Pro-Inflammatory Profile of Adipokines in Obesity Contributes to Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
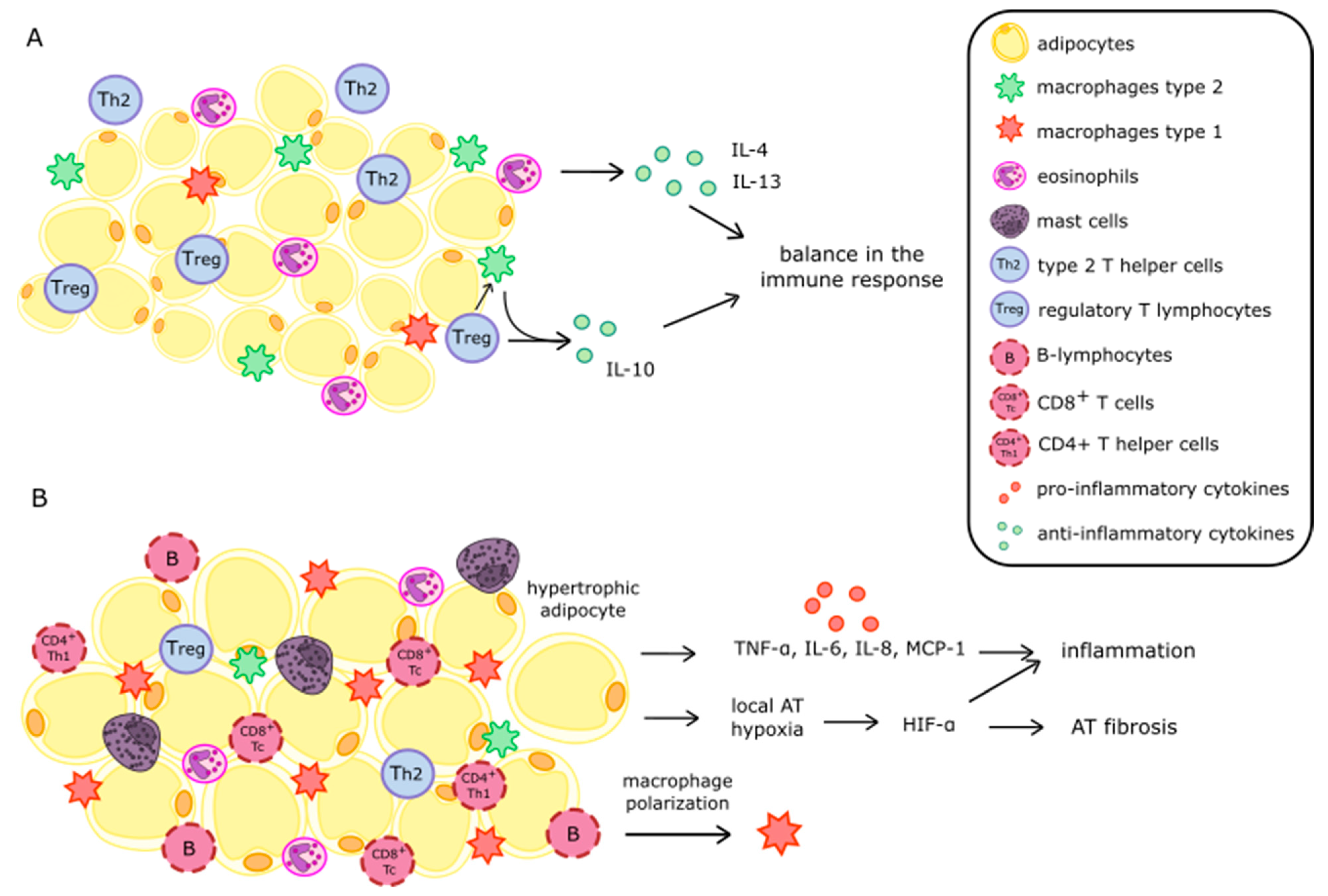
2. Heterogeneity of Adipose Tissue
3. Obesity-Induced Changes in Adipose Tissue
4. Sexual Dimorphism in the Obesity-Induced Metabolic Profile
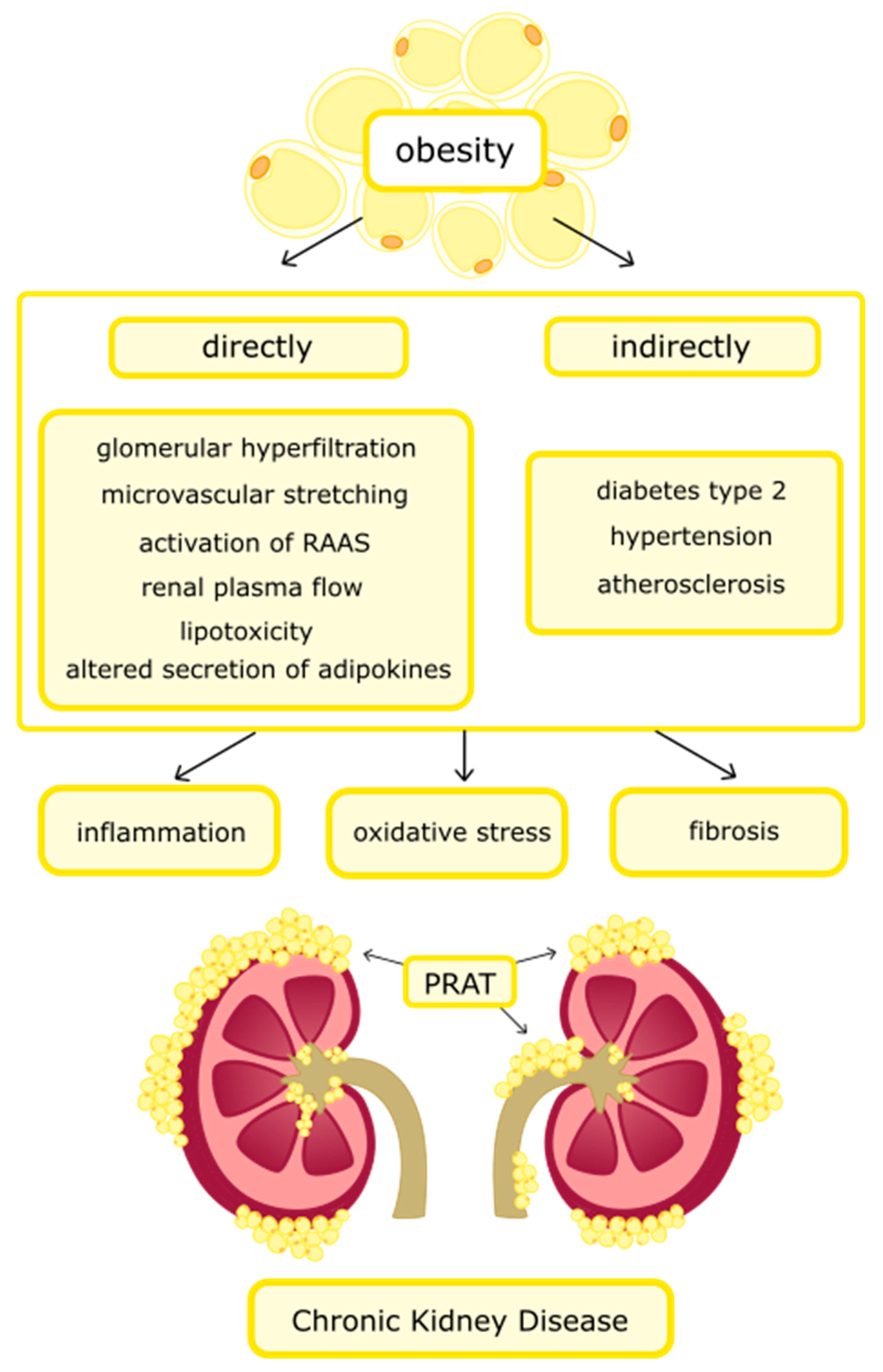
5. Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease
6. Adipokines and Their Influence on Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease
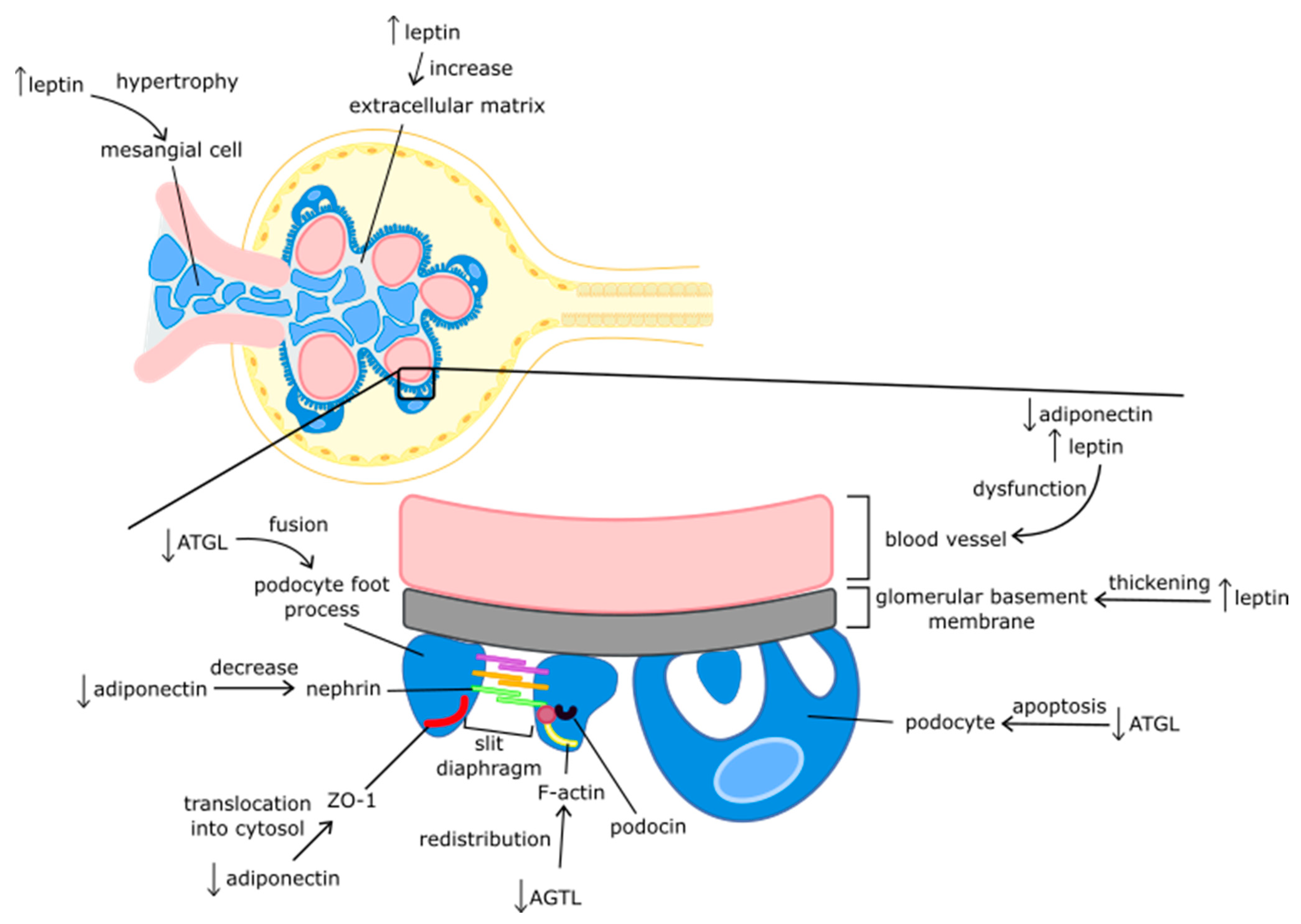
6.1. Leptin
6.2. Adiponectin
6.3. Zinc-α2-Glycoprotein
6.4. Adipose Triglyceride Lipase
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Statistics 2021: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Mattioli, A.V.; Sciomer, S.; Cocchi, C.; Maffei, S.; Gallina, S. Quarantine during COVID-19 outbreak: Changes in diet and physical activity increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Ponzo, V.; Rosato, R.; Scumaci, E.; Goitre, I.; Benso, A.; Belcastro, S.; Crespi, C.; De Michieli, F.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Changes in Weight and Nutritional Habits in Adults with Obesity during the “Lockdown” Period Caused by the COVID-19 Virus Emergency. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divino, V.; Ramasamy, A.; Anupindi, V.R.; Eriksen, K.T.; Olsen, A.H.; DeKoven, M.; Meincke, H.H. Complication-specific direct medical costs by body mass index for 13 obesity-related complications: A retrospective database study. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, J.; Biener, A.; Meyerhoefer, C.; Ding, Y.; Zvenyach, T.; Smolarz, B.G.; Ramasamy, A. Direct medical costs of obesity in the United States and the most populous states. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lainščak, M. Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease. EJIFCC 2009, 20, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Kaze, A.D.; McMullan, C.J.; Isakova, T.; Waikar, S.S. Uric Acid and the Risks of Kidney Failure and Death in Individuals with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Sceppa, C.; Sarnak, M.J.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Madero, M.; Kusek, J.W.; Beck, G.; Kopple, J.D.; Levey, A.S.; Menon, V. Role of adipose tissue in determining muscle mass in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Podkowińska, A.; Formanowicz, D. Chronic kidney disease as oxidative stress-and inflammatory-mediated cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Taboada, M.; Vila-Bedmar, R.; Medina-Gómez, G. From Obesity to Chronic Kidney Disease: How Can Adipose Tissue Affect Renal Function? Nephron 2021, 145, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.D.; Zheng, C.J.; Dong, Y.H.; Zou, Z.Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Yang, Z.G.; Wang, S.; Dong, B.; Ma, J. Sex difference in the mediation roles of an inflammatory factor (hsCRP) and adipokines on the relationship between adiposity and blood pressure. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Arts, I.C.W.; Peeters, R.L.M.; de Kok, T.M.; Ertaylan, G. Adipose tissue in health and disease through the lens of its building blocks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Hadi, H.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Food Ingredients Involved in White-to-Brown Adipose Tissue Conversion and in Calorie Burning. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartelt, A.; Bruns, O.T.; Reimer, R.; Hohenberg, H.; Ittrich, H.; Peldschus, K.; Kaul, M.G.; Tromsdorf, U.I.; Weller, H.; Waurisch, C.; et al. Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.L.; Molica, F.; Kwak, B.R. Browning of White Adipose Tissue as a Therapeutic Tool in the Fight against Atherosclerosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orava, J.; Nuutila, P.; Lidell, M.E.; Oikonen, V.; Noponen, T.; Viljanen, T.; Scheinin, M.; Taittonen, M.; Niemi, T.; Enerbäck, S.; et al. Different metabolic responses of human brown adipose tissue to activation by cold and insulin. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwick, R.K.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Horsley, V.; Plikus, M.V. Anatomical, Physiological, and Functional Diversity of Adipose Tissue. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zitsman, J.L.; Hou, J.; Fennoy, I.; Guo, K.; Feinberg, J.; Leibel, R.L. Fat cell size and adipokine expression in relation to gender, depot, and metabolic risk factors in morbidly obese adolescents. Obesity 2014, 22, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction as Determinant of Obesity-Associated Metabolic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Góralska, M.; Majewska-Szczepanik, M.; Szczepanik, M. Immunological mechanisms involved in obesity and their role in metabolic syndrome. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 1384–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.; Apovian, C. Macrophage functions in lean and obese adipose tissue. Metabolism 2017, 72, 120–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuryłowicz, A.; Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M. Induction of Adipose Tissue Browning as a Strategy to Combat Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.; Varghese, M.; Singer, K. Gender and Sex Differences in Adipose Tissue. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. The sexual dimorphism of obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: Mechanistic links. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Murakami, M.; Shirai, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Kawada, T.; Matsui, T.; Funaba, M. Role of estradiol and testosterone in Ucp1 expression in brown/beige adipocytes. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2018, 36, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; McClusky, R.; Chen, J.; Beaven, S.W.; Tontonoz, P.; Arnold, A.P.; Reue, K. The number of x chromosomes causes sex differences in adiposity in mice. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walicka, M.; Bik, W.; Wolińska-Witort, E.; Marcinowska-Suchowierska, E. Gender dependent dimorphism in adipokines levels and its correlations with insulin resistance in extremely obese patients. Postępy Nauk. Med. 2013, 24, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Selthofer-Relatić, K.; Radić, R.; Stupin, A.; Šišljagić, V.; Bošnjak, I.; Bulj, N.; Selthofer, R.; Delić Brkljačić, D. Leptin/adiponectin ratio in overweight patients—gender differences. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2018, 15, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecelbarger, C.M. Sex Differences in Renal Physiology and Pathophysiology. In Sex Differences in Physiology; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease: Evaluation, Classification and Stratification. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 1–266.
- Rhee, C.M.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. The dual roles of obesity in chronic kidney disease: A review of the current literature. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y. Kidney Damage Caused by Obesity and Its Feasible Treatment Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; Morales, E. The Fatty Kidney: Obesity and Renal Disease. Nephron 2017, 136, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, A.; Glassock, R.J. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy and Single-Nephron GFR. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cao, C.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Z. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy: A Latent Change in Obesity Requiring More Attention. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2020, 45, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Edelstein, M.; Weinstein, T.; Chagnac, A. Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy: Clinical Management. Semin. Nephrol. 2021, 41, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caus, M.; Eritja, À.; Bozic, M. Role of microRNAs in Obesity-Related Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnac, A.; Zingerman, B.; Rozen-Zvi, B.; Herman-Edelstein, M. Consequences of Glomerular Hyperfiltration: The Role of Physical Forces in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes and Obesity. Nephron 2019, 143, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobar, A.; Ori, Y.; Benchetrit, S.; Milo, G.