Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Preparation of an Ethanolic Extract of D. moldavica
2.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.4. Materials
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Analysis of Cell Viability
2.7. Determination of Nitric Oxide Production
2.8. PGE2, IL-6 and IL-1β Assays
2.9. RNA Extraction and Real Time-Quantative PCR (RT-PCR)
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. LPS-Induced Septic Shock Mice
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
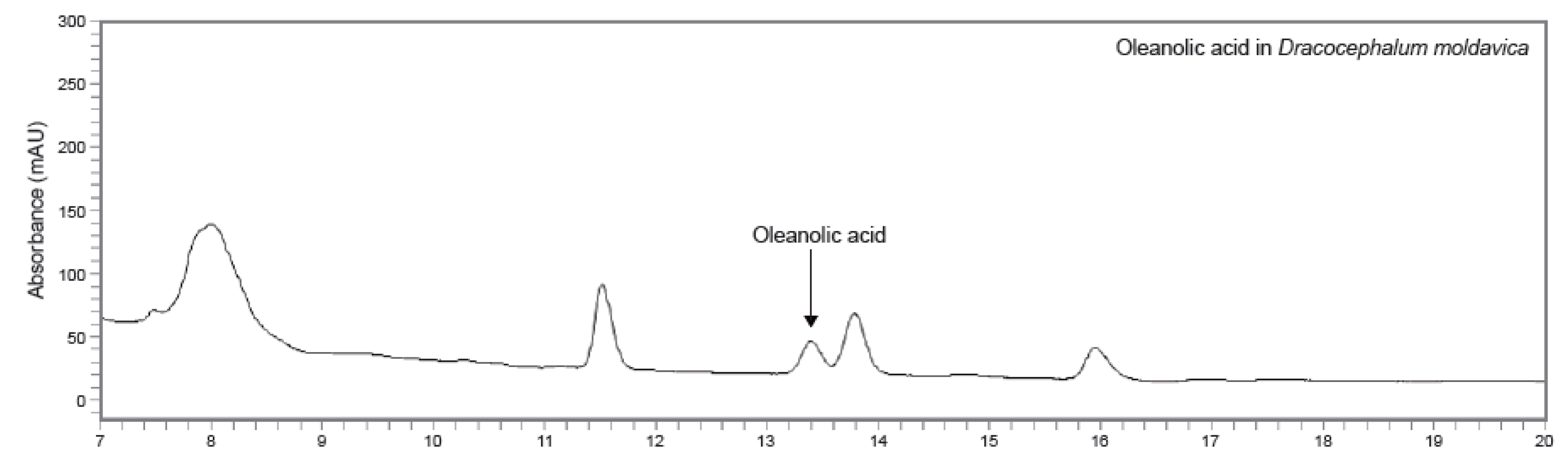
3.1. HPLC-UV Chromatograms Analysis of Oleanolic Acid in DMEE
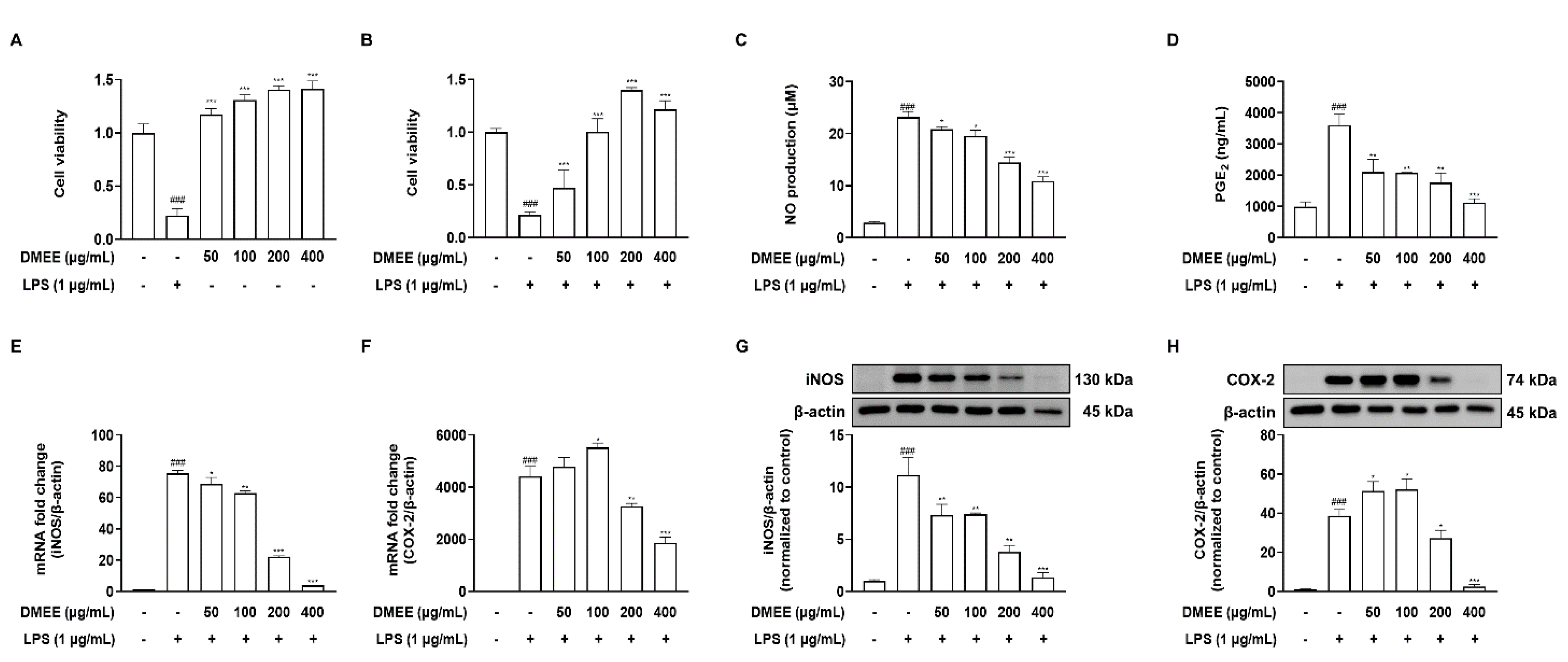
3.2. DMEE Inhibits the LPS-Stimulated Production of Inflammatory Mediators and iNOS and COX-2 Expression in RAW 264.7 Cells
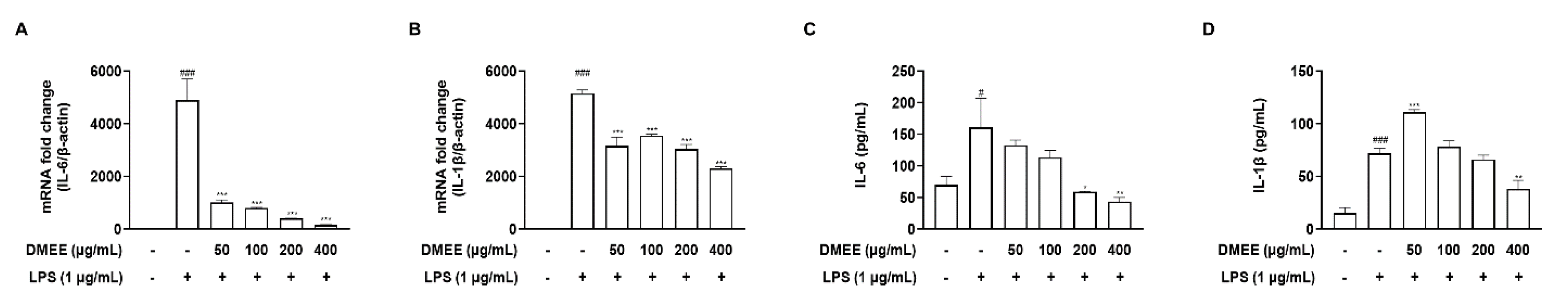
3.3. DMEE Reduced the Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells
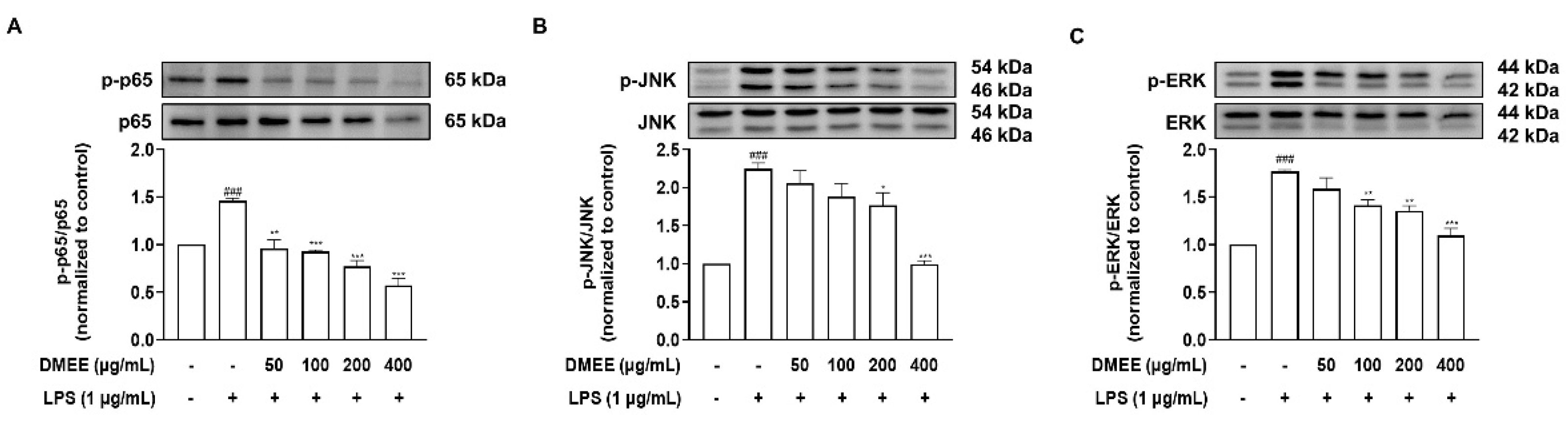
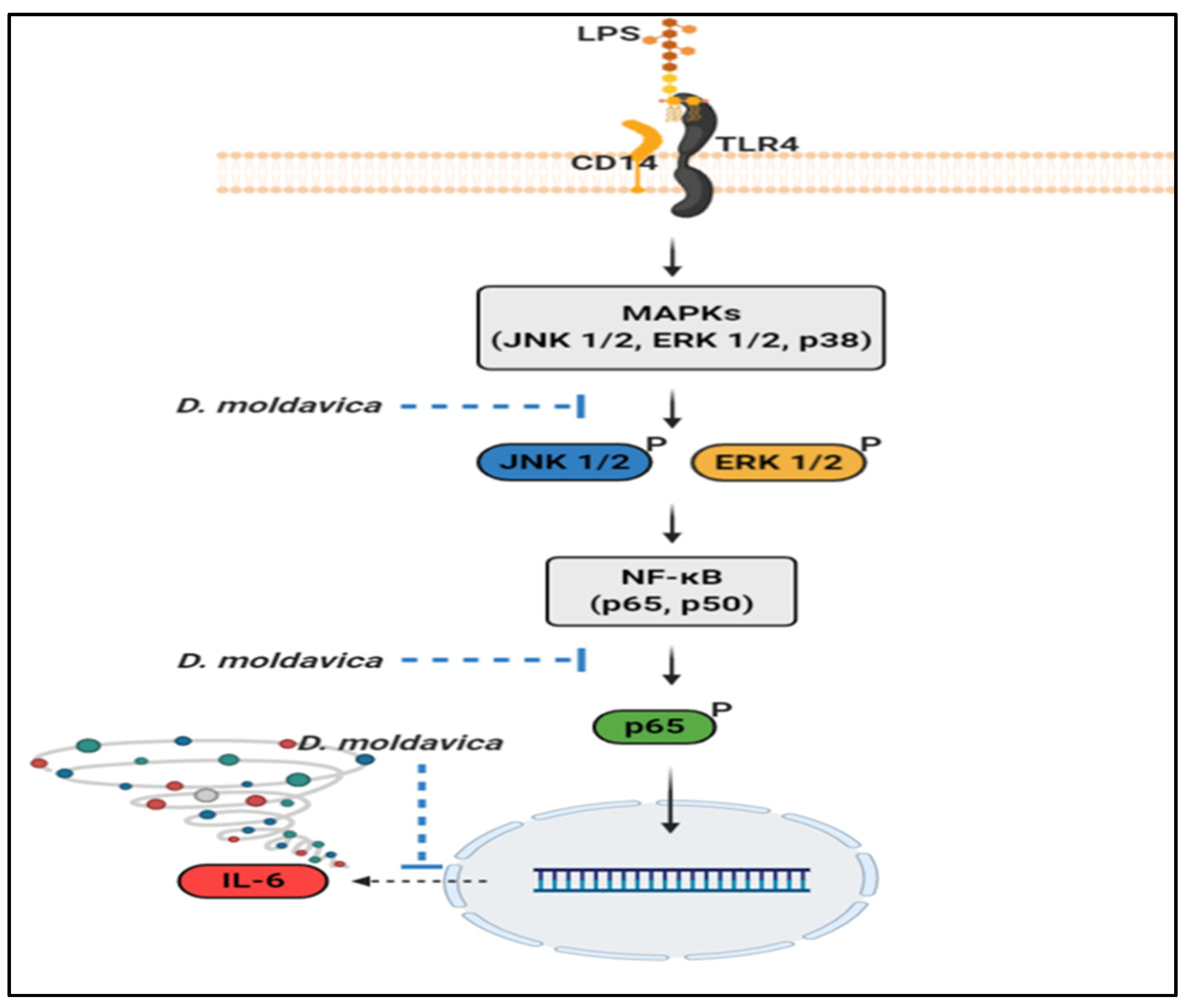
3.4. DMEE Suppresses the MAPK/NF-κB Pathway
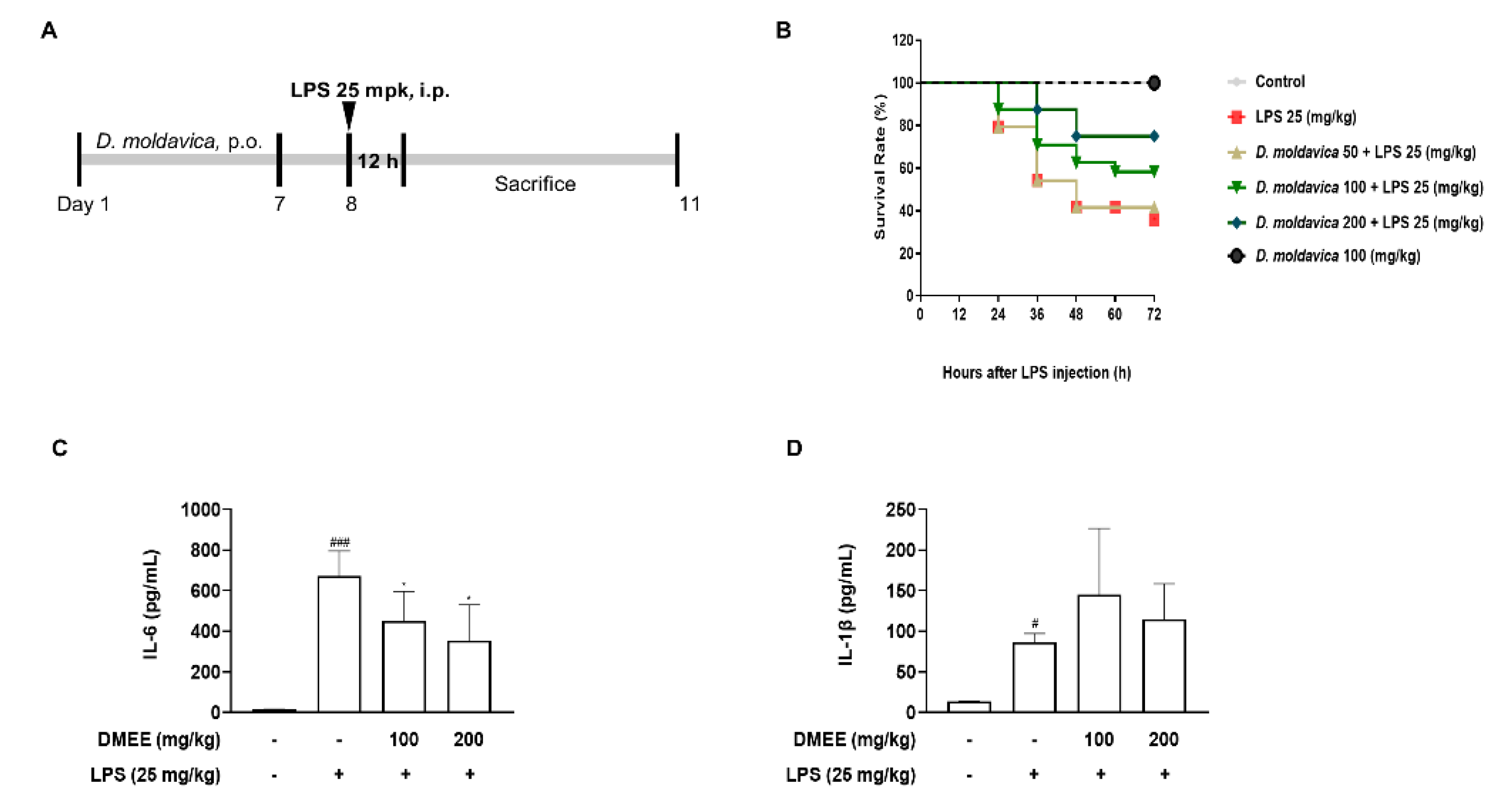
3.5. DMEE Enhances the Survival Rate and Reduces the Level of IL-6 in Plasma in LPS-Stimulated Septic Shock in Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, E.H.; Gu, W.; Kim, D.H. Echinocystic acid ameliorates lung inflammation in mice and alveolar macrophages by inhibiting the binding of LPS to TLR4 in NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol 2012, 84, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Xiong, S.; Lan, H.; Xu, L.; Wei, X. Molecular mechanism underlying anti-inflammatory activities of lirioresinol B dimethyl ether through suppression of NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling in in vitro and in vivo models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.; Lienenklaus, S.; Rosati, O.; Martin, M.U. IL-1beta-induced phosphorylation of PKB/Akt depends on the presence of IRAK-1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 3689–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, I.; Beattie, M.C.; O’Buckley, T.K.; Aurelian, L.; Morrow, A.L. Endogenous Neurosteroid (3alpha,5alpha)3-Hydroxypregnan-20-one Inhibits Toll-like-4 Receptor Activation and Pro-inflammatory Signaling in Macrophages and Brain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kwak, J.A.; Jung, S.H.; Ahn, B.; Cho, W.J.; Yun, C.Y.; Na, C.