Epidemiology of Malnutrition among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Settings
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2.2. Sociodemographic and Clinical Characteristics
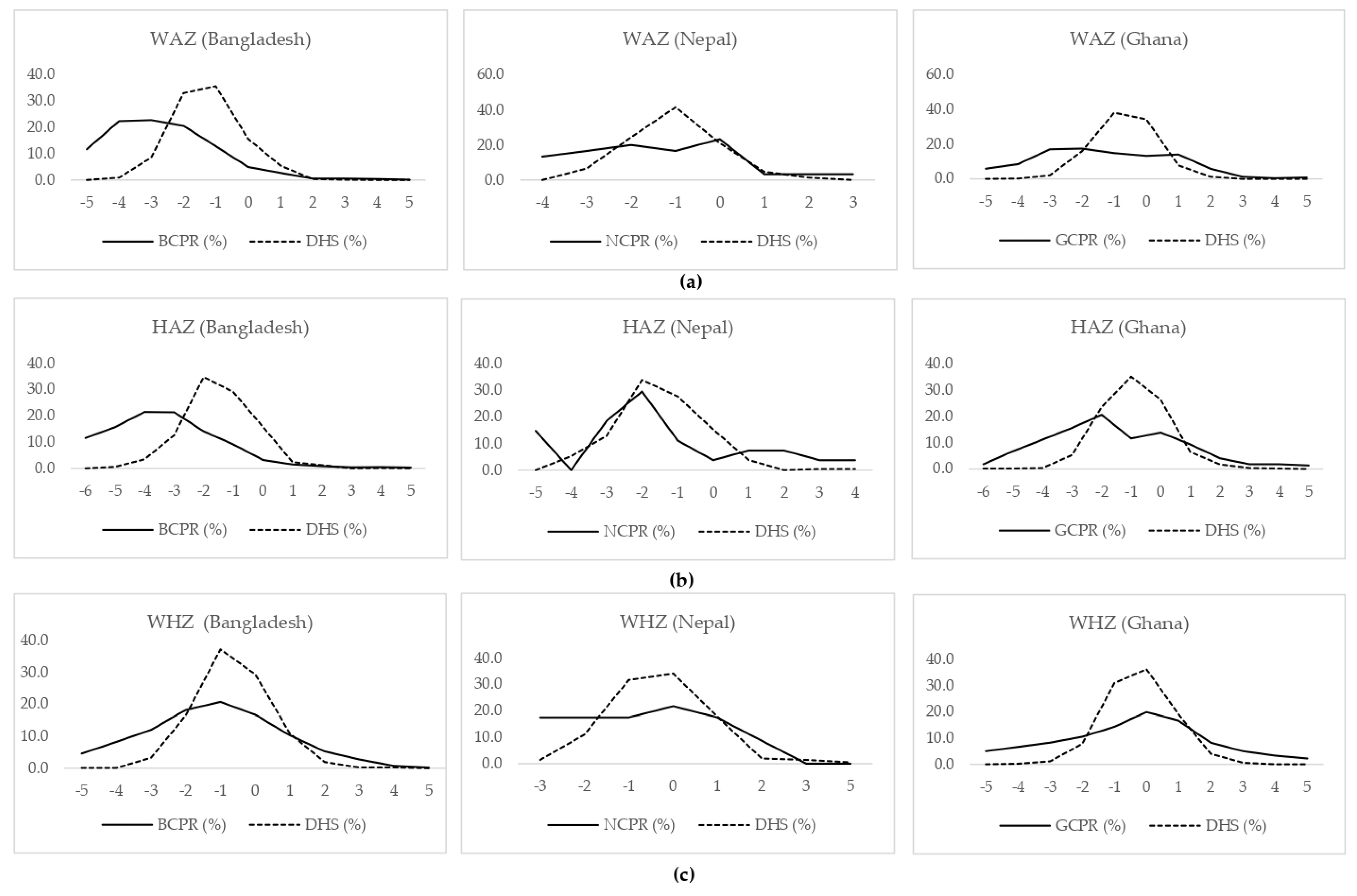
2.2.3. Secondary Data from Demographic and Health Survey (DHS)
2.3. Data Management and Analysis
2.3.1. Indicators Used to Assess Nutritional Status
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Consideration
3. Results
3.1. Overall Nutritional Status
3.2. Nutritional Status of Children with CP Aged Five Years or Less
3.3. Factors Related to Underweight, Stunting, and Thinness among Children with CP Registered into the GLM CPR
3.3.1. Sociodemographic Characteristics
Age and Sex of the Child
Parental Education, Occupation, and Family Income
Access to Drinking Water and Sanitation
3.3.2. Clinical Factors
3.4. Predictors of Undernutrition among Children with CP Registered into the GLM CPR
3.4.1. Underweight
3.4.2. Stunting
3.4.3. Thinness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olusanya, B.O.; Wright, S.M.; Nair, M.; Boo, N.-Y.; Halpern, R.; Kuper, H.; Abubakar, A.A.; Almasri, N.A.; Arabloo, J.; Arora, N.K. Global burden of childhood epilepsy, intellectual disability, and sensory impairments. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20192623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Hardianto, D.; Laryea, F.; Chhetri, A.B.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; McIntyre, S.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Epidemiology of cerebral palsy in low-and middle-income countries: Preliminary findings from an international multi-centre cerebral palsy register. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2021, 61, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakooza-Mwesige, A.; Andrews, C.; Peterson, S.; Wabwire Mangen, F.; Eliasson, A.C.; Forssberg, H. Prevalence of cerebral palsy in Uganda: A population-based study. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1275–e1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khandaker, G.; Muhit, M.; Karim, T.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Novak, I.; Jones, C.; Badawi, N. Epidemiology of cerebral palsy in Bangladesh: A population-based surveillance study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2019, 61, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, S.; Chadha, R.; Pathak, R. Nutritional status and growth in children with cerebral palsy: A review. Int. J. Med. Sci. Public Health 2015, 4, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpato, E.; Staiano, A.; Molteni, M.; Terrone, G.; Mazzocchi, A.; Agostoni, C. Nutritional assessment and intervention in children with cerebral palsy: A practical approach. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakooza-Mwesige, A.; Tumwine, J.K.; Eliasson, A.-C.; Namusoke, H.K.; Forssberg, H. Malnutrition is common in Ugandan children with cerebral palsy, particularly those over the age of five and those who had neonatal complications. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karim, T.; Jahan, I.; Dossetor, R.; Giang, N.T.H.; Van Anh, N.T.; Dung, T.Q.; Chau, C.M.; Van Bang, N.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Nutritional Status of Children with Cerebral Palsy-Findings from Prospective Hospital-Based Surveillance in Vietnam Indicate a Need for Action. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz Brunner, M.d.l.M.; Cieri, M.E.; Rodriguez Marco, M.P.; Schroeder, A.S.; Cuestas, E. Nutritional status of children with cerebral palsy attending rehabilitation centers. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2020, 62, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Karim, T.; Al Imam, M.H.; Das, M.C.; Ali, K.M.; Muhit, M.; Khandaker, G. Childhood disability and nutrition: Findings from a population-based case control study in Rural Bangladesh. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahan, I.; Karim, T.; Das, M.C.; Muhit, M.; Mcintyre, S.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Mortality in children with cerebral palsy in rural Bangladesh: A population-based surveillance study. