Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Poorer Cardiometabolic Profile and Lower Physical Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Study Population
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Handgrip Strength Parameters
2.4. Cardiometabolic Risk Factors
2.5. Mediterranean Diet Adherence
2.6. Pubertal Stage
2.7. Statistical Analysis
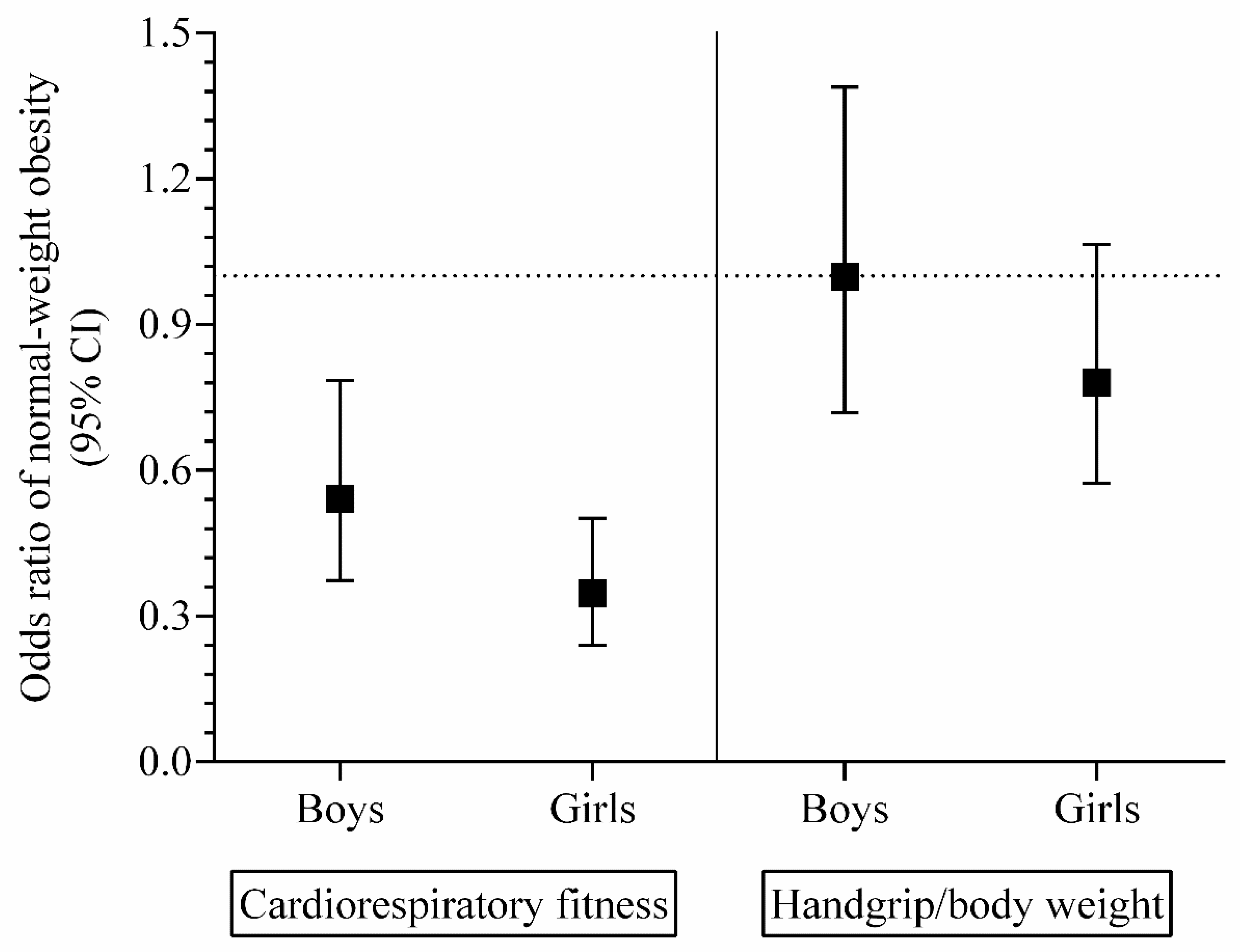
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://www.who.int/chp/ncd_global_status_report/en/ (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Field, A.E.; Laird, N.; Steinberg, E.; Fallon, E.; Semega-Janneh, M.; Yanovski, J.A. Which metric of relative weight best captures body fatness in children? Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.S.; Mei, Z.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Berenson, G.S.; Dietz, W.H. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Excess Adiposity Among Overweight Children and Adolescents: The Bogalusa Heart Study. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 12–17.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, W.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heshka, S. Percentage body fat ranges associated with metabolic syndrome risk: Results based on the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988-1994). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, E.; Somers, V.K.; Sochor, O.; Goel, K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. The concept of normal weight obesity. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.P.; Morais, C.C.; Cominetti, C. Normal-weight obesity syndrome: Diagnosis, prevalence, and clinical implications. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintjens, S.; Menting, M.D.; Daams, J.G.; van Poppel, M.N.M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence Affects Future Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies. Sport Med. 2018, 48, 2577–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Izquierdo, M. Is Muscular Fitness Associated with Future Health Benefits in Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Sport Med. 2019, 49, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, A.S.; Torfadottir, J.E.; Arngrimsson, S.A. Health behavior and metabolic risk factors associated with normal weight obesity in adolescents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Anzola, A.; Martinez-Torres, J.; Vivas, A.; Tordecilla-Sanders, A.; Prieto-Benavides, D.; Izquierdo, M.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Garcia-Hermoso, A. Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Factors in a Population-Based Sample of Schoolchildren in Colombia: The FUPRECOL Study. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2016, 14, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Rodrigues-Bezerra, D.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Izquierdo, M.; Lobelo, F. Reliability of Health-Related Physical Fitness Tests among Colombian Children and Adolescents: The FUPRECOL Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Cardozo, G.D.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; González-Jiménez, E.; Schmidt-RioValle, J.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Percentiles of body fat measured by bioelectrical impedance in children and adolescents from Bogotá (Colombia): The FUPRECOL study. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2016, 114, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 metre shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.; Chan, L.; Bruce, L.C. A preliminary study of the 20-m multistage shuttle run as a predictor of peak VO2 in Hong Kong Chinese students. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1993, 5, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Mota, J.; Garcia-Hermoso, A. Comparison of Different Maximal Oxygen Uptake Equations to Discriminate the Cardiometabolic Risk in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2018, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Peña, J.; Torres, J.M.; Tordecilla-Sanders, A.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Lobelo, F.; García-Hermoso, A. Handgrip strength cutoff for cardiometabolic risk index among Colombian children and adolescents: The FUPRECOL Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.B.; Harro, M.; Sardinha, L.B.; Froberg, K.; Ekelund, U.; Brage, S.; Anderssen, S.A. Physical activity and clustered cardiovascular risk in children: A cross-sectional study (The European Youth Heart Study). Lancet 2006, 368, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, H.A.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet in a sample of Colombian schoolchildren: An evaluation of the psychometric properties of the KIDMED questionnaire. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 37, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.M.; Whitehouse, R.H. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch. Dis. Child. 1976, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Cerjak, D.; Kent, J.W.; James, R.; Blangero, J.; Zhang, Y. Obesity, central adiposity and cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents: A family-based study. Pediatr. Obes. 2014, 9, e58–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camhi, S.M.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Tracking of cardiometabolic risk factor clustering from childhood to adulthood. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 5, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutin, B. Diet vs exercise for the prevention of pediatric obesity: The role of exercise. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, V.; Rinaldi, R.L.; Torrance, B.; Maximova, K.; Ball, G.D.C.; Majumdar, S.R.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Veugelers, P.J.; Boulé, N.G.; Wozny, P.; et al. Vigorous physical activity and longitudinal associations with cardiometabolic risk factors in youth. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Rodríguez, M.; González-Ruíz, K.; Rincón-Pabón, D.; Izquierdo, M.; García-Hermoso, A.; Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Sánchez-Capacho, N.; Roa-Cubaque, M.A.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Increased Cardiometabolic Risk in Young Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Schumann, M.; Huang, T.; Törmäkangas, T.; Cheng, S. Normal weight obesity and physical fitness in Chinese university students: An overlooked association. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
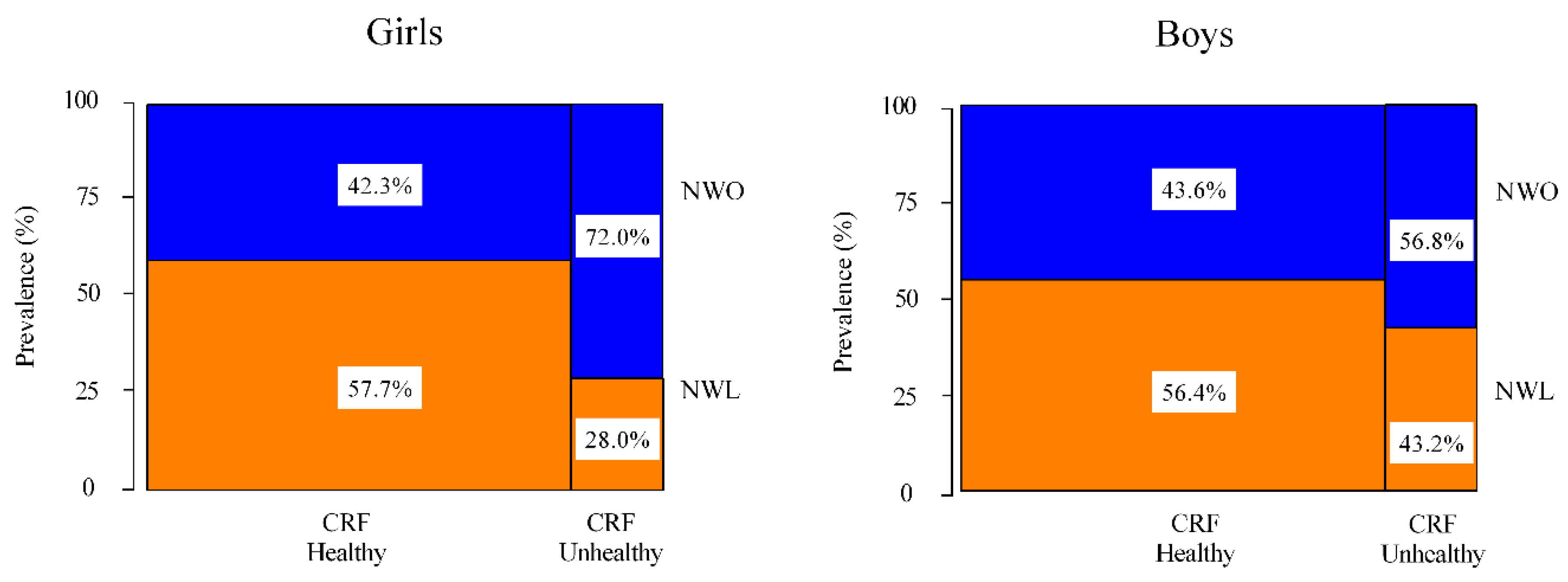
| Characteristics | NWL (n = 1030) | NWO (n = 889) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 12.82 ± 2.11 | 13.86 ± 2.21 | <0.001 |
| Girls, % | 53.0 | 47.0 | 0.264 |
| Anthropometric parameters | |||
| Body weight, kg | 41.09 ± 9.32 | 47.79 ± 9.66 | <0.001 |
| Height, m | 1.50 ± 0.12 | 1.55 ± 1.12 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 17.86 ± 1.85 | 19.67 ± 1.91 | <0.001 |
| Body fat, kg | 7.24 ± 3.09 | 9.89 ± 3.56 | <0.001 |
| Pubertal stage, % | |||
| Pre-pubertal stage | 6.7 | 4.7 | <0.001 |
| Pubertal stage | 57.2 | 43.6 | |
| Late/post-pubertal stage | 36.1 | 51.7 | |
| Mediterranean diet adherence | |||
| KIDMED index score, points | 4.0 ± 1.7 | 3.4 ± 1.6 | 0.001 |
| KIDMED index score (poor/average/good), % | 53.7/36.5/9.9 | 49.0/41.0/10.0 | 0.099 |
| Sex | Groups | p Value | p Value * | |
| Boys (n = 902) | NWL (n = 496) | NWO (n = 406) | ||
| Cardiometabolic parameters | ||||
| Waist circumference, cm | 61.78 ± 5.12 | 65.85 ± 6.13 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 76.72 ± 30.8 | 85.32 ± 38.13 | <0.001 | 0.017 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 49.60 ± 12.99 | 45.72 ± 11.75 | <0.001 | 0.317 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 83.36 ± 14.95 | 81.91 ± 17.04 | 0.122 | 0.472 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 111.44 ± 14.98 | 1114.60 ± 13.34 | 0.001 | 0.994 |
| Cardiometabolic risk score | −0.97 ± 2.10 | −0.15 ± 2.31 | <0.001 | 0.019 |
