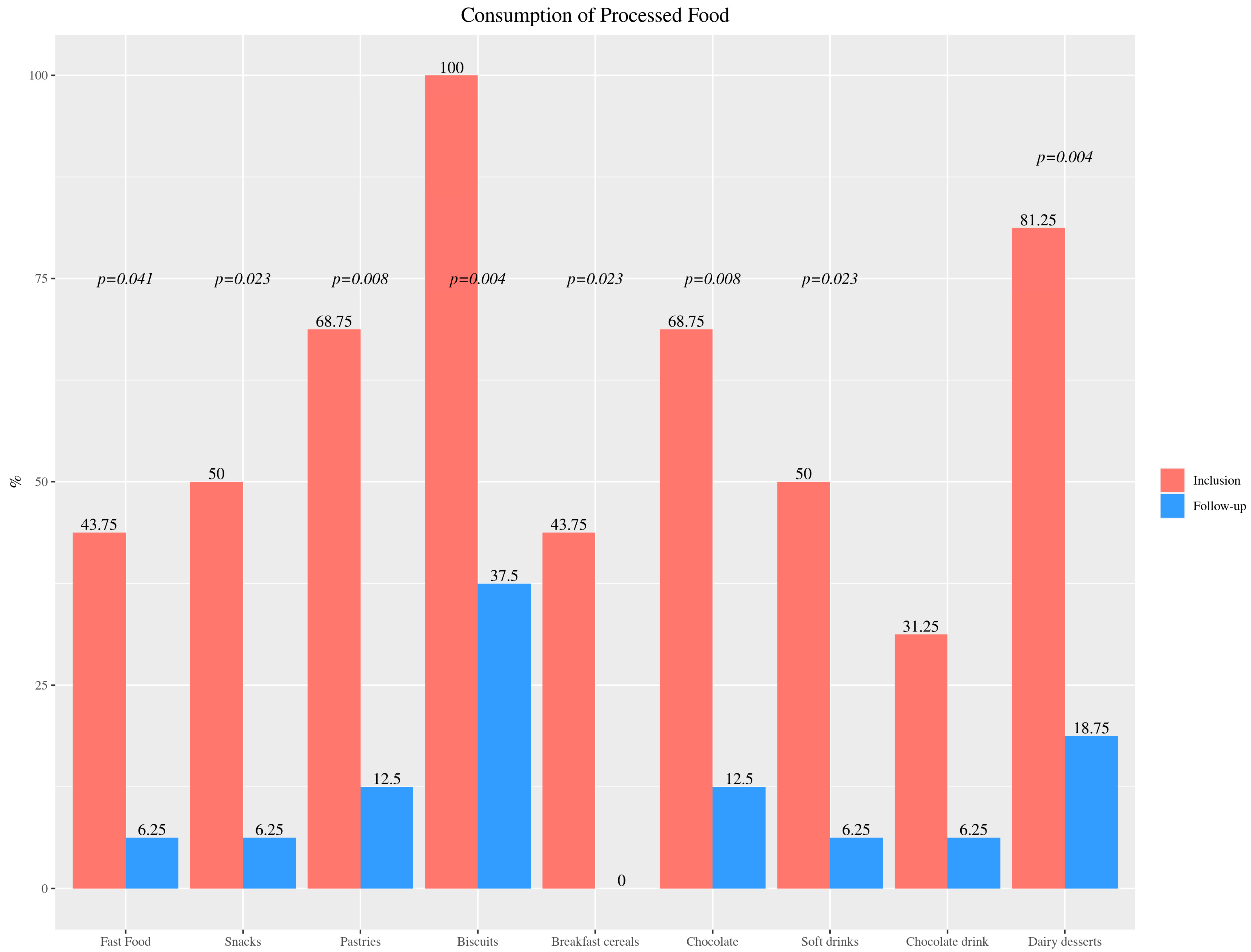
3.2.2. Foods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidelines–KDIGO. Available online: https://kdigo.org/guidelines/ (accessed on 23 April 2022).
