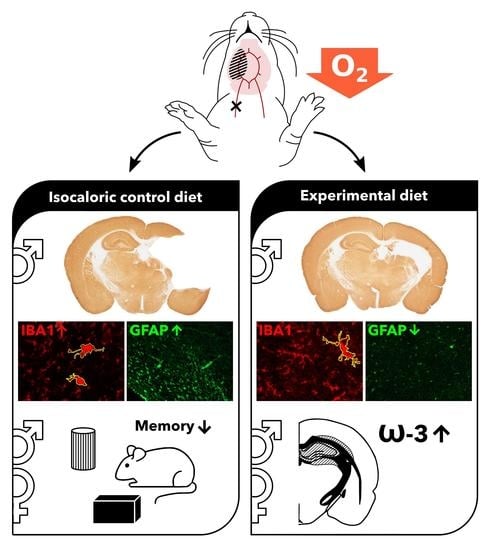
Nutritional Supplementation Reduces Lesion Size and Neuroinflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in a Mouse Model of Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Behavioral Testing
2.2.1. Accelerating Rotarod
2.2.2. Novel Object Recognition Task
2.2.3. Modified Hole Board
2.2.4. Cylinder Rearing Task
2.3. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Thin Layer Chromatography
2.6. Fatty Acid Analysis
2.7. Phospholipid-Bound Fatty Acids
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
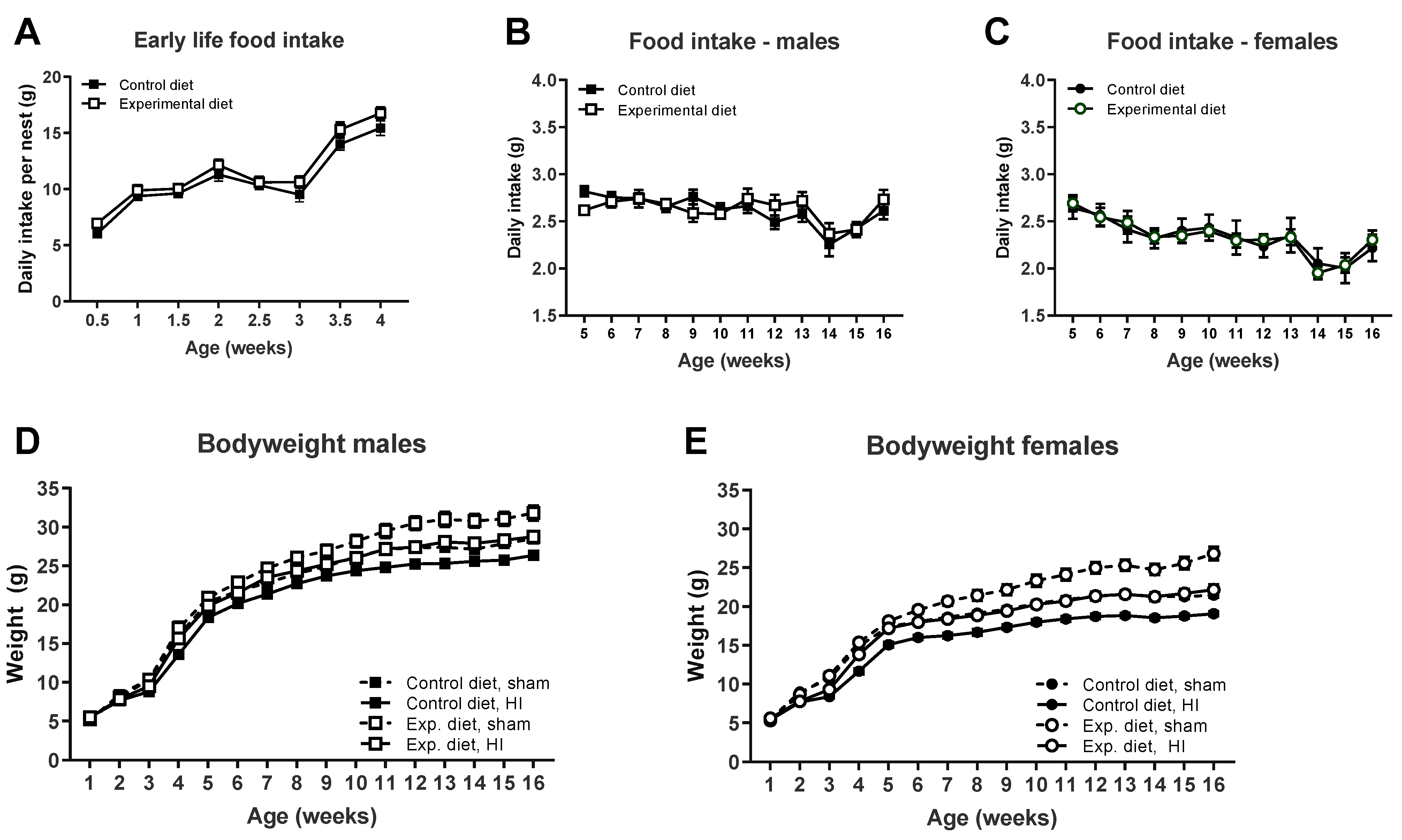
3.1. Food Intake and Bodyweight
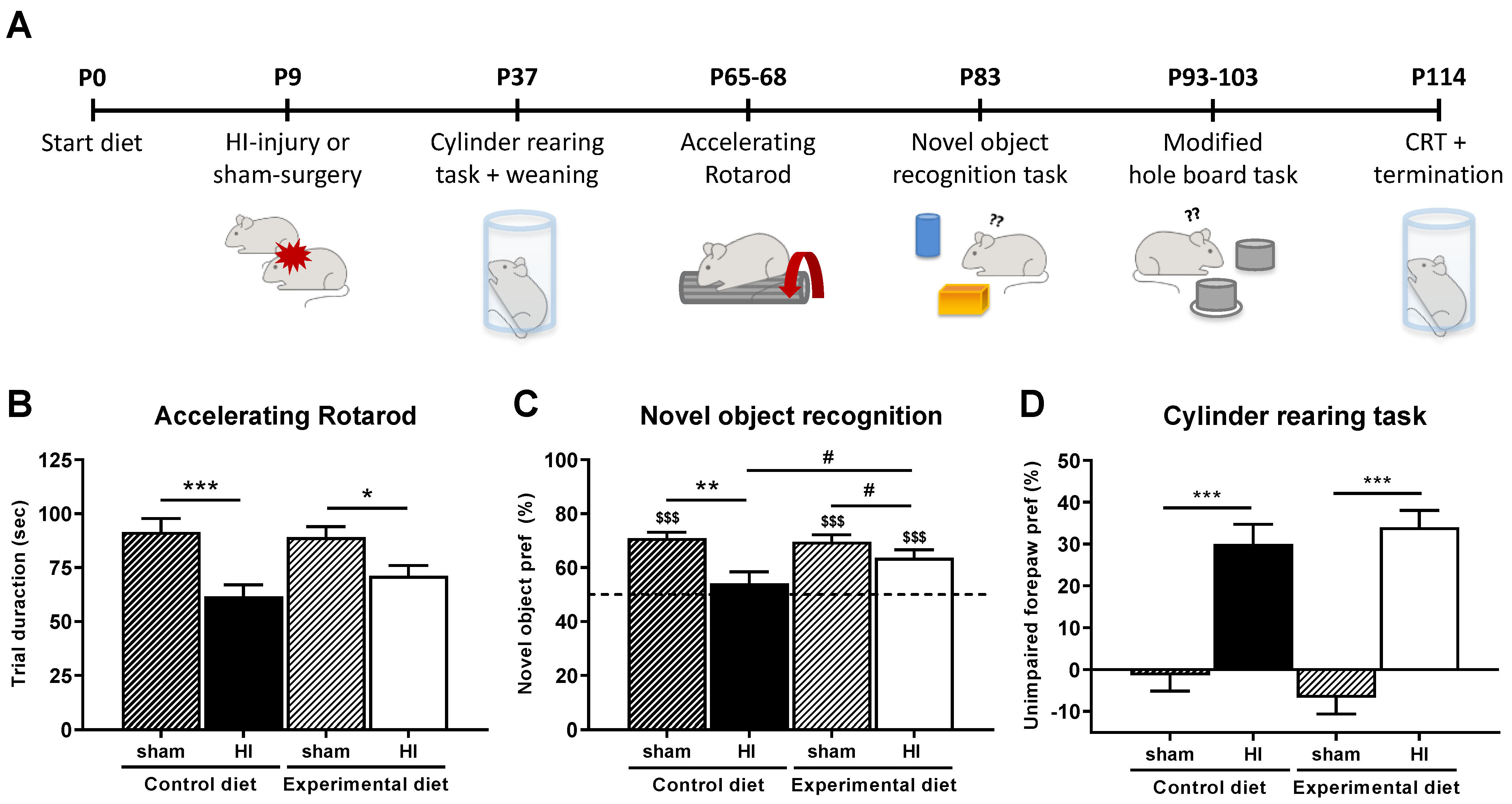
3.2. Behavioral Parameters
3.2.1. Motor Performance
3.2.2. Cognitive Performance
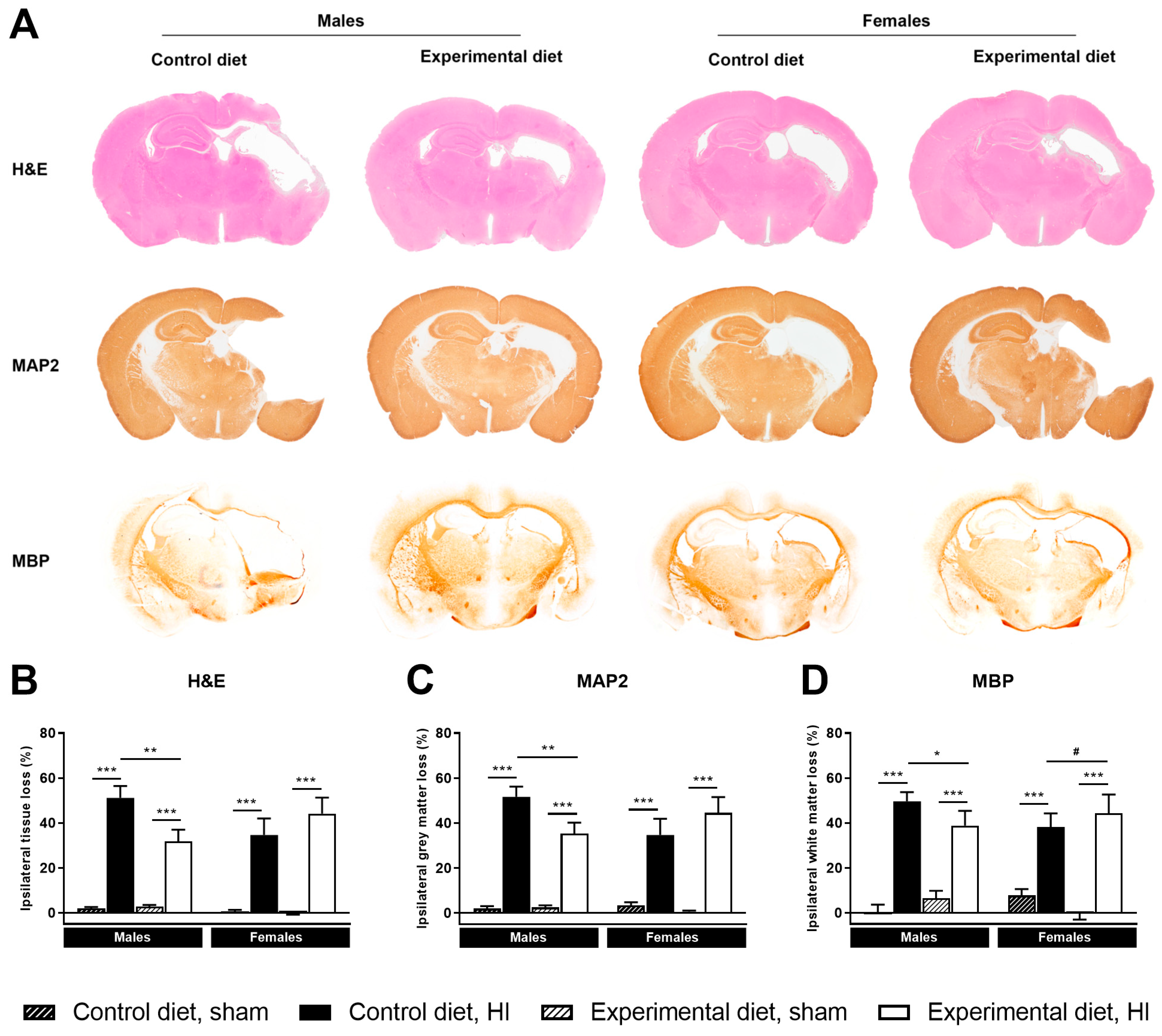
3.3. Histology
3.3.1. Ipsilateral Tissue Loss
3.3.2. Ipsilateral Grey Matter Loss
3.3.3. Ipsilateral White Matter Loss
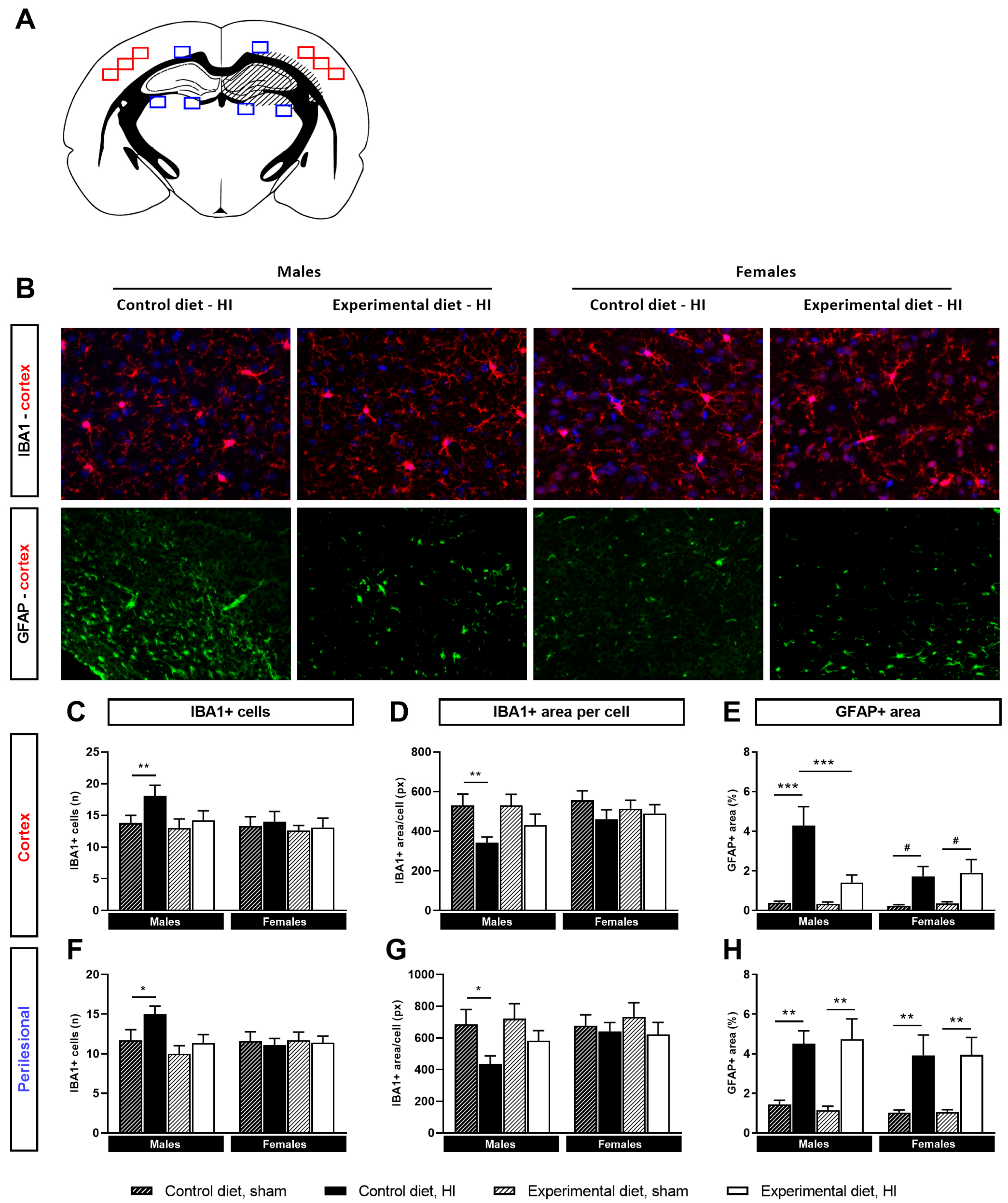
3.4. Neuroinflammation
3.4.1. Microglial Activation
3.4.2. Astrocyte Reactivity
3.5. Synaptic Markers
3.6. Fatty Acids
3.6.1. Fatty Acid Ratios
3.6.2. EPA (20:5n-3)
3.6.3. DPA (22:5n-3)
3.6.4. DHA (22:6n-3)
3.7. Phospholipids
4. Discussion
4.1. Neuroinflammation
4.2. Phospholipids & Fatty Acids
4.3. Functional Outcome
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, A.C.C.; Kozuki, N.; Blencowe, H.; Vos, T.; Bahalim, A.; Darmstadt, G.L.; Niermeyer, S.; Ellis, M.; Robertson, N.J.; Cousens, S.; et al. Intrapartum-related neonatal encephalopathy incidence and impairment at regional and global levels for 2010 with trends from 1990. Pediatr. Res. 2013, 74, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Handel, M.; Swaab, H.; de Vries, L.S.; Jongmans, M.J. Long-term cognitive and behavioral consequences of neonatal encephalopathy following perinatal asphyxia: A review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2007, 166, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Concepcion, K.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L. Brain-immune interactions in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 159, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.A.; Ritzel, R.; Xu, Y.; McCullough, L.D.; Liu, F. Sexually dimorphic outcomes and inflammatory responses in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, A.; Yu, H.; Romana, S.; Liu, F. Inflammatory Responses are Sex Specific in Chronic Hypoxic–Ischemic Encephalopathy. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaran, S.; Natarajan, G.; Chalak, L.; Pappas, A.; McDonald, S.A.; Laptook, A.R. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy: NICHD Neonatal Research Network contribution to the field. Semin. Perinatol. 2016, 40, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassink, G.; Davidson, J.O.; Dhillon, S.K.; Zhou, K.Q.; Bennet, L.; Thoresen, M.; Gunn, A.J. Therapeutic Hypothermia in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas-Escobar, M.; Weiss, M.D. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A review for the clinician. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keunen, K.; van Elburg, R.; Van Bel, F.; Benders, M.J.N.L. Impact of nutrition on brain development and its neuroprotective implications following preterm birth. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, R.J. A Nutrient Combination that Can Affect Synapse Formation. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, R.J.; Cansev, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Ulus, I.H. Use of Phosphatide Precursors to Promote Synaptogenesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhobale, M.V.; Pisal, H.R.; Mehendale, S.S.; Joshi, S.R. Differential expression of human placental neurotrophic factors in preterm and term deliveries. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.E. Phospholipid methylation in mammals: From biochemistry to physiological function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, M.; Bainbridge, S.; Fontaine-Bisson, B. A crucial role for maternal dietary methyl donor intake in epigenetic programming and fetal growth outcomes. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.J.; Parr, J.R.; Montague-Johnson, C.; Laler, K.; Qi, C.; Baker, B.; Sullivan, P.B. Nutritional intervention and neurodevelopmental outcome in infants with suspected cerebral palsy: The Dolphin infant double-blind randomized controlled trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenna, J.T. Animal studies of the functional consequences of suboptimal polyunsaturated fatty acid status during pregnancy, lactation and early post-natal life. Matern. Child Nutr. 2011, 7, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layé, S.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Bazinet, R.P. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Brain: Physiological Mechanisms and Relevance to Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 12–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Kevala, K.; Kim, H.