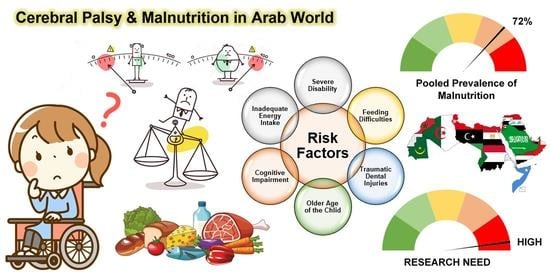
Burden of Malnutrition among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy in Arabic-Speaking Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
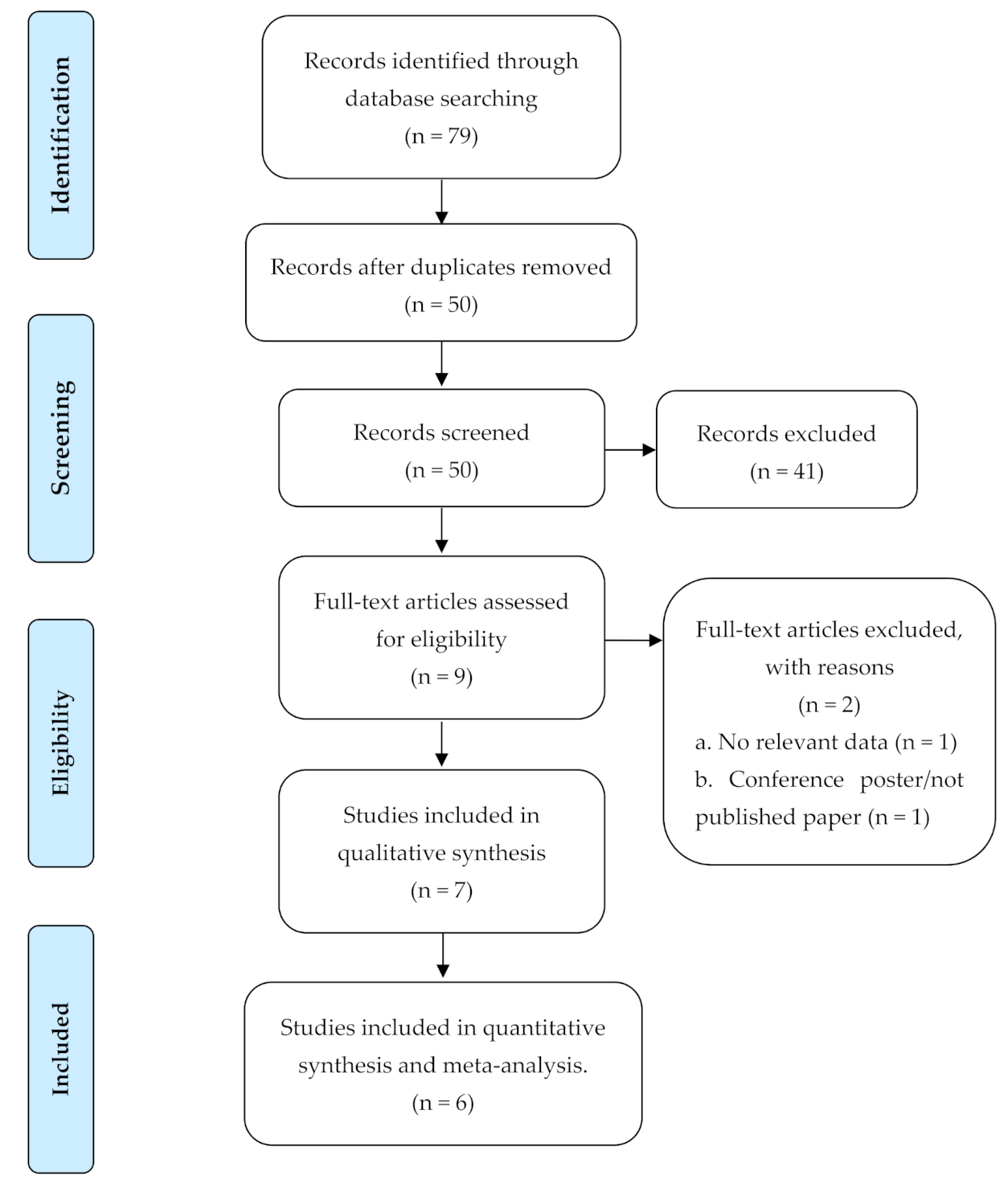
2.2. Study Selection and Inclusion
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Participants
3.2. Measurements Used for Nutritional Assessment
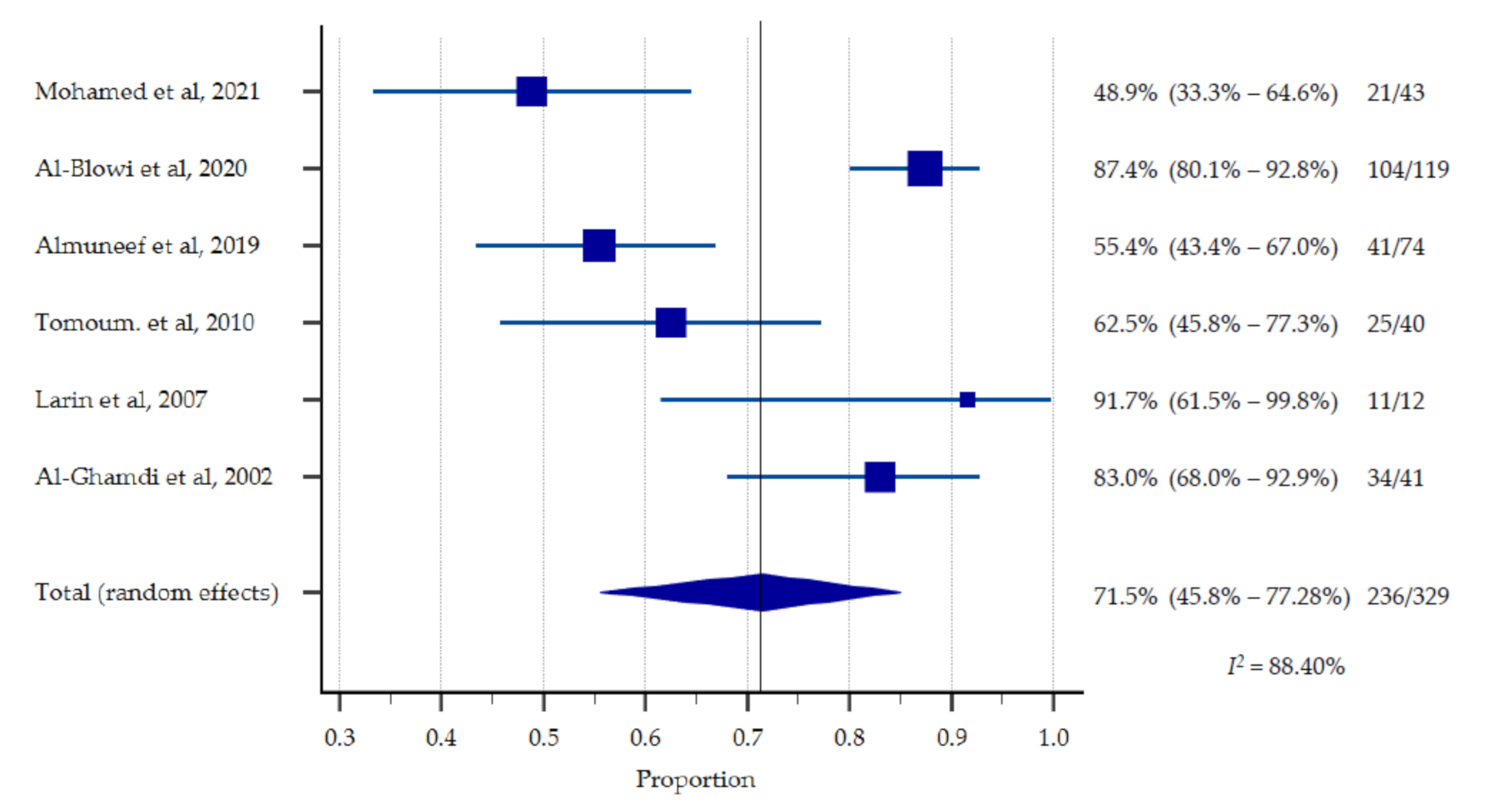
3.3. Malnutrition Rate among Children with CP
3.4. Underlying Risk Factors of Malnutrition
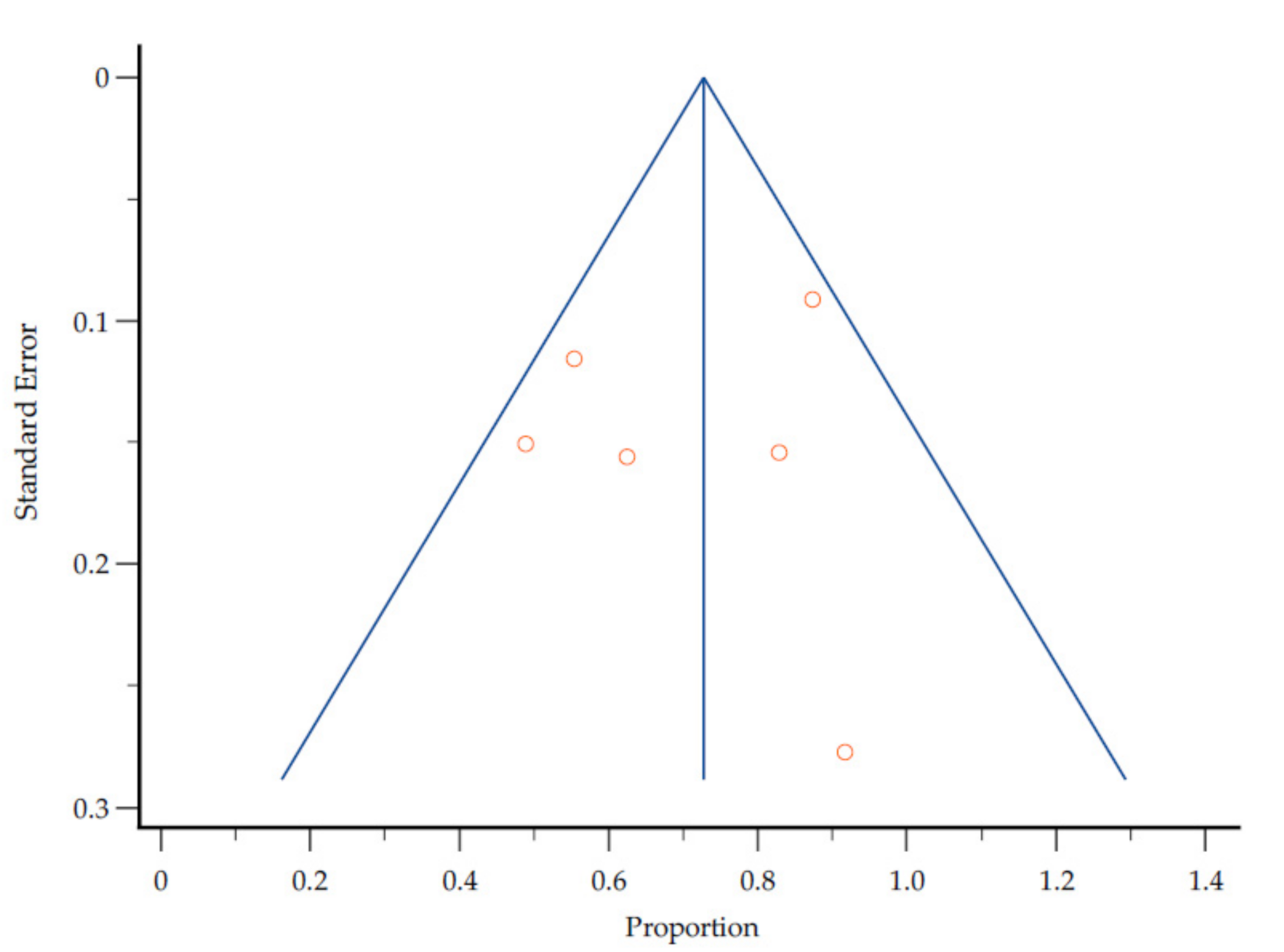
3.5. Study Quality and Heterogeneity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Database
Appendix A
| 1 | exp Cerebral Palsy/ |
| 2 | (cerebral adj pals$).tw. |
| 3 | CP.tw. |
| 4 | 1 or 2 or 3 |
| 5 | exp Nutritional Status/ |
| 6 | exp Nutritional Sciences/ |
| 7 | nutriti$.tw. |
| 8 | exp Malnutrition/ |
| 9 | (malnutrition$ or malnourish$).tw. |
| 10 | undernourish$.tw. |
| 11 | undernutriti$.tw. |
| 12 | exp Thinness/ |
| 13 | (thin$ or lean$ or underweight$).tw. |
| 14 | exp Growth Disorders/ |
| 15 | (grow$ adj5 disorder$).tw. |
| 16 | stunt$.tw. |
| 17 | exp Cachexia/ |
| 18 | (cachexia$ or wasting or wasted).tw. |
| 19 | exp Body Mass Index/ |
| 20 | (“body mass index$” or BMI).tw. |
| 21 | “anthropometric measur$”.tw. |
| 22 | exp Overweight/ |
| 23 | exp Obesity/ |
| 24 | (overweight or obese or obesit$).tw. |
| 25 | 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 |
| 26 | 4 and 25 |
| 27 | exp Jordan/ |
| 28 | jordan$.tw. |
| 29 | exp United Arab Emirates/ |
| 30 | emirate$.tw. |
| 31 | uae.tw. |
| 32 | exp Bahrain/ |
| 33 | bahrain$.tw. |
| 34 | exp Tunisia/ |
| 35 | tunisia$.tw. |
| 36 | exp Algeria/ |
| 37 | algeria$.tw. |
| 38 | exp Djibouti/ |
| 39 | djibouti$.tw. |
| 40 | exp Saudi Arabia/ |
| 41 | (saudi adj1 arabia$).tw. |
| 42 | exp Sudan/ |
| 43 | sudan$.tw. |
| 44 | exp Syria/ |
| 45 | syria$.tw. |
| 46 | exp Somalia/ |
| 47 | somalia$.tw. |
| 48 | exp Iraq/ |
| 49 | iraq$.tw. |
| 50 | exp Oman/ |
| 51 | oman$.tw. |
| 52 | palestin$.tw. |
| 53 | exp Qatar/ |
| 54 | qatar$.tw. |
| 55 | exp Comoros/ |
| 56 | comoros$.tw. |
| 57 | exp Kuwait/ |
| 58 | kuwait$.tw. |
| 59 | exp Lebanon/ |
