Associations of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Esophageal Precancerous Lesions and Esophageal Squamous-Cell Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. DII Score Calculation
2.3. Covariate Assessment
2.4. EPL and ESCC Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Associations of DII Scores with EPLs and ESCC
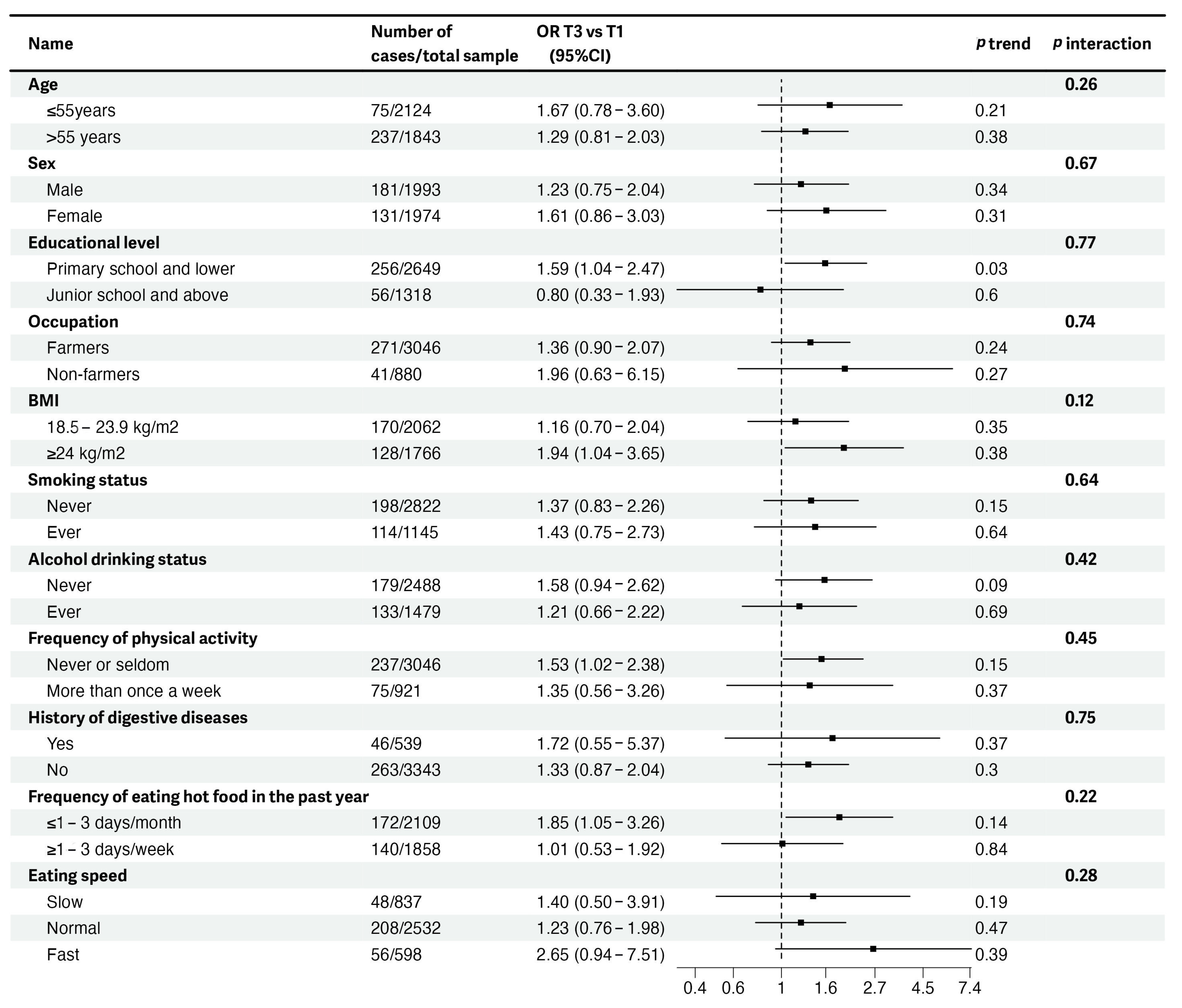
3.3. Stratified Analyses of Associations of DII Scores with EPLs and ESCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Fact Sheets: Oesophagus. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/6-Oesophagus-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Wang, S.M.; Abnet, C.C.; Qiao, Y.L. What have we learned from Linxian esophageal cancer etiological studies? Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Ferlay, J.; Forman, D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 2015, 64, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, W.; Chen, X. Recent advances in esophageal squamous cell precancerous conditions: A review. Medicine 2022, 101, e32192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of oesophageal and gastric cancer by histology and subsite in 2018. Gut 2020, 69, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.R.; Abnet, C.C.; Dawsey, S.M. Squamous dysplasia–the precursor lesion for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.K.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; He, Y.M.; Jiang, C.P.; Jiang, H.D.; Qu, C.X. Adverse effects of preserved vegetables on squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus and precancer lesions in a high risk area. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, J.; Song, M.; Shimazu, T.; Inoue, M.; Charvat, H.; Yamaji, T.; Sawada, N.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Karimi, P.; Dawsey, S.M.; et al. Prediagnostic circulating inflammation biomarkers and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A case-cohort study in Japan. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Song, Q.; Jia, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, P.; Min, R.; Cheng, Y. The clinical significance of systemic inflammation score in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccand, E.; Vollenweider, P.; Guessous, I.; Marques-Vidal, P. Association between dietary intake and inflammatory markers: Results from the CoLaus study. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawsey, S.M.; Fagundes, R.B.; Jacobson, B.C.; Kresty, L.A.; Mallery, S.R.; Paski, S.; van den Brandt, P.A. Diet and esophageal disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1325, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Tabung, F.; Hébert, J.R. A population-based dietary inflammatory index predicts levels of C-reactive protein in the Seasonal Variation of Blood Cholesterol Study (SEASONS). Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Biomarkers of Lipoprotein Metabolism, Inflammation and Glucose Homeostasis in Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Zhao, A.; Liang, W.; Xiao, R.; Xi, Y. Association of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Blood Inflammation: The Prospective Markers on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Shivappa, N.; Lin, Y.; Lagergren, J.; Hébert, J.R. Diet-related inflammation and oesophageal cancer by histological type: A nationwide case-control study in Sweden. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Rashidkhani, B. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer in a Case-Control Study from Iran. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; Rao, W.; Hu, Z. Dietary Inflammatory Nutrients and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Zucchetto, A.; Serraino, D.; Rossi, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of esophageal squamous cell cancer in a case-control study from Italy. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ma, S.; Guan, C.; Song, G.; Ma, Q.; Xie, S.; Wang, M.; Shao, D.; Li, X.; Wei, W. The National Cohort of Esophageal Cancer-Prospective Cohort Study of Esophageal Cancer and Precancerous Lesions based on High-Risk Population in China (NCEC-HRP): Study protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Yan, F.; Jin, M.; Chang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z.; Song, Q.; Li, J.; He, Y.; et al. Pre-diagnosis consumption of preserved vegetables and prognosis of invasive oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective cohort study in one high-risk area in China. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 4306–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, J.C.; Wang, A.R.; Leng, Y.; Li, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.F.; Ren, Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in Yanting–regional report of a national screening programme in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2429–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Dou, L.; Zhou, J.; Song, G.; Li, B.; Zhao, D.; Hua, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hao, C.; et al. Optimal starting age of endoscopic screening for esophageal cancer in China: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 9988–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Song, Q.; Lao, X.; Yu, I.T. Reproducibility and Validity of a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessing Dietary Consumption via the Dietary Pattern Method in a Chinese Rural Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Guo, Y.; Pei, P.; Du, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Shi, Z.; Qi, L.; Chen, J.; et al. The Relative Validity and Reproducibility of Food Frequency Questionnaires in the China Kadoorie Biobank Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y. China Food Composition Table; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tabung, F.K.; Steck, S.E.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liese, A.D.; Agalliu, I.; Hingle, M.; Hou, L.; Hurley, T.G.; Jiao, L.; et al. Construct validation of the dietary inflammatory index among postmenopausal women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawsey, S.M.; Fleischer, D.E.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhou, B.; Kidwell, J.A.; Lu, N.; Lewin, K.J.; Roth, M.J.; Tio, T.L.; Taylor, P.R. Mucosal iodine staining improves endoscopic visualization of squamous dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus in Linxian, China. Cancer 1998, 83, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.Q.; Hao, C.Q.; Guan, C.T.; Song, G.H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, D.L.; Li, B.Y.; Bai, W.L.; Hou, P.Y.; Wang, J.W.; et al. Esophageal Histological Precursor Lesions and Subsequent 8.5-Year Cancer Risk in a Population-Based Prospective Study in China. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.A.; Liu, F.S.; Zhao, H.Z. Histological classification of intraepithelial neoplasias and microinvasive squamous carcinoma of the esophagus. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1989, 13, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Du, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jin, M.; Ma, F.; Li, W.; et al. Association between methionine cycle metabolite-related diets and mild cognitive impairment in older Chinese adults: A population-based observational study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, F.; Chao, L.; et al. Risk factors for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its histological precursor lesions in China: A multicenter cross-sectional study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xue, L.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, N.; Wang, G. Risk factors for complications after endoscopic treatment in Chinese patients with early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.J.; Ou, L.; Li, K.; Ou, F.R. Meta-analysis of the relationship between Dietary Inflammatory Index and esophageal cancer risk. Medicine 2020, 99, e23539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desquilbet, L.; Mariotti, F. Dose-response analyses using restricted cubic spline functions in public health research. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.Y.; Zhang, S.; Suo, Z.; Yang, C.S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.A.; Hu, D.; Ji, X.Z.; Zhai, M. PLCE1 gene in esophageal cancer and interaction with environmental factors. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2745–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Merchant, A.T.; Wirth, M.D.; Zhang, J.; Antwi, S.O.; Shoaibi, A.; Shivappa, N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Hebert, J.R.; Steck, S.E. Inflammatory potential of diet and risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Lee, A.H.; Xu, F.; Binns, C.W. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of oesophageal cancer in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Zeng, R.; Cao, W.; Luo, R.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y. Hot beverage and food intake and esophageal cancer in southern China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 2189–2192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, I.T.; Christiani, D.C. Consumption of salted meat and its interactions with alcohol drinking and tobacco smoking on esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhao, L.; Song, G.; Shao, Y.; Hao, C.; Niu, C.; Ruan, X.; Zang, Z.; Nakyeyune, R.; et al. Estimating Individualized Absolute Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Study in High-Risk Areas of China. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 598603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budach, W.; Hehr, T.; Budach, V.; Belka, C.; Dietz, K. A meta-analysis of hyperfractionated and accelerated radiotherapy and combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy regimens in unresected locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Y.; Cai, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y. Natural phenolic compounds from medicinal herbs and dietary plants: Potential use for cancer prevention. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Cross, A.J.; Graubard, B.I.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A. Meat intake and mortality: A prospective study of over half a million people. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.H. Health-promoting components of fruits and vegetables in the diet. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 384s–392s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Doherty, M.G.; Freedman, N.D.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. A prospective cohort study of obesity and risk of oesophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma in the NIH–AARP Diet and Health Study. Gut 2012, 61, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Q.; Abnet, C.C.; Shen, Q.; Lewin, K.J.; Sun, X.D.; Roth, M.J.; Qiao, Y.L.; Mark, S.D.