Influence of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Platelet Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quantification of TMAO and Its Precursors
2.1.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.1.2. Human Samples
2.1.3. LC-MS/MS
2.1.4. Method Validation
2.2. TMAO In-Vivo Pre-Analytics
2.2.1. Participants and Exclusion Criteria
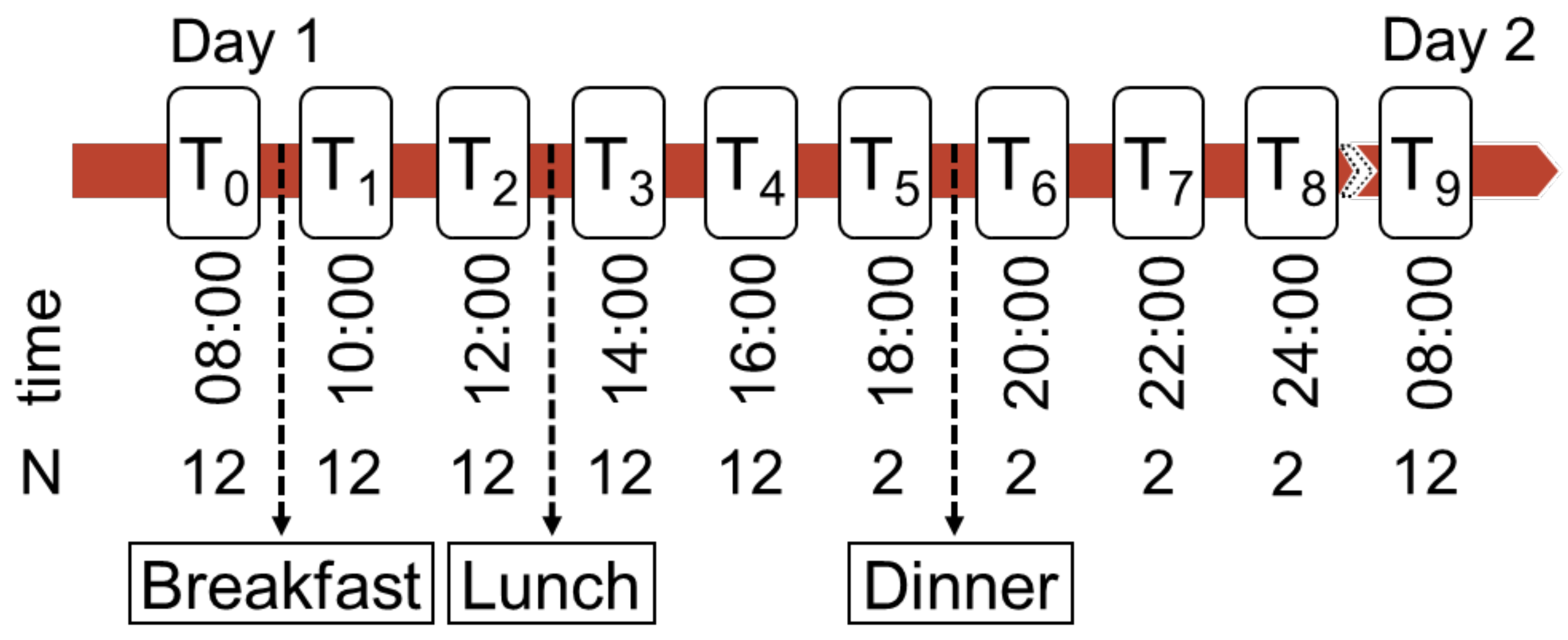
2.2.2. Sampling and Experimental Procedure
2.3. Platelet Activation
2.3.1. Participants and Exclusion Criteria
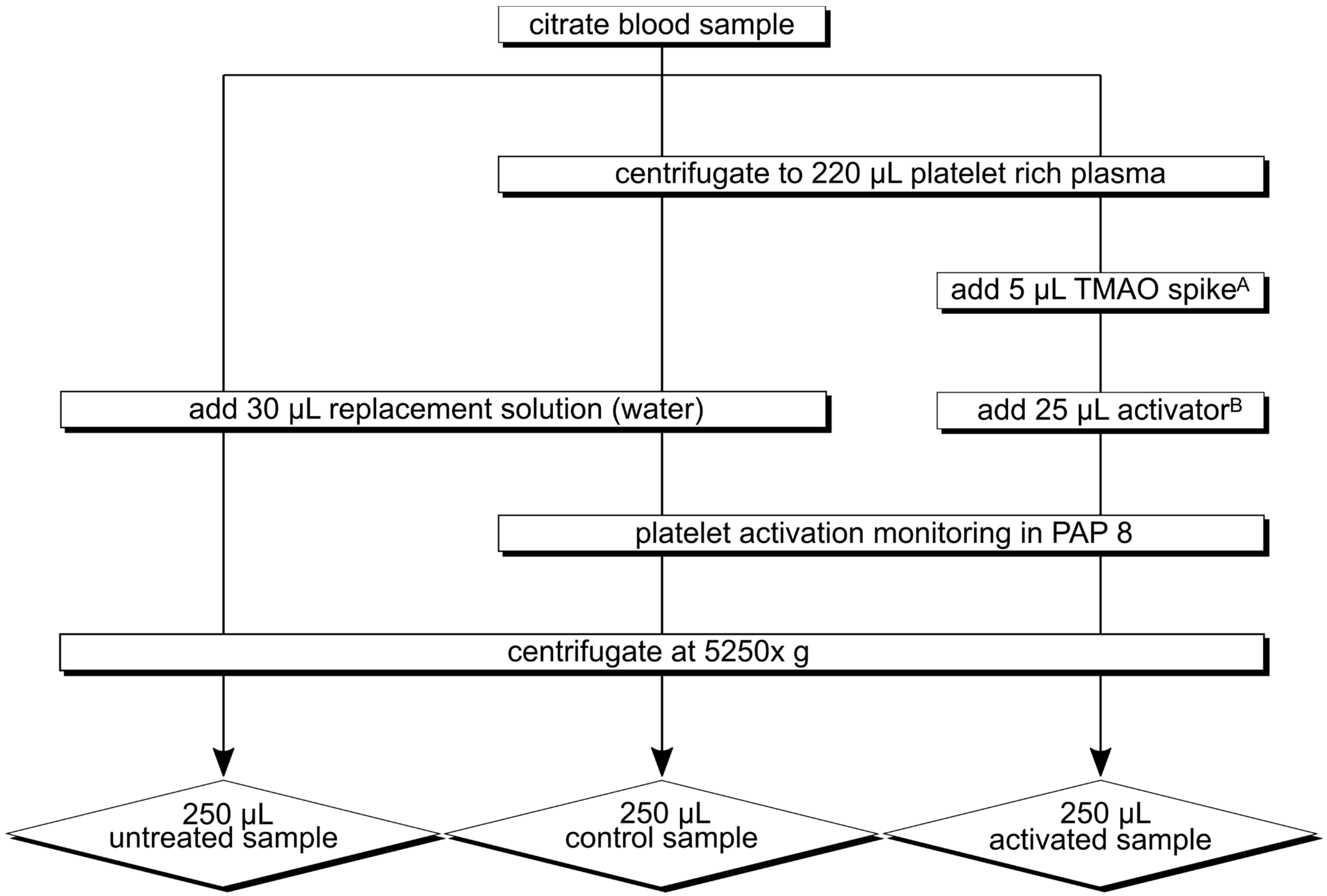
2.3.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3.3. Experimental Series
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LC-MS/MS
3.2. TMAO In-Vivo Pre-Analytics
3.2.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2.2. TMAO, Precursors, and Amino Acids Progressions
3.2.3. Correlation of TMAO, Precursors, and Amino Acids
3.3. Platelet Activation Experiment
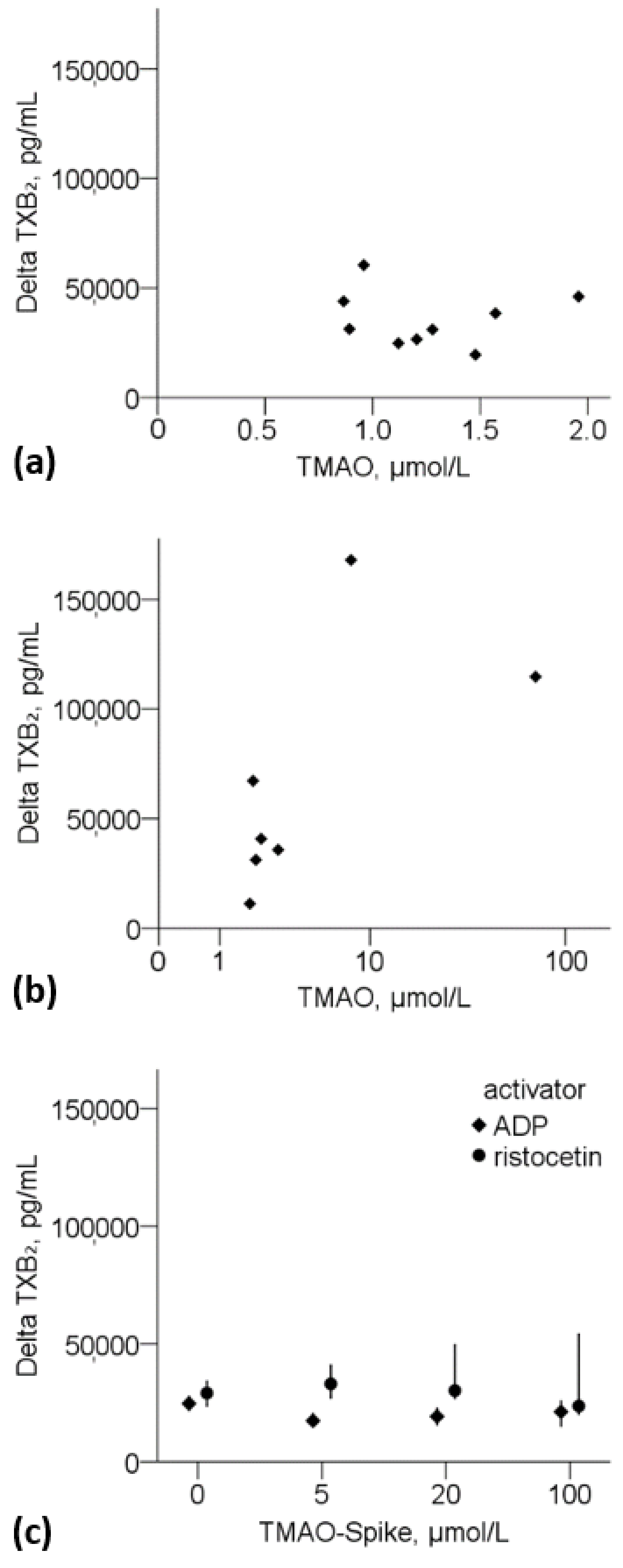
3.3.1. Thromboxane B2 and TMAO
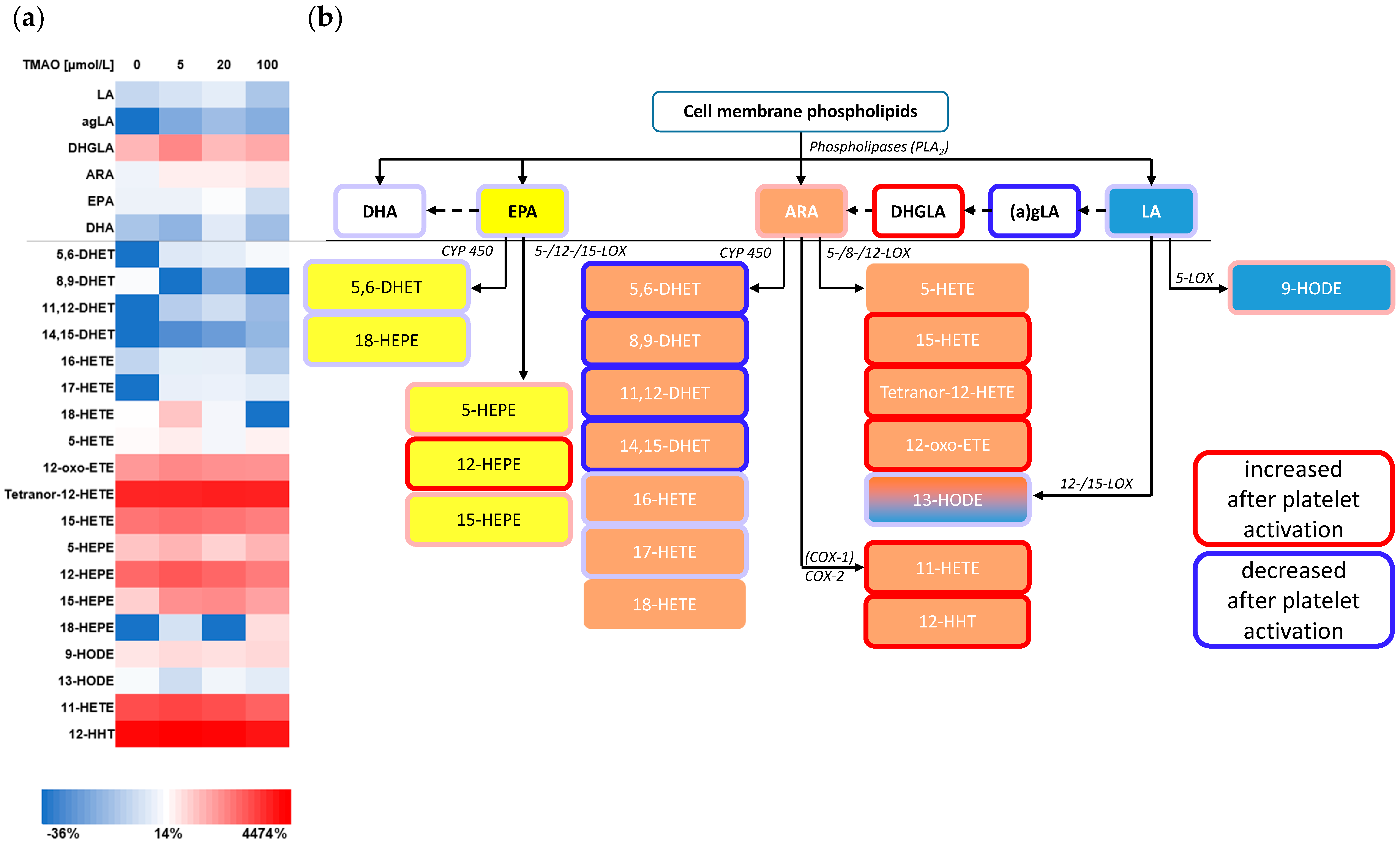
3.3.2. Eicosanoids
4. Discussion
4.1. LC-MS/MS
4.2. In-Vivo Pre-Analytics
4.3. Platelet Activation
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.-M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gatarek, P.; Kaluzna-Czaplinska, J. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) in human health. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, M.; Aulisa, G.; Marcon, D.; Rizzo, G.; Tarsisano, M.G.; Di Renzo, L.; Federici, M.; Caprio, M.; de Lorenzo, A. Association of Urinary and Plasma Levels of Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) with Foods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.C.; Hullar, M.A.J.; Randolph, T.W.; Franke, A.A.; Monroe, K.R.; Cheng, I.; Wilkens, L.R.; Shepherd, J.A.; Madeleine, M.M.; Le Marchand, L.; et al. Associations of plasma trimethylamine N-oxide, choline, carnitine, and betaine with inflammatory and cardiometabolic risk biomarkers and the fecal microbiome in the Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Q.; Cai, L. The gut microbiota and its interactions with cardiovascular disease. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rath, S.; Rud, T.; Pieper, D.H.; Vital, M. Potential TMA-Producing Bacteria Are Ubiquitously Found in Mammalia. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.S.; Fernandez, M.L. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO), Diet and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernetti, L.; Gough, A.; Baetz, N.; Blutt, S.; Broughman, J.R.; Brown, J.A.; Foulke-Abel, J.; Hasan, N.; In, J.; Kelly, E.; et al. Functional Coupling of Human Microphysiology Systems: Intestine, Liver, Kidney Proximal Tubule, Blood-Brain Barrier and Skeletal Muscle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeisel, S.H.; Warrier, M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide, the Microbiome, and Heart and Kidney Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2017, 37, 157–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seldin, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Z.; Hazen, S.L.; Lusis, A.J.; Shih, D.M. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-κB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Jiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Chen, Y. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 481, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kühn, T.; Rohrmann, S.; Sookthai, D.; Johnson, T.; Katzke, V.; Kaaks, R.; von Eckardstein, A.; Müller, D. Intra-individual variation of plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), betaine and choline over 1 year. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, C.E.; Taesuwan, S.; Malysheva, O.V.; Bender, E.; Tulchinsky, N.F.; Yan, J.; Sutter, J.L.; Caudill, M.A. Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) response to animal source foods varies among healthy young men and is influenced by their gut microbiota composition: A randomized controlled trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Davies, S.K.; Revell, V.L.; Keun, H.; Skene, D.J. Diurnal rhythms in the human urine metabolome during sleep and total sleep deprivation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brauer, R.; Leichtle, A.B.; Fiedler, G.M.; Thiery, J.; Ceglarek, U. Preanalytical standardization of amino acid and acylcarnitine metabolite profiling in human blood using tandem mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2011, 7, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuko, M.; Kozioł, I.; Kotlęga, D.; Brodowski, J.; Drozd, A. The Role of Thromboxane in the Course and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrono, C.; Rocca, B. Measurement of Thromboxane Biosynthesis in Health and Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, P.; Zufferey, A.; Daali, Y.; Reny, J.