Influence of Socio-Economic and Psychosocial Profiles on the Human Breast Milk Bacteriome of South African Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Settings: Drakenstein Child Health Study
2.2. Clinical Data and Sample Collection
2.3. Bacterial Nucleic Acid Extraction and Quantification
2.4. Extraction and Sequencing Controls
2.5. 16S Ribosomal Ribonucleic Acid (rRNA) Gene Amplicon Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.6. Processing of 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Sequencing Results and OTU Analysis
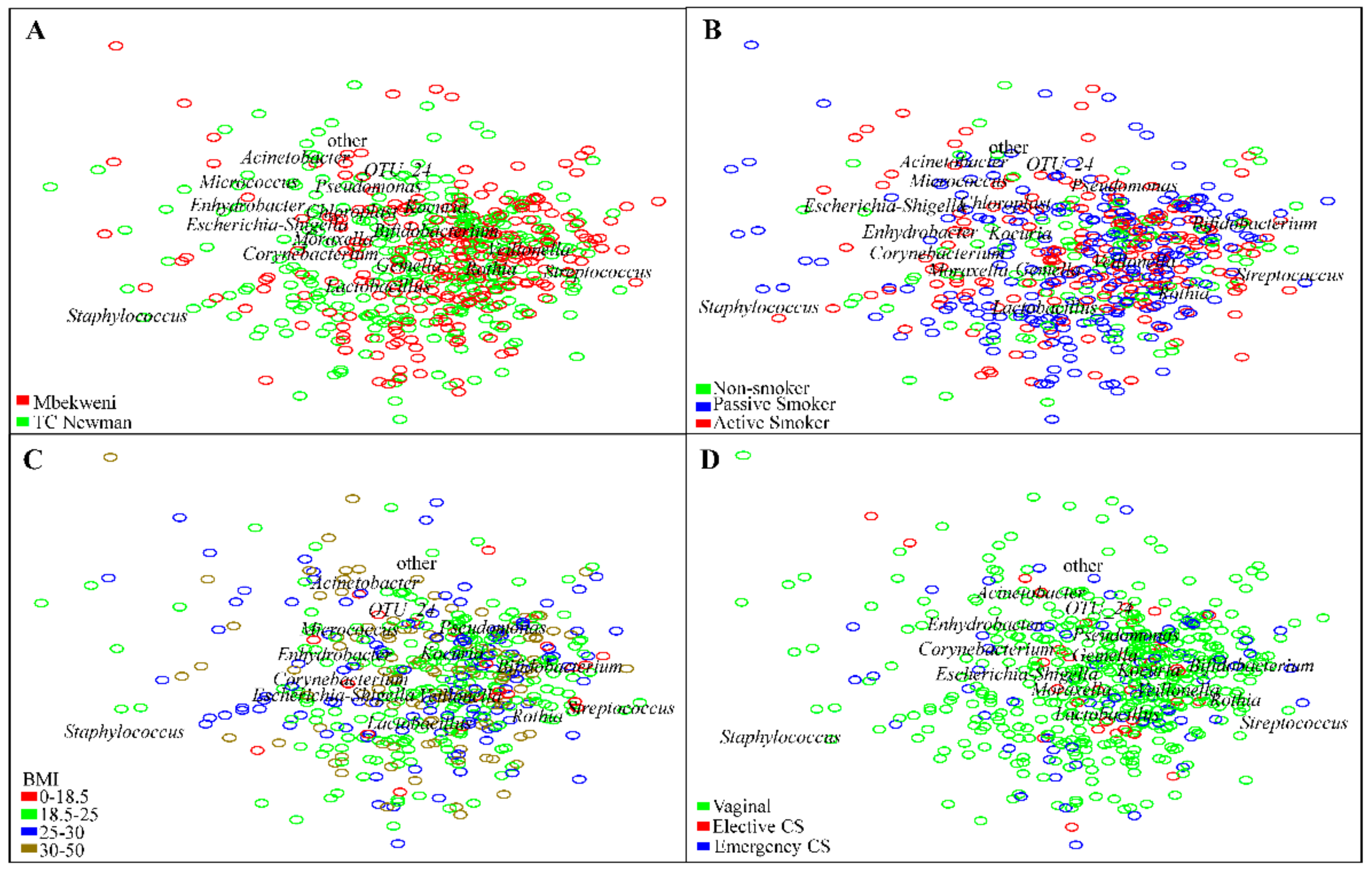
3.3. Profiling of Human Breast Milk Bacteriome
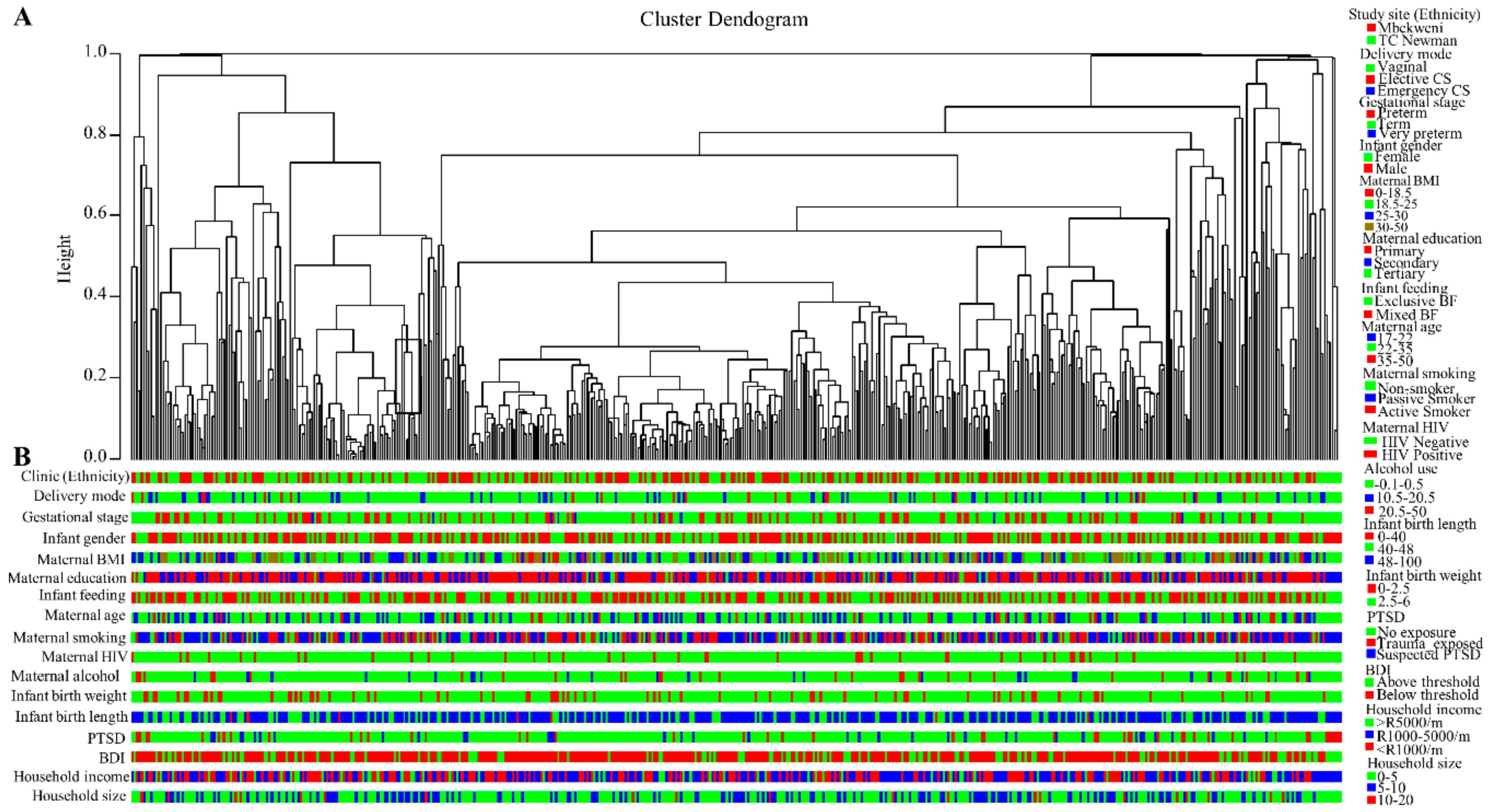
3.4. Breast Milk Bacteriome Profiles Segregate into Three Major Clusters
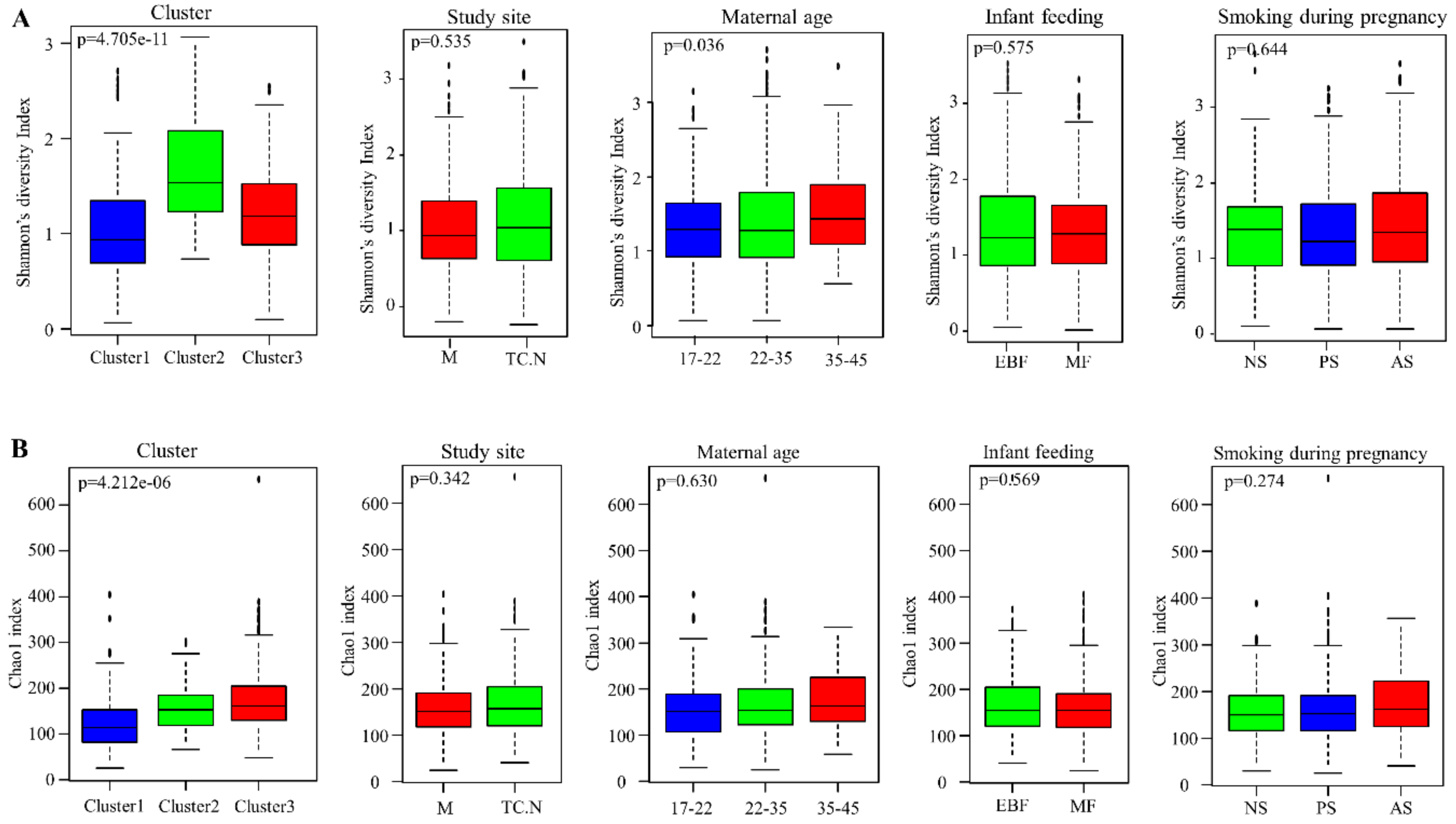
3.5. Alpha Diversity of Bacterial Communities within the DCHS Cohort Study
3.6. Human Breast Milk Bacterial Profiles in Relation to Demographic, Socio-Economic, and Psychosocial Variables
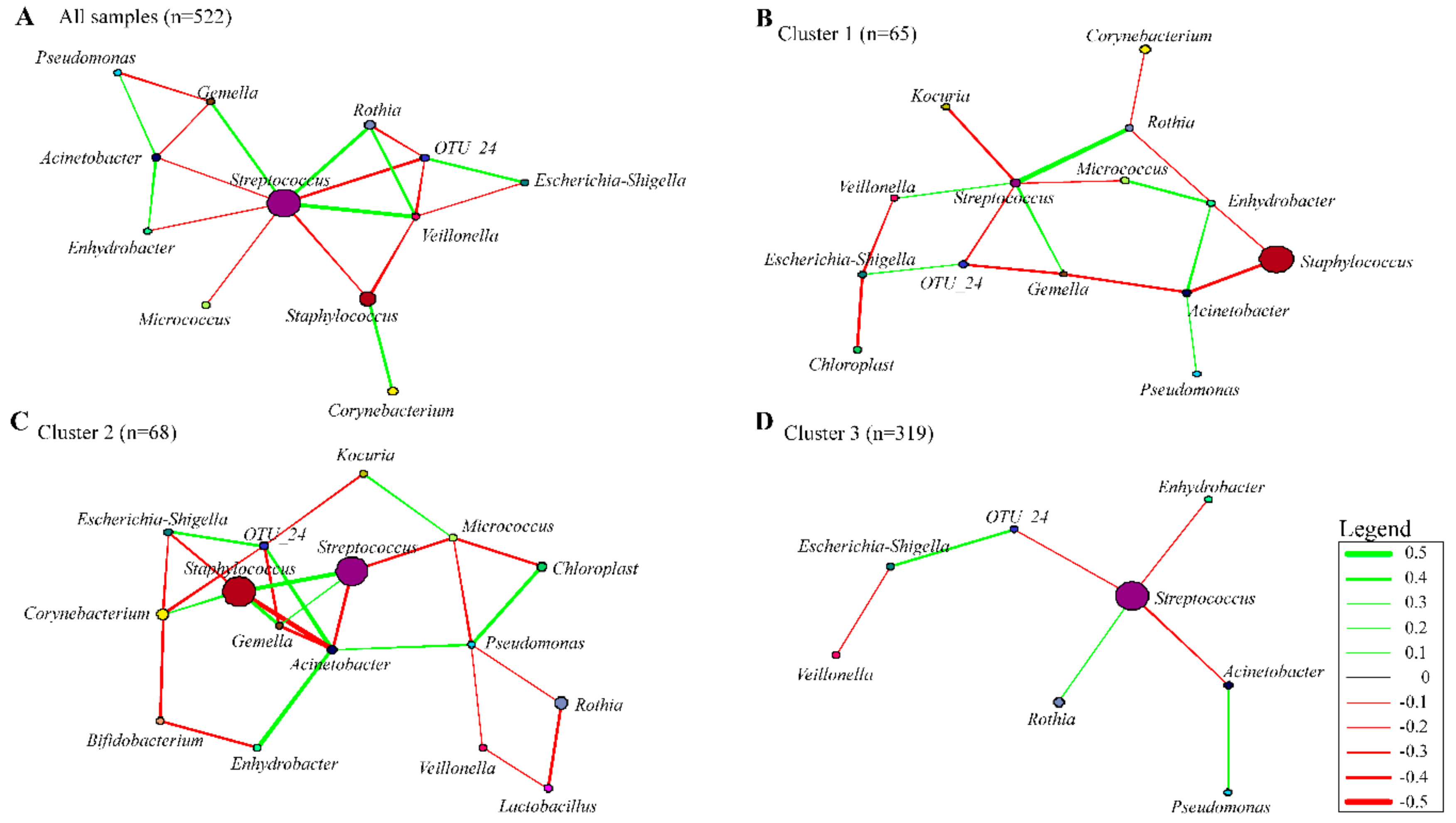
3.7. Co-occurrence Networks in Human Breast Milk Bacterial Communities
3.8. Reproducibility of Bacterial Profiling
4. Discussion
4.1. Bacterial Interactions within the Human Breast Milk Bacterial Community
4.2. Impact of Maternal and Infant Factors on Human Breast Milk Bacterial Profiles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association between breast milk bacterial communities and establishment and development of the infant gut microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; de Andres, J.; Manrique, M.; Pareja-Tobes, P.; Tobes, R.; Martinez-Blanch, J.F.; Codoner, F.M.; Ramon, D.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Metagenomic analysis of milk of healthy and mastitis-suffering women. J. Hum. Lact. 2015, 31, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, H.; Kushiro, A.; Ishikawa, E.; Muylaert, D.; Kubota, H.; Sakai, T.; Oishi, K.; Martin, R.; Amor, K.B.; Oozeer, R. Transmission of intestinal bifidobacterium longum subsp. Longum strains from mother to infant determined by multilocus sequencing typing and amplified fragment length polymorphism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6788–6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, R.; Jiménez, E.; Heilig, H.; Fernández, L.; Marín, M.L.