- Group, K.W. KDOQI Work Group KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in Children with CKD: 2008 Update. Executive Summary. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2009, 53, S11–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biljon, I.; Meyers, A.M. Paediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. South Afr. Med. J. 2015, 105, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akchurin, O.M. Chronic Kidney Disease and Dietary Measures to Improve Outcomes. Pediatr. Clin. 2019, 66, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.; Hashmi, S.; Shah, S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Plant-Based Diets for Prevention and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Adler, S.; Caggiula, A.W.; England, B.K.; Greene, T.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Kusek, J.W.; Rogers, N.L.; Teschan, P.E. Effects of Dietary Protein Restriction on the Progression of Advanced Renal Disease in the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1996, 27, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Maeda, Y.; Matsuki, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Akazawa, M.; Kuyama, T. Urinary Phosphorus Excretion per Creatinine Clearance as a Prognostic Marker for Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Greene, T.; Beck, G.J.; Caggiula, A.W.; Kusek, J.W.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Klahr, S. Dietary Protein Restriction and the Progression of Chronic Renal Disease: What Have All of the Results of the MDRD Study Shown? Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 1999, 10, 2426–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Patient Education for Phosphorus Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2013, 7, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.R.; Draper, H.H.; Tzeng, D.Y.; Shin, H.K.; Schmidt, G.R. Physiological Responses of Human Adults to Foods Containing Phosphate Additives. J. Nutr. 1977, 107, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketteler, M.; Block, G.A.; Evenepoel, P.; Fukagawa, M.; Herzog, C.A.; McCann, L.; Moe, S.M.; Shroff, R.; Tonelli, M.A.; Toussaint, N.D.; et al. Executive Summary of the 2017 KDIGO Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Guideline Update: What’s Changed and Why It Matters. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauveau, P.; Aparicio, M.; Bellizzi, V.; Campbell, K.; Hong, X.; Johansson, L.; Kolko, A.; Molina, P.; Sezer, S.; Wanner, C.; et al. Mediterranean Diet as the Diet of Choice for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2018, 33, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Joshi, S.; Schlueter, R.; Cooke, J.; Brown-Tortorici, A.; Donnelly, M.; Schulman, S.; Lau, W.-L.; Rhee, C.M.; Streja, E.; et al. Plant-Dominant Low-Protein Diet for Conservative Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warady, B.A.; Alexander, S.R.; Watkins, S.; Kohaut, E.; Harmon, W.E. Optimal Care of the Pediatric End-Stage Renal Disease Patient on Dialysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1999, 33, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajarmeh, S.; Er, L.; Brin, G.; Djurdjev, O.; Dionne, J.M. The Effect of a Multidisciplinary Care Clinic on the Outcomes in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2012, 27, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, L.; Mak, R.H. Nutrition and Growth in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Davenport, A. Hemodialysis for Infants, Children, and Adolescents. Hemodial. Int. Int. Symp. Home Hemodial. 2014, 18, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-González, M.; Bousoño García, C.; Jiménez Treviño, S.; Iglesias Cabo, T.; Díaz Martín, J.J. Influence of Nutrition Education in Paediatric Coeliac Disease: Impact of the Role of the Registered Dietitian: A Prospective, Single-Arm Intervention Study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. Off. J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 2020, 33, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, S.; Sichert-Hellert, W.; Kersting, M. Measuring the Effects of Nutritional Counseling on Total Infant Diet in a Randomized Controlled Intervention Trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 45, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obarzanek, E.; Kimm, S.Y.; Barton, B.A.; Van Horn, L.; Kwiterovich, P.O.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Hunsberger, S.A.; Lasser, N.L.; Robson, A.M.; Franklin, F.A.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of a Cholesterol-Lowering Diet in Children with Elevated Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: Seven-Year Results of the Dietary Intervention Study in Children (DISC). Pediatrics 2001, 107, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.; Victora, C.G.; Martines, J.; Gonçalves, H.; Gigante, D.P.; Valle, N.J.; Pelto, G. Nutrition Counseling Increases Weight Gain among Brazilian Children. