The Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on Releasing Minerals and Trace Elements from Wheat Flakes: The Extended Study of Dietary Intakes for Individual Life Stage Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Production of Non-Traditional Wheat Flakes
2.4. Simulated In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.5. Preparation of Undigested Parts of Non-Traditional Wheat Flakes
2.6. ICP-MS Analysis
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Quality Control
2.6.3. ICP-MS Instrumentation
2.7. Effect of the Thermal Treatment and Flaking Process on the Mineral and Trace Element Content of Wheat Flakes
2.8. Contribution of Elements to the RDA, AI, PTWI, and PTMI Values
2.9. Effect of In Vitro Digestion on the Element Content of Wheat Flakes
2.10. Metal Pollution Index Evaluation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dry Matter and Ash Contents and Digestibility Assessment of Non-Traditional Wheat Flakes
3.2. Mineral and Trace Element Content of Non-Traditional Wheat Grains
3.3. Mineral and Trace Element Contents of Non-Traditional Wheat Flakes
3.4. Effect of the Thermal Treatment and Flaking on the Mineral and Trace Element Contents of Wheat Flakes
3.5. Estimations of the Dietary Intake of Elements
3.5.1. Estimation of the Dietary Intake of Essential Elements
3.5.2. Estimation of the Dietary Intake of Toxic Elements
3.5.3. Estimation of the Dietary Intake of Other Elements
3.6. Effect of the In Vitro Digestibility on the Mineral and Trace Element Retention in Wheat Flakes
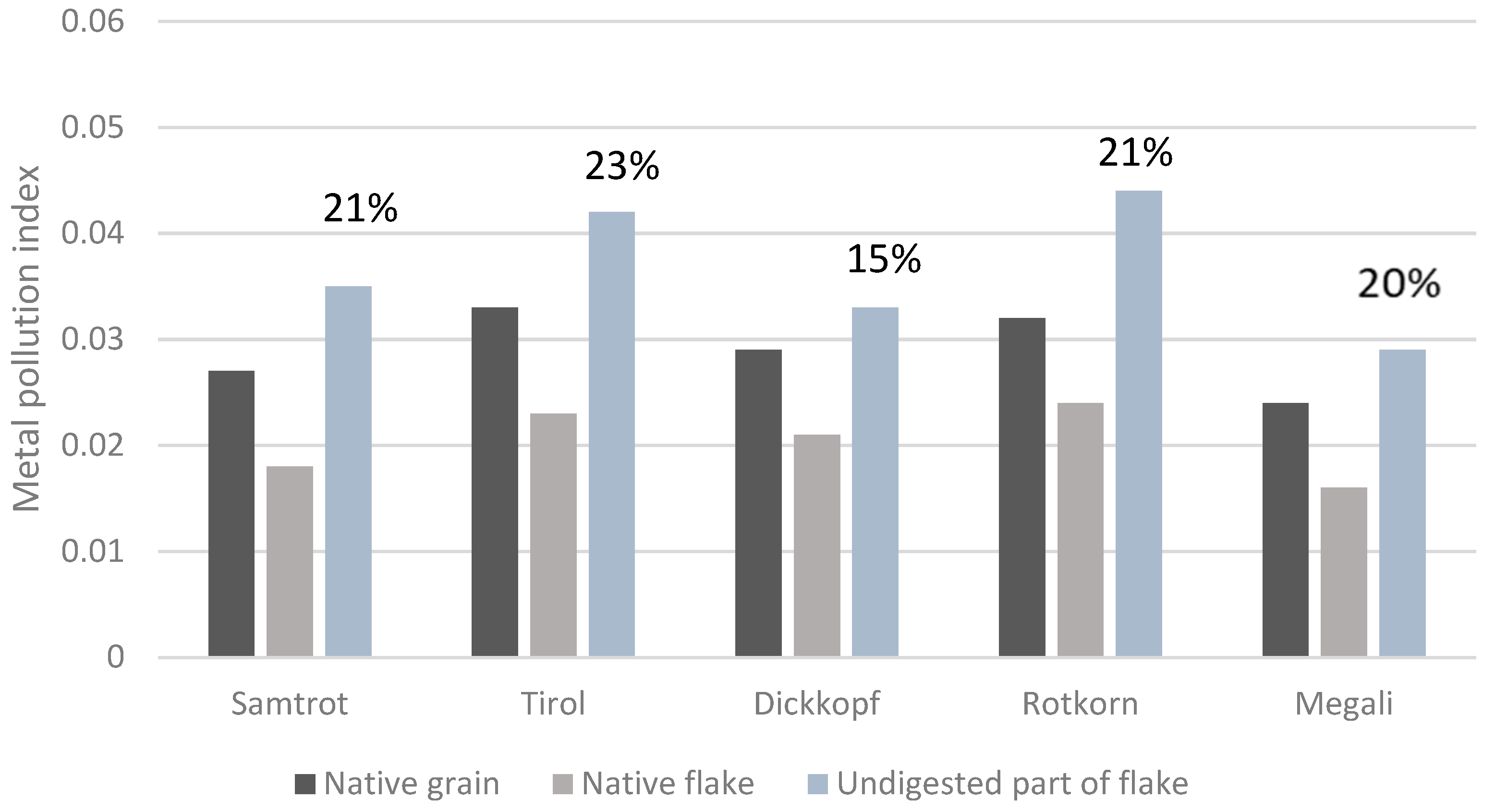
3.7. Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on the Metal Pollution Index
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drawbridge, P.C.; Apea-Bah, F.; Hornung, P.S.; Beta, T. Bioaccessibility of phenolic acids in Canadian hulless barley varieties. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, E.; Deleu, L.J.; De Brier, N.; Smolders, E.; Delcour, J.A. Mineral bio-accessibility and intrinsic saccharides in breakfast flakes manufactured from sprouted wheat. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 143, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiewlitz, J.; Rybicka, I. Minerals and their bioavailability in relation to dietary fiber, phytates and tannins from gluten and gluten-free flakes. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.-E.; Xu, H.; Gao, D.; Zhang, G.; Chen, P.; Liu, D. Effect of wheat pearling on flour phytate activity, phytic acid, iron and zinc content. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficco, D.B.M.; Borrelli, G.M.; Miedico, O.; Giovanniello, V.; Tarallo, M.; Pompa, C.; De Vita, P.; Chiaravalle, A.E. Effect of grain debranning on bioactive compounds, antioxidant capacity and essential and toxic trace elements in purple durum wheats. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 118, 108734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Prado Ferreira, M.; Teixeira Tarley, C.R. Bioaccessibility estimation of metallic macro and micronutrients Ca, Mg, Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn in flours of oat and passion fruit peel. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 150, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dost, K.; Tokul, O. Determination of phytic acid in wheat and wheat products by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 558, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affonfere, M.; Chadare, F.J.; Fassinou, F.T.K.; Linnemann, A.R.; Duodu, K.G. In-vitro digestibility methods and factors affecting minerals bioavailability: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1014–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetola, O.Y.; Kruger, J.; White, Z.; Taylor, J.R.N. Comparison between food-to-food fortification of pearl millet porridge with moringa leaves and baobab fruit and with adding ascorbic and citric acid on iron, zinc and other mineral bioaccessibility. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 106, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, F. Phytic acid and whole grains for health controversy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sęczyk, Ł.; Sugier, D.; Świeca, M.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. The effect of in vitro digestion, food matrix, and hydrothermal treatment on the potential bioaccessibility of selected phenolic compounds. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. Effect of household cooking process on mineral, vitamin B, and phytic acid contents and mineral bioaccessibility in rice. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koláčková, T.; Sumczynski, D.; Minařík, A.; Yalçin, E.; Orsavová, J. The effect of in vitro digestion on matcha tea (Camellia sinensis) active components and antioxidant activity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumczynski, D.; Koubová, E.; Sneyd, J.; Erb-Weber, S.; Orsavová, J. Preparation of non-traditional Dickkopf and Richard wheat flakes: Phenolic and vitamin profiles and antioxidant activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists International, 5th ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sumczynski, D.; Koubová, E.; Šenkárová, L.; Orsavová, J. Rice flakes produced from commercial wild rice: Chemical composition, vitamin B compounds, mineral and trace element contents and their dietary intake evaluation. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate; The National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Contaminants: Sixty-Fourth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No. 930; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Seventy-Second Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No. 959; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Seventy-Fourth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No. 966; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Seventy-Seventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No. 983; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Orecchio, S.; Amorello, D.; Raso, M.; Barreca, S.; Lino, C.; Di Gaudio, F. Determination of trace elements in gluten-free food for celiac people by ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Yadav, J.S.; Kumar, I.; Kumar, U.; Sharma, R.K. Carpet industry irrigational sources risk assessment: Heavy metal contaminated vegetables and cereal crops in northern India. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1906–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation No 18; Regulation for Cereal and Cereal Products, Pasta and Bakery Products. Ministry of Agriculture: Prague, Czech Republic, 2020.
