Association between Dietary Behaviors and BMI Stratified by Sex and the ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Japanese Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Genotyping of the rs671 Polymorphism in Participants
2.3. QC of Genotyping Data
2.4. Phenotypes Based on Data Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Associations between DBs and BMI
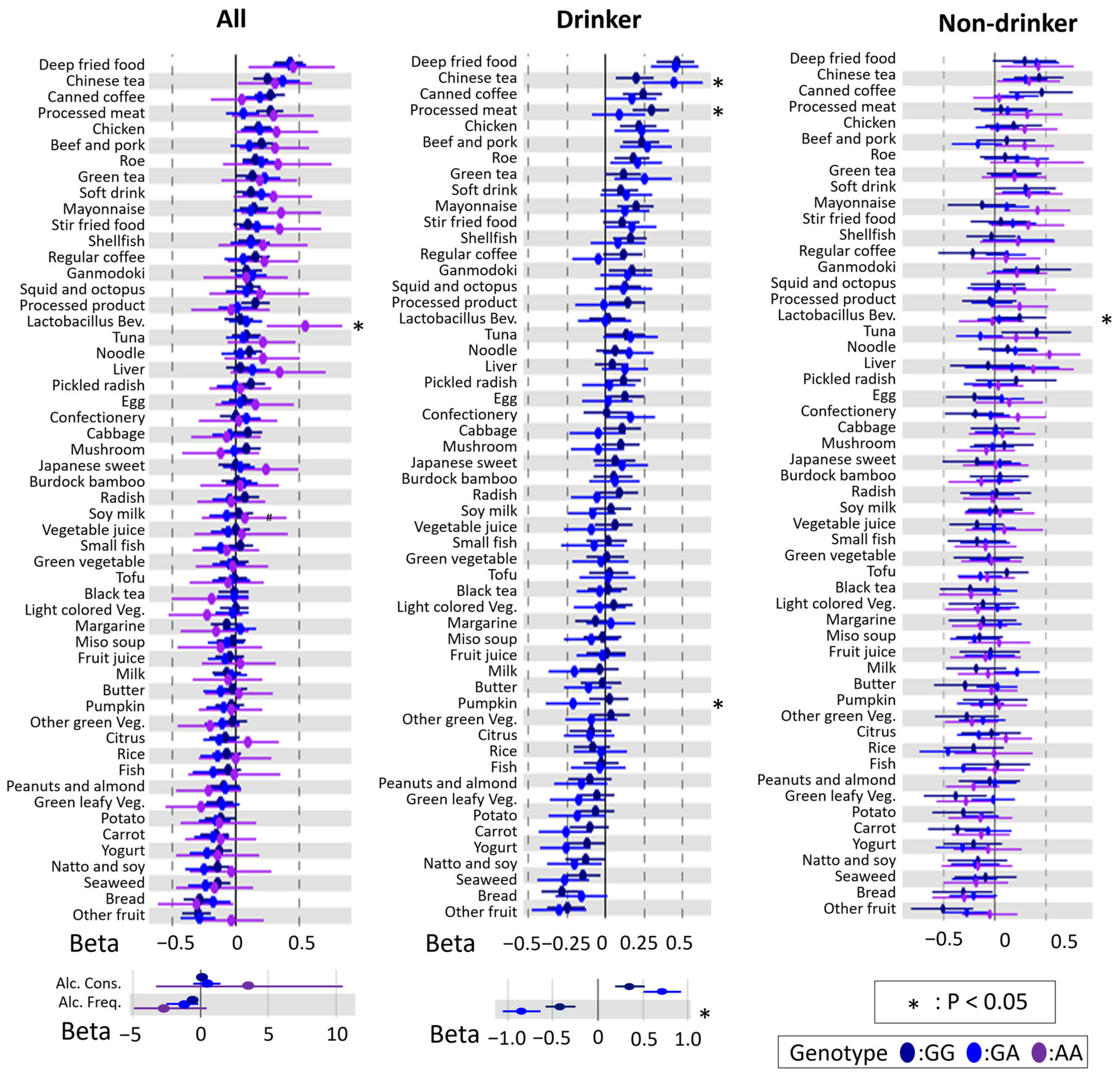
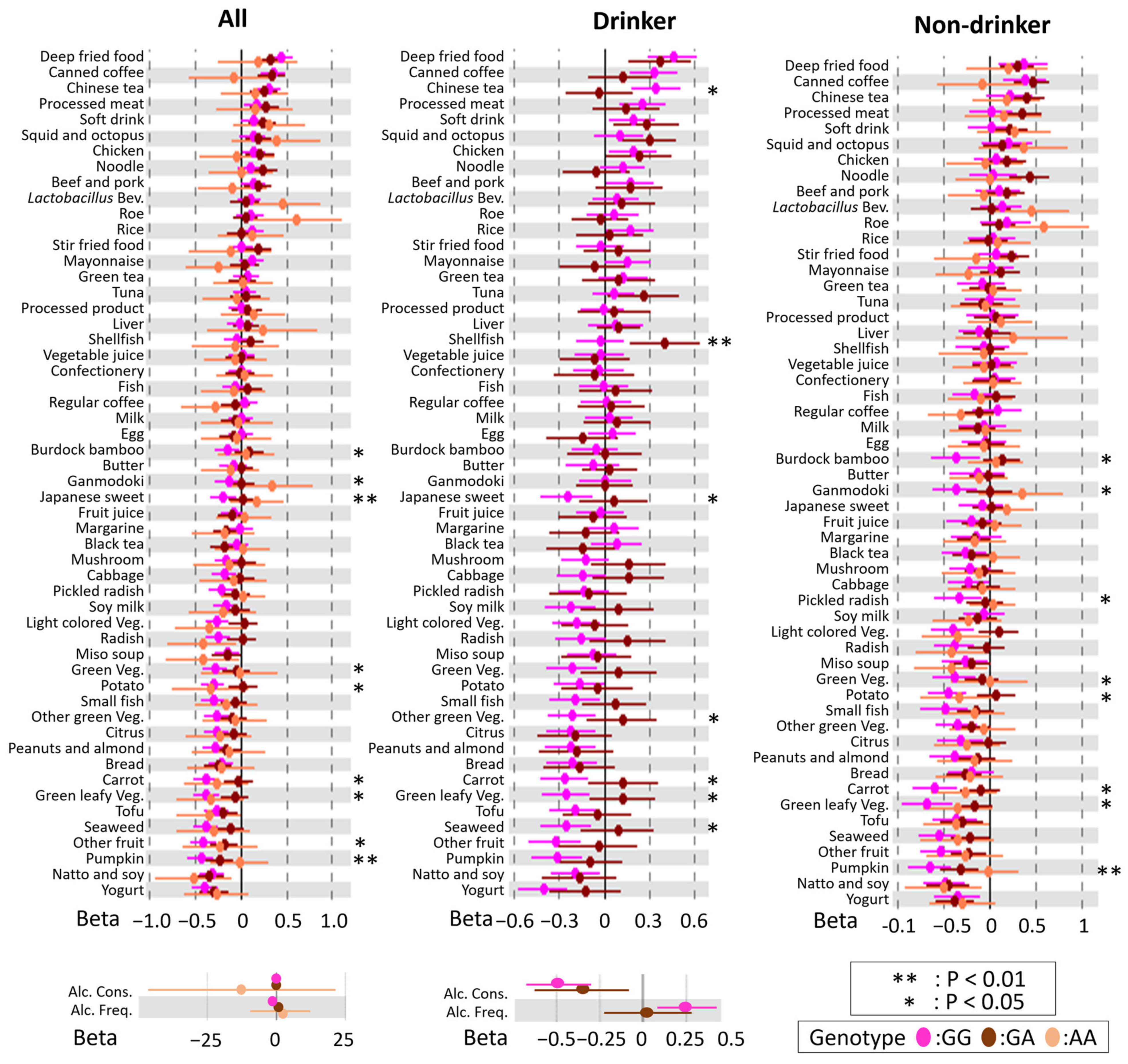
3.3. Modification of rs671 Polymorphism with Respect to the Association between DB and BMI
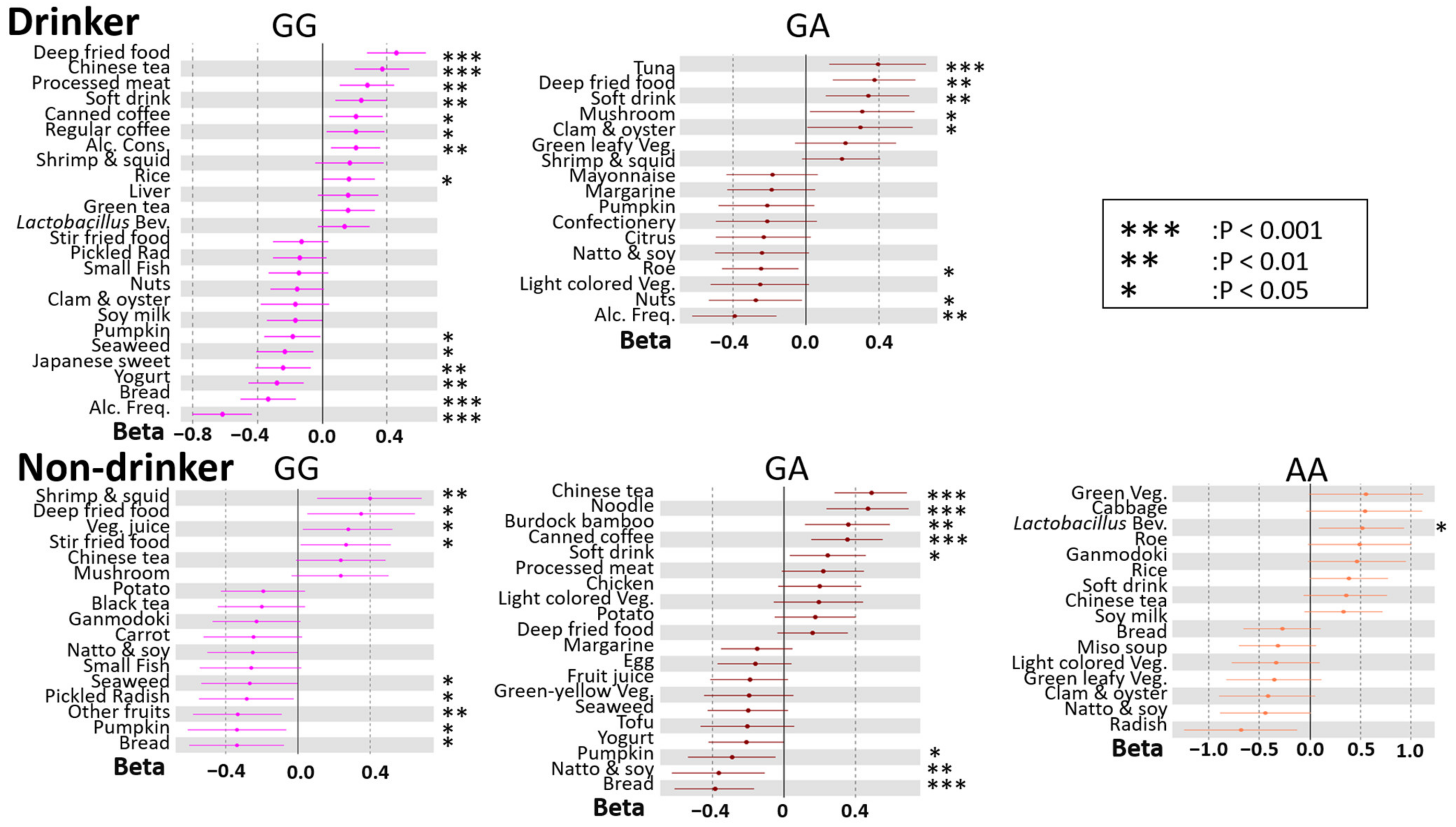
3.4. rs671 Genotype-Specific Associations between DBs and BMI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodgers, G.P.; Collins, F.S. Precision Nutrition-the Answer to “What to Eat to Stay Healthy”. JAMA 2020, 324, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Cristobal, R.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ordovas, J.M.; Martínez, J.A. Contribution of macronutrients to obesity: Implications for precision nutrition. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. 2020–2030 Strategic Plan for NIH Nutrition Research: A Report of the NIH Nutrition Research Task Force [Internet]; NIH: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/about-niddk/strategic-plans-reports/strategic-plan-nih-nutrition-research (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Wall, T.L.; Luczak, S.E.; Hiller-Sturmhöfel, S. Biology, genetics, and environment: Underlying factors influencing alcohol metabolism. Alcohol. Res. 2016, 38, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, F.; Isono, M.; Nabika, T.; Katsuya, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Ogihara, T.; Yamori, Y.; Fujioka, A.; et al. Confirmation of ALDH2 as a Major locus of drinking behavior and of its variants regulating multiple metabolic phenotypes in a Japanese population. Circ. J. 2011, 75, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Jia, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Identification of the 12q24 locus associated with fish intake frequency by genome-wide meta-analysis in Japanese populations. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Igarashi, M.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. GWAS of habitual coffee consumption reveals a sex difference in the genetic effect of the 12q24 locus in the Japanese population. BMC Genet. 2019, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Igarashi, M.; Jia, H.; Nogawa, S.; Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. A genome-wide association study identifies the association between the 12q24 locus and black tea consumption in Japanese populations. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawafune, K.; Hachiya, T.; Nogawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Jia, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Strong association between the 12q24 locus and sweet taste preference in the Japanese population revealed by genome-wide meta-analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, N.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Takahashi, A.; Momozawa, Y.; Ikegawa, S.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N.; Hirata, M.; et al. GWAS of 165,084 Japanese individuals identified nine loci associated with dietary habits. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2020, 4, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa-Senda, H.; Hachiya, T.; Shimizu, A.; Hosono, S.; Oze, I.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuo, K.; Ito, H.; Hara, M.; Nishida, Y.; et al. A genome-wide association study in the Japanese population identifies the 12q24 locus for habitual coffee consumption: The J-MICC Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Oze, I.; Doi, Y.; Narita, A.; Shimizu, A.; Imaeda, N.; Goto, C.; Matsui, K.; et al. A genome-wide association study on fish consumption in a Japanese population-the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Doi, Y.; Narita, A.; Shimizu, A.; Imaeda, N.; Goto, C.; Matsui, K.; Kadota, A.; Miura, K.; et al. A genome-wide association study on confection consumption in a Japanese population: The Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Wu, J.; Cai, Q.; Chen, E.Z.; Jiang, Z.Y. Association between Glu504Lys polymorphism of ALDH2 gene and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, A.; Sasazuki, S.; Matsuo, K.; Ito, H.; Sawada, N.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Inoue, M.; Tsugane, S.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of ADH1B, ADH1C and ALDH2, alcohol consumption, and the risk of gastric cancer: The Japan Public Health Center-based prospective study. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X.; Matsuo, K.; Takezaki, T.; Tajima, K.; Cao, J. A novel polymorphism rs1329149 of CYP2E1 and a known polymorphism rs671 of ALDH2 of alcohol metabolizing enzymes are associated with colorectal cancer in a southwestern Chinese population. Cancer Eepidemio. Bbiomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Oze, I.; Hosono, S.; Ito, H.; Watanabe, M.; Ishioka, K.; Ito, S.; Tajima, M.; Yatabe, Y.; Yasumasa, N.; et al. The aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) Glu504Lys polymorphism interacts with alcohol drinking