Abstract
The purpose of this study was to examine the relative validity of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) for estimating nutrient intake. Dietary data were obtained from 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men, using the online MDHQ and the 4-non-consecutive-day weighed dietary record (DR). The number of nutrients (total n = 46) showing no significant mean differences between estimates from the online MDHQ and DR (with energy adjustment by the density model) was 17 among women and 12 among men. The median value (25th and 75th percentiles) of the Pearson correlation coefficients between the online MDHQ and DR estimates was 0.54 (0.35–0.57) among women and 0.45 (0.25–0.53) among men. Bland–Altman plots for energy-providing nutrients indicated wide limits of agreement (and proportional bias for protein) with overall underestimation of protein and fat and overestimation of carbohydrate by the online MDHQ. Similar results were found when the paper version of the MDHQ (completed after the DR) was examined. For example, the median value of the Pearson correlation coefficients was 0.54 for women and 0.45 for men. This study suggests that the MDHQ has an acceptable ability to rank individuals according to intakes of a wide range of nutrients.
1. Introduction
It is broadly recognized that suboptimal dietary intake is a leading modifiable risk factor contributing to both morbidity and early mortality, making the improvement of dietary quality a worldwide priority at present [1]. The accurate evaluation of habitual dietary intake is fundamental to investigating the diet–disease relationship and to facilitating positive changes in dietary behavior [2]. It is often considered that the dietary record (DR) and 24-h dietary recall are the most accurate methods for capturing intakes of a wide variety of foods and nutrients [3,4]. However, assessing habitual dietary intake on an individual level is not always viable because these methods involve the collection of multiple days of dietary data and, despite technological advances, are still burdensome [4,5]. Conversely, dietary assessment questionnaires are the most commonly used tool in large-scale epidemiologic and intervention studies to capture dietary intake [6,7]. Unlike the DR and 24-h dietary recall, dietary assessment questionnaires can capture long-term dietary intake in a single administration and are less cumbersome to complete [8]. However, dietary assessment questionnaires do not necessarily collect information on actual dietary intake but ultimately measure only the memory and perception of usual diet [9]. Another limitation of dietary assessment questionnaires is that participants cannot report foods not included in the questionnaire [4]. Researchers must always find a balance between reducing participant burden and how comprehensive the list of food items should be. Therefore, a successful dietary assessment questionnaire is inevitably a final product of a careful development and validation evaluation process.
As a tool to assess the dietary habits of Japanese people, we recently designed the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) [10,11]. There are several features of the MDHQ. First, the MDHQ separately assesses dietary intake for each type of meal (i.e., breakfast, morning snack, lunch, afternoon snack, dinner and evening snack). This is mainly based on previous observations in Japanese adults, in which the selection, amount and combination of foods consumed are markedly different between meal types [12,13,14,15,16]. There are complex cognitive tasks demanded during meal recall, such as understanding the information being sought and searching for and evaluating the retrieved information [17]. Thus, compared with questions asking about overall dietary intake in typical dietary assessment questionnaires, questions arranged for each meal type separately in the MDHQ may be easier to answer, facilitating better estimation of dietary intake [18]. Second, the MDHQ is a data-driven system. That is, the structure of the questionnaire, food items and the development of the dietary intake computation algorithm are based on in-depth dietary information retrieved from the 16-day weighed DR collected from 242 Japanese adults (comprising 206,837 food item entries) [10]. This may also contribute to providing better estimation of dietary intake. Third, the MDHQ, originally developed as a paper self-administered questionnaire [10], can be self-administered online [11]. This feature provides several advantages, including reducing paper use, postage costs and the space, security and organization required for paper file storage [19], as well as the ability to communicate with a geographically dispersed population and groups often difficult to sample [20]. Given that, to our knowledge, only a single online dietary assessment questionnaire is available for the Japanese [21], the MDHQ may be a promising candidate in nutritional epidemiologic research in Japan. Finally, we have recently developed a web-based personalized dietary feedback system that integrates dietary assessment using the MDHQ [11], which might be useful in online intervention trials for promoting favorable changes in dietary behaviors.