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Zingerman, B.; Lev, N.; Gafter, U.; Chagnac, A. Proximal tubular hypertrophy and enlarged glomerular and proximal tubular urinary space in obese subjects with proteinuria. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogna, A.; Forni Ogna, V.; Bochud, M.; Guessous, I.; Paccaud, F.; Burnier, M.; Wuerzner, G. Association between obesity and glomerular hyperfiltration: The confounding effect of smoking and sodium and protein intakes. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helal, I.; Fick-Brosnahan, G.; Reed-Gitomer, B.; Schrier, R.W. Glomerular hyperfiltration: Definitions, mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo-Ríos, L.; Mas, S.; Marín-Royo, G.; Mezzano, S.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Moreno, J.A.; Egido, J. Lipotoxicity and Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vries, A.P.; Ruggenenti, P.; Ruan, X.Z.; Praga, M.; Cruzado, J.M.; Bajema, I.M.; D’Agati, V.D.; Lamb, H.J.; Pongrac Barlovic, D.; Hojs, R.; et al. Fatty kidney: Emerging role of ectopic lipid in obesity-related renal disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoraș, A.; Balan, R.A.; Căruntu, I.D.; Giușcă, S.E.; Lozneanu, L.; Avadanei, R.E.; Rusu, A.; Riscanu, L.A.; Amalinei, C. Perirenal Adipose Tissue-Current Knowledge and Future Opportunities. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, J.K.; Soares, R.N.; Power, G.; Harper, J.L.; Smith, J.A.; Shariffi, B.; Jacob, D.W.; Manrique-Acevedo, C.; Padilla, J. Hyperinsulinemia blunts sympathetic vasoconstriction: A possible role of β-adrenergic activation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2021, 320, R771–R779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.S.; Noh, M.R.; Kim, J.; Padanilam, B.J. Defective Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation and Lipotoxicity in Kidney Diseases. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, N.; Mao, E.W.; Hou, N.N.; Liu, Y.P.; Han, F.; Sun, X.D. Novel insight into perirenal adipose tissue: A neglected adipose depot linking cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease. World J. Diabetes 2020, 11, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Llorens, S.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. An Overview of the Role of Adipokines in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, M.P.; Ziyadeh, F.N. Overview of the physiology and pathophysiology of leptin with special emphasis on its role in the kidney. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrahian, S.M.; Falkner, B. Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 956, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Scherer, P.E. Immunologic and endocrine functions of adipose tissue: Implications for kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podestà, M.A.; Ponticelli, C. Autoimmunity in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: A Long-Standing Yet Elusive Association. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 604961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüster, C.; Wolf, G. Adipokines promote chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procaccini, C.; Jirillo, E.; Matarese, G. Leptin as an immunomodulator. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Teo, B.W.; Tai, E.S.; Lim, S.C.; Chan, C.M.; Sethi, S.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Elevated serum leptin, adiponectin and leptin to adiponectin ratio is associated with chronic kidney disease in Asian adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambarkar, M.; Pemmaraju, S.V.; Gouroju, S.; Manohar, S.M.; Bitla, A.R.; Yajamanam, N.; Vishnubhotla, S. Adipokines and their Relation to Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, BC04–BC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korczyńska, J.; Czumaj, A.; Chmielewski, M.; Śledziński, M.; Mika, A.; Śledziński, T. Increased Expression of the Leptin Gene in Adipose Tissue of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease-The Possible Role of an Abnormal Serum Fatty Acid Profile. Metabolites 2020, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navaneethan, S.D.; Kirwan, J.P.; Remer, E.M.; Schneider, E.; Addeman, B.; Arrigain, S.; Horwitz, E.; Fink, J.C.; Lash, J.P.; McKenzie, C.A.; et al. Adiposity, Physical Function, and Their Associations with Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Adipokines in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamadi, F.; Bosorgmehr, R.; Razeghi, E. Relationship between serum leptin level and laboratory and anthropometric indices of malnutrition in patients on hemodialysis. Indian J. Nephrol. 