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2866–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutrición en la Enfermedad Renal Crónica. Nefrología al Día. Available online: http://www.nefrologiaaldia.org/es-articulo-nutricion-enfermedad-renal-cronica-220 (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Tuttle, K.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Bilous, R.W.; Chiang, J.L.; de Boer, I.H.; Goldstein-Fuchs, J.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Narva, A.S.; Navaneethan, S.D.; et al. Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Report From an ADA Consensus Conference. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2864–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkera, H.A.; Mandarino, L.J. Calcineurin Inhibition and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus after Transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 95, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkera, H.A.; Weil, E.J.; Pham, P.-T.; Pomeroy, J.; Knowler, W.C. Can New-Onset Diabetes after Kidney Transplant Be Prevented? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TODAY Study Group. Rapid Rise in Hypertension and Nephropathy in Youth with Type 2 Diabetes: The TODAY Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovecchio, M.L.; Woodside, J.; Jones, T.; Daneman, D.; Neil, A.; Prevost, T.; Dalton, R.N.; Deanfield, J.; Dunger, D.B.; AdDIT Investigators. Adolescent Type 1 Diabetes Cardio-Renal Intervention Trial (AdDIT): Urinary Screening and Baseline Biochemical and Cardiovascular Assessments. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, F.; Tepe, D.; Kara, O.; Esen, I. Microvascular Complications in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Fouque, D. Nutritional Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, D.E.; Pritchett, Y.; Molitch, M.; Wen, S.; Garimella, T.; Audhya, P.; Andress, D.L. Addition of Atrasentan to Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade Reduces Albuminuria in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2011, 22, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briasoulis, A.; Bakris, G. The Future of Interventional Management of Hypertension: Threats and Opportunities. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, D.J.; Talton, J.; Dabelea, D.; Divers, J.; Imperatore, G.; Lawrence, J.M.; Liese, A.D.; Linder, B.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Pihoker, C.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes in U.S. Youth in 2009: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabelea, D.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Saydah, S.; Imperatore, G.; Linder, B.; Divers, J.; Bell, R.; Badaru, A.; Talton, J.W.; Crume, T.; et al. Prevalence of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes among Children and Adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA 2014, 311, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaede, P.; Lund-Andersen, H.; Parving, H.-H.; Pedersen, O. Effect of a Multifactorial Intervention on Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaede, P.; Vedel, P.; Larsen, N.; Jensen, G.V.H.; Parving, H.-H.; Pedersen, O. Multifactorial Intervention and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K. The Association among Smoking, Heavy Drinking, and Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.; Fernández, J.M.; Ferrández, A.; López-Siguero, J.P.; López, D.; Sánchez, E. Estudios_Españoles_de_Crecimiento_2010. An Pediatr (Barc). 2010, 68, pp. 1–46. Available online: https://www.seep.es/images/site/publicaciones/oficialesSEEP/Estudios_Españoles_de_Crecimiento_2010.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Carrascosa, A.; Fernández-Cancio, M.; Yeste, D.; Gussinye, M.; Bosch-Castañe, J.; Moreno, A.; Ferránez, A.; Clemente, M.; Campos, A. Millennial’ Growth. Estudio Longitudinal de Crecimiento. Barcelona 1995–2017. 2017. Available online: https://www.endocrinologiapediatrica.org/modules/editorial/files/millennialsgrowth2017esp_copy1.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- SEGHNP. Aplicación Nutricional. Available online: https://www.seghnp.org/nutricional/ (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Organizador Dietético Metabólico. Available online: http://www.odimet.es/ (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- EFSA. Dietary Reference Values. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/dietary-reference-values (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Grupo Colaborativo de la Sociedad Española de Nutrición Comunitaria (SENC); Aranceta Bartrina, J.; Arija Val, V.; Maíz Aldalur, E.; Martínez de la Victoria Muñoz, E.; Ortega Anta, R.M.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Quiles Izquierdo, J.; Rodríguez Martín, A.; Román Viñas, B.; et al. Dietary guidelines for the Spanish population (SENC, December 2016); the new graphic icon of healthy nutrition. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvard T.H. Chan. El Plato Para Comer Saludable (Spanish). Available online: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-eating-plate/translations/spanish/ (accessed on 27 December 2019).