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2019, 61, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namaganda, L.H.; Almeida, R.; Kajungu, D.; Wabwire-Mangen, F.; Peterson, S.; Andrews, C.; Eliasson, A.C.; Kakooza-Mwesige, A.; Forssberg, H. Excessive premature mortality among children with cerebral palsy in rural Uganda: A longitudinal, population-based study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson-Fang, L.; Fung, E.; Stallings, V.A.; Conaway, M.; Worley, G.; Rosenbaum, P.; Calvert, R.; O’donnell, M.; Henderson, R.C.; Chumlea, W.C. Relationship of nutritional status to health and societal participation in children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatrics 2002, 141, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, M.H.A.; Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Hardianto, D.; Laryea, F.; Chhetri, A.B.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; McIntyre, S.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Predictors of Rehabilitation Service Utilisation among Children with Cerebral Palsy (CP) in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC): Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Karim, T.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Novak, I.; Jones, C.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. What makes children with cerebral palsy vulnerable to malnutrition? Findings from the Bangladesh cerebral palsy register (BCPR). Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandaker, G.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Islam, J.; Alam, M.; Jung, J.; Novak, I.; Booy, R.; Jones, C.; Badawi, N.; Muhit, M. Bangladesh Cerebral Palsy Register (BCPR): A pilot study to develop a national cerebral palsy (CP) register with surveillance of children for CP. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ICF. Demographic and Health Surveys (Various) [Datasets]. Funded by USAID; ICF [Distributor]: Rockville, MD, USA, 2014–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghana Statistical Service (GSS); Ghana Health Service (GHS); ICF International. Ghana Demographic and Health Survey 2014; GSS, GHS amd ICF International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health, Nepal; New ERA; ICF. Nepal Demographic and Health Survey 2016; Ministry of Health, Nepal.: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- NIPORT; ICF. Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2017–18; NIPORT: Dhaka, Bangladesh; ICF: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, K.; Vanneman, R. Maternal education and the multidimensionality of child health outcomes in India. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2020, 52, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.S.; Khan, N.Z.; Begum, S.A.; Wirz, S.L.; Hesketh, T.; Pring, T.R. Feeding difficulties in children with cerebral palsy: Low-cost caregiver training in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Child. Care Health Dev. 2012, 38, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurmond, M.; O’Banion, D.; Gladstone, M.; Carsamar, S.; Kerac, M.; Baltussen, M.; Tann, C.J.; Gyamah Nyante, G.; Polack, S. Evaluating the impact of a community-based parent training programme for children with cerebral palsy in Ghana. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkor, C.M.; Lee, J.; Lelijveld, N.; Adams, M.; Baltussen, M.M.; Nyante, G.G.; Kerac, M.; Polack, S.; Zuurmond, M. Improving nutritional status of children with Cerebral palsy: A qualitative study of caregiver experiences and community-based training in Ghana. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlinda, S.J.; Leyna, G.H.; Massawe, A. The effect of a practical nutrition education programme on feeding skills of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy at Muhimbili National Hospital, in Tanzania. Child. Care Health Dev. 2018, 44, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, S.; Adams, M.; O’Banion, D.; Baltussen, M.; Asante, S.; Kerac, M.; Gladstone, M.; Zuurmond, M. Children with cerebral palsy in Ghana: Malnutrition, feeding challenges, and caregiver quality of life. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2018, 60, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfer, K.A.; Weir, K.A.; Bell, K.L.; Ware, R.S.; Davies, P.S.; Boyd, R.N. Oropharyngeal dysphagia and gross motor skills in children with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1553–e1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troughton, K.; Hill, A. Relation between objectively measured feeding competence and nutrition in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2001, 43, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferluga, E.D.; Sathe, N.A.; Krishnaswami, S.; McPheeters, M.L. Surgical intervention for feeding and nutrition difficulties in cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2014, 56, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Contreras, A.A.; Vasquez-Garibay, E.M.; Romero-Velarde, E.; Ibarra-Gutierrez, A.I.; Troyo-Sanroman, R.; Sandoval-Montes, I.E. Intensive nutritional support improves the nutritional status and body composition in severely malnourished children with cerebral palsy. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 29, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Imam, M.H.; Jahan, I.; Das, M.C.; Muhit, M.; Akbar, D.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Situation analysis of rehabilitation services for persons with disabilities in Bangladesh: Identifying service gaps and scopes for improvement. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFP; LAPAN. Food Security Monitoring Bulletin INDONESIA, Special Focus: Estimating Impact of Disasters on Market Access; WFP: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, J.; Kuter, H.; Campbell, M.; Canoy, D. Reliability of anthropometric measurements in children with special needs. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minocha, P.; Sitaraman, S.; Choudhary, A.; Yadav, R. Subjective Global Nutritional Assessment: A Reliable Screening Tool for Nutritional Assessment in Cerebral Palsy Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhy, M.S.; Jamaluddin, R.; Abd Rasyid Ismail, W.Y.S.; Sulaiman, N.; Adznam, S.N.A.; Ismail, I.H. Anthropometry Measurements to Determine Nutritional Status Among Cerebral Palsy Children: A Scoping Review. Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 16 (Suppl. 6), 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.; Day, S.; Shavelle, R.; Strauss, D. Low weight, morbidity, and mortality in children with cerebral palsy: New clinical growth charts. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e299–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egenolf, P.; Duran, I.; Stark, C.; Martakis, K.; Hamacher, S.; Schoenau, E.; Semler, O. Development of disorder-specific normative data for growth in children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Indicator | Weight-for-Age Z Score (WAZ) 1 | Height-for-Age Z Score (HAZ) | BMI-for-Age Z Score (BAZ) | Weight-for-Height Z Score (WHZ) 1 | MUAC-for-Age Z Score (MUACZ) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bangladesh | |||||
| n | 1971 | 2800 | 2794 | 979 | 1012 |
| Mean (SD) | −3.0 (2.3) | −3.8 (2.9) | −0.8 (3.9) | −1.2 (2.7) | −1.3 (1.7) |
| Median (IQR) | −3.1 (−4.3, −1.8) | −3.7 (−5.4, −2.1) | −1.2 (−2.6, 0.3) | −1.2 (−2.6, 0.1) | −1.1 (−2.1, −0.3) |
| Nutritional status, n (%) | |||||
| Severely undernourished 2 | 1033 (52.4) | 1708 (61.0) | 575 (20.6) | 197 (20.1) | 104 (10.3) |
| Undernourished 2 | 398 (20.2) | 453 (16.2) | 386 (13.8) | 123 (12.6) | 159 (15.7) |
| Normal 2 | 511 (25.9) | 600 (21.4) | 1589 (56.9) | 598 (61.1) | 733 (72.4) |
| Overnourished 2 | 29 (1.5) | 39 (1.4) | 244 (8.7) | 61 (6.2) | 16 (1.6) |
| Indonesia | |||||
| n | 80 | 128 | 127 | 32 | 37 |
| Mean (SD) | −4.1 (2.0) | −5.5 (2.9) | −0.9 (3.3) | −0.8 (2.6) | −1.5 (1.9) |
| Median (IQR) | −4.2 (−5.0, −3.1) | −5.6 (−7.0, −4.1) | −1.0 (−2.6, 0.8) | −0.4 (−2.2, 1.1) | −1.3 (−2.1, −0.3) |
| Nutritional status, n (%) | |||||
| Severely undernourished 2 | 63 (78.8) | 110 (85.9) | 25 (19.7) | 7 (21.9) | 6 (16.2) |
| Undernourished 2 | 8 (10.0) | 9 (7.0) | 21 (16.5) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (10.8) |
| Normal 2 | 8 (10.0) | 7 (5.5) | 65 (51.2) | 18 (56.3) | 27 (73.0) |
| Overnourished 2 | 1 (1.3) | 2 (1.6) | 16 (12.6) | 6 (18.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| Nepal | |||||
| n | 87 | 170 | 164 | 26 | 28 |
