Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dependent Variables: Cognitive Scores
2.3. Explanatory Variable: Use of VKAs
2.4. Covariables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
- Study concept and design: C.A.
- Acquisition of data: A.B. and C.A.
- Analysis and interpretation of data: A.B. and C.A.
- Drafting of the manuscript: C.A. and A.B.
- Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: G.F., Y.R., J.G. and C.F.
- Statistical expertise: J.G. and C.A.
- Obtained funding: not applicable.
- Administrative, technical, or material support: C.A.
- Study supervision: C.A.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansell, J.; Hirsh, J.; Hylek, E.; Jacobson, A.; Crowther, M.; Palareti, G. Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2008, 133, 160S–198S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French National Security Agency of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM). Anticoagulants in France in 2012: Inventory and Monitoring. Available online: http://ansm.sante.fr/var/ansm_site/storage/original/application/901e9c291a545dff52c0b41365c0d6e2.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2018).
- Ferland, G. Vitamin K, an emerging nutrient in brain function. Biofactors 2012, 38, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferland, G. Vitamin K and the nervous system: An overview of its actions. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presse, N.; Shatenstein, B.; Kergoat, M.J.; Ferland, G. Low vitamin K intakes in community-dwelling elders at an early stage of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 2095–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.G.; Pauli, R.M.; Wilson, K.M. Maternal and fetal sequelae of anticoagulation during pregnancy. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annweiler, C.; Denis, S.; Duval, G.; Bartha, R.; Beauchet, O. Use of Vitamin K Antagonists and Brain Volumetry in Older Adults: Preliminary Results From the GAIT Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annweiler, C.; Ferland, G.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Brangier, A.; Rolland, Y.; Beauchet, O. Vitamin K antagonists and cognitive impairment: Results from a cross-sectional pilot study among geriatric patients. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchet, O.; Launay, C.P.; Allali, G.; Watfa, G.; Gallouj, K.; Herrmann, F.R.; Annweiler, C. Anti-dementia drugs and changes in gait: A pre-post quasi-experimental pilot study. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier-Nitenberg, C.; Dauphinot, V.; Bongue, B.; Sass, C.; Rouch, I.; Beauchet, O.; Krolak-Salmon, P.; Fantino, B. Early detection of memory impairment in people over 65 years old consulting at Health Examination Centers for the French health insurance: The EVATEM protocol. BMC Geriatr. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. Mini-mental state: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Slachevsky, A.; Litvan, I.; Pillon, B.F.A.B. The FAB: A frontal assessment battery at bedside. Neurology 2000, 55, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, T.G.; Hall, J.E.; Appel, L.J.; Falkner, B.E.; Graves, J.; Hill, M.N.; Jones, D.W.; Kurtz, T.; Sheps, S.G.; Roccella, E.J. Recommendations for blood pressure measurment in humans and experimental animals: Part 1: Blood pressure measurement in humans: A statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 2005, 111, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pérès, K.; Chrysostome, V.; Fabrigoule, C.; Orgogozo, J.M.; Dartigues, J.F.; Barberger-Gateau, P. Restriction in complex activities of daily living in MCI: Impact on outcome. Neurology 2006, 67, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: A preliminary report. Bull. World Health Organ. 1976, 54, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahlund, L.O.; Barkhof, F.; Fazekas, F.; Bronge, L.; Augustin, M.; Sjögren, M.; Wallin, A.; Ader, H.; Leys, D.; Pantoni, L.; et al. A new rating scale for age-related white matter changes applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 2001, 32, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamadon-Nejad, S. Warfarin-Induced Vitamin K Deficiency Is Associated with Cognitive and Behavioral Perturbations, and Alterations in Brain Sphingolipids in Rats. Université de Montréal 2013. Available online: https://papyrus.bib.umontreal.ca/xmlui/handle/1866/10871 (accessed on 21 March 2018).