However, a rigorous evaluation of the validity of the MDHQ has not been conducted yet, except for food group intake [22]. The main objective of this study was to examine the relative validity of nutrient intake obtained through the web version of the MDHQ (web MDHQ) using the 4-non-consecutive-day weighed DR as a reference. In the real world, not all study participants would complete the questionnaire online. Thus, the secondary objective was to similarly examine the relative validity of the paper version of the MDHQ (paper MDHQ).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Procedure and Participants
Details on the survey procedure and participants have been described elsewhere [22]. In brief, a team of research dietitians with expertise in DR data collection (n = 66) [23,24] collected data in 14 (of 47) prefectures from August to October 2021. For each prefecture, 8 community-dwelling couples, i.e., 2 women from each of the 4 age categories (30–39, 40–49, 50–59 and 60–69 years) and their husbands (irrespective of age), were recruited. Thus, 112 women and 112 men were invited. Although dietary data from cohabiting couples may reduce gender differences in dietary intake, we chose a priori to separate all analyses into women and men, so we do not consider this issue problematic in this study. We decided our sample size principally based on the recommendations of Cade et al. that for validation studies, a sample size of at least 50 and preferably much larger (e.g., 100 or more subjects) is desirable [4]. Our exclusion criteria were dietitians, people living with a dietitian, people receiving dietary counseling from a physician or dietitian, people with diabetes and receiving insulin therapy, people receiving dialysis treatment, people without adequate access to the Internet, people who had difficulty completing the web-based questionnaire and pregnant or lactating women. Due to snowball sampling, the number of individuals approached for this study and those excluded from the survey were not recorded.
We first asked each participant to complete the web MDHQ. After a 7- to 10-day interval to ensure completion of the web MDHQ, participants were asked to complete the weighed DR on four non-consecutive days within two weeks. Finally, after an interval of at least one day, participants were asked to complete the paper MDHQ. The study protocol was completed by 111 women aged 30 to 69 years and 111 men aged 30 to 76 years. This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and all procedures involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Tokyo Faculty of Medicine (protocol code: 2020326NI; date of approval: 29 January 2021). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
2.2. Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire
The MDHQ has been presented in detail elsewhere [10,11]. In short, the MDHQ is a self-administered questionnaire that is designed to assess dietary intake in the previous month for each meal type (breakfast, morning snack, lunch, afternoon snack, dinner and night snack). The MDHQ is comprised of three parts. In Part 1 of the MDHQ, quantitative questions regarding the frequency of consumption of common food groups (i.e., Tier 1 food groups) for each meal type are included (n = 11–24 for common food groups depending on meal type), which can be answered from 0 to 7 days/week. In Part 2 of the MDHQ, there are questions about the relative frequency of consumption of sub-food groups within Tier 1 food groups (i.e., Tier 2 food groups; n = 0–19 according to Tier 1 food groups), which can be answered as “always”, “often”, “sometimes”, “rarely”, or “never”. The information obtained from Part 1 and Part 2 can be combined to increase the number of foods that can be effectively estimated within a restricted number of questions. In Part 3 of the MDHQ, the respondents are asked about general eating behaviors, such as the relative frequency of consumption of brown rice and whole grain bread and whether they eat their bread with jam, honey, or spread fat on it. At the end, the MDHQ involves an assessment of basic attributes (i.e., sex, age, height, weight, education level and current smoking status).
The MDHQ does not gather information on portion sizes (except for alcoholic beverages for which overall consumption frequency and portion sizes are assessed in Part 2). Our rationale for this decision was rooted in our previous finding: a simplified diet history questionnaire (brief-type diet history questionnaire, BDHQ), which assesses the frequency of consumption of 58 food items but collects no information on portion size and applies fixed portion sizes in the calculation of dietary intake, is as effective in estimating food and nutrient intake as a comprehensive diet history questionnaire (DHQ), which not only assesses frequency of consumption but also portion size for 150 food items [25,26,27]. Several previous studies support the limited utility of portion size information [28,29]. All the food groups in the MDHQ and sex-specific and meal-type specific fixed portion size were derived from the 16-day weighed DR data collected from 242 Japanese adults [10].
Two delivery modes of the MDHQ used in this study (web MDHQ and paper MDHQ) were identical in terms of content. The web MDHQ was created using Google Forms. Every question was answered by each participant; no non-responses were allowed. All responses to the web MDHQ, which were automatically allocated to a spreadsheet format, were downloaded from Google Drive. The paper MDHQ utilized in this study was a 21-page A4 questionnaire. The responses to all questions were verified by the research dietitians and the research center staff. Where answers were missing, we asked participants to re-answer the questions in person or over the phone. All responses to the paper MDHQ were typed by hand in duplicate on a spreadsheet and any inconsistencies were checked and corrected. The data obtained using the web and paper versions of the MDHQ were then transformed into a dataset that was suitable for dietary intake calculations.
