Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
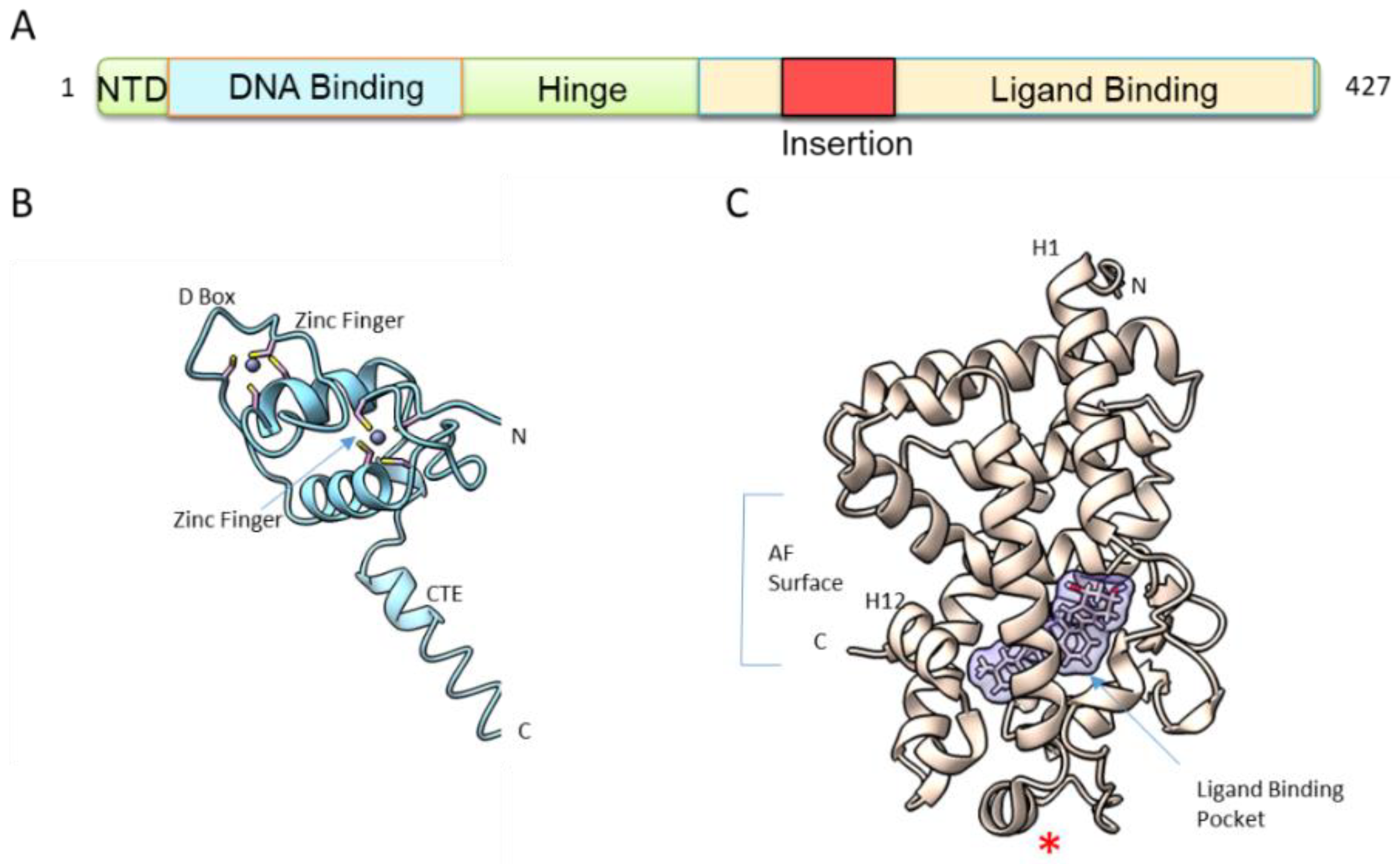
2. Structure and Mechanism of Activation of the Vitamin D Receptor
3. DNA Binding
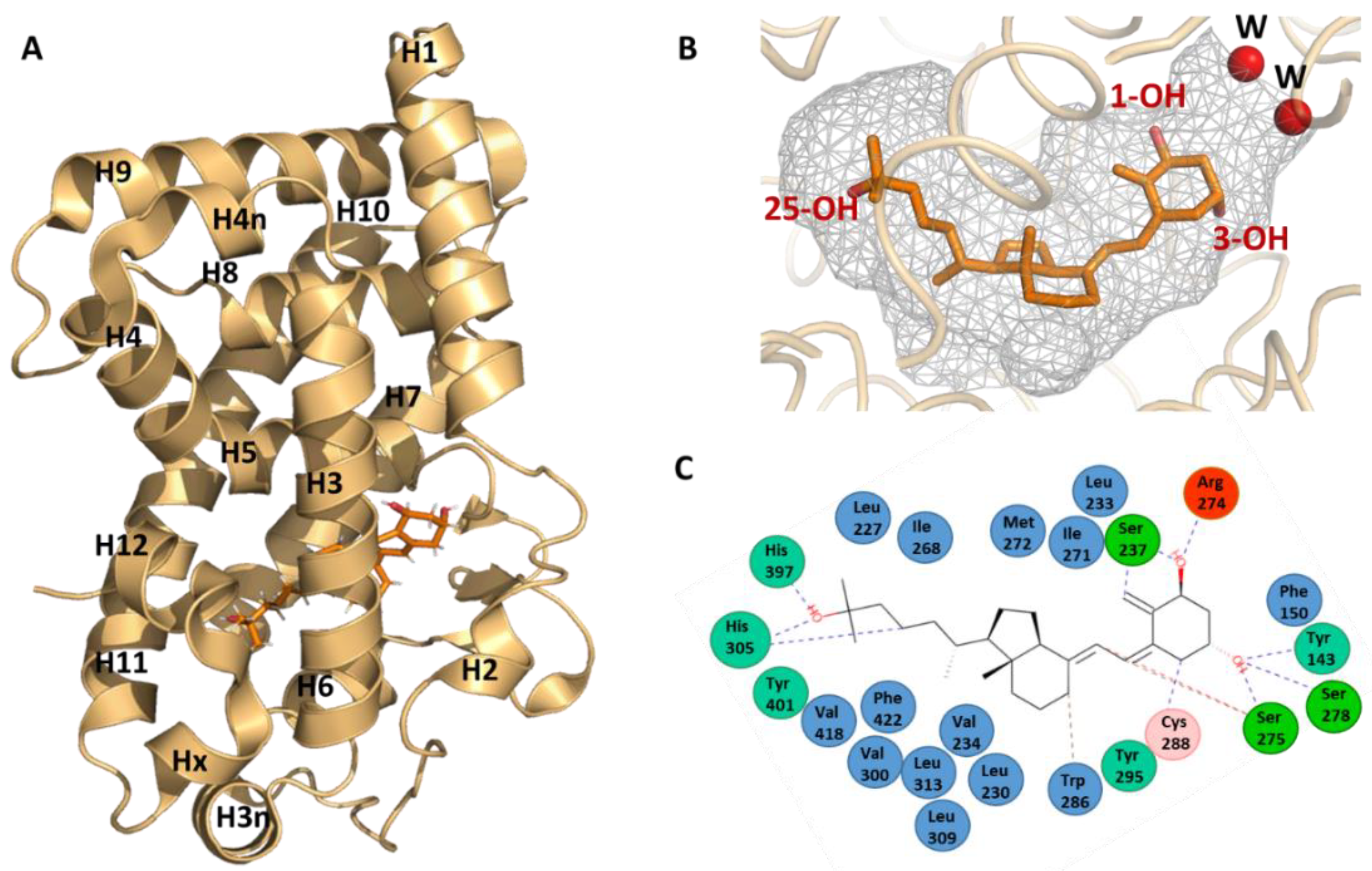
4. Ligand Binding
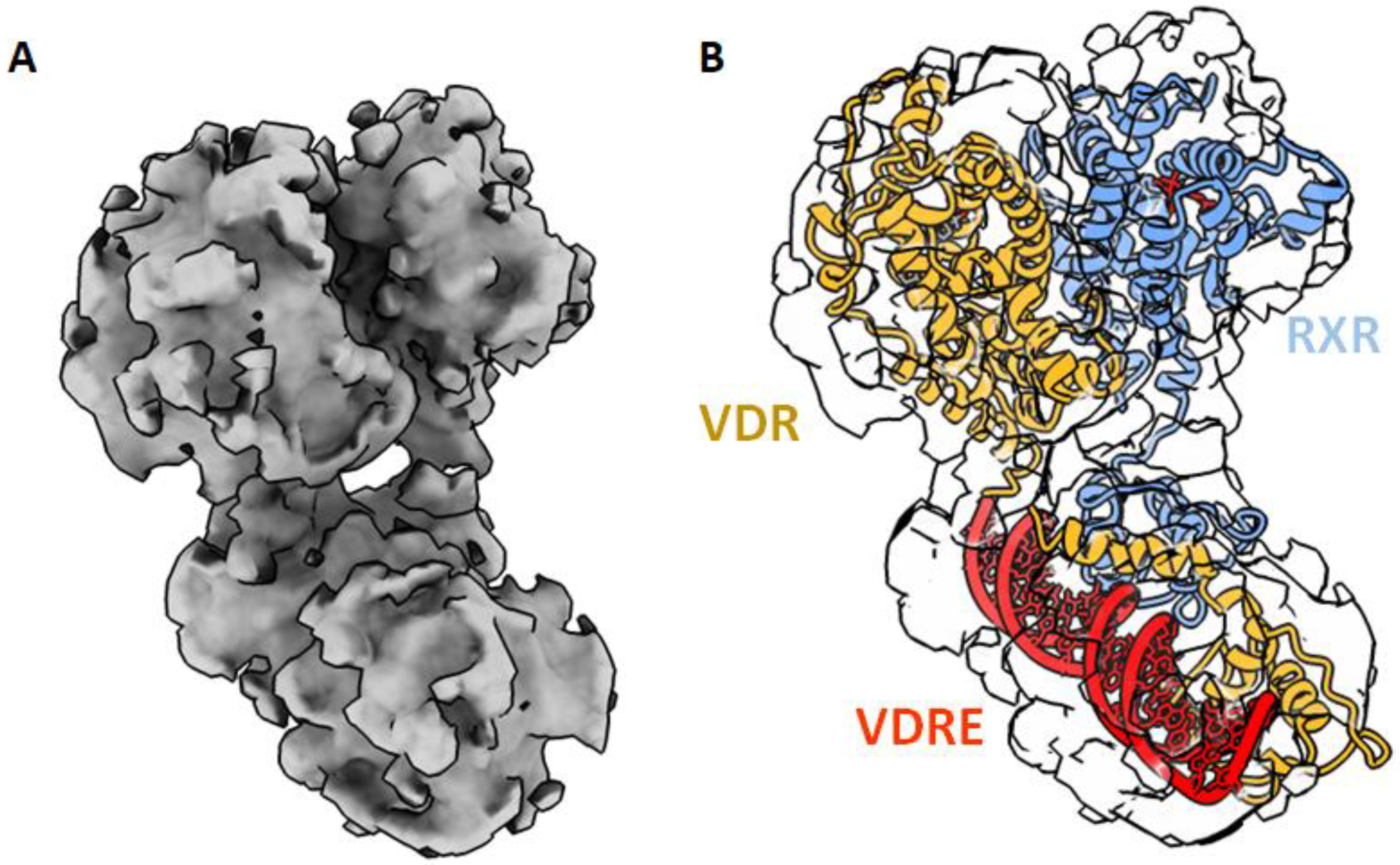
5. Structure of Full-Length VDR Complex
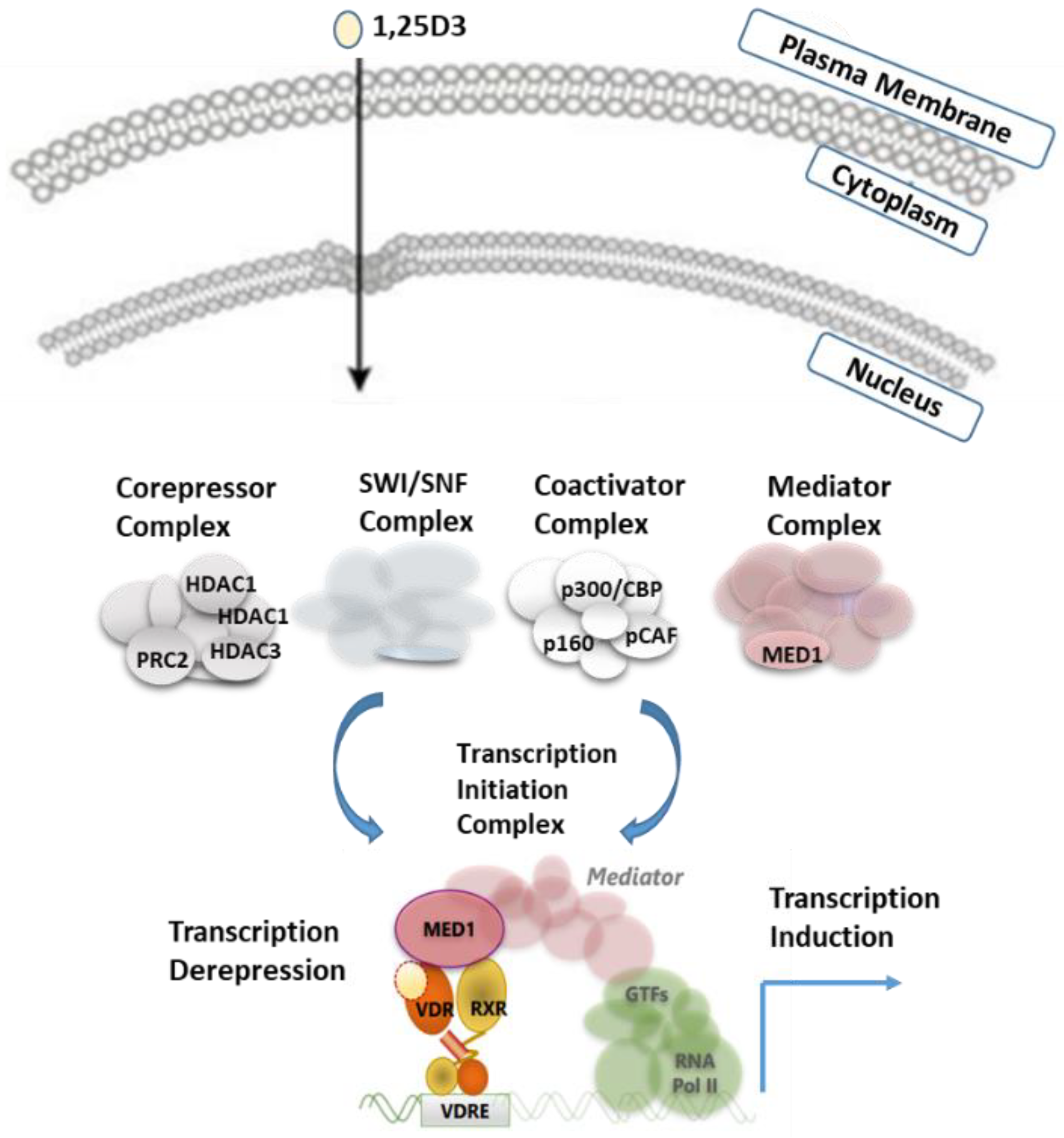
6. VDR–Coregulatory Complexes
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D: Production, Metabolism and Mechanisms of Action. In Endotext [Internet]; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, D.P.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Pike, J.W.; Haussler, M.R.; O’Malley, B.W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science 1987, 235, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmester, J.K.; Maeda, N.; DeLuca, H.F. Isolation and expression of rat 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peleg, S.; Pike, J.W.; O’Malley, B.W. Characterization of the chromosomal gene of the mouse vitamin D receptor. In Vitamin D, Molecular Cellular and Clinical Endocrinology; Norman, A., Schaefer, K., Grigoleit, Herrath, D., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 242–243. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, A.R.; McDonnell, D.P.; Hughes, M.; Crisp, T.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Haussler, M.R.; Pike, J.W.; Shine, J.; O’Malley, B.W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3294–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleet, J.C. The role of vitamin D in the endocrinology controlling calcium homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 453, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D. Functions of vitamin D in bone. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2018, 149, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.; Christakos, S. New aspects of vitamin D metabolism and action—Addressing the skin as source and target. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.A.; Anderson, P.H. Autocrine and paracrine actions of vitamin D. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2010, 31, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B. The unsettled science of nonrenal calcitriol production and its clinical relevance. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4519–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckey, R.C.; Cheng, C.Y.S.; Slominski, A.T. The serum vitamin D metabolome: What we know and what is still to discover. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 186, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Bikle, D. Vitamin D Metabolism Revised: Fall of Dogmas. J. Bone Min. Res. 2019, 34, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Sastry, K.S.; Chouchane, A.I. Role of Vitamin D Beyond the Skeletal Function: A Review of the Molecular and Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leyssens, C.; Verlinden, L.; Verstuyf, A. The future of vitamin D analogs. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maestro, M.A.; Molnár, F.; Carlberg, C. Vitamin D and Its Synthetic Analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6854–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, M.R.; Whitfield, G.K.; Kaneko, I.; Haussler, C.A.; Hsieh, D.; Hsieh, J.C.; Jurutka, P.W. Molecular mechanisms of vitamin D action. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 92, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Vitamin D and Its Target Genes. Nutrients 2022, 4, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, N.A.; Qi, J.C.; Tokita, A.; Kelly, P.J.; Crofts, L.; Nguyen, T.V.; Sambrook, P.N.; Eisman, J.A. Prediction of bone density from vitamin D receptor alleles. Nature 1994, 367, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochel, N.; Tocchini-Valentini, G.; Egea, P.F.; Juntunen, K.; Garnier, J.M.; Vihko, P.; Moras, D. Functional and structural characterization of the insertion region in the ligand binding domain of the vitamin D nuclear receptor. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochel, N.; Wurtz, J.M.; Mitschler, A.; Klaholz, B.; Moras, D. The crystal structure of the nuclear receptor for vitamin D bound to its natural ligand. Mol. Cell. 2000, 5, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, P.L.; Gewirth, D.T. Structural basis of VDR-DNA interactions on direct repeat response elements. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2242–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLuca, H.F.; Zierold, C. Mechanisms and functions of vitamin D. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. What do we learn from the genome-wide perspective on vitamin D3? Anticancer. Res. 2015, 35, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B.; Benkusky, N.A.; Lee, S.M.; St John, H.; Carlson, A.; Onal, M.; Shamsuzzaman, S. Genomic Determinants of Vitamin D-Regulated Gene Expression. Vitam. Horm. 2016, 100, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramagopalan, S.V.; Heger, A.; Berlanga, A.J.; Maugeri, N.J.; Lincoln, M.R.; Burrell, A.; Handunnetthi, L.; Handel, A.E.; Disanto, G.; Orton, S.M.; et al. A ChIP-seq defined genome-wide map of vitamin D receptor binding: Associations with disease and evolution. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, M.B.; Goetsch, P.D.; Pike, J.W. VDR/RXR and TCF4/β-catenin cistromes in colonic cells of colorectal tumor origin: Impact on c-FOS and c-MYC gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S.; Väisänen, S.; Pehkonen, P.; Seuter, S.; Benes, V.; Carlberg, C. Nuclear hormone 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 elicits a genome-wide shift in the locations of VDR chromatin occupancy. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2011, 39, 9181–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, N.; Yu, R.T.; Subramaniam, N.; Sherman, M.H.; Wilson, C.; Rao, R.; Leblanc, M.; Coulter, S.; He, M.; Scott, C.; et al. A vitamin D receptor/SMAD genomic circuit gates hepatic fibrotic response. Cell 2013, 153, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, M.D.; Campbell, M.J. Integrative genomic approaches to dissect clinically-significant relationships between the VDR cistrome and gene expression in primary colon cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 173, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warwick, T.; Schulz, M.H.; Gilsbach, R.; Brandes, R.P.; Seuter, S. Nuclear receptor activation shapes spatial genome organization essential for gene expression control: Lessons learned from the vitamin D receptor. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, 3745–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El Maaty, M.A.; Grelet, E.; Keime, C.; Rerra, A.I.; Gantzer, J.; Emprou, C.; Terzic, J.; Lutzing, R.; Bornert, J.M.; Laverny, G.; et al. Single-cell analyses unravel cell type-specific responses to a vitamin D analog in prostatic precancerous lesions. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singarapu, K.K.; Zhu, J.; Tonelli, M.; Rao, H.; Assadi-Porter, F.M.; Westler, W.M.; DeLuca, H.F.; Markley, J.L. Ligand-specific structural changes in the vitamin D receptor in solution. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 11025–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chalmers, M.J.; Stayrook, K.R.; Burris, L.L.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Pascal, B.D.; Burris, T.P.; Dodge, J.A.; Griffin, P.R. Hydrogen/deuterium exchange reveals distinct agonist/partial agonist receptor dynamics within vitamin D receptor/retinoid X receptor heterodimer. Structure 2010, 18, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, A.; Itoh, T.; Anami, Y.; Egawa, D.; Yamamoto, K. Helix12-Stabilization Antagonist of Vitamin D Receptor. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belorusova, A.Y.; Chalhoub, S.; Rovito, D.; Rochel, N. Structural Analysis of VDR Complex with ZK168281 Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9457–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowski, M.D.; Ai, N.; Hagey, L.R.; Kollitz, E.M.; Kullman, S.W.; Reschly, E.J.; Ekins, S. The evolution of farnesoid X, vitamin D, and pregnane X receptors: Insights from the green-spotted pufferfish (Tetraodon nigriviridis) and other non-mammalian species. BMC Biochem. 