2008, 18, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppe, L.; Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Kidney cachexia or protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease: Facts and numbers. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, Y.T.; Lin, Y.L.; Kuo, C.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Wang, C.H.; Hsu, B.G. Low serum leptin levels are associated with malnutrition status according to malnutrition-inflammation score in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial. Int. 2020, 24, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.A.; Romanovsky, A.A. Leptin: At the crossroads of energy balance and systemic inflammation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2007, 46, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, A.; Hernández-Coronado, C.G.; Rosales-Torres, A.M.; Hernández-Medrano, J.H. Leptin regulates neuropeptides associated with food intake and GnRH secretion. Ann. Endocrinol. 2019, 80, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, R.H.; Cheung, W.; Cone, R.D.; Marks, D.L. Orexigenic and anorexigenic mechanisms in the control of nutrition in chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2005, 20, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Reed, F.; Herzog, H. Leptin signalling on arcuate NPY neurones controls adiposity independent of energy balance or diet composition. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32, e12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zou, Y.C.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.F.; Chen, D.X.; Wei, L.B. Neuropeptide Y levels are associated with nutritional status and cardiovascular events in adults with chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Ortiz, A.; Blumbyte, I.A.; Rudolf, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Malyszko, J.; Spasovski, G.; Carriazo, S.; Viggiano, D.; Kurganaite, J.; et al. Neuropeptide Y as a risk factor for cardiorenal disease and cognitive dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: Translational opportunities and challenges. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 37, ii14–ii23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; D’Arrigo, G.; Leonardis, D.; Pizzini, P.; Postorino, M.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F. Neuropeptide Y predicts cardiovascular events in chronic kidney disease patients: A cohort study. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markaki, A.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Venihaki, M.; Kyriazis, J.; Perakis, K.; Stylianou, K. Associations of adiponectin and leptin levels with protein-energy wasting, in end stage renal disease patients. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.B.; Liabeuf, S.; Okazaki, H.; Lenglet, A.; Desjardins, L.; Lemke, H.D.; Vanholder, R.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. The clinical impact of plasma leptin levels in a cohort of chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Kidney J. 2013, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, T.T.; Liao, S.C.; Lee, W.C.; Lee, P.S.; Ng, H.Y.; Chien, Y.S.; Lee, C.T. Gelsolin and adipokines are associated with protein-energy wasting in hemodialysis patients. Artif. Organs 2015, 39, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korczyńska, J.; Czumaj, A.; Chmielewski, M.; Świerczyński, J.; Śledziński, T. The Causes and Potential Injurious Effects of Elevated Serum Leptin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, G. Cardiovascular effects of leptin. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.W.; Chi, P.J.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, C.H.; Hsu, B.G. Serum leptin levels are positively associated with aortic stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 3–5. Adipocyte 2020, 9, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.P.; Lee, M.