Acute Cognitive Performance and Mood Effects of Coffeeberry Extract: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Healthy Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
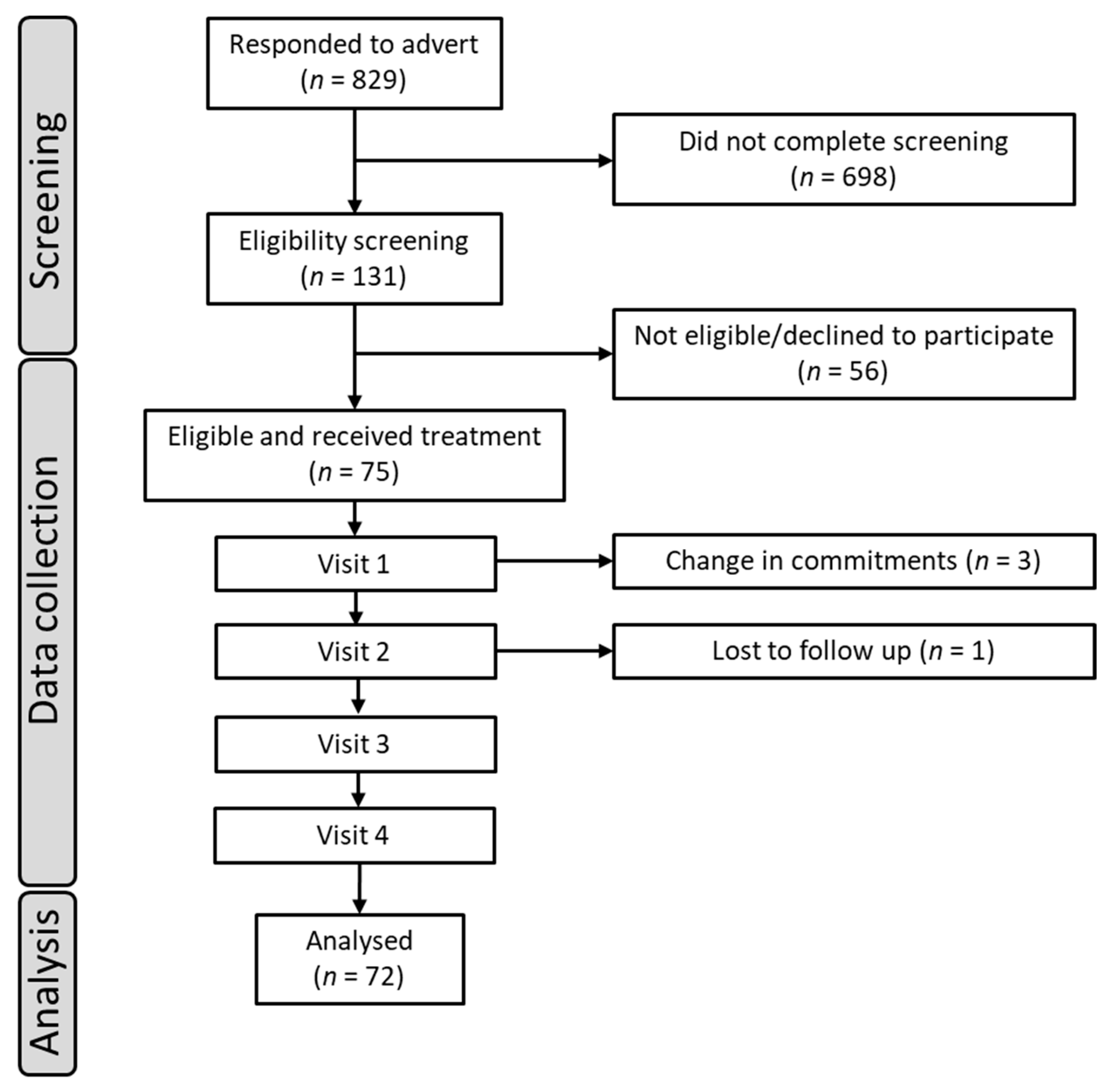
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Cognitive and Mood Assessment
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Response to Coffeeberry
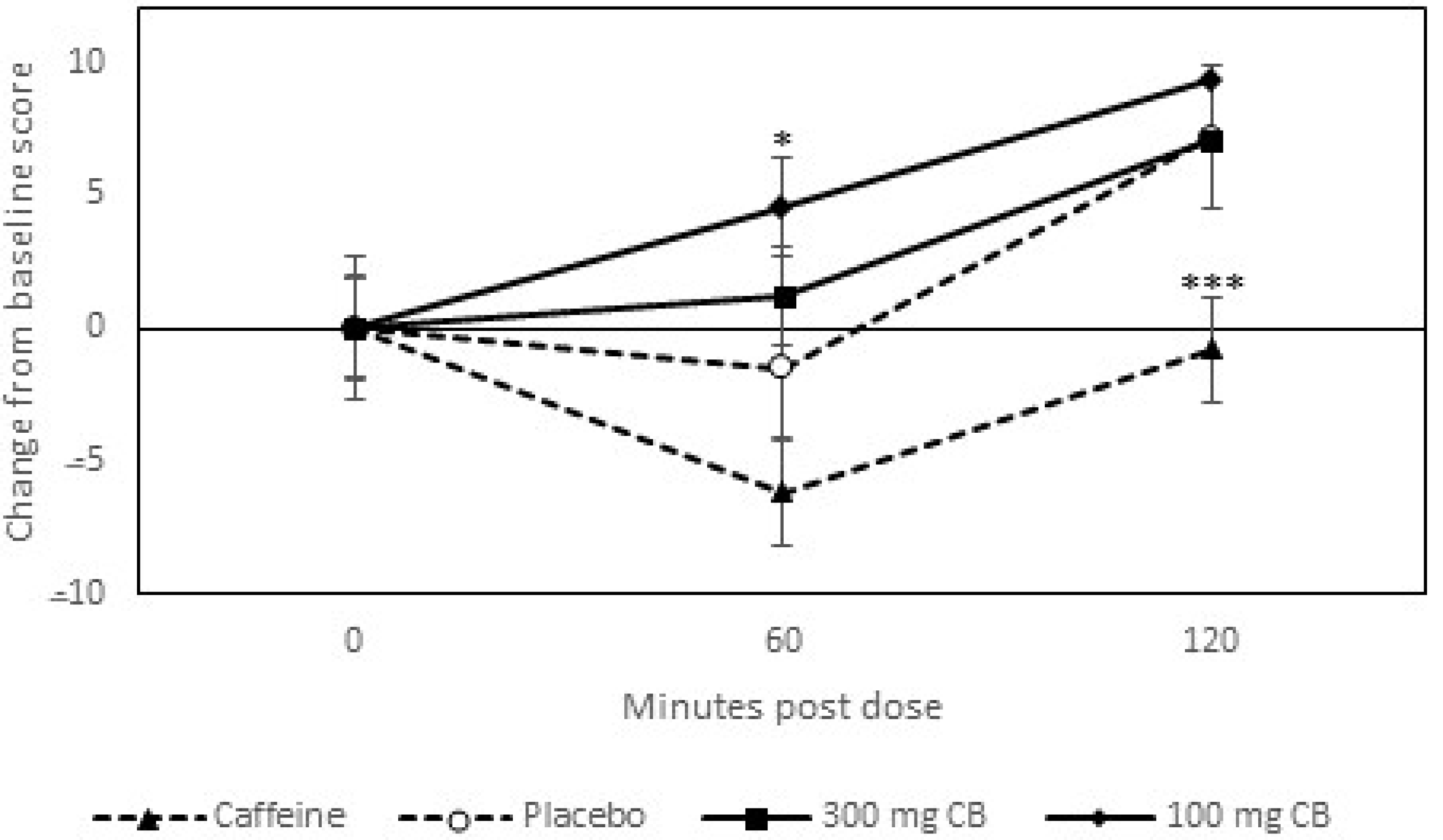
3.1.1. Mood and Psychological State
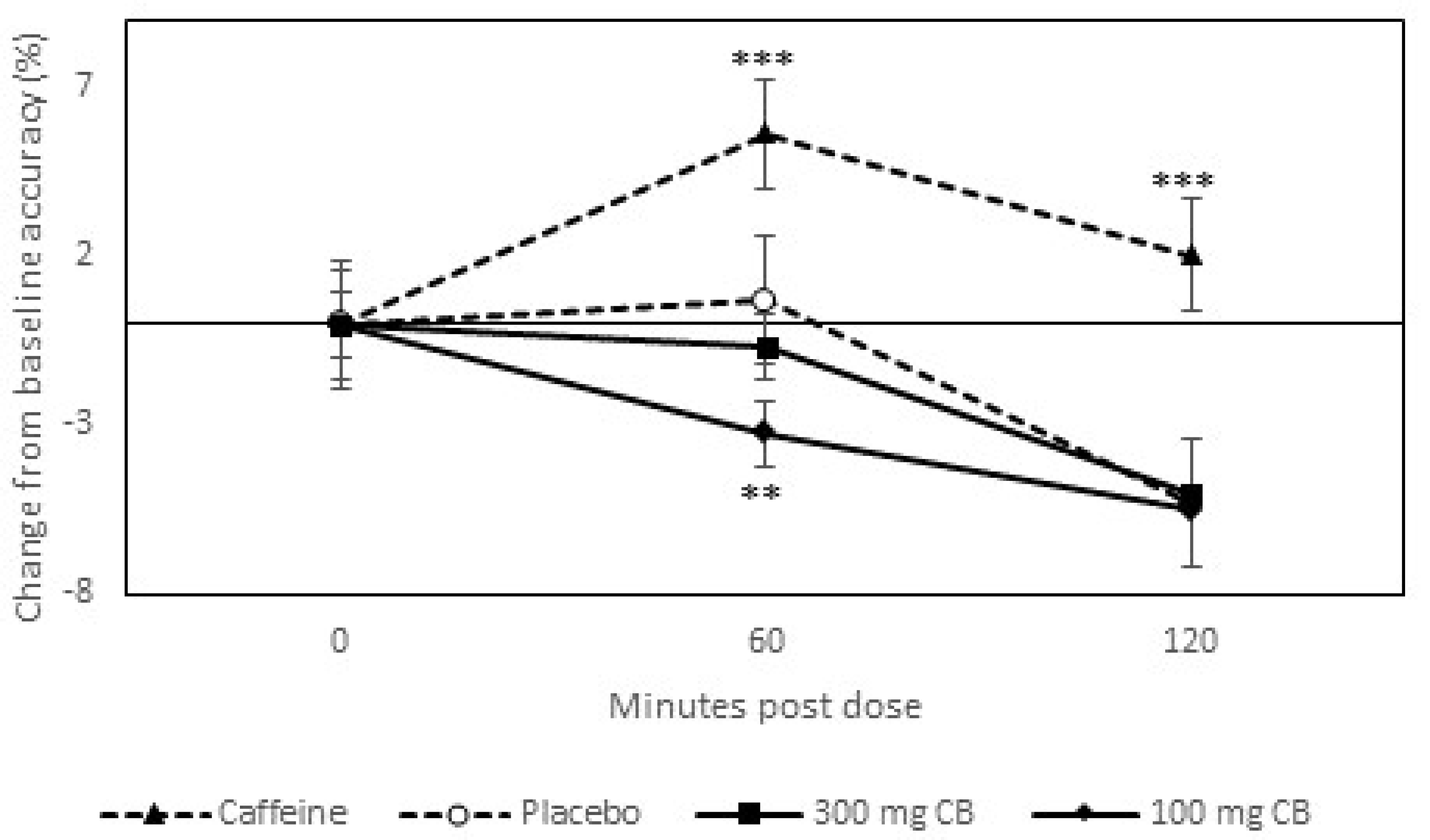
3.1.2. Cognitive Performance
3.2. Response to Caffeine (Positive Control)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Medina-Remon, A.; Quintana, M.; Corella, D.; Pinto, X.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E. Polyphenol-rich foods in the Mediterranean diet are associated with better cognitive function in elderly subjects at high cardiovascular risk. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 29, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesse-Guyot, E.; Fezeu, L.; Andreeva, V.A.; Touvier, M.; Scalbert, A.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P. Total and specific polyphenol intakes in midlife are associated with cognitive function measured 13 years later. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.B.; French, S.J.; Morris, P.J.; Kennedy, D.O.; Milne, A.L.; Haskell, C.F. Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in acute improvements in mood and cognitive performance during sustained mental effort. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamport, D.J.; Pal, D.; Macready, A.L.; Barbosa-Boucas, S.; Fletcher, J.M.; Williams, C.M.; Spencer, J.P.; Butler, L.T. The effects of flavanone-rich citrus juice on cognitive function and cerebral blood flow: An acute, randomised, placebo-controlled cross-over trial in healthy, young adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, E.L.; Jackson, P.A.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Wiebe, J.C.; Gericke, N.; Kennedy, D.O. Acute effects of a polyphenol-rich leaf extract of mangifera indica l.(zynamite) on cognitive function in healthy adults: A double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.J.; Williams, C.M. Polyphenols and cognition in humans: An overview of current evidence from recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Brain Plast. 2020, 6, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pase, M.P.; Scholey, A.B.; Pipingas, A.; Kras, M.; Nolidin, K.; Gibbs, A.; Wesnes, K.; Stough, C. Cocoa polyphenols enhance positive mood states but not cognitive performance: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell-Ramsay, C.; Stuart, R.; Okello, E.; Watson, A. Cognitive and mood improvements following acute supplementation with purple grape juice in healthy young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2621–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Izquierdo, T.; Argumedo, R.; Shu, C.; Nemzer, B.; Pietrzkowski, Z. Stimulatory effect of whole coffee fruit concentrate powder on plasma levels of total and exosomal brain-derived neurotrophic factor in healthy subjects: An acute within-subject clinical study. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 36447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camfield, D.A.; Silber, B.Y.; Scholey, A.B.; Nolidin, K.; Goh, A.; Stough, C. A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial to Differentiate the Acute Cognitive and Mood Effects of Chlorogenic Acid from Decaffeinated Coffee. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, K.; Ochiai, R.; Kozuma, K.; Sato, H.; Koikeda, T.; Osaki, N.; Katsuragi, Y. Effect of Chlorogenic Acids on Cognitive Function: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropley, V.; Croft, R.; Silber, B.; Neale, C.; Scholey, A.; Stough, C.; Schmitt, J. Does coffee enriched with chlorogenic acids improve mood and cognition after acute administration in healthy elderly? A pilot study. Psychopharmacology 2012, 219, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, J.-A.; Hong, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Jo, T.-H.; Park, Y.-I.; Lee, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-Y.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid on scopolamine-induced amnesia via anti-acetylcholinesterase and anti-oxidative activities in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Rammal, H.; Dicko, A.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R. Chlorogenic acid, a polyphenol from Prunus domestica (Mirabelle), with coupled anxiolytic and antioxidant effects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 262, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.A.; Wightman, E.L.; Veasey, R.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Saunders, C.; Mitchell, S.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O. A randomized, crossover study of the acute cognitive and cerebral blood flow effects of phenolic, nitrate and botanical beverages in young, healthy humans. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, T.; Clarke, C.; Nuzum, N.; Teo, W.-P. Acute effects of combined Bacopa, American ginseng and whole coffee fruit on working memory and cerebral haemodynamic response of the prefrontal cortex: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Dodd, F.L.; Robertson, B.C.; Okello, E.J.; Reay, J.L.; Scholey, A.B.; Haskell, C.F. Monoterpenoid extract of sage (Salvia lavandulaefolia) with cholinesterase inhibiting properties improves cognitive performance and mood in healthy adults. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkeaw, C.; Dilokthornsakul, P.; Thanarangsarit, P.; Limpeanchob, N.; Scholfield, C.N. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on cognitive effects of Bacopa monnieri extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.; Williamson, E.M.; Putnam, S.; Farrimond, J.; Whalley, B.J. Effects and mechanisms of ginseng and ginsenosides on cognition. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.A.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Veasey, R.; Kennedy, D.O.; Wilson, A.R.; Saunders, C.; Wightman, E.L. Acute cognitive performance and mood effects of coffee berry and apple extracts: A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover study in healthy humans. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 25, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, R.A.; Mitchell, E.S.; Saunders, C.; O’Connor, P.J. Acute low and moderate doses of a caffeine-free polyphenol-rich coffeeberry extract improve feelings of alertness and fatigue resulting from the performance of fatiguing cognitive tasks. J. Cogn. Enhanc. 2019, 3, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Veasey, R.; Watson, A.; Dodd, F.; Jones, E.; Maggini, S.; Haskell, C.F. Effects of high-dose B vitamin complex with vitamin C and minerals on subjective mood and performance in healthy males. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, J.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B. Single doses of Panax ginseng (G115) reduce blood glucose levels and improve cognitive performance during sustained mental activity. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, E.L.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Thompson, K.G.; Blackwell, J.R.; Winyard, P.G.; Forster, J.; Jones, A.M.; Kennedy, D.O. Dietary nitrate modulates cerebral blood flow parameters and cognitive performance in humans: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 149, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensalem, J.; Dudonné, S.; Etchamendy, N.; Pellay, H.; Amadieu, C.; Gaudout, D.; Dubreuil, S.; Paradis, M.-E.; Pomerleau, S.; Capuron, L. Polyphenols from grape and blueberry improve episodic memory in healthy elderly with lower level of memory performance: A bicentric double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2019, 74, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, A.R.; Cheng, N.; Fromentin, E.; Williams, C.M. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study to compare the safety and efficacy of low dose enhanced wild blueberry powder and wild blueberry extract (ThinkBlue™) in maintenance of episodic and working memory in older adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Jackson, P.A.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Grothe, T.; Perrinjaquet-Moccetti, T.