Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter?
Abstract
1. Introduction
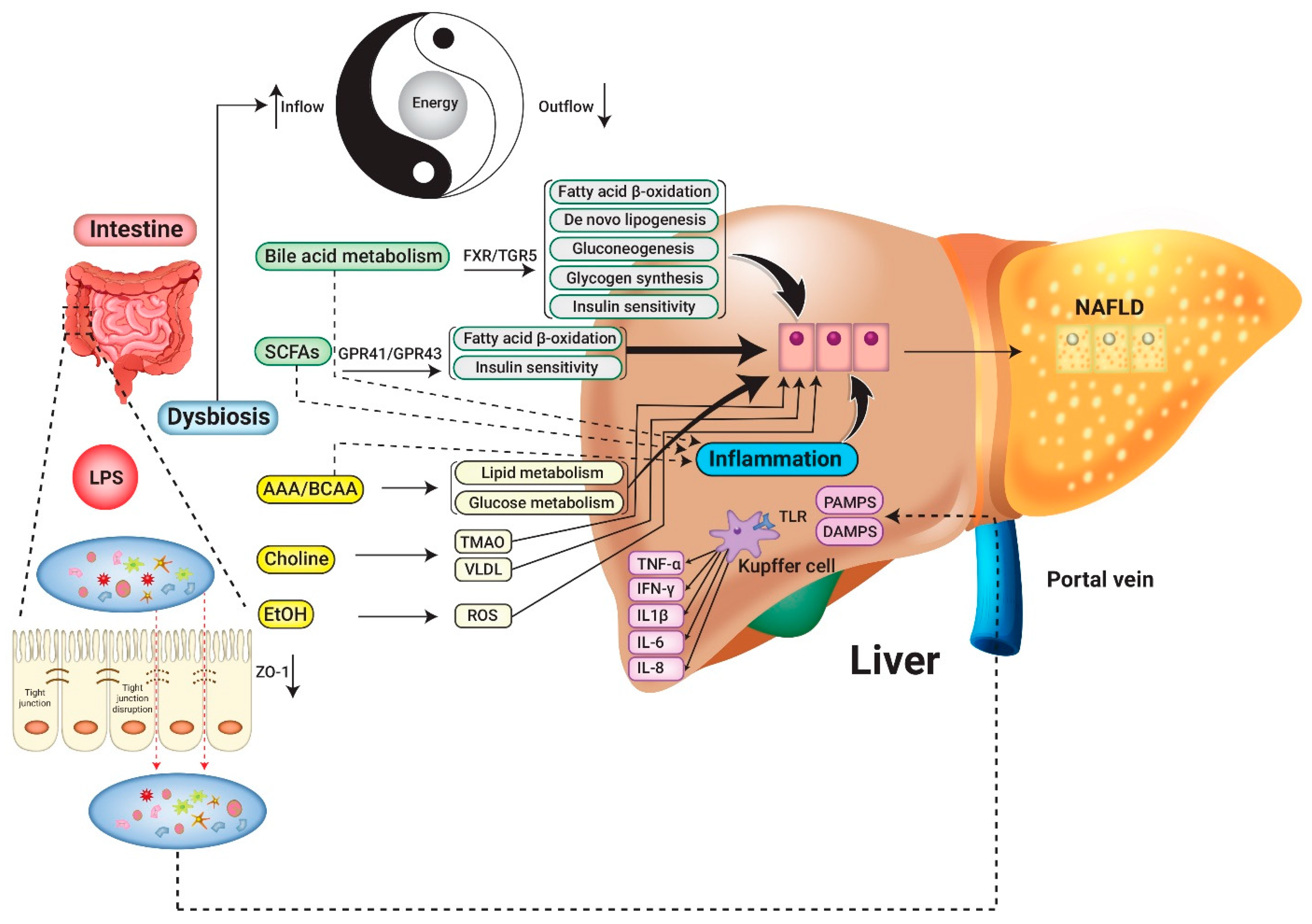
2. Pathogenesis: The Links between NAFLD and Microbiome
2.1. Interplay with Intestinal Microbiota and the Host Immune System
2.2. Crosstalk between Intestinal Microbiota and Metabolite
2.2.1. Bile Acids
2.2.2. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
2.2.3. Aromatic Amino Acid Derivatives and Branched-Chain Amino Acids
2.2.4. Choline
2.2.5. Microbial Synthesis of Ethanol
2.3. Energy Extraction and Consumption Balance Disrupted by GM
3. Clinical Application of Probiotics and Synbiotics in NAFLD/NASH Patients
3.1. Biochemistry Evaluation
3.2. Imaging Modalities to Assess Hepatic Steatosis and Stiffness
3.3. Histologic Evaluation
3.4. Safety and Tolerability of Probiotics in NAFLD Patients
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, G.C.; Wong, V.W.; Chitturi, S. NAFLD in Asia-as common and important as in the West. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, E.; Yatsuji, S.; Tobari, M.; Taniai, M.; Torii, N.; Tokushige, K.; Shiratori, K. Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44 (Suppl. 19), 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Tokushige, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Taniai, M.; Shiratori, K. Hepatic and extrahepatic malignancies in cirrhosis caused by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37 (Suppl. 1), E247–E252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranagua-Vezozzo, D.C.; Ono, S.K.; Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Farias, A.Q.; Cunha-Silva, M.; Franca, J.I.; Alves, V.A.; Sherman, M.; Carrilho, F.J. Epidemiology of HCC in Brazil: Incidence and risk factors in a ten-year cohort. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuji, S.; Hashimoto, E.; Tobari, M.; Taniai, M.; Tokushige, K.; Shiratori, K. Clinical features and outcomes of cirrhosis due to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis compared with cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.P.; Jacobson, I.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Duseja, A.; Eguchi, Y.; Wong, V.W.; Negro, F.; Yilmaz, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is the Fastest Growing Cause of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplant Candidates. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 748–755.e743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangouni, A.A.; Ghavamzadeh, S. A review of synbiotic efficacy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a therapeutic approach. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2917–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.; Oakley, F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Day, C.P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Disease Spectrum. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 451–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Ramos, S.; Lopez-Contreras, B.E.; Canizales-Quinteros, S. Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Metabolic Abnormalities: A Matter of Composition or Functionality? Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Gewirtz, A.T. Microbiota-liver axis in hepatic disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Nunez, G. Regulation of the immune system by the resident intestinal bacteria. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, J.; Mondot, S.; Levenez, F.; Pelletier, E.; Caron, C.; Furet, J.P.; Ugarte, E.; Munoz-Tamayo, R.; Paslier, D.L.; Nalin, R.; et al. Towards the human intestinal microbiota phylogenetic core. Env. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Kashiwagi, K.; Takagi, T.; Andoh, A.; Inoue, R. Intestinal Dysbiosis Secondary to Proton-Pump Inhibitor Use. Digestion 2018, 97, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.M.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Kober, O.I.; Juge, N.; Avershina, E.; Rudi, K.; Narbad, A.; Jenmalm, M.C.; et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Naito, Y.; Takagi, T. Intestinal microbiome as a novel therapeutic target for local and systemic inflammation. Pharmcol. Ther. 2019, 199, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Loomba, R. Insights into the evolving role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Rationale and prospects for therapeutic intervention. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigg, A.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Dymock, R.B.; McCarthy, P.J.; Grose, R.H.; Cummins, A.G. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumour necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2001, 48, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.; Callewaert, C.; Marotz, C.; Hyde, E.R.; Debelius, J.W.; McDonald, D.; Sogin, M.L. The Microbiome and Human Biology. Ann. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2017, 18, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandona, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Youn, G.S.; Shin, M.J.; Suk, K.T. Role of Gut Microbiota in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, Z.Y.; Lal, S.K. The Human Gut Microbiome—A Potential Controller of Wellness and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. The role of microbiota in hepatic encephalopathy. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Masciana, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavekar, A.S.; Raje, D.V.; Manohar, T.; Lavekar, A.A. Role of Probiotics in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-analysis. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2017, 7, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgio, V.; Miele, L.; Principessa, L.; Ferretti, F.; Villa, M.P.; Negro, V.; Grieco, A.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V. Intestinal permeability is increased in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and correlates with liver disease severity. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Inokuchi, S.; Schnabl, B.; Aoyama, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Olefsky, J.M.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of interleukin-1beta in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 323–334.e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Ohnishi, H. Role of gut microbiota and Toll-like receptors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7381–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay-Kumar, M.; Aitken, J.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Cullender, T.C.; Mwangi, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 2010, 328, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Velayudham, A.; Romics, L., Jr.; Mandrekar, P. Modulation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by pattern recognition receptors in mice: The role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 140S–145S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathy, J.; Detloff, S.J.; Ao, M.; Khan, N.; French, S.; Sirajuddin, H.; Nair, T.; Rao, M.C. The Yin and Yang of bile acid action on tight junctions in a model colonic epithelium. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Just, S.; Gau, L.; Mueller, H.; Gerard, P.; Lepage, P.; Clavel, T.; Rohn, S. Rapid analysis of bile acids in different biological matrices using LC-ESI-MS/MS for the investigation of bile acid transformation by mammalian gut bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Talavera, O.; Tailleux, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Bile Acid Control of Metabolism and Inflammation in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1679–1694.e1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, J.P.; Karpen, S.J.; Dawson, P.A.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Bile acids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. Hepatology 2017, 65, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Gioiello, A.; Noriega, L.; Strehle, A.; Oury, J.; Rizzo, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Mataki, C.; Pruzanski, M.; et al. TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pathak, P.; Boehme, S.; Chiang, J.Y. Cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase protects the liver from inflammation and fibrosis by maintaining cholesterol homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Harnish, D.C. Farnesoid X receptor agonist WAY-362450 attenuates liver inflammation and fibrosis in murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, R.H.; Wang, X.X.; Cheng, L.L.; Krisko, T.; Smith, M.; El Kasmi, K.; Pruzanski, M.; Adorini, L.; Golden-Mason, L.; Levi, M.; et al. Bile acid receptor activation modulates hepatic monocyte activity and improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11761–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.S.; Anderson, J.W.; Bridges, S.R. Propionate inhibits hepatocyte lipid synthesis. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1990, 195, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demigne, C.; Morand, C.; Levrat, M.A.; Besson, C.; Moundras, C.; Remesy, C. Effect of propionate on fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis and on acetate metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 74, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Saccomanno, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; De Minicis, S.; Candelaresi, C.; Faraci, G.; Pacetti, D.; Vivarelli, M.; Nicolini, D.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation stimulates hepatic lipid oxidation and restores hepatic signalling alteration induced by a high-fat diet in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonfeld, P.; Wojtczak, L. Short- and medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: The cellular perspective. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, H.; Tsutsui, W.; Fujioka, Y. Are Short Chain Fatty Acids in Gut Microbiota Defensive Players for Inflammation and Atherosclerosis? J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Ohata, A.; Miyoshi, M.; Aoyama, M.; Fueda, Y.; Kotani, J. Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor kappaB activation and tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, U.H.; Lee, S.O.; Sridharan, G.; Lee, K.; Davidson, L.A.; Jayaraman, A.; Chapkin, R.S.; Alaniz, R.; Safe, S. Microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolites and their aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent agonist and antagonist activities. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 85, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Olivares, M.; Rodriguez, J.; de Rocca Serra, A.; Roumain, M.; Bindels, L.B.; Cani, P.D.; Evenepoel, P.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. The gut microbiota metabolite indole alleviates liver inflammation in mice. FASEB J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Ding, Y.; Saedi, N.; Choi, M.; Sridharan, G.V.; Sherr, D.H.; Yarmush, M.L.; Alaniz, R.C.; Jayaraman, A.; Lee, K. Gut Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Modulate Inflammatory Response in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.R.; Duncan, S.H.; Scobbie, L.; Duncan, G.; Cantlay, L.; Calder, A.G.; Anderson, S.E.; Flint, H.J. Major phenylpropanoid-derived metabolites in the human gut can arise from microbial fermentation of protein. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, L.; Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Federici, M.; Serino, M.; Abbott, J.; Charpentier, J.; Heymes, C.; Luque, J.L.; Anthony, E.; Barton, R.H.; et al. Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic steatosis in non-diabetic obese women. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, H.K.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Nielsen, H.B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Nielsen, T.; Jensen, B.A.; Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Prifti, E.; Falony, G.; et al. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 2016, 535, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaie, S.; Ghaffari, P.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sen, P.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; de Wouters, T.; Juste, C.; Rizkalla, S.; Chilloux, J.; et al. Quantifying Diet-Induced Metabolic Changes of the Human Gut Microbiome. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, R.F.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, C.; Tan, X.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Zheng, R.D.; Zhang, H.W.; Ling, W.H.; et al. Associations of gut-flora-dependent metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide, betaine and choline with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duseja, A.; Acharya, S.K.; Mehta, M.; Chhabra, S.; Shalimar; Rana, S.; Das, A.; Dattagupta, S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Chawla, Y.K. High potency multistrain probiotic improves liver histology in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A randomised, double-blind, proof of concept study. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.L.; Dubin, M.D.; Moukarzel, A.A.; Jenden, D.J.; Roch, M.; Rice, K.M.; Gornbein, J.; Ament, M.E. Choline deficiency: A cause of hepatic steatosis during parenteral nutrition that can be reversed with intravenous choline supplementation. Hepatology 1995, 22, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y. Dietary trimethylamine N-oxide exacerbates impaired glucose tolerance in mice fed a high fat diet. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, M.E.; Barton, R.H.; Toye, A.; Cloarec, O.; Blancher, C.; Rothwell, A.; Fearnside, J.; Tatoud, R.; Blanc, V.; Lindon, J.C.; et al. Metabolic profiling reveals a contribution of gut microbiota to fatty liver phenotype in insulin-resistant mice. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12511–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Cope, K.; Risby, T.H.; Diehl, A.M. Obesity and female gender increase breath ethanol concentration: Potential implications for the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynets, V.; Kuper, M.A.; Strahl, S.; Maier, I.B.; Spruss, A.; Wagnerberger, S.; Konigsrainer, A.; Bischoff, S.C.; Bergheim, I. Nutrition, intestinal permeability, and blood ethanol levels are altered in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begriche, K.; Igoudjil, A.; Pessayre, D.; Fromenty, B. Mitochondrial dysfunction in NASH: Causes, consequences and possible means to prevent it. Mitochondrion 2006, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, E.; Masclee, A.; Troost, F.; Dekker, J.; Jonkers, D. Cytotoxicity and metabolic stress induced by acetaldehyde in human intestinal LS174T goblet-like cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G286–G294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeders, E.P.; Nascimento, E.B.; Havekes, B.; Brans, B.; Roumans, K.H.; Tailleux, A.; Schaart, G.; Kouach, M.; Charton, J.; Deprez, B.; et al. The Bile Acid Chenodeoxycholic Acid Increases Human Brown Adipose Tissue Activity. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boets, E.; Deroover, L.; Houben, E.; Vermeulen, K.; Gomand, S.V.; Delcour, J.A.; Verbeke, K. Quantification of in Vivo Colonic Short Chain Fatty Acid Production from Inulin. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8916–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; van der Beek, C.M.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Goossens, G.H.; Holst, J.J.; Olde Damink, S.W.M.; Lenaerts, K.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Blaak, E.E. Colonic infusions of short-chain fatty acid mixtures promote energy metabolism in overweight/obese men: A randomized crossover trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, F.H. The US Food and Drug Administration and probiotics: Regulatory categorization. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46 (Suppl. 2), S133–S136; discussion S144–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olveira, G.; Gonzalez-Molero, I. An update on probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in clinical nutrition. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, C.; Yang, Q. Oral Administration of Compound Probiotics Ameliorates HFD-Induced Gut Microbe Dysbiosis and Chronic Metabolic Inflammation via the G Protein-Coupled Receptor 43 in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rats. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez-Pinto, H.; Borralho, P.; Machado, J.; Lopes, M.T.; Gato, I.V.; Santos, A.M.; Guerreiro, A.S. Microbiota Modulation with Synbiotic Decreases Liver Fibrosis in a High Fat Choline Deficient Diet Mice Model of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 23, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Ni, X.; Yi, D.; Pan, K.; Jing, B. Preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 by attenuating inflammation and mitochondrial injury and improving gut environment in obese mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6817–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudham, A.; Dolganiuc, A.; Ellis, M.; Petrasek, J.; Kodys, K.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. VSL#3 probiotic treatment attenuates fibrosis without changes in steatohepatitis in a diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model in mice. Hepatology 2009, 49, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Watkins, P.A.; Moser, A.B.; Desimone, C.; Song, X.Y.; Diehl, A.M. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Vajro, P.; Mandato, C.; Licenziati, M.R.; Franzese, A.; Vitale, D.F.; Lenta, S.; Caropreso, M.; Vallone, G.; Meli, R. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG in pediatric obesity-related liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Vacante, M.; Antic, T.; Giordano, M.; Chisari, G.; Acquaviva, R.; Mastrojeni, S.; Malaguarnera, G.; Mistretta, A.; Li Volti, G.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavakhi, A.; Minakari, M.; Firouzian, H.; Assali, R.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Ferns, G. Effect of a Probiotic and Metformin on Liver Aminotransferases in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Won, G.L.; Chim, A.M.; Chu, W.C.; Yeung, D.K.; Li, K.C.; Chan, H.L. Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with probiotics. A proof-of-concept study. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisi, A.; Bedogni, G.; Baviera, G.; Giorgio, V.; Porro, E.; Paris, C.; Giammaria, P.; Reali, L.; Anania, F.; Nobili, V. Randomised clinical trial: The beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharm. 2014, 39, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Rafraf, M.; Somi, M.H.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M. Effects of probiotic yogurt consumption on metabolic factors in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7386–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccheli, A.; Capuani, G.; Marini, F.; Tomassini, A.; Pratico, G.; Ceccarelli, S.; Gnani, D.; Baviera, G.; Alisi, A.; Putignani, L.; et al. Urinary (1)H-NMR-based metabolic profiling of children with NAFLD undergoing VSL#3 treatment. Int. J. Obes (Lond) 2015, 39, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, A.; Askari, G.; Esmailzade, A.; Feizi, A.; Mohammadi, V. The Effect of Symbiotic Supplementation on Liver Enzymes, C-reactive Protein and Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferolla, S.M.; Couto, C.A.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.N.; Pereira, C.A.; Martins, F.S.; Ferrari Mde, L.; Vilela, E.G.; Torres, H.O.; Cunha, A.S.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepideh, A.; Karim, P.; Hossein, A.; Leila, R.; Hamdollah, M.; Mohammad, E.G.; Mojtaba, S.; Mohammad, S.; Ghader, G.; Seyed Moayed, A. Effects of Multistrain Probiotic Supplementation on Glycemic and Inflammatory Indices in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll Nutr. 2016, 35, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Monem, S.M. Probiotic Therapy in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Zagazig University Hospitals. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2017, 7, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouz, V.; Jazayeri, S.; Aryaeian, N.; Zahedi, M.J.; Hosseini, F. Effects of Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplementation on Leptin, Adiponectin, and Glycemic Parameters in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Middle East. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 9, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhlasi, G.; Zarrati, M.; Agah, S.; Hosseini, A.F.; Hosseini, S.; Shidfar, S.; Soltani Aarbshahi, S.S.; Razmpoosh, E.; Shidfar, F. Effects of synbiotics and vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure, nitric oxide and inflammatory factors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famouri, F.; Shariat, Z.; Hashemipour, M.; Keikha, M.; Kelishadi, R. Effects of Probiotics on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzhalii, E.; Virchenko, O.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Beregova, T.; Stremmel, W. Treatment efficacy of a probiotic preparation for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot trial. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshimoghaddam, F.; Shateri, K.; Sina, M.; Hashemian, M.; Alizadeh, M. Daily Consumption of Synbiotic Yogurt Decreases Liver Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, L.; Khoshbaten, M.; Safaiyan, A.; Ghavami, M.; Abbasi, M.M.; Gargari, B.P. Pro- and prebiotic effects on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Boccuto, L.; Kononenko, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Komisarenko, I.; Dynnyk, O. Beneficial effects of probiotic combination with omega-3 fatty acids in NAFLD: A randomized clinical study. Minerva Med. 2018, 109, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Kononenko, L.; Boccuto, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Dynnyk, O. A Multi-strain Probiotic Reduces the Fatty Liver Index, Cytokines and Aminotransferase levels in NAFLD Patients: Evidence from a Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2018, 27, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, S.; Neishaboori, H.; Jameshorani, M. Combined effects of synbiotic and sitagliptin versus sitagliptin alone in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Shi, L.P.; Shi, L.; Xu, L. Efficacy of probiotics on the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2018, 57, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.J. Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, B.R.; Hernandez-Saavedra, D.; An, R.; Rector, R.S. Prebiotic and probiotic treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.; Mihali, A.B.; Rawala, M.S.; Aslam, A.; Siddiqui, W.J. The promising role of probiotic and synbiotic therapy in aminotransferase levels and inflammatory markers in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 31, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutnikova, H.; Genser, B.; Monteiro-Sepulveda, M.; Faurie, J.M.; Rizkalla, S.; Schrezenmeir, J.; Clement, K. Impact of bacterial probiotics on obesity, diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease related variables: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e017995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Maraj, B.; Harding-Theobald, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Terrault, N.A. Gut microbiome-targeted therapies in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, R.M.S.; Liau, J.; Kaffas, A.E.; Chammas, M.C.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound Elastography: Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1303–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idilman, I.S.; Aniktar, H.; Idilman, R.; Kabacam, G.; Savas, B.; Elhan, A.; Celik, A.; Bahar, K.; Karcaaltincaba, M. Hepatic steatosis: Quantification by proton density fat fraction with MR imaging versus liver biopsy. Radiology 2013, 267, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.; Ruelaz, A.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.; Suttorp, M.J.; Johnsen, B.; Shanman, R.; Slusser, W.; Fu, N.; et al. Safety of probiotics used to reduce risk and prevent or treat disease. Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. (Full Rep.) 2011, 200, 1–645. [Google Scholar]
- Doron, S.; Snydman, D.R. Risk and safety of probiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60 (Suppl. 2), S129–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Design/Population (N = Included in the Trial) | Bacterial Species | Duration | Main Outcome Related to NAFLD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serology | Imaging or Biopsy | ||||
| Aller et al. [89], 2011 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 28) | Lactobacillus bulgaricus Streptococcus thermophilus | 3 months | (↓) ALT, AST, GGT (-) Anthropometric parameters and cardiovascular risk factors | N/A |
| Vajro et al. [90], 2011 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD obese children (N = 20) | Lactobacillus rhamnosus | 8 weeks | (↓) ALT (-) BMI, TNF-α, peptidoglycanpolysaccharide antibody | N/A |
| Malaguarnera et al. [91], 2012 | RCT/NASH (N = 66) | Bifidobacterium longum + Prebiotics (Fructo-oligosaccharides) | 24 weeks | (↓) AST, LDL-C, CRP, TNF-α, endotoxin, HOMA-IR (-) ALT, bilirubin, HDL-C, TC, TG, glucose, insulin, C-peptide, BMI | The liver biopsy indicated that steatosis and NASH activity improved |
| Shavakhi et al. [92], 2013 | Double-blind RCT/NASH on metformin (N = 64) | Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus | 6 months | (↓) ALT, AST, TG, TC, BMI (-) FBS | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Wong et al. [93], 2013 | RCT/NASH (N = 20) | Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus deslbrueckii Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus rhamnosus Bifidobacterium bifidum | 6 months | (↓) ALT (-) AST, BMI, waist circumference, glucose, and lipid levels | Proton-magnetic resonance spectroscopy-measured that intrahepatic triglyceride content (IHTG) improved |
| Alisi et al. [94], 2014 | Double-blind RCT/NAFJD children (N = 44) | Streptococcus thermophilus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Bifidobacterium infantis Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus plantarum Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus bulgaricus | 4 months | (↓) BMI (↑) GLP-1, activated GLP-1 (-) ALT, triglycerides, HOMA | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Eslamparast et al. [95], 2014 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD with lifestyle modification (N = 52) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus + prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharide) | 28 weeks | (↓) ALT, AST, CRP, TNF-ɑ, NF-κB p65 (-) BMI | Transient elastography- measured fibrosis score improved |
| Nabvi et al. [96], 2014 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 72) | Lactobacillus acidophilus Bifidobacterium lactis | 8 weeks | (↓) ALT, AST, TC, LDL-C (-) Glucose, TG, HDL-C | N/A |