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Ho, G.J.; Shih, M.H.; Hsu, B.G. Hyperleptinemia is a risk factor for the development of central arterial stiffness in kidney transplant patients. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Lee, C.J.; Wang, C.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Liou, H.H.; Hsu, B.G. Hyperleptinemia positively associated with central arterial stiffness in hemodialysis patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoccali, C.; Postorino, M.; Marino, C.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; Tripepi, G. Waist circumference modifies the relationship between the adipose tissue cytokines leptin and adiponectin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in haemodialysis patients. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 269, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, A.; Rattensperger, D.; Zidek, W.; Tepel, M. Low serum leptin predicts mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5. Obesity 2007, 15, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, M.Z.; Nagy, K.; Remport, A.; Gaipov, A.; Fülöp, T.; Czira, M.E.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mucsi, I.; Mathe, Z. Association Between Serum Leptin Level and Mortality in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2017, 27, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christou, G.A.; Kiortsis, D.N. The role of adiponectin in renal physiology and development of albuminuria. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, R49–R61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin/AdipoR Research and Its Implications for Lifestyle-Related Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cammisotto, P.G.; Bendayan, M. Adiponectin stimulates phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha in renal glomeruli. J. Mol. Histol. 2008, 39, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, T.; De, S.; Tanigawa, S.; Miike, K.; Islam, M.; Soga, M.; Era, T.; Shiona, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Nakazato, H.; et al. Impaired NEPHRIN localization in kidney organoids derived from nephrotic patient iPS cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y. Advances in understanding the role of adiponectin in renal fibrosis. Nephrology 2021, 26, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M.; et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappaB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Ramachandrarao, S.; Qiu, G.; Usui, H.K.; Zhu, Y.; Dunn, S.R.; Ouedraogo, R.; Hough, K.; McCue, P.; Chan, L.; et al. Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, D.L.; Green, N.H.; Danesh, F.R. The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miricescu, D.; Balan, D.G.; Tulin, A.; Stiru, O.; Vacaroiu, I.A.; Mihai, D.A.; Popa, C.C.; Enyedi, M.; Nedelea, A.S.; Nica, A.E.; et al. Impact of adipose tissue in chronic kidney disease development (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.W.; Yen, C.J.; Chiang, H.W.; Hung, K.Y.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, K.D. Adiponectin in peritoneal dialysis patients: A comparison with hemodialysis patients and subjects with normal renal function. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudek, J.; Adamczak, M.; Karkoszka, H.; Budziński, G.; Ignacy, W.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Cierpka, L.; Kokot, F.; Wiecek, A. Plasma adiponectin concentration before and after successful kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 2186–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, M.A.; Canziani, M.E.; Sanches, F.R.; Velludo, C.M.; Carrero, J.J.; Bazanelli, A.P.; Draibe, S.A.; Cuppari, L. Variations in adiponectin levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: A prospective study of 12 months. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2012, 34, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaynar, K.; Kural, B.V.; Ulusoy, S.; Cansiz, M.; Akcan, B.; Misir, N.; Yaman, S.; Kaya, N. Is there any interaction of resistin and adiponectin levels with protein-energy wasting among patients with chronic kidney disease. Hemodial. Int. 2014, 18, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.H.; Oh, T.R.