On the basis of a series of ad hoc computer algorithms in the MDHQ [10], estimated intakes of Tier 1 and 2 food groups were calculated. Estimated intakes of energy and nutrients were calculated using food intake information and the 2015 version of the Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan [30]. For food items with unavailable data on the added sugar content, added sugar values were calculated based on the same or similar food in the 2011–2012 Food Patterns Equivalents Database [31]. Teaspoon equivalents in the Food Patterns Equivalents Database were converted into grams by multiplying by 4.2 (grams of added sugar per teaspoon). The number of food codes used during the calculations was 763 for breakfast, 909 for lunch, 965 for dinner, 695 for morning snack and 703 for afternoon and night snacks [10]. The calculation was made for each meal type and the overall intake was calculated as the sum of the intake of each meal type.
2.3. Weighed Dietary Record
Details on the 4-non-consecutive-day weighed DR used as the reference method in this validation study have been presented elsewhere [22]. Briefly, each recording period comprised three weekdays (Monday to Friday) and one weekend day (Saturday or Sunday) within two weeks. Each couple was issued recording sheets and a digital scale (KS-274, Dretec, Japan; ±2 g accuracy for 0–500 g, ±3 g accuracy for 500–2000 g). Upon receiving written and verbal instructions from the research dietitian and a sample diary entry, each participant was asked to document and weigh everything they ate and drank, both inside and outside the home, for each day of record keeping. In cases where weighing is difficult, such as eating out, the participants were instructed to record as much information as possible, including the brand name of the food, the amount consumed (using typical household scales) and the contents of leftovers.
The recording forms used for each survey day were submitted directly to the research dietitian after the survey was completed, who reviewed the forms and, if necessary, requested additional information or revised records by telephone or in person. All records collected were checked by the research dietitians and trained staff at the study center. Following the standard procedure, estimated portions by using a household scale were transformed into weights and individual food items were coded according to the 2015 version of the Standard Tables of Food Composition of Japan [30]. In total, 1297 food codes were used in the DR. As in the MDHQ, estimated energy and nutrient intakes were calculated using the 2015 version of the Standard Tables of Food Composition of Japan [30] and the 2011–2012 Food Pattern Equivalents Database [31]. We used the average daily value for each individual over the four-day period for all dietary variables.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the SAS statistical software (version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). A two-tailed p value of <0.05 was considered significant. All analyses were conducted for women and men separately. The dietary variables examined in this study included 46 nutrients. Dietary data were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD). Analyses were conducted using energy-adjusted values by the residual and density models [32], as well as using crude values. In this study, nutrient intake from dietary supplements was not considered, mainly because of a lack of reliable food composition database in Japan.
To assess the estimation ability at the group level, the mean values of estimates derived from the MDHQ were compared with those derived from the DR using the paired t-test. In order to assess the ability of the MDHQ to rank individuals in the population, Pearson correlation coefficients between the MDHQ and DR estimates were used. Additionally, the agreement between the MDHQ and DR for protein, fat and carbohydrate estimates from the density model (% of energy) was evaluated using Bland–Altman plots [33]. We also used linear regression analysis to examine proportional bias between the MDHQ and DR [34]. We performed identical analyses to evaluate the web MDHQ and paper MDHQ; we provide our findings for the web MDHQ in the Section 3 and for the paper MDHQ in the Supplementary Materials.
3. Results
Table 1 shows the basic characteristics of the study subjects. The mean body mass index (BMI) values (kg/m2) were 22.7 (SD: 3.3) for women and 23.8 (SD: 3.6) for men. For both women and men, the mean energy intakes estimated from the web MDHQ and paper MDHQ were significantly (p < 0.001) lower than that estimated from the DR.

Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the study subjects 1.