| Miccheli et al. [97], 2015 | Triple-blind RCT/NAFLD children (N = 31) | Streptococcus thermophilus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Bifidobacterium infantis Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus plantarum Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus bulgaricus | 4 months | (↓) AST, total and active GLP-1, BMI (-) ALT, TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, glucose, insulin | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Asgharian et al. [98], 2016 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 80) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus + prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharide) | 8 weeks | Prevent ASL and ALT elevation (-) CRP, BMI | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Ferolla et al. [99], 2016 | RCT/NASH (N = 50) | Lactobacillus reuteri + prebiotic (inulin) | 3 months | (↓) BMI (-) AST, ALT, ALP, GGT, TC, TG, HDL-C, VDL-C, LPS, and intestinal permeability measured by lactulose/mannitol urinary excretion | MRI-PDFF- measured steatosis improved but liver fibrosis had no significant change |
| Sepideh et al. [100], 2016 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 42) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus | 8 weeks | (↓) IL-6, FBS, insulin, insulin resistance (-) TNF-alpha | N/A |
| Abdel et al. [101], 2017 | RCT/NASH with obesity (N = 30) | Lactobacillus acidophilus | 1 month | (↓) ALT, AST (-) TG, TC, FBS Bilirubin, HDL-C | N/A |
| Behrouz et al. [102], 2017 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 89) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus acidophilus Bifidobacterium longum Bifidobacterium breve | 12 weeks | (↓) Leptin, insulin, and HOMA-IR (-) Adiponectin, FBS | N/A |
| Ekhlasi et al. [103], 2017 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD with Vitamin E (N = 60) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Stretococcus thermophilus Bifidobacterium breve Lactobacillus acidophilus Bifidobacterium longum Lactobacillus bulgaricus + prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharide) | 8 weeks | (↓) ALT, AST, ALP, sytolic BP, malondialdehyde, TNF-alpha (-) Diastolic Blood Pressure, nitric oxide, BMI | N/A |
| Famouri et al. [104], 2017 | Triple-Blind RCT/NAFLD obese children (N = 64) | Lactobacillus acidophilus Bifidobacterium lactis Bifidobacterium bifidum Lactobacillus rhamnosus | 12 weeks | (↓) ALT, AST, cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-C, and waist circumference (-) BMI, weight | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Manzhalii et al. [105], 2017 | RCT/NASH with low-fat/low-calorie diet (N = 75) | Lactobacilli Bifidobacteria Streptococcus thermophilus | 12 weeks | (↓) ALT, BMI and cholesterol (-) GGT | Liver stiffness based on US measurement improved |
| Mofidi et al. [106], 2017 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 50) | Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus + prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharide) | 28 weeks | (↓) AST, ALT, GGT, glucose, triglyceride, Total cholesterol, CRP, NF-κB p65 (-) HDL-C, LDL-C, TNF-α | Transient elastography-measured hepatic steatosis and fibrosis improved |
| Bakhshimoghaddam et al. [107], 2018 | RCT/NAFLD (N = 102) | Bifidobacterium animalis + prebiotic (inulin) | 24 weeks | (↓) AST, ALT, GGT, ALP, TG, TC | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement improved |
| Javadi et al. [108], 2018 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 75) | Bifidobacterium longum Lactobacillus acidophilus + prebiotic (inulin) | 3 months | (↓) CRP, TNF-α, BMI (↑) TAC (-) IL-6, MDA | N/A |
| Kobyliak et al. [109], 2018 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD with type II DM (N = 48) | Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Lactococcus Propionibacterium Acetobacter + omega-3 fatty acids | 8 weeks | (↓) GGT, TG, TC, VLDL-C, TNF-α, IL-6 (-) AST, ALT, LDL-C, HDL-C, INF-γ, IL-1β, IL-8 | Shear Wave Elastography-measured fatty liver index improvement but no significant change in liver stiffness |
| Kobyliak et al. [110], 2018 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD with type II DM (N = 58) | Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Lactococcus Propionibacterium Acetobacter | 8 weeks | (↓) AST, GTT, TNF-α, IL-6 (-) ALT, TC, TG, VLDL-C, HDL-C, IL-1β, IL-8, IFN- γ | Shear Wave Elastography-measured fatty liver index improvement but no significant change in liver stiffness |
