Effects of a Web-Based Weight Loss Program on the Healthy Eating Index-NVS in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and the Association with Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants and Recruitment
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Outcome
2.5. Sample Size, Randomization and Blinding
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Recruitment, Drop-Outs and Baseline Characteristics
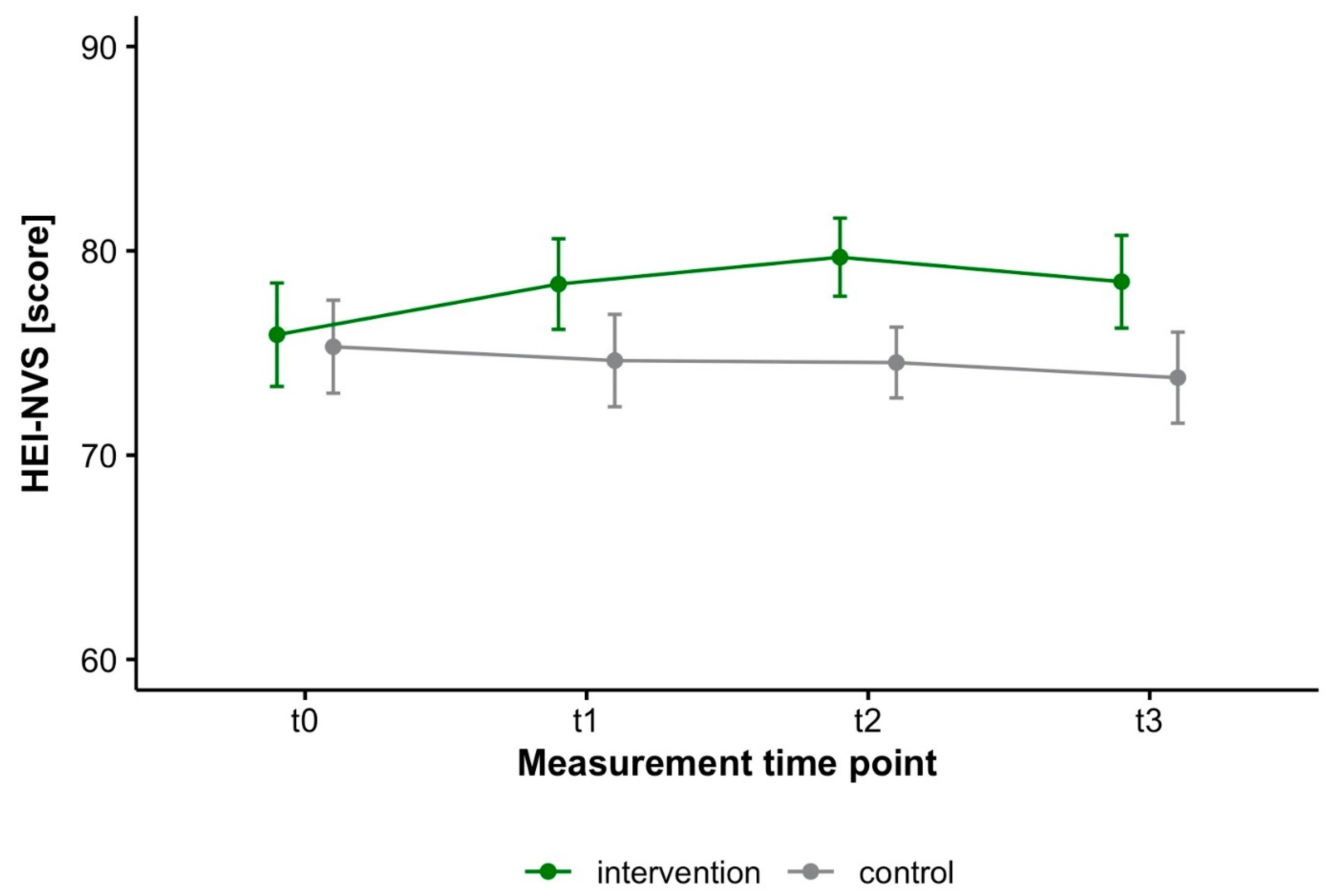
3.2. Effects of Web-Based Weight Loss Programs on HEI-NVS
3.3. Associations between HEI-NVS and Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwingshackl, L.; Bogensberger, B.; Hoffmann, G. Diet Quality as Assessed by the Healthy Eating Index, Alternate Healthy Eating Index, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Score, and Health Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 118, 74–100.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Obbagy, J.E.; Altman, J.M.; Essery, E.V.; McGrane, M.M.; Wong, Y.P.; Spahn, J.M.; Williams, C.L. Dietary Energy Density and Body Weight in Adults and Children: A Systematic Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.H.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Surkan, P.J.; Azadbakht, L. Associations between dietary energy density and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Rodacki, T.; Dobrowolska-Iwanek, J.; Brzozowska, A.; Walkowiak, J.; Wojtanowska-Krosniak, A.; Zagrodzki, P.; Bechthold, A.; Mardas, M.; Boeing, H. Link between Food Energy Density and Body Weight Changes in Obese Adults. Nutrients 2016, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Khuttan, M.; McFarland-Lesser, I.; Patel, Z.; Jones, A. Calorie reformulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the effect of manipulating food energy density on daily energy intake. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2022, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.H.; Surkan, P.J.; Azadbakht, L. The effect of preload/meal energy density on energy intake in a subsequent meal: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Behav. 2017, 26, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Mendez, M.A.; Gomez, S.F.; Fíto, M.; Ribas, L.; Aranceta, J.; Serra-Majem, L. Energy density, diet quality, and central body fat in a nationwide survey of young Spaniards. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.; Pereira, J.L.; Fisberg, R.; Marchioni, D.M.L. Dietary energy density was associated with diet quality in Brazilian adults and older adults. Appetite 2015, 97, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, L.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary energy density is inversely associated with the diet quality indices among Iranian young adults. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2012, 58, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smethers, A.D.; Rolls, B.J. Dietary Management of Obesity: Cornerstones of Healthy Eating Patterns. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Giovannucci, E.; Boffetta, P.; Fadnes, L.T.; Keum, N.; Norat, T.; Greenwood, D.C.; Riboli, E.; Vatten, L.J.; Tonstad, S. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1029–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelino, D.; Godos, J.; Ghelfi, F.; Tieri, M.; Titta, L.; Lafranconi, A.; Marventano, S.; Alonzo, E.; Gambera, A.; Sciacca, S.; et al. Fruit and vegetable consumption and health outcomes: An umbrella review of observational studies. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, T.; Krems, C.; Moon, K.; Brombach, C.; Hoffmann, I. Food consumption of adults in Germany: Results of the German National Nutrition Survey II based on diet history interviews. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRI. German National Nutrition Survey II 2005–2007. 2008. Available online: https://www.mri.bund.de/fileadmin/MRI/Institute/EV/NVSII_Abschlussbericht_Teil_2.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung (DGE). Food-Related Recommendations, 1st ed.; DGE: Bonn, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- US Department of Agriculture; US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025, 9th ed.; 2020. Available online: https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G.; Iqbal, K.; Schwedhelm, C.; Boeing, H. Food groups and intermediate disease markers: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, S.; Neuenschwander, M.; Schwedhelm, C.; Hoffmann, G.; Bechthold, A.; Boeing, H.; Schwingshackl, L. Food Groups and Risk of Overweight, Obesity, and Weight Gain: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2019, 10, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittig, F.; Heuer, T.; Claupein, E.; Pfau, C.; Cordts, A.; Schulze, B.; Padilla Bravo, C.A.; Spiller, A. (Eds.) Auswertung der Daten der Nationalen Verzehrsstudie II (NVS II): Eine Integrierte Verhaltens- und Lebensbasierte Analyse des Bio-Konsums; Rubner-Institut: Karlsruhe, Germany; Georg-August-University Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2010; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, E.T.; Ohls, J.; Carlson, S.; Fleming, K. The Healthy Eating Index: Design and applications. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1995, 95, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsten, A.V.; Illner, A.K.; Boeing, H.; Flothkötter, M. Evaluation of food intake based on a “Healthy Eating Index” [HEI-EPIC]. Ernahr. Umsch. 2009, 56, 450–456. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, L.; Martin, N.; Jimoh, O.F.; Kirk, C.; Foster, E.; Abdelhamid, A.S. Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 5, CD011737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, H.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Botek, M.; McKune, A.J.; Sergi, D.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Mellor, D.D.; Naumovski, N. The Effects of Dietary Polyphenols on Circulating Cardiovascular Disease Biomarkers and Iron Status: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2019, 12, 1178638819882739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.; Mann, J.; Cummings, J.; Winter, N.; Mete, E.; Te Morenga, L. Carbohydrate quality and human health: A series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet 2019, 393, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, P.; Royall, D.; Rodrigues, A. Use of the Healthy Eating Index in Intervention Studies for Cardiometabolic Risk Conditions: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2021, 12, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, H.-W.; Klem, M.L.; Costacou, T.; Burke, L.E. Healthy Eating Index Diet Quality in Randomized Weight Loss Trials: A Systematic Review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2023, 123, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, V.K.; Petersen, K.S.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Eren, F.; Cassens, M.E.; Bunczek, M.T.