Long-Term Dietary Intake of Chia Seed Is Associated with Increased Bone Mineral Content and Improved Hepatic and Intestinal Morphology in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compliance with Ethical Standards
2.2. Dietary Ingredients and Animals
2.3. Preparation of the Food Pellets
2.4. Body Weight and Composition
2.5. Chemical Analysis of Chia Seeds
2.6. Bone Assessment
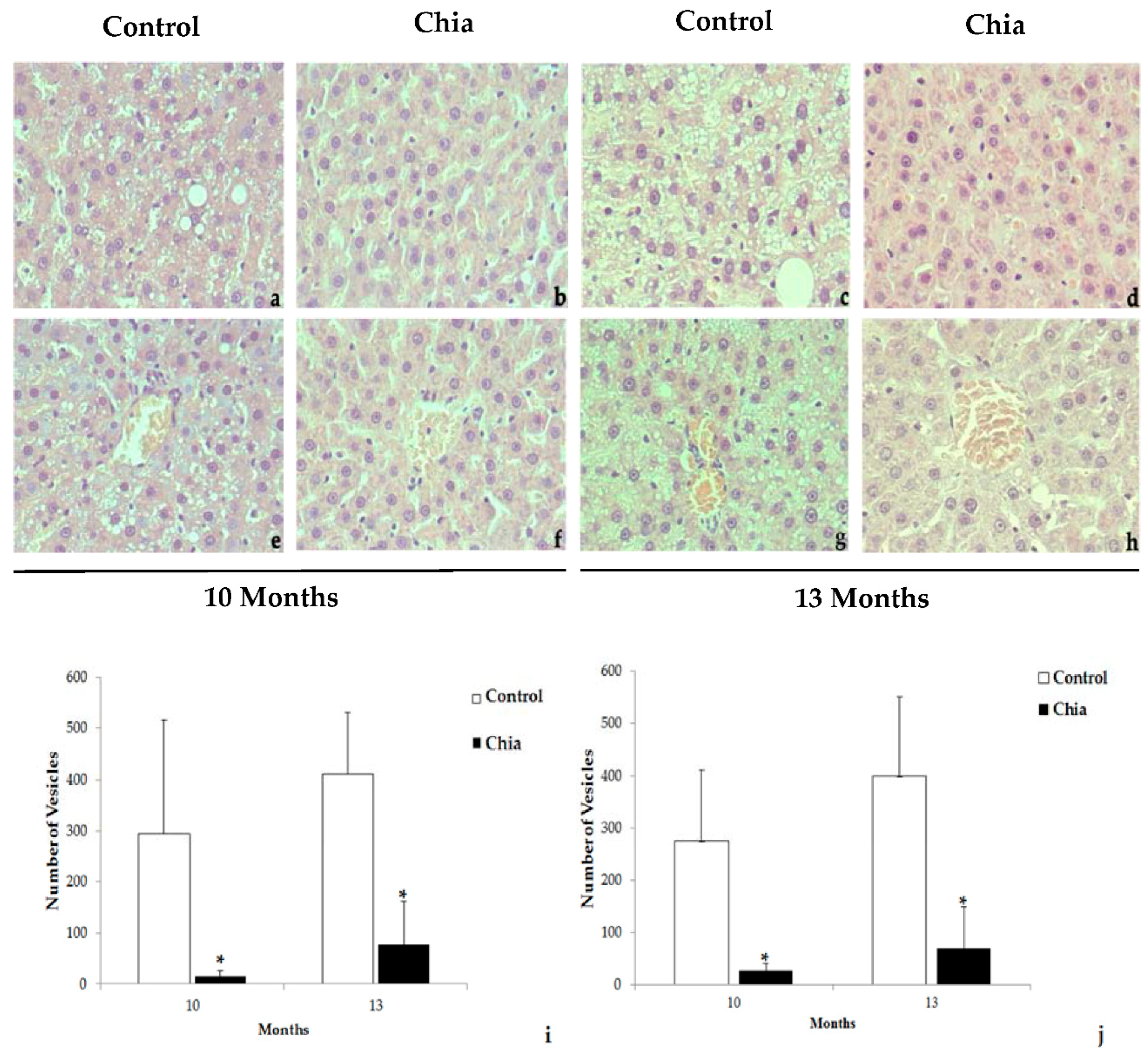
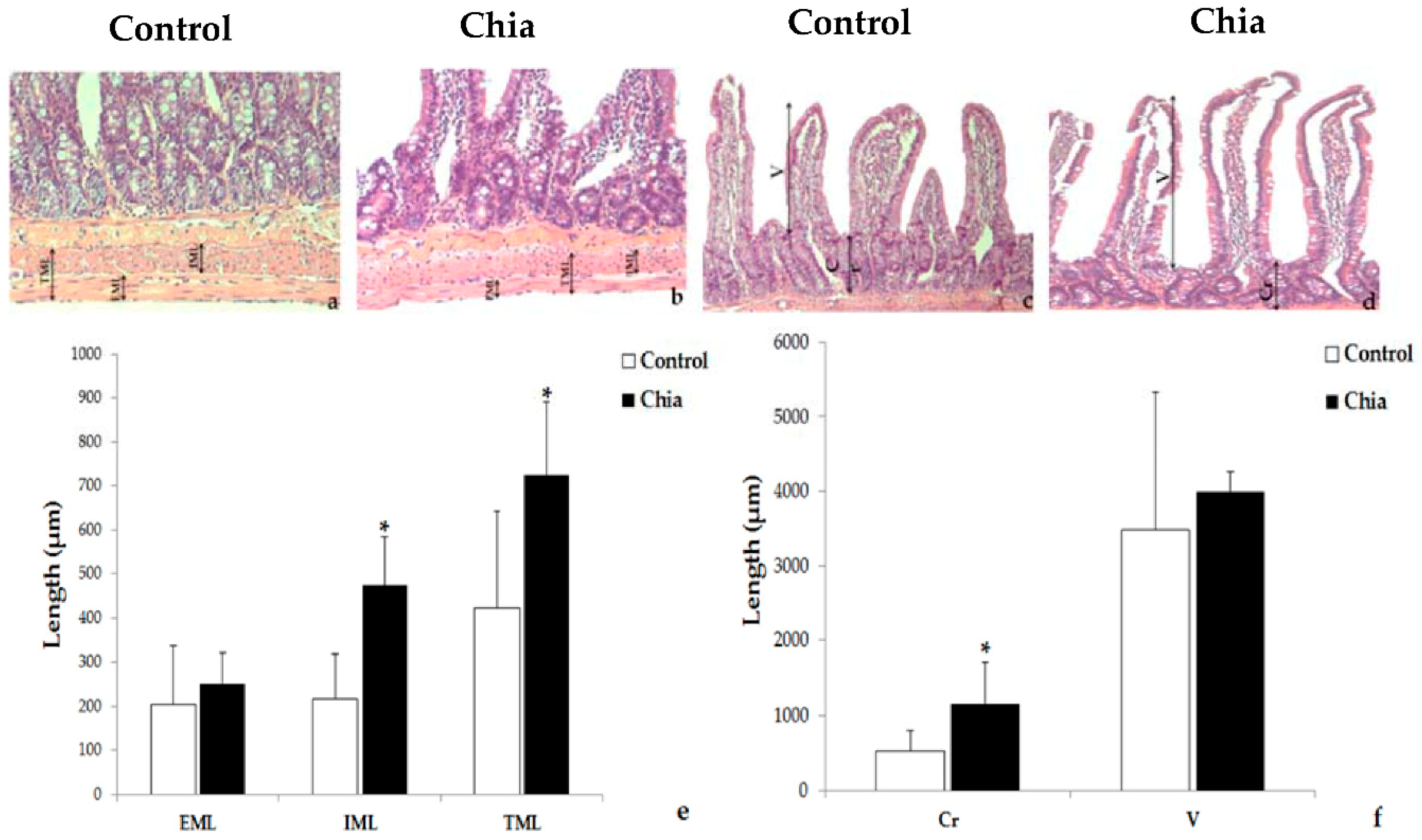
2.7. Liver and Intestine Morphology
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, K.H.; Herzog, W.; MacDonald, G.Z.; Reimer, R.A.; Rios, J.L.; Smith, I.C.; Zernicke, R.F.; Hart, D.A. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and musculoskeletal disease: Common inflammatory pathways suggest a central role for loss of muscle integrity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, S.O.S.; Pacheco, F.J.; Zapata, G.M.; Garcia, J.M.; Previale, C.A.; Cura, H.E.; Craig, W.J. Food habits, lifestyle factors, and risk of prostate cancer in central Argentina: A case control study involving self-motivated health behavior modifications after diagnosis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, D.E.; Chambi, F.R.; Chañi, E.M.; Craig, W.J.; Pacheco, S.O.; Pacheco, F.J. Risk factors for chronic diseases and multimorbidity in a primary care context of central Argentina: A web-based interactive and cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.; Schellenberger, A.N.; Roe, A.L.; Oketch-Rabah, H.; Calderón, A.I. Therapeutic perspectives on chia seed and its oil: A review. Planta Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd, A.N.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Tan, S.W.; Tan, S.G. The promising future of chia, Salvia hispanica L. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Alves, S.C.; Vendramini-Costa, D.B.; Betim Cazarin, C.B.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R.; Borges Ferreira, J.P.; Silva, A.B.; Prado, M.A.; Bronze, M.R. Characterization of phenolic compounds in chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds, fiber flour and oil. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayerza, R. The seed’s protein and oil content, fatty acid composition, and growing cycle length of a single genotype of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) as affected by environmental factors. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz Loreto, A.; Cobos, A.; Diaz, O.; Aguilera, J.M. Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica): An ancient grain and a new functional food. Food Rev. Int. 2013, 29, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia-López, M.Á.; Tecante, A. Chia (Salvia hispanica): A Review of Native Mexican Seed and its Nutritional and Functional Properties. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 75, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannice, G.; Rasmussen, H. Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: Dietary fatty acids for healthy adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Schilling, T.F. Tendon development and musculoskeletal assembly: Emerging roles for the extracellular matrix. Development 2015, 142, 4191–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Tan, N.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disuse osteoporosis. Bone 2017, 97, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, A.; Behler-Janbeck, F.; Beil, F.T.; Koehne, T.; Müller, B.; Schmidt, T.; Heine, M.; Ochs, L.; Yilmaz, T.; Dietrich, M.; et al. Lrp1 in osteoblasts controls osteoclast activity and protects against osteoporosis by limiting PDGF-RANKL signaling. Bone Res. 2018, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, E.; Söderlund, A. What is the role of lifestyle behaviour change associated with non-communicable disease risk in managing musculoskeletal health conditions with special reference to chronic pain? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieboer, M.F.; Gosens, T. Effect of smoking on orthopaedic conditions: An overview for everyday practice. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2017, 161, D925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedno, S.A.; Jackson, R.; Feng, X.; Walton, I.L.; Boivin, M.R.; Cowan, D.N. Meta-analysis of Cigarette Smoking and Musculoskeletal Injuries in Military Training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2191–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintermeyer, E.; Ihle, C.; Ehnert, S.; Stöckle, U.; Ochs, G.; de Zwart, P.; Flesch, I.; Bahrs, C.; Nussler, A.K. Crucial Role of Vitamin D in the Musculoskeletal System. Nutrients 2016, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hant, F.N.; Bolster, M.B. Drugs that may harm bone: Mitigating the risk. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.I.; Kalisinska, E.; Sokolowski, S.; Kolodziej, L.; Budis, H.; Safranow, K.; Kot, K.; Ciosek, Z.; Tomska, N.; et al. Influence of Environmental Factors and Relationships between Vanadium, Chromium, and Calcium in Human Bone. BioMed Res. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellmeyer, D.E.; Civitelli, R.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Khosla, S.; Lecka-Czernik, B.; Schwartz, A.V. Skeletal Metabolism, Fracture Risk, and Fracture Outcomes in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.; Cooper, M.S. Bone loss in inflammatory disorders. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 201, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Pérez, A.; Franco-Trepat, E.; Guillán-Fresco, M.; Jorge-Mora, A.; López, V.; Pino, J.; Gualillo, O.; Gómez, R. Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4 on Osteoblast Metabolism and Function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, F.J.; Almaguel, F.G.; Evans, W.; Rios-Colon, L.; Filippov, V.; Leoh, L.S.; Rook-Arena, E.; Mediavilla-Varela, M.; De Leon, M.; Casiano, C.A. Docosahexanoic acid antagonizes TNF-α-induced necroptosis by attenuating oxidative stress, ceramide production, lysosomal dysfunction, and autophagic features. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaguel, F.G.; Liu, J.W.; Pacheco, F.J.; Casiano, C.A.; De Leon, M. Activation and reversal of lipotoxicity in PC12 and rat cortical cells following exposure to palmitic acid. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veselinovic, M.; Vasiljevic, D.; Vucic, V.; Arsic, A.; Petrovic, S.; Tomic-Lucic, A.; Savic, M.; Zivanovic, S.; Stojic, V.; Jakovljevic, V. Clinical Benefits of n-3 PUFA and γ-Linolenic Acid in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, K.; Singh, A.K.; Jabeen, R. Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods: The Foods for the Future World. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2617–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troesch, B.; Biesalski, H.K.; Bos, R.; Buskens, E.; Calder, P.C.; Saris, W.H.; Spieldenner, J.; Verkade, H.J.; Weber, P.; Eggersdorfer, M. Increased Intake of Foods with High Nutrient Density Can Help to Break the Intergenerational Cycle of Malnutrition and Obesity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6016–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso Monteiro Bezerra, M.; Hellwig, N.; da Rocha Castelar Pinheiro, G.; Souza Lopes, C. Prevalence of chronic musculoskeletal conditions and associated factors in Brazilian adults—National Health Survey. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, K.M.; Sahni, S.; Kerstetter, J.E.; Kenny, A.M.; Hannan, M.T. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their relation with bone and muscle health in adults. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2013, 11, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, A.M.; Rodríguez, J.P. Is fatty acid composition of human bone marrow significant to bone health? Bone 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donlon, C.M.; LeBoff, M.S.; Chou, S.H.; Cook, N.R.; Copeland, T.; Buring, J.E.; Bubes, V.; Kotler, G.; Manson, J.E. Baseline characteristics of participants in the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL): Effects on Bone Structure and Architecture. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2018, 67, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iolascon, G.; Gimigliano, R.; Bianco, M.; De Sire, A.; Moretti, A.; Giusti, A.; Malavolta, N.; Migliaccio, S.; Migliore, A.; Napoli, N.; et al. Are Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals Effective for Musculoskeletal Health and Cognitive Function? A Scoping Review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.A.; Loeser, R.F. Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.B.; Taylor, M.J.; Hill, S.J. Cross-sectional examination of musculoskeletal conditions and multimorbidity: Influence of different thresholds and definitions on prevalence and association estimates. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Ha, Y.C.; Yoo, J.I. Health-related Quality of Life in Accordance with Fracture History and Comorbidities in Korean Patients with Osteoporosis. J. Bone Metab. 2016, 23, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraya, A.M.; Dwibedi, N.; Sambamoorthi, U. Polypharmacy and Health-Related Quality of Life among US Adults with Arthritis, Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, 2010–2012. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosch, M.; Jeske, M.; Kammerlander, C.; Roth, T. Osteoporosis and polypharmacy. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 45, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacar, S.; Itani, T.; Hajal, J.; Saliba, Y.; Louka, N.; Faivre, J.F.; Maroun, R.; Fares, N. The impact of long-term intake of phenolic compounds-rich grape pomace on rat gut microbiota. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Okereke, O.; Devore, E.; Rosner, B.; Breteler, M.; Grodstein, F. Long-term intake of nuts in relation to cognitive function in older women. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Wallin, A.; Bottai, M.; Askling, J.; Wolk, A. Long-term intake of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective cohort study of women. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudyal, H.; Panchal, S.K.; Waanders, J.; Ward, L.; Brown, L. Lipid redistribution by α-linolenic acid-rich chia seed inhibits stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 and induces cardiac and hepatic protection in diet-induced obese rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, B.P.; Dias, D.M.; de Castro Moreira, M.E.; Toledo, R.C.; da Matta, S.L.; Lucia, C.M.; Martino, H.S. Chia seed shows good protein quality, hypoglycemic effect and improves the lipid profile and liver and intestinal morphology of Wistar rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossio-Bolaños, M.A.; Gómez, R.; Rojas, J.; Flores, H. Proposed equations for predicting body composition of male Wistar rats. An. Fac. Med. 2010, 71, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis AOAC; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wronski, T.J.; Ratkus, A.M.; Thomsen, J.S.; Vulcan, Q.; Mosekilde, L. Sequential treatment with basic fibroblast growth factor and parathyroid hormone restores lost cancellous bone mass and strength in the proximal tibia of aged ovariectomized rats. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, C.L.; Más, R.M.; Rodeiro, I.; Noa, M.; Hernández, C.; Menéndez, R.; Gámez, R. Reference database of the main physiological parameters in Sprague-Dawley rats from 6 to 32 months. Lab. Anim. 1998, 32, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletzko, B.; Aggett, P.J.; Bindels, J.G.; Bung, P.; Ferré, P.; Gil, A.; Lentze, M.J.; Roberfroid, M.; Strobel, S. Development and differentiation: A functional food science approach. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, S5–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, T.Y.; Baum, J.I.; Huang, Y. Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on myogenesis and mitochondrial biosynthesis during murine skeletal muscle cell differentiation. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treit, D.; Spetch, M.L.; Deutsch, J.A. Variety in the flavor of food enhances eating in the rat: A controlled demonstration. Physiol. Behav. 1983, 30, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, H.A.; Epstein, L.H. Dietary variety, energy regulation, and obesity. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 127, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.; Sello, C.T.; Qin, G.X.; Che, D.; Han, R. Does dietary fiber affect the levels of nutritional components after feed formulation? Fibers 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Bäckhed, F. The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umu, Ö.C.O.; Rudi, K.; Diep, D.B. Modulation of the gut microbiota by prebiotic fibres and bacteriocins. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2017, 28, 1348886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Grasset, E.; Mannerås Holm, L.; Karsenty, G.; Macpherson, A.J.; Olofsson, L.E.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates maturation of the adult enteric nervous system via enteric serotonin networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6458–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.N.; Martin, R.J.; Keim, N.L. Does Whole Grain Consumption Alter Gut Microbiota and Satiety. Healthcare 2011, 3, 364–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasbalg, T.L.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Ramsden, C.E.; Majchrzak, S.F.; Rawlings, R.R. Changes in consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the United States during the 20th century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J. Polyunsaturated fatty acids intake, omega-6/omega-3 ratio and mortality: Findings from two independent nationwide cohorts. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.X.; Liu, A. The role of the tissue omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in regulating tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S. Health benefits of plant-derived α-linolenic acid. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 443S–448S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceló-Coblijn, G.; Murphy, E.J. Alpha-linolenic acid and its conversion to longer chain n-3 fatty acids: Benefits for human health and a role in maintaining tissue n-3 fatty acid levels. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.R.; Alvarez, S.M.; Illesca, P.; Giménez, M.S.; Lombardo, Y.B. Dietary Salba (Salvia hispanica L.) ameliorates the adipose tissue dysfunction of dyslipemic insulin-resistant rats through mechanisms involving oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 57, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.; Rüfer, C.E.; Le Grandois, J.; Roth, A.; Aoude-Werner, D.; Marchioni, E.; Bub, A.; Barth, S.W. Dietary walnut oil modulates liver steatosis in the obese Zucker rat. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandra, S.; Yeh, M.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Ünalp-Arida, A.; Wilson, L.A.; Chalasani, N. Presence and significance of microvesicular steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Functional roles of fatty acids and their effects on human health. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 18S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasilva, G.; Pazos, M.; García-Egido, E.; Gallardo, J.M.; Rodríguez, I.; Cela, R.; Medina, I. Healthy effect of different proportions of marine ω-3 PUFAs EPA and DHA supplementation in Wistar rats: Lipidomic biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeyens, J.C.; Deepak, V.; Chua, W.H.; Kruger, M.C.; Joubert, A.M.; Coetzee, M. Effects of ω3- and ω6-polyunsaturated fatty acids on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells: A comparative in vitro study. Nutrients 2014, 6, 2584–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, A.; Koehne, T.; Tödter, K.; Reimer, R.; Müller, B.; Behler-Janbeck, F.; Heeren, J.; Scheja, L.; Niemeier, A. Quantification of Bone Fatty Acid Metabolism and Its Regulation by Adipocyte Lipoprotein Lipase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Eerden, B.; van Wijnen, A. Meeting report of the 2016 bone marrow adiposity meeting. Adipocyte 2017, 6, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, M.; Harris, S.S.; Must, A.; Naumova, E.N.; Phillips, S.M.; Rand, W.M.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Leptin, body composition and bone mineral density in premenopausal women. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 73, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.H.; Venners, S.A.; Terwedow, H.A.; Feng, Y.; Niu, T.; Li, Z.; Laird, N.; Brain, J.D.; Cummings, S.R.; Bouxsein, M.L.; et al. Relation of body composition, fat mass, and serum lipids to osteoporotic fractures and bone mineral density in Chinese men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taes, Y.E.; Lapauw, B.; Vanbillemont, G.; Bogaert, V.; De Bacquer, D.; Zmierczak, H.; Goemaere, S.; Kaufman, J.M. Fat mass is negatively associated with cortical bone size in young healthy male siblings. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelt, A.; Beil, F.T.; Schinke, T.; Roeser, K.; Ruether, W.; Heeren, J.; Niemeier, A. Apolipoprotein E-dependent inverse regulation of vertebral bone and adipose tissue mass in C57Bl/6 mice: Modulation by diet-induced obesity. Bone 2010, 47, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, E.; Swinton, P.A.; Sale, C.; Healy, A.; O’Reilly, J. Influence of adipose tissue mass on bone mass in an overweight or obese population: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Cell biology of fat storage. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefterova, M.I.; Haakonsson, A.K.; Lazar, M.A.; Mandrup, S. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuda, O.; Rossmeisl, M.; Kopecky, J. Omega-3 fatty acids and adipose tissue biology. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 17, S0098–S2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavado-García, J.; Roncero-Martin, R.; Moran, J.M.; Pedrera-Canal, M.; Aliaga, I.; Leal-Hernandez, O.; ico-Martin, S.; Canal-Macias, M.L. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid dietary intake is positively associated with bone mineral density in normal and osteopenic Spanish women. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högström, M.; Nordström, P.; Nordström, A. n-3 fatty acids are positively associated with peak bone mineral density and bone accrual in healthy men: The NO2 Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiuri, S.P.B.; Parikh, M.; Stamenkovic, A.; Pierce, G.N.; Aukema, H.M. Dietary modulation of oxylipins in cardiovascular disease and aging. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 313, H903–H918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Bartali, B.; Cherubini, A.; Iorio, A.D.; Blè, A.; Giacomini, V.; Corsi, A.M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids predict accelerated decline of peripheral nerve function in older persons. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, R.A. Osteoporosis in men: A review. Bone Res. 2014, 2, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roager, H.M.; Hansen, L.B.; Bahl, M.I.; Frandsen, H.L.; Carvalho, V.; Gøbel, R.J.; Dalgaard, M.D.; Plichta, D.R.; Sparholt, M.H.; Vestergaard, H.; et al. Colonic transit time is related to bacterial metabolism and mucosal turnover in the gut. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannenberg, G.; Mallon, C.; Edwards, H.; Yeadon, D.; Yan, K.; Johnson, H.; Ismail, A. Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content and Oxidation State of Fish Oil Supplements in New Zealand. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosqvist, F.; Iggman, D.; Kullberg, J.; Cedernaes, J.; Johansson, H.E.; Larsson, A.; Johansson, L.; Ahlström, H.; Arner, P.; Dahlman, I.; et al. Overfeeding polyunsaturated and saturated fat causes distinct effects on liver and visceral fat accumulation in humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, J.I.; Hord, N.G.; Ghosh, S.; Gurzell, E.A. Immunomodulation by dietary long chain omega-3 fatty acids and the potential for adverse health outcomes. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 89, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Gillitt, N.; Jin, F.; Henson, D.A.; Kennerly, K.; Shanely, R.A.; Ore, B.; Su, M.; Schwartz, S. Chia seed supplementation and disease risk factors in overweight women: A metabolomics investigation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.S.; Salas-Mellado, M.L. Addition of chia seed mucilage for reduction of fat content in bread and cakes. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparra, J.M.; Haros, M. Inclusion of ancient Latin-American crops in bread formulation improves intestinal iron absorption and modulates inflammatory markers. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.; Yip, E.L.; Reghunathan, R.; Mohan, S.; Sabaté, J. Effect of Altering Dietary n-6:n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio with Plant and Marine-Based Supplement on Biomarkers of Bone Turnover in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ingredients (g/kg) | Control Diet | Chia Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Cornstarch | 463.0 | 428.0 |
| Casein | 151.0 | 139.0 |
| Dextrinized corn starch | 141.0 | 129.0 |
| Whole chia seed | - | 100.0 |
| Dextrose monohydrate | 86.0 | 80.0 |
| Soybean oil | 60.0 | 30.0 |
| Fiber | 60.0 | 60.0 |
| Mineral complex | 31.5 | 28.0 |
| Multivitamins | 5.1 | 5.1 |
| l-cystine | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Nutrients (Unit/kg) | Control Diet | Chia Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Total energy (kcal) | 3678 | 3663 |
| Energy as protein (%) | 17.0 | 17.0 |
| Energy as carbohydrate (%) | 68.0 | 68.0 |
| Energy as fat (%) | 15.0 | 15.0 |
| Total fat (g) | 64.7 | 65.3 |
| Saturated fats (g) | 9.3 | 7.8 |