- European Environment Agency. R Core Team (2020). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/oxygen-consuming-substances-in-rivers/r-development-core-team-2006 (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Evans, P.D.; Taal, M.W. Epidemiology and Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease. Medicine 2015, 43, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naber, T.; Purohit, S. Chronic Kidney Disease: Role of Diet for a Reduction in the Severity of the Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Paglialonga, F.; Edefonti, A. Assessment of Nutritional Status in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease and on Dialysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kogon, A.J.; Kumar, J.; Sethna, C.B.; Hammad, H.T.; Christos, P.J.; Mahan, J.D.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Woroniecki, R. Approach to Growth Hormone Therapy in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease Varies across North America: The Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium Report. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe PMC. Assessment of Dietary Intake of Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/pmc/5642285 (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Uribarri, J. Dietary Phosphorus and Kidney Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1301, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.N. High-Protein Diets: Potential Effects on the Kidney in Renal Health and Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2004, 44, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouque, D.; Aparicio, M. Eleven Reasons to Control the Protein Intake of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Low-protein Diet for Conservative Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F. Potassium Binders for Hyperkalemia in Chronic Kidney Disease-Diet, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitor Therapy, and Hemodialysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; Ster, I.C.; Kaski, J.-C.; Anderson, L.; Banerjee, D. The LIFT Trial: Study Protocol for a Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial of K+-Binder Lokelma for Maximisation of RAAS Inhibition in CKD Patients with Heart Failure. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy y Goldman. What We Eat in America, NHANES 2009-2010.Pdf. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400530/pdf/0910/tables_1-40_2009-2010.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Martínez-Pineda, M.; Yagüe-Ruiz, C.; Caverni-Muñoz, A.; Vercet-Tormo, A. Reduction of Potassium Content of Green Bean Pods and Chard by Culinary Processing. Tools for Chronic Kidney Disease. Nefrol. Engl. Ed. 2016, 36, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Ávila, J.M.; Valero, T.; Del Pozo, S.; Rodriguez, P.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gil, Á.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Macronutrient Distribution and Dietary Sources in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melse-Boonstra, A. Bioavailability of Micronutrients From Nutrient-Dense Whole Foods: Zooming in on Dairy, Vegetables, and Fruits. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Kidney damage markers | Albuminuria (ACR > 30 mg/g) Abnormal urine sediment (e.g., hematuria, red cell casts, etc.) Electrolyte and different anomalies because of tubular issues Irregularities recognized by histology Structural abnormalities distinguished by imaging History of kidney transplantation |
| Decreased GFR | GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (GFR categories G3a-G5) |
| GFR Category | GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | Terms |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | >90 | Normal or high |
| G2 | 60–89 | Mildly diminished |
| G3a | 45–59 | Mildly to moderately diminished |