| Mean (SD) | −2.2 (1.9) | −2.9 (2.6) | −0.5 (4.1) | −0.5 (1.6) | −0.9 (1.4) |
| Median (IQR) | −2.1 (−3.8, −0.9) | −2.8 (−4.5, −1.4) | −1.1 (−2.5, 0.6) | −0.1 (−1.7, 0.6) | −0.6 (−2.2, 0.1) |
| Nutritional status, n (%) | |||||
| Severely undernourished 2 | 34 (39.1) | 79 (46.5) | 29 (17.7) | 2 (7.7) | 4 (14.3) |
| Undernourished 2 | 11 (12.6) | 30 (17.6) | 19 (11.6) | 2 (7.7) | 3 (10.7) |
| Normal 2 | 38 (43.7) | 55 (32.4) | 103 (62.8) | 21 (80.8) | 21 (75.0) |
| Overnourished 2 | 4 (4.6) | 6 (3.5) | 13 (7.9) | 1 (3.8) | 0 (0.0) |
| Ghana | |||||
| n | 376 | 439 | 438 | 212 | 191 |
| Mean (SD) | −1.5 (2.2) | −2.2 (2.8) | −0.4 (3.0) | −0.9 (3.2) | −1.6 (1.8) |
| Median (IQR) | −1.5 (−2.9, -0.1) | −2.1 (−3.7, −0.8) | −0.2 (−1.9, 1.2) | −0.5 (−2.8, 0.9) | −1.7 (−2.8, −0.4) |
| Nutritional status, n (%) | |||||
| Severely undernourished 2 | 86 (22.9) | 148 (33.7) | 66 (15.1) | 48 (22.6) | 42 (22.0) |
| Undernourished 2 | 60 (16.0) | 77 (17.5) | 38 (8.7) | 21 (9.9) | 37 (19.4) |
| Normal 2 | 215 (57.2) | 194 (44.2) | 261 (59.6) | 108 (50.9) | 108 (56.5) |
| Overnourished 2 | 15 (4.0) | 20 (4.6) | 73 (16.7) | 35 (16.5) | 4 (2.1) |
| Characteristics | Underweight (WAZ < −2SD) 1, n (%) | Stunted (HAZ < −2SD), n (%) | Thin (BAZ < −2SD), n (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population-Based | Institution-Based | Population-Based | Institution-Based | Population-Based | Institution-Based | |||||||
| Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | |
| n | 1431 | 71 | 45 | 146 | 2161 | 119 | 109 | 194 | 961 | 46 | 48 | 104 |
| Age | ||||||||||||
| 0–4 | 683 (48.1) | 30 (42.3) | 9 (20.0) | 87 (61.7) | 770 (35.8) | 33 (27.7) | 12 (11.0) | 95 (43.8) | 256 (26.9) | 9 (19.6) | 5 (10.6) | 62 (63.3) |
| 5–9 | 722 (50.8) | 40 (56.3) | 35 (77.8) | 54 (38.3) | 726 (33.8) | 41 (34.5) | 38 (34.9) | 64 (29.5) | 331 (34.8) | 12 (26.1) | 16 (34.0) | 27 (27.6) |
| 10–14 | 14 (1.0) | 1 (1.4) | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 438 (20.4) | 30 (25.2) | 38 (34.9) | 40 (18.4) | 260 (27.3) | 18 (39.1) | 14 (29.8) | 9 (9.2) |
| 15 and above | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 215 (10.0) | 15 (12.6) | 21 (19.3) | 18 (8.3) | 104 (10.9) | 7 (15.2) | 12 (25.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| p-value | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.20 | <0.001 | 0.41 | 0.49 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.001 |
| Sex of the child | ||||||||||||
| Male | 871 (60.9) | 38 (53.5) | 23 (51.1) | 92 (63.4) | 1312 (60.7) | 67 (56.3) | 62 (56.9) | 138 (61.6) | 602 (62.6) | 25 (54.3) | 29 (60.4) | 70 (67.3) |
| Female | 560 (39.1) | 33 (46.5) | 22 (48.9) | 53 (36.6) | 849 (39.3) | 52 (43.7) | 47 (43.1) | 86 (38.4) | 359 (37.4) | 21 (45.7) | 19 (39.6) | 34 (32.7) |
| p-value | 0.70 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.02 |
| Maternal education level (formal schooling) | ||||||||||||
| None | 379 (26.5) | 5 (7.0) | 11 (25.0) | 40 (27.8) | 657 (30.5) | 15 (12.6) | 43 (41.7) | 79 (35.3) | 328 (34.2) | 8 (17.4) | 22 (45.8) | 28 (27.5) |
| Primary | 602 (42.2) | 36 (50.7) | 17 (38.6) | 57 (39.6) | 876 (40.6) | 59 (49.6) | 34 (33.0) | 78 (34.8) | 381 (39.8) | 21 (45.7) | 11 (22.9) | 39 (38.2) |
| Secondary | 381 (26.7) | 11 (15.5) | 0 (0.0) | 28 (19.4) | 526 (24.4) | 19 (16.0) | 5 (4.9) | 33 (14.7) | 205 (21.4) | 7 (15.2) | 1 (2.1) | 22 (21.6) |
| ≥Higher secondary | 66 (4.6) | 19 (26.8) | 16 (36.4) | 19 (13.2) | 96 (4.5) | 26 (21.8) | 21 (20.4) | 34 (15.2) | 44 (4.6) | 10 (21.7) | 14 (29.2) | 13 (12.7) |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.39 | 0.22 |
| Paternal education level (formal schooling) | ||||||||||||
| None | 510 (35.9) | 10 (14.7) | 9 (20.5) | 24 (17.1) | 846 (39.5) | 17 (14.9) | 21 (21.0) | 41 (18.4) | 415 (43.4) | 8 (18.6) | 7 (15.2) | 17 (17.0) |
| Primary | 496 (35.0) | 32 (47.1) | 12 (27.3) | 47 (33.6) | 686 (32.1) | 57 (50.0) | 25 (25.0) | 83 (37.2) | 299 (31.2) | 18 (41.9) | 12 (26.1) | 28 (28.0) |
| Secondary | 296 (20.9) | 10 (14.7) | 5 (11.4) | 38 (27.1) | 438 (20.5) | 13 (11.4) | 19 (19.0) | 47 (21.1) | 173 (18.1) | 5 (11.6) | 9 (19.6) | 34 (34.0) |
| ≥Higher secondary | 117 (8.2) | 16 (23.5) | 18 (40.9) | 31 (22.1) | 170 (7.9) | 27 (23.7) | 35 (35.0) | 52 (23.3) | 70 (7.3) | 12 (27.9) | 18 (39.1) | 21 (21.0) |