| Monounsaturated fats (g) | 13.6 | 8.9 |
| Polyunsaturated fats (g) | 34.6 | 40.6 |
| n-6 fatty acids (g) | 30.3 | 21.0 |
| n-3 fatty acids (g) | 4.0 | 19.5 |
| n-6/n-3 ratio * | 7.4 | 1.0 |
| Total carbohydrate (g) | 648.4 | 621.4 |
| Total protein (g) | 150.4 | 154.9 |
| Vitamins, minerals, fiber, choline ** | Based on the AIN-93M guidelines | |
| Variables (U) | 10 Months | 13 Months | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Chia | Control | Chia | |
| Body weight # (g) | 745.9 ± 110.9 | 786.8 ± 74.6 | 711.0 ± 58.5 | 918.2 ± 75.4 * |
| Body weight gain (%) | 497.4 ± 157.1 | 550.3 ± 93.4 | 473.0 ± 42.2 | 608.3 ± 51.5 * |
| Daily food intake (g/day) | 25.6 ± 1.4 | 30.9 ± 1.7 * | 26.6 ± 1.2 | 31.0 ± 0.7 * |
| Fat free weight (g) | 365.6 ± 24.3 | 365.0 ± 23.1 | 356.3 ± 20.3 | 430.6 ± 44.1 * |
| Fat weight (g) | 204.1 ± 43.3 | 243.2 ± 25.5 | 203.4 ± 27.2 | 288.5 ± 37.1 * |
| Residual weight (g) | 176.1 ± 55.2 | 178.5 ± 34.0 | 151.2 ± 14.4 | 199.0 ± 41.1 * |
| Water intake (mL/day) | 61.9 ± 31.7 | 61.9 ± 21.4 | 57.3 ± 26.9 | 57.9 ± 17.8 |
| Variables | 10 Months | 13 Months | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Chia | p Value for t-Test | Control | Chia | p Value for t-Test | |
| BMD (mg/cm2) | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | NS | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | NS |
| BMC | 8.69 ± 0.94 | 9.02 ± 1.01 | NS | 8.77 ± 1.31 | 10.05 ± 0.93 | NS |
| BMC tibia left total | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.36 ± 0.15 | NS * | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.019 |
| BMD tibia left total (mg/cm2) | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | NS | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.052 |
| BMC tibia left proximal | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | NS | 0.14 ± 0.20 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.019 |
| BMD tibia left proximal (mg/cm2) | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | NS | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.44 ± 0.06 | NS * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montes Chañi, E.M.; Pacheco, S.O.S.; Martínez, G.A.; Freitas, M.R.; Ivona, J.G.; Ivona, J.A.; Craig, W.J.; Pacheco, F.J. Long-Term Dietary Intake of Chia Seed Is Associated with Increased Bone Mineral Content and Improved Hepatic and Intestinal Morphology in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070922
Montes Chañi EM, Pacheco SOS, Martínez GA, Freitas MR, Ivona JG, Ivona JA, Craig WJ, Pacheco FJ. Long-Term Dietary Intake of Chia Seed Is Associated with Increased Bone Mineral Content and Improved Hepatic and Intestinal Morphology in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nutrients. 2018; 10(7):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070922
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontes Chañi, Evelyn M., Sandaly O. S. Pacheco, Gustavo A. Martínez, Maykon R. Freitas, Joaquin G. Ivona, Javier A. Ivona, Winston J. Craig, and Fabio J. Pacheco. 2018. "Long-Term Dietary Intake of Chia Seed Is Associated with Increased Bone Mineral Content and Improved Hepatic and Intestinal Morphology in Sprague-Dawley Rats" Nutrients 10, no. 7: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070922
APA StyleMontes Chañi, E. M., Pacheco, S. O. S., Martínez, G. A., Freitas, M. R., Ivona, J. G., Ivona, J. A., Craig, W. J., & Pacheco, F. J. (2018). Long-Term Dietary Intake of Chia Seed Is Associated with Increased Bone Mineral Content and Improved Hepatic and Intestinal Morphology in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nutrients, 10(7), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070922





