Association of Serum Magnesium with Blood Pressure in Patients with Hypertensive Crises: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
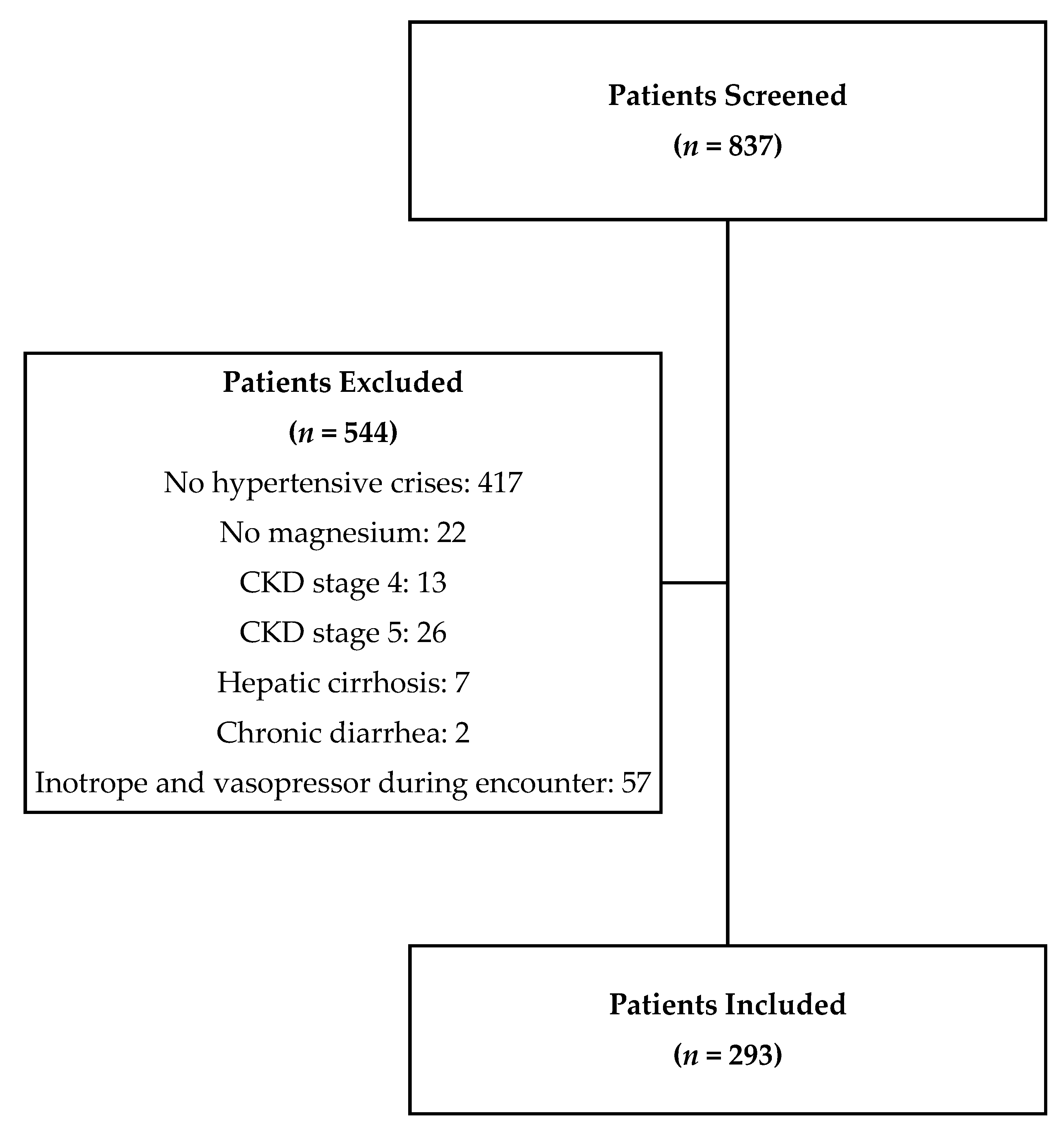
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, C.G.; Taler, S.J. Initial treatment of hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 636–644. [Google Scholar]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004.