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Ma, S.K.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, E.H. High serum adiponectin as a biomarker of renal dysfunction: Results from the KNOW-CKD study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.M.; Nguyen, D.V.; Moradi, H.; Brunelli, S.M.; Dukkipati, R.; Jing, J.; Nakata, T.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Brent, G.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association of Adiponectin with Body Composition and Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Otsuka, H.; Yanai, M.; Haketa, A.; Hara, M.; Hishiki, M.; Abe, M.; Soma, M. Adiponectin is not associated with renal function decline in community-dwelling elderly adults. Medicine 2018, 97, e10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, S.; Ishimura, E.; Norimine, K.; Tsuboniwa, N.; Kagitani, S.; Yamakawa, K.; Yamakawa, T.; Sato, K.K.; Hayashi, T.; Shoji, S.; et al. Serum adiponectin and bone mineral density in male hemodialysis patients. Osteoporos. Int. 2012, 23, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, K.B.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Park, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Yoo, T.H.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.H. Serum adiponectin and protein-energy wasting in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Nutrition 2017, 33, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Cho, S.; Kim, S.R. The association between serum adiponectin levels and nutritional status of hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2011, 33, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervisoglu, E.; Eraldemir, C.; Kalender, B.; Kir, H.M.; Caglayan, C. Adipocytokines leptin and adiponectin, and measures of malnutrition-inflammation in chronic renal failure: Is there a relationship? J. Ren. Nutr. 2008, 18, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Li, L.; Tighiouart, H.; Jaber, B.L.; Pereira, B.J.; Balakrishnan, V.S. Plasma adiponectin levels and clinical outcomes among haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, B.; Kronenberg, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Haller, H.; Morath, C.; Ritz, E.; Fliser, D. Renal insulin resistance syndrome, adiponectin and cardiovascular events in patients with kidney disease: The mild and moderate kidney disease study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, E.; Waked, E.; Nabil, M.; El-Bendary, O. Adiponectin and cardiovascular outcomes among hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2012, 35, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, H.O. An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Balakrishnan, V.; Madero, M.; Pereira, A.A.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; et al. Adiponectin and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.Y.; Bae, E.H.; Ma, S.K.; Chae, D.W.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, S.W. Association of serum adiponectin level with albuminuria in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2016, 20, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Ku, E.J.; Hong, E.S.; Lim, S.; Kim, K.W.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Park, Y.J.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. High serum adiponectin concentration and low body mass index are significantly associated with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in an elderly cohort, “adiponectin paradox”: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 183, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Yun, H.R.; Park, S.; Jhee, J.H.; Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Sung, S.A.; Lee, J.; et al. High serum adiponectin is associated with anemia development in chronic kidney disease: The results from the KNOW-CKD study. Cytokine 2018, 103, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, O.; Fujita, M.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Asano, Y.; Ogai, A.; Okazaki, H.; Asai, M.; Nagamachi, Y.; Maeda, N.; et al. Natriuretic peptides enhance the production of adiponectin in human adipocytes and in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Kim, J.K.