-L. Antiplatelet therapy: Targeting the TxA2 pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2014, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Khan, H.; Xiao, J.; Cheang, W.S. Effects of Arachidonic Acid Metabolites on Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mütze, U.; Beblo, S.; Kortz, L.; Matthies, C.; Koletzko, B.; Bruegel, M.; Rohde, C.; Thiery, J.; Kiess, W.; Ceglarek, U. Metabolomics of Dietary Fatty Acid Restriction in Patients with Phenylketonuria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kortz, L.; Dorow, J.; Becker, S.; Thiery, J.; Ceglarek, U. Fast liquid chromatography-quadrupole linear ion trap-mass spectrometry analysis of polyunsaturated fatty acids and eicosanoids in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 927, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, D.M.; Allenspach, M.; Othman, A.; Saely, C.H.; Muendlein, A.; Vonbank, A.; Drexel, H.; von Eckardstein, A. Plasma levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide are confounded by impaired kidney function and poor metabolic control. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BORN, G.V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature 1962, 194, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasti, L.; Galliazzo, S.; Molaro, M.; Visconti, E.; Pennella, B.; Gaudio, G.V.; Lupi, A.; Grandi, A.M.; Squizzato, A. TMAO as a biomarker of cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, R.A.; Koh, A.Y.; Zia, A. The gut microbiome and thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 2020, 189, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, C.; Dittrich, J.; Gaudl, A.; Schellong, P.; Beuchel, C.F.; Baber, R.; Beutner, F.; Teren, A.; Engel, C.; Wirkner, K.; et al. Association of plasma trimethylamine N-oxide levels with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and factors of the metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2021, 335, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocque, A.J.; Stubbs, J.R.; Nolin, T.D. Development