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Hong, J.T.; Han, S.B.; et al. Piperidylmethyloxychalcone improves immune-mediated acute liver failure via inhibiting TAK1 activity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotch, C.; Barrett, D.; Teachey, D.T. Tocilizumab for the treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced cytokine release syndrome. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.K.; Khan, M.A.; Singh, S.K. Constitutive Inflammatory Cytokine Storm: A Major Threat to Human Health. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020, 40, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Lee, K.H.; Effenberger, M.; Szpirt, W.; Kronbichler, A.; Shin, J.I. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Theranostics 2021, 11, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeley, A.; Hine, P.; Nsutebu, E. The recognition and management of sepsis and septic shock: A guide for non-intensivists. Postgrad. Med. J. 2017, 93, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, M.; Evans, L.; Levy, M.; Rhodes, A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 2018, 392, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, A.; Park, P.; Cherry-Bukowiec, J.R. Early Goal-Directed Therapy: The History and Ongoing Impact on Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Surg. Infect. 2018, 19, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arens, C.; Bajwa, S.A.; Koch, C.; Siegler, B.H.; Schneck, E.; Hecker, A.; Weiterer, S.; Lichtenstern, C.; Weigand, M.A.; Uhle, F. Sepsis-induced long-term immune paralysis—Results of a descriptive, explorative study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, K.; Venkatesh, B.; Finfer, S. Sepsis and septic shock: Current approaches to management. Intern. Med. J. 2019, 49, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, M.G.; Heil, E.L.; Hayes, B.D. Appropriate Antibiotic Therapy. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 35, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molano Franco, D.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Roque, I.F.M.; Montero Oleas, N.G.; Nuvials, X.; Zamora, J. Plasma interleukin-6 concentration for the diagnosis of sepsis in critically ill adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, CD011811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, P.T.N.; Tra, T.T.; Son, N.T.; Wada, K. Reduction in the IL-6 level at 24 h after admission to the intensive care unit is a survival predictor for Vietnamese patients with sepsis and septic shock: A prospective study. BMC Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.E.; He, C.H.; Jiang, W.; Zeng, C.; Yu, N.; Huang, W.; Gao, Z.G.; Xing, J.G. Development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing total flavonoid extract from Dracocephalum moldavica L. and their therapeutic effect against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miernisha, A.; Bi, C.W.; Cheng, L.K.; Xing, J.G.; Liu, J.; Maiwulanjiang, M.; Aisa, H.A.; Dong, T.T.; Lin, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Badiranji Buya Keli, a Traditional Uyghur Medicine, Induces Vasodilation in Rat Artery: Signaling Mediated by Nitric Oxide Production in Endothelial Cells. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, A.; Oniszczuk, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Kocira, S.; Wojtunik, K.; Mitrus, M.; Kocira, A.; Widelski, J.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K. Application of Moldavian dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) leaves addition as a functional component of nutritionally valuable corn snacks. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, E.; Sharifian, F.; Fattahi, M. Process optimization of spray-dried Moldavian balm (Dracocephalum moldavica L.) extract powder. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 6580–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Wan, L.H. Rosmarinic acid ameliorates septic-associated mortality and lung injury in mice via GRP78/IRE1alpha/JNK pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 73, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.L.; Chen, X.G.; Qu, G.W.; Yue, X.D.; Zhu, H.B.; Tian, J.W.; Fu, F.H. Rosmarinic acid protects against experimental sepsis by inhibiting proinflammatory factor release and ameliorating hemodynamics. Shock 2009, 32, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yang, E.J.; Ku, S.K.; Song, K.S.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of oleanolic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation 2013, 36, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Ren, C.H.; Feng, J.; Ou, C.H.; Liu, L. Oleanolic acid inhibits mouse spinal cord injury through suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via the blockage of p38 and JNK MAPKs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, M.; Huang, C.; Wu, T.; Yan, R.; Hu, X. Abietane diterpenoids from Dracocephalum moldavica L. and their anti-inflammatory activities in vitro. Phytochemistry 2021, 184, 112680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Anwaier, G.; Cao, Y.; Lian, G.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Tuerdi, N.; Qi, R. Atheroprotective Mechanisms of Tilianin by Inhibiting Inflammation Through Down-Regulating NF-kappaB Pathway and Foam Cells Formation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, P.; Bae, H.J.; Park, H.B.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Liu, X.Q.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, S.J. Dracocephalum moldavica attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment through activation of hippocampal ERK-CREB signaling in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 253, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Wang, H.M.; Shen, Y.C.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; Wang, C.K. Anti-inflammatory properties of fermented pine (Pinus morrisonicola Hay.) needle on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, W.U.; Cho, C.S.; Woo, J.M.; Yoon, C.