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Yoo, D.E.; Lee, M.J.; Shin, D.H.; Han, S.H.; Han, D.S.; et al. Leptin/adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of mortality in nondiabetic peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2013, 33, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, B.; Becerril, S.; Salvador, J.; Colina, I.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin Ratio is a Functional Biomarker of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, S.T.; Tisdale, M.J. The role of glucocorticoids in the induction of zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein expression in adipose tissue in cancer cachexia. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaszak, M.; Górna, I.; Przysławski, J. Zinc and the Innovative Zinc-α2-Glycoprotein Adipokine Play an Important Role in Lipid Metabolism: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elattar, S.; Dimri, M.; Satyanarayana, A. The tumor secretory factor ZAG promotes white adipose tissue browning and energy wasting. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4727–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.M.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.Y.; Liu, C.Y. Adipokine zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein as a novel urinary biomarker presents earlier than microalbuminuria in diabetic nephropathy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woźny, Ł.A.; Morawiecka-Pietrzak, M.; Jaszczura, M.; Ziora, K.; Grzeszczak, W. The new adipokine zinc-α2-glycoprotein (ZAG) as a link between adipose tissue and kidney? Endokrynol. Pol. 2019, 70, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mracek, T.; Ding, Q.; Tzanavari, T.; Kos, K.; Pinkney, J.; Wilding, J.; Trayhurn, P.; Bing, C. The adipokine zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein (ZAG) is downregulated with fat mass expansion in obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörensen-Zender, I.; Beneke, J.; Schmidt, B.M.; Menne, J.; Haller, H.; Schmitt, R. Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein in patients with acute and chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelletier, C.C.; Koppe, L.; Croze, M.L.; Kalbacher, E.; Vella, R.E.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Géloën, A.; Badet, L.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. White adipose tissue overproduces the lipid-mobilizing factor zinc α2-glycoprotein in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, D.; Trayhurn, P.; Bing, C. Macrophage-secreted factors inhibit ZAG expression and secretion by human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 325, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchara, A.; Yi, D.; Pastural, M.; Granjon, S.; Selag, J.C.; Laville, M.; Arkouche, W.; Pelletier, S.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O.; et al. Serum levels of the adipokine zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein (ZAG) predict mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, F.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Deng, J.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Pan, H.; Li, N.S.; Shi, Y.F. Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein is involved in regulation of body weight through inhibition of lipogenic enzymes in adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, C.; Mo, L.; Wang, H.; Peng, X.; Deng, F.; Chen, L. Expression and Function of Zinc-α2-Glycoprotein. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, D.C.; Lam, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Tso, A.W.; Xu, A. Serum zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein correlates with adiposity, triglycerides, and the key components of the metabolic syndrome in Chinese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J.; Mahdavi-Mazdeh, M.; Yaseri, M.; Zahed, N.S.; Alipoor, E. Comparative Assessment of Serum Adipokines Zinc-α2-glycoprotein and Adipose Triglyceride Lipase, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors Between Normal Weight and Obese Patients with Hemodialysis. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, V.O.; Lobo, J.C.