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Greater Scores for Dietary Fat and Grain Quality Components Underlie Higher Total Healthy Eating Index-2015 Scores, While Whole Fruits, Seafood, and Plant Proteins Are Most Favorably Associated with Cardiometabolic Health in US Adults. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2021, 5, nzab015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artegoitia, V.M.; Krishnan, S.; Bonnel, E.L.; Stephensen, C.B.; Keim, N.L.; Newman, J.W. Healthy eating index patterns in adults by sex and age predict cardiometabolic risk factors in a cross-sectional study. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.; Webb, P.; Micha, R.; Mozaffarian, D. Defining diet quality: A synthesis of dietary quality metrics and their validity for the double burden of malnutrition. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e352–e370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gose, M.; Krems, C.; Heuer, T.; Hoffmann, I. Trends in food consumption and nutrient intake in Germany between 2006 and 2012: Results of the German National Nutrition Monitoring (NEMONIT). Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelnuovo, G.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manzoni, G.M.; Corti, S.; Ceccarini, M.; Borrello, M.; Giusti, E.M.; Novelli, M.; Cattivelli, R.; Middleton, N.A.; et al. Chronic care management of globesity: Promoting healthier lifestyles in traditional and mHealth based settings. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.G.; Glasgow, R.E. The Delivery of Public Health Interventions via the Internet: Actualizing Their Potential. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2009, 30, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E. Web-Based Interventions for Behavior Change and Self-Management: Potential, Pitfalls, and Progress. Medicine 2.0 2012, 1, e1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, V.; Tran, H.; Downing, K.L.; Hesketh, K.D.; Moodie, M. A systematic review of economic evaluations of web-based or telephone-delivered interventions for preventing overweight and obesity and/or improving obesity-related behaviors. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kercher, V.M.; Kercher, K.; Bennion, T.; Levy, P.; Alexander, C.; Amaral, P.C.; Li, Y.-M.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. 2022 Fitness Trends from Around the Globe. ACSM’S Health Fit. J. 2022, 26, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakoulis, A. European survey of fitness trends for 2020. ACSM’S Health Fit. J. 2019, 23, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgente, A.; Pietrabissa, G.; Manzoni, G.M.; Rethlefsen, M.; Simpson, S.; Perona, S.; Rossi, A.; Cattivelli, R.; Innamorati, M.; Jackson, J.B.; et al. Web-Based Interventions for Weight Loss or Weight Loss Maintenance in Overweight and Obese People: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, J.; Eckert, T.; Wunsch, K.; Woll, A. Key facets to build up eHealth and mHealth interventions to enhance physical activity, sedentary behavior and nutrition in healthy subjects—An umbrella review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelanotte, C.; Müller, A.M.; Short, C.E.; Hingle, M.; Nathan, N.; Williams, S.L.; Lopez, M.L.; Parekh, S.; Maher, C.A. Past, Present, and Future of eHealth and mHealth Research to Improve Physical Activity and Dietary Behaviors. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, 219–228.