Butaphosphan Effects on Glucose Metabolism Involve Insulin Signaling and Depends on Nutritional Plan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
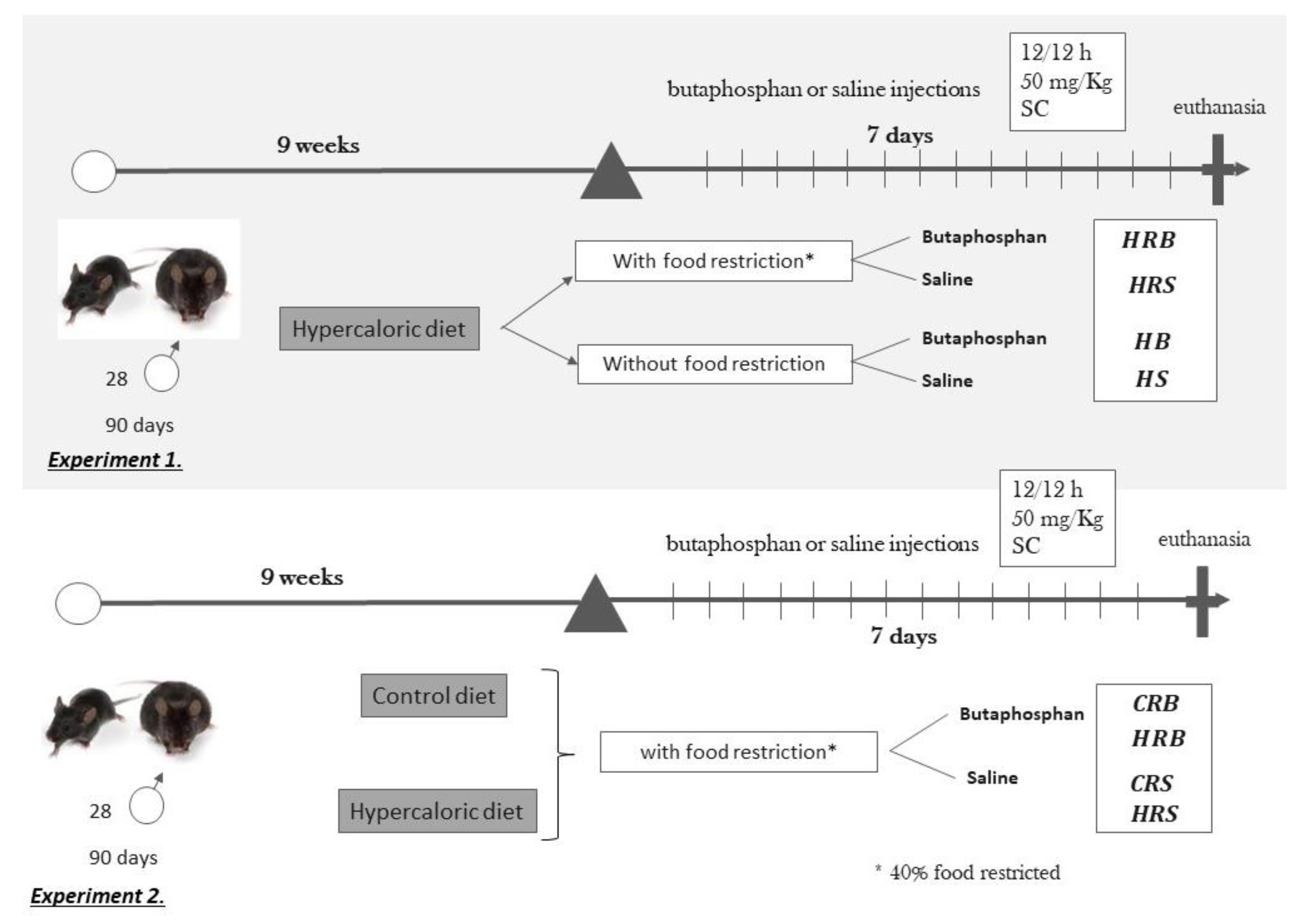
2.1. Experimental Design
2.1.1. Experiment 1
2.1.2. Experiment 2
2.2. Butaphosphan Treatment and Nutritional Management
2.3. Diet
2.4. Samples Collection
2.5. Blood Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1
3.2. Experiment 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdallah, A.G.; El-Husseiny, O.M.; Abdel-Latif, K.O. Influence of some dietary organic mineral supplementations. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2009, 8, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątkiewicz, S.; Arczewska-Włosek, A.; Jozefiak, D. The efficacy of organic minerals in poultry nutrition: Review and implications of recent studies. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2014, 70, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leese, H.J.; Baumann, C.G.; Brison, D.R.; McEvoy, T.G.; Sturmey, R.G. Metabolism of the viable mammalian embryo: Quietness revisited. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 14, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, T.; Pierce, J.L.; Pescatore, A.J.; Cantor, A.H.; Dawson, K.A.; Ford, M.J. Effects of feeding reduced levels of organic minerals (Bioplex®) on the development of white layer pullets. Poultry Sci. 2009, 88, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furll, M.; Deniz, A.; Westphal, B.; Illing, C.; Constable, P.D. Effect of multiple intravenous injections of butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin on the metabolism of periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 2010, 93, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasi, S.-R.; Jiang, J.-S.; Du, X.-Y. Studies on Effects of Compound Butaphosphan Solution on Endurance Capability and Energy Metabolism in Mice. Acta Vet. Et Zoot. Sin. 2004, 35, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Coppo, J.A.; Gapel, E.R. Results of using Catosal® B12 to treat racehorses in Argentina. Hora Veterinária 2000, 19, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Deniz, A.; Spiecker-Hauser, U.; Rehagen, M. Efficacy of a butafosfan and vitamin B12 combination (Catosal®) on biochemical and hematological blood parameters in dogs treated with dexamethasone. Intern. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2009, 7, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Nuber, U.; van Dorland, H.A.; Bruckmaier, R. Effects of butafosfan with or without cyanocobalamin on the metabolism of early lactating cows with subclinical ketosis. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.A.; Fensterseifer, S.; Barcelos, V.B.; Martins, C.F.; Schneider, A.; Schmitt, E.; Pfeifer, L.F.M.; Del Pino, F.B.; Corrêa, M.N. Metabolic parameters and dry matter intake of ewes treated with butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin in the early postpartum period. Small Ruminant Res. 2013, 114, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Staay, F.; De Groot, J.; Van Reenen, C.; Hoving-Bolink, A.; Schuurman, T.; Schmidt, B. Effects of Butafosfan on salivary cortisol and behavioral response to social stress in piglets 1. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.L.; Duffield, T.F.; Herdt, T.H.; Kelton, D.F.; Neuder, L.; LeBlanc, S.J. Effects of a combination butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin product and insulin on ketosis resolution and milk production. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.A.; Silveira, P.A.; Montagner, P.; Schneider, A.; Schmitt, E.; Rabassa, V.R.; Pfeifer, L.F.; Del Pino, F.A.; Pulga, M.E.; Correa, M.N. Effect of butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin on postpartum metabolism and milk production in dairy cows. Animal 2013, 7, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollin, E.; Berghaus, R.D.; Rapnicki, P.; Godden, S.M.; Overton, M.W. The effect of injectable butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin on postpartum serum β-hydroxybutyrate, calcium, and phosphorus concentrations in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakahashi, O.; Kagawa, T.; Ishiguro, M.; Masuda, M.; Kozai, M.; Ikeda, S.; Taketani, Y.; Takeda, E. Dietary phosphate restriction induces hepatic lipid accumulation through dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism in mice. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhalabi, M.M.A. The Role of Phosphorus in the Development and Progression of High Fat Diet Induced NAFLD in Rats. Master’s Thesis, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, J.E.; Huh, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Sung, K.C.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Park, J.R.; Rhee, E.J.; et al. Serum phosphate levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome: A double-edged sword. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuang, Y.H.; Kao, T.W.; Peng, T.C.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, P.K.; Wu, L.W. Serum Phosphorus as a Risk Factor of Metabolic Syndrome in the Elderly in Taiwan: A Large-Population Cohort Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglin, L. Hypophosphataemia: Cause of the disturbed metabolism in the metabolic syndrome. Med. Hypotheses 2001, 56, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.Y.; Sitrin, M.D.; Te, H.S. Serum phosphorus levels predict clinical outcome in fulminant hepatic failure. Liver Transpl. 2003, 9, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Tran, T.L.; Finegoog, D.T.; Van de Werve, G. Dietary P(i) deprivation in rats affects liver CAMP, glycogen, key steps of gluconeogenesis and glucose production. Biochem. J. 2000, 352, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Méchin, M.-C.; Dewerve, G.V. Up-regulation of liver glucose-6-phosphatase in rats fed with a Pi-deficient diet. Biochem. J. 1999, 343, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballou, M.A.; Gomes, R.C.; Juchem, S.O.; De Peters, E.J. Effects of dietary supplemental fish oil during the peripartum period on blood metabolites and hepatic fatty acid compositions and total triacylglycerol concentrations of multiparous Holstein cows. J. Dairy. Sci. 2009, 92, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Zhi, X.; Hossain, T.; Bartke, A.; Spong, A.; Gesing, A.; Masternak, M.M. The contribution of visceral fat to improved insulin signaling in Ames dwarf mice. Aging cell 2014, 13, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ramakers, C.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Karlen, Y.; Bakker, O.; van den Hoff, M.J.; Moorman, A.F. Amplification efficiency: Linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In Biochemistry, 6th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 433–474. [Google Scholar]