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk population. Gut 2005, 54, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.Q.; Abnet, C.C.; Lu, N.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Dye, B.A.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; Albert, P.; Qiao, Y.L.; et al. Risk factors for oesophageal squamous dysplasia in adult inhabitants of a high risk region of China. Gut 2005, 54, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, K.; Gao, L.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for esophageal squamous cell cancer and precursor lesions in Anyang, China: A population-based endoscopic survey. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abnet, C.C.; Chen, W.; Dawsey, S.M.; Wei, W.Q.; Roth, M.J.; Liu, B.; Lu, N.; Taylor, P.R.; Qiao, Y.L. Serum 25(OH)-vitamin D concentration and risk of esophageal squamous dysplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 1889–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Su, M.; Zhang, T.; Miao, C.; Fu, L.; Yang, L.; Song, G.; Raine, P.J.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. A Distinct Epidemiologic Pattern of Precancerous Lesions of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-risk Area of Huai’an, Jiangsu Province, China. Cancer Prev. Res. 2019, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulpen, M.; Peeters, P.H.; van den Brandt, P.A. Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer subtypes in the Netherlands Cohort Study. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Park, Y.; Wu, J.W.; Ren, J.S.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Freedman, N.D.; Abnet, C.C. Index-based dietary patterns and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer in a large cohort study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1130–1136.e1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Liu, F.; Chao, L.; et al. Dietary patterns and severity of symptom with the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its histological precursor lesions in China: A multicenter cross-sectional latent class analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, F.; Fedirko, V.; Tramacere, I.; Bagnardi, V.; Jenab, M.; Scotti, L.; Rota, M.; Corrao, G.; Garavello, W.; Schüz, J.; et al. Alcohol drinking and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with focus on light-drinkers and never-smokers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology 2011, 129, 2473–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stornetta, A.; Guidolin, V.; Balbo, S. Alcohol-Derived Acetaldehyde Exposure in the Oral Cavity. Cancers 2018, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Pei, Z.; et al. Drinking alcohol is associated with variation in the human oral microbiome in a large study of American adults. Microbiome 2018, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishehsari, F.; Magno, E.; Swanson, G.; Desai, V.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol and Gut-Derived Inflammation. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, M.; Patsias, A.; Posner, M.; Sikora, A. The role of inflammation in head and neck cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 816, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Miles, E.A. Diet and Immune Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Pischon, T.; Hankinson, S.E.; Rifai, N.; Joshipura, K.