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dening, J.; Islam, S.M.S.; George, E.; Maddison, R. Web-Based Interventions for Dietary Behavior in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Shang, B.; Liang, W.; Du, G.; Yang, M.; Rhodes, R.E. Effects of eHealth-Based Multiple Health Behavior Change Interventions on Physical Activity, Healthy Diet, and Weight in People With Noncommunicable Diseases: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e23786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleigoli, A.M.; Andrade, A.Q.; Cançado, A.G.; Paulo, M.N.; Diniz, M.D.F.H.; Ribeiro, A.L. Web-Based Digital Health Interventions for Weight Loss and Lifestyle Habit Changes in Overweight and Obese Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brame, J.; Kohl, J.; Wurst, R.; Fuchs, R.; Tinsel, I.; Maiwald, P.; Fichtner, U.; Armbruster, C.; Bischoff, M.; Farin-Glattacker, E.; et al. Health Effects of a 12-Week Web-Based Lifestyle Intervention for Physically Inactive and Overweight or Obese Adults: Study Protocol of Two Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsel, I.; Metzner, G.; Schlett, C.; Sehlbrede, M.; Bischoff, M.; Anger, R.; Brame, J.; König, D.; Wurst, R.; Fuchs, R.; et al. Effectiveness of an interactive web-based health program for adults: A study protocol for three concurrent controlled-randomized trials (EVA-TK-Coach). Trials 2021, 22, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, B.; Braun, W.; Geisler, C.; Both, M.; Klückmann, K.; Müller, M.J.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Limitations of Fat-Free Mass for the Assessment of Muscle Mass in Obesity. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Schautz, B.; Later, W.; Kehayias, J.J.; Gallagher, D.; Müller, M.J. What makes a BIA equation unique? Validity of eight-electrode multifrequency BIA to estimate body composition in a healthy adult population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, S14–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Jensen, B.; Braun, W.; Pourhassan, M.; Gallagher, D.; Müller, M.J. Quantification of whole-body and segmental skeletal muscle mass using phase-sensitive 8-electrode medical bioelectrical impedance devices. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audigier, V.; Resche-Rigon, M. Micemd: Multiple Imputation by Chained Equations with Multilevel Data. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/micemd/index.html (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M. robustlmm: An R Package for Robust Estimation of Linear Mixed-Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 75, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Canty, A.; Ripley, B. Boot: Bootstrap R (S-Plus) Functions; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/boot/citation.html (accessed on 27 November 2022).
- Kohl, J.; Brame, J.; Centner, C.; Wurst, R.; Fuchs, R.; Sehlbrede, M.; Tinsel, I.; Maiwald, P.; Fichtner, U.A.; Armbruster, C.; et al. Effects of a web-based lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight and obesity on weight loss and cardiometabolic risk factors: A randomized controlled clinical trial. JMIR, 2022; preprints. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, K.; Krems, C.; Heuer, T.; Roth, A.; Hoffmann, I. Predictors of BMI Vary along the BMI Range of German Adults–Results of the German National Nutrition Survey II. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.; Jebb, S.; Oke, J.; Nickless, A.; Ahern, A.; Boyland, E.; Caterson, I.; Halford, J.; Hauner, H.; Aveyard, P. How effective is weight loss in reducing cardiometabolic risk? An observational analysis of two randomised controlled trials of community weight loss programmes. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2021, 71, e312–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.L.; Ho, Y.Y.; Rollo, M.E.; Collins, C.E. Validity of Dietary Assessment Methods When Compared to the Method of Doubly Labeled Water: A Systematic Review in Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Dodd, K.W.; Kipnis, V.; Thompson, F.E.; Potischman, N.; Schoeller, D.A.; Baer, D.J.; Midthune, D.; Troiano, R.; Bowles, H.; et al. Comparison of self-reported dietary intakes from the Automated Self-Administered 24-h recall, 4-d food records, and food-frequency questionnaires against recovery biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Kleiser, C.; Uzhova, I.; Peñalvo, J.L.; La Torre, G.; Palys, W.; Lojko, D.; Nimptsch, K.; Suwalska, A.; Linseisen, J.; et al. Seasonality of food groups and total energy intake: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckland, N.J.; Swinnerton, L.F.; Ng, K.; Price, M.; Wilkinson, L.L.; Myers, A.; Dalton, M. Susceptibility to increased high energy dense sweet and savoury food intake in response to the COVID-19 lockdown: The role of craving control and acceptance coping strategies. Appetite 2020, 158, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | All (n = 153) | Intervention (n = 78) | Control (n = 75) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 48.92 (11.17) | 49.12 (11.36) | 48.72 (11.05) |
| Sex | |||
| Male [n] | 44 (28.8%) | 20 (25.7%) | 24 (32.0%) |
| Female [n] | 109 (71.2%) | 58 (74.3%) | 51 (68.0%) |
| Body weight [kg] | 88.39 (10.65) | 88.42 (10.15) | 88.36 (11.21) |
| Body height [m] | 1.69 (0.08) | 1.69 (0.07) | 1.70 (0.08) |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 30.71 (2.13) | 30.88 (2.2) | 30.54 (2.05) |
| Predictors | HEI-NVS | p |
|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 77.33 (2.66) | <0.001 |
| Time | ||
| t0–t1 | 5.23 (2.81) | 0.063 |
| t0–t2 | 9.06 (3.04) | 0.003 |
| t0–t3 | 5.90 (2.82) | 0.037 |
| Group (Control) | −1.10 (1.69) | 0.513 |
| Time * group (Control) | ||
| t0–t1 | −2.84 (1.79) | 0.113 |
| t0–t2 | −4.96 (2.00) | 0.013 |
| t0–t3 | −3.50 (1.81) | 0.054 |
| Group | t0 | t1 | t2 | t3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetables [score], max. 15 points | ||||
| Intervention | 6.24 (3.41) | 7.71 (4.06) | 7.36 (3.01) | 7.60 (3.51) |
| Control | 6.15 (3.15) | 6.67 (3.10) | 5.72 (2.54) | 6.57 (3.08) |
| Fruits [score], max. 15 points | ||||
| Intervention | 7.95 (4.37) | 7.89 (4.36) | 7.75 (3.96) | 7.34 (4.41) |
| Control | 7.31 (4.69) | 7.20 (4.63) | 6.42 (3.61) | 6.77 (3.99) |
| Grains [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 6.67 (2.35) | 6.42 (2.19) | 6.98 (2.05) | 6.56 (2.05) |
| Control | 6.71 (2.33) | 6.35 (2.04) | 7.00 (1.94) | 6.84 (2.30) |
| Dairy [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 7.08 (2.15) | 6.80 (1.95) | 7.14 (1.75) | 7.01 (2.05) |
| Control | 7.15 (1.82) | 7.33 (1.57) | 7.27 (1.66) | 7.14 (1.55) |
| Fish [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 3.29 (3.90) | 3.87 (3.85) | 4.07 (3.36) | 4.15 (3.39) |
| Control | 4.31 (3.93) | 3.18 (3.53) | 3.52 (3.24) | 3.13 (3.33) |
| Beverages [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 8.93 (2.08) | 8.97 (2.17) | 8.87 (2.00) | 8.75 (2.09) |
| Control | 8.19 (2.52) | 8.10 (2.84) | 8.24 (2.48) | 8.22 (2.59) |
| Eggs [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 8.79 (1.92) | 8.91 (1.82) | 8.89 (1.62) | 8.84 (1.75) |
| Control | 8.72 (2.10) | 8.31 (2.31) | 8.90 (1.75) | 8.62 (2.10) |
| Spreadable fats [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 9.83 (0.82) | 9.92 (0.43) | 9.94 (0.37) | 9.95 (0.22) |