| 60 | leban$.tw. |
| 61 | exp Libya/ |
| 62 | libya$.tw. |
| 63 | exp Egypt/ |
| 64 | egypt$.tw. |
| 65 | exp Morocco/ |
| 66 | morocco$.tw. |
| 67 | exp Mauritania/ |
| 68 | mauritania$.tw. |
| 69 | exp Yemen/ |
| 70 | yemen$.tw. |
| 71 | exp Arabs/ |
| 72 | (arab$ adj4 (speak$ or countr$ or world)).tw. |
| 73 | 27 or 28 or 29 or 30 or 31 or 32 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 or 39 or 40 or 41 or 42 or 43 or 44 or 45 or 46 or 47 or 48 or 49 or 50 or 51 or 52 or 53 or 54 or 55 or 56 or 57 or 58 or 59 or 60 or 61 or 62 or 63 or 64 or 65 or 66 or 67 or 68 or 69 or 70 or 71 or 72 |
| 74 | 26 and 73 |
| 75 | limit 74 to "all child (0 to 18 years)" |
| 76 | exp Infant, Newborn/ |
| 77 | exp Infant/ |
| 78 | exp Child, Preschool/ |
| 79 | exp Child/ |
| 80 | exp Adolescent/ |
| 81 | (baby or babies or infant$ or toddler$ or child$ or adolescen$ or pediatric$ or pediatric$).tw. |
| 82 | 76 or 77 or 78 or 79 or 80 or 81 |
| 83 | 74 and 82 |
| 84 | 75 or 83 |
References
- Mushta, S.M.; Khandaker, G.; Power, R.; Badawi, N. Cerebral Palsy in the Middle East: Epidemiology, Management, and Quality of Life. In Handbook of Healthcare in the Arab World; Laher, I., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malnutrition. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/malnutrition (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Kuperminc, M.; Stevenson, R. Growth and nutrition disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2008, 14, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almuneef, A.; Almajwal, A.; Alam, I.; Abulmeaty, M.; Bader, B.; Badr, M.; Almuammar, M.; Razak, S. Malnutrition is common in children with cerebral palsy in Saudi Arabia—A cross-sectional clinical observational study. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larson-Nath, C.; Goday, P. Malnutrition in Children with Chronic Disease. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.; Graham, A.; Harini, S.; Grimble, G.; Forbes, A. Profile and prevalence of malnutrition in children with spinal cord injuries—Assessment of the Screening Tool for Assessment of Malnutrition in Paediatrics (STAMP). Spinal Cord 2011, 50, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.; McKenzie, J.; Bossuyt, P.