- Sumczynski, D.; Bubelova, Z.; Sneyd, J.; Erb-Weber, S.; Mlcek, J. Total phenolics, flavonoids, antioxidant activity, crude fibre and digestibility in non-traditional wheat flakes and muesli. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.-Q.; Wang, F.; Ren, L.-P.; Zhou, Z.-M.; Meng, Q.-X.; Bao, Y.-H. Effect of steam-flaking on chemical compositions, starch gelatinization, in vitro fermentability, and energetic values of maize, wheat and rice. J. Integr. Aric. 2015, 14, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.; Čupić, S. Toxic and essential elements in soft wheat grain cultivated in Serbia. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, M.; Afyuni, M.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Papritz, A.; Schulin, R. Grain zinc, iron, and copper concentrations of wheat grown in central Iran and their relationships with soil and climate variables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10876–10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, G.M.A.; Jasan, R.; Plá, R.; Pignata, M.L. Heavy metal and trace element concentrations in wheat grains: Assessment of potential non-carcinogenic health hazard through their consumption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 193, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvěřina, O.; Kuta, J.; Coufalík, P.; Kosečková, P.; Komárek, J. Simultaneous determination of cadmium and iron in different kinds of cereal flakes using high-resolution continuum source atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 629/2008 of 2 July 2008 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. 2008. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008R0629&qid=1673430422268&from=CS (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1323 of 10 August 2021 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as Regards Maximum Levels of Cadmium in Certain Foodstuffs. 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1323&from=EN (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Cadmium dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2551. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2551 (accessed on 5 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 420/2011 of 29 April 2011 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32011R0420&qid=1673429826655&from=CS (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1317 of 9 August 2021 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as Regards Maximum Levels of Lead in Certain Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1317&qid=1678878875525&from=CS (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/1006 of 25 June 2015 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as Regards Maximum Levels of Inorganic Arsenic in Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32015R1006&qid=1678879433609&from=CS (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Wu, G.; Ashton, J.; Simic, A.; Fang, Z.; Johnson, S.K. Mineral availability is modified by tannin and phytate content in sorghum flaked breakfast cereals. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–153. ISBN 978-1-4200-9368-1. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers, Amending Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and Repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496,EEC, Commission Directive 1990/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02011R1169-20180101&qid=1678014199899&from=CS (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Antoine, J.M.R.; Hoo Fung, L.A.; Grant, C.N.; Dennis, H.T.; Lalor, G.C. Dietary intake of minerals and trace elements in rice on the Jamaican market. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 26, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. European Food Safety Authority. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3846. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3846 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the tolerable upper intake level for selenium. EFSA J. 2023, 21, 7704. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.7704 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on dietary reference values for copper. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4253. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4253 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Mathebula, M.W.; Mandiwana, K.; Panichev, N. Speciation of chromium in bread and breakfast cereals. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the risk to public health related to the presence of chromium in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3595. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3595 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. IRIS Toxicological Review of Hexavalent Chromium (External Review Draft): Support of Summary Information on the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Dong, J.Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.Q. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N. Nutritional neuropathies. Neurol. Clin. 2007, 25, 209–255. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4199287/pdf/nihms549812.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Re-evaluation of the existing health-based guidance values for copper and exposure assessment from all sources. EFSA J. 2023, 21, 7728. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.7728 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on dietary reference values for molybdenum. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3333. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3333 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung—Österreichische Gesellschaft für Ernährung, Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Ernährungsforschung, Schdweizerische Vereinigung für Ernährung: Referenzwerte für die Nährstoffzufuhr; Neuer Umschau Buchverlag: Frankfurt/Main, Germany, 2013.
