Obesity in the Liver Transplant Setting
Abstract
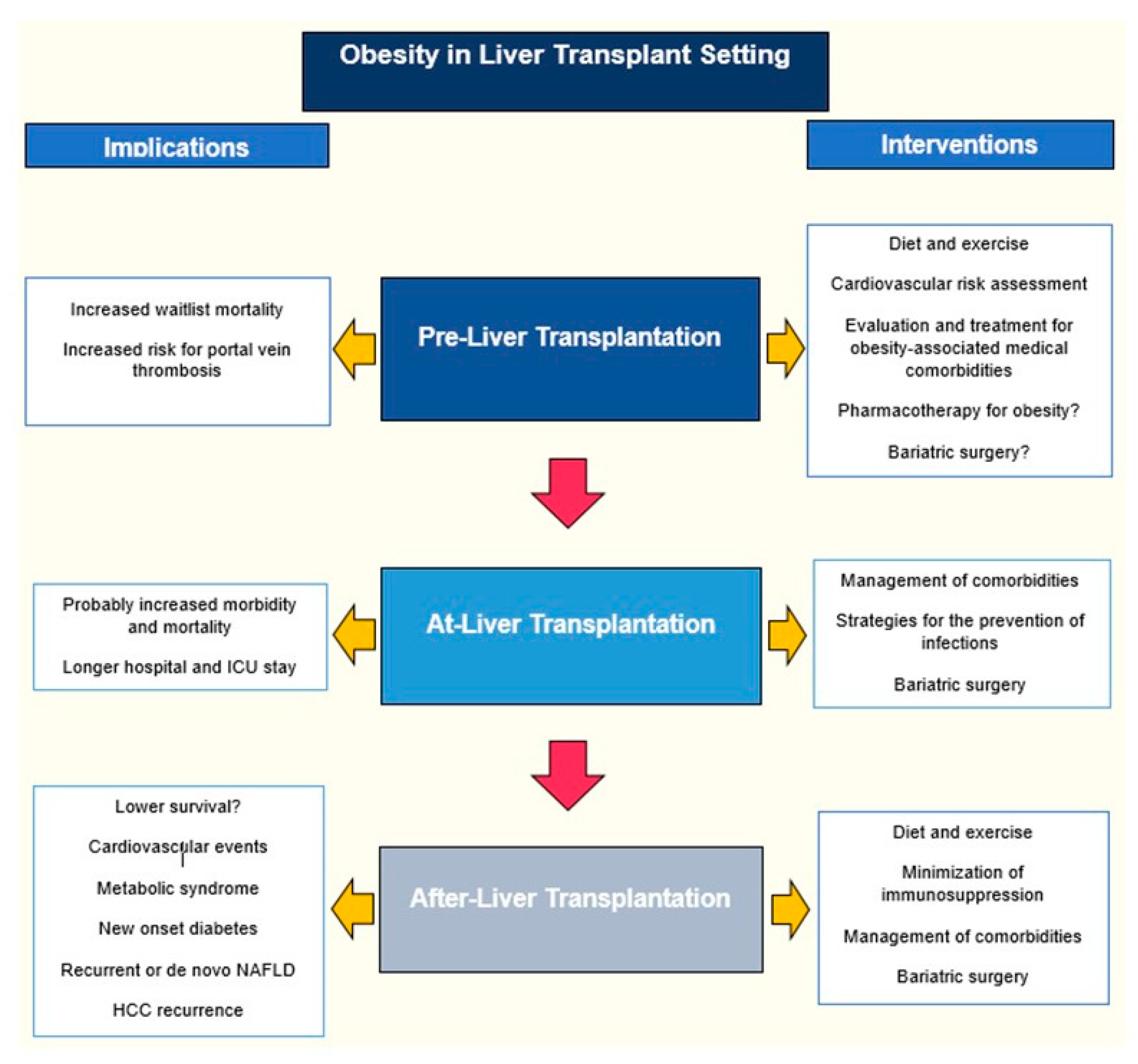
:1. Introduction
2. Obesity Before Liver Transplantation
2.1. How Should Obesity be Defined in Patients with Cirrhosis Considered for LT?
- -
- BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (Asian population: ≥25 kg/m2);
- -
- Percentage of fat mass ≥28% in men and ≥40% in women;
- -
- Waist circumference ˃102 cm in men and ˃88 cm in women (Asian population: A waist circumference ˃90 cm in men and ˃80 cm in women);
- -
- Visceral fat area ≥100 cm2 on abdominal computed tomography.
