Thymus atlanticus: A Source of Nutrients with Numerous Health Benefits and Important Therapeutic Potential for Age-Related Diseases
Abstract
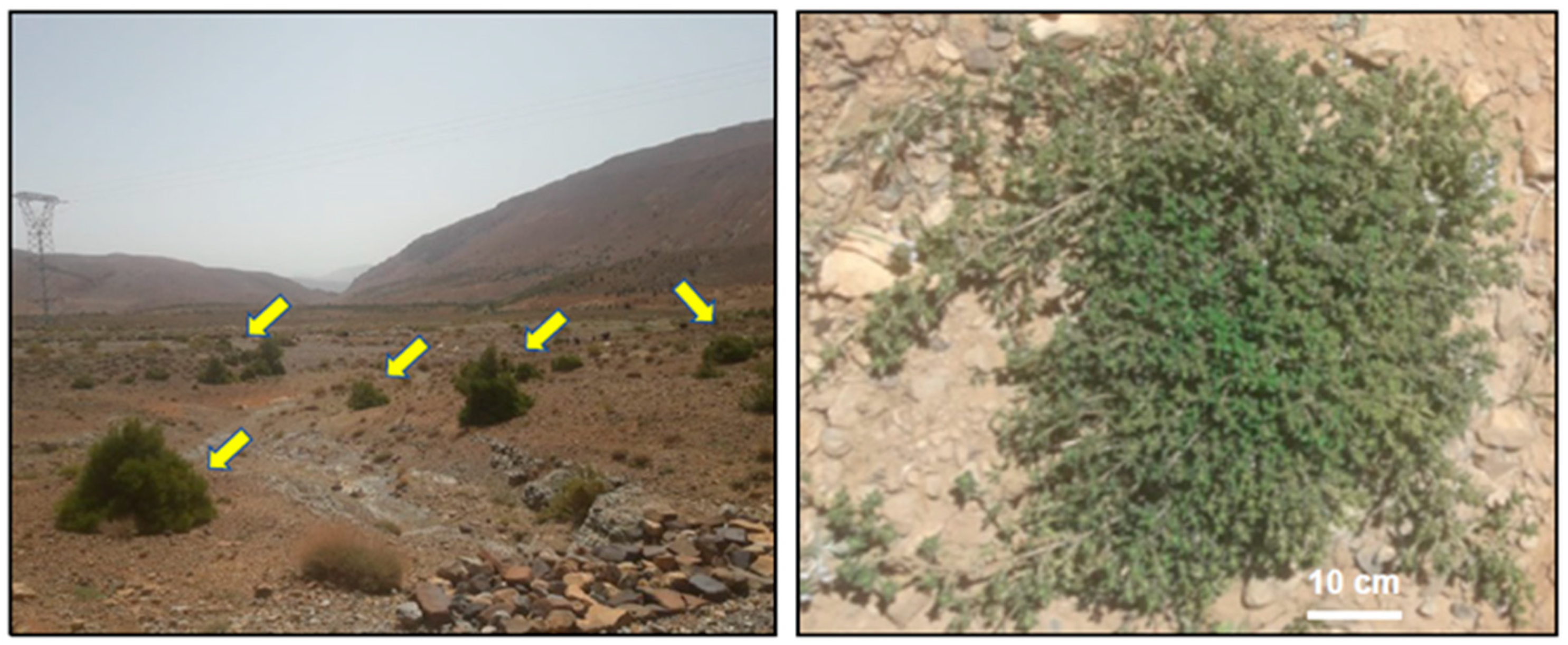
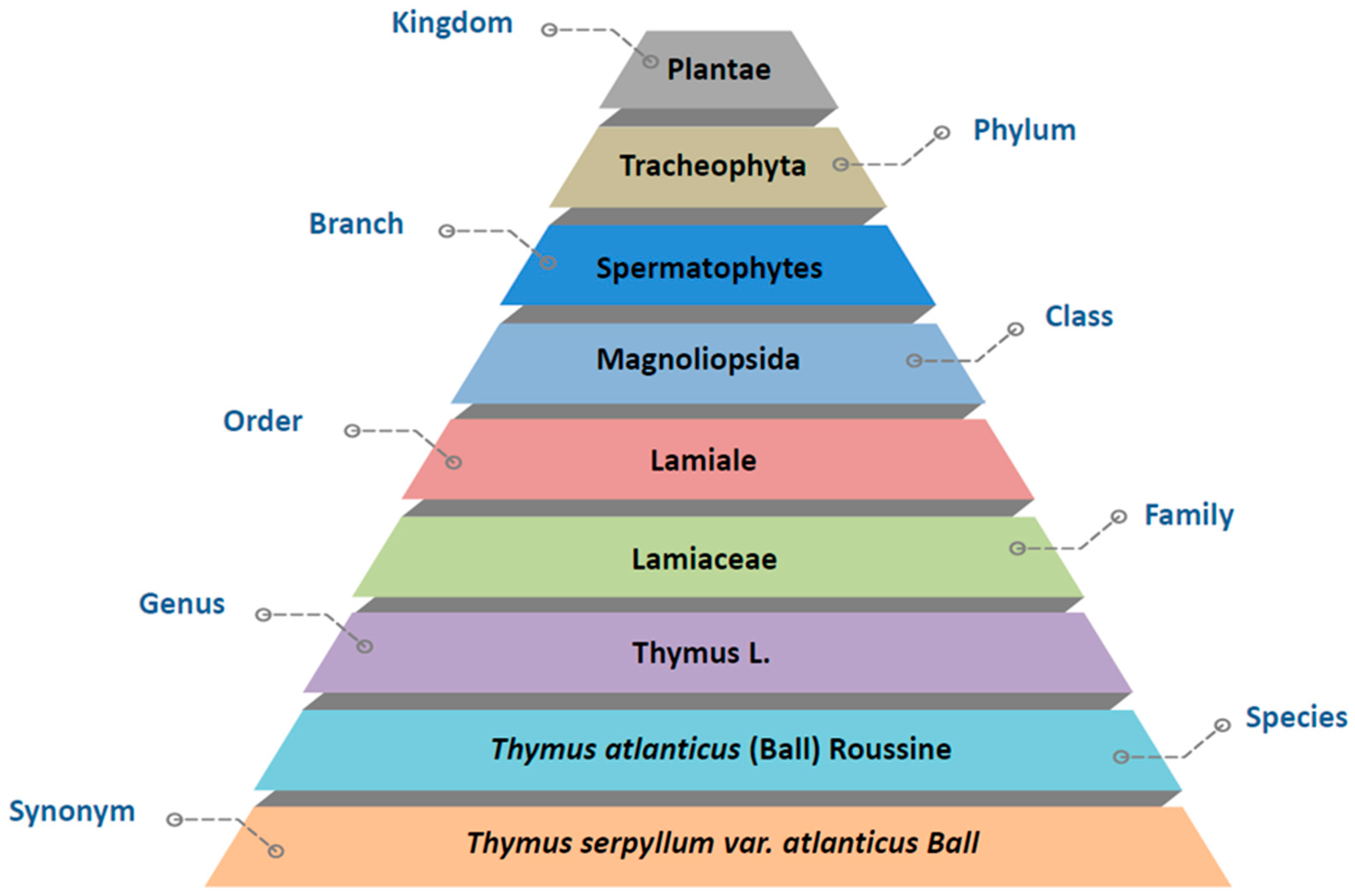
:1. History, Geographical Distribution, and Use of Thymus atlanticus (Lamiaceae) in Traditional Medicine
2. Botany and Cultivation
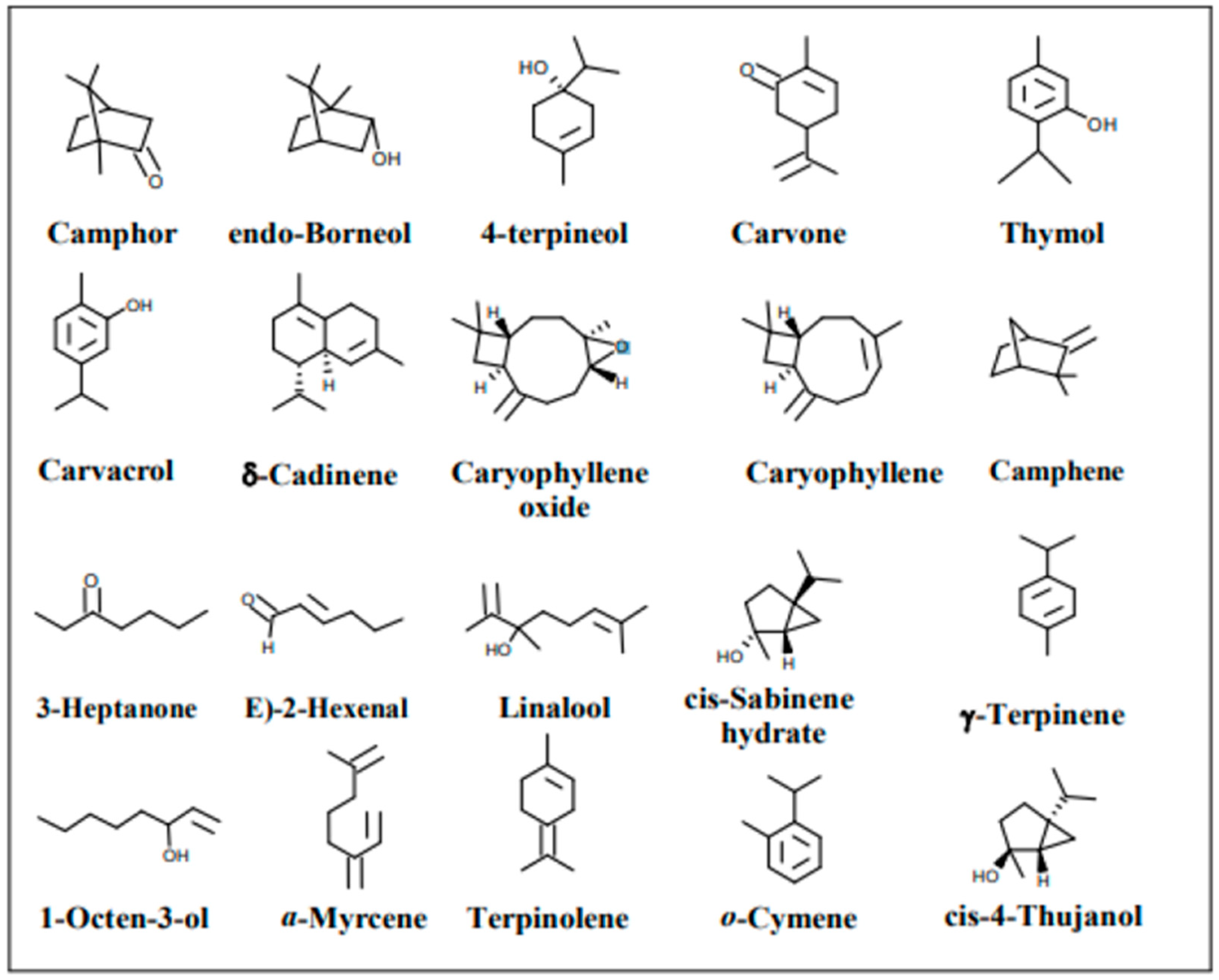
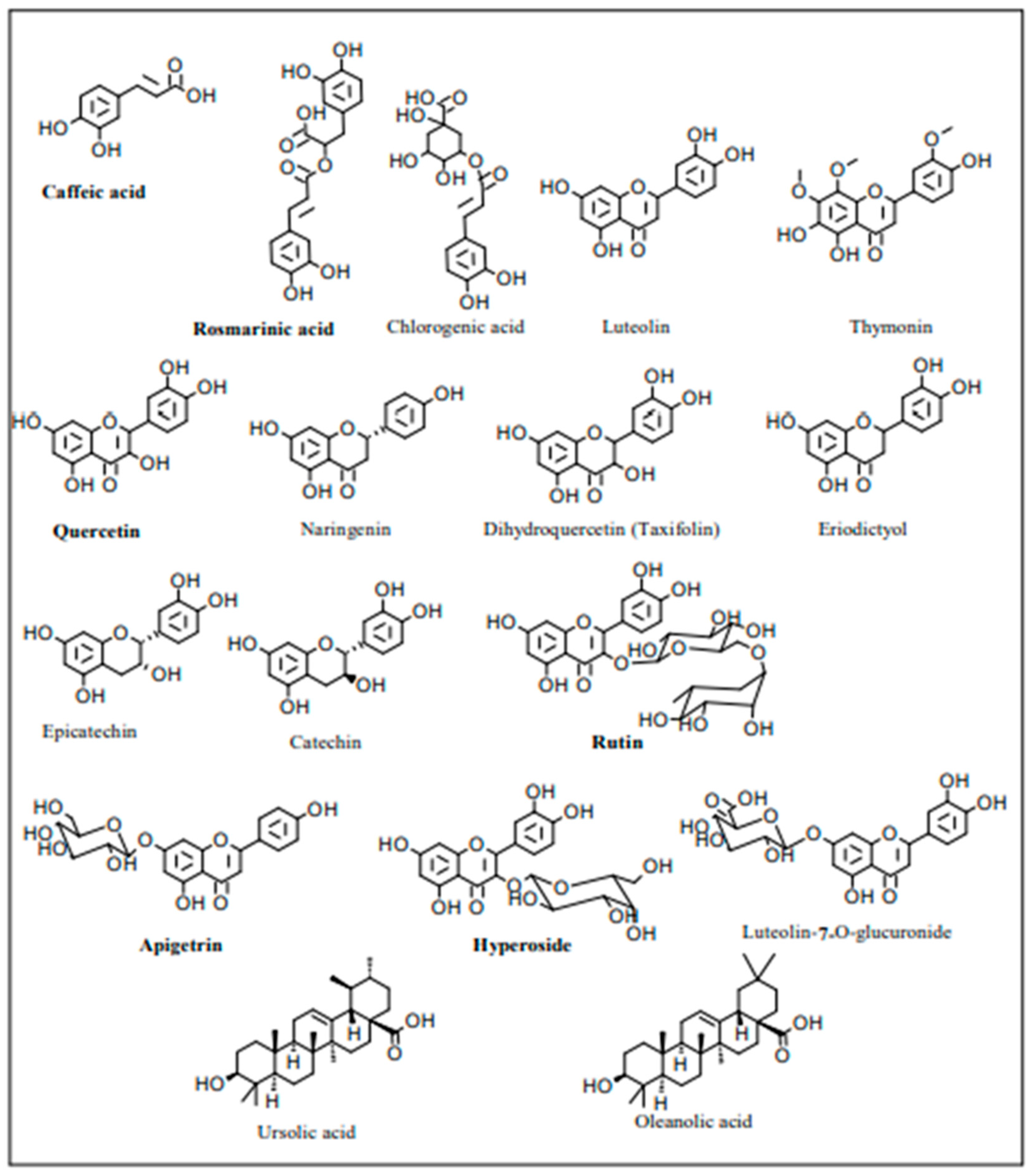
3. Phytochemistry
4. Benefits of Thymus atlanticus on Human Health
4.1. Antimicrobial Activities of Thymus atlanticus
4.2. Benefits of Thymus atlanticus on Age-Related Diseases
4.2.1. Dyslipidemia
4.2.2. Atherosclerosis
4.2.3. Myocardial Infarction
4.2.4. Hypertension
4.2.5. Stroke
4.2.6. Insulin Resistance
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basch, E.; Ulbricht, C.; Hammerness, P.; Bevins, A.; Sollars, D. Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), thymol. J. Herb. Pharmacother 2004, 4, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.M.; Ramu, R.; Shirahatti, P.S.; Shivamallu, C.; Amachawadi, R.G. A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickavar, B.; Mojab, F.; Dolat-Abadi, R. Analysis of the essential oils of two Thymus species from Iran. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl-Biskup, E.; Saez, F.A. Thyme: The Genus Thymus; Taylor & Francis.: Abingdon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tzima, K.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Polyphenols in Lamiaceae Plants—A Review. Plants 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dob, T.; Dahmane, D.; Benabdelkader, T.; Chelghoum, C. Studies on the essential oil composition and antimicrobial activity of Thymus algeriensis Boiss. et Reut. Int. J. Aromather. 2006, 16, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennane, M.; Ibn Tattou, M.; Mathez, J.; Ouyahya, A.; El Oualidi, J. Flore Pratique du Maroc; Institut Scientifique, Mohammed V University: Rabat, Morocco, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bellakhdar, J.; Claisse, R.; Fleurentin, J.; Younos, C. Repertory of standard herbal drugs in the Moroccan pharmacopoea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 35, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellakhdar, J. La pharmacopée marocaine traditionnelle. In Médecine Arabe Ancienne et Savoirs Populaires; Ibis Press: Paris, France, 1997; p. 764. [Google Scholar]
- Dobignard, A. Compte rendu de la 49 ème Session extraordinaire de la Société botanique du Centre-Ouest dans le Grand Atlas marocain. In Proceedings of the Revue Électronique Annuelle de la Société Botanique du Centre-Ouest, Marrakech, Morocco, 7–15 June 2015; pp. 107–252. [Google Scholar]
- Peltier, J.P. Biodiversité Végétale du Sud-Ouest Marocain, Thymus atlanticus, Endémiques du Maroc (2019). 2006–2023. Available online: https://www.teline.fr/ (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Stahl-Biskup, E.; Venskutonis, R.P. Thyme. In Handbook of Herbs and Spices; Peter, K.V., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 499–525. [Google Scholar]