| p-value | 0.005 | 0.74 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.82 | 0.004 |
| Maternal occupation (involved in any income generating activities) | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 171 (12.0) | 54 (79.4) | 27 (64.3) | 120 (82.8) | 252 (11.7) | 97 (83.6) | 63 (63.6) | 186 (83.0) | 117 (12.2) | 41 (91.1) | 26 (59.1) | 88 (84.6) |
| No | 1252 (88.0) | 14 (20.6) | 15 (35.7) | 25 (17.2) | 1896 (88.3) | 19 (16.4) | 36 (36.4) | 38 (17.0) | 842 (87.8) | 4 (8.9) | 18 (40.9) | 16 (15.4) |
| p-value 2 | 0.81 | 0.54 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.94 | 0.19 3 | 0.84 | 0.72 |
| Paternal occupation (involved in any income generating activities) | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 1399 (99.0) | 66 (100.0) | 40 (93.0) | 135 (94.4) | 2110 (99.2) | 112 (100.0) | 98 (97.0) | 213 (96.4) | 938 (98.7) | 45 (100.0) | 45 (97.8) | 99 (96.1) |
| No | 14 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.0) | 8 (5.6) | 16 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (3.0) | 8 (3.6) | 12 (1.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 4 (3.9) |
| p-value 2 | 0.06 | n/a | 0.16 3 | 0.11 | 0.55 | n/a | 0.55 3 | 0.20 | 0.01 | n/a | 0.48 3 | 0.31 3 |
| Source of drinking water | ||||||||||||
| Tubewell/Well/Borhole | 1402 (98.2) | 29 (40.8) | 1 (2.3) | 42 (29.0) | 2114 (98.1) | 45 (37.8) | 3 (2.8) | 57 (26.0) | 940 (98.1) | 15 (32.6) | 2 (4.2) | 28 (27.2) |
| Piped water/Tap water | 22 (1.5) | 5 (7.0) | 34 (77.3) | 90 (62.1) | 35 (1.6) | 10 (8.4) | 90 (84.1) | 146 (66.7) | 16 (1.7) | 4 (8.7) | 40 (83.3) | 64 (62.1) |
| Other sources 4 | 3 (0.2) | 37 (52.1) | 9 (20.5) | 13 (9.0) | 5 (0.2) | 64 (53.8) | 14 (13.1) | 16 (7.3) | 2 (0.2) | 27 (58.7) | 6 (12.5) | 11 (10.7) |
| p-value 2 | 0.58 3 | 0.70 | 0.98 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.80 3 | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| Type of toilet used 5 | ||||||||||||
| Sanitary | 705 (49.4) | 45 (63.4) | 40 (97.6) | 106 (73.1) | 1073 (49.7) | 87 (73.1) | 103 (98.1) | 165 (74.0) | 485 (50.6) | 34 (73.9) | 44 (95.7) | 75 (72.8) |
| Nonsanitary | 685 (48.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.4) | 39 (26.9) | 1028 (47.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 58 (26.0) | 452 (47.1) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 28 (27.8) |
| No toilet facility | 38 (2.7) | 26 (36.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 56 (2.6) | 32 (26.9) | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (2.3) | 12 (26.1) | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| p-value 2 | 0.001 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.92 3 | <0.001 | 0.61 3 | 0.40 3 | 0.19 3 | 1.00 | 0.52 3 | 0.86 3 | 0.393 |
| Monthly family income (USD) | ||||||||||||
| 0 to <73.2 | 223 (15.7) | 56 (80.0) | 13 (29.5) | 59 (52.7) | 352 (16.4) | 96 (82.1) | 34 (31.5) | 106 (53.5) | 156 (16.4) | 38 (82.6) | 12 (25.0) | 39 (50.0) |
| 73.2 to <109.8 | 663 (46.8) | 7 (10.0) | 13 (29.5) | 13 (11.6) | 990 (46.2) | 11 (9.4) | 28 (25.9) | 29 (14.6) | 467 (49.1) | 4 (8.7) | 12 (25.0) | 11 (14.1) |
| ≥109.8 | 532 (37.5) | 7 (10.0) | 18 (40.9) | 40 (35.7) | 800 (37.3) | 10 (8.5) | 46 (42.6) | 63 (31.8) | 329 (34.6) | 4 (8.7) | 24 (50.0) | 28 (35.9) |
| p-value 2 | 0.67 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.46 | 0.92 3 | 0.79 | 0.38 |
| Characteristics | Underweight (WAZ < −2SD) 1, n (%) | Stunted (HAZ < −2SD), n (%) | Thin (BAZ < −2SD), n (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population-Based | Institution-Based | Population-Based | Institution-Based | Population-Based | Institution-Based | |||||||
| Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | |
| n | 1431 | 71 | 45 | 146 | 2161 | 119 | 109 | 225 | 961 | 46 | 48 | 104 |
| Predominant motor type | ||||||||||||
| Spastic | 1113 (77.8) | 52 (73.2) | 39 (86.7) | 104 (71.2) | 1744 (80.7) | 98 (82.4) | 89 (81.7) | 171 (76.0) | 778 (81.0) | 41 (89.1) | 40 (83.3) | 69 (66.3) |
| Dyskinesia | 87 (6.1) | 11 (15.5) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (8.2) | 138 (6.4) | 10 (8.4) | 4 (3.7) | 9 (4.0) | 66 (6.9) | 3 (6.5) | 2 (4.2) | 9 (8.7) |
