An Overview of Diet and Physical Activity for Healthy Weight in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the ACT1ON Consortium
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. ACT1ON Overview
1.2. Role of Combined Diet and PA for Weight Management in T1D
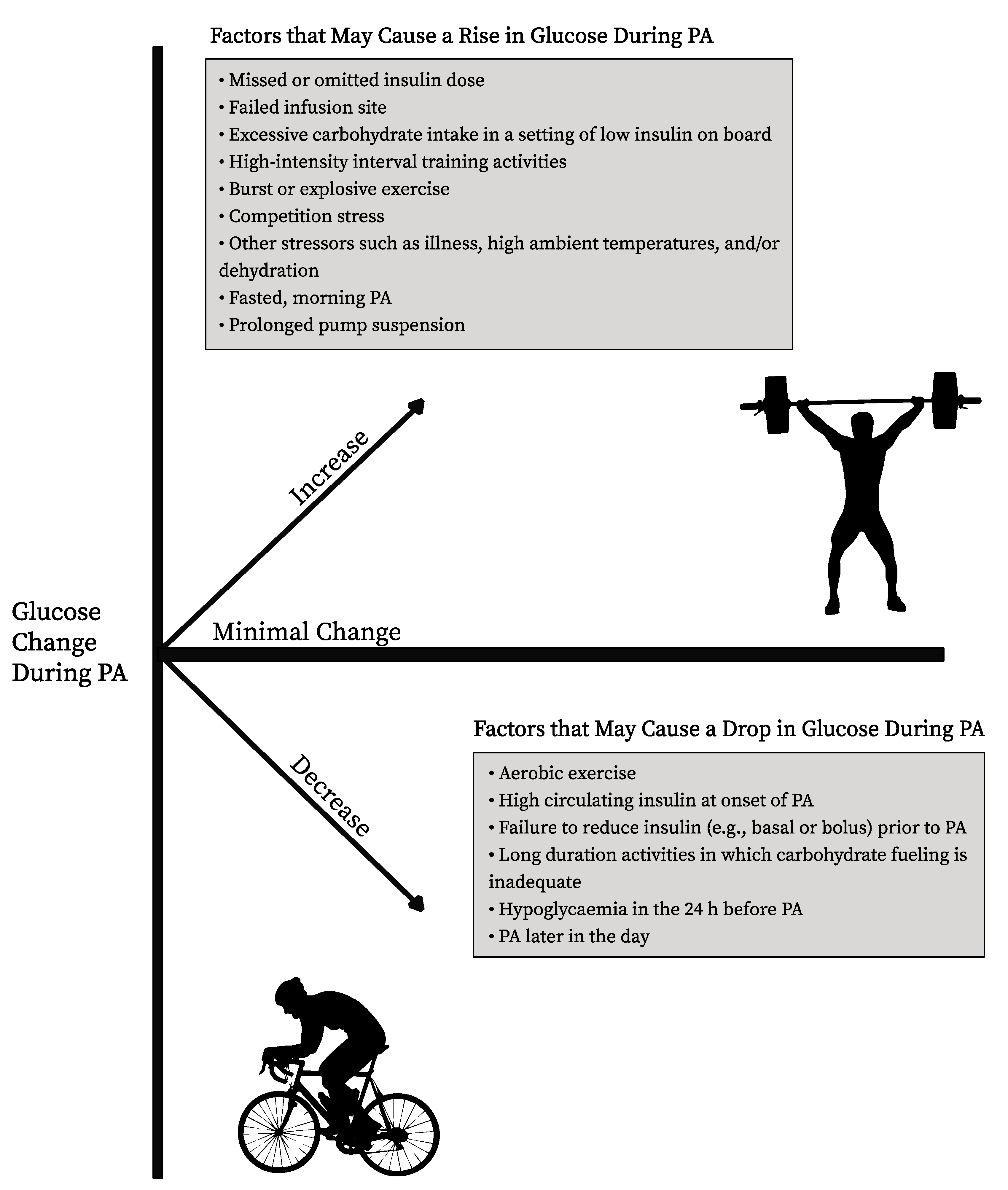
1.3. Current Resources for PA and Glucose Management in T1D
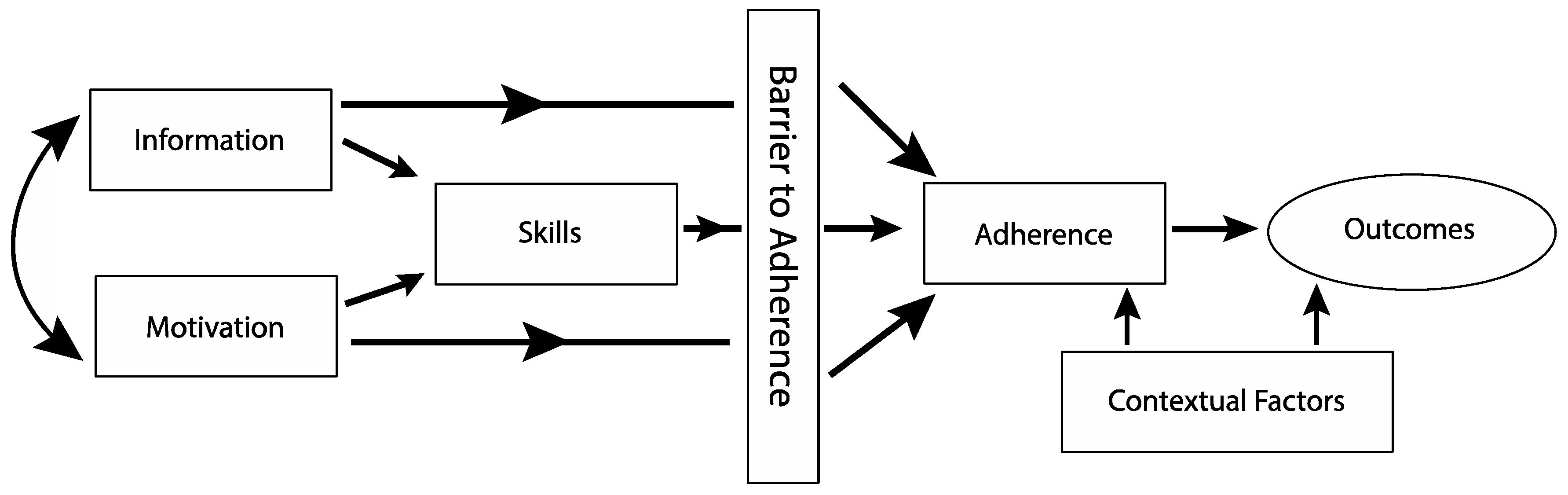
1.4. Integrating Motivational Interviewing and Problem-Solving Skills Training to Address Barriers to PA Adherence
1.5. What Is Needed—Gaps in the Literature
2. Published ACT1ON Study Results
Existing PA Data in T1D
3. Future Directions and Future Steps Ongoing Challenges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.L.; Lawrence, J.M.; Davis, C. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in youth with diabetes in USA: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Pediatr. Diabetes 2010, 11, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBose, S.N.; Hermann, J.M.; Tamborlane, W.V. Obesity in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes in Germany, Austria, and the United States. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.M.; Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W. Current State of Type 1 Diabetes Treatment in the U.S.: Updated Data from the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoye, A.; Gorin, A.A.; LaRose, J.G. Young Adults’ Attitudes and Perceptions of Obesity and Weight Management: Implications for Treatment Development. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maahs, D.M.; Ogden, L.G.; Dabelea, D. Association of glycaemia with lipids in adults with type 1 diabetes: Modification by dyslipidaemia medication. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes, C.; Diabetes, I.; Complications Research, G. Modern-day clinical course of type 1 diabetes mellitus after 30 years’ duration: The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications and Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications experience (1983–2005). Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar]
- De Ferranti, S.D.; De Boer, I.H.; Fonseca, V.; Fox, C.S.; Golden, S.H.; Lavie, C.J.; Magge, S.N.; Marx, N.; McGuire, D.K.; Orchard, T.J.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circ 2014, 130, 1110–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maahs, D.M.; Daniels, S.R.; De Ferranti, S.D.; Dichek, H.L.; Flynn, J.; Goldstein, B.I.; Kelly, A.S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Martyn-Nemeth, P.; Osganian, S.K.; et al. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in youth with diabetes mellitus: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014, 130, 1532–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, M.J.; Foster, N.C.; Libman, I.M. Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in youth with type 1 diabetes and elevated body mass index. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 53, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnell, J.Q.; Braffett, B.H.; Zinman, B. Impact of Excessive Weight Gain on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes: Results from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evert, A.B.; Dennison, M.; Gardner, C.D. Nutrition Therapy for Adults with Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annan, S.F.; Higgins, L.A.; Jelleryd, E.; Hannon, T.; Rose, S.; Salis, S.; Baptista, J.; Chinchilla, P.; Marcovecchio, M.L. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Nutritional management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1297–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppini, G.; Carlini, M.; Muggeo, M. Self-reported exercise and quality of life in young type 1 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 2003, 16, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuchsjager-Mayrl, G.; Pleiner, J.; Wiesinger, G.F. Exercise training improves vascular endothelial function in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimen, M.; Kennedy, A.