-Y. Depletion of Brain Docosahexaenoic Acid Impairs Recovery from Traumatic Brain Injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower-Winter, S.D.; Levenson, C.W. Zinc in the central nervous system: From molecules to behavior. BioFactors 2012, 38, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramel, S.E.; Georgieff, M.K. Preterm Nutrition and the Brain. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 110, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Singh, K.; Avasthi, K.; Kim, J.-J. Neurobiology of zinc and its role in neurogenesis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, P.M.; Marcelino, G.; Santana, L.F.; de Almeida, E.B.; Guimarães, R.D.C.A.; Pott, A.; Hiane, P.A.; Freitas, K.d.C. Minerals in Pregnancy and Their Impact on Child Growth and Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadosh, K.C.; Muhardi, L.; Parikh, P.; Basso, M.; Mohamed, H.J.J.; Prawitasari, T.; Samuel, F.; Ma, G.; Geurts, J.M.W. Nutritional Support of Neurodevelopment and Cognitive Function in Infants and Young Children—An Update and Novel Insights. Nutrients 2021, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall, S.; Mandhair, H.; Fincham, R.; Kerr, D.; Roche, M.; Molina-Holgado, F. Distinctive effects of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in regulating neural stem cell fate are mediated via endocannabinoid signalling pathways. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Leak, R.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Reduce Neonatal Hypoxic/Ischemic Brain Injury by Promoting Phosphatidylserine Formation and Akt Signaling. Stroke 2015, 46, 2943–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, H.; Arai, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Okumura, A.; Shimizu, T. Maternal docosahexaenoic acid-enriched diet prevents neonatal brain injury. Neuropathology 2010, 30, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.J.; Parr, J.R.; Montague-Johnson, C.; Braddick, O.; Laler, K.; Williams, N.; Baker, B.; Sullivan, P.B. Optimising nutrition to improve growth and reduce neurodisabilities in neonates at risk of neurological impairment, and children with suspected or confirmed cerebral palsy. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andrew, M.J.; Parr, J.R.; Montague-Johnson, C.; Laler, K.; Holmes, J.; Baker, B.; Sullivan, P.B. Neurodevelopmental outcome of nutritional intervention in newborn infants at risk of neurodevelopmental impairment: The Dolphin neonatal double-blind randomized controlled trial. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, R.C.; Vannucci, S.J. Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage: Evolution of an Animal Model. Dev. Neurosci. 2005, 27, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Sert, N.P.