and validation of a simple UHPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of trimethylamine N-oxide, choline, and betaine in human plasma and urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 109, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L.; Yin, Y. Simultaneous targeted analysis of trimethylamine-N-oxide, choline, betaine, and carnitine by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1035, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, A.; Di Giuseppe, R.; Koch, M.; Fromm, M.F.; Lieb, W.; Maas, R. Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) determined by LC-MS/MS: Distribution and correlates in the population-based PopGen cohort. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustad, S.; Eussen, S.; Midttun, Ø.; Ulvik, A.; van de Kant, P.M.; Mørkrid, L.; Gislefoss, R.; Ueland, P.M. Kinetic modeling of storage effects on biomarkers related to B vitamin status and one-carbon metabolism. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi Park, E.; Lee, E.; Jin Joo, H.; Oh, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.S. Inter- and intra-individual variations of urnary endogenous metabolites in healthy male college students using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, K.; Kesmarky, G.; Feher, G.; Tibold, A.; Toth, K. Platelet Aggregometry Testing: Molecular Mechanisms, Techniques and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badimon, L.; Vilahur, G.; Rocca, B.; Patrono, C. The key contribution of platelet and vascular arachidonic acid metabolism to the pathophysiology of atherothrombosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, K.; Yokomizo, T. Identification, Signaling, and Functions of LTB4 Receptors. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 33, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Fuchs, D.; Tan, S.; Trauelsen, M.; Schwartz, T.W.; Wheelock, C.E.; Li, N.; Haeggström, J.Z. Activation of Metabolite Receptor GPR91 Promotes Platelet Aggregation and Transcellular Biosynthesis of Leukotriene C4. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rund, K.M.; Nolte, F.; Doricic, J.; Greite, R.; Schott, S.