Structural Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Digalactosyldiacylglycerol-Monoestolide, a Characteristic Glycolipid in Oats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Isolation of a Major DGDG-Monoestolide (Compound X) from Powdered Oat
2.3. Structural Analysis of Compound X
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Analysis of Nitric Oxide (NO) Production and Cell Viability
2.6. Analysis of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
2.7. Analysis of Cellular Uptake
2.8. Protein Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
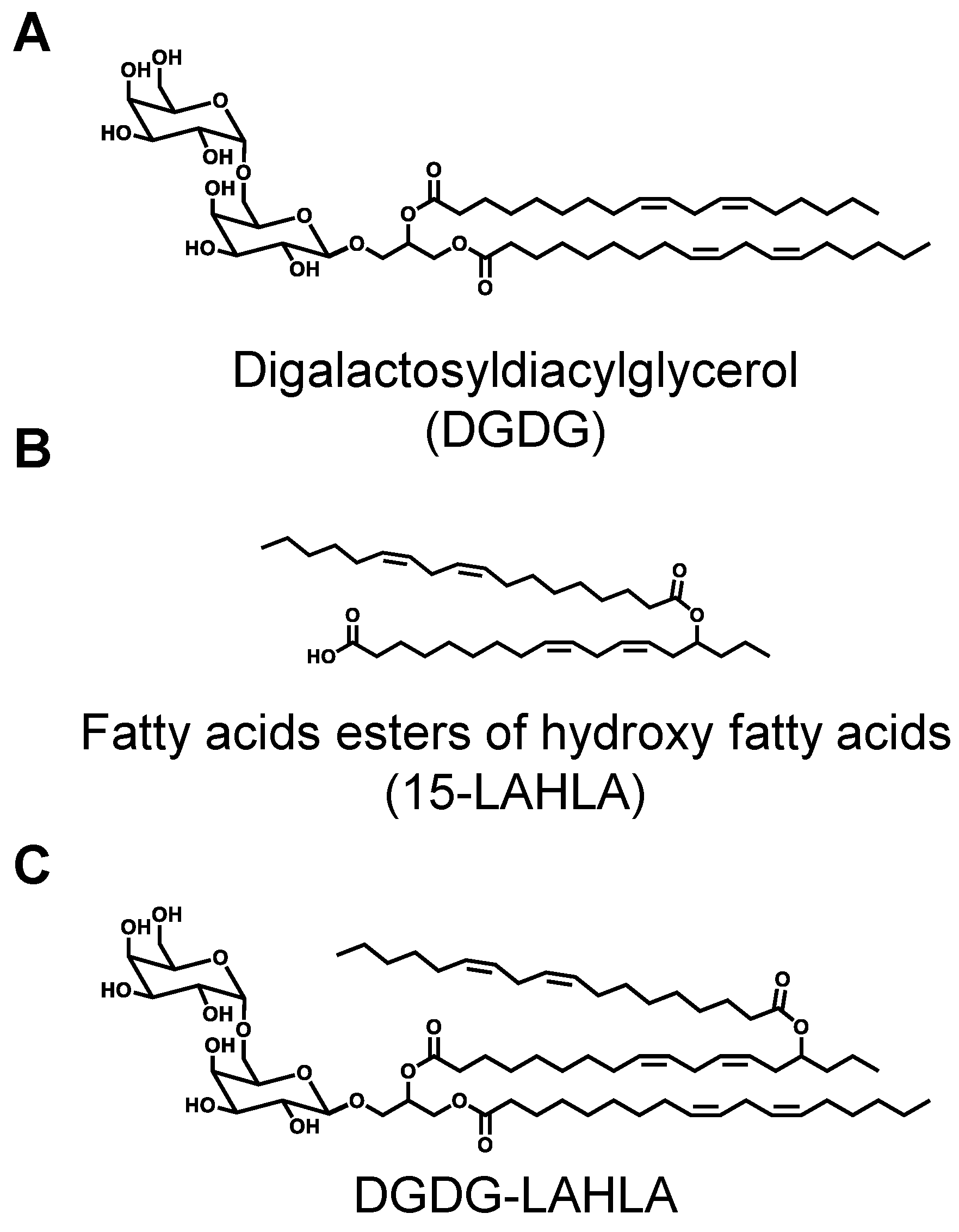
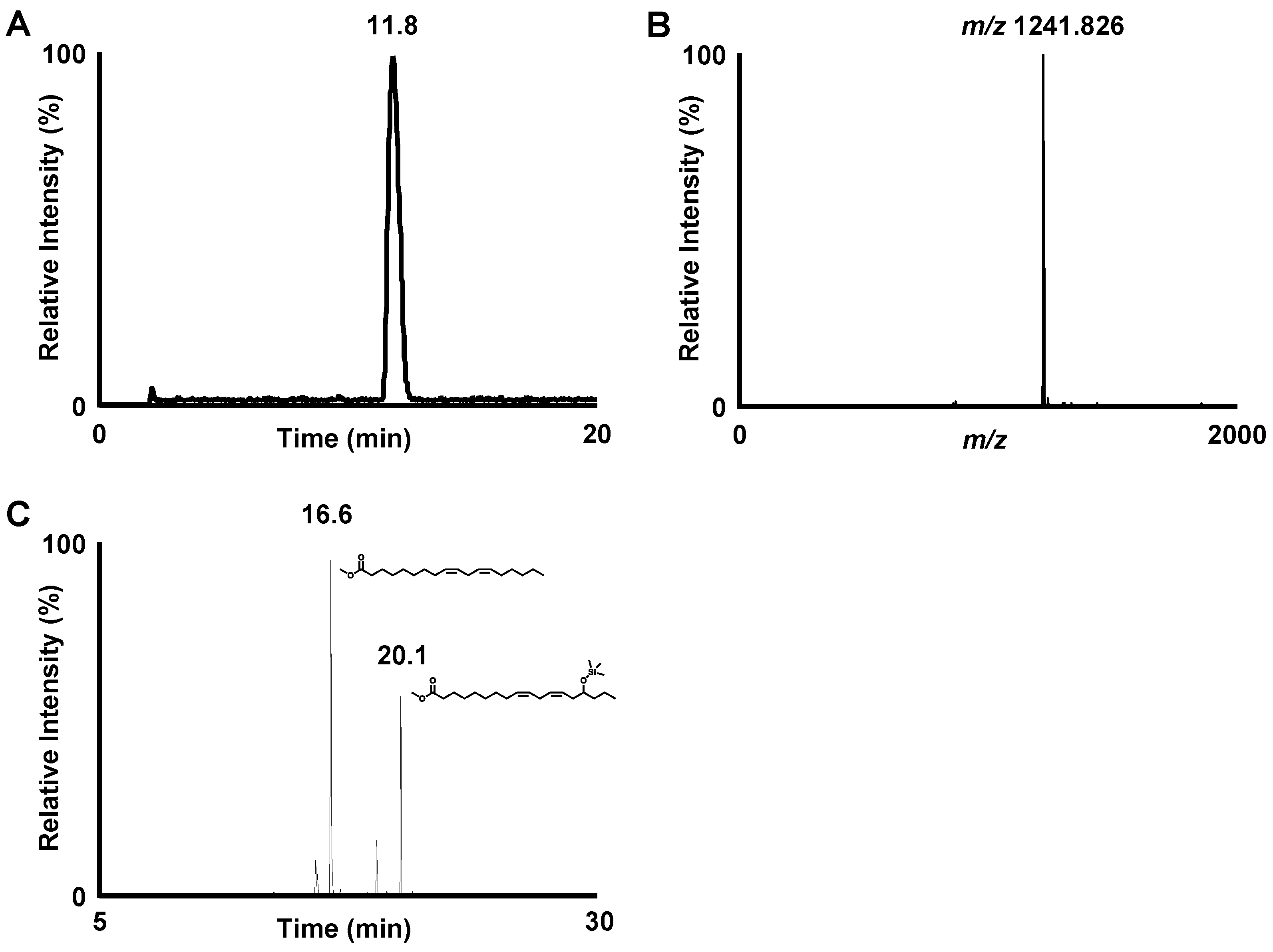
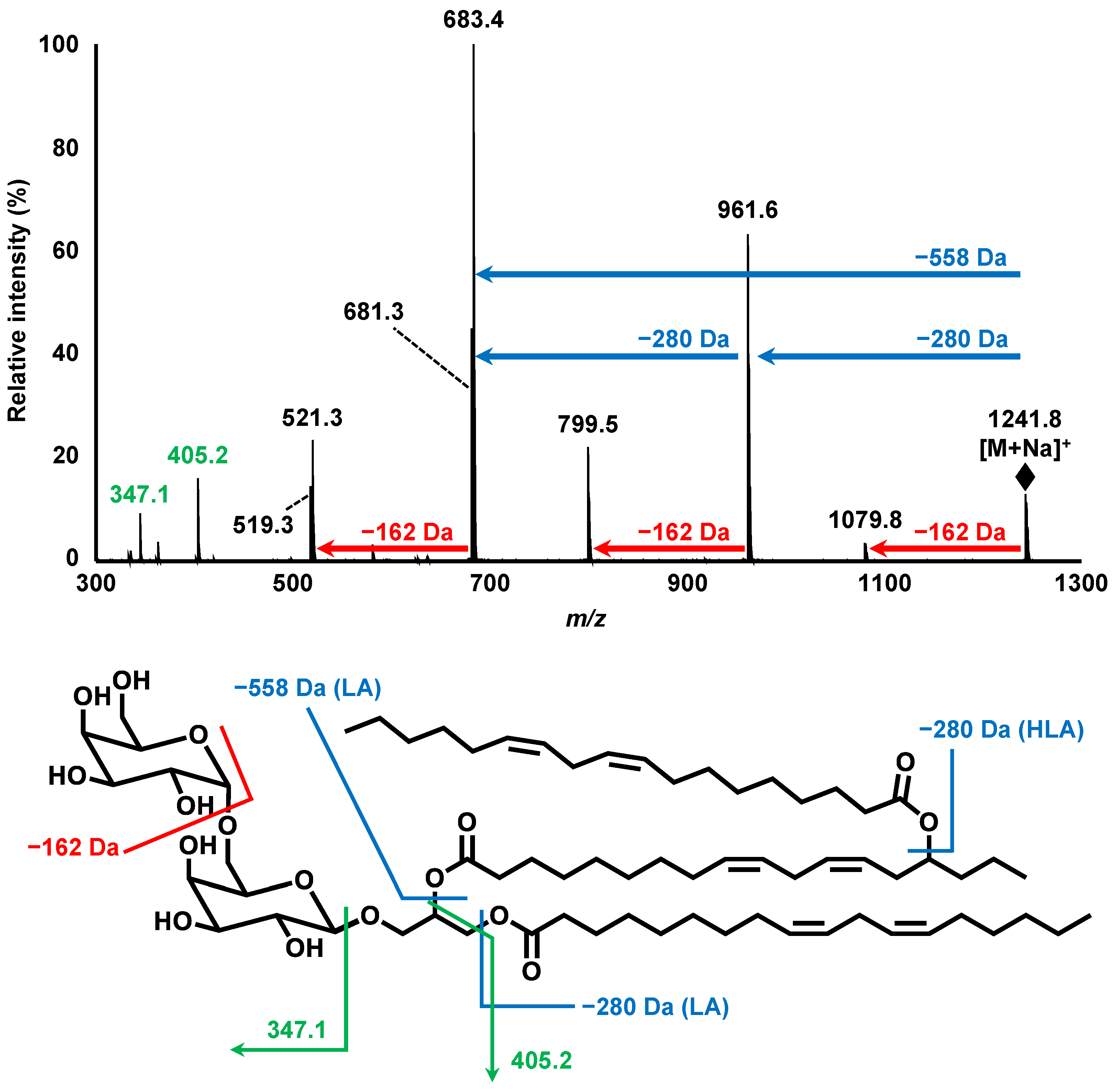
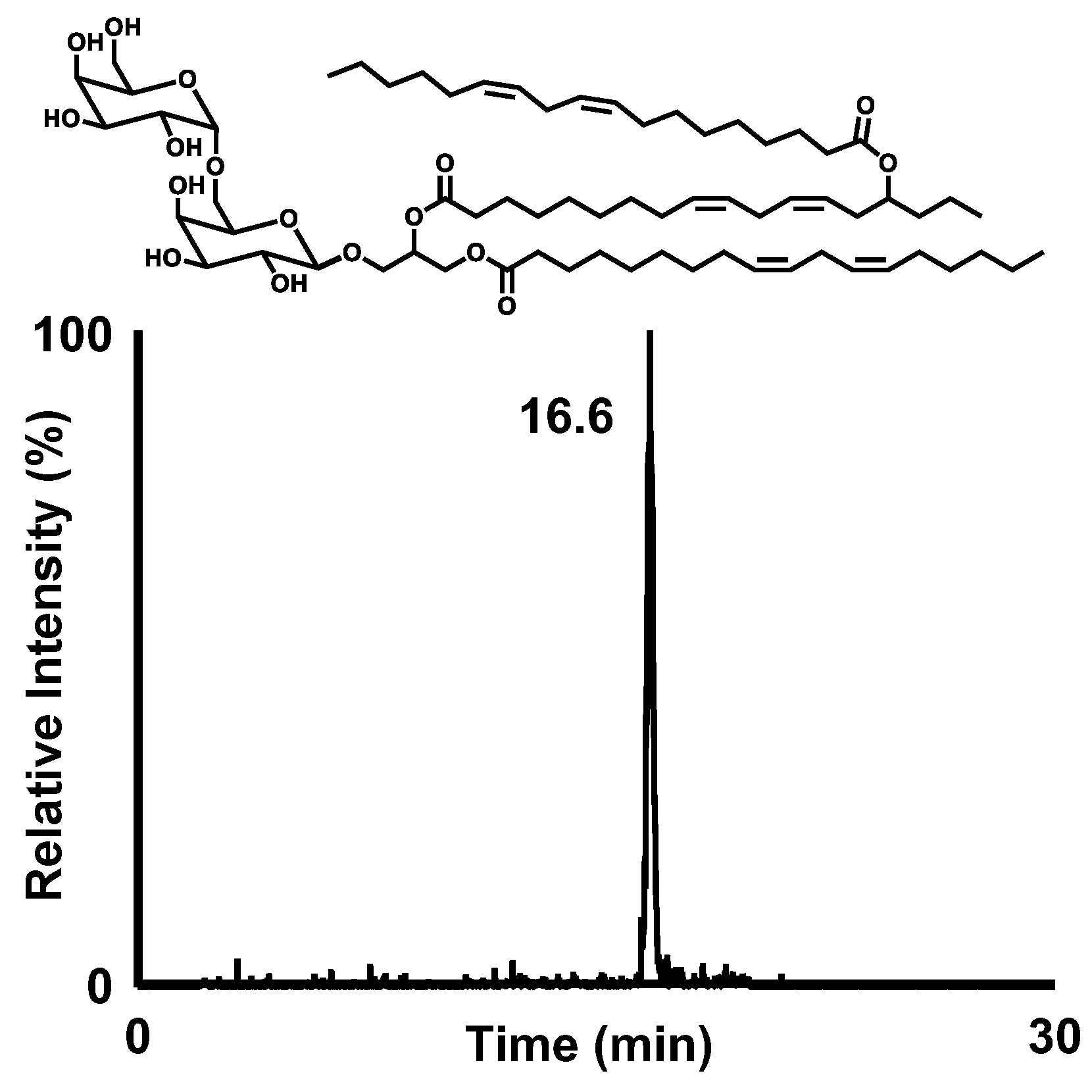
3.1. Isolation and Structural Analysis of a Major DGDG-Monoestolide (Compound X) Contained in Oat
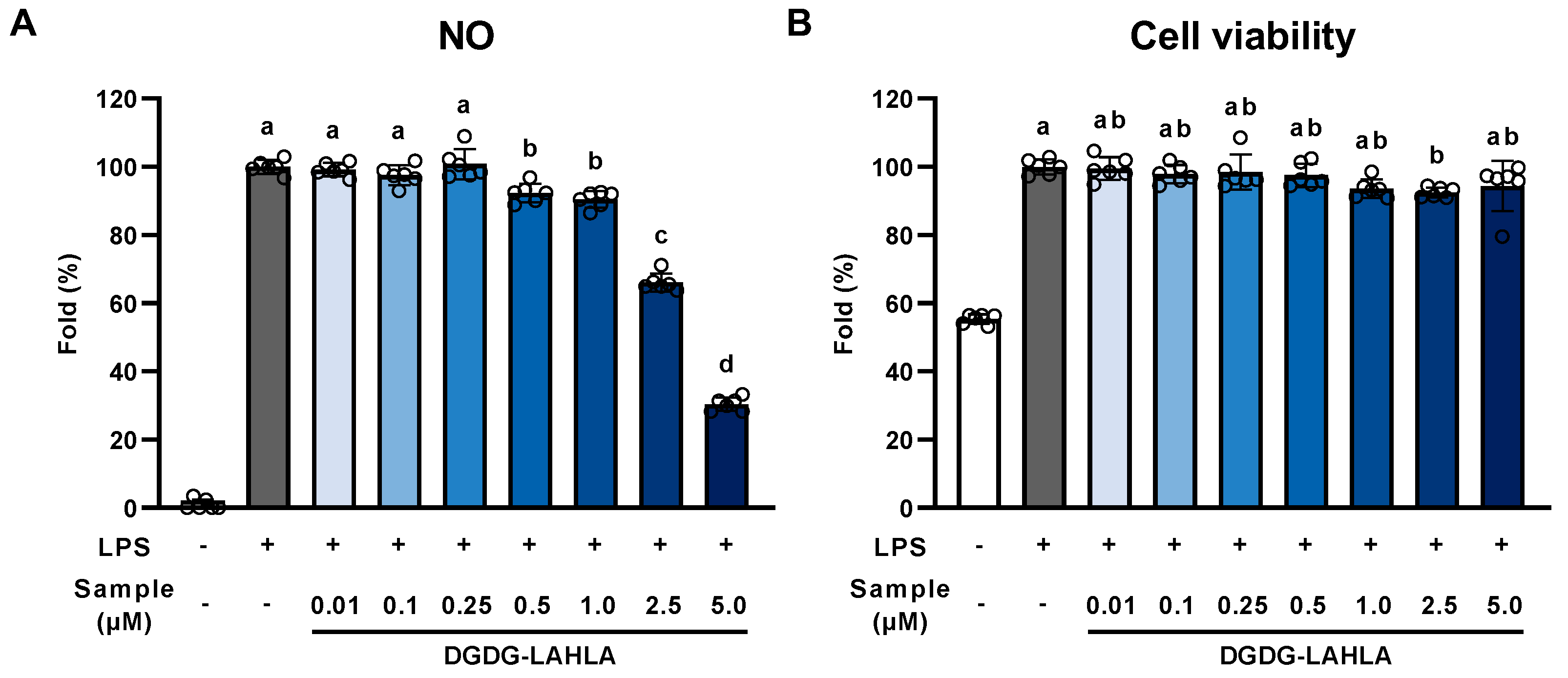
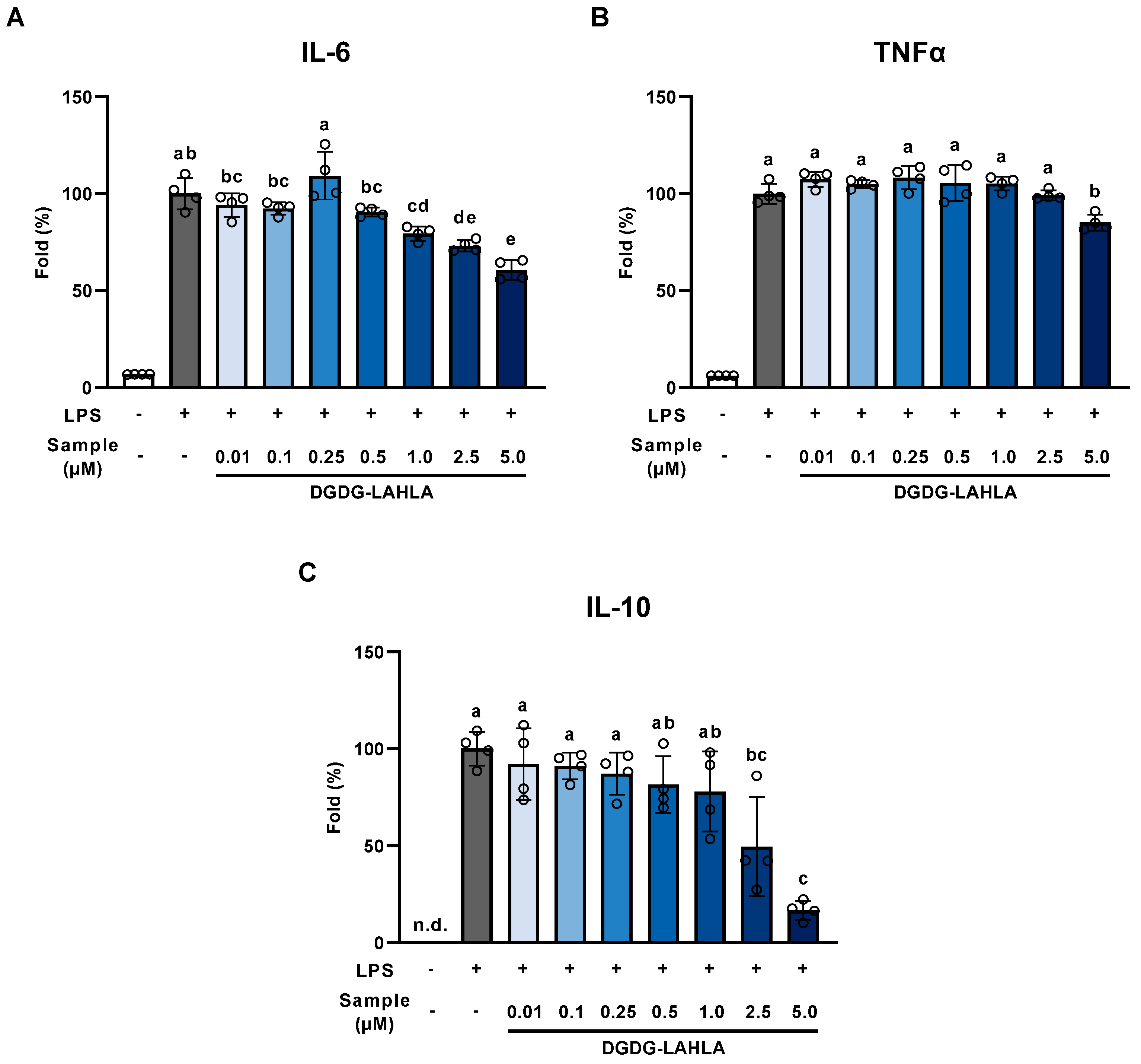
3.2. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of DGDG-LAHLA
3.3. Evaluation of the Cellular Uptake of DGDG-LAHLA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Ellis, P.R. Oat β-Glucan: Physico-chemical characteristics in relation to its blood-glucose and cholesterol-lowering properties. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, S4–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ni, T.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Consumption of avenanthramides extracted from oats reduces weight gain, oxidative stress, inflammation and regulates intestinal microflora in high fat diet-induced mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauksson, J.B.; Bergqvist, M.H.J.; Rilfors, L. Structure of digalactosyldiacylglycerol from oats. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1995, 78, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, M.J.; Konduri, S.; Chang, T.; Wang, H.; McNerlin, C.; Ohlsson, L.; Härröd, M.; Siegel, D.; Saghatelian, A. Linoleic acid esters of hydroxy linoleic acids are anti-inflammatory lipids found in plants and mammals. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10698–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamberg, M.; Liepinsh, E.; Otting, G.; Griffiths, W. Isolation and structure of a new galactolipid from oat seeds. Lipids 1998, 33, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.C.; Chen, Y.P.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, N.S.; Shyur, L.F. A Galactolipid possesses novel cancer chemopreventive effects by suppressing inflammatory mediators and mouse B16 melanoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6907–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Stefanova, R.; Sperker, S.; Melanson, R.; Osborne, J.A.; O’Leary, S.J.B. Five new galactolipids from the freshwater microalga porphyridium aerugineum and their nitric oxide inhibitory activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Los Reyes, C.; Ortega, M.J.; Rodríguez-Luna, A.; Talero, E.; Motilva, V.; Zubía, E. Molecular characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of galactosylglycerides and galactosylceramides from the microalga isochrysis galbana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yore, M.M.; Syed, I.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Zhang, T.; Herman, M.A.; Homan, E.A.; Patel, R.T.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; Peroni, O.D.; et al. Discovery of a class of endogenous mammalian lipids with anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. Cell 2014, 159, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuda, O.; Brezinova, M.; Rombaldova, M.; Slavikova, B.; Posta, M.; Beier, P.; Janovska, P.; Veleba, J.; Kopecky, J.; Kudova, E.