Serum Lutein is related to Relational Memory Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ethical Approval
2.3. Procedure
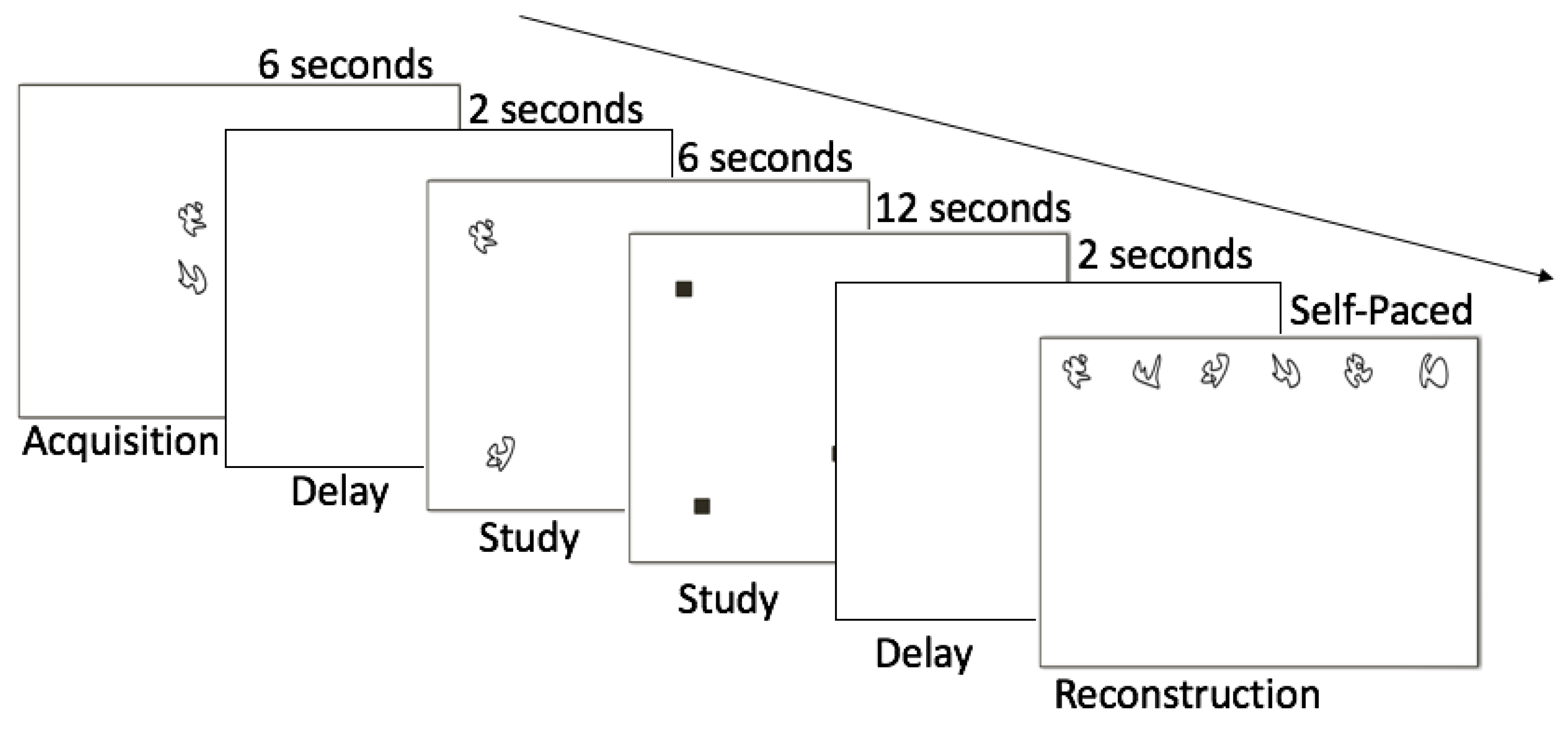
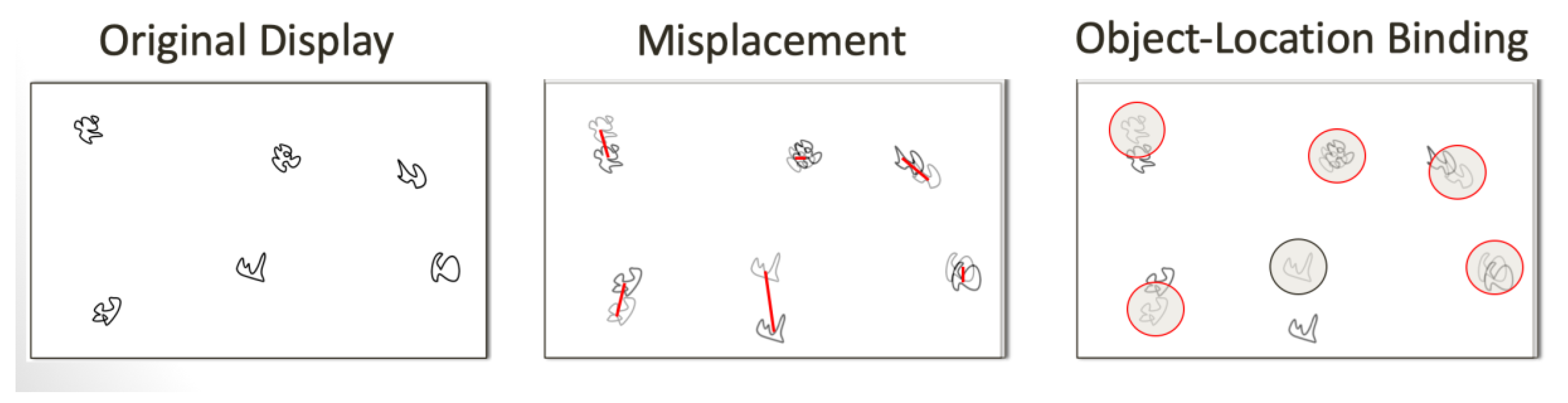
2.4. Relational Memory Assessment
2.5. Intelligence Assessment
2.6. Dietary Assessment
2.7. Serum Carotenoid Assessment
2.8. Retinal Carotenoid Assessment
2.9. Weight Status and Adiposity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity Among Adults and Youth: United States, 2015–2016. NCHS Data Brief 2017, 288, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhalter, T.M.; Hillman, C.H. A Narrative Review of Physical Activity, Nutrition, and Obesity to Cognition and Scholastic Performance across the Human Lifespan. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 201S–206S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Davidson, T.L. Western diet consumption and cognitive impairment: Links to hippocampal dysfunction and obesity. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 103, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Baym, C.L.; Monti, J.M.; Raine, L.B.; Drollette, E.S.; Scudder, M.R.; Moore, R.D.; Kramer, A.F.; Hillman, C.H.; Cohen, N.J. Central adiposity is negatively associated with hippocampal-dependent relational memory among overweight and obese children. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupret, D.; Revest, J.-M.; Koehl, M.; Ichas, F.; De Giorgi, F.; Costet, P.; Abrous, D.N.; Piazza, P.V. Spatial Relational Memory Requires Hippocampal Adult Neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, J.M.; Cooke, G.E.; Watson, P.D.; Voss, M.W.; Kramer, A.F.; Cohen, N.J. Relating Hippocampus to Relational Memory Processing across Domains and Delays. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 27, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassevoort, K.M.; Khazoum, S.E.; Walker, J.A.; Barnett, S.M.; Raine, L.B.; Hammond, B.R.; Renzi-Hammond, L.M.; Kramer, A.F.; Khan, N.A.; Hillman, C.H.; et al. Macular Carotenoids, Aerobic Fitness, and Central Adiposity Are Associated Differentially with Hippocampal-Dependent Relational Memory in Preadolescent Children. J. Pediatr. 2017, 183, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baym, C.L.; Khan, N.A.; Monti, J.M.; Raine, L.B.; Drollette, E.S.; Moore, R.D.; Scudder, M.R.; Kramer, A.F.; Hillman, C.H.; Cohen, N.J. Dietary lipids are differentially associated with hippocampal-dependent relational memory in prepubescent children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.; Akhtar, H.; Zaheer, K.; Ali, R. Dietary Sources of Lutein and Zeaxanthin Carotenoids and Their Role in Eye Health. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwanathan, R.; Kuchan, M.J.; Sen, S.; Johnson, E.J. Lutein and Preterm Infants With Decreased Concentrations of Brain Carotenoids. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.J.; Vishwanathan, R.; Johnson, M.A.; Hausman, D.B.; Davey, A.; Scott, T.M.; Green, R.C.; Miller, L.S.; Gearing, M.; Woodard, J.; et al. Relationship between Serum and Brain Carotenoids, α-Tocopherol, and Retinol Concentrations and Cognitive Performance in the Oldest Old from the Georgia Centenarian Study. J. Aging Res. 2013, 2013, 951786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, J.; Smith, J.; Kuchan, M.; Mohn, E.; Johnson, E.; Rubakhin, S.; Wang, L.; Sweedler, J.; Neuringer, M. Lutein and Brain Function. Foods 2015, 4, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M.; Ajani, U.A.; Sperduto, R.D.; Hiller, R.; Blair, N.; Burton, T.C.; Farber, M.D.; Gragoudas, E.S.; Haller, J.; Miller, D.T.; et al. Dietary Carotenoids, Vitamins A, C, and E, and Advanced Age-Related Macular Degeneration. JAMA 1994, 272, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoshita, M.; Toda, E.; Osada, H.; Narimatsu, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Tsubota, K.; Ozawa, Y. Lutein acts via multiple antioxidant pathways in the photo-stressed retina. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, S.; Nolan, J.; Kavanagh, H.; O’Donovan, O. Macular pigment optical density and its relationship with serum and dietary levels of lutein and zeaxanthin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 430, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwanathan, R.; Neuringer, M.; Snodderly, D.M.; Schalch, W.; Johnson, E.J. Macular lutein and zeaxanthin are related to brain lutein and zeaxanthin in primates. Nutr. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Walk, A.M.; Edwards, C.G.; Jones, A.R.; Cannavale, C.N.; Thompson, S.V.; Reeser, G.E.; Holscher, H.D. Macular xanthophylls are related to intellectual ability among adults with overweight and obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzi, L.M.; Dengler, M.J.; Puente, A.; Miller, L.S.; Hammond, B.R. Relationships between macular pigment optical density and cognitive function in unimpaired and mildly cognitively impaired older adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwanathan, R.; Iannaccone, A.; Scott, T.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Jennings, B.J.; Carboni, G.; Forma, G.; Satterfield, S.; Harris, T.; Johnson, K.C.; et al. Macular pigment optical density is related to cognitive function in older people. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamroziewicz, M.K.; Paul, E.J.; Zwilling, C.E.; Johnson, E.J.; Kuchan, M.J.; Cohen, N.J.; Barbey, A.K. Parahippocampal Cortex Mediates the Relationship between Lutein and Crystallized Intelligence in Healthy, Older Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horecka, K.M.; Dulas, M.R.; Schwarb, H.; Lucas, H.D.; Duff, M.; Cohen, N.J. Reconstructing relational information. Hippocampus 2018, 28, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, R.I.; Chelune, G.J.; Tucker, G.D. Validity of the Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test. Psychol. Assess. 1993, 5, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Kaufman, A.S. Changes in Fluid and Crystallized Intelligence Across the 20- to 90-Year Age Range on the K-Bit. J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 1993, 11, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Neuringer, M.; Kuchan, M.J.; Erdman, J.W. Relationships of carotenoid-related gene expression and serum cholesterol and lipoprotein levels to retina and brain lutein deposition in infant rhesus macaques following 6 months of breastfeeding or formula feeding. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 654, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, B.R.; Hammond, B.R., Jr.; Land, R.I.; Snodderly, D.M. A Practical Method for Measuring Macular Pigment Optical Density. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar]
- Renzi-Hammond, L.; Bovier, E.; Fletcher, L.; Miller, L.; Mewborn, C.; Lindbergh, C.; Baxter, J.; Hammond, B. Effects of a Lutein and Zeaxanthin Intervention on Cognitive Function: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Younger Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaulmann, A.; Bohn, T. Carotenoids, inflammation, and oxidative stress—Implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 907–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandona, P. Inflammation: The link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindbergh, C.A.; Renzi-Hammond, L.M.; Hammond, B.R.; Terry, D.P.; Mewborn, C.M.; Puente, A.N.; Miller, L.S. Lutein and Zeaxanthin Influence Brain Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2018, 24, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.J. Role of lutein and zeaxanthin in visual and cognitive function throughout the lifespan. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran-Celentano, J.; Hammond, B.R.; Ciulla, T.A.; Cooper, D.A.; Pratt, L.M.; Danis, R.B. Relation between dietary intake, serum concentrations, and retinal concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin in adults in a Midwest population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Sex, F/M | 45, 54 |