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 1975, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, G.; Casagrande, M. Effects of Blood Pressure on Cognitive Performance in Aging: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, M.; Mingarelli, A.; Guarino, A.; Favieri, F.; Boncompagni, I.; Germanò, R.; Germanò, G.; Forte, G. Alexithymia: A facet of uncontrolled hypertension. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2019, 146, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, M.; Boncompagni, I.; Mingarelli, A.; Favieri, F.; Forte, G.; Germanò, R.; Germanò, G.; Guarino, A. Coping styles in individuals with hypertension of varying severity. Stress Health 2019, 35, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, W.J.; Haxby, E.J.; Male, D.A. Magnesium: Physiology and pharmacology. Br. J. Anaesth. 1999, 83, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.M. Magnesium in hypertension, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and other conditions: A review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupetsky-Rincon, E.A.; Uitto, J. Magnesium: Novel applications in cardiovascular disease—A review of the literature. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 61, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, H.; Wanner, C. Magnesium in disease. CKJ Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i25–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, L.M.; Gupta, R.K.; Laragh, J.H. Intracellular free magnesium in erythrocytes of essential hypertension: Relation to blood pressure and serum divalent cations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 6511–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, L.M.; Bardicef, O.; Altura, B.T.; Alderman, M.H.; Altura, B.M. Serum ionized magnesium: Relation to blood pressure and racial factors. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Folsom, A.R.; Melnick, S.L.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Sharrett, A.R.; Nabulsi, A.A.; Hutchinson, R.G.; Metcalf, P.A. Associations of serum and dietary magnesium with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, insulin, and carotid arterial wall thickness: The aric study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1995, 48, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Milne, F.J.; Seftel, H.C.; Reinach, S.G. Magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium status in normotensive and hypertensive Johannesburg residents. S. Afr. Med. J. 1987, 72, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, I.R.; Salim-ul-Haque; Kausar, M.W.; Karira, K.A.; Zubari, N.A. Correlation of divalent Cat ions (Ca++, Mg++) and Serum Renin in pateints of essential hypertension. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2012, 62, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, M.C.; Harper, K.J. Potassium, magnesium, and calcium: Their role in both the cause and treatment of hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2008, 10, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, M. The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinner, M.D.; Spliet-van Laar, L.; Kromhout, D. Serum sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium and blood pressure in a Dutch population. J. Hypertens. 1989, 7, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Sullivan, L.; McCabe, E.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. Lack of association between serum magnesium and the risks of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Am. Heart J. 2010, 160, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, J.M.; Folsom, A.R.; Arnett, D.K.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Szklo, M. Relationship of serum and dietary magnesium to incident hypertension: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 1999, 9, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Hernández-Ronquillo, G.; Gómez-Díaz, R.; Pizano-Zarate, M.L.; Wacher, N.H.; Mondragón-González, R.; Simental-Mendia, L.E.; Salinas Martínez, A.M.; Álvarez Villaseñor, A.S.; et al. Low Serum Magnesium Levels and Its Association with High Blood Pressure in Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 168, 93–98.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Fang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Fan, Z.; Aaseth, J.; Hiyoshi, A.; He, J.; et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake, serum magnesium concentration and risk of hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, M.M.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Mukamal, K.J.; Kootstra-Ros, J.E.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.L. Urinary magnesium excretion and risk of hypertension: The prevention of renal and vascular end-stage disease study. Hypertension 2013, 61, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, B.; Schroll, M.; Christiansen, C.; Transbøl, I. Serum and Erythrocyte Magnesium in Normal Elderly Danish People: Relationship to Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids. Acta Med. Scand. 