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of essential oils extracted from Chamaecyparis obtusa on murine models of inflammation and RAW 264.7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3335–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, W.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jo, M.J.; Kumar, H.; Han, I.B.; Sohn, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, H.S.; Min, H.J.; Hong, V.S.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Novel PIM Kinase Inhibitor KMU-470 in RAW 264.7 Cells through the TLR4-NF-kappaB-NLRP3 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, S.; Horii, S.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Ono, S.; Shimmura, Y.; Sato, K.; Egashira, Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of pyroglutamyl-leucine on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Life Sci. 2014, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.T.; Huang, S.S.; Lin, S.S.; Amagaya, S.; Ho, H.Y.; Hou, W.C.; Shie, P.H.; Wu, J.B.; Huang, G.J. Anti-inflammatory activities of tormentic acid from suspension cells of Eriobotrya Japonicaex vivo and in vivo. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Na, K.S.; Myint, A.M.; Leonard, B.E. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in neuroinflammation, neurogenesis and the neuroendocrine system in major depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyati, K.K.; Masuda, K.; Zaman, M.M.; Dubey, P.K.; Millrine, D.; Chalise, J.P.; Higa, M.; Li, S.; Standley, D.M.; Saito, K.; et al. TLR4-induced NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling regulate the IL-6 mRNA stabilizing protein Arid5a. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huet, O.; Chin-Dusting, J.P. Septic shock: Desperately seeking treatment. Clin. Sci. 2014, 126, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perner, A.; Gordon, A.C.; De Backer, D.; Dimopoulos, G.; Russell, J.A.; Lipman, J.; Jensen, J.U.; Myburgh, J.; Singer, M.; Bellomo, R.; et al. Sepsis: Frontiers in diagnosis, resuscitation and antibiotic therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor anf treatment of the septic shock syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, X.; Xiao, J.