| Ataxia | 48 (3.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | 15 (10.3) | 62 (2.9) | 1 (0.8) | 2 (1.8) | 23 (10.2) | 26 (2.7) | 1 (2.2) | 3 (6.3) | 12 (11.5) |
| Hypotonia | 183 (12.8) | 8 (11.3) | 5 (11.1) | 15 (10.3) | 216 (10.0) | 10 (8.4) | 14 (12.8) | 22 (9.8) | 91 (9.5) | 1 (2.2) | 3 (6.3) | 14 (13.5) |
| p-value 2 | 0.32 | 0.54 3 | 0.02 3 | 0.81 | 0.19 | 0.313 | <0.001 3 | 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.15 3 | 0.42 3 | 0.50 |
| Spastic Topography | ||||||||||||
| Mono/hemiplegia | 234 (21.0) | 8 (15.4) | 11 (28.2) | 17 (16.3) | 346 (19.8) | 14 (14.3) | 26 (29.2) | 27 (15.8) | 178 (22.9) | 6 (14.6) | 12 (30.0) | 16 (23.2) |
| Diplegia | 194 (17.4) | 8 (15.4) | 5 (12.8) | 25 (24.0) | 298 (17.1) | 19 (19.4) | 10 (11.2) | 35 (20.5) | 128 (16.5) | 8 (19.5) | 3 (7.5) | 16 (23.2) |
| Tri/quadriplegia | 685 (61.5) | 36 (69.2) | 23 (59.0) | 62 (59.6) | 1100 (63.1) | 65 (66.3) | 53 (59.6) | 109 (63.7) | 472 (60.7) | 27 (65.9) | 25 (7.5) | 37 (53.6) |
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | 0.91 | 0.53 | 0.52 | <0.001 | 0.65 | 0.002 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.97 | 0.18 3 | 0.65 |
| GMFCS level | ||||||||||||
| I–II | 272 (19.1) | 7 (9.9) | 13 (28.9) | 48 (33.8) | 406 (18.9) | 19 (16.0) | 37 (33.9) | 63 (28.3) | 227 (23.8) | 8 (17.4) | 15 (31.3) | 44 (43.1) |
| III–V | 1153 (80.9) | 64 (90.1) | 32 (71.1) | 94 (66.2) | 1746 (81.1) | 100 (84.0) | 72 (66.1) | 160 (71.7) | 727 (76.2) | 38 (82.6) | 33 (68.8) | 58 (56.9) |
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | <0.001 | 0.33 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.82 |
| Associated impairment | ||||||||||||
| None | 215 (15.0) | 9 (12.7) | 0 (0.0) | 38 (26.0) | 336 (15.5) | 15 (12.6) | 2 (1.8) | 37 (16.4) | 140 (14.6) | 4 (8.7) | 0 (0.0) | 32 (30.8) |
| One | 400 (28.0) | 26 (36.6) | 15 (33.3) | 48 (32.9) | 599 (27.7) | 52 (43.7) | 33 (30.3) | 100 (44.4) | 288 (30.0) | 20 (43.5) | 15 (31.3) | 34 (32.7) |
| Two and more | 815 (57.0) | 36 (50.7) | 30 (66.7) | 60 (41.1) | 1226 (56.7) | 52 (43.7) | 74 (67.9) | 88 (39.1) | 532 (55.4) | 22 (47.8) | 33 (68.8) | 38 (36.5) |
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | 0.10 | 0.52 3 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.99 | 0.82 3 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.31 3 | 0.61 3 | 0.33 |
| Dysphagia | ||||||||||||
| No | 958 (67.0) | 43 (61.4) | 24 (54.5) | n/a | 1457 (67.6) | 73 (61.9) | 67 (61.5) | n/a | 650 (68.0) | 25 (54.3) | 29 (61.7) | n/a |
| Yes | 472 (33.0) | 27 (38.6) | 20 (45.5) | n/a | 697 (32.4) | 45 (38.1) | 42 (38.5) | n/a | 306 (32.0) | 21 (45.7) | 18 (38.3) | n/a |
| p-value 2 | <0.001 | 0.37 | 0.43 | n/a | <0.001 | 0.47 | 0.11 | n/a | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.48 | n/a |
| Gastro-esophageal reflux | ||||||||||||
| No | 1088 (76.1) | 64 (92.8) | 24 (64.9) | n/a | 1642 (76.3) | 107 (93.0) | 67 (76.1) | n/a | 749 (78.4) | 37 (86.0) | 30 (75.0) | n/a |
| Yes | 341 (23.9) | 5 (7.2) | 13 (35.1) | n/a | 511 (23.7) | 8 (7.0) | 21 (23.9) | n/a | 206 (21.6) | 6 (14.0) | 10 (25.0) | n/a |
| p-value 2 | 0.001 | 0.57 | 0.11 | n/a | <0.001 | 0.42 | 0.04 | n/a | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.34 | n/a |
| Predictors | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | ||||||||
| 0–4 | Ref | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | ||
| 5–9 | 1.4 (1.1,1.8) | 0.02 | 14.9 (1.4, 162.0) | 0.03 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| 10–14 | 1.2 (0.4, 3.8) | 0.74 | - | 1.00 | ||||
| Sex of the child | ||||||||
| Male | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | n/a | n/a | |
| Female | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.5 (0.9, 6.5) | 0.06 | n/a | n/a |
| Maternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| None | 2.8 (1.5, 5.4) | 0.002 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.1 (1.1, 4.3) | 0.03 |
| Primary | 2.6 (1.4, 4.8) | 0.002 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.9 (1.5, 5.7) | 0.002 |
| Secondary | 2.1 (1.2, 3.8) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.7 (0.8, 3.5) | 0.16 |