| Physical fitness parameters | ||||
| Cardiorespiratory fitness, mL·kg−1·min−1 | 51.36 ± 2.97 | 50.67 ± 3.19 | 0.001 | 0.009 |
| Handgrip strength/body weight | 0.50 ± 0.09 | 0.51 ± 0.11 | 0.785 | <0.001 |
| Girls (n = 1017) | NWL (n = 539) | NWO (n = 478) | p Value | |
| Cardiometabolic parameters | ||||
| Waist circumference, cm | 59.12 ± 5.07 | 63.94 ± 5.89 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 87.16 ± 36.61 | 97.86 ± 62.59 | <0.001 | 0.065 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 49.63 ± 12.51 | 47.15 ± 12.21 | <0.001 | 0.484 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 81.96 ± 15.16 | 80.47 ± 16.86 | 0.055 | 0.051 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 107.81 ± 12.31 | 110.58 ± 12.36 | <0.001 | 0.268 |
| Cardiometabolic risk score | −1.08 ± 2.31 | −0.12 ± 2.38 | <0.001 | 0.044 |
| Physical fitness parameters | ||||
| Cardiorespiratory fitness, mL·kg−1·min−1 | 36.86 ± 2.33 | 35.56 ± 2.37 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| Handgrip strength/body weight | 0.43 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.06 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Hermoso, A.; Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Camargo-Villalba, G.E.; González-Jiménez, N.M.; Izquierdo, M.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Poorer Cardiometabolic Profile and Lower Physical Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041171
García-Hermoso A, Agostinis-Sobrinho C, Camargo-Villalba GE, González-Jiménez NM, Izquierdo M, Correa-Bautista JE, Ramírez-Vélez R. Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Poorer Cardiometabolic Profile and Lower Physical Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients. 2020; 12(4):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041171
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Hermoso, Antonio, Cesar Agostinis-Sobrinho, Gloria Eugenia Camargo-Villalba, Nubia Mercedes González-Jiménez, Mikel Izquierdo, Jorge Enrique Correa-Bautista, and Robinson Ramírez-Vélez. 2020. "Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Poorer Cardiometabolic Profile and Lower Physical Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents" Nutrients 12, no. 4: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041171
APA StyleGarcía-Hermoso, A., Agostinis-Sobrinho, C., Camargo-Villalba, G. E., González-Jiménez, N. M., Izquierdo, M., Correa-Bautista, J. E., & Ramírez-Vélez, R. (2020). Normal-Weight Obesity Is Associated with Poorer Cardiometabolic Profile and Lower Physical Fitness Levels in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients, 12(4), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041171