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.; Mulrow, C.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.; Akl, E.; Brennan, S.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.; Mulrow, C.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.; Akl, E.; Brennan, S.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Member States, the League of Arab States. Available online: http://www.lasportal.org/ar/aboutlas/Pages/CountryData.aspx (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Mohamed, R.; Basha, S.; Al-Thomali, Y.; AlZahrani, F.; Ashour, A.; Almutair, N. Association Between Dental Caries and Obesity among Children with Special Health Care Needs. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2021, 19, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Blowi, A.; Al-Mutairi, R.; Ghabbany, R.; Manaa, A.; Aloufi, M.; Ternati, G.; Al-Raddady, B.; Al-Rufai, A. The prevalence of malnutrition and the nutritional status in children with cerebral palsy and its causes in Madinah Maternity and Children Hospital. Curr. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 24, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tomoum, H.; Badawy, N.; Hassan, N.; Alian, K. Anthropometry and body composition analysis in children with cerebral palsy. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larin, H.; Bell, P.; Duncan, C.; Shahin, M. Bone mineral density of children with physical disabilities in the United Arab Emirates: A feasibility study. Emir. Med. J. 2007, 25, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.; Hawamdeh, Z. Evaluation of physical growth in cerebral palsied children and its possible relationship with gross motor development. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2007, 30, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghamdi, Y.; Omer, M.; Khalil, M.; Ali, S.; Barmada, R.; Abdelgader, M. Clinical evaluation of disabled children in Al-Qassim region, Saudi Arabia. Neurosciences 2002, 7, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Bank Country and Lending Groups—World Bank Data Help Desk. Available online: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Karim, T.; Jahan, I.; Dossetor, R.; Giang, N.; Van Anh, N.; Dung, T.; Chau, C.; Van Bang, N.