Lactoferrin Prevents Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis via the Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Development and Screening of Transgenic Rats
2.3. Animal Treatments and Biochemical Analysis
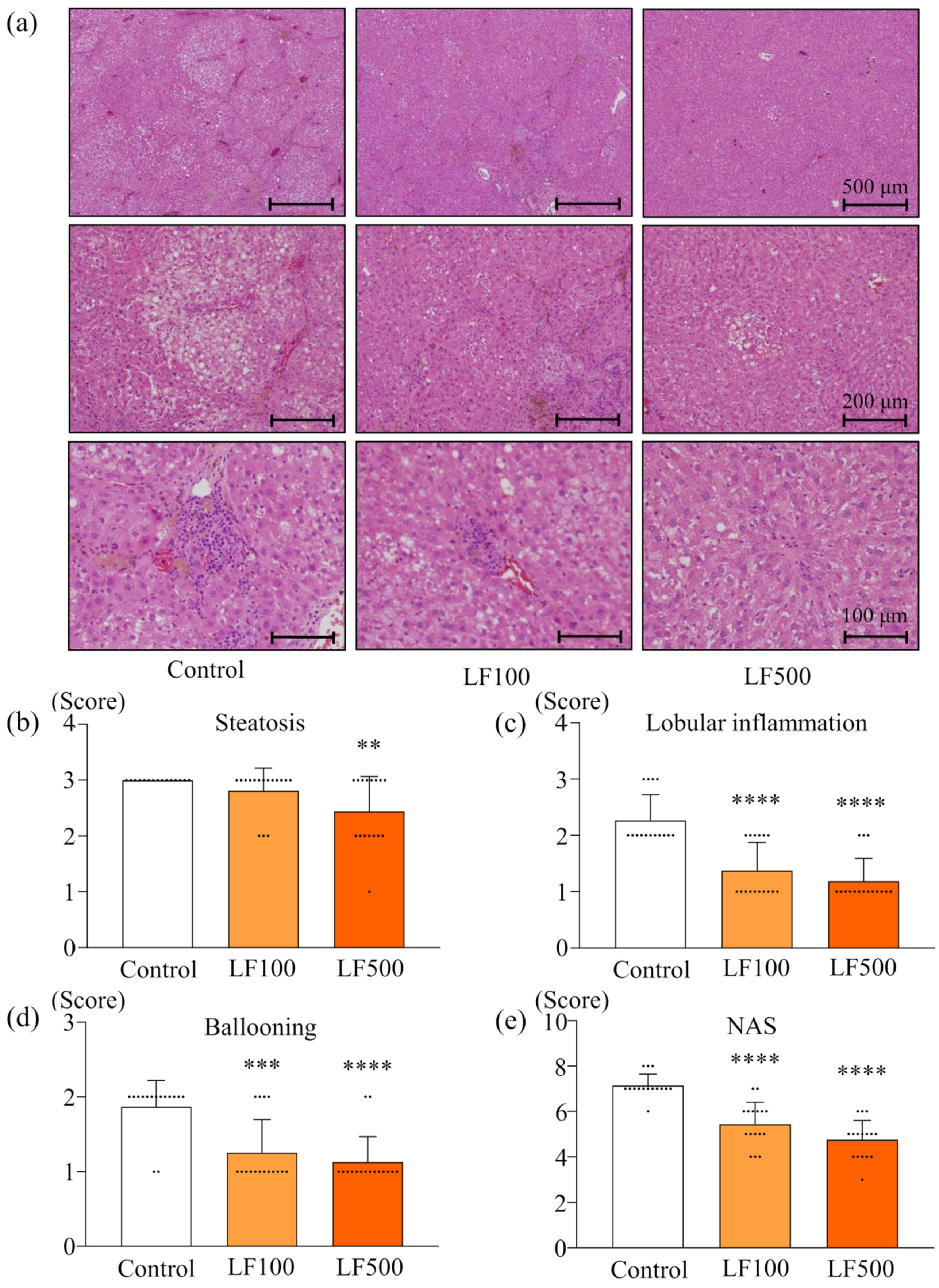
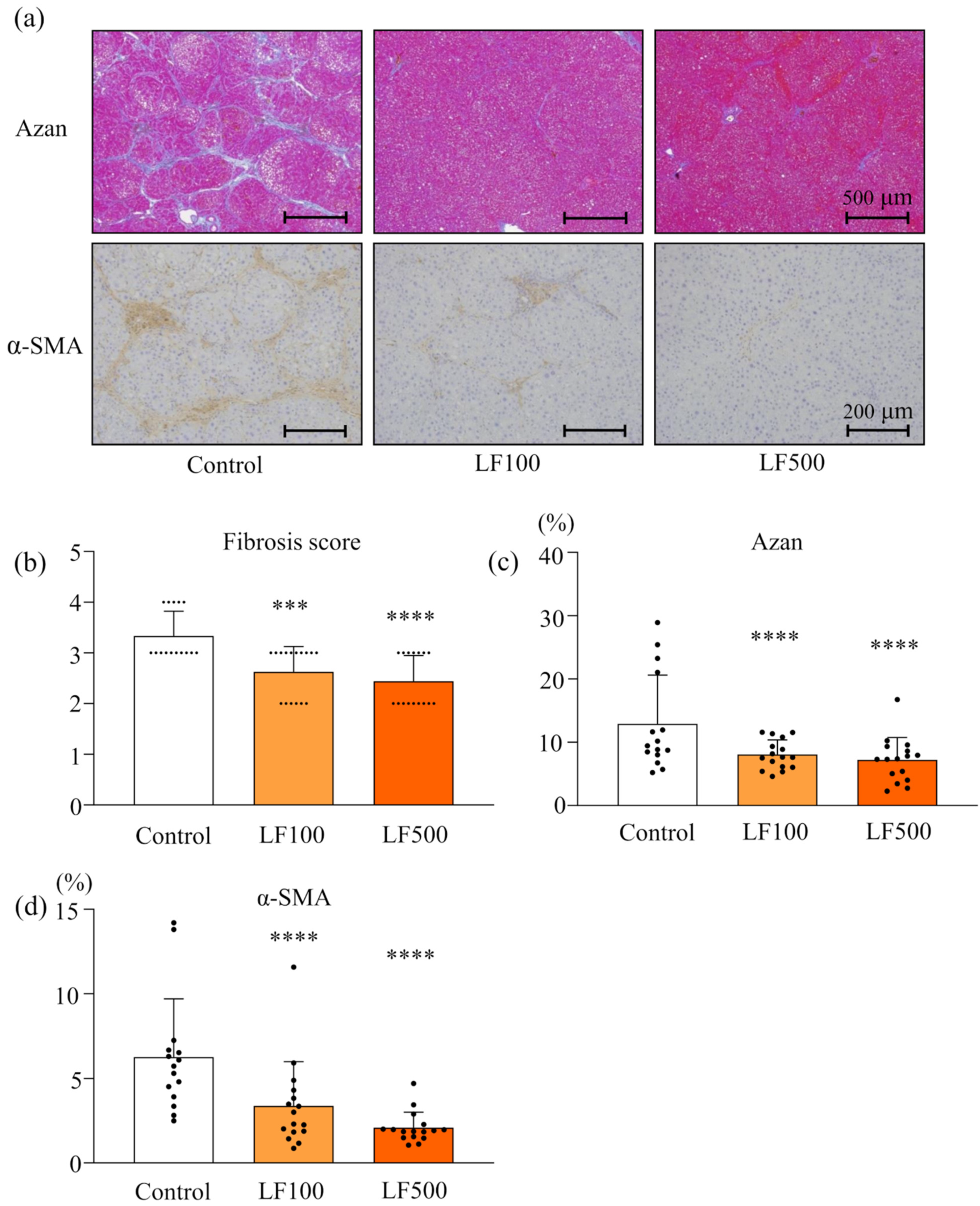
2.4. Histology of NASH
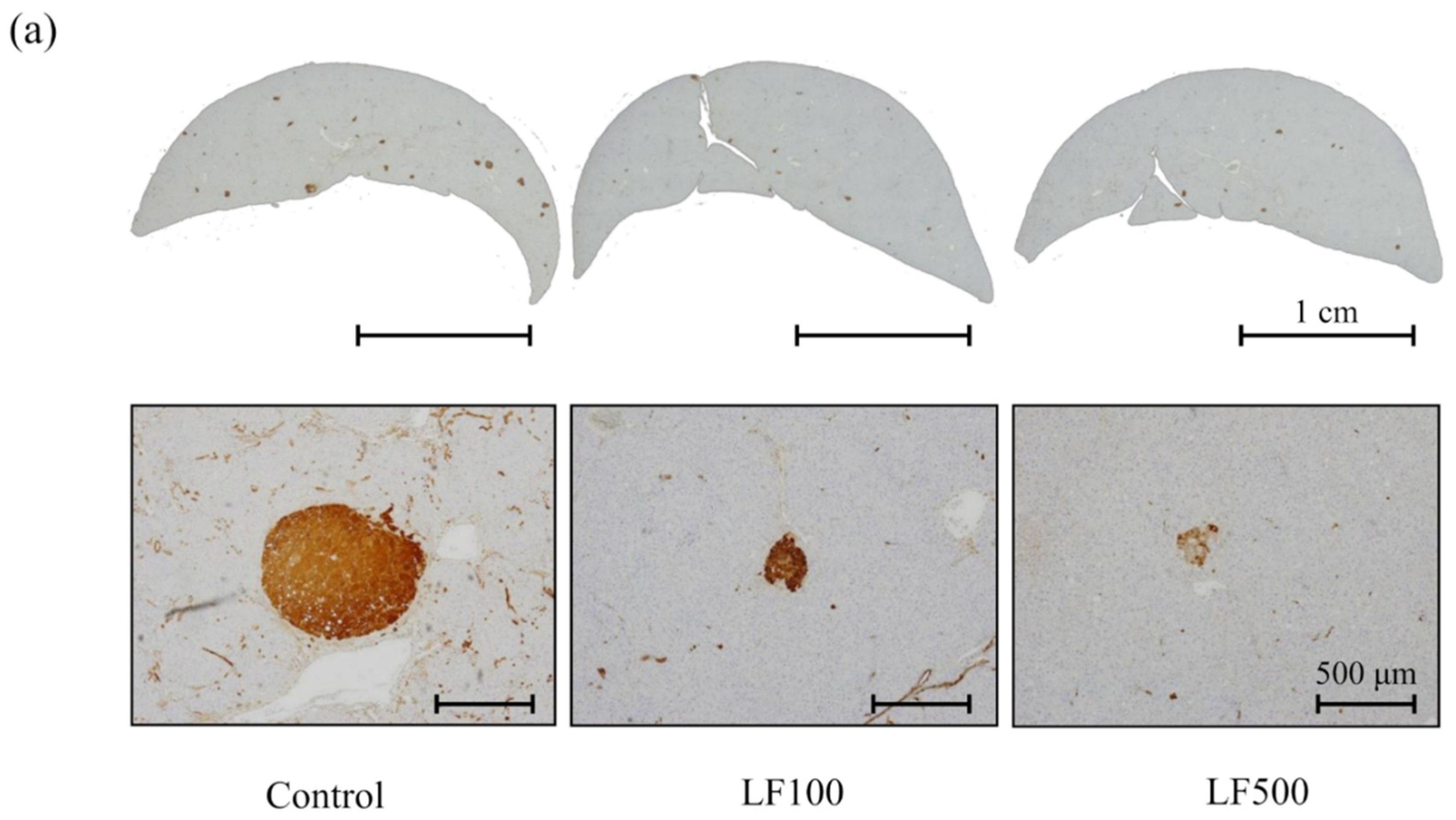
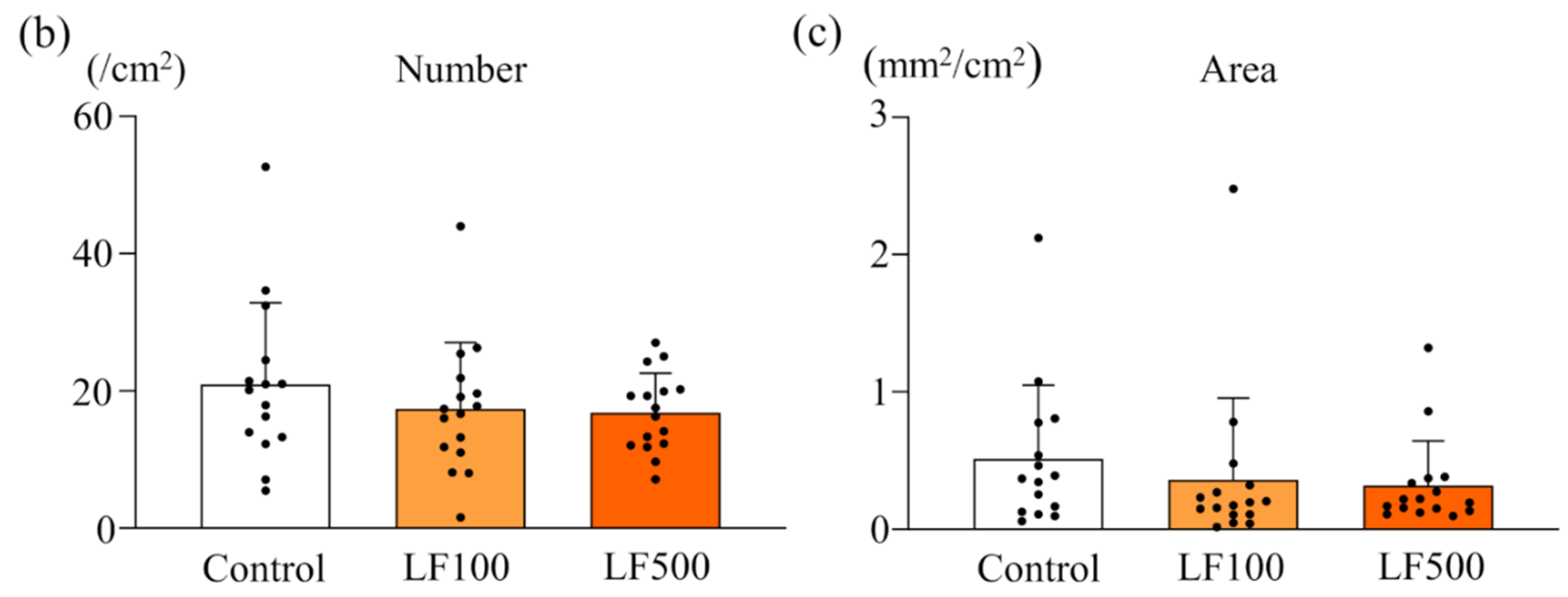
2.5. Evaluation of Preneoplastic Foci in the Liver
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
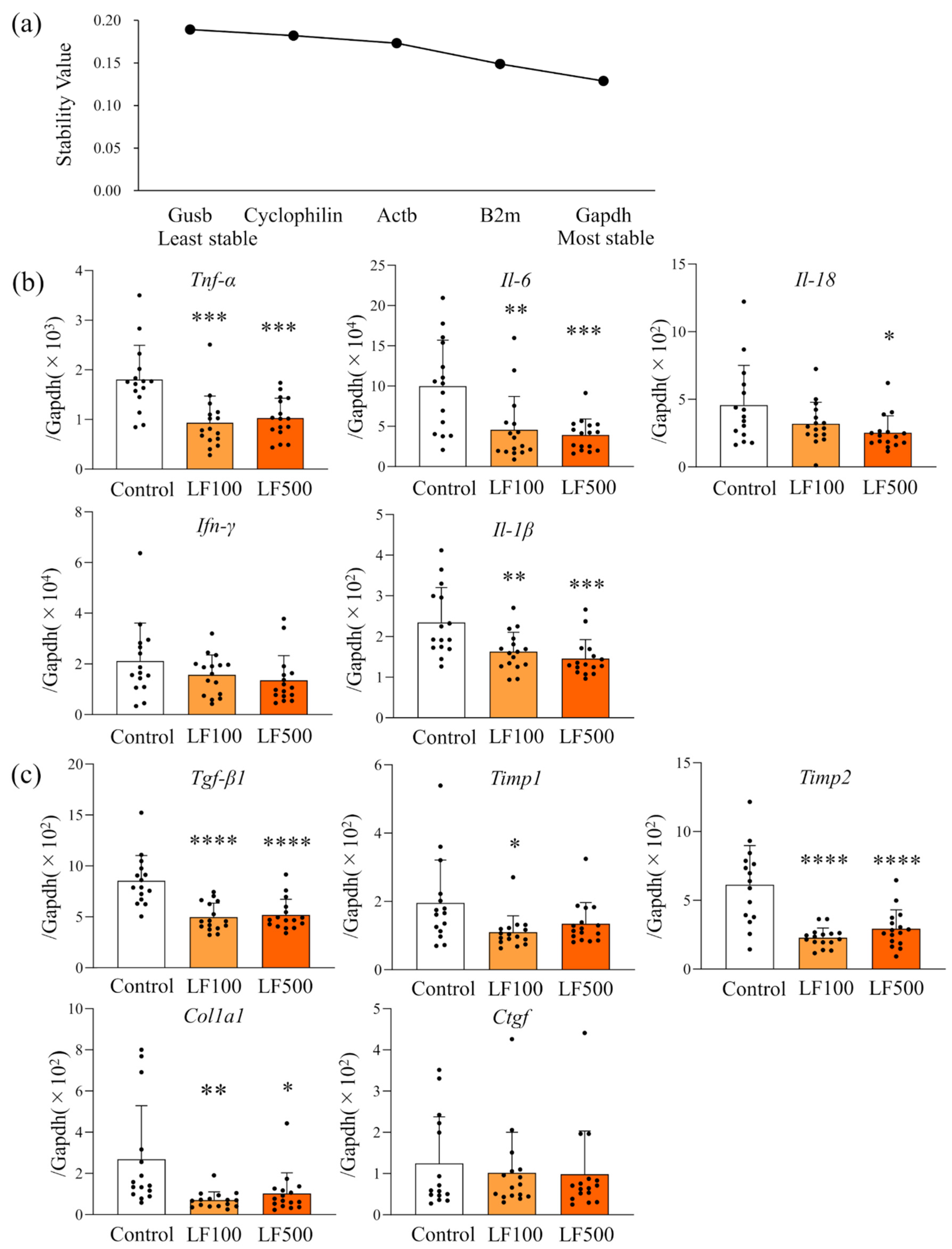
2.8. Selection of a Candidate Reference Gene
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LF Prevents Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis in Cx32ΔTg Rats
3.2. LF Tends to Decrease the Induction of Preneoplastic Lesions in Cx32ΔTg Rats
3.3. LF Down-Regulates mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines in Cx32ΔTg Rats
3.4. LF Administration Reduces NF-κB Signaling in Cx32ΔTg Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Alb | Albumin |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| Bex1 | Brain expressed, X-linked 1 |
| Cx | Connexin |
| Cx32ΔTg | Cx32 dominant negative transgenic |
| DEN | Diethylnitrosamine |
| DMN | Dimethylnitrosamine |
| GST-P | Glutathione S-transferase placental form |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| HSC | Hepatic stellate cell |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LF | Lactoferrin |
| MCDD | Methionine choline-deficient diet |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NAS | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease activity score |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| Wt | Wild-type |