3.1. Results on the Web Version of Meal-Based Diet History Questionnaire
3.1.1. Mean Estimation
The mean estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of nutrients derived from the DR and web MDHQ are shown in Table 2 for women and Table 3 for men. Among women, the number of nutrients (n = 46 in total) that showed no significant mean differences between the web MDHQ and DR estimates was 12 (26%) for the residual model and 17 (37%) for the density model. The corresponding value among men was 7 (15%) and 13 (28%), respectively. When the crude values were examined (Table S1), the results were similar to those based on the residual model; the corresponding value was 12 (26%) among women and 7 (15%) among men.

Table 2.
Mean estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of nutrients obtained from the 4-day weighed dietary record (DR) and those obtained from the web version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese women 1.

Table 3.
Mean estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of nutrients obtained from the 4-day weighed dietary record (DR) and those obtained from the web version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese men 1.
3.1.2. Pearson Correlations
Table 4 shows the Pearson correlation coefficients between crude and energy-adjusted estimates of daily intakes of nutrients derived from the DR and web MDHQ. For crude estimates of nutrient intakes, the median values of the Pearson correlation coefficients (25th and 75th percentiles) were 0.37 (0.30–0.46) among women and 0.33 (0.21–0.40) among men. Higher correlations were observed when energy-adjusted values of nutrient intakes were examined than when using crude estimates, particularly among women. The median values of the Pearson correlation coefficients (25th and 75th percentiles) among women were 0.50 (0.34–0.56) for the residual model and 0.54 (0.35–0.57) for the density model. The corresponding values among men were 0.37 (0.26–0.49) and 0.45 (0.25–0.53), respectively.

Table 4.
Pearson correlation coefficients between crude and energy-adjusted estimates of daily intakes of nutrients obtained from the 4-day weighed dietary record and those obtained from the web version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire in 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men 1.
3.1.3. Bland–Altman Plots
Figure 1 shows Bland–Altman plots assessing the agreement between estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of protein, fat and carbohydrate (% of energy) derived from the DR and those derived from the web MDHQ. Overall, compared to the DR, the web MDHQ underestimated protein and fat intakes, with a range from 1.5% of energy (for protein in women) to 3.9% of energy (for fat in men). Conversely, carbohydrate intake was overestimated by the web MDHQ compared with the DR, by 2.1% of energy among women and 3.3% of energy among men. Further, regardless of sex and nutrient, the limits of agreement (mean difference ± 1.96 SD of the difference) were generally wide, indicating poor agreement at the individual level. There was no indication of proportional bias between the web MDHQ and DR, except for protein intake which tended to be underestimated by the web MDHQ as the average intake increased in both sexes.
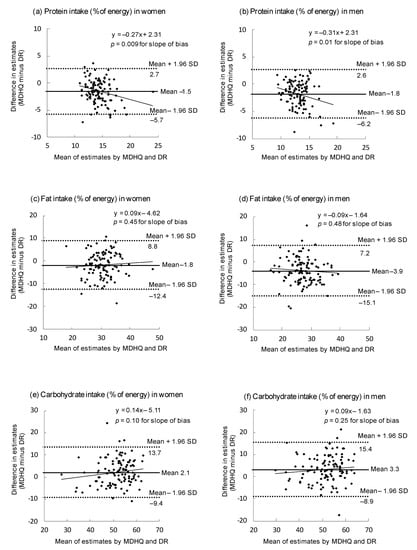
Figure 1.
Bland–Altman plots assessing the agreement between estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of protein (a,b), fat (c,d) and carbohydrate (e,f) obtained from the 4-day weighed dietary record (DR) and those obtained from the web version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men. Energy adjustment was made using the density model. SD, standard deviation.
3.2. Results from the Paper Version of Meal-Based Diet History Questionnaire
Identical analyses of the paper MDHQ were conducted (Tables S2 and S3 for mean estimations, Table S4 for Pearson correlation coefficients and Figure S1 for Bland–Altman plots for protein, fat and carbohydrate intakes). The results for the paper MDHQ were generally similar to those for the web MDHQ, except for somewhat higher Pearson correlation coefficients between the paper MDHQ and DR, particularly in the crude and residual models. The median values of the Pearson correlation coefficients (25th and 75th percentiles) among women were 0.45 (0.38–0.49) for the crude model, 0.56 (0.46–0.61) for the residual model and 0.54 (0.42–0.59) for the density model. The corresponding values among men were 0.42 (0.35–0.50), 0.43 (0.34–0.55) and 0.45 (0.32–0.57), respectively.