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Nutritional Status of Children with Cerebral Palsy—Findings from Prospective Hospital-Based Surveillance in Vietnam Indicate a Need for Action. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz Brunner, M.; Cieri, M.; Rodriguez Marco, M.; Schroeder, A.; Cuestas, E. Nutritional status of children with cerebral palsy attending rehabilitation centers. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Chadha, R.; Pathak, R. Nutritional status and growth in children with cerebral palsy: A review. Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health 2015, 4, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Anaya, E.; Angarita-Fonseca, A.; Herrera-Galindo, V.; Martínez-Marín, R.; Rodríguez-Bayona, C. Association between gross motor function and nutritional status in children with cerebral palsy: A cross-sectional study from Colombia. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benfer, K.; Weir, K.; Bell, K.; Ware, R.; Davies, P.; Boyd, R. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia and Gross Motor Skills in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1553–e1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, O.; Assem, H.; Ahmed, D.; Abd Elmaksoud, M. Lactoferrin versus iron hydroxide polymaltose complex for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Pediatrics 2021, 180, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Country | Official Name | Total Populations * | Population Aged ≤ 19 years * (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algeria | People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria | 43,851,043 | 16,409,237 (37) |
| Bahrain | Kingdom of Bahrain | 1,701,583 | 399,990 (24) |
| Comoros | Union of the Comoros | 869,595 | 428,906 (49) |
| Djibouti | Republic of Djibouti | 988,002 | 376,430 (38) |
| Egypt | Arab Republic of Egypt | 102,334,403 | 43,413,971 (42) |
| Emirates | United Arab Emirates | 9,890,400 | 1,854,704 (19) |
| Iraq | Republic of Iraq | 40,222,503 | 19,320,987 (48) |
| Jordan | Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan | 10,203,140 | 4,392,416 (43) |
