Exercise-Induced ADAR2 Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through miR-34a
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatments
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.4. Vector Construction
2.5. Vector Transfection
2.6. Nile Red Staining
2.7. Quantification of TGs
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exercise Mitigates Liver Steatosis in Mice
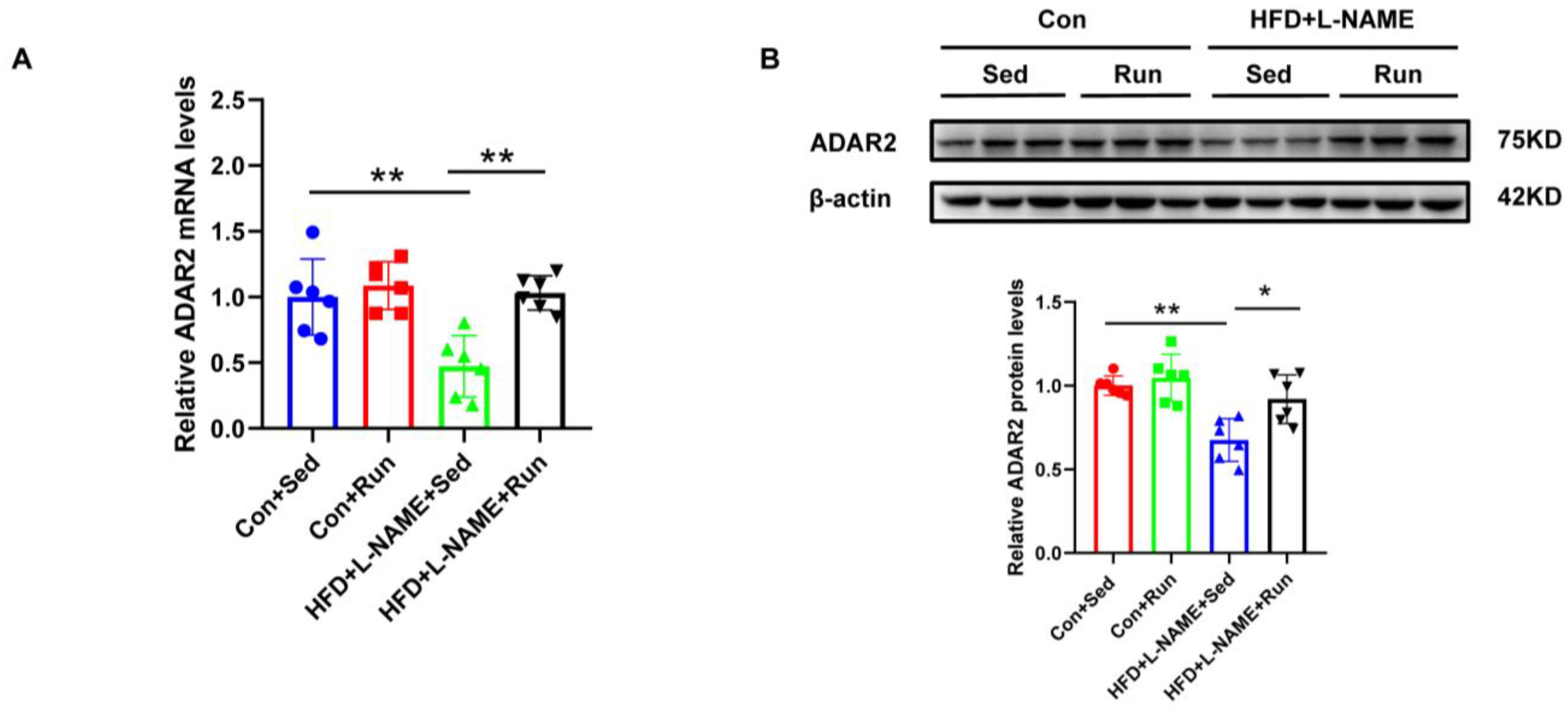
3.2. Hepatic ADAR2 Was Ameliorated by Exercise in the Group with Diet-Induced NAFLD Mice
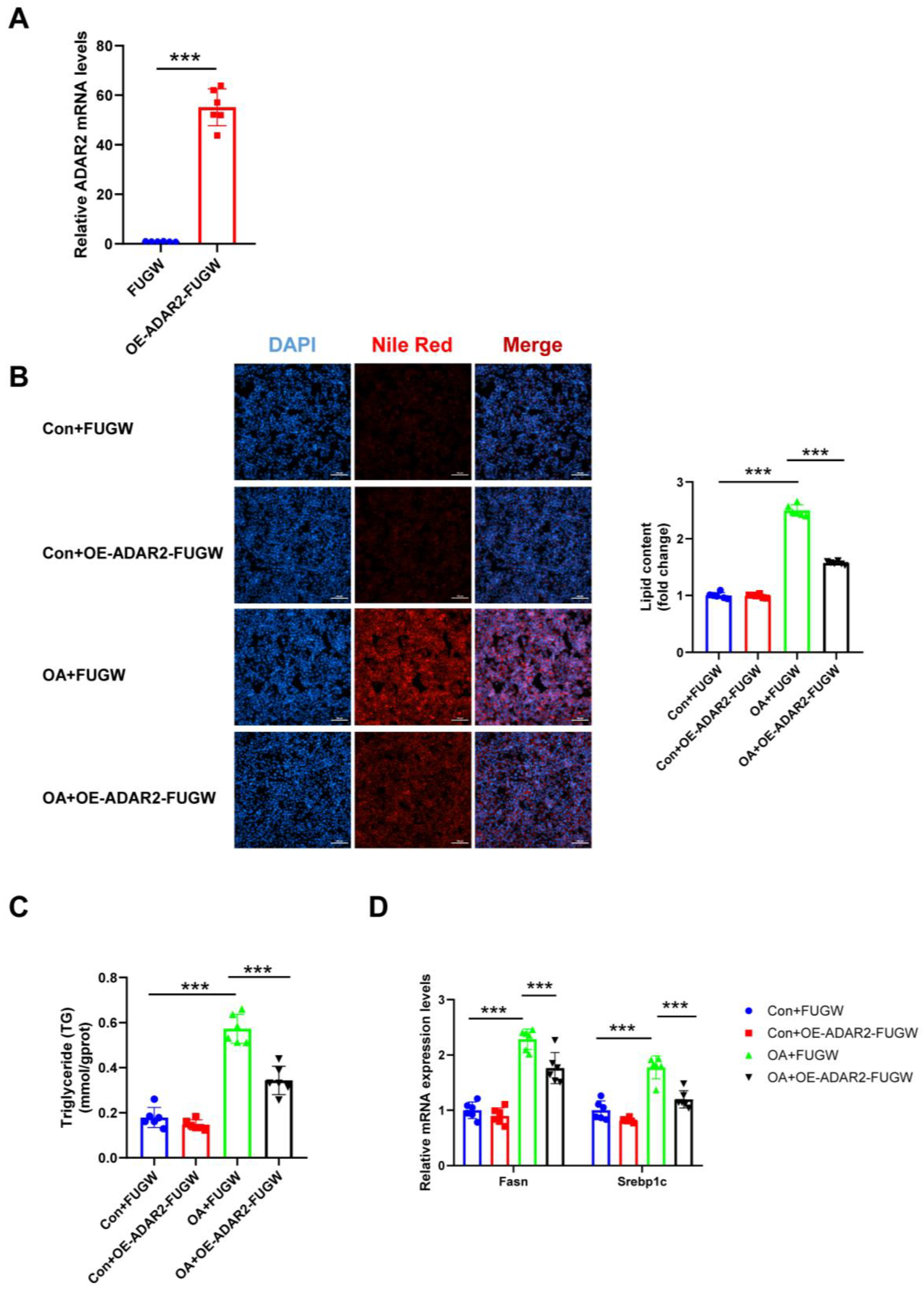
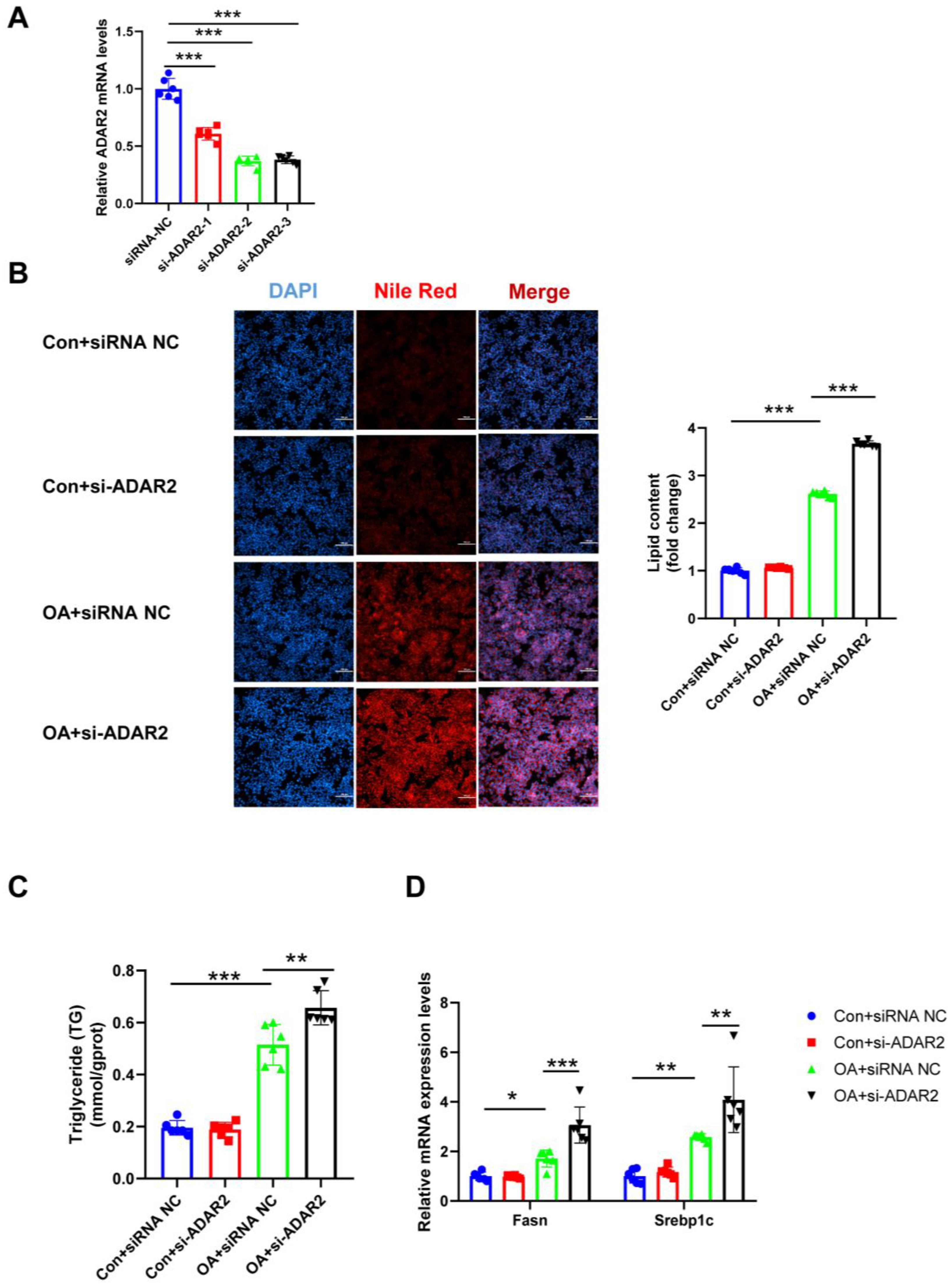
3.3. ADAR2 Prevents Hepatocyte from Lipid Accumulation In Vitro
3.4. miR-34a Is Regulated by ADAR2 In Vitro and In Vivo
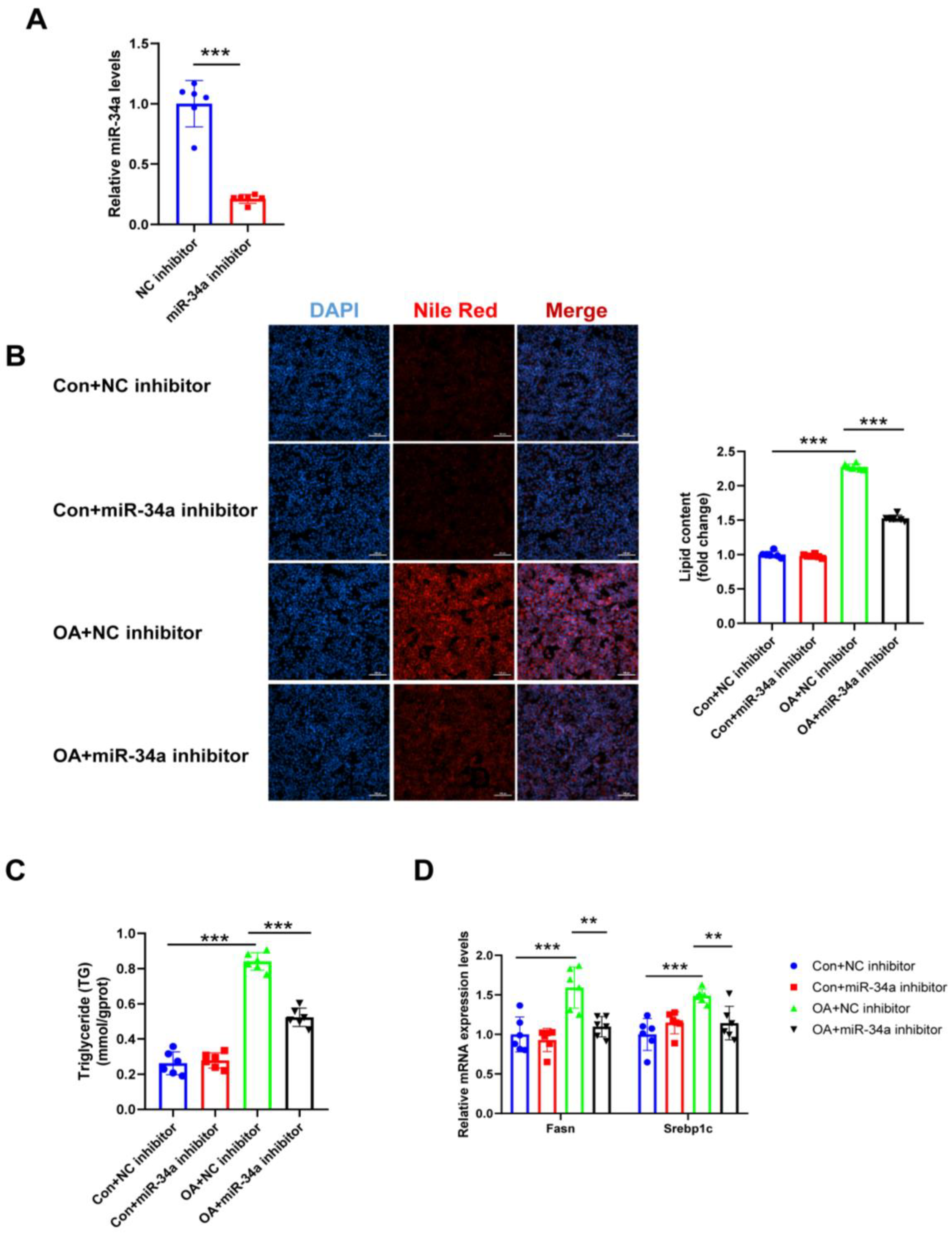
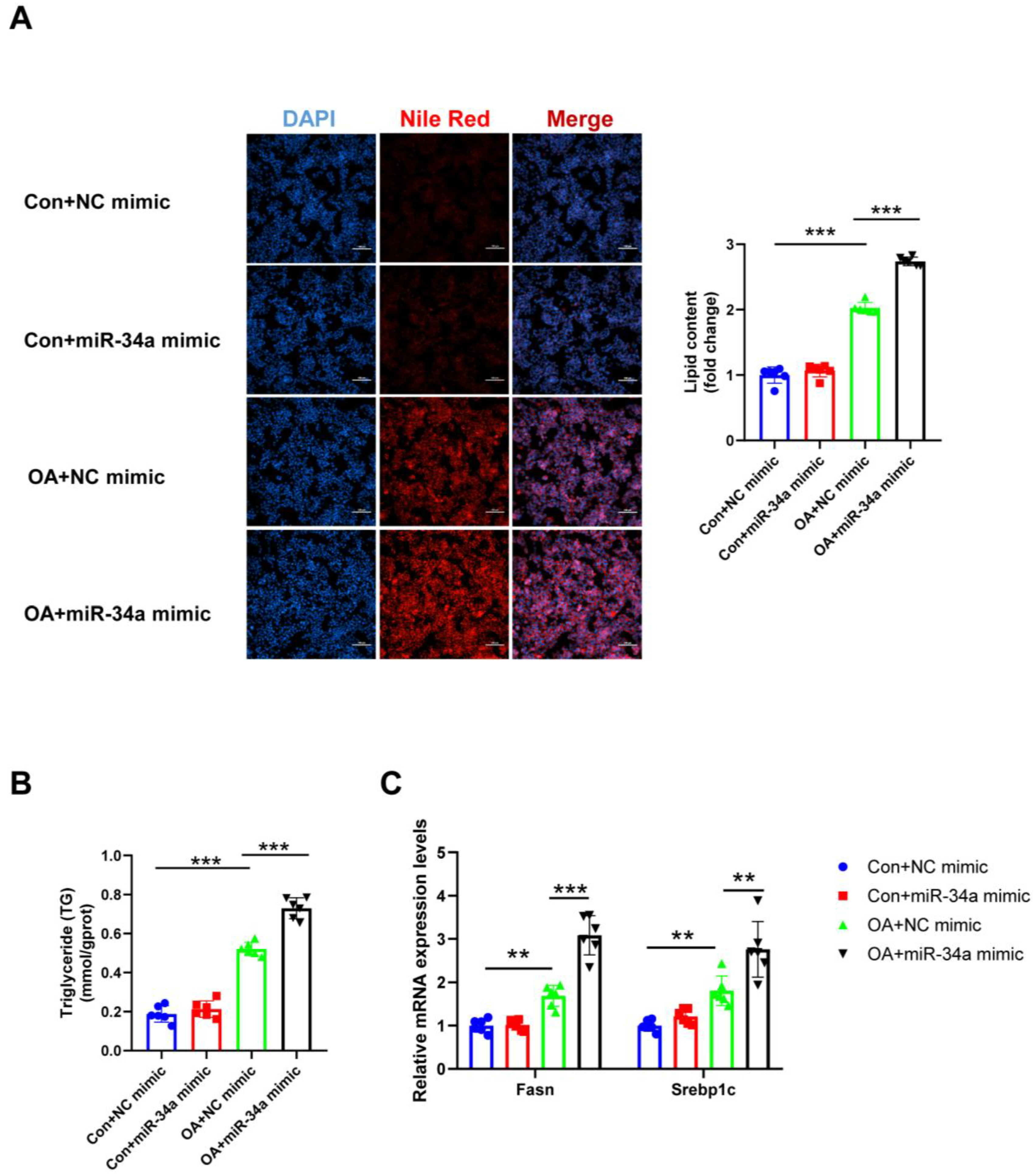
3.5. ADAR2 Inhibits Hepatocyte Lipid Droplet Accumulation by Regulating miR-34a In Vitro
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, J.A.; George, J.; on behalf of the International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, T.G.; Rinella, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease 2020: The State of the Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, R.S.; Shu, S.S.; Cheung, B.H.; Li, L.S.; Chim, A.M.; Chan, C.K.; Leung, J.K.; Chu, W.C.; et al. Beneficial effects of lifestyle intervention in non-obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Corey, K.E.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Lifestyle Modification Using Diet and Exercise to Achieve Weight Loss in the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, S.E.; Hackett, D.A.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Sahar, N.E.; Javaid, H.M.A.; Pak, E.S.; Liang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ha, H.; Huh, J.Y. Exercise-Induced Irisin Decreases Inflammation and Improves NAFLD by Competitive Binding with MD2. Cells 2021, 10, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.; Liu, M.; Xi, Y.; Chen, M.; Tian, L.; Xie, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; Yu, Z.; et al. Long-term exercise prevents hepatic steatosis: A novel role of FABP1 in regulation of autophagy-lysosomal machinery. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 11870–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dun, Y.; Zhang, W.; You, B.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, J.; Ripley-Gonzalez, J.W.; Liu, S. Exercise improves lipid droplet metabolism disorder through activation of AMPK-mediated lipophagy in NAFLD. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, A.; Fealy, C.E.; Axelrod, C.L.; Haus, J.M.; Flask, C.A.; McCullough, A.J.; Kirwan, J.P. Exercise Training Rapidly Increases Hepatic Insulin Extraction in NAFLD. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajo-Pescador, S.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Juarez-Fernández, M.; Cuevas, M.J.; Mauriz, J.L.; González-Gallego, J.; Nistal, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Beneficial effects of exercise on gut microbiota functionality and barrier integrity, and gut-liver crosstalk in an in vivo model of early obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dis. Models Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise. J. Hepatol 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; He, J.; Pan, L.L.; Ma, Z.M.; Han, C.K.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Han, H.W.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Vigorous Exercise on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2016, 176, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayir, A. RNA A-to-I editing, environmental exposure, and human diseases. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2021, 51, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikura, K. Functions and regulation of RNA editing by ADAR deaminases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Nakajima, M. Significance of A-to-I RNA editing of transcripts modulating pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 181, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarini, V.; Silvestris, D.A.; Tassinari, V.; Tomaselli, S.; Alon, S.; Eisenberg, E.; Locatelli, F.; Gallo, A. ADAR2/miR-589-3p axis controls glioblastoma cell migration/invasion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2045–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.B.; Liao, X.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Wang, F.; Qin, H.D.; Zhang, L.; Shugart, Y.Y.; Zeng, Y.X.; Jia, W.H. ADAR2 functions as a tumor suppressor via editing IGFBP7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Varanasi, S.M.; Patil, S.S.; Srinivas, S.; Hernández-Cuervo, H.; Czachor, A.; Bulkhi, A.; Fukumoto, J.; Galam, L.; Lockey, R.F.; et al. Lung fibrosis is induced in ADAR2 overexpressing mice via HuR-induced CTGF signaling. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Chen, R.; Wu, X.; Ni, G.; Liu, C.; Das, S.; Sluijter, J.P.G.; et al. ADAR2 increases in exercised heart and protects against myocardial infarction and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terajima, H.; Yoshitane, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Fukada, Y. A-to-I RNA editing enzyme ADAR2 regulates light-induced circadian phase-shift. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terajima, H.; Yoshitane, H.; Ozaki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimba, S.; Kuroda, S.; Iwasaki, W.; Fukada, Y. ADARB1 catalyzes circadian A-to-I editing and regulates RNA rhythm. Nat. Genet 2017, 49, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.H.; Lin, C.H.; Qi, L.; Fei, J.; Li, Y.; Yong, K.J.