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Pang, T.T.; Andrews, R.; Narendran, P. What are the health benefits of physical activity in type 1 diabetes mellitus? A literature review. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPorte, R.E.; Dorman, J.S.; Tajima, N. Pittsburgh Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Morbidity and Mortality Study: Physical activity and diabetic complications. Pediatrics 1986, 78, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, C.S.; Songer, T.J.; LaPorte, R.E. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, physical activity, and death. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1993, 137, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, M.C.; Peters, A.L. Exercise in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriska, A.M.; LaPorte, R.E.; Patrick, S.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Orchard, T.J. The association of physical activity and diabetic complications in individuals with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: The Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study–VII. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1991, 44, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, S.; Roche, D.; Stratton, G.; Wallymahmed, K.; Glenn, S.M. Physical activity and psychological well-being in children with Type 1 diabetes. Psychol. Health Med. 2007, 12, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imayama, I.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Courneya, K.S.; Johnson, J.A. Determinants of quality of life in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2011, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, M.; Gallardo-Alfaro, L.; Bibiloni, M.D.M.; Tur, J.A. Efficacy of dietary intervention or in combination with exercise on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakicic, J.M.; Rogers, R.J.; Collins, A.M.; Jackson, R. Strategies for Physical Activity Interventions in the Treatment of Obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, M.C.; Bar-Or, O.; Hollidge-Horvat, M.; Schwarcz, H.P.; Heigenhauser, G.J. Glucose ingestion and substrate utilization during exercise in boys with IDDM. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 88, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguso, C.A.; Coggan, A.R.; Gastaldelli, A.; Sidossis, L.S.; Bastyr, E.J.; Wolfe, R.R. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in IDDM during moderate and intense exercise. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fel, S.; Rochette, E.; Walther, G.; Echaubard, S.; Pereira, B.; Merlin, E.; Terral, D.; Duché, P. Maximal Fat Oxidation During Exercise Is Already Impaired in Pre-pubescent Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 664211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenni, S.; Oetliker, C.; Allemann, S.; Ith, M.; Tappy, L.; Wuerth, S.; Egger, A.; Boesch, C.; Schneiter, P.; Diem, P.; et al. Fuel metabolism during exercise in euglycaemia and hyperglycaemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus—A prospective single-blinded randomised crossover trial. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitaille, M.; Dubé, M.C.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Prud’Homme, D.; Massicotte, D.; Péronnet, F.; Lavoie, C. Substrate source utilization during moderate intensity exercise with glucose ingestion in Type 1 diabetic patients. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livny, R.; Said, W.; Shilo, S.; Bar-Yoseph, R.; Gal, S.; Oren, M.; Levy, M.; Weiss, R.; Shehadeh, N.; Zuckerman-Levin, N.; et al. Identifying sources of support and barriers to physical activity in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Igudesman, D.; Addala, A.; Casu, A.; Crandell, J.; Kosorok, M.R.; Maahs, D.M.; Pokaprakarn, T.; Pratley, R.E.; Souris, K.J.; et al. Design of the Advancing Care for Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity Network energy metabolism and sequential multiple assignment randomized trial nutrition pilot studies: An integrated approach to develop weight management solutions for individuals with type 1 diabetes. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2022, 117, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Driscoll, K.A.; Pratley, R.E.; Smith, S.R.; Maahs, D.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Obesity in Type 1 Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Clinical Impact, and Mechanisms. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 629–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, K.A.; Corbin, K.D.; Maahs, D.M. Biopsychosocial Aspects of Weight Management in Type 1 Diabetes: A Review and Next Steps. Curr. Diab Rep. 2017, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igudesman, D.; Crandell, J.; Corbin, K.D.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Thomas, J.M.; Casu, A.; Kirkman, M.S.; Pokaprakarn, T.; Riddell, M.C.; et al. Weight Management in Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The Advancing Care for Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity Network Sequential Multiple Assignment Randomized Trial Pilot Results. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 25, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntis, F.R.; Igudesman, D.; Sarteau, A.C.; Thomas, J.; Arrizon-Ruiz, N.; Hooper, J.; Addala, A.; Crandell, J.L.; Riddell, M.C.; Maahs, D.M.; et al. Relationship Between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Glycemia Among Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes and Overweight or Obesity: Results from the Advancing Care for Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity Network (ACT1ON) Study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2022, 24, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilingiris, D.; Tzeravini, E.; Koliaki, C.; Dalamaga, M.; Kokkinos, A. The Role of Mitochondrial Adaptation and Metabolic Flexibility in the Pathophysiology of Obesity and Insulin Resistance: An Updated Overview. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Bredin, S.S.; Guan, Y.; Dickinson, K.; Kim, D.D.; Chua, Z.; Kaufman, K.; Warburton, D.E. Cardiovascular Health Benefits of Exercise Training in Persons Living with Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, V.; Gingras, V.; Leroux, C.; Bertrand, A.; Desjardins, K.; Mircescu, H.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Adult Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: An Observational Study. Can. J. Diabetes 2016, 40, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Liese, A.D.; Liu, L.; Dabelea, D.; Anderson, A.; Imperatore, G.; Bell, R. Weight-loss practices and weight-related issues among youth with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, L.M.; Murphy, S.A.; Strecher, V. The multiphase optimization strategy (MOST) and the sequential multiple assignment randomized trial (SMART): New methods for more potent eHealth interventions. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2007, 32 (5 Suppl), S112–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.E. Role of Physical Activity for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, M.C.; Gallen, I.W.; Smart, C.E.; Taplin, C.E.; Adolfsson, P.; Lumb, A.N.; Kowalski, A.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Hume, C.; et al. Exercise management in type 1 diabetes: A consensus statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolfsson, P.; Taplin, C.E.