2.2. Should Morbidly Obese Patients be Listed for LT?
2.3. How does Obesity Impact LT Assessment?
2.4. How does Obesity Impact Patients while on the Waiting List?
2.5. How should Overweight/Obesity be Managed in Patients Listed for LT?
2.5.1. Diet and Exercise
2.5.2. Pharmacologic Treatment
2.5.3. Bariatric Surgery in the Pre-LT Setting
2.5.4. Use of Intragastric Balloons for Obesity Management
2.6. Obesity-Related Comorbidities in the Pre-LT Setting
3. Obesity at the Time of Liver Transplantation
3.1. Are Obese Patients at Increased Risk of Peri-Operative Morbidity and Mortality?
3.2. Bariatric Surgery at the Time of LT
3.3. Obesity and Organ Allocation
4. Obesity After Liver Transplantation
4.1. What is the Impact of Pre-LT BMI on Post-LT Patient and Graft Survival?
4.2. What is the Impact of Pre-LT BMI on Other Post-LT Outcomes?
4.3. How should Obesity be Treated after LT?
4.4. How should Immunosuppression be Managed in the Obese Recipient?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LT | Liver transplant |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| ELTR | European Liver Transplant Registry |
| OPTN | Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network |
| SRTR | Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| LDLT | Living donor liver transplant |
| GWRW | Graft weight/recipient weight |
| MELDa | Model for End-Stage Liver Disease |
| HVPG | Hepatic venous pressure gradient |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| BS | Bariatric surgery |
| RYGB | Roux-en-Y gastric bypass |
| LAGB | Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding |
| SG | Sleeve gastrectomy |
| CSPH | Clinically significant portal hypertension |
| MMF | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| PKs | Pharmacokinetics |
References
- Dick, A.A.; Spitzer, A.L.; Seifert, C.F.; Deckert, A.; Carithers, R.L., Jr.; Reyes, J.D.; Perkins, J.D. Liver transplantation at the extremes of the body mass index. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, R.; Bugianesi, E. Should we undertake surveillance for HCC in patients with NAFLD? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Larson, J.J.; Watt, K.D.; Allen, A.M.; Wiesner, R.H.; Gores, G.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.A.; Leise, M.D. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is the Most Common Indication for Liver Transplantation and Placement on the Waitlist in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, W.J.; Wang, J.; Steuer, J.; Tapper, E.B.; Konerman, M.; Singal, A.G.; Hutton, D.W.; Byon, E.; Lavieri, M.S. Projected increase in obesity and non-alcoholic-steatohepatitis-related liver transplantation waitlist additions in the United States. Hepatology 2019, 70, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, D.; Kern, B.; Hodson, J.; Armstrong, M.J.; Adam, R.; Berlakovich, G.; Fritz, J.; Feurstein, B.; Popp, W.; Karam, V.; et al. Outcomes of liver transplantation for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A European Liver Transplant Registry study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.R.; Lake, J.R.; Smith, J.M.; Schladt, D.P.; Skeans, M.A.; Noreen, S.M.; Robinson, A.M.; Miller, E.; Snyder, J.J.; Israni, A.K.; et al. OPTN/SRTR 2017 Annual Data Report: Liver. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19 (Suppl. 2), 184–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eslamparast, T.; Montano-Loza, A.J.; Raman, M.; Tandon, P. Sarcopenic obesity in cirrhosis-The confluence of 2 prognostic titans. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Garcia-Juarez, I.; Soto-Solis, R.; Hernandez-Cortes, J.; Torre, A. Nutritional assessment and treatment of patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Baracos, V.E.; Bain, V.G.; Sawyer, M.B. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 166–173.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Heimbach, J.K.; Malinchoc, M.; Watt, K.; Charlton, M. The impact of obesity on long-term outcomes in liver transplant recipients-results of the NIDDK liver transplant database. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Tandon, P.; Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Ghosh, S.; Baracos, V.E.; Mazurak, V.C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Low subcutaneous adiposity associates with higher mortality in female patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terjimanian, M.N.; Harbaugh, C.M.; Hussain, A.; Olugbade, K.O., Jr.; Waits, S.A.; Wang, S.C.; Sonnenday, C.J.; Englesbe, M.J. Abdominal adiposity, body composition and survival after liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 30, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, N.; Iwasa, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Mifuji-Moroka, R.; Yoshikawa, K.; Terasaka, E.; Hattori, A.; Ishidome, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity Are Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients with Cirrhosis. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Angulo, P.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Ma, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, N.; Kaido, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Okumura, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Shirai, H.; Yao, S.; Yagi, S.; Uemoto, S. Impact of sarcopenic obesity on outcomes in patients undergoing living donor liver transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vater, Y.; Dembo, G.; Martay, K.; Vitin, A.; Amar, E.; Weinbroum, A.A. Ascites characterizes perioperative clinical indices better than preoperative body mass index. A study in orthotopic liver transplant candidates. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 910–919. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Renner, E.L.; Selzner, N.; Therapondos, G.; Lilly, L.B. The impact of obesity as determined by modified body mass index on long-term outcome after liver transplantation: Canadian single-center experience. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halegoua-De Marzio, D.L.; Wong, S.Y.; Fenkel, J.M.; Doria, C.; Sass, D.A. Listing Practices for Morbidly Obese Patients at Liver Transplantation Centers in the United States. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 14, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.F.; Carithers, R.L., Jr.; AASLD. AASLD practice guidelines: Evaluation of the patient for liver transplantation. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1407–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlansky, B.; Naugler, W.E.; Orloff, S.L.; Enestvedt, C.K. Higher Mortality and Survival Benefit in Obese Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2016, 100, 2648–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 433–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsochatzis, E.; Coilly, A.; Nadalin, S.; Levistky, J.; Tokat, Y.; Ghobrial, M.; Klinck, J.; Berenguer, M. International Liver Transplantation Consensus Statement on End-stage Liver Disease Due to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagai, S.; Collins, K.; Chau, L.C.; Safwan, M.; Rizzari, M.; Yoshida, A.; Abouljoud, M.S.; Moonka, D. Increased Risk of Death in First Year After Liver Transplantation Among Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis vs Liver Disease of Other Etiologies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, K.D. Reducing the load: The evolution and management of obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis before liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2012, 18 (Suppl. 2), S52–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konerman, M.A.; Fritze, D.; Weinberg, R.L.; Sonnenday, C.J.; Sharma, P. Incidence of and Risk Assessment for Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes After Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentine, K.L.; Costa, S.P.; Weir, M.R.; Robb, J.F.; Fleisher, L.A.; Kasiske, B.L.; Carithers, R.L.; Ragosta, M.; Bolton, K.; Auerbach, A.D.; et al. Cardiac disease evaluation and management among kidney and liver transplantation candidates: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology Foundation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 434–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, Y.; Guler, N.; Dayangac, M.; Taskesen, F.; Yaprak, O.; Emek, E.; Akyildiz, M.; Altaca, G.; Yuzer, Y.; Tokat, Y. Living donor liver transplantation for obese patients: Challenges and outcomes. Liver Transpl. 2014, 20, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Abraldes, J.G. Impact of obesity and insulin-resistance on cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 36, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Albillos, A.; Villanueva, C.; Genesca, J.; Ardevol, A.; Augustin, S.; Calleja, J.L.; Banares, R.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Mesonero, F.; et al. Effects of an intensive lifestyle intervention program on portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis and obesity: The SportDiet study. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1293–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berzigotti, A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J.; Grace, N.D.; Burroughs, A.K.; Morillas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Patch, D.; Matloff, D.S.; et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for clinical decompensation in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelletier, S.J.; Schaubel, D.E.; Wei, G.; Englesbe, M.J.; Punch, J.D.; Wolfe, R.A.; Port, F.K.; Merion, R.M. Effect of body mass index on the survival benefit of liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 1678–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everhart, J.E.; Lok, A.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Morgan, T.R.; Lindsay, K.L.; Chung, R.T.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Ghany, M.G.; Group, H.-C.T. Weight-related effects on disease progression in the hepatitis C antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis trial. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segev, D.L.; Thompson, R.E.; Locke, J.E.; Simpkins, C.E.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Montgomery, R.A.; Maley, W.R. Prolonged waiting times for liver transplantation in obese patients. Ann. Surg. 2008, 248, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardashian, A.A.; Dodge, J.L.; Roberts, J.; Brandman, D. Weighing the risks: Morbid obesity and diabetes are associated with increased risk of death on the liver transplant waiting list. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, R.; Grande, S.; Bustelos, R.; Ribera, C.; Garcia-Sesma, A.; Jimenez, C.; Moreno, E.; Martinez-Lopez, J. Obesity is an independent risk factor for pre-transplant portal vein thrombosis in liver recipients. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagozian, R.; Bhardwaj, G.; Wakefield, D.B.; Baffy, G. Obesity paradox in advanced liver disease: Obesity is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Choudhary, N.S. Treating morbid obesity in cirrhosis: A quest of holy grail. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2819–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Valdes, D.; Watt, K.D.; Kellogg, T.A.; Poterucha, J.J.; Di Cecco, S.R.; Francisco-Ziller, N.M.; Taner, T.; Rosen, C.B.; Heimbach, J.K. Long-term outcomes of patients undergoing simultaneous liver transplantation and sleeve gastrectomy. Hepatology 2018, 68, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Watt, K.D.; Poterucha, J.J.; Ziller, N.F.; Cecco, S.D.; Charlton, M.R.; Hay, J.E.; Wiesner, R.H.; Sanchez, W.; Rosen, C.B.; et al. Combined liver transplantation and gastric sleeve resection for patients with medically complicated obesity and end-stage liver disease. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, P.; Bemeur, C.; Butterworth, R.; Cordoba, J.; Kato, A.; Montagnese, S.; Uribe, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Morgan, M.Y. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus. Hepatology 2013, 58, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, E.K. The Author’s Reply: Very low-calorie diet, the morbidly obese with liver cirrhosis and bariatric surgery. Transplantation 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, E.K.; O’Leary, J.G.; Te, H.S.; Rogal, S.; Pillai, A.A.; Al-Osaimi, A.; Desai, A.; Fleming, J.N.; Ganger, D.; Seetharam, A.; et al. Liver Transplantation in the Obese Cirrhotic Patient. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmerman, J.C.; Friedman, A.N. Very low calorie ketogenic weight reduction diet in patients with cirrhosis: A case series. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; Zamora, J.; Martinez, J.; Arroyo, D.; Ahmad, I.; De-la-Pena, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Lo, G.H.; Sarin, S.; Sharma, B.; et al. Stratifying risk in the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage: Results of an individual patient meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bandi, J.C.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Escorsell, A.; Francois, E.; Moitinho, E.; Rodes, J.; Bosch, J. Effects of propranolol on the hepatic hemodynamic response to physical exercise in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998, 28, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Rodriguez, R.U.; Ilarraza-Lomeli, H.; Ruiz-Margain, A.; Ponce-de-Leon-Rosales, S.; Vargas-Vorackova, F.; Garcia-Flores, O.; Torre, A.; Duarte-Rojo, A. Changes in Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Induced by Physical Exercise in Cirrhosis: Results of a Pilot Randomized Open Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Momoki, C.; Yuikawa, M.; Okada, G.; Hamakawa, E.; Kawamura, E.; Hagihara, A.; Toyama, M.; Fujii, H.; et al. Physical inactivity and insufficient dietary intake are associated with the frequency of sarcopenia in patients with compensated viral liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenith, L.; Meena, N.; Ramadi, A.; Yavari, M.; Harvey, A.; Carbonneau, M.; Ma, M.; Abraldes, J.G.; Paterson, I.; Haykowsky, M.J.; et al. Eight weeks of exercise training increases aerobic capacity and muscle mass and reduces fatigue in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1920–1926.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, E.; Torrades, M.T.; Nadal, M.J.; Cardenas, G.; Nieto, J.C.; Vidal, S.; Bascunana, H.; Juarez, C.; Guarner, C.; Cordoba, J.; et al. Randomized pilot study: Effects of an exercise programme and leucine supplementation in patients with cirrhosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Saran, U.; Dufour, J.F. Physical activity and liver diseases. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Landaverde, C.; Wells, J.T.; Poordad, F. Lorcaserin Use in the Management of Morbid Obesity in a Pre-Liver Transplant Patient. Hepatology 2016, 64, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, T.S.; Rice, T.C.; Heimbach, J.K.; Schauer, D.P. Liver Transplantation and Bariatric Surgery: Timing and Outcomes. Liver Transpl. 2018, 24, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebibo, L.; Gerin, O.; Verhaeghe, P.; Dhahri, A.; Cosse, C.; Regimbeau, J.M. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in patients with NASH-related cirrhosis: A case-matched study. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2014, 10, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallal, R.M.; Mattar, S.G.; Lord, J.L.; Watson, A.R.; Cottam, D.R.; Eid, G.M.; Hamad, G.; Rabinovitz, M.; Schauer, P.R. Results of laparoscopic gastric bypass in patients with cirrhosis. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodford, R.M.; Burton, P.R.; O’Brien, P.E.; Laurie, C.; Brown, W.A. Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding In Patients with Unexpected Cirrhosis: Safety and Outcomes. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1858–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosko, J.D.; Nguyen, G.C. Increased perioperative mortality following bariatric surgery among patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, A.; Iannelli, A.; Schneck, A.S.; Nelson, A.C.; Katsahian, S.; Gugenheim, J.; Azoulay, D. Bariatric surgery and liver transplantation: A systematic review a new frontier for bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Terrault, N.A.; Posselt, A.M. Outcomes of Sleeve Gastrectomy in Obese Liver Transplant Candidates. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sesma, A.; Calvo, J.; Manrique, A.; Cambra, F.; Justo, I.; Caso, O.; Marcacuzco, A.; Loinaz, C.; Jimenez, C. Morbidly Obese Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation-Sleeve Gastrectomy: Safety and Efficacy From a Liver Transplant Unit Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Phuong, V.; Maia, M.; Kroh, M.; Chand, B.; Schauer, P.R.; Brethauer, S.A. Bariatric surgery in patients with liver cirrhosis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, L.; Swain, J.; Dierkhising, R.; Kendrick, M.L.; Kamath, P.S.; Watt, K.D. Bariatric surgery in patients with cirrhosis with and without portal hypertension: A single-center experience. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voican, C.S.; Lebrun, A.; Maitre, S.; Lainas, P.; Lamouri, K.; Njike-Nakseu, M.; Gaillard, M.; Tranchart, H.; Balian, A.; Dagher, I.; et al. Predictive score of sarcopenia occurrence one year after bariatric surgery in severely obese patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, R.; Hasse, J.; Wu, T.; Khan, F.; Saracino, G.; McKenna, G.; Testa, G.; Trotter, J.; Klintmalm, G.; Asrani, S.K. Impact of Prior Bariatric Surgery on Perioperative Liver Transplant Outcomes. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Addeo, P.; Cesaretti, M.; Anty, R.; Iannelli, A. Liver transplantation for bariatric surgery-related liver failure: A systematic review of a rare condition. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Albuquerque, L.A.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Wahle, R.C.; de Oliveira Souza, E.; Mancero, J.M.; de Oliveira e Silva, A. Liver transplantation for subacute hepatocellular failure due to massive steatohepatitis after bariatric surgery. Liver Transpl. 2008, 14, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, D.; Dutson, E.; Saab, S. Liver Transplantation and Bariatric Surgery: Best Approach. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, J.M.; Devaud, N.; Jarufe, N.P.; Boza, C.; Perez, G.; Torres, J.; Perez-Ayuso, R.M.; Arrese, M.; Martinez, J. Sleeve gastrectomy as treatment for severe obesity after orthotopic liver transplantation. Obes. Surg. 2007, 17, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.S.; Puri, R.; Saraf, N.; Saigal, S.; Kumar, N.; Rai, R.; Rastogi, A.; Goja, S.; Bhangui, P.; Ramchandra, S.K.; et al. Intragastric balloon as a novel modality for weight loss in patients with cirrhosis and morbid obesity awaiting liver transplantation. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 35, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.S.; Saigal, S.; Saraf, N.; Puri, R.; Soin, A. Innovative approach using an intragastric balloon for weight loss in a morbidly obese patient undergoing liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Cohen, D.B.; Cohen, M.P.; Tan, H.; Maley, W.; Thuluvath, P.J. Postoperative morbidity, mortality, costs, and long-term survival in severely obese patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakeem, A.R.; Cockbain, A.J.; Raza, S.S.; Pollard, S.G.; Toogood, G.J.; Attia, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Hidalgo, E.L.; Prasad, K.R.; Menon, K.V. Increased morbidity in overweight and obese liver transplant recipients: A single-center experience of 1325 patients from the United Kingdom. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMattina, J.C.; Foley, D.P.; Fernandez, L.A.; Pirsch, J.D.; Musat, A.I.; D’Alessandro, A.M.; Mezrich, J.D. Complications associated with liver transplantation in the obese recipient. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, A.; Wilson, G.C.; Wima, K.; Quillin, R.C.; Cuffy, M.; Anwar, N.; Kaiser, T.E.; Paterno, F.; Diwan, T.S.; Woodle, E.S.; et al. Impact of recipient morbid obesity on outcomes after liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, D.F.; Yoshida, E.M.; Buczkowski, A.K.; Chung, S.W.; Steinbrecher, U.P.; Erb, S.E.; Scudamore, C.H. Surgical morbidity in severely obese liver transplant recipients—A single Canadian Centre Experience. Ann. Hepatol. 2009, 8, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.G.; Pelletier, S.J.; Pruett, T.L. Increased early morbidity and mortality with acceptable long-term function in severely obese patients undergoing liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 1999, 13, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Vanatta, J.M.; Arteh, J.; Eason, J.D. Effects of obesity, diabetes, and prior abdominal surgery on resource utilization in liver transplantation: A single-center study. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, J. Pretransplant obesity: A weighty issue affecting transplant candidacy and outcomes. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2007, 22, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrero, B.; Ramirez, P.; Espinosa, F.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Rios, A.; Robles, R.; Sanchez-Bueno, F.; Cascales, P.; Lujan, J.; Parrilla, P. Risk of Respiratory Complications in Obese Liver Transplant Patients: A Study of 343 Patients. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 2385–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneck, M.; Afonso, R.C.; Coelho, G.R.; Sboarini, C.; Coelho, M.P.; Thome, T.; Lisboa, L.F.; Ferraz Neto, B.H. Obese and nonobese recipients had similar need for ventilatory support after liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunfeld, M.Y.; Chan, S.; Pregler, J.; Neelakanta, G.; Sopher, M.J.; Busuttil, R.W.; Csete, M. Liver transplantation in the morbidly obese. J. Clin. Anesth. 1996, 8, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.W.; Choi, G.S.; Kim, J.M.; Kwon, C.H.D.; Joh, J. Comparison of Posttransplant Outcomes in Living Donor Liver Transplantation for Obese and Nonobese Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 2679–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Goyal, N.; Nayeem, M.; Pareek, S.; Gupta, S. Living donor liver transplantation in patients weighing >/=100 kg: Low graft weight and obesity do not impact outcomes. Liver Transpl. 