1977, 201, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. The effect of lowering blood pressure by magnesium supplementation in diabetic hypertensive adults with low serum magnesium levels: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2009, 23, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuliani, A.F.; De Abreu Fagundes, V.G.; Francischetti, E.A. Effects of magnesium on blood pressure and intracellular ion levels of Brazilian hypertensive patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 1996, 56, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Takishita, S.; Omae, T. Effects of magnesium supplementation in hypertensive patients: Assessment by office, home, and ambulatory blood pressures. Hypertension 1998, 32, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.; Weekes, J.; Carpenter, L. Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Rosanoff, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trials. Hypertension 2016, 68, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, S.H.A.; Miller, E.R.; Guallar, E.; Singh, V.K.; Appel, L.J.; Klag, M.J. The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanoff, A.; Plesset, M.R. Oral magnesium supplements decrease high blood pressure (SBP > 155 mmHg) in hypertensive subjects on anti-hypertensive medications: A targeted meta-analysis. Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, H.O.; Nicolson, D.; Campbell, F.; Beyer, F.R.; Mason, J. Potassium supplementation for the management of primary hypertension in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3, CD004641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, P.; Vermeier, W.; Kesteloot, H.; Stroobandt, R. Effect of the infusion of magnesium sulfate during atrial pacing on ECG intervals, serum electrolytes, and blood pressure. Am. Heart J. 1989, 117, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorde, R.; Sundsfjord, J.; Fitzgerald, P.; Bønaa, K.H. Serum calcium and cardiovascular risk factors and diseases: The Tromso Study. Hypertension 1999, 34, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesteloot, H.; Joossens, J.V. Relationship of serum sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus with blood pressure. Belgian Interuniversity Research on Nutrition and Health. Hypertension 1988, 12, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Jakobsson, S.; Lithell, H.; Wengle, B.; Ljunghall, S. Relation of serum calcium concentration to metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Br. Med. J. 1988, 297, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, R.; Huisman, H.W.; Schutte, A.E.; Malan, N.T.; Van Rooyen, J.M.; Fourie, C.M.T.; Malan, L. Serum calcium revisited: Associations with 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and cardiovascular reactivity in Africans. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessen, J.; Sartor, F.; Roels, H.; Bulpitt, C.J.; Claeys, F.; Ducoffre, G.; Fagard, R.; Lauwerijs, R.; Lijnen, P.; Rondia, D.; et al. The association between blood pressure, calcium and other divalent cations: A population study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1991, 5, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cormick, G.; Belizán, J.M. Calcium intake and health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabanayagam, C.; Shankar, A. Serum calcium levels and hypertension among US adults. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Yamada, K.; Nagoshi, H.; Ishiyama, A.; Minami, M.; Uehara, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Hirata, Y.; Kimura, K.; Omata, M. Relation of 24-h ambulatory blood pressure with plasma potassium in essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pikilidou, M.I.; Lasaridis, A.N.; Sarafidis, P.A.; Tziolas, I.M.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Dombros, N.V.; Giannoulis, E. Blood pressure and serum potassium levels in hypertensive patients receiving or not receiving antihypertensive treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2007, 29, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulpitt, C.J.; Shipley, M.J.; Semmence, A. Blood pressure and plasma sodium and potassium. Clin. Sci. 1981, 61, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danziger, J.; William, J.H.; Scott, D.J.; Lee, J.; Lehman, L.-W.; Mark, R.G.; Howell, M.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mukamal, K.J. Proton-pump inhibitor use is associated with low serum magnesium concentrations. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic Variables | |
|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD years; (range)) | 56.70 ± 12.86 (19–97) |
| Sex, n (%) | Male: 146 (49.8%) |
| Female: 147 (50.2%) | |
| Race, n (%) | White: 62 (21.2%) |
| Black/African American: 213 (72.7%) | |
| Asian: 3 (1.0%) | |
| Other: 15 (5.1%) | |
| Hypertensive Crises Diagnosis, n (%) | Hypertensive Urgency: 220 (75.1%) |
| Hypertensive Emergency: 73 (24.9%) | |
| History of Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | Diabetic: 102 (34.8%) |
| Non-diabetic: 191 (65.2%) | |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) (Mean ± SD kg/m2; (range)) (N = 290) | 30.59 ± 9.33 (16.70–69.10) |
| Use of Home Proton Pump Inhibitors (N = 259), n (%) | 53 (20.5%) |
| Use of Home Blood Pressure Medications (N = 264), n (%) | 227 (85.9%) |
| Use of Hospital Blood Pressure Medications, n (%) | 283 (96.6%) |