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Rodríguez, J.M. Isolation of bifidobacteria from breast milk and assessment of the bifidobacterial population by pcr-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and quantitative real-time pcr. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; du Toit, E.; Kulkarni, A.; Aakko, J.; Linderborg, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Nicol, M.P.; Isolauri, E.; Yang, B.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Distinct patterns in human milk microbiota and fatty acid profiles across specific geographic locations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Mira-Pascual, L.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C. Impact of mode of delivery on the milk microbiota composition of healthy women. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2016, 7, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, K.M.; Foster, J.A.; Forney, L.J.; Schutte, U.M.; Beck, D.L.; Abdo, Z.; Fox, L.K.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, C.; Angelini, M.; Gloor, G.B.; Reid, G. Human milk microbiota profiles in relation to birthing method, gestation and infant gender. Microbiome 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Curley, D.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; O’Shea, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. The composition of human milk and infant faecal microbiota over the first three months of life: A pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo-Okunola, A.; Nicol, M.; du Toit, E. Human breast milk bacteriome in health and disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Collado, M.C.; Laitinen, K.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Mira, A. The human milk microbiome changes over lactation and is shaped by maternal weight and mode of delivery. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, M.; Albrecht, S.; De Palma, G.; Ferrer, M.D.; Castillejo, G.; Schols, H.A.; Sanz, Y. Human milk composition differs in healthy mothers and mothers with celiac disease. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.E.; Carrothers, J.M.; Lackey, K.A.; Beatty, N.F.; York, M.A.; Brooker, S.L.; Shafii, B.; Price, W.J.; Settles, M.L.; McGuire, M.A.; et al. Human milk microbial community structure is relatively stable and related to variations in macronutrient and micronutrient intakes in healthy lactating women. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, R.; Mandomando, I.; Fumadó, V.; Sacoor, C.; Macete, E.; Alonso, P.L.; Menendez, C. Breast milk and gut microbiota in african mothers and infants from an area of high hiv prevalence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, H.J.; Barnett, W.; Myer, L.; Stein, D.J.; Nicol, M.P. Investigating the early-life determinants of illness in africa: The drakenstein child health study. Thorax 2015, 70, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A.; Tamehana, M.; Singh, H.; Munro, P.A. Effect of interactions between denatured whey proteins and casein micelles on the formation and rheological properties of acid skim milk gels. J. Dairy Res. 1998, 65, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, D.; Keijser, B.; Huse, S.; Rossen, J.; Veenhoven, R.; van Gils, E.; Bruin, J.; Montijn, R.; Bonten, M.; Sanders, E. Variability and diversity of nasopharyngeal microbiota in children: A metagenomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16s rrna diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen-Weitz, S.; Gardner-Lubbe, S.; Nicol, P.; Botha, G.; Mounaud, S.; Shankar, J.; Nierman, W.C.; Mulder, N.; Budree, S.; Zar, H.J. Hiv-exposure, early life feeding practices and delivery mode impacts on faecal bacterial profiles in a south african birth cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wen, C.; Qin, Y.; Yin, H.; Tu, Q.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Yuan, T.; Yuan, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J. Phasing amplicon sequencing on illumina miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina, P. Miseq® System User Guide; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. Fastqc: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: Http://www.Bioinformatics.Babraham.Ac.Uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 30 October 2018).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Kaller, M. Multiqc: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Uparse: Highly accurate otu sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than blast. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rrna sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The silva ribosomal rna gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Chatzou, M.; Floden, E.W.; Barja, P.P.; Palumbo, E.; Notredame, C. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.Org/ (accessed on 22 September 2018).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Package ‘vegan’. In Community Ecology Package, Version; 2013; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J.A. Clustering Algorithms; John Willey and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 113129. [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh, F. Multidimensional Clustering Algorithms; Compstat Lectures; Physika Verlag: Vienna, Austria, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2.4-4; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliński, T.; Harabasz, J. A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.J. Biplots in Practice; Fundacion BBVA: Fundacion, Dominica, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J.C.; Lubbe, S.G.; Le Roux, N.J. Understanding Biplots; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, D.F.; Parker, R.A.; Kendrick, J.S. The box plot: A simple visual method to interpret data. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989, 110, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butts, C.T. Network: A package for managing relational data in r. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 24, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J.; Tolosana-Delgado, R. Modeling and Analysis of Compositional Data; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison, J.; Barceló-Vidal, C.; Martín-Fernández, J.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. Logratio analysis and compositional distance. Math. Geol. 2000, 32, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templ, M.; Hron, K.; Filzmoser, P. Robcompositions: An R-Package for Robust Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa, L.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.; Vazquez-Barquero, J.; Dıez-Manrique, F.; Dowrick, C. The use of the beck depression inventory to screen for depression in the general population: A preliminary analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2000, 57, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Beck depression inventory-ii. San Antonio 1996, 78, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Beusenberg, M.; Orley, J.H.; World Health Organization. A