| G3b | 30–44 | Moderately to severely diminished |
| G4 | 15–29 | Severely diminished |
| G5 | <15 | Kidney failure |
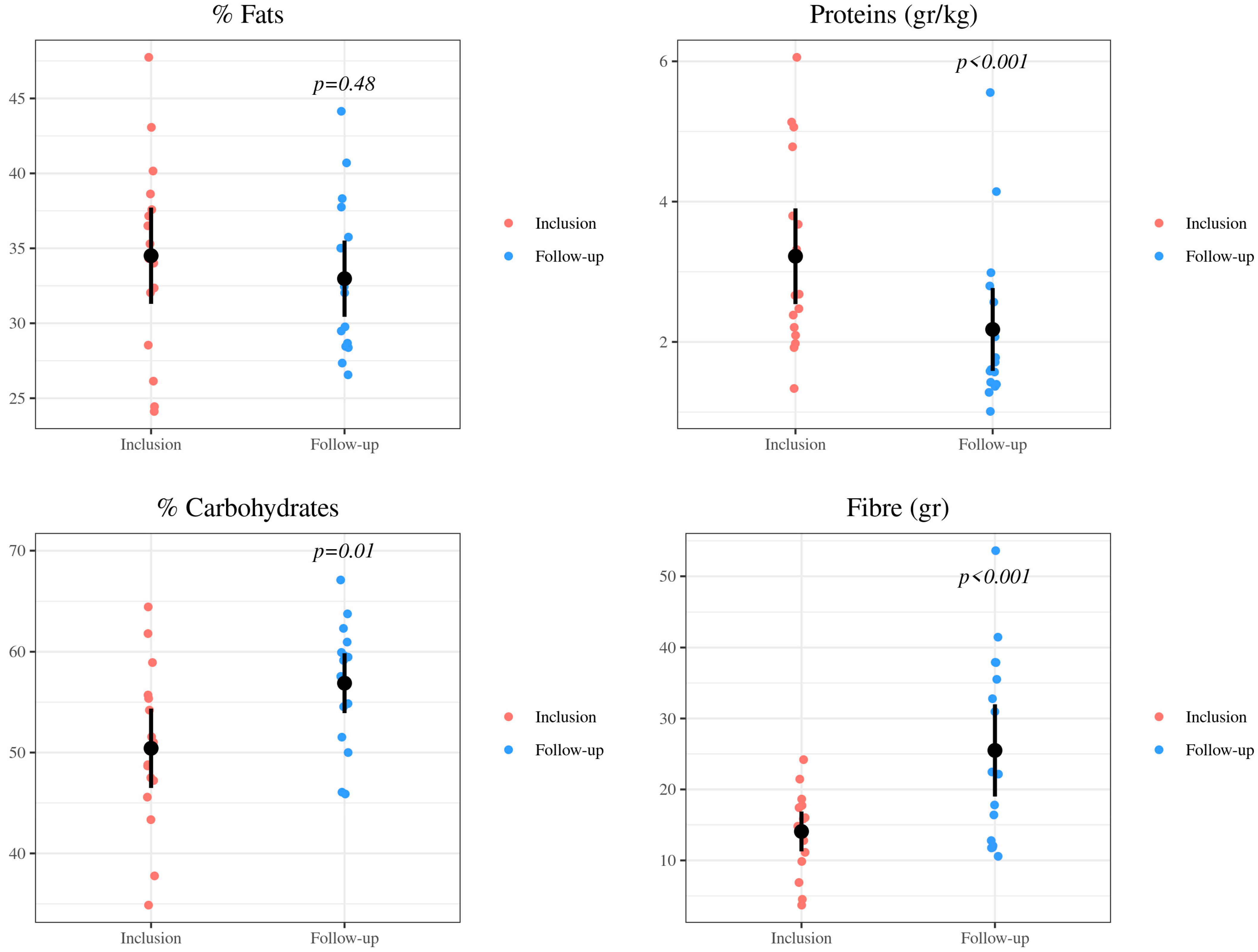
| Energy and Nutrients | Inclusion | Follow-Up | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Energy (kcal) | 1683.64 (511.89) | 1783.22 (694.03) | 0.4 |
| Proteins | Proteins (g) | 67.34 (20.45) | 53.21 (19.77) | 0.01 |
| Proteins/kg (g) | 3.22 (1.39) | 2.18 (1.21) | <0.001 | |
| Proteins (%) | 16.29 (1.91) | 12.48 (2.30) | <0.001 | |
| Fats | Fats (g) | 64.20 (23.03) | 64.29 (27.38) | 0.99 |
| Fats (%) | 34.51 (6.55) | 32.97 (5.19) | 0.48 | |
| Saturated fat (g) | 20.53 (8.32) | 16.02 (7.96) | 0.14 | |
| Saturated fat (%) | 11.03 (2.81) | 8.29 (3.38) | 0.05 | |
| MUFAs (g) | 25.23 (11.56) | 30.50 (14.34) | 0.14 | |
| MUFAs (%) | 13.54 (4.67) | 16.28 (3.27) | 0.11 | |
| PUFAs (g) | 7.31 (4.18) | 11.74 (13.44) | 0.18 | |
| PUFAs (%) | 4.04 (2.33) | 4.66 (1.94) | 0.44 | |
| Carbohydrates | Carbohydrates (g) | 209.19 (66.81) | 247.93 (102.21) | 0.03 |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 50.42 (8.03) | 56.88 (6.06) | 0.01 | |
| Fiber (g) | 14.08 (5.73) | 25.50 (13.26) | <0.001 | |
| Minerals | Sodium (mg) | 963.81 (464.00) | 861.19 (502.50) | 0.37 |
| Potassium (mg) | 2215.91 (884.50) | 2795.19 (958.63) | 0.01 | |
| Calcium (mg) | 734.42 (279.28) | 578.40 (235.18) | 0.07 | |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 961.33 (670.36) | 851.08 (283.28) | 0.82 | |
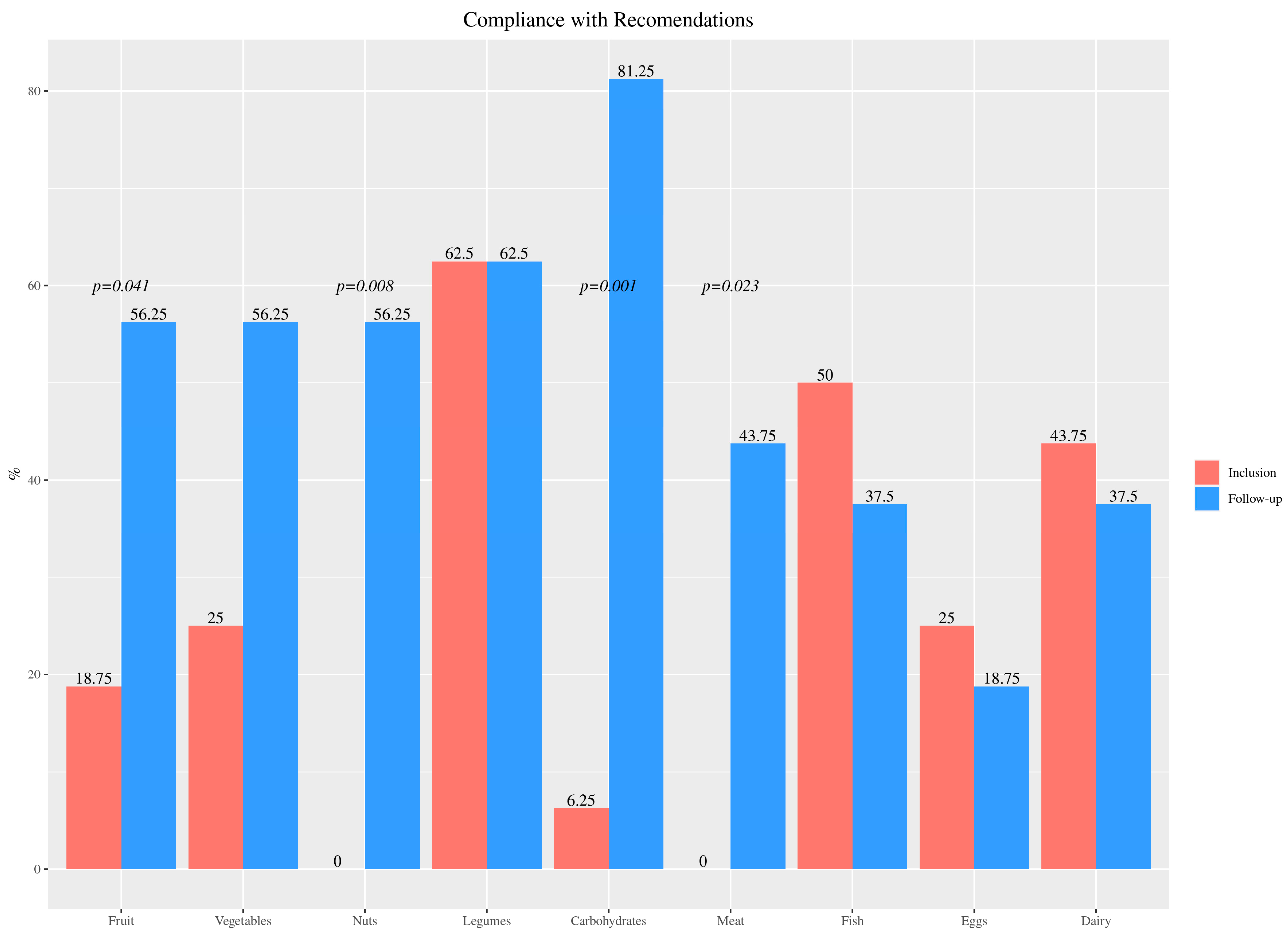
| Food Group | Foods | Inclusion | Follow-Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruit and vegetables | Fruit/day | 1.59 (1.29) | 2.72 (0.84) | <0.001 |
| Vegetable/day | 0.78 (0.86) | 1.72 (0.36) | <0.001 | |
| Plan protein sources | Legume/week | 3.28 (1.37) | 3.03 (1.02) | 0.68 |
| Nuts/week | 0.19 (0.40) | 2.72 (2.62) | 0.01 | |
| Animal protein sources | Meat/week | 6.75 (0.68) | 3.29 (2.08) | <0.001 |
| Fish/week | 2.56 (1.12) | 2.5 (0.98) | 0.79 | |
