In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Brewers’ Spent Grain from Different Types of Malt
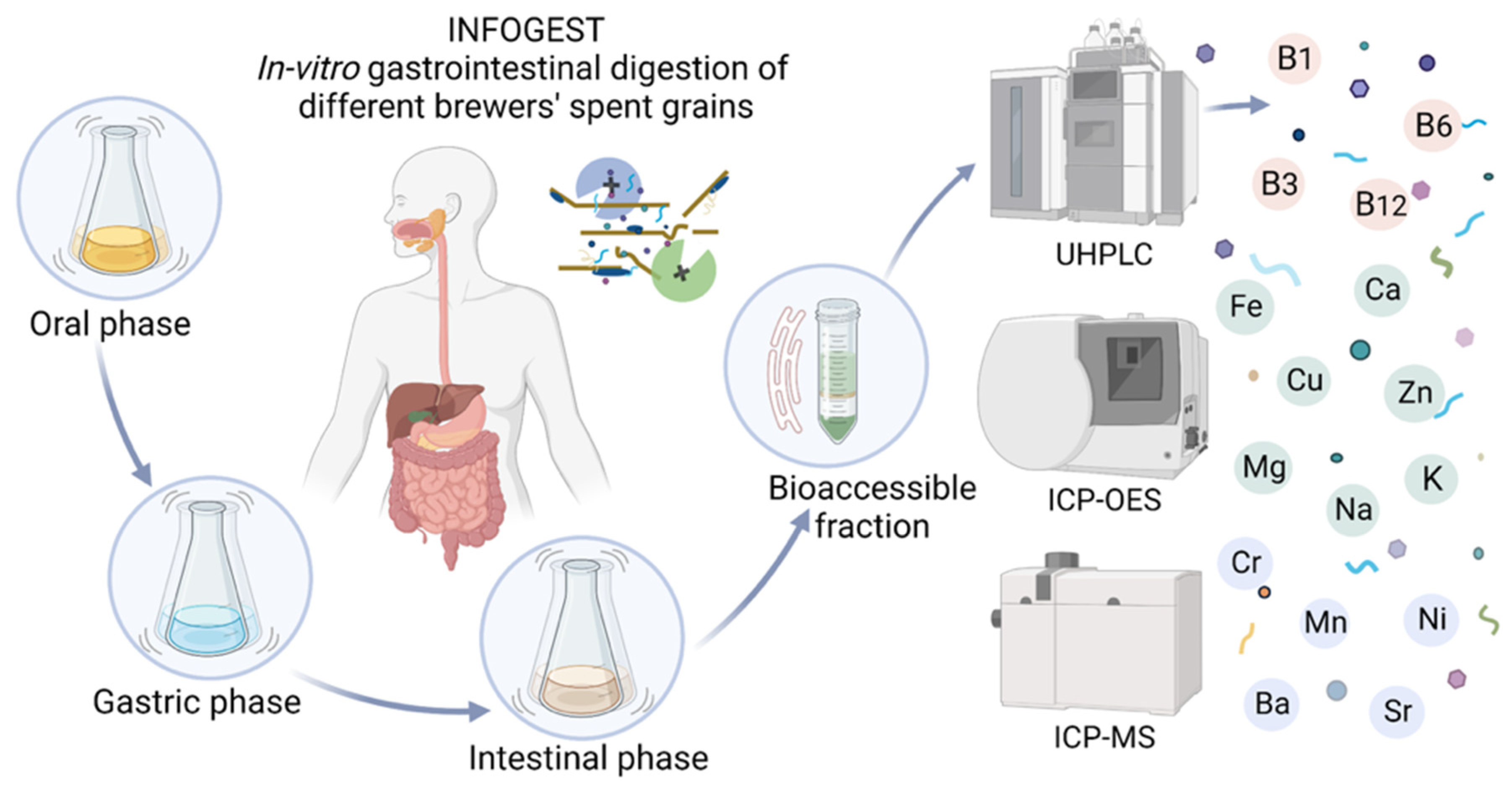
2.3. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.4. Mineral Determination
2.5. B Vitamins Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
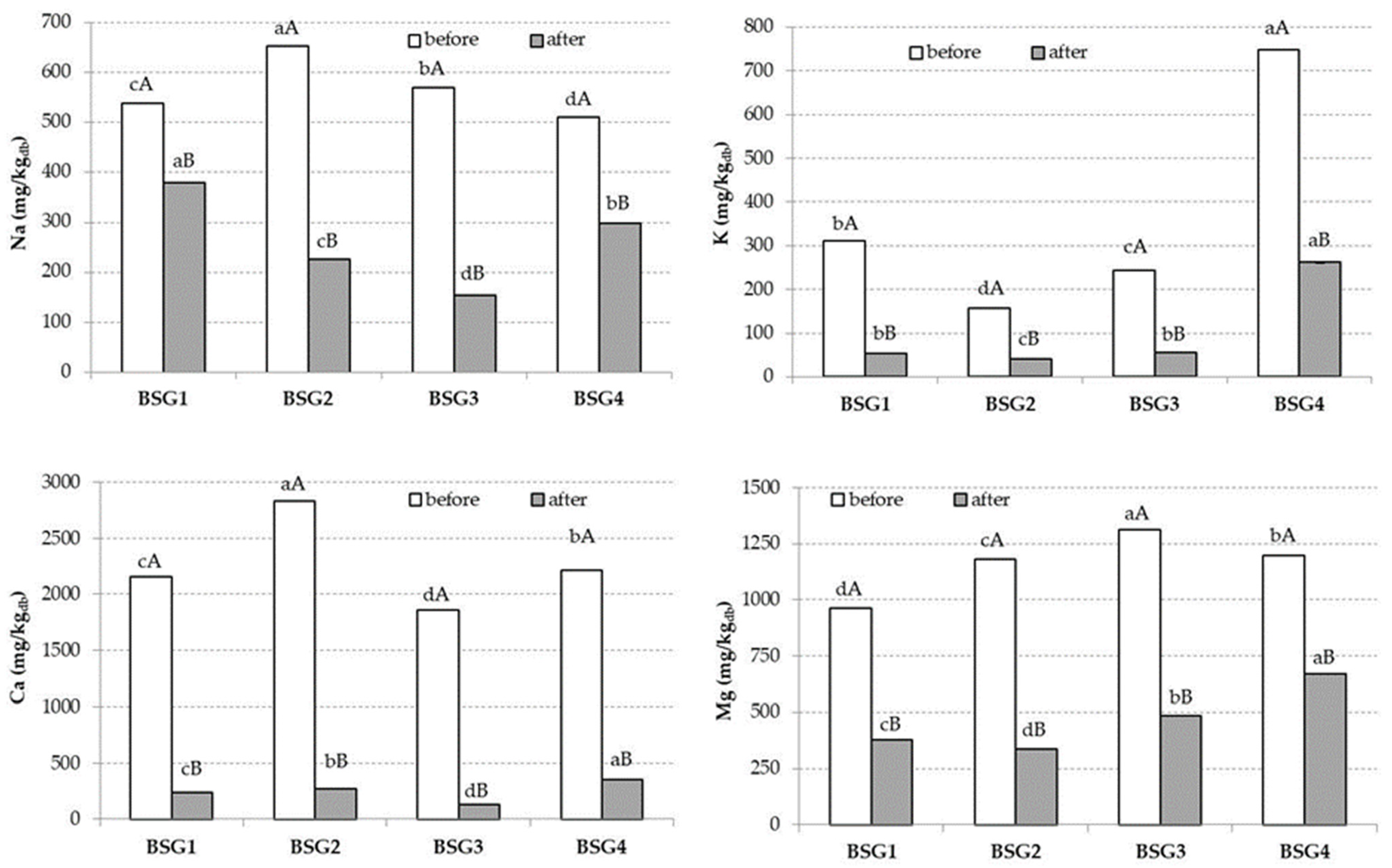
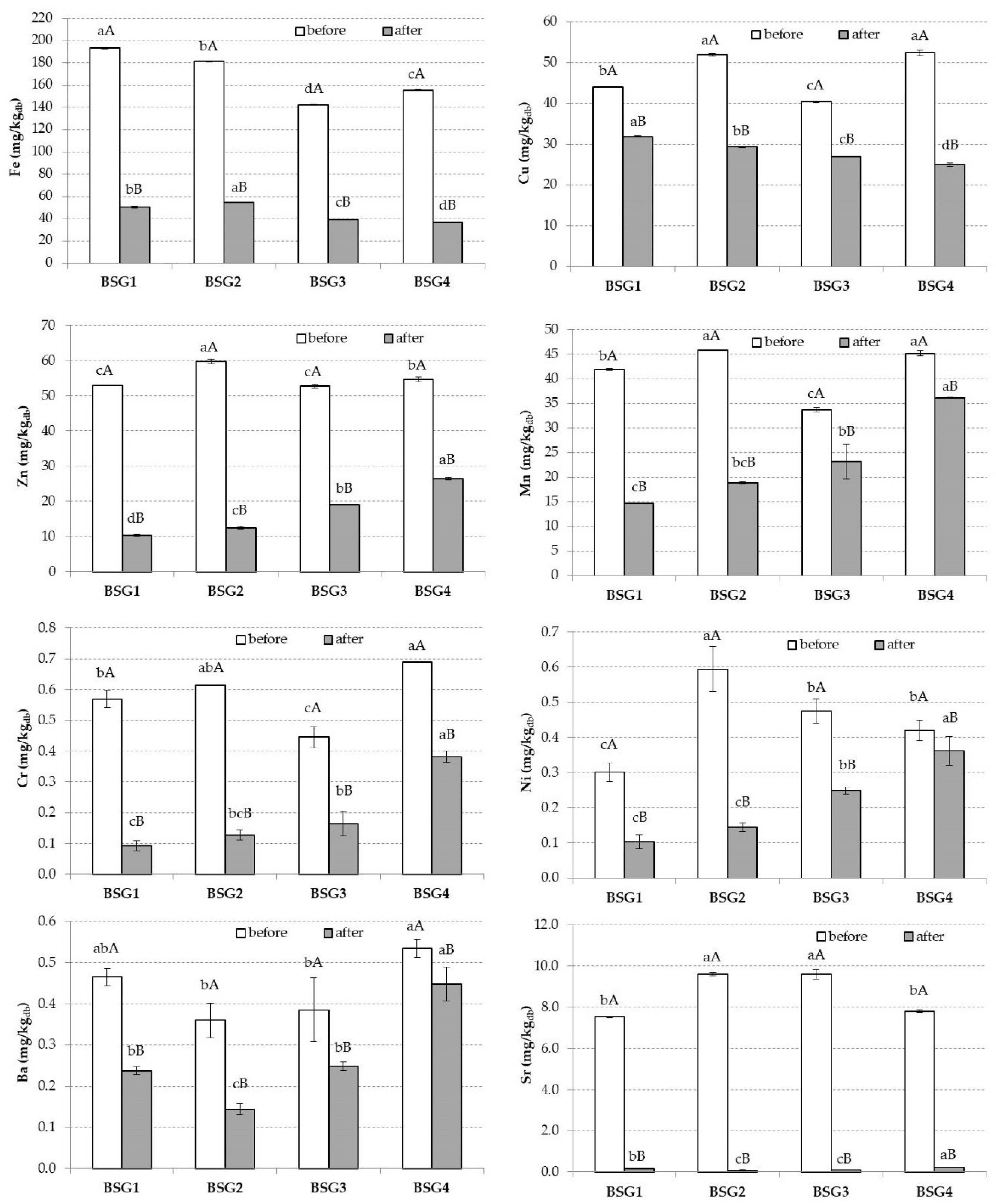
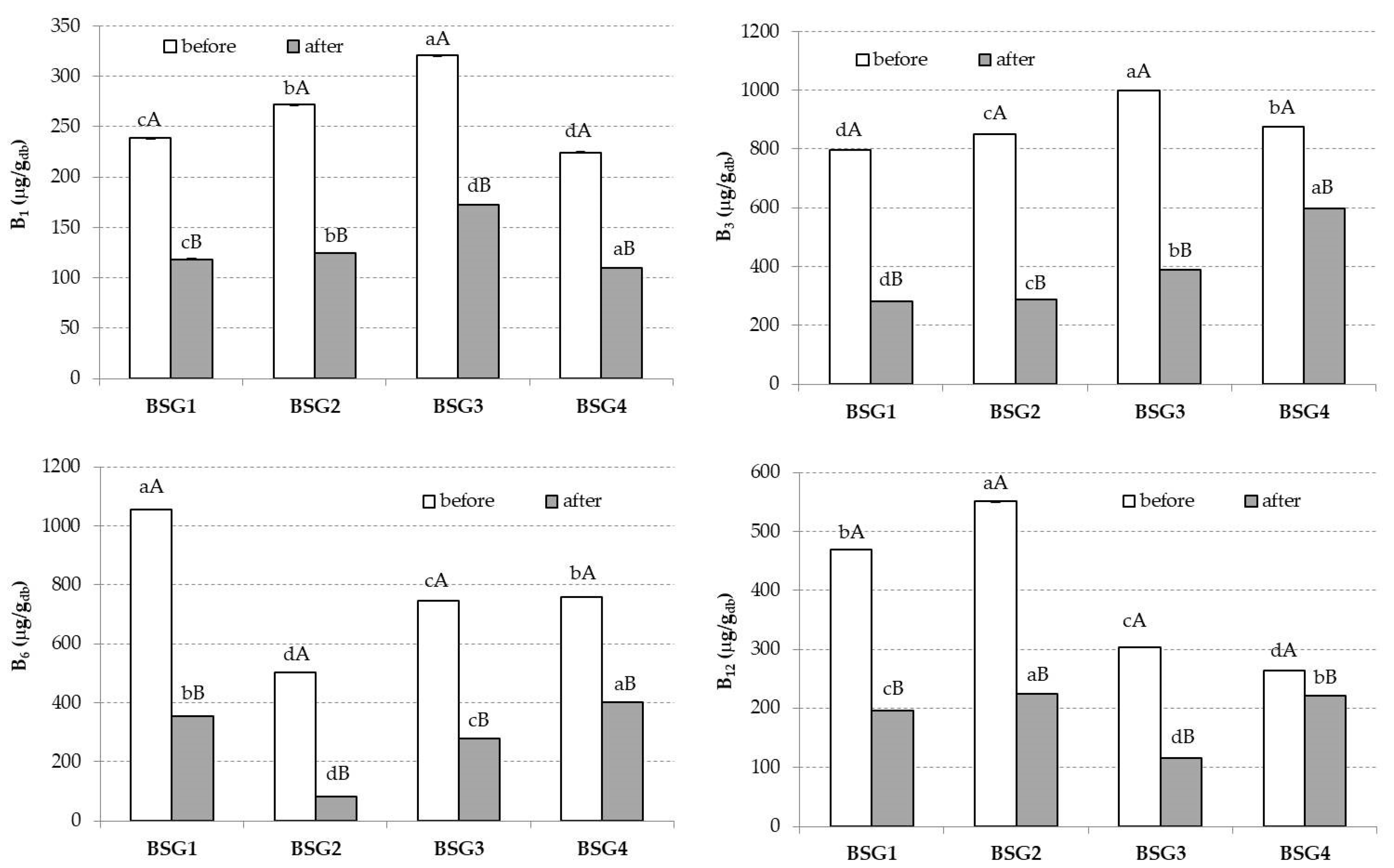
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, Y.X.; Mok, W.K.; Chen, W.N. In Vitro Evaluation of Enriched Brewers’ Spent Grains Using Bacillus subtilis WX-17 as Potential Functional Food Ingredients. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegretti, C.; Bellinetto, E.; D’arrigo, P.; Griffini, G.; Marzorati, S.; Rossato, L.A.M.; Ruffini, E.; Schiavi, L.; Serra, S.; Strini, A.; et al. Towards a Complete Exploitation of Brewers’ Spent Grain from a Circular Economy Perspective. Fermentation 2022, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Chiș, M.S.; Pop, O.L.; Fogarasi, M.; Păucean, A.; Igual, M.; Michiu, D. Reintegration of brewers spent grains in the food chain: Nutritional, functional and sensorial aspects. Plants 2021, 10, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, A.I.; Petron, M.J.; Lopez, A.M.; Timon, M.L. Optimization of extraction conditions to improve phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity in craft brewers’ spent grain using response surface methodology (rsm). Foods 2020, 9, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoriello, T.; Mellara, F.; Galli, V.; Amoriello, M.; Ciccoritti, R. Technological properties and consumer acceptability of bakery products enriched with brewers⇔ spent grains. Foods 2020, 9, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, S.; Huang, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, M. Composition and Nutrient Value Proposition of Brewers Spent Grain. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocente, F.; Taddei, F.; Galassi, E.; Gazza, L. Upcycling of brewers’ spent grain by production of dry pasta with higher nutritional potential. Lwt 2019, 114, 108421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jin, Y. Optimization of Brewer’s spent grain-enriched biscuits processing formula. J. Food Process Eng. 2014, 37, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Sandoval, N.G.; Granados-Nevárez, M.d.C.; Calderón de la Barca, A.M.; Vásquez-Lara, F.; Malunga, L.N.; Apea-Bah, F.B.; Beta, T.; Islas-Rubio, A.R. Phenolic Acids, Antioxidant Capacity, and Estimated Glycemic Index of Cookies Added with Brewer’s Spent Grain. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fărcaş, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Tofană, M.; Mureşan, C.; Mudura, E.; Salanţă, L.; Scrob, S. Nutritional properties and volatile profile of brewer’s spent grain supplemented bread. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 19, 9705–9714. [Google Scholar]