| Sayari et al. [111], 2018 | RCT/NAFLD with sitagliptin (N = 138) | Lactobacillus casei Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus bulgaricus Bifidobacterium breve Bifidobacterium longum Streptococcus thermophilus + prebiotic (fructo-oligosaccharide) | 16 weeks | (↓) AST, TC, LDL-C, FBS (-) ALT, HDL-C, TG, BMI | N/A |
| Wang et al. [112], 2018 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 200) | Bifidobacterium Lactobacillus Enterococcus Bacillus subtilis | 1 month | (↓) AST, ALT, TC, TG, glucose, VLDL-C, TNF-α (↑) High molecular weight adiponectin (-) HDL-C | Grading of steatosis based on US measurement showed no significant difference |
| Ahn et al. [113], 2019 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD with obesity (N = 68) | Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lactobacillus paracasei Pediococcus pentosaceus Bifidobacterium lactis Bifidobacterium breve | 12 weeks | (↓) TG (-) AST, ALT, TC, HDL-C, glucose, insulin, TNF-α, IL-6, LPS | MRI-PDFF-measured intrahepatic fat fraction (IHF) and mean IHF reduced compared with control, but no significant change in liver stiffness |
| Duseja et al. [69], 2019 | Double-blind RCT/NAFLD (N = 30) | Lactobacillus paracasei Lactobacillus plantarum Lactobacillus acidophilus Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus Bifidobacterium longum Bifidobacterium infantis Bifidobacterium breve Streptococcus thermophilus | 1 year | (↓) ALT, ALP, leptin, TNF-α, and LPS (-) AST, Bilirubin, Adiponectin, IL-1β, IL-6 | The biopsy indicated hepatocyte ballooning, NAS score and fibrosis improved, but not steatosis or lobular inflammation |
| Study | Population | Study Period | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loman et al. [114], 2018 | Included 25 studies (most are RCT): Among them, 9 studies used prebiotics, 11 studies used probiotics, and 7 studies used synbiotics. 1309 patients were included. | Up to December 14, 2017 | Microbial therapies significantly reduced AST and ALT, but not CRP. The results of serum cholesterol and LDL-C are mixed among prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics. |
| Khan et al. [115], 2019 | Included 12 probiotics/synbiotics RCTs for NAFLD. 748 patients were included. | Up to June 10, 2018 | Probiotics/synbiotics were associated with a significant improvement in ALT, AST, and liver fibrosis score graded by fibroscan. There was a reduction in CRP with synbiotics. The TNF-α, LDL-C, TG, and TC significantly improved with synbiotics but not with probiotics in a subgroup analysis. There were no significant changes in HDL-C, HOMA-IR, or FBS in either group. |
| Koutnikova et al. [116], 2019 | Included 105 articles with 111 RCTs representing 6826 subjects (includes metabolic syndrome, type II DM, and NAFLD patients). Among them, about 658 patients had NAFLD. | January 1990 to June 2018 | In subjects with fatty liver diseases, probiotics reduced AST and ALT, but not GGT. |
| Liu et al. [117], 2019 | Included 15 probiotics and synbiotic RCTs, involving 782 patients with NAFLD. | Up to April 2018 | Probiotics and synbiotics supplementation could significantly improve AST, ALT, TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance, TNF-α, liver steatosis, and liver stiffness. However, probiotics and synbiotics could not ameliorate BMI, waist circumference, or FBS. |
| Sharpton et al. [118], 2019 | Included 21 RCTs (1252 participants) with NAFLD. 9 trials evaluated probiotics and 12 trials evaluated synbiotics. | January 1, 2005 to December 1, 2018 | Probiotics/synbiotics could improve AST and ALT. Probiotics/synbiotics were also associated with hepatic steatosis improvement when graded with ultrasound. Last, probiotics/synbiotics were associated with liver stiffness improvement when measured by elastography, although analyses showed heterogeneity. Probiotics, but not synbiotics, were associated with a significant reduction in body mass index. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, C.; Halegoua-DeMarzio, D. Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112837
Xie C, Halegoua-DeMarzio D. Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter? Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112837
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Chencheng, and Dina Halegoua-DeMarzio. 2019. "Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter?" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112837
APA StyleXie, C., & Halegoua-DeMarzio, D. (2019). Role of Probiotics in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Does Gut Microbiota Matter? Nutrients, 11(11), 2837. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112837