User’s Guide to the Self Reporting Questionnaire (srq); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Harpham, T.; Reichenheim, M.; Oser, R.; Thomas, E.; Hamid, N.; Jaswal, S.; Ludermir, A.; Aidoo, M. Measuring mental health in a cost-effective manner. Health Policy Plan. 2003, 18, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foa, E.B.; Riggs, D.S.; Dancu, C.V.; Rothbaum, B.O. Reliability and validity of a brief instrument for assessing post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Trauma Stress 1993, 6, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.J.; Koen, N.; Donald, K.; Adnams, C.M.; Koopowitz, S.; Lund, C.; Marais, A.; Myers, B.; Roos, A.; Sorsdahl, K. Investigating the psychosocial determinants of child health in africa: The drakenstein child health study. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 252, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budree, S.; Stein, D.; Brittain, K.; Goddard, E.; Koen, N.; Barnett, W.; Myer, L.; Zar, H. Maternal and infant factors had a significant impact on birthweight and longitudinal growth in a south african birth cohort. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 326. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, E.; Delgado, S.; Fernández, L.; García, N.; Albújar, M.; Gómez, A.; Rodríguez, J.M. Assessment of the bacterial diversity of human colostrum and screening of staphylococcal and enterococcal populations for potential virulence factors. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, T.L.; Hosid, S.; Ioshikhes, I.; Altosaar, I. Human milk metagenome: A functional capacity analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-W.; Watanabe, K.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chao, S.-H.; Yang, Z.-H.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Cao, Y.-M.; Huang, H.-C.; Chang, C.-H. Bacterial composition and diversity in breast milk samples from mothers living in taiwan and mainland china. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansson, H.; Kumar, H.; Collado, M.C.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E.; Rautava, S. Breast milk microbiota is shaped by mode of delivery and intrapartum antibiotic exposure. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J.; et al. Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in a population with varied ethnic origins but shared geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakwinska, O.; Moine, D.; Delley, M.; Combremont, S.; Rezzonico, E.; Descombes, P.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Thakkar, S.K. Microbiota in breast milk of chinese lactating mothers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Huang, M.S. Profiles of commensal and opportunistic bacteria in human milk from healthy donors in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzstevens, J.L.; Smith, K.C.; Hagadorn, J.I.; Caimano, M.J.; Matson, A.P.; Brownell, E.A. Systematic review of the human milk microbiota. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Delgado, S.; Maldonado, A.; Rodríguez, J.M. Assessment of the bacterial diversity of breast milk of healthy women by quantitative real-time pcr. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodayar-Pardo, P.; Mira-Pascual, L.; Collado, M.C.; Martínez-Costa, C. Impact of lactation stage, gestational age and mode of delivery on breast milk microbiota. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, L.; Langa, S.; Martín, V.; Jiménez, E.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. The microbiota of human milk in healthy women. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013, 59, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.F.; Boris, S.; Barbes, C. Probiotic properties of human lactobacilli strains to be used in the gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Huo, G.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Duan, C. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in infants during the first six months of life. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Guan, Q.; Ye, C.; Zhang, C.; Foster, J.A.; Forney, L.J. Network analysis suggests a potentially ‘evil’ alliance of opportunistic pathogens inhibited by a cooperative network in human milk bacterial communities. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediano, P.; Fernández, L.; Jiménez, E.; Arroyo, R.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Marín, M. Microbial diversity in milk of women with mastitis: Potential role of coagulase-negative staphylococci, viridans group streptococci, and corynebacteria. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacho, N.T.; Harrison, N.A.; Parker, L.A.; Padgett, K.A.; Lemas, D.J.; Marcial, G.E.; Li, N.; Carr, L.E.; Neu, J.; Lorca, G.L. Personalization of the microbiota of donor human milk with mother’s own milk. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Gonzalez, E.; Solomons, N.; Scott, M.E.; Koski, K. Human breast milk microbiota is influenced by maternal age and bmi, stage of lactation and infant feeding practices. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 965. [Google Scholar]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linløkken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and depression. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, K.M.B.; Krych, L.; Sørensen, D.B.; Pang, W.; Nielsen, D.S.; Josefsen, K.; Hansen, L.H.; Sørensen, S.J.; Hansen, A.K. Gut microbiota composition is correlated to grid floor induced stress and behavior in the balb/c mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46231. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, S.; Liang, Y. Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: A cross-sectional study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, H.-M.; Li, P.; McDonald, D.; Sheng, H.-F.; Chen, M.-X.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ji, G.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-D.-X.; et al. Regional variation limits applications of healthy gut microbiome reference ranges and disease models. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulke, C.A.; Sharpton, T.J. The influence of ethnicity and geography on human gut microbiome composition. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Covariates | Phylum (p-Value) | Class | Order | Family (p-Value) | Genus (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (p-Value) | (p-Value) | ||||
| Study site (Ethnicity) | 0.041 * | 0.0628 | 0.0036 * | 0.004 * | 0.0028 * |
| Mode of delivery | 0.9756 | 0.9492 | 0.8276 | 0.8358 | 0.793 |
| Gestational age | 0.1266 | 0.126 | 0.944 | 0.3424 | 0.3538 |
| Infant gender | 0.7818 | 0.8142 | 0.3084 | 0.9608 | 0.7898 |
| Infant feeding options | 0.1716 | 0.2244 | 0.9502 | 0.2888 | 0.4662 |
| Maternal education | 0.275 | 0.3486 | 0.2202 | 0.189 | 0.1734 |
| Maternal employment | 0.7434 | 0.7192 | 0.2346 | 0.6372 | 0.7988 |
| Maternal BMI | 0.3886 | 0.3806 | 0.6206 | 0.714 | 0.5788 |
| Infant birth weight | 0.836 | 0.933 | 0.6886 | 0.719 | 0.7824 |