| Kuwait | State of Kuwait | 4,270,563 | 1,141,552 (27) |
| Lebanon | Lebanese Republic | 6,825,442 | 2,287,154 (34) |
| Libya | State of Libya | 6,871,287 | 2,471,165 (36) |
| Mauritania | Islamic Republic of Mauritania | 4,649,660 | 2,315,383 (50) |
| Morocco | Kingdom of Morocco | 36,910,558 | 12,849,811 (35) |
| Oman | Sultanate of Oman | 5,106,662 | 1,362,877 (27) |
| Palestine | State of Palestine | 5,101,416 | 2,474,021 (48) |
| Qatar | State of Qatar | 2,881,060 | 498,936 (17) |
| Saudi Arabia | Kingdom of Saudi Arabia | 34,813,867 | 10,816,497 (31) |
| Somalia | Federal Republic of Somalia | 15,893,219 | 9,152,954 (58) |
| Sudan | Republic of Sudan | 43,849,269 | 22,252,463 (51) |
| Syria | Syrian Arab Republic | 17,500,657 | 6,961,028 (40) |
| Tunisia | Republic of Tunisia | 11,818,618 | 3,657,697 (31) |
| Yemen | Republic of Yemen | 29,825,968 | 14,783,682 (50) |
| Author | Selection Max 4 Stars | Comparability Max 2 Stars | Outcome Max 3 Stars | Score * Max 9 Stars |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohamed et al., 2021 [11] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 |
| Al-Blowi et al., 2020 [12] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★★ | 7 |
| Almuneef et al., 2019 [4] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 |
| Tomoum. et al., 2010 [13] | ★★★★ | ★ | ★★★ | 8 |
| Larin et al., 2007 [14] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 |
| Ibrahim et al., 2007 [15] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 8 |
| Al-Ghamdi et al., 2002 [16] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 |
| ID | Authors | Country | Study Period | Study Design | Study Settings | Study Population | Sample Size | Age of Participants | Female: Male (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mohamed et al., 2021 [11] | Saudi Arabia | Sep 2018–Mar 2019 | Cross-sectional | School based | Children with special health care needs including CP | N = 400, CP: n = 43 | Range: 6–16 years | CP information not reported |
| 2. | Al-Blowi et al., 2020 [12] | Saudi Arabia | 2012–2016 | Retrospective record review | Hospital/institution-based | Children with CP | N = 119 | Mean (standard deviation [SD]): 5.9 (3.8) years | F: 53.0; M: 47 |