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B. Dietary intake of trans fatty acids and systemic inflammation in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Lim, T.G.; Lee, K.W. Molecular mechanisms of chemopreventive phytochemicals against gastroenterological cancer development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietkau, R.; Lewitzki, V.; Kuhnt, T.; Hölscher, T.; Hess, C.F.; Berger, B.; Wiegel, T.; Rödel, C.; Niewald, M.; Hermann, R.M.; et al. A disease-specific enteral nutrition formula improves nutritional status and functional performance in patients with head and neck and esophageal cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy: Results of a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Cancer 2013, 119, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Ying, S.; Zhang, C.; Lin, R.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, G.; Tian, D.; Guo, Y.; Du, C.; et al. Genetic Alterations in Esophageal Tissues From Squamous Dysplasia to Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierziak, J.; Kostyn, K.; Boba, A.; Czemplik, M.; Kulma, A.; Wojtasik, W. Influence of the Bioactive Diet Components on the Gene Expression Regulation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlenhopp, D.J.; Then, E.O.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzo, A.J.; Fuller, A.M.; Makowski, L. Contribution of Adipose Tissue to Development of Cancer. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 237–282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mwachiro, M.M.; Burgert, S.L.; Lando, J.; Chepkwony, R.; Bett, C.; Bosire, C.; Abnet, C.C.; Githanga, J.; Waweru, W.; Giffen, C.A.; et al. Esophageal Squamous Dysplasia is Common in Asymptomatic Kenyans: A Prospective, Community-Based, Cross-Sectional Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | DII Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tertile 1 (−3.694–1.994) | Tertile 2 (1.995–2.944) | Tertile 3 (2.945–5.474) | |
| N | 1322 | 1323 | 1322 |
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | |
| Age (years) | 54.86 ± 7.77 | 56.37 ± 7.94 | 56.24 ± 7.84 |
| Total energy intake (kcal/day) | 1321.22 ± 220.38 | 1095.68 ± 179.01 | 896.78 ± 214.48 |
| N (%) a | N (%) a | N (%) a | |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 858 (64.9) | 616 (46.6) | 519 (39.3) |
| Female | 464 (35.1) | 707 (53.4) | 803 (60.7) |
| Marital status b | |||
| Married | 1269 (96.0) | 1268 (95.8) | 1281 (96.9) |
| Not married | 53 (4.0) | 55 (4.2) | 41 (3.1) |
| Educational level | |||
| Primary school and lower | 794 (60.1) | 920 (69.5) | 935 (70.7) |
| Junior school | 462 (35.0) | 372 (28.1) | 339 (25.6) |
| High school and above | 66 (5.0) | 31 (2.3) | 48 (3.6) |
| Occupation | |||
| Farmers | 917 (69.4) | 1096 (82.8) | 1033 (78.1) |
| Non-farmers | 405 (30.6) | 227 (17.2) | 289 (21.9) |
| Household income (CNY/year) | |||
| <50,000 | 954 (72.2) | 1152 (87.1) | 1185 (89.6) |
| ≥50,000 | 368 (27.8) | 171 (12.9) | 137 (10.4) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| <18.5 | 15 (1.2) | 39 (3.0) | 45 (3.4) |
| 18.5–23.9 | 640 (49.0) | 721 (55.0) | 701 (53.4) |
| 24.0–27.9 | 502 (38.5) | 459 (35.0) | 477 (36.4) |
| ≥28.0 | 148 (11.3) | 91 (7.0) | 89 (6.8) |
| Smoking status | |||
| Never | 804 (60.8) | 973 (73.5) | 1045 (79.1) |
| Past | 74 (5.6) | 80 (6.1) | 64 (4.8) |
| Current | 444 (33.6) | 270 (20.4) | 213 (16.1) |
| Alcohol drinking status | |||
| Never | 633 (47.9) | 831 (62.8) | 1024 (77.5) |
| Ever | 689 (52.1) | 492 (37.2) | 298 (22.5) |
| Frequency of physical activity c | |||
| Never or seldom | 921 (69.7) | 941 (71.1) | 1184 (89.6) |
| More than once a week | 401 (30.3) | 382 (28.9) | 138 (10.4) |
| Self-rated health status | |||
| Good | 167 (12.6) | 195 (14.8) | 113 (8.5) |