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Gueler, F.; Schebb, N.H. Clinical Blood Sampling for Oxylipin Analysis—Effect of Storage and Pneumatic Tube Transport of Blood on Free and Total Oxylipin Profile in Human Plasma and Serum. Analyst 2020, 145, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cebo, M.; Schlotterbeck, J.; Gawaz, M.; Chatterjee, M.; Lämmerhofer, M. Simultaneous Targeted and Untargeted UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS Method with Data-Independent Acquisition for Quantification and Profiling of (Oxidized) Fatty Acids Released upon Platelet Activation by Thrombin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1094, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.T.; Miura, H.; Hatoum, O.A.; Campbell, W.B.; Hammock, B.D.; Zeldin, D.C.; Falck, J.R.; Gutterman, D.D. Epoxyeicosatrienoic and Dihydroxyeicosatrienoic Acids Dilate Human Coronary Arterioles via BKCa Channels: Implications for Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H491–H499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Experimental Series | Participants, n | Activator | Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | ristocetin | Samples were collected on nine subsequent days at the same daytime. |
| 2 | 7 | ristocetin | Samples were collected on different days at the same daytime. |
| 3 | 1 | ristocetin, ADP | Samples were collected on one day in three runs and spiked with different TMAO-concentrations |
| Between Day | Within Run | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betaine | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N |
| Val native | 29 | 5.6% | 30 | 29 | 4.7% | 30 | ||
| Val spike level 1 | 63 | 6.2% | 80% | 30 | 66 | 4.4% | 88% | 30 |
| Val spike level 2 | 96 | 6.8% | 79% | 30 | 97 | 5.6% | 80% | 27 |
| QC native | 28 | 4.6% | 116 | |||||
| QC spike level 1 | 111 | 3.8% | 97% | 96 | ||||
| Carnitine | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N |
| Val native | 41 | 5.5% | 30 | 40 | 4.1% | 30 | ||
| Val spike level 1 | 72 | 6.3% | 101% | 30 | 74 | 4.3% | 110% | 30 |
| Val spike level 2 | 102 | 6.9% | 99% | 30 | 102 | 5.7% | 100% | 27 |
| QC native | 39 | 4.5% | 116 | |||||
| QC spike level 1 | 99 | 4.1% | 96% | 96 | ||||
| Choline | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N |
| Val native | 9.2 | 7.8% | 30 | 8.8 | 3.2% | 30 | ||