| Use of Home Magnesium (Oral) (N = 292), n (%) | 31 (10.6%) |
| Use of Hospital Magnesium (Intravenous) (N = 292), n (%) | 95 (32.5%) |
| Serum Magnesium at Crises (Mean ± SD mg/dL; (range)) | 1.93 ± 0.36 (0.80–3.90) |
| Serum Calcium at Crises (Mean ± SD mg/dL; (range)) | 8.92 ± 0.92 (0.80–13.10) |
| Corrected Calcium at Crises (Mean ± SD mg/dL; (range)) (N = 207) | 9.33 ± 0.90 (1.12–13.34) |
| Serum Potassium at Crises (Mean ± SD mg/dL; (range)) | 3.92 ± 0.64 (1.40–6.30) |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (Mean ± SD mmHg; (range)) | 194.2 ± 21.31 (136–265) |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (Mean ± SD mmHg; (range)) | 113.7 ± 21.38 (53–180) |
| SBP at Crises | |||
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| Serum Magnesium | 0.143 | 0.020 | 0.014 |
| Serum Calcium | 0.187 | 0.035 | 0.001 |
| Corrected Calcium (N = 207) | 0.049 | 0.002 | 0.482 |
| Serum Potassium | −0.076 | 0.006 | 0.195 |
| DBP at Crises | |||
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| Serum Magnesium | 0.033 | 0.001 | 0.570 |
| Serum Calcium | 0.090 | 0.008 | 0.124 |
| Corrected Calcium (N = 207) | −0.011 | 0.000 | 0.873 |
| Serum Potassium | −0.113 | 0.013 | 0.053 |
| SBP at Crises | ||
| Variables | β ± SE | p-Value |
| Serum Magnesium (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 11.25 ± 4.67 | 0.017 |
| DBP at Crises | ||
| Variables | β ± SE | p-Value |
| Serum Magnesium (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 2.56 ± 4.93 | 0.603 |
| SBP at Crises | ||
|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | β ± SE | p-Value |
| Serum Magnesium (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 11.25 ± 4.67 | 0.017 |
| Serum Calcium (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 9.50 ± 3.37 | 0.006 |
| Corrected Calcium (per 1 mg/dL increase) (N = 207) | −7.82 ± 3.54 | 0.029 |
| Use of Home Proton Pump Inhibitors | 9.13 ± 3.85 | 0.019 |
| DBP at Crises | ||
|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | β ± SE | p-Value |
| Serum Calcium (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 16.21 ± 3.56 | <0.001 |
| Corrected Calcium (per 1 mg/dL increase) (N = 207) | −14.12 ± 3.74 | <0.001 |
| Age | −0.53 ± 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Serum Magnesium at Crises | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| SBP at Crises | 0.143 | 0.020 | 0.014 |
| SBP Maximum (24 h) | 0.104 | 0.011 | 0.074 |
| SBP Minimum (24 h) | −0.034 | 0.001 | 0.563 |
| DBP at Crises | 0.033 | 0.001 | 0.570 |
| DBP Maximum (24 h) | 0.041 | 0.002 | 0.480 |
| DBP Minimum (24 h) | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.726 |
| Serum Calcium at Crises | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| SBP at Crises | 0.187 | 0.035 | 0.001 |
| SBP Maximum (24 h) | 0.134 | 0.018 | 0.022 |
| SBP Minimum (24 h) | 0.237 | 0.056 | <0.001 |
| DBP at Crises | 0.090 | 0.008 | 0.124 |
| DBP Maximum (24 h) | 0.121 | 0.015 | 0.038 |
| DBP Minimum (24 h) | 0.183 | 0.033 | 0.002 |
| Corrected Calcium at Crises | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| SBP at Crises | 0.049 | 0.002 | 0.482 |
| SBP Maximum (24 h) | −0.028 | 0.001 | 0.690 |
| SBP Minimum (24 h) | 0.256 | 0.066 | <0.001 |
| DBP at Crises | −0.011 | 0.000 | 0.873 |
| DBP Maximum (24 h) | −0.000 | 0.000 | 0.996 |
| DBP Minimum (24 h) | 0.177 | 0.031 | 0.011 |
| Serum Potassium at Crises | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | r | R2 | p-Value |
| SBP at Crises | −0.076 | 0.006 | 0.195 |
| SBP Maximum (24 h) | −0.074 | 0.005 | 0.209 |
| SBP Minimum (24 h) | −0.130 | 0.017 | 0.026 |
| DBP at Crises | −0.113 | 0.013 | 0.053 |
| DBP Maximum (24 h) | −0.065 | 0.004 | 0.265 |
| DBP Minimum (24 h) | −0.175 | 0.031 | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onor, I.O.; Hill, L.M.; Famodimu, M.M.; Coleman, M.R.; Huynh, C.H.; Beyl, R.A.; Payne, C.J.; Johnston, E.K.; Okogbaa, J.I.; Gillard, C.J.; et al. Association of Serum Magnesium with Blood Pressure in Patients with Hypertensive Crises: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124213
Onor IO, Hill LM, Famodimu MM, Coleman MR, Huynh CH, Beyl RA, Payne CJ, Johnston EK, Okogbaa JI, Gillard CJ, et al. Association of Serum Magnesium with Blood Pressure in Patients with Hypertensive Crises: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124213
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnor, IfeanyiChukwu O., Lashira M. Hill, Modupe M. Famodimu, Mallory R. Coleman, Carolkim H. Huynh, Robbie A. Beyl, Casey J. Payne, Emily K. Johnston, John I. Okogbaa, Christopher J. Gillard, and et al. 2021. "Association of Serum Magnesium with Blood Pressure in Patients with Hypertensive Crises: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124213
APA StyleOnor, I. O., Hill, L. M., Famodimu, M. M., Coleman, M. R., Huynh, C. H., Beyl, R. A., Payne, C. J., Johnston, E. K., Okogbaa, J. I., Gillard, C. J., Sarpong, D. F., Borghol, A., Okpechi, S. C., Norbert, I., Sanne, S. E., & Guillory, S. G. (2021). Association of Serum Magnesium with Blood Pressure in Patients with Hypertensive Crises: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients, 13(12), 4213. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124213