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.H.; Martin, P.E. Gap junctions: Structure and function (Review). Mol. Membr. Biol. 2002, 19, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstein, W.R. Junctional intercellular communication: The cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol. Rev. 1981, 61, 829–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H. Gap junctional intercellular communication and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trosko, J.E.; Chang, C.C. Role of stem cells and gap junctional intercellular communication in human carcinogenesis. Radiat. Res. 2001, 155, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 103, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagawa, H.; Naiki-Ito, A.; Kato, H.; Naiki, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, S.; Shiomi, K.; Kato, A.; Kuno, T.; et al. Connexin 32 and luteolin play protective roles in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development and its related hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Ono, T.; Yamanoi, A.; El-Assal, O.N.; Kohno, H.; Nagasue, N. Expression of gap junction protein connexin32 in chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoto, M.; Hokaiwado, N.; Murasaki, T.; Shirai, T. Connexin 32 dominant-negative mutant transgenic rats are resistant to hepatic damage by chemicals. Hepatology 2004, 40, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokaiwado, N.; Asamoto, M.; Ogawa, K.; Shirai, T. Transgenic disruption of gap junctional intercellular communication enhances early but not late stage hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 33, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokaiwado, N.; Asamoto, M.; Futakuchi, M.; Ogawa, K.; Takahashi, S.; Shirai, T. Both early and late stages of hepatocarcinogenesis are enhanced in Cx32 dominant negative mutant transgenic rats with disrupted gap junctional intercellular communication. J. Membr. Biol. 2007, 218, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Kato, H.; Naiki, T.; Yeewa, R.; Aoyama, Y.; Nagayasu, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Inaguma, S.; Takahashi, S. A novel