| 3. | Almuneef et al., 2019 [4] | Saudi Arabia | Jan–Aug 2015 | Cross-sectional | Hospital/institution-based | Children with CP | N = 74 | Range: 1–12 years | F: 41.0; M: 59 |
| 4. | Tomoum. et al., 2010 [13] | Egypt | Apr–Oct 2007 | Cross-sectional | Hospital/institution-based | Children with CP and controls | N = 80, CP: n = 40 | Range: 2–8 years | F: 47.5; M: 52.5 |
| 5. | Larin et al., 2007 [14] | United Arab Emirates | Not reported | Cross sectional | Population based | Children with physical disability including CP | N = 17, CP: n = 12 | Range: 4.2–18.4 years;mean (SD): 10.4 (4.6) years | F: 41.7; M: 58.3 |
| 6. | Ibrahim et al., 2007 [15] | Jordan | Mar 2005–Mar 2006 | Cross sectional | Hospital/institution-based | Children with spastic CP and control group without CP | N = 151, CP: n = 71 | Range: 3–7 years | Not reported |
| 7. | Al-Ghamdi et al., 2002 [16] | Saudi Arabia | 1998 | Not reported | Hospital/institution-based | Children with disability including CP | N = 111, CP: n = 41 | Range: 1.1- just over 13 years; Mean (SD): 6.0 (2.7) years | F: 48.2; M: 51.8 |
| ID | Authors | Anthropometric Measurements Used | Nutritional Indicator Reported |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mohamed et al., 2021 [11] | (i) weight, (ii) height | BMI |
| 2. | Al-Blowi et al., 2020 [12] | (i) weight, (ii) height, (iii) head circumference | weight-for age (underweight) |
| 3. | Almuneef et al., 2019 [4] | (i) weight, (ii) height, (iii) arm circumference, (iv) arm muscle circumference, and (v) triceps skinfold thickness | weight-for age z-score, weight-for-height z-score, height-for-age z-score, BMI-for-age z-score, arm circumference, arm muscle circumference, triceps skinfold thickness |
| 4. | Tomoum. et al., 2010 [13] | (i) body weight, (ii) head circumference, (iii) mid-upper arm circumference, (iv) waist and hip circumferences | (i) weight percentile, (ii) height percentile, (iii) BMI percentile, (iv) hip circumference, (v) waist-to-hip circumference ratio |
| 5. | Larin et al., 2007 [14] | (i) weight, (ii) height | BMI, BMI-for-age percentile |