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F. Acute effects of a wild green-oat (Avena sativa) extract on cognitive function in middle-aged adults: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, within-subjects trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Wightman, E.L.; Forster, J.; Khan, J.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Jackson, P.A. Cognitive and mood effects of a nutrient enriched breakfast bar in healthy adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel groups study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veasey, R.; Gonzalez, J.; Kennedy, D.; Haskell, C.; Stevenson, E. Breakfast consumption and exercise interact to affect cognitive performance and mood later in the day. A randomized controlled trial. Appetite 2013, 68, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.; Lader, M. The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1974, 47, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P. Mental and Physical State and Trait Energy and Fatigue Scales. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.L.; Yanes, J.A.; Reid, M.A.; Murphy, J.E.; Busler, J.N.; Mumford, P.W.; Young, K.C.; Pietrzkowski, Z.J.; Nemzer, B.V.; Hunter, J.M.; et al. Neurophysiological Effects of Whole Coffee Cherry Extract in Older Adults with Subjective Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Pilot Study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, C.M.; Cornelis, M.C. Caffeine in the Diet: Country-Level Consumption and Guidelines. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Salazar, N.; Ruiz-Saavedra, S.; Gómez-Martín, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Gueimonde, M. Long-Term Coffee Consumption is Associated with Fecal Microbial Composition in Humans. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, T.; Sela, D.A.; Xiao, J.; Boyacioglu, D.; Chen, F.; Capanoglu, E. The Reciprocal Interactions between Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota and Effects on Bioaccessibility. Nutrients 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Hunter, J.M.; Reyes-Izquierdo, T.; Argumedo, R.; Brizuela-Bastien, J.; Keller, R.; Pietrzkowski, Z.J. Cognitive short-and long-term effects of coffee cherry extract in older adults with mild cognitive decline. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2020, 27, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrime, M.G.; Bauer, S.R.; McDonald, A.C.; Chowdhury, N.H.; Coltart, C.E.; Ding, E.L. Flavonoid-rich cocoa consumption affects multiple cardiovascular risk factors in a meta-analysis of short-term studies. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Wightman, E.L.; Reay, J.L.; Lietz, G.; Okello, E.J.; Wilde, A.; Haskell, C.F. Effects of resveratrol on cerebral blood flow variables and cognitive performance in humans: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.W.