| Control | 9.76 (1.03) | 9.91 (0.57) | 9.93 (0.24) | 9.90 (0.41) |
| Alcohol [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 9.23 (1.79) | 9.29 (1.54) | 9.57 (1.17) | 9.45 (1.17) |
| Control | 9.04 (1.93) | 9.11 (1.75) | 9.30 (1.57) | 9.18 (1.65) |
| Meat [score], max. 10 points | ||||
| Intervention | 7.96 (2.43) | 8.52 (1.98) | 8.85 (1.51) | 8.15 (1.94) |
| Control | 7.95 (2.31) | 8.13 (2.14) | 8.08 (1.94) | 7.83 (2.26) |
| Group | t0–t1 | t0–t2 | t0–t3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEI-NVS | |||
| Intervention | 0.24 [−0.08, 0.55] | 0.38 [0.06, 0.70] | 0.24 [−0.07, 0.56] |
| Control | −0.07 [−0.39, 0.25] | −0.09 [−0.41, 0.23] | −0.15 [−0.48, 0.17] |
| Δt0–t1 | Δt0–t3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Correlation Coefficient | 95% Confidence Interval | Correlation Coefficient | 95% Confidence Interval |
| Energy density | −0.228 * | −0.359, −0.097 | −0.312 * | −0.451, −0.165 |
| Energy intake | 0.089 | −0.079, 0.256 | 0.076 | −0.098, 0.247 |
| Body weight | −0.052 | −0.203, 0.122 | −0.070 | −0.235, 0.101 |
| Waist circumference | 0.068 | −0.086, 0.216 | −0.014 | −0.203, 0.189 |
| Fat mass | 0.040 | −0.103, 0.226 | 0.042 | −0.111, 0.193 |
| Fat free mass | −0.045 | −0.209, 0.148 | −0.190 * | −0.334, −0.041 |
| Total cholesterol | −0.041 | −0.185, 0.127 | −0.018 | −0.177, 0.133 |
| HDL-cholesterol | −0.013 | −0.165, 0.159 | 0.011 | −0.163, 0.189 |
| LDL-cholesterol | −0.087 | −0.228, 0.065 | 0.001 | −0.137, 0.151 |
| Fasting blood glucose | −0.116 | −0.258, 0.056 | 0.161 * | 0.038, 0.275 |
| HbA1c | −0.083 | −0.217, 0.059 | −0.055 | −0.166, 0.081 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.104 | −0.057, 0.264 | −0.042 | −0.221, 0.125 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.176 | −0.009, 0.365 | −0.117 | −0.297, 0.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohl, J.; Brame, J.; Hauff, P.; Wurst, R.; Sehlbrede, M.; Fichtner, U.A.; Armbruster, C.; Tinsel, I.; Maiwald, P.; Farin-Glattacker, E.; et al. Effects of a Web-Based Weight Loss Program on the Healthy Eating Index-NVS in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and the Association with Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010007
Kohl J, Brame J, Hauff P, Wurst R, Sehlbrede M, Fichtner UA, Armbruster C, Tinsel I, Maiwald P, Farin-Glattacker E, et al. Effects of a Web-Based Weight Loss Program on the Healthy Eating Index-NVS in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and the Association with Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohl, Jan, Judith Brame, Pascal Hauff, Ramona Wurst, Matthias Sehlbrede, Urs Alexander Fichtner, Christoph Armbruster, Iris Tinsel, Phillip Maiwald, Erik Farin-Glattacker, and et al. 2023. "Effects of a Web-Based Weight Loss Program on the Healthy Eating Index-NVS in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and the Association with Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010007
APA StyleKohl, J., Brame, J., Hauff, P., Wurst, R., Sehlbrede, M., Fichtner, U. A., Armbruster, C., Tinsel, I., Maiwald, P., Farin-Glattacker, E., Fuchs, R., Gollhofer, A., & König, D. (2023). Effects of a Web-Based Weight Loss Program on the Healthy Eating Index-NVS in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and the Association with Dietary, Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Variables: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 15(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010007