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on dietary reference values for manganese. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3419. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3419 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- EFSA Scientific Committee; More, S.J.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Hernández-Jerez, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lambré, C.; et al. Content of toxic elements in 12 group of rice products available on Polish market: Human health risk assessment. Foods 2020, 9, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. ATSDR’s Substance Priority List. 2022. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html#2022spl (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Cadmium in food. Scientific Opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain. EFSA J. 2009, 980, 1–139. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.980 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion. Statement on tolerable weekly intake for cadmium. EFSA J 2011, 9, 1975. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.1975 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific opinion on the risk for public health related to the presence of mercury and methylmercury in food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2985. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2985 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Safety of aluminium from dietary intake. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Food Contact Materials (AFC). EFSA J. 2008, 754, 1–34. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2008.754 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Filippini, T.; Tancredi, S.; Malagoli, C.; Cilloni, S.; Malavolti, M.; Violi, F.; Vescovi, L.; Bargellini, A.; Vinceti, M. Aluminium and tin: Food contamination and dietary intake in an Italian population. J. Trace. Elem Med. Biol. 2019, 52, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubová, E.; Sumczynski, D.; Šenkárová, L.; Orsavová, J.; Fišera, M. Dietary intakes of minerals, essential and toxic trace elements for adults from Eragrostis tef L.: A nutritional assessment. Nutrients 2018, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies on a request from the Commission related to the tolerable upper intake level of tin. EFSA J. 2005, 254, 1–25. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2005.254 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02006R1881-20230101&qid=1678820563695&from=CS (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Seventy-Third Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series No. 960; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on lead in food. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1570. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1570 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Report of EFSA. Lead dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2831. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2831 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Report of EFSA. Dietary exposure to inorganic arsenic in the European population. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3597. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3597 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on arsenic in food. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1351. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1351 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4002. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4002 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Update of the risk assessment of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6268. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.6268 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Akinyele, I.O.; Shokunbi, O.S. Concentrations of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Cr, Cd, Pb, Ni in selected Nigerian tubers, legumes and cereals and estimates of the adult daily intakes. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, P.L.; Hazelwood, K.J. Exposure-related health effects of silver and silver compounds: A review. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 49, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Silver in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/350935/WHO-HEP-ECH-WSH-2021.7-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Dawson, P.A.; Elliot, A.; Bowling, F.G. Sulphate in pregnancy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, E.; Givelet, L.; Amlund, H.; Sloth, J.J.; Hansen, M. Risk assessment of rare earth elements, antimony, barium, boron, lithium, tellurium, thallium and vanadium in teas. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200410. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2022.e200410 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Antimony in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/antimony.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Wu, F.; Fu, Z.; Liu, B.; Mo, C.; Chen, B.; Corns, W.; Liao, H. Health risk associated with dietary co-exposure to high levels of antimony and arsenic in the world’s largest antimony mine area. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3344–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks SCHER. Assessment of the Tolerable Daily Intake of Barium; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 22 March 2012; Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/176688a8-869f-4a9e-b590-f8fcf09fc1c2/language-en (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- World Health Organization. Strontium and Strontium Compounds: Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 77; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44280/9789241530774_eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Kołodziejska, B.; Stępień, J.; Kolmas, J. The influence of strontium on bone metabolism and its application in osteoporosis treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Inorganic Contaminant Accumulation in Potable Water Distribution Systems; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-05/documents/issuepaper_tcr_inorganicaccumulation_posted.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Tolerable Upper Intake Levels for Vitamins and Minerals: Scientific Committee on Food; Scientific Panel on Dietetics products, Nutrition and Allergies, 2006; p. 482. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/assets/ndatolerableuil.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Szklarska, D.; Rzymski, P. Is lithium a micronutrient? From biological activity and epidemiological observation to food fortification. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 18–27. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12011-018-1455-2 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Lithium: Occurrence, dietary intakes, nutritional essentiality. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2002, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies on a request from the Commission related to the tolerable upper intake level of boron (sodium borate and boric acid). EFSA J. 2004, 820, 1–22. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2004.80 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Nielsen, F.H. Update on human health effects of boron. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. Boron. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Boron-HealthProfessional/ (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- World Health Organization. Boron: Trace Elements in Human Nutrition and Health; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- World Health Organization & International Programme on Chemical Safety. Boron: Environmental Health Criteria 204; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; p. 201. ISBN 92-4157-204-3.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Toxicological Review of Thallium and Compounds; (CAS No. 7440-28-0); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. Available online: https://iris.epa.gov/static/pdfs/1012tr.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Cvjetko, P.; Cvjetko, I.; Pavlica, M. Thallium toxicity in humans. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 2010, 61, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Review of potentially toxic rare earth elements, thallium and tellurium in plant-based foods. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e181101. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.e181101 (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn TO RS TE, N.; Bourlieu, C.; Brodkorb, A. Standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food–an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafi, K.; Nodehi, R.N.; Mahvi, A.H.; Pirsaheb, M.; Nazmara, S.; Mahmoudi, B.; Yunesian, M. Bioacessibility analysis of toxic metals in consumed rice through an in vitro human digestion model—Comparison of calculated human health risk from raw, cooked and digested rice. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioca, A.-A.; Langerholc, T.; Tušar, L. Implementation of food matrix effects into chemical food contaminant risk assessment. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200905. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2022.e200905 (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Prijanka; Shukla, V.; Kumar, S.; Ram, R.B.; Kumar, N. Metal pollution index and daily dietary intake of metals through consumption of vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 3271–3278. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13762-019-02594-y (accessed on 8 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, F.; Amin, M.M.; Alavijeh, Z.P.; Esfahani, R.A.; Sadeghi, M.; Bandarrig, N.S.; Rezakazemi, M. Health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements intake via food crops consumption: Monte Carlo simulation-based probabilistic and heavy metal pollution index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
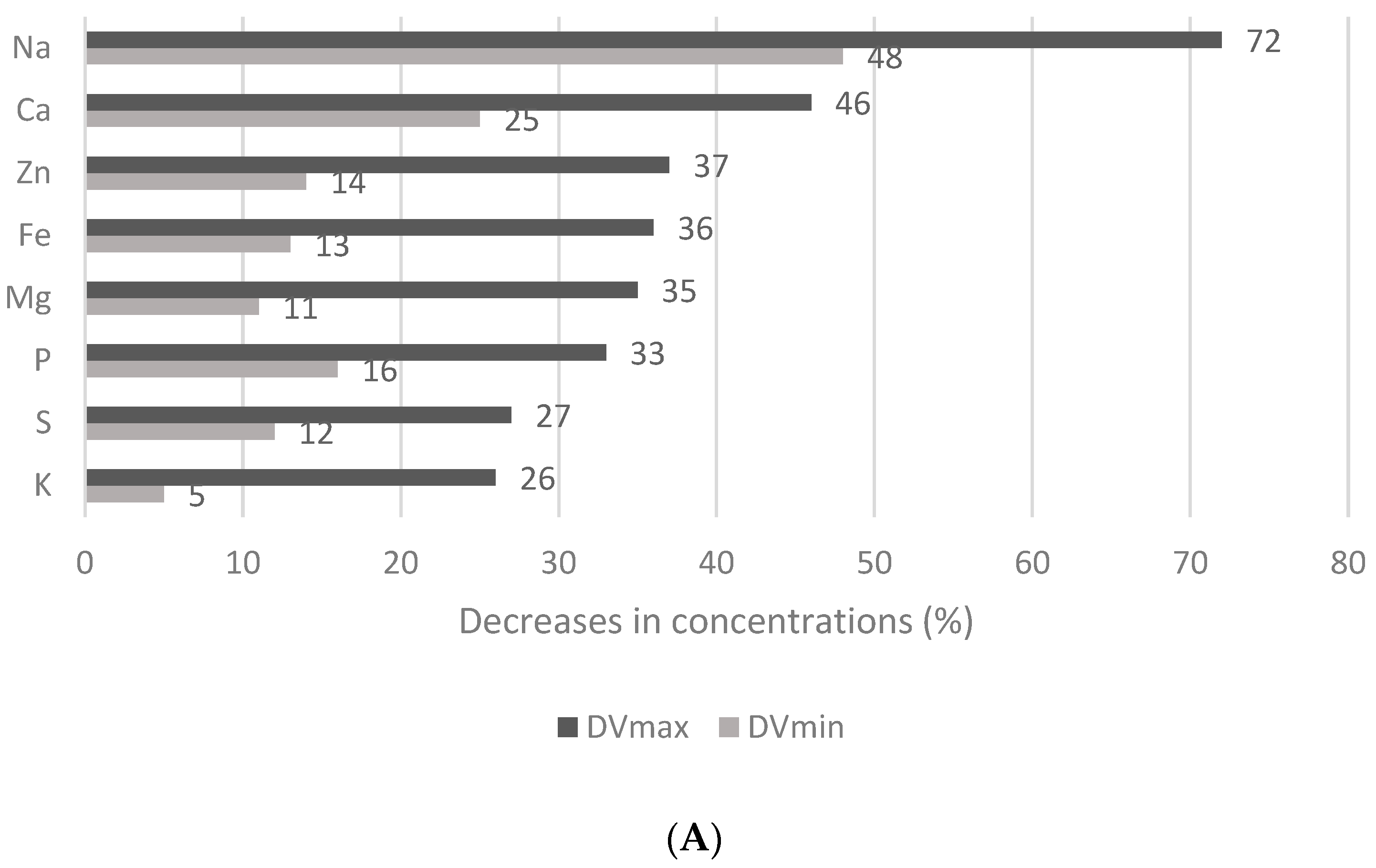
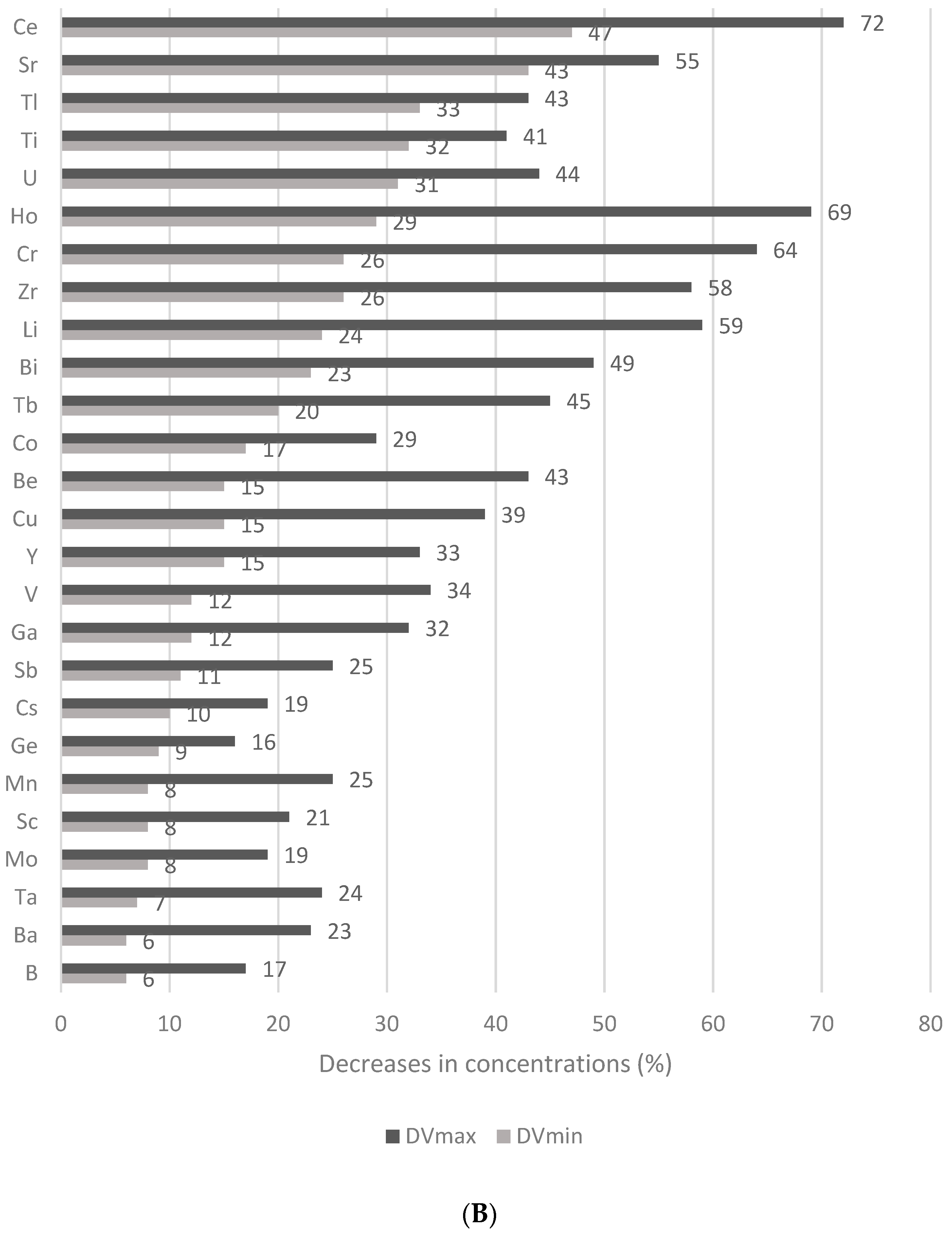



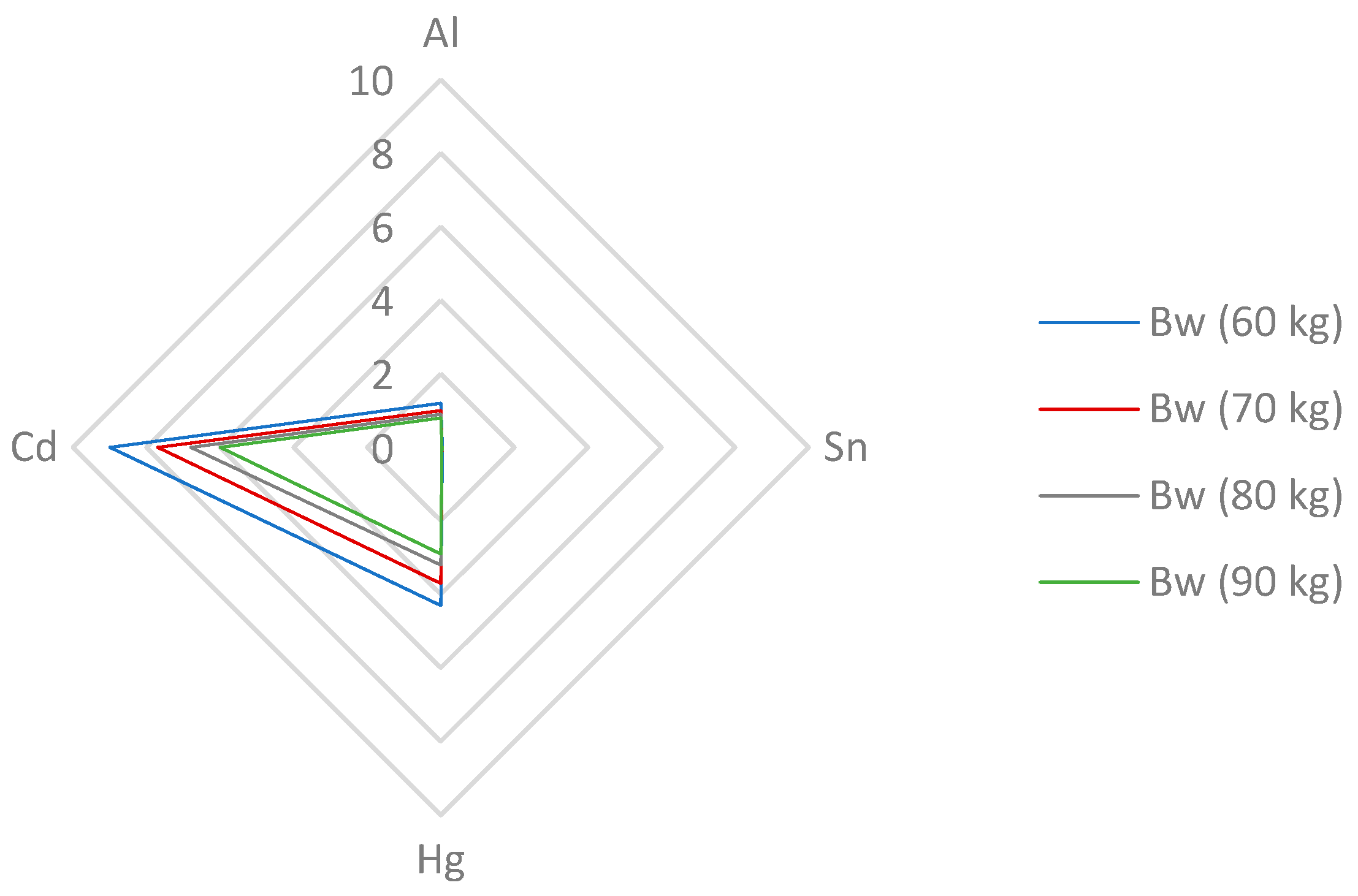

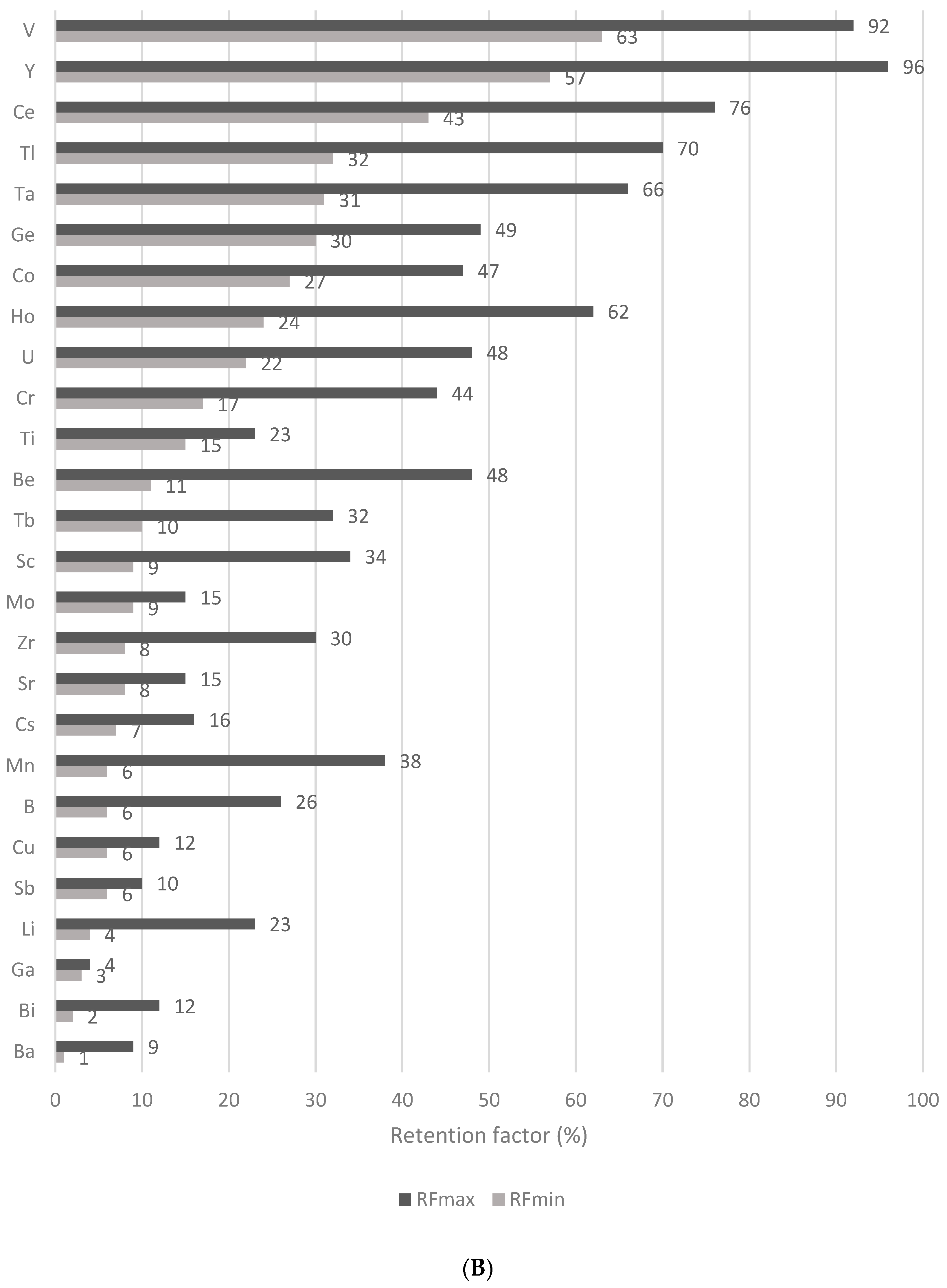

| Analyte | Native Grains | Native Flakes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samtrot | Tirol | Dickkopf | Rotkorn | Megali | Samtrot | Tirol | Dickkopf | Rotkorn | Megali | |
| (µg/g) | ||||||||||
| 23Na | 4.13 ± 0.10 a | 4.42 ± 0.10 b | 10.6 ± 0.2 c | 6.01 ± 0.10 d | 4.44 ± 0.12 b | 1.33 ± 0.05 A | 1.35 ± 0.04 A | 5.51 ± 0.20 B | 1.74 ± 0.04 C | 1.26 ± 0.04 D |
| 24Mg | 1020 ± 20 a | 978 ± 15 b | 981 ± 15 b | 1090 ± 20 c | 878 ± 15 d | 658 ± 15 A | 690 ± 12 B | 758 ± 10 C | 967 ± 15 D | 679 ± 12 E |
| 27Al | 1.56 ± 0.03 a | 2.05 ± 0.10 b | 1.60 ± 0.06 a,d | 2.33 ± 0.04 c | 1.67 ± 0.05 d | 1.45 ± 0.05 A | 1.86 ± 0.06 B | 1.52 ± 0.03 C | 2.01 ± 0.04 D | 1.59 ± 0.02 E |
| 31P | 192 ± 5 a | 192 ± 5 a | 191 ± 4 a | 205 ± 4 b | 176 ± 2 c | 129 ± 3 A | 150 ± 5 B | 154 ± 5 B | 172 ± 5 C | 140 ± 5 D |
| 32S | 6.11 ± 0.10 a | 6.63 ± 0.12 b | 6.51 ± 0.12 c | 7.52 ± 0.12 d | 6.24 ± 0.14 e | 4.45 ± 0.20 A | 5.12 ± 0.20 B | 5.70 ± 0.20 C | 6.55 ± 0.12 D | 5.17 ± 0.10 B |
| 39K | 574 ± 10 a | 651 ± 12 b | 725 ± 20 c | 744 ± 14 d | 728 ± 12 c | 424 ± 10 A | 589 ± 15 B | 616 ± 14 C | 710 ± 12 D | 621 ± 12 C |