| Age, years | 34.9 ± 6.1 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 33.3 ± 6.6 |
| Fat, % | 40.2 ± 8.42 |
| Intelligence Quotient | 107 ± 12.1 |
| Macular Pigment Optical Density | 0.438 ± 0.20 |
| Dietary Lutein + Zeaxanthin, mcg/day | 2283 ± 3382 |
| Serum Lutein, µmol/L | 0.129 ± 0.06 |
| Misplacement, pixels | 219.3 ± 77.0 |
| Object-location binding | 2.67 ± 0.83 |
| Misplacement | Object-Location Binding | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.33 ** | −0.25 ** |
| Sex | −0.17 | 0.10 |
| %Fat | 0.19 * | −0.11 |
| IQ | −0.37 ** | 0.32 ** |
| Dietary L + Z | −0.21 * | 0.21 * |
| Dietary Beta-Carotene | −0.24 ** | 0.20 * |
| Dietary Beta-Cryptoxanthin | −0.06 | 0.05 |
| MPOD | −0.110 | 0.083 |
| Serum Lutein | −0.266 ** | 0.223 * |
| Serum Zeaxanthin | −0.027 | 0.002 |
| Serum Beta-Carotene | −0.202 * | 0.137 |
| Serum Cryptoxanthin | −0.103 | 0.076 |
| Step & Variable | β | ΔR2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Age | 0.179 ** | 0.142 ** |
| %Fat | 0.019 | ||
| IQ | −0.363 ** | ||
| Step 2 | Serum Lutein | −0.152 * | 0.207 * |
| Step & Variable | β | ΔR2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Age | 0.290 ** | 0.142 ** |
| IQ | −0.197 * | ||
| Step 2 | Serum Lutein | 0.159 * | 0.166 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cannavale, C.N.; Hassevoort, K.M.; Edwards, C.G.; Thompson, S.V.; Burd, N.A.; Holscher, H.D.; Erdman, J.W., Jr.; Cohen, N.J.; Khan, N.A. Serum Lutein is related to Relational Memory Performance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040768
Cannavale CN, Hassevoort KM, Edwards CG, Thompson SV, Burd NA, Holscher HD, Erdman JW Jr., Cohen NJ, Khan NA. Serum Lutein is related to Relational Memory Performance. Nutrients. 2019; 11(4):768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040768
Chicago/Turabian StyleCannavale, Corinne N., Kelsey M. Hassevoort, Caitlyn G. Edwards, Sharon V. Thompson, Nicholas A. Burd, Hannah D. Holscher, John W. Erdman, Jr., Neal J. Cohen, and Naiman A. Khan. 2019. "Serum Lutein is related to Relational Memory Performance" Nutrients 11, no. 4: 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040768
APA StyleCannavale, C. N., Hassevoort, K. M., Edwards, C. G., Thompson, S. V., Burd, N. A., Holscher, H. D., Erdman, J. W., Jr., Cohen, N. J., & Khan, N. A. (2019). Serum Lutein is related to Relational Memory Performance. Nutrients, 11(4), 768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040768