model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with fibrosis and carcinogenesis in connexin 32 dominant-negative transgenic rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 4085–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Gunasekaran, S.; Saleh, D.M.; Alexander, W.T.; Alexander, D.B.; Ohara, H.; Tsuda, H. Effects of oral bovine lactoferrin on a mouse model of inflammation associated colon cancer. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 99, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togawa, J.; Nagase, H.; Tanaka, K.; Inamori, M.; Nakajima, A.; Ueno, N.; Saito, T.; Sekihara, H. Oral administration of lactoferrin reduces colitis in rats via modulation of the immune system and correction of cytokine imbalance. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, A.S.; El Shemy, M.A.; Nafie, E.; Hegazy, A.M.; Abdelhiee, E.Y. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and hepatoprotective effects of lactoferrin in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.A.; Chiu, C.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Tzang, B.S. Lactoferrin Increases Antioxidant Activities and Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis in Lupus-Prone Mice Fed with a High-Cholesterol Diet. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.C.; Nicolau, A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. The effect of bovine milk lactoferrin on human breast cancer cell lines. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.X.; Jiang, H.R.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, T.N.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, N. Apoptosis of stomach cancer cell SGC-7901 and regulation of Akt signaling way induced by bovine lactoferrin. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 2344–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Monitto, C.L.; Minhas, K.M.; Sidransky, D. Lactoferrin down-regulates G1 cyclin-dependent kinases during growth arrest of head and neck cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8683–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozu, T.; Iinuma, G.; Ohashi, Y.; Saito, Y.; Akasu, T.; Saito, D.; Alexander, D.B.; Iigo, M.; Kakizoe, T.; Tsuda, H. Effect of orally administered bovine lactoferrin on the growth of adenomatous colorectal polyps in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Kato, H.; Asamoto, M.; Naiki, T.; Shirai, T. Age-dependent carcinogenic susceptibility in rat liver is related to potential of gap junctional intercellular communication. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dela Pena, A.; Leclercq, I.; Field, J.; George, J.; Jones, B.; Farrell, G. NF-kappaB activation, rather than TNF, mediates hepatic inflammation in a murine dietary model of steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Kluwe, J.; Osawa, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieckowska, A.; Papouchado, B.G.; Li, Z.; Lopez, R.; Zein, N.N.; Feldstein, A.E. Increased hepatic and circulating interleukin-6 levels in human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Alisi, A.; Valenti, L.; Miele, L.; Feldstein, A.E.; Alkhouri, N. NAFLD in children: New genes, new diagnostic modalities and new drugs. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, R.E.; Zaitoun, A.M.; Aithal, G.P.; Ryder, S.D.; Beckingham, I.J.; Lobo, D.N. Association of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis without significant fibrosis with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Fontana, R.J.; Su, G.L.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Emick, D.M.; Lok, A.S. NAFLD may be a common underlying liver disease in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, G.P.; Thomas, J.A.; Kaye, P.V.; Lawson, A.; Ryder, S.D.; Spendlove, I.; Austin, A.S.; Freeman, J.G.; Morgan, L.; Webber, J. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ratziu, V.; Giral, P.; Jacqueminet, S.; Charlotte, F.; Hartemann-Heurtier, A.; Serfaty, L.; Podevin, P.; Lacorte, J.M.; Bernhardt, C.; Bruckert, E.; et al. Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: One-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled Fatty Liver Improvement with Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, S.A.; Torgerson, S.; Hayashi, P.; Ward, J.; Schenker, S. Vitamin E and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Gossios, T.D.; Griva, T.; Anagnostis, P.; Kargiotis, K.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Theocharidou, E.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Safety and efficacy of long-term statin treatment for cardiovascular events in patients with coronary heart disease and abnormal liver tests in the Greek Atorvastatin and Coronary Heart Disease Evaluation (GREACE) Study: A post-hoc analysis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filozof, C.; Goldstein, B.J.; Williams, R.N.; Sanyal, A. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: Limited Available Treatment Options but Promising Drugs in Development and Recent Progress Towards a Regulatory Approval Pathway. Drugs 2015, 75, 1373–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Son, B.; Jeon, J.; Park, G.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Youn, H.; Jo, S.; Song, J.Y.; Youn, B. Decreased Hepatic Lactotransferrin Induces Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2233–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.Q.; Qin, L.Q.; Sun, Z.Z.; Zuo, W.T.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J.Y. Effects of Metformin Combined with Lactoferrin on Lipid Accumulation and Metabolism in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, L.; Ren, F.