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. BMJ Open Sci. 2020, 4, e100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.E.; Vannucci, R.C.; Brierley, J.B. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 9, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donega, V.; Nijboer, C.H.; van Velthoven, C.; Youssef, S.A.; De Bruin, A.; Van Bel, F.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Assessment of long-term safety and efficacy of intranasal mesenchymal stem cell treatment for neonatal brain injury in the mouse. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooij, M.A.; Ohl, F.; Arndt, S.S.; Kavelaars, A.; van Bel, F.; Heijnen, C.J. Mild neonatal hypoxia–ischemia induces long-term motor- and cognitive impairments in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M. Measuring Motor Coordination in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 75, e2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-H.; Langley, S.A.; Huang, Y.; Hang, M.; Bouchard, K.E.; Celniker, S.E.; Brown, J.B.; Jansson, J.; Karpen, G.H.; Snijders, A.M. Identification of genetic factors that modify motor performance and body weight using Collaborative Cross mice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2011, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Stackman, R.W., Jr. Assessing rodent hippocampal involvement in the novel object recognition task. A review. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 285, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueptow, L.M. Novel Object Recognition Test for the Investigation of Learning and Memory in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 2017, e55718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labots, M.; Van Lith, H.A.; Ohl, F.; Arndt, S.S. The Modified Hole Board—Measuring Behavior, Cognition and Social Interaction in Mice and Rats. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 98, e52529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallert, T.; Fleming, S.M.; Leasure, J.L.; Tillerson, J.L.; Bland, S.T. CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanier, E.R.; Fumagalli, S.; Perego, C.; Pischiutta, F.; De Simoni, M.-G. Shape descriptors of the “never resting” microglia in three different acute brain injury models in mice. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2015, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deranieh, R.M.; Joshi, A.S.; Greenberg, M.L. Thin-Layer Chromatography of Phospholipids. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1033, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, S.; Sharma, S.; Fisette, A.; Fernandes, M.F.; Daneault, C.; Rosiers, C.D.; Fulton, S. Perinatal deficiency in dietary omega-3 fatty acids potentiates sucrose reward and diet-induced obesity in mice. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 64, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cansev, M.; van Wijk, N.; Turkyilmaz, M.; Orhan, F.; Sijben, J.W.; Broersen, L.M. A specific multi-nutrient enriched diet enhances hippocampal cholinergic transmission in aged rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deijk, A.-L.F.; Broersen, L.M.; Verkuyl, J.M.; Smit, A.B.; Verheijen, M.H.G. High Content Analysis of Hippocampal Neuron-Astrocyte Co-cultures Shows a Positive Effect of Fortasyn Connect on Neuronal Survival and Postsynaptic Maturation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmann, M.; Zinnhardt, B.; Reinhardt, D.; Eligehausen, S.; Wachsmuth, L.; Hermann, S.; Dederen, P.J.; Hellwich, M.; Kuhlmann, M.T.; Broersen, L.M.; et al. A specific dietary intervention to restore brain structure and function after ischemic stroke. Theranostics 2017, 7, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Elst, K.; Bruining, H.; Birtoli, B.; Terreaux, C.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Kas, M.J. Food for thought: Dietary changes in essential fatty acid ratios and the increase in autism spectrum disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 45, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.A.; Fitch, R.H. Sex Differences in Mechanisms and Outcome of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia in Rodent Models: Implications for Sex-Specific Neuroprotection in Clinical Neonatal Practice. Neurol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 867531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijboer, C.H.; Kavelaars, A.; Van Bel, F.; Heijnen, C.J.; Groenendaal, F. Gender-Dependent Pathways of Hypoxia-Ischemia-Induced Cell Death and Neuroprotection in the Immature P3 Rat. Dev. Neurosci. 2007, 29, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Leconte, C.; Csaba, Z.; Chafa, L.; Pansiot, J.; Talatizi, M.; Simon, K.; Moretti, R.; Marchand-Leroux, C.; Baud, O.; et al. Sex differences in the effects of PARP inhibition on microglial phenotypes following neonatal stroke. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirpoli, H.; Chang, C.L.; Carpentier, Y.A.; Michael-Titus, A.T.; Ten, V.S.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Novel Approaches for Omega-3 Fatty Acid Therapeutics: Chronic versus Acute Administration to Protect Heart, Brain, and Spinal Cord. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 40, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrogliosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agut, J.; G.-Coviella, I.L.; Ortiz, J.A.; Wurtman, R.J. Oral Cytidine 5′-Diphosphate Choline Administration to Rats Increases Brain Phospholipid Levels. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 695, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thau-Zuchman, O.; Gomes, R.; Dyall, S.; Davies, M.; Priestley, J.V.; Groenendijk, M.; de Wilde, M.C.; Lopez-Tremoleda, J.; Michael-Titus, A.T. Brain Phospholipid Precursors Administered Post-Injury Reduce Tissue Damage and Improve Neurological Outcome in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.T.; Orr, S.K.; Bazinet, R.P. The emerging role of group VI calcium-independent phospholipase A2 in releasing docosahexaenoic acid from brain phospholipids. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Simonyi, A.; Fritsche, K.L.; Chuang, D.Y.; Hannink, M.; Gu, Z.; Greenlief, C.M.; Yao, J.K.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Beversdorf, D.Q. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): An essential nutrient and a nutraceutical for brain health and diseases. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 136, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, H.; Okumura, A.; Kitamura, Y.; Shoji, H.; Shimizu, T. Effect of Hypoxic-Ischemic Insults on the Composition of Fatty Acids in the Brain of Neonatal Rats. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 62, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Bazinet, R.P. β-oxidation and rapid metabolism, but not uptake regulate brain eicosapentaenoic acid levels. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 92, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, J.J.; Loepke, A.W.; Miles, L.; Joseph, B.; Hughes, E.; Vorhees, C. Desflurane, Isoflurane, and Sevoflurane Provide Limited Neuroprotection against Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia in a Delayed Preconditioning Paradigm. Anesthesiology 2009, 111, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinboth, B.S.; Köster, C.; Abberger, H.; Prager, S.; Bendix, I.; Felderhoff-Müser, U.; Herz, J. Endogenous hypothermic response to hypoxia reduces brain injury: Implications for modeling hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal mice. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.; Braddick, O.; Montague-Johnson, C.; Baker, B.; Parr, J.R.; Sullivan, P.; Andrew, M.J. Visual attention and dietary supplementation in children with perinatal brain injury. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griva, M.; Lagoudaki, R.; Touloumi, O.; Nousiopoulou, E.; Karalis, F.; Georgiou, T.; Kokaraki, G.; Simeonidou, C.; Tata, D.A.; Spandou, E. Long-term effects of enriched environment following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia on behavior, BDNF and synaptophysin levels in rat hippocampus: Effect of combined treatment with G-CSF. Brain Res. 2017, 1667, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krick, J.; Murphy-Miller, P.; Zeger, S.; Weight, E. Pattern of Growth in Children with Cerebral Palsy. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, J.L.; Emerson, J.A.; Murdock, F.; Petroski, G.F. Growth characteristics in cerebral palsy subtypes: A comparative assessment. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaardingerbroek, H.; Vermeulen, M.; Carnielli, V.P.; Vaz, F.; Akker, C.V.D.; van Goudoever, J.B. Growth and Fatty Acid Profiles of VLBW Infants Receiving a Multicomponent Lipid Emulsion from Birth. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Rodriguez-Palmero, M.; Demmelmair, H.; Fidler, N.; Jensen, R.; Sauerwald, T. Physiological aspects of human milk lipids. Early Hum. Dev. 2001, 65, S3–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition: Nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredients | Control Diet | Experimental Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | ||
| Cornstarch, pre-gelatinized | 27.47 | 25.11 |
| Maltodextrin | 15.50 | 15.50 |
| Sucrose | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Dextrose | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Cellulose powder | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Proteins | ||
| Casein | 20.00 | 20.00 |
| Fats | ||
| Soy oil | 2.66 | 2.00 |
| Coconut oil | 1.26 | 0.10 |
| Corn oil | 3.08 | 1.70 |
| Fish oil (HiDHA 25N + EPA) | - | 3.20 |
| Vitamins & Minerals | ||
| Mineral & trace element premix (AIN-93G-MX) | 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Vitamin mix (AIN-93-VX) | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Supplemented Vit. B12 (Cyanocobalamin 0.1%) | - 1 | 0.0125 |
| Supplemented Zinc | - 1 | 0.1269 |
| Supplemented Iodide | - 1 | 0.0080 |
| Additions | ||
| L-cystine | 0.300 | 0.300 |
| Choline chloride (0.434g/g) | 0.230 | 0.922 |
| Tert-butylhydroquinone | 0.0014 | 0.0014 |
| Soy lecithin (Emulpur) | - | 0.7547 |
| UMP disodium (24% H2O) | - | 0.5000 |
| Cytidine 5MP free acid | - | 0.2634 |