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, B.; Teng, H. Sonchus oleraceus Linn protects against LPS-induced sepsis and inhibits inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Hunter, C.A. Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Hu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, P. Effects of Tilianin on Proliferation, Migration and TGF-beta/Smad Signaling in Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Induced with Angiotensin II. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Peng, K.; Cao, W.; Lian, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Effects of total flavonoids from Dracocephalum moldavica on the proliferation, migration, and adhesion molecule expression of rat vascular smooth muscle cells induced by TNF-alpha. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Yan, X.S.; Jin, M.; Huo, D.S.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.J. The inhibitory effects of Dracocephalum moldavica L. (DML) on rat cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2017, 80, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, X.; Han, Y.; He, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, G. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Three Triterpene from Hippophae rhamnoides L. in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Song, J.; Kim, H.R.; Hwang, K.A. Oleanolic acid regulates NF-kappaB signaling by suppressing MafK expression in RAW 264.7 cells. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, S.J.; Jin, U.H.; Kim, K.W.; Son, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Son, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, C.H. Triterpenoid saponin, oleanolic acid 3-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-alpha-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1→2)-alpha-l-arabinopy ranoside (OA) from Aralia elata inhibits LPS-induced nitric oxide production by down-regulated NF-kappaB in raw 264.7 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 467, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, A.R.; Kim, J.B.; Jeong, H.G.; Jin, C.H. Rosmarinic Acid Methyl