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Chow, R.K.; Ng, V.H.; et al. A disrupted RNA editing balance mediated by ADARs (Adenosine DeAminases that act on RNA) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2014, 63, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Kumar, V.; Sud, N.; Mahato, R.I. MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of progressive liver injury in NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 129, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Gao, B. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 2021, 70, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Bei, Y.; Liu, J.; Dimitrova-Shumkovska, J.; Kuang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. miR-212 downregulation contributes to the protective effect of exercise against non-alcoholic fatty liver via targeting FGF-21. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Lv, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Song, M.; Liu, J.; Bei, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Yang, C. miR-149 controls non-alcoholic fatty liver by targeting FGF-21. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikura, K. A-to-I editing of coding and non-coding RNAs by ADARs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Mojumdar, K.; Zhou, Z.; Jeong, K.J.; Mangala, L.S.; Yu, S.; Tsang, Y.H.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. A-to-I-edited miRNA-379-5p inhibits cancer cell proliferation through CD97-induced apoptosis. J. Clin. Invest 2019, 129, 5343–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.D.; Padilla, J.; Jenkins, N.T.; Laughlin, M.H.; Rector, R.S. Chronic NOS inhibition accelerates NAFLD progression in an obese rat model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G540–G549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Deng, J.; Yao, J.; Song, J.; Meng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, M.; Liang, Y.; Xu, J.; Sluijter, J.P.; et al. Exercise downregulates HIPK2 and HIPK2 inhibition