| ≥Higher secondary | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| Paternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| None | 0.8 (0.5, 1.5) | 0.58 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Primary | 1.1 (0.6, 1.8) | 0.76 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Secondary | 0.8 (0.5, 1.3) | 0.31 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| ≥Higher secondary | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Predominant motor type | ||||||||
| Spastic | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | n/a | n/a | |
| Dyskinesia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Ataxia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Hypotonia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Spastic Topography | ||||||||
| Mono/hemiplegia | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Diplegia | 1.7 (1.2, 2.4) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Tri/quadriplegia | 3.1 (2.2, 4.5) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| GMFCS level | ||||||||
| I–II | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | ||||
| III–V | 1.8 (1.3, 2.5) | <0.001 | 14.9 (2.2, 102.3) | 0.01 | 3.2 (1.2, 8.1) | 0.01 | 1.3 (0.8, 2.2) | 0.29 |
| Associated impairment | ||||||||
| None | Ref | Ref | n/a | n/a | Ref | |||
| One | 1.6 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.9 (0.5, 1.7) | 0.88 |
| Two or more | 1.6 (1.1, 2.2) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.9 (1.0, 3.5) | 0.05 |
| Dysphagia | ||||||||
| No | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Yes | 1.0 (0.7, 1.5) | 0.95 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | ||||||||
| No | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Yes | 1.2 (0.8, 1.8) | 0.41 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Predictors | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age group (years) | ||||||||
| 0–4 | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| 5–9 | 0.7 (0.5, 1.0) | 0.02 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.7 (0.5, 1.2) | 0.25 |
| 10–14 | 0.5 (0.3, 0.6) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.8 (1.3, 6.4) | 0.01 |
| 15 and above | 1.5 (0.9, 2.6) | 0.09 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 9.0 (1.9, 42.4) | 0.01 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.3 (1.0, 5.1) | 0.05 | n/a | n/a |
| Male | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | n/a | n/a | |
| Maternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| None | 2.1 (1.2, 3.5) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.7 (0.7, 4.3) | 0.26 |
| Primary | 2.5 (1.5, 4.1) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.3 (0.6, 3.1) | 0.47 |
| Secondary | 2.0 (1.2, 3.4) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.6 (0.3, 1.4) | 0.25 |
| ≥Higher secondary | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| Paternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| None | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.5 (0.2, 1.3) | 0.18 |
| Primary | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.9 (0.4, 2.0) | 0.81 |
| Secondary | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.0 (0.5, 2.1) | 0.96 |
| ≥Higher secondary | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| Predominant motor type | ||||||||
| Spastic | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | n/a | n/a | |
| Dyskinesia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.0 (0.2, 5.2) | 0.97 | n/a | n/a |
| Ataxia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.1 (0.0, 0.4) | 0.002 | n/a | n/a |
| Hypotonia | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.4 (0.5, 11.9) | 0.28 | n/a | n/a |
| Spastic topography | ||||||||
| Mono/hemiplegia | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Diplegia | 1.8 (1.3, 2.5) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Tri/quadriplegia | 4.7 (3.4, 6.5) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| GMFCS level | ||||||||
| I–II | Ref | n/a | n/a | Ref | Ref | |||
| III–V | 2.6 (2.0, 3.4) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | 3.4 (1.6, 7.1) | 0.001 | 1.6 (1.0, 2.8) | 0.06 |
| Associated impairment | ||||||||
| None | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| One | 1.0 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.79 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.7 (1.4, 5.1) | 0.002 |