in the risk of stomach cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, P.K.; Yang, L.; Kartsonaki, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Du, H.; Kerosi, R.; Hacker, A.; Liu, J.; Yu, C.; et al. Alcohol metabolism genes and risks of site-specific cancers in Chinese adults: An 11-year prospective study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.J.; Cho, Y.; Davey Smith, G.D. Alcohol consumption, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene polymorphisms, and cardiovascular health in Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Won, S.; Relton, C.L.; Davey Smith, G.; Shin, M.J. Alcohol intake and cardiovascular risk factors: A Mendelian randomisation study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cai, X.; Lian, F.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Y.; Cao, C.; Shao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liangwen, X.; et al. Interactions between ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism and lifestyle behaviors on coronary artery disease risk in a Chinese Han population with dyslipidemia: A guide to targeted heart health management. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, R.; Sun, X.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, S.; Yan, D.; He, Z.; et al. Effects of obesity related genetic variations on visceral and subcutaneous fat distribution in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchihashi-Makaya, M.; Serizawa, M.; Yanai, K.; Katsuya, T.; Takeuchi, F.; Fujioka, A.; Yamori, Y.; Ogihara, T.; Kato, N. Gene–environmental interaction regarding alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in the Japanese general population. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Q. Associations between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) rs671 genetic polymorphisms, lifestyles and hypertension risk in Chinese Han people. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Park, S.; Jin, H.S. Interaction between ALDH2 rs671 and life habits affects the risk of hypertension in Koreans: A STROBE observational study. Medicine 2021, 100, e26664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Qian, L.; Jie, L.; Fang, Z. Association between ALDH-2 rs671 and essential hypertension risk or blood pressure levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zheng, W.; Okada, Y.; Takeuchi, F.; Tabara, Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Dorajoo, R.; Li, H.; Tsai, F.J.; Yang, X.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in East Asian-ancestry populations identifies four new loci for body mass index. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5492–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zeng, Q. The association and interaction of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphisms with food group intake and probability of having non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.L.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, M.E.J.; Vlachou, P.; Govan, L.; Han, T.S. Different associations between body composition and alcohol when assessed by exposure frequency or by quantitative estimates of consumption. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traversy, G.; Chaput, J.P. Alcohol consumption and obesity: An update. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeomans, M.R. Alcohol, appetite and energy balance: Is alcohol intake a risk factor for obesity? Physiol. Behav. 2010, 100, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Xu, X.Y.; Tang, G.Y.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, H.B. Dietary plants, gut microbiota, and obesity: Effects and mechanisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Ferreira, D.M.T.P.; Rosado, E.L.; Soares-Mota, M. Effect of Lactobacillus on body weight and body fat in overweight subjects: A systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny Núñez, I.; Maldonado Galdeano, C.; de Moreno de LeBlanc, A.; Perdigón, G. Lactobacillus casei CRL 431 administration decreases inflammatory cytokines in a diet-induced obese mouse model. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ağagündüz, D.; Yılmaz, B.; Şahin, T.Ö.; Güneşliol, B.E.; Ayten, Ş.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; Rocha, J.M.; Bartkiene, E.; Özogul, F. Dairy lactic acid bacteria and their potential function in dietetics: The food–gut-health axis. Foods 2021, 10, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Hu, J.T.; Chiu, C.F.; Hung, S.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Chuang, H.L. Aldehyde dehydrogenase mutation exacerbated high-fat-diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with gut microbiota remodeling in male mice. Biology 2021, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Rios, E.; Castro, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y.; Dixon, D. Genistein: Dual role in women’s health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.R.; Chen, K.H. Utilization of isoflavones in soybeans for women with menopausal syndrome: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F.; Clegg, D.J. The sexual dimorphism of obesity. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2015, 402, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizcano, F.; Guzmán, G. Estrogen deficiency and the origin of obesity during menopause. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 757461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Male | Female | pinteractionc | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype a | Beta | SE | p Trend b | Genotype a | Beta | SE | p Trend b | ||||||