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid-derived fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAS) with anti-inflammatory properties. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chang, T.; Konduri, S.; Huang, J.; Saghatelian, A.; Siegel, D. Synthesis of chemically edited derivatives of the endogenous regulator of inflammation 9-PAHSA. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, M.; Watanabe, A.; Yoshida, I.; Mishima, T.; Nakamura, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Morimoto, Y. Evaluation of aculeatin and toddaculin isolated from toddalia asiatica as anti-inflammatory agents in LPS-stimulated RAW264 macrophages. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doehlert, D.C.; Moreau, R.A.; Welti, R.; Roth, M.R.; McMullen, M.S. Polar lipids from oat kernels. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Miyazawa, T. Separation and determination of glycolipids from edible plant sources by high-performance liquid chromatography and evaporative light-scattering detection. Lipids 1999, 34, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Hao, C.; Liu, S.; Voinov, V.G.; Kalinovskaya, N.I. Electrospray ionization multiple-stage tandem mass spectrometric analysis of diglycosyldiacylglycerol glycolipids from the bacteria bacillus pumilus. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, J.S.; Kim, M.S. Structural characterization of sulfoquinovosyl, monogalactosyl and digalactosyl diacylglycerols by FAB-CID-MS / MS. J. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 32, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Svensson, I.; Adlercreutz, P. Enzymatic fatty acid exchange in digalactosyldiacylglycerol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 104, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, R.A.; Doehlert, D.C.; Welti, R.; Isaac, G.; Roth, M.; Tamura, P.; Nuñez, A. The Identification of Mono-, Di-, Tri-, and tetragalactosyl-diacylglycerols and their natural estolides in oat kernels. Lipids 2008, 43, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banskota, A.H.; Stefanova, R.; Gallant, P.; McGinn, P.J. Mono- and Digalactosyldiacylglycerols: Potent Nitric Oxide Inhibitors from the Marine Microalga Nannochloropsis Granulata. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Ahn, E.K.; Hong, S.S.; Oh, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effect of tribulusamide D isolated from tribulus terrestris in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4421–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.-W.; Wang, R.; Yao, L.-W.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Sun, P.-L.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Y.-F. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Mytilus Coruscus Polysaccharide on RAW264.7 Cells and DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröter, D.; Neugart, S.; Schreiner, M.; Grune, T.; Rohn, S.; Ott, C. Amaranth’s 2-Caffeoylisocitric Acid-An Anti-Inflammatory Caffeic Acid Derivative That Impairs NF-ΚB Signaling in LPS-Challenged RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Nutrients 2019, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 | Condition 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | Column A | Column A | Column B | Column C |
| Mobile phase | M.P. A | M.P. B | M.P. C | M.P. D |
| Flow rate | 20 mL/min | 20 mL/min | 1 mL/min | 1 mL/min |
| Oven temperature | 40 °C | |||
| UV | 210 nm | 210 nm | - | - |
| Parameter | Condition 1 | Condition 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis mode | Q1 mass scan | Product ion scan |
| Source | ESI | ESI |
| Polarity | Positive | Positive |
| Scan range (m/z) | 50–2000 | 50–2000 |
| End plate offset (V) | −500 | −500 |
| Capillary | 4500 | 4500 |
| Nebulizer (Bar) | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Dry gas (L/min) | 6 | 6 |
| Dry temp (°C) | 180 | 180 |
| Collision RF (Vpp) | 1100 | 600 |
| Precursor ion (m/z) | - | 1241.826 |
| Collision energy (V) | - | 80 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Analysis mode | Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) |
| Source | ESI |
| Polarity | Positive |
| Precursor ion (m/z) | 1241.8 |
| Product ion (m/z) | 961.5 |
| Curtain gas (psi) | 20 |
| Ion spray voltage (V) | 5500 |
| Turbo gas temperature (oC) | 600 |
| Ion source gas 1 (psi) | 40 |
| Ion source gas 2 (psi) | 80 |
| Collision-activated dissociation gas (psi) | 9 |
| Declustering potential (V) | 266 |
| Entrance potential (V) | 10 |
| Collision energy (V) | 81 |
| Collision cell exit potential (V) | 24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, H.; Ito, J.; Shimizu, N.; Takahashi, T.; Kato, C.; Parida, I.S.; Jutanom, M.; Ishihara, K.; Nakagawa, K. Structural Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Digalactosyldiacylglycerol-Monoestolide, a Characteristic Glycolipid in Oats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194153
Yamada H, Ito J, Shimizu N, Takahashi T, Kato C, Parida IS, Jutanom M, Ishihara K, Nakagawa K. Structural Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Digalactosyldiacylglycerol-Monoestolide, a Characteristic Glycolipid in Oats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194153
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Hiroki, Junya Ito, Naoki Shimizu, Takumi Takahashi, Chikara Kato, Isabella Supardi Parida, Mirinthorn Jutanom, Katsuyuki Ishihara, and Kiyotaka Nakagawa. 2022. "Structural Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Digalactosyldiacylglycerol-Monoestolide, a Characteristic Glycolipid in Oats" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194153
APA StyleYamada, H., Ito, J., Shimizu, N., Takahashi, T., Kato, C., Parida, I. S., Jutanom, M., Ishihara, K., & Nakagawa, K. (2022). Structural Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Digalactosyldiacylglycerol-Monoestolide, a Characteristic Glycolipid in Oats. Nutrients, 14(19), 4153. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194153