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Farage, N.E.; Abdalla, D.S.; Leite, M.J.; Mafra, D. Is zinc-α2-glycoprotein a cardiovascular protective factor for patients undergoing hemodialysis? Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, S.J.; Yuan, G.Y.; Zhou, L.B.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.Z.; Chen, J.J. Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 6746–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoiswohl, G.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; Menke, M.N.; Wills, R.C.; Surlow, B.A.; Basantani, M.K.; Sitnick, M.T.; Cai, L.; Yazbeck, C.F.; Stolz, D.B.; et al. Impact of Reduced ATGL-Mediated Adipocyte Lipolysis on Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3610–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, Y.; Han, J.; Hu, J.; He, T.; Yan, T.; Huang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Mei, H.; Liao, Y.; et al. ATGL deficiency induces podocyte apoptosis and leads to glomerular filtration barrier damage. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Näf, S.; Escoté, X.; Caubet, E.; Gomez, J.M.; Miranda, M.; Chacon, M.R.; Gonzalez-Clemente, J.M.; Gallart, L.; Gutierrez, C.; et al. Circulating and adipose tissue gene expression of zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein in obesity: Its relationship with adipokine and lipolytic gene markers in subcutaneous and visceral fat. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5062–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alipoor, E.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Mahdavi-Mazdeh, M.; Yaseri, M.; Zahed, N.S.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. The relationship of serum adipokines with malnutrition inflammation score in haemodialysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salatzki, J.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Bentele, K.; Blumrich, A.; Smeir, E.; Ban, Z.; Brix, S.; Grune, J.; Beyhoff, N.; Klopfleisch, R.; et al. Adipose tissue ATGL modifies the cardiac lipidome in pressure-overload-induced left ventricular failure. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Meyer, C.; Rozman, J.; Heldmaier, G.; Maier, R.; Theussl, C.; Eder, S.; et al. Defective lipolysis and altered energy metabolism in mice lacking adipose triglyceride lipase. Science 2006, 312, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölkart, G.; Schrammel, A.; Dörffel, K.; Haemmerle, G.; Zechner, R.; Mayer, B. Cardiac dysfunction in adipose triglyceride lipase deficiency: Treatment with a PPARα agonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Activity | Leptin | Adiponectin | ZAG | ATGL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma levels in obesity | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Plasma levels in CKD | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | U |
| Malnutrition/PEW | ↑/↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Oxidative stress | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Inflammation | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| CVR | ↑ | ↑/↓ | ↑ | U |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czaja-Stolc, S.; Potrykus, M.; Stankiewicz, M.; Kaska, Ł.; Małgorzewicz, S. Pro-Inflammatory Profile of Adipokines in Obesity Contributes to Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071457
Czaja-Stolc S, Potrykus M, Stankiewicz M, Kaska Ł, Małgorzewicz S. Pro-Inflammatory Profile of Adipokines in Obesity Contributes to Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071457
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzaja-Stolc, Sylwia, Marta Potrykus, Marta Stankiewicz, Łukasz Kaska, and Sylwia Małgorzewicz. 2022. "Pro-Inflammatory Profile of Adipokines in Obesity Contributes to Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 14, no. 7: 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071457
APA StyleCzaja-Stolc, S., Potrykus, M., Stankiewicz, M., Kaska, Ł., & Małgorzewicz, S. (2022). Pro-Inflammatory Profile of Adipokines in Obesity Contributes to Pathogenesis, Nutritional Disorders, and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 14(7), 1457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071457