| GG | GA | AA | GG | GA | AA | ||||||||
| Number | 3474 | 2556 | 495 | 3203 | 2163 | 380 | |||||||
| Age, years d | 50.41 ± 13.58 | 50.71 ± 13.4 | 51.49 ± 13.31 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 49.46 ± 12.76 | 50.35 ± 12.61 | 50.49 ± 13.01 | 0.7 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.48 |
| BMI, kg/m2 d | 23.96 ± 3.38 | 23.88 ± 3.53 | 23.53 ± 3.33 | −0.16 | 0.07 | 0.002 | 22.25 ± 3.85 | 21.98 ± 3.70 | 22.05 ± 3.67 | −0.18 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.82 |
| Alcohol intake d | |||||||||||||
| Alcohol frequency, times/week | 3.67 ± 2.79 | 2.05 ± 2.57 | 0.08 ± 0.38 | −1.71 | 0.05 | <0.001 | 2.27 ± 2.58 | 0.88 ± 1.82 | 0.03 ± 0.11 | −1.25 | 0.05 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol frequency, times/week | 13.57 ± 15.37 | 6.09 ± 10.48 | 0.11 ± 0.60 | −7.06 | 0.25 | <0.001 | 6.32 ± 10.06 | 2.07 ± 6.17 | 0.02 ± 0.13 | −3.68 | 0.18 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Igarashi, M.; Nogawa, S.; Hachiya, T.; Furukawa, K.; Takahashi, S.; Jia, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Association between Dietary Behaviors and BMI Stratified by Sex and the ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Japanese Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235116
Igarashi M, Nogawa S, Hachiya T, Furukawa K, Takahashi S, Jia H, Saito K, Kato H. Association between Dietary Behaviors and BMI Stratified by Sex and the ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Japanese Adults. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235116
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgarashi, Maki, Shun Nogawa, Tsuyoshi Hachiya, Kyohei Furukawa, Shoko Takahashi, Huijuan Jia, Kenji Saito, and Hisanori Kato. 2022. "Association between Dietary Behaviors and BMI Stratified by Sex and the ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Japanese Adults" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235116
APA StyleIgarashi, M., Nogawa, S., Hachiya, T., Furukawa, K., Takahashi, S., Jia, H., Saito, K., & Kato, H. (2022). Association between Dietary Behaviors and BMI Stratified by Sex and the ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Japanese Adults. Nutrients, 14(23), 5116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235116