| 40Ca | 261 ± 5 a | 270 ± 6 b | 302 ± 6 c | 324 ± 5 d | 300 ± 5 c | 141 ± 3 A | 171 ± 5 B | 204 ± 7 C | 244 ± 6 D | 195 ± 5 E |
| 48Ti | 2.00 ± 0.10 a | 2.78 ± 0.11 b | 2.24 ± 0.10 c | 3.06 ± 0.20 d | 2.26 ± 0.14 c | 1.18 ± 0.10 A | 1.75 ± 0.07 B | 1.52 ± 0.07 C | 2.04 ± 0.02 D | 1.41 ± 0.02 E |
| 55Mn | 38.7 ± 0.5 a | 31.9 ± 0.5 b | 25.2 ± 0.4 c | 36.8 ± 0.5 d | 31.5 ± 0.5 b | 29.2 ± 0.5 A | 29.3 ± 0.6 A | 20.2 ± 0.3 B | 32.9 ± 0.4 C | 25.8 ± 0.3 D |
| 57Fe | 12.3 ± 0.1 a | 17.6 ± 0.2 b | 11.9 ± 0.2 c | 11.2 ± 0.3 d | 10.2 ± 0.2 e | 7.89 ± 0.15 A | 12.5 ± 0.3 B | 9.07 ± 0.20 C | 9.65 ± 0.10 D | 7.46 ± 0.10 E |
| 63Cu | 8.56 ± 0.05 a | 4.57 ± 0.05 b | 9.73 ± 0.05 c | 6.45 ± 0.10 d | 8.16 ± 0.12 e | 5.28 ± 0.12 A | 3.79 ± 0.12 B | 6.25 ± 0.14 C | 5.51 ± 0.07 D | 5.00 ± 0.05 E |
| 66Zn | 9.01 ± 0.20 a | 7.45 ± 0.20 b | 15.4 ± 0.3 c | 7.38 ± 0.20 b | 7.89 ± 0.10 d | 6.37 ± 0.30 A,D | 6.07 ± 0.20 B | 9.67 ± 0.20 C | 6.34 ± 0.10 A | 6.44 ± 0.10 D |
| (ng/g) | ||||||||||
| 7Li | 30.8 ± 0.3 a | 55.2 ± 0.7 b | 59.8 ± 1.0 c | 60.8 ± 0.6 d | 35.7 ± 0.4 e | 16.8 ± 0.4 A | 42.1 ± 0.9 B | 43.6 ± 1.0 C | 30.1 ± 0.3 D | 14.7 ± 0.2 E |
| 9Be | 0.13 ± 0.02 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.01 c | 0.07 ± 0.01 c | 0.09 ± 0.01 d | 0.11 ± 0.01 A | ≤0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.01 B | ≤0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.01 B |
| 11B | 242 ± 4 a | 231 ± 5 b | 282 ± 5 c | 393 ± 5 d | 279 ± 4 c | 224 ± 4 A | 217 ± 6 B | 234 ± 4 C | 341 ± 6 D | 260 ± 4 E |
| 45Sc | 65.6 ± 0.4 a | 65.1 ± 0.5 a | 73.6 ± 0.5 b | 73.7 ± 0.4 b | 74.4 ± 0.4 c | 51.9 ± 1.0 A | 58.9 ± 1.2 B | 63.4 ± 1.5 C | 67.8 ± 1.2 D | 62.6 ± 1.2 E |
| 51V | 23.5 ± 0.2 a | 169 ± 5 b | 25.3 ± 0.3 c | 65.9 ± 0.7 d | 20.5 ± 0.2 e | 20.2 ± 0.3 A | 112 ± 4 B | 21.4 ± 0.2 C | 58.3 ± 0.8 D | 17.4 ± 0.3 E |
| 52Cr | 169 ± 2 a | 100 ± 4 b | 142 ± 5 c | 98.6 ± 1.0 d | 117 ± 3 e | 60.5 ± 0.7 A | 74.5 ± 0.7 B | 67.0 ± 0.7 C | 70.3 ± 0.8 D | 61.1 ± 0.7 E |
| 59Co | 9.51 ± 0.20 a | 21.5 ± 0.3 b | 8.61 ± 0.40 c | 8.75 ± 0.25 c | 9.17 ± 0.12 d | 7.19 ± 0.50 A | 15.5 ± 0.6 B | 6.11 ± 0.40 C | 7.23 ± 0.20 A | 7.39 ± 0.20 D |
| 60Ni | 299 ± 7 a | 169 ± 6 b | 286 ± 8 c | 291 ± 5 c | 115 ± 3 d | 197 ± 8 A | 138 ± 7 B | 183 ± 6 C | 208 ± 8 D | 62.8 ± 3.4 E |
| 71Ga | 13.6 ± 0.2 a | 16.9 ± 0.3 b | 13.4 ± 0.3 a | 17.0 ± 0.3 b | 12.6 ± 0.2 c | 9.25 ± 0.32 A | 14.7 ± 0.42 B | 11.0 ± 0.5 C | 15.0 ± 0.5 D | 9.56 ± 0.30 E |
| 73Ge | 4.95 ± 0.08 a | 4.36 ± 0.09 b | 4.85 ± 0.09 c | 5.99 ± 0.10 d | 4.29 ± 0.09 e | 4.33 ± 0.20 A | 3.87 ± 0.20 B | 4.35 ± 0.20 A | 5.03 ± 0.03 C | 3.90 ± 0.05 B |
| 75As | 10.7 ± 0.2 a | 17.5 ± 0.3 b | 8.03 ± 0.10 c | 6.70 ± 0.20 d | 10.7 ± 0.3 a | 9.28 ± 0.10 A | 10.9 ± 0.2 B | 6.40 ± 0.20 C | 5.86 ± 0.14 D | 8.86 ± 0.20 E |
| 77Se | 36.6 ± 0.3 a | 29.4 ± 0.5 b | 65.3 ± 1.0 c | 36.5 ± 0.5 a | 25.3 ± 0.4 d | 32.8 ± 0.5 A | 20.8 ± 0.7 B | 56.3 ± 0.5 C | 32.8 ± 0.5 A | 20.8 ± 0.4 B |
| 88Sr | 1460 ± 20 a | 2500 ± 30 b | 1850 ± 30 c | 2760 ± 30 d | 1650 ± 20 e | 756 ± 10 A | 1130 ± 20 B | 1060 ± 30 C | 1430 ± 30 D | 809 ± 15 E |
| 89Y | 0.53 ± 0.02 a | 0.55 ± 0.03 b | 0.49 ± 0.04 c | 1.08 ± 0.02 d | 0.41 ± 0.02 e | 0.42 ± 0.05 A,C | 0.38 ± 0.03 B | 0.40 ± 0.04 C | 0.72 ± 0.04 D | 0.35 ± 0.02 E |
| 90Zr | 42.7 ± 0.5 a | 21.0 ± 0.4 b | 45.0 ± 0.6 c | 12.1 ± 0.3 d | 35.1 ± 0.6 e | 19.7 ± 0.5 A | 12.3 ± 0.4 B | 33.1 ± 0.4 C | 6.14 ± 0.06 D | 14.8 ± 0.2 E |
| 95Mo | 568 ± 5 a | 460 ± 5 b | 657 ± 5 c | 671 ± 10 d | 326 ± 8 e | 458 ± 7 A | 409 ± 8 B | 574 ± 8 C | 614 ± 11 D | 282 ± 7 E |
| 107Ag | 4.40 ± 0.20 a | 1.25 ± 0.10 b | 6.70 ± 0.25 c | 4.78 ± 0.15 d | 7.84 ± 0.22 e | 2.12 ± 0.10 A | 0.89 ± 0.04 B | 3.98 ± 0.12 C | 3.60 ± 0.10 D | 5.07 ± 0.12 E |