| Infant birth length | 0.9876 | 0.971 | 0.9006 | 0.895 | 0.9414 |
| Maternal age | 0.3286 | 0.3986 | 0.8976 | 0.641 | 0.7316 |
| Dwelling type | 0.5846 | 0.4892 | 0.6306 | 0.136 | 0.1158 |
| Marital status | 0.4194 | 0.4406 | 0.1362 | 0.7608 | 0.7778 |
| Household income | 0.6062 | 0.6988 | 0.663 | 0.0922 | 0.0988 |
| Maternal HIV status | 0.7238 | 0.6582 | 0.0836 | 0.9242 | 0.9252 |
| Antibiotics | 0.4178 | 0.4446 | 0.951 | 0.3334 | 0.2128 |
| Household size | 0.559 | 0.4248 | 0.3374 | 0.9198 | 0.8276 |
| Maternal smoking | 0.867 | 0.8698 | 0.837 | 0.7986 | 0.7448 |
| Alcohol score | 0.1216 | 0.0974 | 0.8012 | 0.2018 | 0.8706 |
| IPV-emotional | 0.9198 | 0.9132 | 0.806 | 0.8394 | 0.3256 |
| IPV-physical | 0.2504 | 0.2432 | 0.1708 | 0.6604 | 0.817 |
| IPV-sexual | 0.7438 | 0.8552 | 0.8676 | 0.2556 | 0.8092 |
| PTSD | 0.847 | 0.6846 | 0.724 | 0.3232 | 0.1342 |
| BDI score | 0.127 | 0.876 | 0.2598 | 0.3168 | 0.3246 |
| SRQ | 0.7408 | 0.5376 | 0.2576 | 0.8204 | 0.3012 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojo-Okunola, A.; Claassen-Weitz, S.; Mwaikono, K.S.; Gardner-Lubbe, S.; Stein, D.J.; Zar, H.J.; Nicol, M.P.; du Toit, E. Influence of Socio-Economic and Psychosocial Profiles on the Human Breast Milk Bacteriome of South African Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061390
Ojo-Okunola A, Claassen-Weitz S, Mwaikono KS, Gardner-Lubbe S, Stein DJ, Zar HJ, Nicol MP, du Toit E. Influence of Socio-Economic and Psychosocial Profiles on the Human Breast Milk Bacteriome of South African Women. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061390
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjo-Okunola, Anna, Shantelle Claassen-Weitz, Kilaza S. Mwaikono, Sugnet Gardner-Lubbe, Dan J. Stein, Heather J. Zar, Mark P. Nicol, and Elloise du Toit. 2019. "Influence of Socio-Economic and Psychosocial Profiles on the Human Breast Milk Bacteriome of South African Women" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061390
APA StyleOjo-Okunola, A., Claassen-Weitz, S., Mwaikono, K. S., Gardner-Lubbe, S., Stein, D. J., Zar, H. J., Nicol, M. P., & du Toit, E. (2019). Influence of Socio-Economic and Psychosocial Profiles on the Human Breast Milk Bacteriome of South African Women. Nutrients, 11(6), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061390