| Fair | 1111 (84.0) | 1018 (77.0) | 1085 (82.0) |
| Poor and very poor | 44 (3.3) | 109 (8.2) | 125 (9.4) |
| History of digestive diseases d | |||
| Yes | 162 (12.3) | 163 (12.3) | 260 (19.7) |
| No | 1144 (86.5) | 1148 (86.8) | 1051 (79.5) |
| Missing | 16 (1.2) | 12 (0.9) | 11 (0.8) |
| Frequency of eating hot food in the past year e | |||
| ≤1–3 days/month | 970 (73.4) | 718 (54.3) | 421 (31.8) |
| ≥1–3 days/week | 352 (26.6) | 605 (45.7) | 901 (68.2) |
| Texture of staple food f | |||
| Hard | 118 (13.7) | 105 (7.9) | 132 (10.0) |
| Soft or liquid | 1141 (86.3) | 1218 (92.1) | 1190 (90.0) |
| Eating speed | |||
| Slow | 337 (25.5) | 260 (19.7) | 240 (18.2) |
| Normal | 759 (57.4) | 863 (65.2) | 910 (68.8) |
| Fast | 226 (17.1) | 200 (15.1) | 172 (13.0) |
| Tertile 1 | Tertile 2 | Tertile 3 | ORcontinuous a | ptrend b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall EPLs | |||||
| Mean (range) c | 1.11 (−3.69–1.99) | 2.45 (2.00–2.94) | 3.44 (2.95–5.47) | ||
| Cases/Total Sample | 99/1322 | 95/1323 | 118/1322 | ||
| Model 1, OR (95%CI) d | Ref. | 0.98 (0.71–1.35) | 1.53 (1.05–2.23) | 1.15 (1.00–1.34) | 0.05 |
| Model 2, OR (95%CI) e | Ref. | 0.94 (0.68–1.31) | 1.45 (1.01–2.09) | 1.12 (0.96–1.31) | 0.15 |
| Mild EPLs | |||||
| Mean (range) c | 1.10 (−3.69–1.99) | 2.45 (2.00–2.94) | 3.44 (2.95–5.47) | ||
| Cases/Total Sample | 76/1299 | 69/1297 | 79/1283 | ||
| Model 1, OR (95%CI) d | Ref. | 0.95 (0.66–1.38) | 1.39 (0.90–2.16) | 1.14 (0.96–1.36) | 0.14 |
| Model 2, OR (95%CI) e | Ref. | 0.94 (0.65–1.37) | 1.31 (0.83–2.06) | 1.11 (0.93–1.34) | 0.21 |
| Moderate and Severe EPLs | |||||
| Mean (range) c | 1.10 (−3.69–1.99) | 2.45 (2.00–2.94) | 3.44 (2.95–5.47) | ||
| Cases/Total Sample | 23/1245 | 26/1254 | 39/1242 | ||
| Model 1, OR (95%CI) d | Ref. | 1.07 (0.58–1.97) | 1.97 (0.99–3.92) | 1.18 (0.92–1.53) | 0.20 |
| Model 2, OR (95%CI) e | Ref. | 0.96 (0.52–1.79) | 1.77 (0.86–3.61) | 1.15 (0.87–1.51) | 0.33 |
| ESCC | |||||
| Mean (range) c | 1.11 (−3.69–1.99) | 2.45 (2.00–2.94) | 3.44 (2.95–5.47) | ||
| Cases/Total Sample | 19/1322 | 21/1323 | 32/1322 | ||
| Model 1, OR (95%CI) d | Ref. | 1.08 (0.55–2.11) | 1.93 (0.90–4.11) | 1.13 (0.85–1.49) | 0.40 |
| Model 2, OR (95%CI) e | Ref. | 0.96 (0.48–1.92) | 1.80 (0.82–3.97) | 1.14 (0.84–1.55) | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Gao, M.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Chen, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J. Associations of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Esophageal Precancerous Lesions and Esophageal Squamous-Cell Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184078
Dong J, Gao M, Li L, Pan X, Chen S-Y, Li J, Smith-Warner SA, Li X, Wang H, Zheng J. Associations of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Esophageal Precancerous Lesions and Esophageal Squamous-Cell Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184078
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jingwen, Min Gao, Lin Li, Xiaoyu Pan, Sheng-Yin Chen, Jun Li, Stephanie A. Smith-Warner, Xiaoguang Li, Hui Wang, and Jiali Zheng. 2023. "Associations of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Esophageal Precancerous Lesions and Esophageal Squamous-Cell Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184078
APA StyleDong, J., Gao, M., Li, L., Pan, X., Chen, S.-Y., Li, J., Smith-Warner, S. A., Li, X., Wang, H., & Zheng, J. (2023). Associations of Dietary Inflammatory Potential with Esophageal Precancerous Lesions and Esophageal Squamous-Cell Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 15(18), 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184078