| 111Cd | 19.7 ± 0.3 a | 9.35 ± 0.20 b | 52.9 ± 1.0 c | 28.4 ± 0.7 d | 6.66 ± 0.3 e | 15.4 ± 0.9 A | 7.84 ± 0.09 B | 45.2 ± 1.0 C | 26.1 ± 0.9 D | 5.60 ± 0.5 E |
| 118Sn | 146 ± 4 a | 314 ± 7 b | 143 ± 3 a | 530 ± 7 c | 180 ± 2 d | 107 ± 3 A | 178 ± 6 B | 110 ± 6 A | 467 ± 10 C | 117 ± 4 D |
| 121Sb | 4.66 ± 0.22 a | 4.15 ± 0.22 b | 4.76 ± 0.22 a | 4.28 ± 0.12 c | 6.14 ± 0.14 d | 4.15 ± 0.10 A | 3.61 ± 0.20 B | 4.03 ± 0.20 C | 3.21 ± 0.10 D | 5.45 ± 0.12 E |
| 133Cs | 0.31 ± 0.05 a | 1.65 ± 0.07 b | 0.36 ± 0.05 c | 0.94 ± 0.05 d | 0.36 ± 0.04 c | 0.28 ± 0.03 A,E | 1.35 ± 0.03 B | 0.31 ± 0.04 C,E | 0.78 ± 0.04 D | 0.29 ± 0.03 E |
| 137Ba | 283 ± 4 a | 254 ± 5 b | 978 ± 11 c | 1140 ± 20 d | 274 ± 5 e | 218 ± 7 A | 240 ± 7 B | 810 ± 12 C | 1050 ± 15 D | 228 ± 7 E |
| 140Ce | 1.89 ± 0.05 a | 22.2 ± 0.2 b | 1.19 ± 0.05 c | 5.68 ± 0.10 d | 1.54 ± 0.04 e | 0.63 ± 0.03 A | 6.88 ± 0.30 B | 0.63 ± 0.05 A | 1.58 ± 0.10 C | 0.60 ± 0.04 A |
| 159Tb | ≤0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.02 a | ≤0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.02 |
| 165Ho | ≤0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | ≤0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 b | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.01 A | ≤0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 B | ≤0.02 |
| 181Ta | 9.32 ± 0.12 a | 12.9 ± 0.2 b | 9.65 ± 0.13 c | 7.36 ± 0.09 d | 8.07 ± 0.07 e | 8.26 ± 0.13 A | 9.83 ± 0.14 B | 8.72 ± 0.12 C | 6.10 ± 0.20 D | 7.50 ± 0.20 E |
| 202Hg | 20.9 ± 0.3 a | 15.5 ± 0.4 b | 20.6 ± 0.4 a | 14.0 ± 0.3 c | 19.9 ± 0.5 d | 14.8 ± 0.5 A | 11.3 ± 0.3 B | 12.8 ± 0.4 C | 12.2 ± 0.2 D | 12.4 ± 0.2 D |
| 205Tl | 0.07 ± 0.01 a,c | 0.08 ± 0.02 a,b,c | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.01 a,c | 0.06 ± 0.01 c | ≤0.04 | 0.05 ± 0.05 A | 0.06 ± 0.01 A | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 |
| 208Pb | 68.3 ± 1.0 a | 72.1 ± 1.2 b | 50.2 ± 1.4 c | 61.0 ± 1.0 d | 40.8 ± 1.4 e | 57.8 ± 1.4 A | 46.1 ± 1.1 B | 44.9 ± 1.1 C | 34.4 ± 1.0 D | 35.9 ± 1.0 E |
| 209Bi | 2.84 ± 0.12 a | 2.30 ± 0.05 b | 1.24 ± 0.02 c | 2.01 ± 0.04 d | 1.38 ± 0.02 e | 1.44 ± 0.04 A | 1.76 ± 0.05 B | 0.73 ± 0.02 C | 1.41 ± 0.05 A | 0.79 ± 0.02 D |
| 238U | 0.65 ± 0.02 a | 0.21 ± 0.05 b | 0.52 ± 0.03 c | 0.75 ± 0.05 d | 1.03 ± 0.03 e | 0.45 ± 0.02 A | 0.13 ± 0.01 B | 0.35 ± 0.03 C | 0.49 ± 0.03 D | 0.58 ± 0.04 E |
| Undigested Parts of Flakes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | Samtrot | Tirol | Dickkopf | Rotkorn | Megali |
| (µg/g) | |||||
| 23Na | 3.41 ± 0.15 a | 3.75 ± 0.20 b | 25.5 ± 0.3 c | 3.57 ± 0.12 d | 2.90 ± 0.10 e |
| 24Mg | 117 ± 3 a | 252 ± 7 b | 102 ± 3 c | 311 ± 6 d | 112 ± 2 e |
| 27Al | 4.02 ± 0.12 a | 4.90 ± 0.12 b | 2.31 ± 0.10 c | 6.23 ± 0.20 d | 2.10 ± 0.05 e |
| 31P | 38.9 ± 0.3 a | 63.1 ± 0.5 b | 30.4 ± 0.4 c | 65.7 ± 0.7 d | 32.8 ± 0.5 e |
| 32S | 6.78 ± 0.30 a | 16.8 ± 0.5 b | 7.02 ± 0.20 c | 22.8 ± 0.4 d | 6.41 ± 0.20 e |
| 39K | 65.6 ± 0.6 a | 77.4 ± 0.6 b | 63.2 ± 0.6 c | 71.5 ± 0.7 d | 64.5 ± 0.8 e |
| 40Ca | 253 ± 5 a | 490 ± 8 b | 269 ± 6 c | 505 ± 10 d | 250 ± 5 a |
| 48Ti | 2.46 ± 0.09 a | 2.66 ± 0.10 b | 2.40 ± 0.11 a,d | 2.94 ± 0.04 c | 2.38 ± 0.02 d |
| 55Mn | 103 ± 4 a | 14.3 ± 0.4 b | 50.9 ± 0.5 c | 23.5 ± 0.2 d | 75.2 ± 0.8 e |
| 57Fe | 12.1 ± 0.2 a | 14.7 ± 0.3 b | 11.2 ± 0.3 c | 19.4 ± 0.3 d | 11.7 ± 0.2 e |
| 63Cu | 3.76 ± 0.10 a | 3.72 ± 0.10 a | 3.71 ± 0.12 a | 5.95 ± 0.20 b | 3.39 ± 0.12 c |
| 66Zn | 2.46 ± 0.10 a | 3.86 ± 0.12 b | 2.55 ± 0.10 c | 5.52 ± 0.22 d | 3.73 ± 0.10 e |
| (ng/g) | |||||
| 7Li | 15.8 ± 0.5 a | 58.1 ± 1.2 b | 19.3 ± 0.4 c | 61.3 ± 0.6 d | 18.3 ± 0.3 e |
| 9Be | 0.11 ± 0.02 a | 0.15 ± 0.02 b,e | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.17 ± 0.02 d,e | 0.16 ± 0.02 e |
| 11B | 202 ± 5 a | 455 ± 10 b | 162 ± 7 c | 369 ± 10 d | 136 ± 4 e |
| 45Sc | 65.5 ± 1.0 a | 160 ± 5 b | 60.1 ± 1.4 c | 155 ± 3 d | 64.3 ± 1.2 e |