| Two and more | 1.1 (0.8, 1.6) | 0.40 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 3.0 (1.5, 5.8) | 0.002 |
| Dysphagia | ||||||||
| No | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Yes | 1.1 (0.7, 1.6) | 0.66 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Gastroesophageal reflux | ||||||||
| No | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Yes | 1.3 (0.9, 2.1) | 0.17 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Predictors | Bangladesh | Indonesia | Nepal | Ghana | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age group (years) | ||||||||
| 0–4 | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| 5–9 | 1.3 (1.1, 1.7) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.4 (0.2, 0.7) | 0.001 |
| 10–14 | 1.7 (1.4, 2.3) | <0.001 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.5 (0.2, 1.1 | 0.13 |
| 15 and above | 1.6 (1.1, 2.3) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.00 |
| Sex of the child | ||||||||
| Male | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | |
| Female | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.5 (0.3, 0.9) | 0.02 |
| Maternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| No formal schooling | 1.2 (0.7, 2.1) | 0.48 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Primary | 1.1 (0.7, 1.9) | 0.67 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Secondary | 0.9 (0.6, 1.6) | 0.80 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Higher secondary and above | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Paternal educational level (formal schooling) | ||||||||
| No formal schooling | 1.2 (0.8, 1.8) | 0.46 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.9 (0.4, 2.1) | 0.91 |
| Primary | 1.0 (0.7, 1.6) | 0.81 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 1.2 (0.6, 2.4) | 0.59 |
| Secondary | 0.9 (0.6, 1.4) | 0.62 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 2.6 (1.3, 5.3) | 0.01 |
| Higher secondary and above | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | Ref | ||
| Spastic topography | ||||||||
| Mono/hemiplegia | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Diplegia | 1.3 (1.0, 1.7) | 1.00 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Tri/quadriplegia | 1.5 (1.2, 2.0) | 0.002 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| GMFCS level | ||||||||
| I–II | Ref | n/a | n/a | Ref | n/a | n/a | ||
| III–V | 1.0 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.70 | n/a | n/a | 2.4 (1.2, 5.0) | 0.02 | n/a | n/a |
| Associated impairment | ||||||||
| None | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| One | 1.3 (1.0, 1.8) | 0.04 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Two and more | 1.4 (1.1, 1.9) | 0.01 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Dysphagia | ||||||||
| No | Ref | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| Yes | 1.1 (0.9, 1.4) | 0.28 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jahan, I.; Muhit, M.; Hardianto, D.; Laryea, F.; Amponsah, S.K.; Chhetri, A.B.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; McIntyre, S.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Epidemiology of Malnutrition among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113676
Jahan I, Muhit M, Hardianto D, Laryea F, Amponsah SK, Chhetri AB, Smithers-Sheedy H, McIntyre S, Badawi N, Khandaker G. Epidemiology of Malnutrition among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113676
Chicago/Turabian StyleJahan, Israt, Mohammad Muhit, Denny Hardianto, Francis Laryea, Samuel Kofi Amponsah, Amir Banjara Chhetri, Hayley Smithers-Sheedy, Sarah McIntyre, Nadia Badawi, and Gulam Khandaker. 2021. "Epidemiology of Malnutrition among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113676
APA StyleJahan, I., Muhit, M., Hardianto, D., Laryea, F., Amponsah, S. K., Chhetri, A. B., Smithers-Sheedy, H., McIntyre, S., Badawi, N., & Khandaker, G. (2021). Epidemiology of Malnutrition among Children with Cerebral Palsy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Findings from the Global LMIC CP Register. Nutrients, 13(11), 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113676