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O.; Cooney, J.M.; Trower, T.; Scheepens, A. Acute supplementation with blackcurrant extracts modulates cognitive functioning and inhibits monoamine oxidase-B in healthy young adults. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalmach, A.; Williamson, G.; Crozier, A. Impact of dose on the bioavailability of coffee chlorogenic acids in humans. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Haskell, C.F.; Robertson, B.; Reay, J.; Brewster-Maund, C.; Luedemann, J.; Maggini, S.; Ruf, M.; Zangara, A.; Scholey, A.B. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added guarana (Paullinia cupana). Appetite 2008, 50, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B. A glucose-caffeine ‘energy drink’ ameliorates subjective and performance deficits during prolonged cognitive demand. Appetite 2004, 42, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, J.L.; Kennedy, D.O.; Scholey, A.B. Effects of Panax ginseng, consumed with and without glucose, on blood glucose levels and cognitive performance during sustained ‘mentally demanding’ tasks. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.; Okello, E.; Chazot, P.; Howes, M.-J.; Ohiomokhare, S.; Jackson, P.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.; Khan, J.; Forster, J.; Wightman, E. Volatile terpenes and brain function: Investigation of the cognitive and mood effects of Mentha× piperita l. essential oil with in vitro properties relevant to central nervous system function. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jackson, P.A.; Kenney, C.; Forster, J.; Smith, E.F.; Elcoate, R.; Spittlehouse, B.; Johnson, J.; Kennedy, D.O. Acute Cognitive Performance and Mood Effects of Coffeeberry Extract: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Healthy Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112418
Jackson PA, Kenney C, Forster J, Smith EF, Elcoate R, Spittlehouse B, Johnson J, Kennedy DO. Acute Cognitive Performance and Mood Effects of Coffeeberry Extract: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Healthy Humans. Nutrients. 2023; 15(11):2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112418
Chicago/Turabian StyleJackson, Philippa A., Charlotte Kenney, Joanne Forster, Ellen F. Smith, Rian Elcoate, Bethany Spittlehouse, Jodee Johnson, and David O. Kennedy. 2023. "Acute Cognitive Performance and Mood Effects of Coffeeberry Extract: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Healthy Humans" Nutrients 15, no. 11: 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112418
APA StyleJackson, P. A., Kenney, C., Forster, J., Smith, E. F., Elcoate, R., Spittlehouse, B., Johnson, J., & Kennedy, D. O. (2023). Acute Cognitive Performance and Mood Effects of Coffeeberry Extract: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Healthy Humans. Nutrients, 15(11), 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15112418