| Val spike level 1 | 17 | 6.2% | 79% | 29 | 17 | 3.8% | 82% | 30 |
| Val spike level 2 | 31 | 5.8% | 76% | 29 | 30 | 4.7% | 75% | 27 |
| QC native | 8.6 | 4.9% | 116 | |||||
| QC spike level 1 | 56 | 3.9% | 98% | 96 | ||||
| TMAO | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N | Mean [µmol/L] | CV | Recovery | N |
| Val native | 4.0 | 7.8% | 30 | 3.7 | 5.2% | 30 | ||
| Val spike level 1 | 5.2 | 6.3% | 90% | 30 | 5.2 | 5.0% | 111% | 30 |
| Val spike level 2 | 10 | 6.9% | 94% | 30 | 10 | 6.5% | 94% | 27 |
| QC native | 3.7 | 5.3% | 116 | |||||
| QC spike level 1 | 10 | 4.8% | 97% | 96 | ||||
| N | ILM Leipzig | IKC Zurich | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Betaine [µmol/L] | 31 | 29 (21–47) | 26 (20–44) | 0.678 |
| Choline [µmol/L] | 31 | 13 (7.3–29) | 12 (7.7–28) | 0.860 |
| TMAO [µmol/L] | 29 | 4.8 (3.0–10) | 5.1 (3.3–10) | 0.852 |
| Metabolite | Intra-Individual Coefficient of Variation 1 | Inter-Individual Coefficient of Variation 2 |
|---|---|---|
| TMAO | 28% | 37% |
| Betaine | 7.3% | 32% |
| Choline | 11% | 25% |
| Carnitine | 6.5% | 21% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emonds, J.J.; Ringel, C.; Reinicke, M.; Müller, D.; Von Eckardstein, A.; Meixensberger, J.; Ceglarek, U.; Gaudl, A. Influence of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Platelet Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163261
Emonds JJ, Ringel C, Reinicke M, Müller D, Von Eckardstein A, Meixensberger J, Ceglarek U, Gaudl A. Influence of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Platelet Activation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163261
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmonds, Julian Josef, Clemens Ringel, Madlen Reinicke, Daniel Müller, Arnold Von Eckardstein, Jürgen Meixensberger, Uta Ceglarek, and Alexander Gaudl. 2022. "Influence of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Platelet Activation" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163261
APA StyleEmonds, J. J., Ringel, C., Reinicke, M., Müller, D., Von Eckardstein, A., Meixensberger, J., Ceglarek, U., & Gaudl, A. (2022). Influence of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Platelet Activation. Nutrients, 14(16), 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163261