4. Discussion
As a companion paper on the relative validity of the MDHQ at the food level [22], here we examined the relative validity of the MDHQ at the nutrient level, using the same dataset. We observed that, for many nutrients (63% to 85% of nutrients examined), energy-adjusted mean values derived from the web MDHQ were significantly different from those derived from the 4-day weighed DR, irrespective of energy adjustment model and sex. These findings suggest that the web MDHQ is acceptable for estimating mean values for only a limited number of nutrients. Similar results (50% to 90% of nutrients examined showing significant differences) have been obtained in previous relative validation analyses of the DHQ and BDHQ, which are among the most widely used dietary assessment questionnaires in Japan [26].
Additionally, on the basis of Bland–Altman plots for energy-providing nutrients, we found poor agreement between the web MDHQ and DR at the individual level, which is consistent with our analysis of the web MDHQ for food groups [22]. This may be mainly due to the use of the fixed portion sizes during dietary intake calculation. In any case, irrespective of energy adjustment, the estimates of nutrient intakes derived from the web MDHQ should be interpreted with considerable caution not only at the individual level but also as at the group level.
Nevertheless, we observed that, for many nutrients, the Pearson correlation coefficients between energy-adjusted estimates derived from the web MDHQ and DR were greater than 0.40 in both women (70% for the residual model and 67% for the density model) and men (43% for the residual model and 57% for the density model). These findings suggest that the web MDHQ has an acceptable ability to rank individuals according to intakes of a wide range of nutrients. Somewhat better results (57% to 83% of nutrients examined) have been obtained in previous validation analyses of the DHQ and BDHQ using the 16-day DR as a reference [26].
For ranking ability of dietary assessment questionnaires in Japan, a review published in 2009 showed that the median of correlation coefficients between dietary assessment questionnaires and DR ranged from 0.31 to 0.56 [35]. Similar results have been reported in more recent studies, with a range of median of correlation coefficients from 0.44 to 0.52 [21,26,36,37]. Particularly, in a validation study on intakes of energy and 53 nutrients derived from an online food frequency questionnaire against a 12-day DR, the median value of correlation coefficients was 0.46 for women and 0.47 for men [21]. The median values of the Pearson correlation coefficients observed in this study (0.37 to 0.54, depending on sex and energy adjustment model) are comparable with these figures. Collectively, we consider that the web MDHQ’s ability for ranking individuals according to nutrient intake is not inferior to that of existing dietary assessment questionnaires in Japan, as in the case of food intake estimation [22].
However, being “non-inferior” to other questionnaires does not necessarily justify the use of the web MDHQ. For example, we observed that the correlation coefficients were rather low (<0.30) for such nutrients as n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (only men), marine-origin n-3 fatty acids (including individual fatty acids; only men), α-linolenic acid, water, retinol, cryptoxanthin, retinol equivalent, vitamin D (only men), niacin (only men) and vitamin B-12 (only men), which may be mainly due to the limited validity of major food sources of these nutrients (e.g., fish, vegetable oils and meat) [22]. The low correlations may also be due to high within-person variability in intakes of these nutrients [38]. Most of these nutrients are fat-related and difficulty in assessing intakes of these nutrients has also been observed in a recent meta-analysis of correlation coefficients between food frequency questionnaires and reference methods (DR or 24-h dietary recall) [3]. Conversely, we observed that the correlation coefficients were rather high (>0.60) for some nutrients, including marine-origin n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (only women), carbohydrate, alcohol, pantothenic acid (only women), vitamin C (only men), sodium (only women), potassium, magnesium (only women), iron and copper (only women), which may be mainly due to a high validity of major food sources of these nutrients (e.g., rice, miso soup, fruit, dairy products and alcoholic beverages) [22]. These findings should be carefully considered when selecting the web MDHQ (or another questionnaire) as a dietary assessment tool in nutrition research in Japan.
It should be noted that the analyses based on the web MDHQ and on the paper MDHQ showed similar results, despite the fact that the Pearson correlation coefficients with the DR were somewhat high for the paper MDHQ, as was observed in the validation analysis of food group intake [22]. Apparently higher correlations for the paper MDHQ are reasonable since the web MDHQ and paper MDHQ are filled out before and after the experience of dietary recording, respectively. In general, administrative and cost considerations favor online surveys, but not all research participants will cooperate with online surveys in the real world. Therefore, we plan to directly compare the food and nutrient intakes provided by the web and paper versions of MDHQ to evaluate the comparability or compatibility of these two modes of delivery.