protects against myocardial infarction. EBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehri, A.S.; El-Kott, A.F.; El-Kenawy, A.E.; Khalifa, H.S.; AlRamlawy, A.M. Cadmium chloride induces non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by stimulating miR-34a/SIRT1/FXR/p53 axis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zalzala, M.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y. A metabolic stress-inducible miR-34a-HNF4α pathway regulates lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.G.; Kim, S.U.; Wong, V.W. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.; Finck, B.N. Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzanegi, P.; Dana, A.; Ebrahimpoor, Z.; Asadi, M.; Azarbayjani, M.A. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, R.; Che, L.; Fan, Z.; Gao, W.; Liang, Q.; Lin, S.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Animal exercise studies in cardiovascular research: Current knowledge and optimal design-A position paper of the Committee on Cardiac Rehabilitation, Chinese Medical Doctors’ Association. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Fuente, F.P.; Quezada, L.; Sepúlveda, C.; Monsalves-Alvarez, M.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Sacristán, C.; Chiong, M.; Llanos, M.; Espinosa, A.; Troncoso, R. Exercise regulates lipid droplet dynamics in normal and fatty liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 158519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Morris, R.T.; Laye, M.J.; Borengasser, S.J.; Booth, F.W.; Ibdah, J.A. Daily exercise increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents steatosis in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Am J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G619–G626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor Antony Santiago, J.; Jayachitra, J.; Shenbagam, M.; Nalini, N. Dietary d-limonene alleviates