| Energetic value (kcal/100g) | 384.1 | 374.6 |
| % saturated fatty acids | 26.55 | 26.10 |
| % n-3 of total fatty acids | 2.54 | 22.44 |
| % n-6 of total fatty acids | 46.82 | 26.72 |
| n-6/n-3 ratio | 18.53 | 1.19 |
| Control Diet | Experimental Diet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Behavior | Histo|Mol | Behavior | Histo|Mol |
| HI-injured | 29 | 20|13 | 31 | 20|16 |
| Males | 14 (1) | 10|6 | 16 (1) | 10|8 |
| Females | 15 (1) | 10|7 | 15 (1) | 10|8 |
| Sham-operated | 26 | 20|12 | 28 | 21|14 |
| Males | 12 | 10|6 | 13 | 9|7 |
| Females | 14 | 10|6 | 15 | 12|7 |
| Litters | 12 | 12 | ||
| Litter size (M ± SD) | 5.9 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | ||
| Litter size (range) | 3–7 | 5–7 | ||
| Adult mice per cage (M ± SD) | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 2.8 ± 1.0 | ||
| Adult mice per cage (range) | 1–5 | 1–4 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandt, M.J.V.; Nijboer, C.H.; Nessel, I.; Mutshiya, T.R.; Michael-Titus, A.T.; Counotte, D.S.; Schipper, L.; van der Aa, N.E.; Benders, M.J.N.L.; de Theije, C.G.M. Nutritional Supplementation Reduces Lesion Size and Neuroinflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in a Mouse Model of Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Nutrients 2022, 14, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010176
Brandt MJV, Nijboer CH, Nessel I, Mutshiya TR, Michael-Titus AT, Counotte DS, Schipper L, van der Aa NE, Benders MJNL, de Theije CGM. Nutritional Supplementation Reduces Lesion Size and Neuroinflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in a Mouse Model of Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010176
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandt, Myrna J. V., Cora H. Nijboer, Isabell Nessel, Tatenda R. Mutshiya, Adina T. Michael-Titus, Danielle S. Counotte, Lidewij Schipper, Niek E. van der Aa, Manon J. N. L. Benders, and Caroline G. M. de Theije. 2022. "Nutritional Supplementation Reduces Lesion Size and Neuroinflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in a Mouse Model of Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010176
APA StyleBrandt, M. J. V., Nijboer, C. H., Nessel, I., Mutshiya, T. R., Michael-Titus, A. T., Counotte, D. S., Schipper, L., van der Aa, N. E., Benders, M. J. N. L., & de Theije, C. G. M. (2022). Nutritional Supplementation Reduces Lesion Size and Neuroinflammation in a Sex-Dependent Manner in a Mouse Model of Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. Nutrients, 14(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010176