Several limitations in the present study have been described in detail elsewhere [22]; thus, a brief description is provided here. First, the subjects of this study are not a nationally representative sample of the Japanese population and may be biased toward those who are more health conscious. Thus, further research needs to be conducted with a more representative sample. Second, the reference method of this study, weighed DR, is not without measurement error, especially because of incorrect recording and potential changes in eating behavior [4]. However, the weighed DR is broadly regarded as the first method for validating diet assessment questionnaires since the errors in weighed DR should be less correlated with the errors in dietary assessment questionnaires than the errors in other memory-based diet assessment tools [3,4]. Nevertheless, we cannot rule out the possibility that the weighed DR and MDHQ share sources of bias, which could affect the present results, including the calculation of correlation coefficients. Finally, because the MDHQ is designed to assess dietary habits during the previous month, the tool does not account for intra-individual variation in dietary intake during the year (e.g., changes in dietary intake for the same person due to seasonal or temporal differences in foods). However, our earlier work has demonstrated that a one-time administering of questionnaires which assess dietary intake during the preceding month (i.e., DHQ and BDHQ) may be able to capture longer-term (i.e., one year) habitual dietary intake [25,26,27,39] and these results may also be extrapolated to the MDHQ.
In summary, consistent with the analysis at the food group level [22], we showed that the web version (as well as the paper version) of the MDHQ had acceptable relative validity in terms of nutrient intakes against the 4-day weighed DR. For a wide range of nutrients, the MDHQ’s ability to rank individuals was acceptable, whereas its ability to estimate mean intakes appeared limited for only a small number of nutrients, as well as a limited ability to estimate nutrient intakes at the individual level. To our knowledge, there is no purpose-built, dedicated dietary assessment questionnaire to collect data on dietary intake at each meal type, which is also inexpensive to implement and less burdensome for participants. Thus, we consider that the MDHQ, a novel, purpose-built, dedicated dietary assessment questionnaire to collect data on dietary intake at each meal type, might be useful for future nutritional epidemiologic research. In this context, this analysis of nutrient intakes, as well as that on food group intakes [22], might lend support to the use of the MDHQ in large-scale epidemiologic and intervention studies in Japan to capture dietary intake.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu14204270/s1, Table S1: Mean estimates of crude intakes of nutrients derived from the 4-day weighed dietary record (DR) and those derived from the web version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men, Table S2: Mean estimates of crude and energy-adjusted intakes of nutrients derived from the paper version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese women, Table S3: Mean estimates of crude and energy-adjusted intakes of nutrients derived from the paper version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese men, Table S4: Pearson correlation coefficients between crude and energy-adjusted estimates of daily intakes of nutrients derived from the 4-day weighed dietary record and those derived from the paper version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire in 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men, Figure S1: Bland–Altman plots assessing the agreement between estimates of energy-adjusted intakes of protein (a, b), fat (c, d), and carbohydrate (e, f) derived from the 4-day weighed dietary record (DR) and those derived from the paper version of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire (MDHQ) in 111 Japanese women and 111 Japanese men.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.M. and N.S.; methodology, K.M., N.S., N.K., S.M. and S.S.; software, K.M.; formal analysis, K.M.; investigation, K.M. and N.S.; resources, K.M. and S.M.; data curation, K.M., N.S., N.K., S.M. and S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, K.M.; writing—review and editing, N.S.; visualization, K.M. and N.S.; supervision, K.M.; project administration, K.M., N.S., N.K., S.M. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Institute for Food and Health Science, Yazuya Co., Ltd. The Institute for Food and Health Science, Yazuya Co., Ltd. had no role in the design, analysis, or writing of this manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Tokyo, Faculty of Medicine (protocol code: 2020326NI; date of approval: 29 January 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the present study are not publicly available because of privacy and ethical restrictions imposed by the Ethics Committee of the University of Tokyo, Faculty of Medicine, but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The web and paper versions of the MDHQ used in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the research dietitians who conducted data collection: Tamotsu Noshiro *, Fuki Kudo, Erika Iwasaki, Kazue