insulin resistance and oxidative stress-induced liver injury in high-fat diet and L-NAME-treated rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, I.; Yamamoto, S.; Kakimoto, M.; Fujii, M.; Honma, K.; Kumazaki, S.; Matsui, M.; Nakayama, H.; Kirihara, S.; Ran, S.; et al. Suppression of nitric oxide synthase aggravates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and atherosclerosis in SHRSP5/Dmcr rat via acceleration of abnormal lipid metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Locatelli, F. ADARs: Allies or enemies? The importance of A-to-I RNA editing in human disease: From cancer to HIV-1. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos Soc. 2012, 87, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shoshan, S.O.; Kagan, P.; Sultan, M.; Barabash, Z.; Dor, C.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Harmelin, A.; Pappo, O.; Marcu-Malina, V.; Ben-Ari, Z.; et al. ADAR1 deletion induces NFκB and interferon signaling dependent liver inflammation and fibrosis. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Chan, T.H.; Tenen, D.G.; Chen, L. RNA editome imbalance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Luo, R.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Peng, J.; Huang, K. ADAR1 inhibits adipogenesis and obesity by interacting with Dicer to promote the maturation of miR-155-5P. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs259333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jin, Y. ADAR-mediated RNA editing in non-coding RNA sequences. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, S.; Pan, X.; Bawa, F.C.; Wang, H.H.; Wang, D.Q.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y. Hepatocyte miR-34a is a key regulator in the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Metab. 2021, 51, 101244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, M.; Cao, Y.; Ma, L.; Shen, Y.; Velikanova, A.A.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y. miR-34a regulates lipid metabolism by targeting SIRT1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with iron overload. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.E.; Duan, L.; He, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, T.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C. Saturated Fatty Acids Promote Hepatocytic Senecence through Regulation of miR-34a/Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e2000383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.L.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, R.N.; Shen, F.; Yan, S.Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, Z.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Fan, J.G. Disease-specific miR-34a as diagnostic marker of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in a Chinese population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9844–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, L.; Li, J.; Song, M.; Yang, C. Exercise-Induced ADAR2 Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through miR-34a. Nutrients 2023, 15, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010121
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Xia L, Li J, Song M, Yang C. Exercise-Induced ADAR2 Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through miR-34a. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhijing, Yaru Zhu, Lu Xia, Jing Li, Meiyi Song, and Changqing Yang. 2023. "Exercise-Induced ADAR2 Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through miR-34a" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010121
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhu, Y., Xia, L., Li, J., Song, M., & Yang, C. (2023). Exercise-Induced ADAR2 Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through miR-34a. Nutrients, 15(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010121