- Flakoll, P.J.; Borel, M.J.; Wentzel, L.S.; Williams, P.E.; Lacy, D.B.; Abumrad, N.N. The role of glucagon in the control of protein and amino acid metabolism in vivo. Metabolism 1994, 43, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, S.S.; Armentano, L.E. Insulin and glucagon regulation of gluconeogenesis in preruminating and ruminating bovine. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobe, G.; Ametaj, B.N.; Young, J.W.; Beitz, D.C. Potential treatment of fatty liver with 14-day subcutaneous injections of glucagon. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Glucagon: Acute actions on hepatic metabolism. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse-Patin, A.; Jeromson, S.; Levesque-Damphousse, P.; Secco, B.; Laplante, M.; Estall, J.L. PGC1A regulates the IRS1:IRS2 ratio during fasting to influence hepatic metabolism downstream of insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Șahal, M.; Denİz, A.; Vural, R.; Küplülü, Ș.; Polat, İ.M.; Çolakoğlu, E.Ç.; Öcal, N.; Macun, H.C.; Pekcan, M.; Ocak, M. Evaluation of the effect of different doses of butaphosphan and cyanocobalamin combination in dairy cattle with subclinical ketosis. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2017, 23, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vluggens, A.; Andreoletti, P.; Viswakarma, N.; Jia, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Kulik, W.; Khan, M.; Huang, J.; Guo, D.; Yu, S. Functional significance of the two ACOX1 isoforms and their crosstalks with PPARα and RXRα. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Gavaldà, J.M.; Herrero, L.; Malandrino, M.I.; Pañeda, A.; Sol Rodríguez-Peña, M.; Petry, H.; Asins, G.; Van Deventer, S.; Hegardt, F.G.; Serra, D. Molecular therapy for obesity and diabetes based on a long-term increase in hepatic fatty-acid oxidation. Hepatology 2011, 53, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farese, R.V., Jr.; Zechner, R.; Newgard, C.B.; Walther, T.C. The problem of establishing relationships between hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, L.M.; Rivas, D.A.; Ezzyat, Y.; Gaffney-Stomberg, E.; Young, A.J.; McClung, J.P.; Fielding, R.A.; Pasiakos, S.M. Calorie restricted high protein diets downregulate lipogenesis and lower intrahepatic triglyceride concentrations in male rats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, S.; Oetzel, G.R. Decreased insulin response in dairy cows following a four-day fast to induce hepatic lipidosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, J.A.; Souza, A.H.; Grummer, R.R. Induction of hyperlipidemia by intravenous infusion of tallow emulsion causes insulin resistance in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S. Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome: Insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, T1–T23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H. The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in the pathogenesis of obesity-related insulin resistance. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, P.W.; Loos, R.J. PGC-1α gene and physical activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2006, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-Q.; Tucker, K.L.; Parnell, L.D.; Adiconis, X.; García-Bailo, B.; Griffith, J.; Meydani, M.; Ordovás, J.M. PPARGC1A variation associated with DNA damage, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: The Boston Puerto Rican Health Study. Diabetes 2008, 57, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Matharoo, K.; Kapoor, R.; Bhanwer, A. Association of PGC-1α gene with type 2 diabetes in three unrelated endogamous groups of North-West India (Punjab): A case-control and meta-analysis study. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puigserver, P.; Wu, Z.; Park, C.W.; Graves, R.; Wright, M.; Spiegelman, B.M. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 1998, 92, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Handschin, C.; Arlow, D.; Xie, X.; Pierre, J.S.; Sihag, S.; Yang, W.; Altshuler, D.; Puigserver, P.; Patterson, N. Errα and Gabpa/b specify PGC-1α-dependent oxidative phosphorylation gene expression that is altered in diabetic muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6570–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, F.; Li, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Apelin stimulates glucose uptake through the PI3K/Akt pathway and improves insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 353, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Ward, W.F. PGC-1α: A key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrès, R.; Osler, M.E.; Yan, J.; Rune, A.; Fritz, T.; Caidahl, K.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R. Non-CpG methylation of the PGC-1α promoter through DNMT3B controls mitochondrial density. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB | HRB | HS | HRS | SEM | Treat | Restriction | Treat. × Restriction | |
| a Body weight (g) | 33.28 | 34.71 | 34.85 | 32.2 | 1.76 | 0.766 | 0.699 | 0.205 |
| b Liver (g) | 1.57 | 1.73 | 1.74 | 1.77 | 0.10 | 0.237 | 0.299 | 0.492 |
| c Epididymal WAT mass (g) | 0.88 a,b | 1.11 a | 0.95 a,b | 0.36 b | 0.18 | 0.047 | 0.284 | 0.019 |
| d Muscle (g) | 0.18 a,b | 0.18 a,b | 0.19 a | 0.14 b | 0.01 | 0.324 | 0.018 | 0.016 |
| e Glucose (mmol/L) | 12.61 a | 11.35 a | 11.25 a | 7.51 b | 0.48 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 |
| f NEFA (mmol/L) | 0.80 ab | 0.85 a | 0.85 a | 0.65 b | 0.05 | 0.066 | 0.087 | 0.009 |
| g Insulin (ng/mL) | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.539 | 0.488 | 0.284 |
| h Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 10.14 | 9.28 | 10.14 | 9.94 | 0.69 | 0.125 | 0.925 | 0.672 |
| I HOMA Index | 2.96 a | 2.91 a | 2.82 a | 1.73 b | 0.36 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.045 |
| Gene | Groups | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB | HRB | HS | HRS | SEM | Treat. | Restriction | Treat. × Restriction | |
| Lipid metabolism | ||||||||
| Acaca | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.098 | 0.302 | 0.385 |
| Acox1 | 2.16 | 2.45 | 0.74 | 1.33 | 0.57 | 0.011 | 0.089 | 0.201 |
| Cpt1a | 0.82 | 1.11 | 0.80 | 1.03 | 0.14 | 0.672 | 0.071 | 0.995 |
| Srebp1c | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.384 | 0.626 | 0.248 |
| Glucose metabolism and insulin signaling | ||||||||
| PcK1 | 0.73 | 0.36 | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 0.824 | 0.059 | 0.928 |
| GcK | 0.11 b | 0.39 a | 0.45 a | 0.18 a,b | 0.15 | 0.217 | 0.050 | 0.005 |
| Fbp1 | 2.07 | 3.01 | 1.87 | 2.39 | 0.92 | 0.316 | 0.122 | 0.241 |
| G6Pase | 0.45 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.819 | 0.0002 | 0.921 |
| PI3K | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.340 | 0.400 | 0.617 |
| Irs1 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.135 | <0.0001 | 0.170 |
| Irs2 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.460 | 0.164 | 0.162 |
| Irs1:Irs2 | 6.30 | 1.17 | 3.58 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 0.051 | <0.001 | 0.971 |
| FoxO1 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.124 | 0.517 | 0.757 |
| Transcription Factors | ||||||||
| Pparγ | 0.031 | 0.026 | 0.028 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.223 | 0.577 | 0.593 |
| Ppargc1a | 0.006 | 0.03 | 0.005 | 0.04 | 0.007 | 0.783 | <0.0001 | 0.274 |
| Groups | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRB | HRB | CRS | HRS | SEM | Treat. | Diet | Treat. × Diet | |
| a Body Mass (g) | 29.43 | 34.71 | 28.71 | 32.20 | 1.29 | 0.175 | 0.001 | 0.442 |
| b Liver (g) | 1.62 | 1.73 | 1.61 | 1.77 | 0.09 | 0.832 | 0.132 | 0.744 |
| c WAT mass (g) | 0.21 b | 1.10 a | 0.24 b | 0.36 b | 0.15 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.011 |
| d Muscle (g) | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.063 | 0.485 | 0.068 |