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H. Lactoferrin attenuates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and lipid metabolic dysfunctions by suppressing hepatic lipogenesis and down-regulating inflammation in C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4328–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.C. Lactoferrin dampens high-fructose corn syrup-induced hepatic manifestations of the metabolic syndrome in a murine model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morishita, S.; Ono, T.; Fujisaki, C.; Ishihara, Y.; Murakoshi, M.; Kato, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Nishino, H. Bovine lactoferrin reduces visceral fat and liver triglycerides in ICR mice. J. Oleo Sci. 2013, 62, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, F.H.; Sarhan, N.I.; Soliman, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Abd-Elsalam, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S. Heat shock protein 47 as indispensible participant in liver fibrosis: Possible protective effect of lactoferrin. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hessin, A.; Hegazy, R.; Hassan, A.; Yassin, N.; Kenawy, S. Lactoferrin Enhanced Apoptosis and Protected Against Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegazy, R.R.; Mansour, D.F.; Salama, A.A.; Abdel-Rahman, R.F.; Hassan, A.M. Regulation of PKB/Akt-pathway in the chemopreventive effect of lactoferrin against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.M.; Ramadan, G.; Zoheiry, M.K.; El-Beih, N.M. Antihepatocarcinogenic activity of whey protein concentrate and lactoferrin in diethylnitrosamine-treated male albino mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB signaling, liver disease and hepatoprotective agents. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6228–6244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; An, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. STING-mediated inflammation in Kupffer cells contributes to progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okina, Y.; Sato-Matsubara, M.; Matsubara, T.; Daikoku, A.; Longato, L.; Rombouts, K.; Thanh