| 51V | 162 ± 4 a | 593 ± 10 b | 144 ± 5 c | 327 ± 6 d | 142 ± 3 c |
| 52Cr | 136 ± 5 a | 259 ± 7 b | 121 ± 5 c | 267 ± 7 d | 90.7 ± 1.5 e |
| 59Co | 26.9 ± 0.7 a | 33.6 ± 0.9 b | 19.5 ± 0.6 c | 30.6 ± 0.8 d | 19.1 ± 0.4 e |
| 60Ni | 253 ± 8 a | 123 ± 5 b | 153 ± 6 c | 115 ± 5 d | 130 ± 5 e |
| 71Ga | 3.31 ± 0.10 a | 3.75 ± 0.20 b | 3.33 ± 0.30 a | 4.82 ± 0.16 c | 3.08 ± 0.12 d |
| 73Ge | 13.6 ± 0.3 a | 11.9 ± 0.2 b | 13.6 ± 0.2 a | 21.8 ± 0.5 c | 10.5 ± 0.2 d |
| 75As | 8.37 ± 0.12 a | 14.2 ± 0.2 b | 7.77 ± 0.15 c | 14.7 ± 0.4 d | 6.46 ± 0.10 e |
| 77Se | 54.0 ± 0.6 a | 94.1 ± 1.0 b | 45.6 ± 0.6 c | 54.1 ± 0.6 d | 44.6 ± 0.6 e |
| 88Sr | 1050 ± 20 a | 1300 ± 30 b | 881 ± 12 c | 1370 ± 20 d | 728 ± 10 e |
| 89Y | 3.56 ± 0.25 a | 1.71 ± 0.10 b | 4.04 ± 0.10 c | 3.15 ± 0.10 d | 2.53 ± 0.10 e |
| 90Zr | 35.1 ± 0.6 a | 29.2 ± 0.6 b | 26.3 ± 0.6 c | 4.24 ± 0.04 d | 26.8 ± 0.2 e |
| 95Mo | 655 ± 10 a | 287 ± 4 b | 604 ± 10 c | 490 ± 8 d | 383 ± 8 e |
| 107Ag | 6.45 ± 0.17 a | 1.72 ± 0.10 b | 18.5 ± 0.4 c | 17.0 ± 0.3 d | 20.1 ± 0.3 e |
| 111Cd | 18.7 ± 0.4 a | 21.5 ± 0.3 b | 123 ± 6 c | 74.2 ± 1.2 d | 13.3 ± 0.2 e |
| 118Sn | 281 ± 2 a | 412 ± 5 b | 504 ± 9 c | 1150 ± 30 d | 413 ± 8 b |
| 121Sb | 3.21 ± 0.30 a | 2.18 ± 0.25 b | 3.27 ± 0.30 a | 2.94 ± 0.04 c | 2.84 ± 0.04 d |
| 133Cs | 0.41 ± 0.02 a | 0.72 ± 0.04 b | 0.39 ± 0.05 c | 0.81 ± 0.03 d | 0.36 ± 0.02 e |
| 137Ba | 55.2 ± 1.5 a | 177 ± 7 b | 43.0 ± 0.8 c | 163 ± 7 d | 53.5 ± 1.5 e |
| 140Ce | 4.00 ± 0.10 a | 26.3 ± 0.5 b | 4.18 ± 0.14 c | 6.12 ± 0.12 d | 4.01 ± 0.06 a |
| 159Tb | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 c | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| 165Ho | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 9.83 ± 0.22 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 c | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 d |
| 181Ta | 23.7 ± 0.5 a | 45.2 ± 0.7 b | 37.1 ± 0.7 c | 35.9 ± 0.7 d | 25.4 ± 0.6 e |
| 202Hg | 58.6 ± 0.5 a | 30.8 ± 0.3 b | 26.8 ± 0.3 c | 41.5 ± 0.5 d | 24.3 ± 0.2 e |
| 205Tl | 0.22 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.20 ± 0.02 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 a |
| 208Pb | 215 ± 4 a | 126 ± 2 b | 225 ± 5 c | 179 ± 5 d | 185 ± 5 e |
| 209Bi | 1.61 ± 0.03 a | 0.33 ± 0.02 b | 0.28 ± 0.02 c | 0.53 ± 0.03 d | 0.13 ± 0.01 e |
| 238U | 2.02 ± 0.10 a | 0.23 ± 0.02 b | 1.12 ± 0.12 c | 1.08 ± 0.04 c | 2.15 ± 0.05 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sumczynski, D.; Fišera, M.; Salek, R.N.; Orsavová, J. The Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on Releasing Minerals and Trace Elements from Wheat Flakes: The Extended Study of Dietary Intakes for Individual Life Stage Groups. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112509
Sumczynski D, Fišera M, Salek RN, Orsavová J. The Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on Releasing Minerals and Trace Elements from Wheat Flakes: The Extended Study of Dietary Intakes for Individual Life Stage Groups. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112509
Chicago/Turabian StyleSumczynski, Daniela, Miroslav Fišera, Richardos Nikolaos Salek, and Jana Orsavová. 2023. "The Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on Releasing Minerals and Trace Elements from Wheat Flakes: The Extended Study of Dietary Intakes for Individual Life Stage Groups" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112509
APA StyleSumczynski, D., Fišera, M., Salek, R. N., & Orsavová, J. (2023). The Effect of Flake Production and In Vitro Digestion on Releasing Minerals and Trace Elements from Wheat Flakes: The Extended Study of Dietary Intakes for Individual Life Stage Groups. Nutrients, 15(11), 2509. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112509