- Labiad, M.H.; Belmaghraoui, W.; Ghanimi, A.; El-Guezzane, C.; Chahboun, N.; Harhar, H.; Egea-Gilabert, C.; Zarrouk, A.; Tabyaoui, M. Biological properties and chemical profiling of essential oils of Thymus (vulgaris, algeriensis and broussonettii) grown in Morocco. Chem. Data Collect. 2022, 37, 100797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Ouazzou, A.; Lorán, S.; Bakkali, M.; Laglaoui, A.; Rota, C.; Herrera, A.; Pagán, R.; Conchello, P. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oils of Thymus algeriensis, Eucalyptus globulus and Rosmarinus officinalis from Morocco. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2643–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golparvar, A.; Bahari, B. Effects of phenological stages on herbage yield and quality/quantity of oil in garden thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.). J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 6085–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmakani, M.T.; Rezaei, K. Comparison of microwave-assisted hydrodistillation withthe traditional hydrodistillation method in the extractionof essential oils from Thymus vulgaris L. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Shukla, I.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Contreras, M.D.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fathi, H.; Nasrabadi, N.N.; Kobarfard, F.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: Health and potential uses. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1688–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Golparvar, A.; Hadipanah, A. Effect of Harvest Time on Yield and Quality of Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil in Isfahan Province, Iran. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2014, 79, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.C.; Barroso, J.G.; Pedro, L.G.; Salgueiro, L.; Miguel, M.G.; Faleiro, M.L. Portuguese Thymbra and Thymus species volatiles: Chemical composition and biological activities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3120–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwath, A.B.; Grayer, R.J.; Keith-Lucas, D.M.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Chemical characterisation of wild populations of Thymus from different climatic regions in southeast Spain. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, R.; Gershenzon, J. Genetic Control of Monoterpene Biosynthesis in Mints (Mentha: Lamiaceae). In Genetic Engineering of Plant Secondary Metabolism; Ellis, B.E., Kuroki, G.W., Stafford, H.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 193–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, K.H.C.; Özek, T.; Tümen, G. Essential Oils of Thymus cariensis and Thymus haussknechtii, Two Endemic Species in Turkey. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1992, 4, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, F. Variability in Essential Oils from Populations of Thymus hyemalis Lange in Southeastern Spain. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 1998, 5, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarti, F.; Satrani, B.; Ghanmi, M.; Farah, A.; Aafi, A.; Aarab, L.; Ajjouri, M.E.; Chaouch, A. Composition chimique et activité antimicrobienne des huiles essentielles de Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut. et Thymus ciliatus (Desf.) Benth. du Maroc. Biotechnol. Agron. Société Et Environ. 2010, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Rota, M.; Herrera, A.; Martínez, R.; Sotomayor, J.; Jordán, M. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of Thymus vulgaris, Thymus zygis and Thymus hyemalis essential oils. Food Control 2008, 19, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, C.A.; El Bouzidi, L.; Bekkouche, K.; Lahcen, H.; Markouk, M.; Wohlmuth, H.; Leach, D.; Abbad, A. Chemical composition and antioxidant and anticandidal activities of essential oils from different wild Moroccan Thymus species. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, C.A.; Kasrati, A.; Bekkouche, K.; Hassani, L.; Wohlmuth, H.; Leach, D.; Abbad, A. Phenological changes to the chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil from Moroccan endemic thyme (Thymus maroccanus Ball). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaoui Jamali, C.; Kasrati, A.; Bekkouche, K.; Hassani, L.; Wohlmuth, H.; Leach, D.; Abbad, A. Cultivation and the application of inorganic fertilizer modifies essential oil composition in two Moroccan species of Thymus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S. Chapter 7—Composition of essential oils and other materials. In Essential Chemistry for Aromatherapy, 2nd ed.; Clarke, S., Ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2008; pp. 123–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafis, A.; Iriti, M.; Ouchari, L.; El Otmani, F.; Marraiki, N.; Elgorban, A.M.; Syed, A.; Mezrioui, N.; Hassani, L.; Custódio, L. New Insight into the Chemical Composition, Antimicrobial and Synergistic Effects of the Moroccan Endemic Thymus atlanticus (Ball) Roussine Essential Oil in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics. Molecules 2021, 26, 5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roby, M.H.H.; Sarhan, M.A.; Selim, K.A.-H.; Khalel, K.I. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, total phenols and phenolic compounds in thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), sage (Salvia officinalis L.), and marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, B.; Jakabová, S.; Dörnyei, A.; Horváth, G.; Pluhár, Z.; Kilár, F.; Felinger, A. Determination of polyphenolic compounds by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in Thymus species. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7972–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauqan, E.M.A.; Abdullah, A. Medicinal and Functional Values of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) Herb. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Khouya, T.; Ramchoun, M.; Amrani, S.; Harnafi, H.; Rouis, M.; Couchie, D.; Simmet, T.; Alem, C. Anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects of polyphenol-rich extracts from Thymus atlanticus: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 252, 112475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadli, M.; Saad, A.; Sayadi, S.; Chevalier, J.; Mezrioui, N.E.; Pagès, J.M.; Hassani, L. Antibacterial activity of Thymus maroccanus and Thymus broussonetii essential oils against nosocomial infection—Bacteria and their synergistic potential with antibiotics. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasrati, A.; Alaoui Jamali, C.; Fadli, M.; Bekkouche, K.; Hassani, L.; Wohlmuth, H.; Leach, D.; Abbad, A. Antioxidative activity and synergistic effect of Thymus saturejoides Coss. essential oils with cefixime against selected food-borne bacteria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 61, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Fadli, M.; Bouaziz, M.; Benharref, A.; Mezrioui, N.E.; Hassani, L. Anticandidal activity of the essential oils of Thymus maroccanus and Thymus broussonetii and their synergism with amphotericin B and fluconazol. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadli, M.; Bolla, J.-M.; Mezrioui, N.-E.; Pagès, J.-M.; Hassani, L. First evidence of antibacterial and synergistic effects of Thymus riatarum essential oil with conventional antibiotics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 61, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutakiout, A.; Majdouli, K.; Chafai, Y.; Radi, M.; El Aggadi, S.; El Belghiti, M.A.; Zair, T. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Essential Oil and Phytochemical Screening of Extracts of Aerial Parts of Thymus atlanticus. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2022, 25, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanci, H.; Igan, H. Antimicrobial synergistic effects of apigenin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, myricetin and luteolin in combination with some antibiotics. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2023, 30, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramchoun, M.; Harnafi, H.; Alem, C.; Büchele, B.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M.; Atmani, F.; Amrani, S. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effect of polyphenol-rich extracts from Moroccan thyme varieties. e-SPEN J. 2012, 7, e119–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchoun, M.; Khouya, T.; Harnafi, H.; Alem, C.; Benlyas, M.; Simmet, T.; Ouguerram, K.; Amrani, S. Effect of polyphenol, flavonoid, and saponin fractions from Thymus atlanticus on acute and chronic hyperlipidemia in mice. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchoun, M.; Khouya, T.; Harnafi, H.; Amrani, S.; Alem, C.; Benlyas, M.; Kasbi Chadli, F.; Nazih, E.H.; Nguyen, P.; Ouguerram, K. Effect of Aqueous Extract and Polyphenol Fraction Derived from Thymus atlanticus Leaves on Acute Hyperlipidemia in the Syrian Golden Hamsters. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 3282596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouya, T.; Ramchoun, M.; Hmidani, A.; Amrani, S.; Benlyas, M.; Kasbi Chadli, F.; Ouguerram, K.; Alem, C. Effect of supplementation with polyphenol extract of Thymus atlanticus on paraoxonase-1 activity, insulin resistance, and lipid profile in high-fat diet-fed hamsters. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchoun, M.; Khouya, T.; Alibrahim, E.A.; Hmidani, A.; Sellam, K.; Amrani, S.; Harnafi, H.; Benlyas, M.; Kasbi Chadli, F.; Ouguerram, K.; et al. Thymus atlanticus polyphenol-rich extract regulates cholesterol metabolism by inhibiting its biosynthesis without affecting its excretion in hamsters fed a high-fat diet. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 129, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Tan, Y.Q.; Lin, S.M.; Leung, L.K. Co-administrating apigenin in a high-cholesterol diet prevents hypercholesterolaemia in golden hamsters. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y.; Ali, F. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology 2016, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, A.; Cybulski, M.; Wysokiński, A.P.; Berbeć, H.; Stążka, J.; Zapolski, T. Paraoxonase 1 Activity, Polymorphism and Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tian, J.; Liang, X. Regression of atherosclerosis by Rosmarinic acid via regulating lipid metabolism and anti-inflammatory actions. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 44, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyandwi, J.B.; Ko, Y.S.; Jin, H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.J. Rosmarinic acid inhibits oxLDL-induced inflammasome activation under high-glucose conditions through downregulating the p38-FOXO1-TXNIP pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyandwi, J.B.; Ko, Y.S.; Jin, H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.J. Rosmarinic Acid Increases Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux through Regulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in Different Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, J.A.; Fasae, K.D.; Awe, A.I.; Paimo, O.K.; Adegoke, A.M.; Akintunde, J.K.; Sekhoacha, M.P. The protective roles of citrus flavonoids, naringenin, and naringin on endothelial cell dysfunction in diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, R.; Hua, Y.; Ling, S.; Xu, X. Naringenin ameliorates vascular senescence and atherosclerosis involving SIRT1 activation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, Y.C.; Du, C.; Wang, L.N.; Xiao, Y.H. Effects of Apigenin on the Expression of LOX-1, Bcl-2, and Bax in Hyperlipidemia Rats. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.D.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Sadek, B.; Ojha, S. Pharmacological and Molecular Insight on the Cardioprotective Role of Apigenin. Nutrients 2023, 15, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathiazad, F.; Matlobi, A.; Khorrami, A.; Hamedeyazdan, S.; Soraya, H.; Hammami, M.; Maleki-Dizaji, N.; Garjani, A. Phytochemical screening and evaluation of cardioprotective activity of ethanolic extract of Ocimum basilicum L. (basil) against isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats. Daru 2012, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidanpour, S.; Dianat, M.; Badavi, M.; Mard, S.A. The cardioprotective effect of rosmarinic acid on acute myocardial infarction and genes involved in Ca(2+) homeostasis. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, W.; Liu, H.X.; Zhang, W.; Lou, W.J.; Gong, Y.Z.; Yuan, C.; Shao, Q.; Wang, N.; Guo, C.; Liu, F. Cardioprotective effect of rosmarinic acid against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of the NF-κB inflammatory signalling pathway and ROS production in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2021, 59, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Meng, X.; Fu, F. Protective Effect of RA on Myocardial Infarction-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis via AT1R/p38 MAPK Pathway Signaling and Modulation of the ACE2/ACE Ratio. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6716–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Samtiya, M.; Dhewa, T.; Mishra, V.; Aluko, R.E. Health benefits of polyphenols: A concise review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Wan, S.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.; Xu, T.; He, J.; Mechanick, J.I.; Wu, W.C.; et al. Micronutrient Supplementation to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2269–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, T.; Khan, I.; Iqbal, H.; Usman, S.; Naeem, N.; Faizi, S.; Salim, A. Rutin and quercetagetin enhance the regeneration potential of young and aging bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the rat infarcted myocardium. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2023, 478, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, D.