Thuy, L.T.; Ichikawa, H.; Minamiyama, Y.; Kadota, M.; et al. TGF-beta-driven reduction of cytoglobin leads to oxidative DNA damage in stellate cells during non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, X.; Tao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, X.; Sheng, X.; Xue, D. Xia-yu-xue decoction (XYXD) reduces carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition hepatic stellate cell activation by targeting NF-kappaB and TGF-beta1 signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Symbol | Gene Name | Accession Number | Primers (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | NM_017008.4 | GCATCCTGCACCACCAACTG GCCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTT |
| B2m | Beta-2 microglobulin | NM_012512.2 | CCTTCAGCAAGGACTGGTCT |
| TACATGTCTCGGTCCCAGGT | |||
| Actb | Actin, beta | NM_031144.3 | GCGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAG |
| CATACCCACCATCACACCCTG | |||
| Ppia | Peptidylprolyl isomerase A | NM_017101.1 | TGCTGGACCAAACACAATG GAAGGGGAATGAGGAAAATA |
| Gusb | Glucuronidase, beta | NM_017015.3 | CCGACAGGAGAGTGGTGTTG GCTTGGTGATGTCAGCCTCA |
| No. of rats | Body Weight (g) | Liver | Kidney | Visceral Fat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute (g) | Relative (%) | Absolute (g) | Relative (%) | Absolute (g) | Relative (%) | |||
| Control | 15 | 564.7 ± 67.9 | 12.22 ± 2.70 | 2.14 ± 0.33 | 2.59 ± 0.15 | 0.48 ± 0.09 | 15.34 ± 4.68 | 2.65 ± 0.64 |
| LF100 | 16 | 607.9 ± 63.2 | 14.59 ± 1.91 ** | 2.40 ± 0.18 * | 2.67 ± 0.16 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 16.90 ± 4.56 | 2.74 ± 0.53 |
| LF500 | 16 | 585.8 ± 33.3 | 13.37 ± 1.79 | 2.28 ± 0.22 | 2.66 ± 0.18 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 14.98 ± 3.15 | 2.54 ± 0.44 |