2011, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanhooke, J.L.; Benning, M.M.; Bauer, C.B.; Pike, J.W.; DeLuca, H.F. Molecular structure of the rat vitamin D receptor ligand binding domain complexed with 2-carbon-substituted vitamin D3 hormone analogues and a LXXLL-containing coactivator peptide. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4101–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, F.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D. Adaptability of the Vitamin D nuclear receptor to the synthetic ligand Gemini: Remodelling the LBP with one side chain rotation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigüeiro, R.; Bianchetti, L.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Chalhoub, S.; Dejaegere, A.; Osz, J.; Rochel, N. Advances in Vitamin D Receptor Function and Evolution Based on the 3D Structure of the Lamprey Ligand-Binding Domain. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 5821–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reschly, E.J.; Bainy, A.C.D.; Mattos, J.J.; Hagey, L.R.; Bahary, N.; Mada, S.R.; Ou, J.; Venkataramanan, R.; Krasowski, M.D. Functional evolution of the vitamin D and pregnane X receptors. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitfield, G.K.; Dang, H.T.L.; Schluter, S.F.; Bernstein, R.M.; Bunag, T.; Manzon, L.A.; Hsieh, G.; Encinas Dominguez, C.; Youson, J.H.; Haussler, M.R.; et al. Cloning of a functional vitamin D receptor from the lamprey (Petromyzon marinus), an ancient vertebrate lacking a calcified skeleton and teeth. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2704–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldman, D.J.; Malloy, P. Mutations in the vitamin D receptor and hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets. Bonekey Rep. 2014, 3, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acar, S.; Demir, K.; Shi, Y. Genetic causes of rickets. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristjansson, K.; Rut, A.R.; Hewison, M.; O’Riordan, J.L.; Hughes, M.R. Two mutations in the hormone binding domain of the vitamin D receptor cause tissue resistance to 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aljubeh, J.M.; Wang, J.; Al-Remeithi, S.S.; Malloy, P.J.; Feldman, D. Report of two unrelated patients with hereditary vitamin D resistant rickets due to the same novel mutation in the vitamin D receptor. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 24, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, P.C.; Dingle, E.; Pappas, J.; Raisingani, M. Clinical Phenotype in a Toddler with a Novel Heterozygous Mutation of the Vitamin D Receptor. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 3905905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malloy, P.J.; Eccleshall, T.R.; Gross, C.; Van Maldergem, L.; Bouillon, R.; Feldman, D. Hereditary vitamin D resistant rickets caused by a novel mutation in the vitamin D receptor that results in decreased affinity for hormone and cellular hyporesponsiveness. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andary, R.; El-Hage-Sleiman, A.K.; Farhat, T.; Sanjad, S.; Nemer, G. Hereditary vitamin D-resistant rickets in Lebanese patients: The p.R391S and p.H397P variants have different phenotypes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochel, N.; Molnár, F. Structural aspects of Vitamin D endocrinology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 453, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belorusova, A.Y.; Rochel, N. Structural Basis for Ligand Activity in Vitamin D Receptor. In Vitamin D, 5th ed.; Feldman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Belorusova, A.Y.; Rochel, N. Modulators of vitamin D nuclear receptor: Recent advances from structural studies. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2368–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Makishima, M. Structure-activity relationship of nonsecosteroidal vitamin D receptor modulators. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutchie, T.R.; Yu, O.B.; Di Milo, E.S.; Arnold, L.A. Alternative binding sites at the vitamin D receptor and their ligands. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 485, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, L.; Rehó, B.; Volkó, J.; Bojcsuk, D.; Kolostyák, Z.; Nagy, G.; Müller, G.; Simandi, Z.; Hegedüs, É.; Szabó, G.; et al. Agonist binding directs dynamic competition among nuclear receptors for heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10045–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.D.; Jurutka, P.W.; Haussler, C.A.; Whitfield, G.K.; Haussler, M.R. Heterodimeric DNA binding by the vitamin D receptor and retinoid X receptors is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and inhibited by 9-cis-retinoic acid. Evidence for allosteric receptor interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8483–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bettoun, D.J.; Burris, T.P.; Houck, K.A.; Buck, D.W.; Stayrook, K.R.; Khalifa, B.; Lu, J.; Chin, W.W.; Nagpal, S. Retinoid X receptor is a nonsilent major contributor to vitamin D receptor-mediated transcriptional activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Martínez, R.; Castillo, A.I.; Steinmeyer, A.; Aranda, A. The retinoid X receptor ligand restores defective signalling by the vitamin D receptor. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rochel, N.; Ciesielski, F.; Godet, J.; Moman, E.; Roessle, M.