| 6. | Ibrahim et al., 2007 [15] | (i) stature, (ii) weight, (iii) head circumference, (iv) mid-upper arm circumference | Mean value for each measurement according to motor type of CP |
| 7. | Al-Ghamdi et al., 2002 [16] | (i) weight | weight for height z-score (wasting) |
| ID | Authors | Sample Size | Proportion of Malnutrition among Children with CP | Factors Related to Nutritional Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mohamed et al., 2021 [11] | N = 400, CP: n = 43 |
|
|
| 2. | Al-Blowi et al., 2020 [12] | N = 119 |
|
|
| 3. | Almuneef et al., 2019 [4] | N = 74 |
|
|
| 4. | Tomoum. et al., 2010 [13] | N = 80, CP: n = 40 |
|
|
| 5. | Larin et al., 2007 [14] | N = 17, CP: n = 12 |
|
|
| 6. | Ibrahim et al., 2007 [15] | N = 151, CP: n = 71 |
|
|
| 7. | Al-Ghamdi et al., 2002 [16] | N = 111, CP: n = 41 |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mushta, S.M.; Jahan, I.; Sultana, R.; McIntyre, S.; Badahdah, A.-M.; Almasri, N.A.; King, C.; Rashid, H.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Burden of Malnutrition among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy in Arabic-Speaking Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093199
Mushta SM, Jahan I, Sultana R, McIntyre S, Badahdah A-M, Almasri NA, King C, Rashid H, Badawi N, Khandaker G. Burden of Malnutrition among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy in Arabic-Speaking Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093199
Chicago/Turabian StyleMushta, Sami Mukhdari, Israt Jahan, Risad Sultana, Sarah McIntyre, Al-Mamoon Badahdah, Nihad A. Almasri, Catherine King, Harunor Rashid, Nadia Badawi, and Gulam Khandaker. 2021. "Burden of Malnutrition among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy in Arabic-Speaking Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 13, no. 9: 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093199
APA StyleMushta, S. M., Jahan, I., Sultana, R., McIntyre, S., Badahdah, A.-M., Almasri, N. A., King, C., Rashid, H., Badawi, N., & Khandaker, G. (2021). Burden of Malnutrition among Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy in Arabic-Speaking Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 13(9), 3199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093199