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Administration of rosmarinic acid reduces cardiopathology and blood pressure through inhibition of p22phox NADPH oxidase in fructose-fed hypertensive rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 58, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannarong, M.; Saengsirisuwan, V.; Surapongchai, J.; Buniam, J.; Chukijrungroat, N.; Rattanavichit, Y. Rosmarinic acid improves hypertension and skeletal muscle glucose transport in angiotensin II-treated rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.R.; Woo, E.R.; Hong, S.T.; Chae, H.J.; Chae, S.W. Inhibitory effects of rosmarinic acid on adriamycin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiac muscle cells by inhibiting reactive oxygen species and the activations of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Evora, P.R.B.; Capellini, V.K.; Albuquerque, A.A.; Carvalho, M.T.M.; Gomes, R.; Parolini, M.T.; Celotto, A.C. Effect of rosmarinic acid on the arterial blood pressure in normotensive and hypertensive rats: Role of ACE. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegría-Herrera, E.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Román-Ramos, R.; Zamilpa, A.; Santillán-Urquiza, M.A.; Aguilar, M.I.; Avilés-Flores, M.; Fuentes-Mata, M.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E. Effect of Ocimum basilicum, Ocimum selloi, and Rosmarinic Acid on Cerebral Vascular Damage in a Chronic Hypertension Model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbry, F.; Abdelkawy, K.; Moshirian, N.; Abdel-Megied, A.M. The Antihypertensive Effect of Quercetin in Young Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats; Role of Arachidonic Acid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Saleem, M.Z.; Wei, L.; Xie, Y.; Yan, M.; Chu, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Quercetin attenuates angiotensin II-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and p53 pathway activation in vitro and in vivo. Biofactors 2023, 49, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, T.; Su, B.; Hou, W.; Zhong, H.; Cheng, D.; et al. Rosmarinic acid protects rats against post-stroke depression after transient focal cerebral ischemic injury through enhancing antioxidant response. Brain Res. 2021, 1757, 147336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C.H.; Miao, J.Y.; Chen, R. Rosmarinic acid elicits neuroprotection in ischemic stroke via Nrf2 and heme oxygenase 1 signaling. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Ono, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Iwasa, K.; Nagai, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakamura, H.; Yamada, M. Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Melissa officinalis Extract which Contained Rosmarinic Acid in Healthy Individuals: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, W.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Liao, S.