| No. of rats | TP (g/dL) | ALB (g/dL) | AST (U/L) | ALT (U/L) | ALP (U/L) | GLU (mg/dL) | T-chol (mg/dL) | LDL-C (mg/dL) | HDL-C (mg/dL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 15 | 5.9 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 117.0 ± 86.6 | 45.5 ± 11.8 | 1249.9 ± 516.2 | 136.0 ± 18.2 | 91.1 ± 68.9 | 16.9 ± 15.0 | 46.8 ± 11.4 |
| LF100 | 16 | 6.1 ± 0.2 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 88.9 ± 21.5 | 47.4 ± 14.6 | 922.6 ± 286.9 | 161.2 ± 29.2 * | 74.4 ± 14.4 | 10.6 ± 2.7 | 51.6 ± 11.4 |
| LF500 | 16 | 6.0 ± 0.3 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 91.2 ± 21.0 | 45.4 ± 9.7 | 1061.7 ± 437.1 | 153.0 ± 33.0 | 72.2 ± 13.3 | 11.1 ± 2.9 | 48.6 ± 9.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aoyama, Y.; Naiki-Ito, A.; Xiaochen, K.; Komura, M.; Kato, H.; Nagayasu, Y.; Inaguma, S.; Tsuda, H.; Tomita, M.; Matsuo, Y.; et al. Lactoferrin Prevents Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis via the Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model. Nutrients 2022, 14, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010042
Aoyama Y, Naiki-Ito A, Xiaochen K, Komura M, Kato H, Nagayasu Y, Inaguma S, Tsuda H, Tomita M, Matsuo Y, et al. Lactoferrin Prevents Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis via the Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAoyama, Yoshinaga, Aya Naiki-Ito, Kuang Xiaochen, Masayuki Komura, Hiroyuki Kato, Yuko Nagayasu, Shingo Inaguma, Hiroyuki Tsuda, Mamoru Tomita, Yoichi Matsuo, and et al. 2022. "Lactoferrin Prevents Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis via the Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010042
APA StyleAoyama, Y., Naiki-Ito, A., Xiaochen, K., Komura, M., Kato, H., Nagayasu, Y., Inaguma, S., Tsuda, H., Tomita, M., Matsuo, Y., Takiguchi, S., & Takahashi, S. (2022). Lactoferrin Prevents Hepatic Injury and Fibrosis via the Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in a Rat Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Model. Nutrients, 14(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010042