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Moulin, M.; Haertlein, M.; Callow, P.; Mély, Y.; et al. Common architecture of nuclear receptor heterodimers on DNA direct repeat elements with different spacings. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, I.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure of the full human RXR/VDR nuclear receptor heterodimer complex with its DR3 target DNA. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chalmers, M.J.; Stayrook, K.R.; Burris, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Busby, S.A.; Pascal, B.D.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Bruning, J.B.; Istrate, M.A.; et al. DNA binding alters coactivator interaction surfaces of the intact VDR-RXR complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Hamuro, Y.; Raghuram, S.; Wang, Y.; Burris, T.P.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the intact PPAR-gamma-RXR- nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature 2008, 456, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Potluri, N.; Wu, D.; Kim, Y.; Rastinejad, F. Multidomain integration in the structure of the HNF-4α nuclear receptor complex. Nature 2013, 495, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, X.; Toresson, G.; Benod, C.; Suh, J.H.; Philips, K.J.; Webb, P.; Gustafsson, J.A. Structure of the retinoid X receptor α-liver X receptor β (RXRα-LXRβ) heterodimer on DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Potluri, N.; Kim, Y.; Rastinejad, F. The quaternary architecture of RARβ-RXRα heterodimer facilitates domain-domain signal transmission. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maletta, M.; Orlov, I.; Roblin, P.; Beck, Y.; Moras, D.; Billas, I.M.; Klaholz, B.P. The palindromic DNA-bound USP/EcR nuclear receptor adopts an asymmetric organization with allosteric domain positioning. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasmuth, E.V.; Broeck, A.V.; LaClair, J.R.; Hoover, E.A.; Lawrence, K.E.; Paknejad, N.; Pappas, K.; Matthies, D.; Wang, B.; Feng, W.; et al. Allosteric interactions prime androgen receptor dimerization and activation. Mol. Cell. 2022, 82, 2021–2031.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chang, M.R.; Stites, R.E.; Wang, Y.; Bruning, J.B.; Pascal, B.D.; Novick, S.J.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Stayrook, K.R.; Chalmers, M.J.; et al. HDX reveals the conformational dynamics of DNA sequence specific VDR co-activator interactions. Nat. Comm. 2017, 8, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osz, J.; McEwen, A.G.; Bourguet, M.; Przybilla, F.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Mély, Y.; Cianférani, S.; Jeffries, C.M.; Svergun, D.I.; et al. Structural basis for DNA recognition and allosteric control of the retinoic acid receptors RAR-RXR. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 9969–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonard, D.M.; O’malley, B.W. Nuclear receptor coregulators: Judges, juries, and executioners of cellular regulation. Mol. Cell. 2007, 27, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, J.W.; Christakos, S. Biology and Mechanisms of Action of the Vitamin D Hormone. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 815–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Oda, Y.; Tu, C.L.; Jiang, Y. Novel mechanisms for the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in the skin and in skin cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 148, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachez, C.; Lemon, B.D.; Suldan, Z.; Bromleigh, V.; Gamble, M.; Näär, A.M.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Freedman, L.P. Ligand-dependent transcription activation by nuclear receptors requires the DRIP complex. Nature 1999, 398, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, L.; Kao, H.Y.; Love, J.D.; Li, C.; Banayo, E.; Gooch, J.T.; Krishna, V.; Chatterjee, K.; Evans, R.M.; Schwabe, J.W. Mechanism of corepressor binding and release from nuclear hormone receptors. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3209–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Lazar, M.A. The CoRNR motif controls the recruitment of corepressors by nuclear hormone receptors. Nature 1999, 402, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perissi, V.; Staszewski, L.M.; McInerney, E.M.; Kurokawa, R.; Krones, A.; Rose, D.W.; Lambert, M.H.; Milburn, M.V.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Molecular determinants of nuclear receptor-corepressor interaction. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 3198–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teichert, A.; Arnold, L.A.; Otieno, S.; Oda, Y.; Augustinaite, I.; Geistlinger, T.R.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Guy, R.K.; Bikle, D.D. Quantification of the vitamin D receptor-coregulator interaction. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burakov, D.; Wong, C.W.; Rachez, C.; Cheskis, B.J.; Freedman, L.P. Functional interactions between the estrogen receptor and DRIP205, a subunit of the heteromeric DRIP coactivator complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20928–20934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, F.; Claessens, F.; Fondell, J.D. Regulation of androgen receptor-dependent transcription by coactivator MED1 is mediated through a newly discovered noncanonical binding motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolte, R.T.; Wisely, G.B.; Westin, S.; Cobb, J.E.; Lambert, M.H.; Kurokawa, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Willson, T.M.; Glass, C.K.; Milburn, M.V. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature 1998, 395, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, A.K.; Barstad, D.; Loria, P.M.; Cheng, L.; Kushner, P.J.; Agard, D.A.; Greene, G.L. The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell 1998, 95, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darimont, B.D.; Wagner, R.L.; Apriletti, J.W.; Stallcup, M.R.; Kushner, P.J.; Baxter, J.D.; Fletterick, R.J.; Yamamoto, K.R. Structure and specificity of nuclear receptor-coactivator interactions. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3343–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huet, T.; Laverny, G.; Ciesielski, F.; Molnár, F.; Ramamoorthy, T.G.; Belorusova, A.Y.; Antony, P.; Potier, N.; Metzger, D.; Moras, D.; et al. A vitamin D receptor selectively activated by gemini analogs reveals ligand dependent and independent effects. Cell. Rep. 2015, 10, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egawa, D.; Itoh, T.; Kato, A.; Kataoka, S.; Anami, Y.; Yamamoto, K. SRC2-3 binds to vitamin D receptor with high sensitivity and strong affinity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chou, C.K.; Pintilie, G.D.; Shen, H.; Foulds, C.E.; Fan, G.; Serysheva, I.; Ludtke, S.J.; et al. Structural and Functional Impacts of ER Coactivator Sequential Recruitment. Mol. Cell. 2017, 67, 733–743.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Yi, P.; Hamilton, R.A.; Shen, H.; Chen, M.; Foulds, C.E.; Mancini, M.A.; Ludtke, S.J.; Wang, Z.; O’Malley, B.W. Structural Insights of Transcriptionally Active, Full-Length Androgen Receptor Coactivator Complexes. Mol. Cell. 2020, 79, 812–823.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovito, D.; Belorusova, A.Y.; Chalhoub, S.; Rerra, A.I.; Guiot, E.; Molin, A.; Linglart, A.; Rochel, N.; Laverny, G.; Metzger, D. Cytosolic sequestration of the vitamin D receptor as a therapeutic option for vitamin D-induced hypercalcemia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belorusova, A.Y.; Bourguet, M.; Hessmann, S.; Chalhoub, S.; Kieffer, B.; Cianférani, S.; Rochel, N. Molecular determinants of MED1 interaction with the DNA bound VDR-RXR heterodimer. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11199–11213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rochel, N. Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142847
Rochel N. Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142847
Chicago/Turabian StyleRochel, Natacha. 2022. "Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142847
APA StyleRochel, N. (2022). Vitamin D and Its Receptor from a Structural Perspective. Nutrients, 14(14), 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142847