2017, 23, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare, A.J.; Plank, L.D.; Phillips, A.R.; Gane, E.J.; Harrison, B.; Orr, D.; Jiang, Y.; Bartlett, A.S. Additive effect of pretransplant obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors on outcomes after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014, 20, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.A.; Arauz, O.; Angus, P.W.; Sinclair, M.; MacDonald, G.A.; Chelvaratnam, U.; Wigg, A.J.; Yeap, S.; Shackel, N.; Lin, L.; et al. Additive impact of pre-liver transplant metabolic factors on survival post-liver transplant. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, J.R.; Latchana, N.; Michaels, A.; Hanje, A.J.; Hinton, A.; Elkhammas, E.A.; Black, S.M.; Mumtaz, K. Diagnosis of morbid obesity may not impact healthcare utilization for orthotopic liver transplantation: A propensity matched study. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Viggiani, M.T.; Losurdo, G.; Principi, M.; Leandro, G.; Di Leo, A. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Post-operative complications and mortality risk in liver transplant candidates with obesity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Nieto, R.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Davidson, B.R. Recipient body mass index and infectious complications following liver transplantation. HPB (Oxford) 2019, 21, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, E.S.; Mayorga, M.E.; Wheeler, S.B.; Townsley, R.M.; Toro-Diaz, H.H.; Hayashi, P.H.; Barritt, A.S., IV. Declining liver graft quality threatens the future of liver transplantation in the United States. Liver Transpl. 2015, 21, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapero-Marugan, M.; Little, E.C.; Berenguer, M. Stretching the boundaries for liver transplant in the 21st century. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Gulfo, J.; Romero Gomez, M.; Jimenez-Castro, M.B.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Peralta, C. Use of Steatotic Grafts in Liver Transplantation: Current Status. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segev, D.L.; Kucirka, L.M.; Nguyen, G.C.; Cameron, A.M.; Locke, J.E.; Simpkins, C.E.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Montgomery, R.A.; Maley, W.R. Effect modification in liver allografts with prolonged cold ischemic time. Am. J. Transplant. 2008, 8, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ata, N.; Ayloo, S.; Tsung, A.; Molinari, M. Recipient obesity does not affect survival after deceased donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. A national retrospective cohort study in the United States. HPB (Oxford) 2019, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Verma, S.; Thuluvath, P.J. Obesity and its effect on survival in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation in the United States. Hepatology 2002, 35, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuluvath, P.J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Thompson, R.E. A model to predict survival at one month, one year, and five years after liver transplantation based on pretransplant clinical characteristics. Liver Transpl. 2003, 9, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conzen, K.D.; Vachharajani, N.; Collins, K.M.; Anderson, C.D.; Lin, Y.; Wellen, J.R.; Shenoy, S.; Lowell, J.A.; Doyle, M.B.; Chapman, W.C. Morbid obesity in liver transplant recipients adversely affects longterm graft and patient survival in a single-institution analysis. HPB (Oxford) 2015, 17, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambha, K.M.; Dodge, J.L.; Gralla, J.; Sprague, D.; Biggins, S.W. Low, rather than high, body mass index confers increased risk for post-liver transplant death and graft loss: Risk modulated by model for end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2015, 21, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, L.A.; Majno, P.E.; Berney, T.; Morel, P.; Mentha, G.; Toso, C. The impact of wait list body mass index changes on the outcome after liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Cheung, R.; Perumpail, R.B.; Holt, E.W.; Ahmed, A. Diabetes mellitus, and not obesity, is associated with lower survival following liver transplantation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, K.D.; Pedersen, R.A.; Kremers, W.K.; Heimbach, J.K.; Charlton, M.R. Evolution of causes and risk factors for mortality post-liver transplant: Results of the NIDDK long-term follow-up study. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Protto, S.E.; Quintini, C.; Reynolds, L.F.; You, J.; Cywinski, J.B.; Sessler, D.I.; Miller, C. Comparable graft and patient survival in lean and obese liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustgi, V.K.; Marino, G.; Rustgi, S.; Halpern, M.T.; Johnson, L.B.; Tolleris, C.; Taddei, T.H. Impact of body mass index on graft failure and overall survival following liver transplant. Clin. Transplant. 2004, 18, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.M.; deVera, M.E.; Fontes, P.; Shaikh, O.; Ahmad, J. Outcome after liver transplantation for NASH cirrhosis. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, S.; Lalezari, D.; Pruthi, P.; Alper, T.; Tong, M.J. The impact of obesity on patient survival in liver transplant recipients: A meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, S.; Drent, G.; Ruppar, T.; Nikolic, N.; De Geest, S. Body weight parameters are related to morbidity and mortality after liver transplantation—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transplantation 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuluvath, P.J. Morbid obesity with one or more other serious comorbidities should be a contraindication for liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, K.D. Obesity evolution or revolution: There is more to it than meets the BMI. Liver Transpl. 