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Pemberton, J.; Davis, E.A.; Riddell, M.C.; McGavock, J.; Moser, O.; Szadkowska, A.; Lopez, P.; et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Exercise in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1341–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, R.D.; Alcántara-Cordero, F.J.; Weseen, E.; Maldaner, M.; Hart, S.; Nitz, C.; Boulé, N.G.; Yardley, J.E. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Blood Glucose Response to High-intensity Interval Exercise in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 47, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, M.C.; Pooni, R.; Yavelberg, L.; Li, Z.; Kollman, C.; Brown, R.E.; Li, A.; Aronson, R. Reproducibility in the cardiometabolic responses to high-intensity interval exercise in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 148, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.M.; Gomez, C.; Aschner, P.; Veloza, A.; Muñoz, O.; Rubio, C.; Vallejo, S. Effects of performing morning versus afternoon exercise on glycemic control and hypoglycemia frequency in type 1 diabetes patients on sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardley, J.E. Fasting May Alter Blood Glucose Responses to High-Intensity Interval Exercise in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized, Acute Crossover Study. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghi-Eshghi, S.R.; Yardley, J.E. Morning (Fasting) vs Afternoon Resistance Exercise in Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Crossover Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5217–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, M.C.; Li, Z.; Gal, R.L.; Calhoun, P.; Jacobs, P.G.; Clements, M.A.; Martin, C.K.; Iii, F.J.D.; Patton, S.R.; Castle, J.R.; et al. Examining the Acute Glycemic Effects of Different Types of Structured Exercise Sessions in Type 1 Diabetes in a Real-World Setting: The Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise Initiative (T1DEXI). Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardley, J.E. Reassessing the evidence: Prandial state dictates glycaemic responses to exercise in individuals with type 1 diabetes to a greater extent than intensity. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1994–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, G.; Minnock, D.; Tarantino, G.; Neville, R.D. Delayed effect of different exercise modalities on glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2021, 31, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Luzio, S.; Gray, B.J.; Dunseath, G.; Rees, E.D.; Kilduff, L.P.; Campbell, M.D.; West, D.J.; Bain, S.C.; Bracken, R.M. Impact of single and multiple sets of resistance exercise in type 1 diabetes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, e99–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegemer, J.J.; Squires, R.W.; Marsh, H.M.; Haymond, M.W.; Cryer, P.E.; Rizza, R.A.; Miles, J.M. Differences between prebreakfast and late afternoon glycemic responses to exercise in IDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1990, 13, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 7. Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S111–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, O.; Riddell, M.C.; Eckstein, M.L.; Adolfsson, P.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Boom, L.V.D.; Gillard, P.; Nørgaard, K.; Oliver, N.S.; Zaharieva, D.P.; et al. Glucose management for exercise using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) systems in type 1 diabetes: Position statement of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and of the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD) endorsed by JDRF and supported by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 1375–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houlder, S.K.; Yardley, J.E. Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Exercise in Type 1 Diabetes: Past, Present and Future. Biosensors 2018, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, O.; Eckstein, M.L.; Mueller, A.; Mueller, A.; Birnbaumer, P.; Birnbaumer, P.; Aberer, F.; Aberer, F. Impact of physical exercise on sensor performance of the FreeStyle Libre intermittently viewed continuous glucose monitoring system in people with Type 1 diabetes: A randomized crossover trial. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2019, 36, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, O.; Eckstein, M.L.; McCarthy, O.; Deere, R.; Pitt, J.; Williams, D.M.; Hayes, J.; Sourij, H.; Bain, S.C.; Bracken, R.M. Performance of the Freestyle Libre flash glucose monitoring (flash GM) system in individuals with type 1 diabetes: A secondary outcome analysis of a randomized crossover trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Turksoy, K.; McGaugh, S.M.; Pooni, R.; Vienneau, T.; Ly, T.; Riddell, M.C. Lag Time Remains with Newer Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Technology During Aerobic Exercise in Adults Living with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Riddell, M.C.; Potashner, D.; Brown, R.E.; Aronson, R. Time Lag and Accuracy of Continuous Glucose Monitoring During High Intensity Interval Training in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Riddell, M.C. Insulin management strategies for exercise in diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2017, 41, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsker, J.E.; Kraus, A.; Gianferante, D. Techniques for exercise preparation and management in adults with type 1 diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2016, 40, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichler, J.C.; Seid, M.; Crandell, J. The Flexible Lifestyle Empowering Change (FLEX) intervention for self-management in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Trial design and baseline characteristics. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2018, 66, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, S.; Weil, C.; Holden, G. Psychosocial characteristics of inner-city children with asthma: A description of the NCICAS psychosocial protocol. Natl. Coop. Inn-City Asthma Study Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1997, 24, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigal, J.K.; Stout, C.; Brandon, M. The Knowledge, Attitude, and Self-Efficacy Asthma Questionnaire. Chest 1993, 104, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroyer, C.; Lebrun, T.; Proust, A. Knowledge, self-management, compliance and quality of life in asthma: A cross-sectional study of the French version of the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire. Qual. Life Res. 1998, 7, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.; Sibbald, B.; Anderson, H.R.; Freeling, P. Controlled evaluation of the effects of patient education on asthma morbidity in general practice. Lancet 1986, 1, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Maahs, D.M.; Seid, M. Efficacy of the Flexible Lifestyles Empowering Change intervention on metabolic and psychosocial outcomes in adolescents with type 1 diabetes (FLEX): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A.; Simmons, K.M.; Maahs, D.M. Weight Management in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity: Challenges and Possible Solutions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.M.; Funk, M.; Grey, M. Cardiovascular health in adults with type 1 diabetes. Prev. Med. 2016, 91, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetty, T.; Shetty, V.; Fournier, P.A.; Adolfsson, P.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A. Exercise Management for Young People with Type 1 Diabetes: A Structured Approach to the Exercise Consultation. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, B.; Herbst, A.; Pfeifer, M. Impact of Physical Activity on Glycemic Control and Prevalence of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-sectional Multicenter Study of 18,028 Patients. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czenczek-Lewandowska, E.; Leszczak, J.; Baran, J. Levels of Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in Relation to the Healthy Comparators and to the Method of Insulin Therapy Used. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, I.; Andrews, R.C.; Narendran, P.; Greenfield, S. Patient and Healthcare Professionals Perspectives on the Delivery of Exercise Education for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, P.; Dovc, K.; Braune, K.; Addala, A.; Riddell, M.C.; Dos Santos, T.J.; Zaharieva, D.P. Perceived Knowledge and Confidence for Providing Youth-Specific Type 1 Diabetes Exercise Recommendations amongst Pediatric Diabetes Healthcare Professionals: An International, Cross-Sectional, Online Survey. Pediatr. Diabetes 2023, 2023, 8462291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau, A.S.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Strychar, I.; Mircescu, H. Barriers to physical activity among patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2108–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottalib, A.; Kasetty, M.; Mar, J.Y.; Elseaidy, T.; Ashrafzadeh, S.; Hamdy, O. Weight Management in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Obesity. Curr. Diab Rep. 2017, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical activity/exercise and diabetes: A position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, G.; Quigg, S.; Davoren, P.; Basile, R.; McAuley, S.A.; Coombes, J.S. Resources to Guide Exercise Specialists Managing Adults with Diabetes. Sports Med. Open 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Blackburn, G.; Brancati, F.L. Reduction in weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: One-year results of the look AHEAD trial. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Lasa, A.; Miranda, J.; Bulló, M.; Casas, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Larretxi, I.; Estruch, R.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Portillo, M.P. Comparative effect of two Mediterranean diets versus a low-fat diet on glycaemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, D.; McGaugh, S.; Pooni, R.; Vienneau, T.; Ly, T.; Riddell, M. Improved open-loop glucose control with basal insulin reduction 90 minutes before aerobic exercise in patients with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, R.; Li, A.; Brown, R.E.; McGaugh, S.; Riddell, M.C. Flexible insulin therapy with a hybrid regimen of insulin degludec and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with pump suspension before exercise in physically active adults with type 1 diabetes (FIT Untethered): A single-centre, open-label, proof-of-concept, randomised crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, R.; Brown, R.E.; Li, A.; Riddell, M.C. Optimal Insulin Correction Factor in Post- High Intensity Exercise Hyperglycemia in Adults with Type 1 diabetes: The FIT Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, M.C.; Li, Z.; Beck, R.W.; Gal, R.L.; Jacobs, P.G.; Castle, J.R.; Gillingham, M.B.; Clements, M.A.; Patton, S.R.; Dassau, E.; et al. More Time in Glucose Range During Exercise Days than Sedentary Days in Adults Living with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGavock, J.; Chauhan, B.F.; Rabbani, R.; Dias, S.; Klaprat, N.; Boissoneault, S.; Lys, J.; Wierzbowski, A.K.; Sakib, M.N.; Zarychanski, R.; et al. Layperson-Led vs Professional-Led Behavioral Interventions for Weight Loss in Pediatric Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2010364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.C.; Brown, J.A.; Leslie, G.D.; Ntoumanis, N. Acceptability of Self-Management Group Education to Reduce Fear of Hypoglycemia as a Barrier to Physical Activity in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Mixed Methods Approach. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 46, 16–25.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Addala, A. Current and Novel Strategies to Reduce Fear of Hypoglycemia as a Barrier to Physical Activity in Adults and Youth with Type 1 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2022, 46, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaharieva, D.P.; Messer, L.H.; Paldus, B.; O’Neal, D.N.; Maahs, D.M.; Riddell, M.C. Glucose Control During Physical Activity and Exercise Using Closed Loop Technology in Adults and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2020, 44, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickels, M.R.; DuBose, S.N.; Toschi, E.; Beck, R.W.; Verdejo, A.S.; Cummins, M.J.; Newswanger, B.; Riddell, M.C.; Peleckis, A.; Evangelisti, M.; et al. Mini-Dose Glucagon as a Novel Approach to Prevent Exercise-Induced Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaugh, S.M.; Edwards, S.; Wolpert, H.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Gulati, N.; Riddell, M.C. The Development of an Exercise Advisor App for Type 1 Diabetes: Digitization Facilitates More Individualized Guidance. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2022, 16, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Blood Glucose Level | Aerobic/Low Intensity | Anaerobic/High intensity |
|---|---|---|
| <90 mg/dL (<5.0 mmol/L) | Major hypoglycemia risk ~10–20 g carbohydrates and re-check before starting Consider insulin adjustments | May be OK to start if predictable rise seen before activity ~10–15 g carbohydrates |
| 90–124 mg/dL (5.0–6.9 mmol/L) | ~10 g carbohydrates, then start Consider insulin adjustments | OK to start |
| 126–180 mg/dL (7.0–10.0 mmol/L) | OK to start | OK to start, but blood glucose may ↑ |
| 180–270 mg/dL (10.0–15.0 mmol/L) | OK to start, but performance may ↓ | OK to start, but performance may ↓ Blood glucose may ↑ further |
| >270 mg/dL (>15.0 mmol/L) | If unexplained high, check ketones If small-to-moderate levels, then light intensity OK Consider 50% correction bolus | Avoid exercise |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bishop, F.K.; Addala, A.; Corbin, K.D.; Muntis, F.R.; Pratley, R.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Maahs, D.M.; Zaharieva, D.P. An Overview of Diet and Physical Activity for Healthy Weight in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the ACT1ON Consortium. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112500
Bishop FK, Addala A, Corbin KD, Muntis FR, Pratley RE, Riddell MC, Mayer-Davis EJ, Maahs DM, Zaharieva DP. An Overview of Diet and Physical Activity for Healthy Weight in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the ACT1ON Consortium. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112500
Chicago/Turabian StyleBishop, Franziska K., Ananta Addala, Karen D. Corbin, Franklin R. Muntis, Richard E. Pratley, Michael C. Riddell, Elizabeth J. Mayer-Davis, David M. Maahs, and Dessi P. Zaharieva. 2023. "An Overview of Diet and Physical Activity for Healthy Weight in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the ACT1ON Consortium" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112500
APA StyleBishop, F. K., Addala, A., Corbin, K. D., Muntis, F. R., Pratley, R. E., Riddell, M. C., Mayer-Davis, E. J., Maahs, D. M., & Zaharieva, D. P. (2023). An Overview of Diet and Physical Activity for Healthy Weight in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Lessons Learned from the ACT1ON Consortium. Nutrients, 15(11), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112500