| e Glucose (mmol/L) | 9.02 b | 11.35 a | 8.54 b | 7.5 b | 0.68 | 0.002 | 0.297 | 0.011 |
| f NEFA (mmol/L) | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.65 | 0.1 | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.53 |
| g Insulin (ng/mL) | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.336 | 0.119 | 0.644 |
| h Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 11.06 | 9.28 | 9.56 | 9.94 | 0.69 | 0.453 | 0.236 | 0.118 |
| I HOMA Index | 1.80 | 2.91 | 1.53 | 1.73 | 0.39 | 0.027 | 0.115 | 0.125 |
| Gene | Groups | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRB | HRB | CRS | HRS | SEM | Treat. | Diet | Treat. ×Diet | |
| Lipid metabolism | ||||||||
| Acaca | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.055 | 0.120 | 0.538 |
| Acox1 | 1.55 | 2.45 | 0.98 | 1.33 | 0.52 | 0.026 | 0.113 | 0.726 |
| Cpt1a | 1.32 | 1.11 | 0.84 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 0.034 | 0.844 | 0.100 |
| Srebp1c | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.822 | 0.110 | 0.724 |
| Glucose metabolism and insulin signaling | ||||||||
| PcK1 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.287 | 0.629 | 0.223 |
| GcK | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.014 | 0.020 | 0.839 |
| Fbp1 | 3.29 | 3.01 | 2.12 | 2.39 | 0.69 | 0.332 | 0.603 | 0.478 |
| G6Pase | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.551 | 0.142 | 0.375 |
| PI3K | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.030 | 0.038 | 0.124 |
| Irs1 | 0.56 | 0.19 * | 0.33 | 0.10 * | 0.06 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.840 |
| Irs2 | 0.21 a | 0.18 a | 0.09 b,* | 0.14 a,b,* | 0.02 | 0.003 | 0.202 | 0.028 |
| Irs1:Irs2 | 2.72 a | 1.17 b | 5.20 a | 0.72 b | 0.98 | 0.793 | <0.001 | 0.035 |
| FoxO1 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.272 | 0.300 | 0.939 |
| Transcription Factors | ||||||||
| Pparγ | 0.02 * | 0.02 | 0.01 * | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.278 | 0.710 |
| Ppargc1a | 0.04 a | 0.03 a | 0.01 b | 0.04 a | 0.009 | 0.059 | 0.27 | 0.002 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weiller, M.A.A.; Alvarado-Rincón, J.A.; Jacometo, C.B.; Barros, C.C.; de Souza, I.C.C.; Hax, L.T.; da Silva, T.C.; Mattei, P.; Barbosa, A.A.; Feijó, J.d.O.; et al. Butaphosphan Effects on Glucose Metabolism Involve Insulin Signaling and Depends on Nutritional Plan. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061856
Weiller MAA, Alvarado-Rincón JA, Jacometo CB, Barros CC, de Souza ICC, Hax LT, da Silva TC, Mattei P, Barbosa AA, Feijó JdO, et al. Butaphosphan Effects on Glucose Metabolism Involve Insulin Signaling and Depends on Nutritional Plan. Nutrients. 2020; 12(6):1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061856
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeiller, Maria Amélia Agnes, Joao Alveiro Alvarado-Rincón, Carolina Bespalhok Jacometo, Carlos Castilho Barros, Izabel Cristina Custódio de Souza, Lucas Teixeira Hax, Thaís Casarin da Silva, Patrícia Mattei, Antônio Amaral Barbosa, Josiane de Oliveira Feijó, and et al. 2020. "Butaphosphan Effects on Glucose Metabolism Involve Insulin Signaling and Depends on Nutritional Plan" Nutrients 12, no. 6: 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061856
APA StyleWeiller, M. A. A., Alvarado-Rincón, J. A., Jacometo, C. B., Barros, C. C., de Souza, I. C. C., Hax, L. T., da Silva, T. C., Mattei, P., Barbosa, A. A., Feijó, J. d. O., Pereira, R. A., Brauner, C. C., Rabassa, V. R., Del Pino, F. A. B., & Corrêa, M. N. (2020). Butaphosphan Effects on Glucose Metabolism Involve Insulin Signaling and Depends on Nutritional Plan. Nutrients, 12(6), 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061856