| Eggs/week | 2.44 (1.76) | 2.16 (1.01) | 0.51 | |
| Dairy/day | 3.66 (1.43) | 2.09 (0.92) | <0.001 | |
| Cereal and tubers | Rice/week | 1.16 (0.68) | 2.38 (1.27) | 0.01 |
| Pasta/week | 1.16 (0.77) | 2.84 (1.27) | <0.001 | |
| Potato/week | 4.84 (2.10) | 5.31 (1.67) | 0.47 | |
| Bread/day | 1.13 (0.96) | 2.75 (1.34) | <0.001 | |
| Total carbohydrates/day | 2.47 (1.49) | 4.28 (1.38) | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suárez-González, M.; Ordoñez-Álvarez, F.Á.; Gil-Peña, H.; Carnicero-Ramos, S.; Hernández-Peláez, L.; García-Fernández, S.; Santos-Rodríguez, F. Nutritional Assessment and Support in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Benefits of Working with a Registered Dietitian. Nutrients 2023, 15, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030528
Suárez-González M, Ordoñez-Álvarez FÁ, Gil-Peña H, Carnicero-Ramos S, Hernández-Peláez L, García-Fernández S, Santos-Rodríguez F. Nutritional Assessment and Support in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Benefits of Working with a Registered Dietitian. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030528
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuárez-González, Marta, Flor Ángel Ordoñez-Álvarez, Helena Gil-Peña, Sara Carnicero-Ramos, Lucía Hernández-Peláez, Sonia García-Fernández, and Fernando Santos-Rodríguez. 2023. "Nutritional Assessment and Support in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Benefits of Working with a Registered Dietitian" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030528
APA StyleSuárez-González, M., Ordoñez-Álvarez, F. Á., Gil-Peña, H., Carnicero-Ramos, S., Hernández-Peláez, L., García-Fernández, S., & Santos-Rodríguez, F. (2023). Nutritional Assessment and Support in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: The Benefits of Working with a Registered Dietitian. Nutrients, 15(3), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030528