- Ktenioudaki, A.; Crofton, E.; Scannell, A.G.M.; Hannon, J.A.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Gallagher, E. Sensory properties and aromatic composition of baked snacks containing brewer’s spent grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özvural, E.B.; Vural, H.; Gökbulut, I.; Özboy-Özbaş, Ö. Utilization of brewer’s spent grain in the production of Frankfurters. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, S.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Microencapsulation of extracted bioactive compounds from brewer’s spent grain to enrich fish-burgers. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Cazares, L.A.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Ramírez-Jiménez, A.K.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Campos-Vega, R.; Gaytán-Martínez, M. Influence of extrusion process on the release of phenolic compounds from mango (Mangifera indica L.) bagasse-added confections and evaluation of their bioaccessibility, intestinal permeability, and antioxidant capacity. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affonfere, M.; Chadare, F.J.; Fassinou, F.T.K.; Linnemann, A.R.; Duodu, K.G. In-vitro Digestibility Methods and Factors Affecting Minerals Bioavailability: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Proaño, J.L.; Salgado, P.R.; Mauri, A.N.; Drago, S.R. High iron bioaccessibility from co-microencapsulated iron/ascorbic acid using chelating polypeptides from brewers’ spent grain protein as wall material. Lwt 2021, 139, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, S.; Kyomugasho, C.; Celus, M.; Hendrickx, M.E.G.; Grauwet, T. Barriers impairing mineral bioaccessibility and bioavailability in plant-based foods and the perspectives for food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.G.S.; Rebellato, A.P.; Caramês, E.T.d.S.; Greiner, R.; Pallone, J.A.L. In vitro digestion effect on mineral bioaccessibility and antioxidant bioactive compounds of plant-based beverages. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platel, K.; Eipeson, S.W.; Srinivasan, K. Bioaccessible mineral content of malted finger millet (Eleusine coracana), wheat (Triticum aestivum), and barley (Hordeum vulgare). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8100–8103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, M.; Çatak, J.; Uğur, H.; Gürbüz, M.; Belli, İ.; Tanyıldız, S.N.; Yıldırım, H.; Cengiz, S.; Yavuz, B.B.; Kişmiroğlu, C.; et al. The bioaccessibility of water-soluble vitamins: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaqua, D.; Carnier, R.; Cadore, S.; Sanches, V.L.; Berton, R.S.; Corbi, F.C.A.; Coscione, A.R. In vitro bioaccessibility and bioavailability of selenium in agronomic biofortified wheat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 105, 104253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, C.; Assadpour, E.; Dima, S.; Jafari, S.M. Bioavailability and bioaccessibility of food bioactive compounds; overview and assessment by in vitro methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2862–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igual, M.; Păucean, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; García-Segovia, P.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; Chiş, M.S. In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Bioactive Compounds from Rosehip-Enriched Corn Extrudates. Molecules 2022, 27, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanță, L.C.; Coldea, T.E.; Ignat, M.V.; Pop, C.R.; Tofană, M.; Mudura, E.; Borșa, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Zhao, H. Non-Alcoholic and Craft Beer Production and Challenes. Processes 2020, 8, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.Q.; Liu, S.Q. An overview of selected specialty beers: Developments, challenges and prospects. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltermaier, A.; Waters, D.; Becker, T.; Arendt, E.; Gastl, M. Common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and its use as a brewing cereal—A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastanjević, K.; Šarkanj, B.; Krska, R.; Sulyok, M.; Warth, B.; Mastanjević, K.; Šantek, B.; Krstanović, V. From malt to wheat beer: A comprehensive multi-toxin screening, transfer assessment and its influence on basic fermentation parameters. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabija, A.; Ciocan, M.E.; Chetrariu, A.; Codină, G.G. Buckwheat and Amaranth as Raw Materials for Brewing, a Review. Plants 2022, 11, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.P.; Niccolai, A.; Fradinho, P.; Fragoso, S.; Bursic, I.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Microalgae biomass as an alternative ingredient in cookies: Sensory, physical and chemical properties, antioxidant activity and in vitro digestibility. Algal Res. 2017, 26, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouzam, R.B.; Pohl, P.; Lobinski, R. Bioaccessibility of essential elements from white cheese, bread, fruit and vegetables. Talanta 2011, 86, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chen, X.D. Validation of in vitro bioaccessibility assays—A key aspect in the rational design of functional foods towards tailored bioavailability. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, M.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Trusek, A. Brewer’ s Spent Grains—Valuable Beer Industry By-Product biomolecules Brewer’ s Spent Grains—Valuable Beer Industry By-Product. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetrariu, A.; Dabija, A. Brewer’s spent grains: Possibilities of valorization, a review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio-Lopes, T.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M. Current extraction techniques towards bioactive compounds from brewer’s spent grain–A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naibaho, J.; Korzeniowska, M. Brewers’ spent grain in food systems: Processing and final products quality as a function of fiber modification treatment. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 1532–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s spent grain: A valuable feedstock for industrial applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosek, Ż.; Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Rotter, I. The effects of calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, fluoride, and lead on bone tissue. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Swelm, R.P.L.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Swinkels, D.W. The multifaceted role of iron in renal health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechova, A.; Pavlata, L. Chromium as an essential nutrient: A review. Vet. Med. 2007, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asli, M.; Azizzadeh, M.; Moghaddamjafari, A.; Mohsenzadeh, M. Copper, Iron, Manganese, Zinc, Cobalt, Arsenic, Cadmium, Chrome, and Lead Concentrations in Liver and Muscle in Iranian Camel (Camelus dromedarius). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Shabnam, A.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Gupta, D.K.; et al. Nickel in terrestrial biota: Comprehensive review on contamination, toxicity, tolerance and its remediation approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirabi, A.; Shokuhi Rad, A.; Nourani, S. Application of modified magnetic nanoparticles as a sorbent for preconcentration and determination of nickel ions in food and environmental water samples. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 74, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.H.; Ribeiro Fernandes, M.; De Pádua Melo, E.S.; Granja Arakaki, D.; De Lima, N.V.; Santos Leite, L.C.; Espindola, P.R.; De Souza, I.D.; Do Nascimento, V.A.; Saldanha Tschinkel, P.F.; et al. Determination of Macro- And Microelements in the Inflorescences of Banana Tree Using ICP OES: Evaluation of the Daily Recommendations of Intake for Humans. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 8383612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahifar, A.; Chapman, L.D.; Weber, L.; Samadi, N.; Cooper, D.M.L. Biodistribution of strontium and barium in the developing and mature skeleton of rats. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2019, 37, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Ntoupa, P.S.A.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Recent aspects of the effects of zinc on human health. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, T.; Carriere, F.; Day, L.; Deglaire, A.; Egger, L.; Freitas, D.; Golding, M.; Le Feunteun, S.; Macierzanka, A.; Menard, O.; et al. Correlation between in vitro and in vivo data on food digestion. What can we predict with static in vitro digestion models? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2239–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, P.; Ibanoǧlu, Ş.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, E.; Stojceska, V. Effect of brewers spent grain addition and screw speed on the selected physical and nutritional properties of an extruded snack. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ spent grain: A review with an emphasis on food and health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligundla, P.; Mok, C. Recent advances in biotechnological valorization of brewers’ spent grain. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, F.; Champ, M. Structural and physical properties of dietary fibres, and consequences of processing on human physiology. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligundla, P.; Mok, C.; Park, S. Advances in the valorization of spent brewer’s yeast. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 62, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, E.; De Brier, N.; Goos, P.; Smolders, E.; Delcour, J.A. Steeping and germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). I. Unlocking the impact of phytate and cell wall hydrolysis on bio-accessibility of iron and zinc elements. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 90, 102847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, D. Malting: An indigenous technology used for improving the nutritional quality of grains— A review. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2017, 36, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raes, K.; Knockaert, D.; Struijs, K.; Van Camp, J. Role of processing on bioaccessibility of minerals: Influence of localization of minerals and anti-nutritional factors in the plant. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 37, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.A.; Wyrwisz, J.; Karp, S.; Wierzbicka, A. Particle size of dietary fiber preparation affects the bioaccessibility of selected vitamin B in fortified wheat bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 77, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akça, S.N.; Sargın, H.S.; Mızrak, Ö.F.; Yaman, M. Determination and assessment of the bioaccessibility of vitamins B1, B2, and B3 in commercially available cereal-based baby foods. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Procopio, S.; Becker, T. Influence of malting and lactic acid fermentation on functional bioactive components in cereal-based raw materials: A review paper. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaupa, M.; Scazzina, F.; Dall’Asta, M.; Calani, L.; Del Rio, D.; Bianchi, M.A.; Melegari, C.; De Albertis, P.; Tribuzio, G.; Pellegrini, N.; et al. In vitro bioaccessibility of phenolics and vitamins from durum wheat aleurone fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, M.; Mızrak, Ö.F. Determination and evaluation of in vitro bioaccessibility of the pyridoxal, pyridoxine, and pyridoxamine forms of vitamin B6 in cereal-based baby foods. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, O.Y.; Seregina, N.V.; Ivanova, T.N.; Shuldeshova, N.V.; Zaugolnikova, E.V. Micronutrient value and antioxidant activity of malt wheat sprouts. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 677, 022107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavriša, Ž.; Hristov, H.; Hribar, M.; Žmitek, K.; Kušar, A.; Koroušić Seljak, B.; Gregorič, M.; Blaznik, U.; Gregorič, N.; Zaletel, K.; et al. Dietary Intake and Status of Vitamin B12 in Slovenian Population. Nutrients 2022, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcheverry, P.; Grusak, M.A.; Fleige, L.E. Application of in vitro bioaccessibility and bioavailability methods for calcium, carotenoids, folate, iron, magnesium, polyphenols, zinc, and vitamins B 6, B 12, D, and E. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.N.; Nagaonkar, S.N.; Shah, N.B.; Bhat, T.S.; Almale, B. Study of perception and help seeking behaviour among parents for their children with psychiatric disorder: A community based cross-sectional study. J. Med. Res. 2016, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roasa, J.; De Villa, R.; Mine, Y.; Tsao, R. Phenolics of cereal, pulse and oilseed processing by-products and potential effects of solid-state fermentation on their bioaccessibility, bioavailability and health benefits: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 954–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luithui, Y.; Baghya Nisha, R.; Meera, M.S. Cereal by-products as an important functional ingredient: Effect of processing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Dai, S.; Lian, Z.; Tong, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Qi, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. The Layered Encapsulation of Vitamin B 2 and β -Carotene in Bioaccessibility of Vitamin B 2 and β -Carotene. Foods 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cereal By-Products | Used Grains | Percent | Kilning Temperature °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| BSG 1 | Pale Ale Malt | 40% | 80–85 |
| Munich Malt | 30% | 100–105 | |
| Caramel Malt | 24% | 220 | |
| Black Malt | 6% | 235–250 | |
| BSG 2 | Pale Ale Malt | 65% | 80–85 |
| Vienna Malt | 35% | 100–110 | |
| BSG 3 | Pilsner Malt | 70% | 80–85 |
| Degermed Corn | 30% | - | |
| BSG 4 | Pilsner Malt | 50% | 80–85 |
| Wheat Malt | 50% | 72–80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fărcaș, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Chiș, M.S.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P.; Becze, A.; Török, A.I.; Cadar, O.; Coldea, T.E.; Igual, M. In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173512
Fărcaș AC, Socaci SA, Chiș MS, Martínez-Monzó J, García-Segovia P, Becze A, Török AI, Cadar O, Coldea TE, Igual M. In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains. Nutrients. 2022; 14(17):3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173512
Chicago/Turabian StyleFărcaș, Anca Corina, Sonia Ancuța Socaci, Maria Simona Chiș, Javier Martínez-Monzó, Purificación García-Segovia, Anca Becze, Anamaria Iulia Török, Oana Cadar, Teodora Emilia Coldea, and Marta Igual. 2022. "In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains" Nutrients 14, no. 17: 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173512
APA StyleFărcaș, A. C., Socaci, S. A., Chiș, M. S., Martínez-Monzó, J., García-Segovia, P., Becze, A., Török, A. I., Cadar, O., Coldea, T. E., & Igual, M. (2022). In Vitro Digestibility of Minerals and B Group Vitamins from Different Brewers’ Spent Grains. Nutrients, 14(17), 3512. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173512