Fukushi and Masako Shimooka (Hokkaido); Akiko Sato, Hiromi Kawaguchi, Yuka Takeda and Akiko Matsunaga (Yamagata); Yoko Isaka, Yuka Ota, Hanayo Kadoi, Akiko Seki, Yuko Takano, Toshie Nakayama, Ayami Murakami and Masako Yamaguchi (Ibaraki); Kaoru Goto, Yuka Inaba, Akiko Kato and Miki Hori (Saitama), Hitomi Okahashi, Shinobu Matsui and Yurina Arai (Tokyo); Suzuyo Takeda, Kumiko Ono, Yayoi Hayashi, Kazumi Takagi, Kaori Otomo and Mayuko Sakitsu (Kanagawa); Masako Koike, Reiko Kunimatsu, Keiko Kuribayashi, Keiko Hirayama and Eriko Kiryuu (Niigata); Kazumi Horiguchi, Kotomi Kishikawa, Yasuko Ishii and Miyuki Yokokoji (Yamanashi); Masako Tanaka, Hideko Uchibayashi, Tomoko Suzuki, Ryoko Mizuno and Emi Kajiura (Aichi), Yumiko Noutomi, Atsuko Toyokawa, Yasuka Tabuchi and Junko Ikukawa (Osaka), Sachiko Terao, Mari Matsuda, Mieko Imanaka and Noriyuki Kubota (Okayama); Yoko Fujii, Izumi Hase, Aki Funada and Tomomi Saya (Hiroshima); Kyoko Kaku, Kiyoko Katayama, Miki Hamachi, Yoshiko Yahagi and Chizuru Shibata (Fukuoka); Yuko Soga, Kayoko Iwamoto, Mika Moribe, Miki Hamada and Kaori Nakamura (Oita). The authors also thank the research team staff at the survey center (University of Tokyo): Akiko Hara, Keika Mine and Hiroko Onodera. *Deceased.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- GBD 2017 Diet Collaborators. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdirmid, J.; Blundell, J. Assessing dietary intake: Who, what and why of under-reporting. Nutr. Res. Rev. 1998, 11, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Niu, K.; Zhao, Y. Validity of the food frequency questionnaire for adults in nutritional epidemiological studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, J.; Thompson, R.; Burley, V.; Warm, D. Development, validation and utilisation of food-frequency questionnaires—A review. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, J.E. Measuring diet in the 21st century: Use of new technologies. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satija, A.; Yu, E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Understanding nutritional epidemiology and its role in policy. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinnette, R.; Narita, A.; Manning, B.; McNaughton, S.A.; Mathers, J.C.; Livingstone, K.M. Does personalized nutrition advice improve dietary intake in healthy adults? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subar, A.F. Developing dietary assessment tools. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.B.E.; Prentice, A.M.; Coward, W.A.; Strain, J.J.; Black, A.E.; Davies, P.S.W.; Stewart, C.M.; McKenna, P.G.; Whitehead, R.G. Validation of estimates of energy intake by weighed dietary record and diet history in children and adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Shinozaki, N.; McCaffrey, T.A.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Sasaki, S. Data-driven development of the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire for Japanese adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 126, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Shinozaki, N.; Masayasu, S.; Livingstone, M.B.E. Web-based personalized nutrition system for delivering dietary feedback based on behavior change techniques: Development and pilot study among dietitians. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Shinozaki, N.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Fujiwara, A.; Asakura, K.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Characterisation of breakfast, lunch, dinner and snacks in the Japanese context: An exploratory cross-sectional analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Sasaki, S. Meal-specific dietary patterns and their contribution to overall dietary patterns in the Japanese context: Findings from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Survey, Japan. Nutrition 2019, 59, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Sasaki, S. Establishment of a meal coding system for the characterization of meal-based dietary patterns in Japan. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Shinozaki, N.; Sugimoto, M.; Fujiwara, A.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Food combinations in relation to the quality of overall diet and individual meals in Japanese adults: A nationwide study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Sasaki, S.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Miura, A.; Todoriki, H.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Applying a meal coding system to 16-day weighed dietary record data in the Japanese context: Toward the development of simple meal-based dietary assessment tools. J. Nutr. Sci. 2018, 7, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, M.B.; Robson, P.J.; Wallace, J.M. Issues in dietary intake assessment of children and adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, S213–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, J.E.; Burley, V.J.; Warm, D.L.; Thompson, R.L.; Margetts, B.M. Food-frequency questionnaires: A review of their design, validation and utilisation. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallaize, R.; Forster, H.; Macready, A.L.; Walsh, M.C.; Mathers, J.C.; Brennan, L.; Gibney, E.R.; Gibney, M.J.; Lovegrove, J.A. Online dietary intake estimation: Reproducibility and validity of the Food4Me food frequency questionnaire against a 4-day weighed food record. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, C.; Pynaert, I.; De Keyzer, W.; De Henauw, S. Validity and reproducibility of an adolescent web-based food frequency questionnaire. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.; Takachi, R.; Ishihara, J.; Ishii, Y.; Sasazuki, S.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Shinozawa, Y.; Umezawa, J.; Tanaka, J.; et al. Online version of the self-administered food frequency questionnaire for the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study for the Next Generation (JPHC-NEXT) protocol: Relative validity, usability, and comparison with a printed questionnaire. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Shinozaki, N.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Kimoto, N.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Relative validity of food intake in each meal type and overall food intake derived using the Meal-based Diet History Questionnaire against the 4-day weighed dietary record in Japanese adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, K.; Uechi, K.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Sodium sources in the Japanese diet: Difference between generations and sexes. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Masayasu, S.; Sasaki, S. Eating patterns in a nationwide sample of Japanese aged 1–79 y from MINNADE study: Eating frequency, clock time for eating, time spent on eating and variability of eating patterns. Public Health Nutr. 2022, 25, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Comparison of relative validity for food group intake estimated by comprehensive and brief-type self-administered diet history questionnaires against 16 d dietary records in Japanese adults. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Honda, S.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Both comprehensive and brief self-administered diet history questionnaires satisfactorily rank nutrient intakes in Japanese adults. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Livingstone, M.B.E.; Fujiwara, A.; Sasaki, S. Reproducibility and relative validity of the Healthy Eating Index-2015 and Nutrient-Rich Food Index 9.3 estimated by comprehensive and brief diet history questionnaires in Japanese adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noethlings, U.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.M.; Boeing, H. Portion size adds limited information on variance in food intake of participants in the EPIC-Potsdam study. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlundt, D.G.; Buchowski, M.S.; Hargreaves, M.K.; Hankin, J.H.; Signorello, L.B.; Blot, W.J. Separate estimates of portion size were not essential for energy and nutrient estimation: Results from the Southern Community Cohort food-frequency questionnaire pilot study. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council for Science and Technology; Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. Standard Tables of Food Composition in Japan 2015, 7th ed.; Official Gazette Co-operation of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. (In Japanese)
- Bowman, S.A.; Clemens, J.C.; Friday, J.E.; Thoerig, R.C.; Moshfegh, A. Food Patterns Equivalents Database 2011–2012: Methodology and User Guide. Available online: http://www.ars.usda.gov/nea/bhnrc/fsrg (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Willett, W.C.; Howe, G.R.; Kushi, L.H. Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 65, 1220S–1228S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenij, L.J.; Buhre, W.F.; Jansen, J.R.; Kruitwagen, C.L.; de Waal, E.E. Methodology of method comparison studies evaluating the validity of cardiac output monitors: A stepwise approach and checklist. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 116, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakai, K. A review of food frequency questionnaires developed and validated in Japan. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Takachi, R.; Ishihara, J.; Ishii, Y.; Sasazuki, S.; Sawada, N.; Shinozawa, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Kato, E.; Kitamura, K.; et al. Validity of short and long self-administered food frequency questionnaires in ranking dietary intake in middle-aged and elderly Japanese in the Japan Public Health Center-Based Prospective Study for the Next Generation (JPHC-NEXT) protocol area. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Kokubo, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Iso, H.; Okamura, T.; Miyamoto, Y. The reasonable reliability of a self-administered food frequency questionnaire for an urban, Japanese, middle-aged population: The Suita study. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, A.; Asakura, K.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Todoriki, H.; Miura, A.; Fukui, M.; et al. Within- and between-individual variation in energy and nutrient intake in Japanese adults: Effect of age and sex differences on group size and number of records required for adequate dietary assessment. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Reproducibility and relative validity of dietary glycaemic index and load assessed with a self-administered diet-history questionnaire in Japanese adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).