Ester Inhibits LPS-Induced NO Production via Suppression of MyD88- Dependent and -Independent Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, S.D.; Ping, K.; Ni, H.Y.; Qin, X.Y.; Zhao, C.J.; Wang, W.; Efferth, T.; Fu, Y.J. Cryptochlorogenic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress via upregulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamek-Guzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandins and chronic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Qin, L.P. Triggering of p38 MAPK and JNK signaling is important for oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial death pathway in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | F | 5′-CATGCTACTGGAGGTGGGTG-3′ |
| R | 5′-CATTGATCTCCGTGACAGCC-3′ | |
| COX-2 | F | 5′-TGCTGTACAAGCAGTGGCAA-3 |
| R | 5′-GCAGCCATTTCCTTCTCTCC-3′ | |
| IL-6 | F | 5′-GAGGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC-3′ |
| R | 5′-AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA-3′ | |
| IL-1β | F | 5′-ACCTGCTGGTGTGTGACGTT-3′ |
| R | 5′-TCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTG-3′ | |
| β-actin | F | 5′-ATCACTATTGGCAACGAGCG-3′ |
| R | 5′-TCAGCAATGCCTGGGTACAT-3′ | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Mony, T.J.; Bae, H.J.; Han, S.-D.; Lee, E.-S.; Choi, S.-H.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, S.-D.; Park, S.J. Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124501
Kim K-M, Kim S-Y, Mony TJ, Bae HJ, Han S-D, Lee E-S, Choi S-H, Hong SH, Lee S-D, Park SJ. Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124501
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyeong-Min, So-Yeon Kim, Tamanna Jahan Mony, Ho Jung Bae, Sang-Deok Han, Eun-Seok Lee, Seung-Hyuk Choi, Sun Hee Hong, Sang-Deok Lee, and Se Jin Park. 2021. "Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124501
APA StyleKim, K.-M., Kim, S.-Y., Mony, T. J., Bae, H. J., Han, S.-D., Lee, E.-S., Choi, S.-H., Hong, S. H., Lee, S.-D., & Park, S. J. (2021). Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice. Nutrients, 13(12), 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124501