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Chen, C.J. Quercetin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion and oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation neurotoxicity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zych, M.; Kaczmarczyk-Sedlak, I.; Wojnar, W.; Folwarczna, J. Effect of Rosmarinic Acid on the Serum Parameters of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Estrogen-Deficient Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlavcheski, F.; Naimi, M.; Murphy, B.; Hudlicky, T.; Tsiani, E. Rosmarinic Acid, a Rosemary Extract Polyphenol, Increases Skeletal Muscle Cell Glucose Uptake and Activates AMPK. Molecules 2017, 22, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthy, G.; Roshana Devi, V.; Ilango, K.; Subramanian, S.P. Rosmarinic Acid Mediates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Insulin Resistant Skeletal Muscle Through Activation of AMPK. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Choudhury, S.T.; Seidel, V.; Rahman, A.B.; Aziz, M.A.; Richi, A.E.; Rahman, A.; Jafrin, U.H.; Hannan, J.M.A.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin in the Management of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Life 2022, 12, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Williams, A.; Wei, N. Quercetin ameliorated insulin resistance via regulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of PRKD2 mRNA in skeletal muscle and C2C12 myocyte cell line. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Shih, H.Y.; Chia, Y.C.; Lee, C.H.; Ashida, H.; Lai, Y.K.; Weng, C.F. Rutin potentiates insulin receptor kinase to enhance insulin-dependent glucose transporter 4 translocation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Midaoui, A.; Khallouki, F.; Couture, R.; Moldovan, F.; Ismael, M.A.; Ongali, B.; Akoume, M.Y.; Alem, C.; Ait Boughrous, A.; Zennouhi, W.; et al. Thymus atlanticus: A Source of Nutrients with Numerous Health Benefits and Important Therapeutic Potential for Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184077
El Midaoui A, Khallouki F, Couture R, Moldovan F, Ismael MA, Ongali B, Akoume MY, Alem C, Ait Boughrous A, Zennouhi W, et al. Thymus atlanticus: A Source of Nutrients with Numerous Health Benefits and Important Therapeutic Potential for Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184077
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Midaoui, Adil, Farid Khallouki, Réjean Couture, Florina Moldovan, Mahmoud Ali Ismael, Brice Ongali, Marie Yvonne Akoume, Chakib Alem, Ali Ait Boughrous, Wafa Zennouhi, and et al. 2023. "Thymus atlanticus: A Source of Nutrients with Numerous Health Benefits and Important Therapeutic Potential for Age-Related Diseases" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184077
APA StyleEl Midaoui, A., Khallouki, F., Couture, R., Moldovan, F., Ismael, M. A., Ongali, B., Akoume, M. Y., Alem, C., Ait Boughrous, A., Zennouhi, W., Roqai, M. C., Hajji, L., Ghzaiel, I., Vejux, A., & Lizard, G. (2023). Thymus atlanticus: A Source of Nutrients with Numerous Health Benefits and Important Therapeutic Potential for Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients, 15(18), 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184077