2014, 20, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, T. Obesity and the liver transplant recipient. Liver Transpl. 2002, 8, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, G.; Marchesini, G.; Marzocchi, R.; Pinna, A.D.; Zoli, M. Metabolic syndrome in liver transplantation: Relation to etiology and immunosuppression. Liver Transpl. 2008, 14, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussner, L.A.; Heimbach, J.K.; Fan, C.; Dierkhising, R.; Coss, E.; Leise, M.D.; Watt, K.D. Cardiovascular disease after liver transplantation: When, What, and Who Is at Risk. Liver Transpl. 2015, 21, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.G.; Cheng, C.L.; Wee, A.; Lim, S.G.; Lee, Y.M.; Sutedja, D.S.; Da Costa, M.; Prabhakaran, K.; Wai, C.T. Prevalence and clinical associations of posttransplant fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablecki, J. [Report on the 3rd International Symposium of the Polish Society for Hand Surgery, Bialystok 13–15 June 2003]. Chir. Narzadow Ruchu Ortop. Pol. 2004, 69, 61–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charlton, M. Obesity, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15 (Suppl. 2), S83–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Gunson, B.; Johnson, J.; Neuberger, J. Weight gain and obesity after liver transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2005, 18, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwagner, L.B.; Bhave, M.; Te, H.S.; Feinglass, J.; Alvarez, L.; Rinella, M.E. Patients transplanted for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis are at increased risk for postoperative cardiovascular events. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazuelos, F.; Abril, J.; Zaragoza, C.; Rubio, E.; Moreno, J.M.; Turrion, V.S.; Cuervas-Mons, V. Cardiovascular morbidity and obesity in adult liver transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 1909–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Franco, E.S.; Leone, J.P.; Osman-Mohamed, H.; Rojas, H.; Kemmer, N.; Neff, G.W.; Rosemurgy, A.S.; Alsina, A.E. Obesity portends increased morbidity and earlier recurrence following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford) 2013, 15, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, A.B.; Lim, E.A.; Wang, S.; Brubaker, W.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Goyal, A.; Jacobson, J.S.; Hershman, D.L.; Verna, E.C.; Zaretsky, J.; et al. Diabetes, body mass index, and outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation 2012, 94, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Yoshizumi, T.; Kimura, K.; Okabe, H.; Harimoto, N.; Ikegami, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Shirabe, K.; Nishie, A.; Maehara, Y. Effect of Sarcopenic Obesity on Outcomes of Living-Donor Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.R.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Greenway, F.; Ryan, D.; deJonge, L.; de la Bretonne, J.; Volafova, J.; Bray, G.A. Contributions of total body fat, abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments, and visceral adipose tissue to the metabolic complications of obesity. Metabolism 2001, 50, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, B.; Deng, R.; Ma, Y. The Association of obesity with vascular complications after liver transplantation. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Fujita, S.; Mizuno, S.; Shenkman, E.; Vogel, B.; Lipori, P.; Hemming, A.W.; Nelson, D.; Reed, A.I. Clinical and financial impact of obesity on the outcome of liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 3612–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaydfudim, V.; Feurer, I.D.; Moore, D.E.; Wisawatapnimit, P.; Wright, J.K.; Wright Pinson, C. The negative effect of pretransplant overweight and obesity on the rate of improvement in physical quality of life after liver transplantation. Surgery 2009, 146, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassiman, D.; Roelants, M.; Vandenplas, G.; Van der Merwe, S.W.; Mertens, A.; Libbrecht, L.; Verslype, C.; Fevery, J.; Aerts, R.; Pirenne, J.; et al. Orlistat treatment is safe in overweight and obese liver transplant recipients: A prospective, open label trial. Transpl. Int. 2006, 19, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andalib, A.; Aminian, A.; Khorgami, Z.; Jamal, M.H.; Augustin, T.; Schauer, P.R.; Brethauer, S.A. Early Postoperative Outcomes of Primary Bariatric Surgery in Patients on Chronic Steroid or Immunosuppressive Therapy. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Tavakol, M.M.; Sarin, A.; Amirkiai, S.M.; Rogers, S.J.; Carter, J.T.; Posselt, A.M. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy is safe and efficacious for pretransplant candidates. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamalaidze, L.; Stauffer, J.A.; Arasi, L.C.; Villacreses, D.E.; Franco, J.S.S.; Bowers, S.; Elli, E.F. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy for Morbid Obesity in Patients After Orthotopic Liver Transplant: A Matched Case-Control Study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoraki, J.; Katz, M.G.; Funk, L.M.; Greenberg, J.A.; Fernandez, L.A.; Campos, G.M. Feasibility and outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy after solid organ transplantation. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2016, 12, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nowaylati, A.R.; Al-Haddad, B.J.; Dorman, R.B.; Alsaied, O.A.; Lake, J.R.; Chinnakotla, S.; Slusarek, B.M.; Sampson, B.K.; Ikramuddin, S.; Buchwald, H.; et al. Gastric bypass after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2013, 19, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elli, E.F.; Masrur, M.A.; Giulianotti, P.C. Robotic sleeve gastrectomy after liver transplantation. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2013, 9, e20–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.C.; Alloway, R.R.; Alexander, J.W.; Cardi, M.; Trofe, J.; Vinks, A.A. Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid, tacrolimus and sirolimus after gastric bypass surgery in end-stage renal disease and transplant patients: A pilot study. Clin. Transplant. 2008, 22, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwan, T.S.; Lichvar, A.B.; Leino, A.D.; Vinks, A.A.; Christians, U.; Shields, A.R.; Cardi, M.A.; Fukuda, T.; Mizuno, T.; Kaiser, T.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenetic analysis of immunosuppressive agents after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerut, J.P.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Lai, Q.; Stouffs, V.; Orlando, G.; Juri, J.M.; Ciccarelli, O.; Sempoux, C.; Roggen, F.M.; De Reyck, C.; et al. Is minimal, [almost] steroid-free immunosuppression a safe approach in adult liver transplantation? Long-term outcome of a prospective, double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, investigator-driven study. Ann. Surg. 2014, 260, 886–891, discussion 891–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, C.B.; Doria, C.; Frank, A.M.; Armenti, S.T.; Marino, I.R. Completely steroid-free immunosuppression in liver transplantation: A randomized study. Clin. Transplant. 2013, 27, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgourakis, G.; Dedemadi, G. Corticosteroid-free immunosuppression in liver transplantation: An evidence-based review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10703–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mare-Bredemeijer, E.L.; Metselaar, H.J. Optimization of the use of Calcineurin inhibitors in liver transplantation. Best Pract Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 26, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, M.; Rinella, M.; Patel, D.; McCague, K.; Heimbach, J.; Watt, K. Everolimus Is Associated With Less Weight Gain Than Tacrolimus 2 Years After Liver Transplantation: Results of a Randomized Multicenter Study. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2873–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PRE | DURING | POST | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PROS | -Potential for improvement of liver function and delisting -Potential for decreasing risk of post-LT complications associated with obesity -Weight loss in order to achieve a certain BMI in centers where obesity is a contraindication for LT | -Single intervention and single recovery phase -Less risk of perioperative complications associated with portal hypertension | -Patient is more stable and without portal hypertension |
| CONS | -Potential for increased morbidity and mortality in patients with advanced cirrhosis | -Potential increased risk of staple line complications due to high dose steroids -Rapid weight loss may complicate immunosuppression dosing -May worsen intolerance to oral intake in the immediate postoperative period -Increased surgical time -Potential for increased rate of perioperative complications when compared to LT-only procedure -May worsen accelerated loss of bone mass in the first months after LT -May be cumbersome to the patient to learn post-LT care plus post-BS care | -Technically more challenging surgery because of post-LT adhesions -Increased infection risk due to immunosuppression -Steroids can interfere with healing |
| Gastric Bypass | Sleeve Gastrectomy | Banding | Intragastric Balloon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROS | -The most efficient in terms of weight loss | -Does not cause malabsorption, less risk for malnutrition -Less operative time, reducing anesthesia duration -Technically easier -Does not modify pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus or MMF | -The least invasive, requires minimal dissection -Technically speaking is the easiest of the surgical procedures | -Minimally invasive -Can potentially be used in the decompensated patient -Easiest of all the procedures |
| CONS | -No easy access to the biliary tract or the remnant stomach which may develop variceal bleeding -Potential to lead to malabsorption and undernutrition -Affects the PKs of immunosuppressants -Use of steroids may increase the risk of marginal ulcers | -Risk of perioperative bleeding if there are gastric varices -Risk of bleeding or leakage from staple line | -Risk of complications related to the band (infection, migration) -The least effective in terms of weight loss | -Contraindicated in patients with large esophageal varices, gastric varices, or severe portal gastropathy |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moctezuma-Velazquez, C.; Márquez-Guillén, E.; Torre, A. Obesity in the Liver Transplant Setting. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112552
Moctezuma-Velazquez C, Márquez-Guillén E, Torre A. Obesity in the Liver Transplant Setting. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112552
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoctezuma-Velazquez, Carlos, Ernesto Márquez-Guillén, and Aldo Torre. 2019. "Obesity in the Liver Transplant Setting" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112552
APA StyleMoctezuma-Velazquez, C., Márquez-Guillén, E., & Torre, A. (2019). Obesity in the Liver Transplant Setting. Nutrients, 11(11), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112552