- Barber, M.; Tait, R.C.; Scott, J.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Stott, D.J. Dementia in subjects with atrial fibrillation: Hemostatic function and the role of anticoagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.; Meade, T.W.; Peart, S.; Brennan, P.J.; Mann, A.H. Is there any evidence for a protective effect of antithrombotic medication on cognitive function in men at risk of cardiovascular disease? Some preliminary findings. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantarian, S.; Sternd, T.; Mansour, M.; Ruskin, J.N. Cognitive impairment associated with atrial fibrillation. A meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thijssen, H.H.; Drittij-Reijnders, M.J. Vitamin K distribution in rat tissues: Dietary phylloquinone is a source of tissue menaquinone-4. Br. J. Nutr. 1994, 72, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagami, T.; Ueda, K.; Asakura, K.; Sakaeda, T.; Nakazato, H.; Kuroda, T.; Hata, S.; Sakaguchi, G.; Itoh, N.; Nakano, T.; et al. Gas6 rescues cortical neurons from amyloid beta protein-induced apoptosis. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Griffin, J.H.; Fernandez, J.A.; Zlokovic, B.V. Protein S confers neuronal protection during ischemic/hypoxic injury in mice. Circulation 2003, 107, 1791–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, K.S.; Lev, M. Warfarin administration reduces synthesis of sulfatides and other sphingolipids in mouse brain. J. Lipid Res. 1988, 29, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godefroy, O.; Jeannerod, M.; Allain, P.; Le Gall, D. Frontal lobe, executive functions and cognitive control. Rev. Neurol. 2008, 164, 119S–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffinet, P.; Bordet, R.; Menard, J. Relevance of the evaluation criteria used in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Therapie 2009, 64, 139–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinomais, M.; Celle, S.; Duval, G.T.; Roche, F.; Henni, S.; Bartha, R.; Beauchet, O.; Annweiler, C. Anatomic Correlation of the Mini-Mental State Examination: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study in Older Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A. Novel anticoagulant therapy: Principle and practice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 663, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Total Cohort (n = 378) | Use Vitamin K Antagonists | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 332) | Yes (n = 46) | |||
| Demographic measures | ||||
| Age, years | 82.32 ± 5.60 | 82.11 ± 5.79 | 83.81 ± 3.63 | 0.160 |
| Female gender, n (%) | 227 (60.1) | 202 (60.8) | 25 (54.3) | 0.399 |
| Clinical measures | ||||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.99 ± 18.30 | 27.71 ± 19.49 | 29.91 ± 5.35 | <0.001 |
| Mean arterial pressure, mmHg | 100.12 ± 12.03 | 99.74 ± 12.09 | 102.61 ± 11.45 | 0.196 |
| IADL score, /4 | 1.94 ± 1.40 | 1.94 ± 1.44 | 1.91 ± 1.11 | 0.972 |
| Gait speed, cm/s | 71.56 ± 24.49 | 72.56 ± 24.53 | 65.11 ± 23.60 | 0.094 |
| Number of comorbidities | 3.58 ± 2.12 | 3.46 ± 2.03 | 4.51 ± 2.53 | 0.005 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 56 (14.8) | 19 (5.7) | 37 (80.4) | <0.001 |
| Stroke, n (%) | 42 (11.1) | 30 (9.0) | 12 (26.1) | 0.001 |
| ARWMC score, /3 | 0.68 ± 0.98 | 0.68 ± 0.98 | 0.70 ± 1.01 | 0.904 |
| Carotid artery stenosis, n (%) | 23 (6.1) | 20 (6.0) | 3 (6.5) | 0.751 |
| MMSE score, /30 | 19.84 ± 4.76 | 19.82 ± 4.87 | 19.96 ± 3.90 | 0.778 |
| FAB score *, /18 | 11.78 ± 3.15 | 12.01 ± 3.01 | 10.29 ± 3.59 | 0.006 |
| Use of psychoactive drugs, n (%) | 223 (59.0) | 201 (61.7) | 22 (47.8) | 0.073 |
| Use of antidementia drugs, n (%) | 198 (52.4) | 172 (51.8) | 26 (56.5) | 0.548 |
| Serum measures | ||||
| Creatinine concentration, µmol/L | 86.03 ± 48.26 | 85.34 ± 50.60 | 91.12 ± 24.86 | 0.049 |
| Vitamin B12 concentration, ng/L | 449.13 ± 231.65 | 448.06 ± 236.81 | 457.18 ± 191.59 | 0.483 |
| Use of blood-thinning drugs | ||||
| Total, n (%) | 175 (46.3) | 129 (38.9) | 46 (100.0) | <0.001 |
| Vitamin K antagonists, n (%) | 46 (12.2) | - | - | - |
| Heparin, n (%) | 4 (1.1) | 4 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
| Direct oral anticoagulants, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Antiplatelet medications, n (%) | 129 (34.1) | 126 (38.0) | 3 (6.5) | <0.001 |
| Cognitive Scores | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMSE Score (n = 378) | FAB Score (n = 253) | |||||
| β | [95% CI] | p-Value | β | [95% CI] | p-Value | |
| Use of vitamin K antagonists | 0.51 | [−2.38, 23.26] | 0.655 | −2.12 | [−3.99, −0.25] | 0.026 |
| Age | 0.05 | [−1.75, 2.77] | 0.443 | 0.02 | [−0.07, 0.11] | 0.635 |
| Female gender | 0.80 | [−0.07, 0.16] | 0.228 | 0.59 | [−0.40, 1.59] | 0.242 |
| Body mass index | 0.19 | [0.04, 0.34] | 0.011 | −0.03 | [−0.15, 0.09] | 0.649 |
| Mean arterial pressure | −0.01 | [−0.06, 0.03] | 0.564 | 0.002 | [−0.04, 0.04] | 0.939 |
| Number of comorbidities | 0.08 | [−0.20, 0.35] | 0.578 | −0.03 | [−0.25, 0.20] | 0.823 |
| Disability * | −2.95 | [−4.35, −1.55] | <0.001 | −0.46 | [−1.52, 0.60] | 0.393 |
| Gait Speed | 0.07 | [0.04, 0.10] | <0.001 | 0.05 | [0.03, 0.07] | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | −0.38 | [−2.46, 1.71] | 0.722 | 1.12 | [−0.67, 2.92] | 0.219 |
| Stroke | 0.60 | [−1.46, 2.66] | 0.566 | 1.03 | [−0.64, 2.69] | 0.225 |
| ARWMC score | −0.04 | [−0.60, 0.53] | 0.897 | −0.35 | [−0.80, 0.09] | 0.115 |
| Carotid artery stenosis | −1.59 | [−3.91, 0.73] | 0.178 | −0.79 | [−2.63, 1.06] | 0.402 |
| Use of psychoactive drugs | −0.08 | [−1.27, 1.11] | 0.898 | −0.66 | [−1.57, 0.25] | 0.156 |
| Use of antidementia drugs | −3.63 | [−4.79, −2.48] | <0.001 | −1.57 | [−2.47, −0.67] | 0.001 |
| Creatinine concentration | −0.001 | [−0.02, 0.02] | 0.961 | −0.001 | [−0.02, 0.02] | 0.915 |
| Vitamin B12 concentration | 0.00 | [−0.00, 0.00] | 0.830 | 0.00 | [−0.00, 0.00] | 0.836 |
| Use of antiplatelet medications | 1.07 | [−0.24, 2.38] | 0.109 | 0.02 | [−1.01, 1.06] | 0.963 |
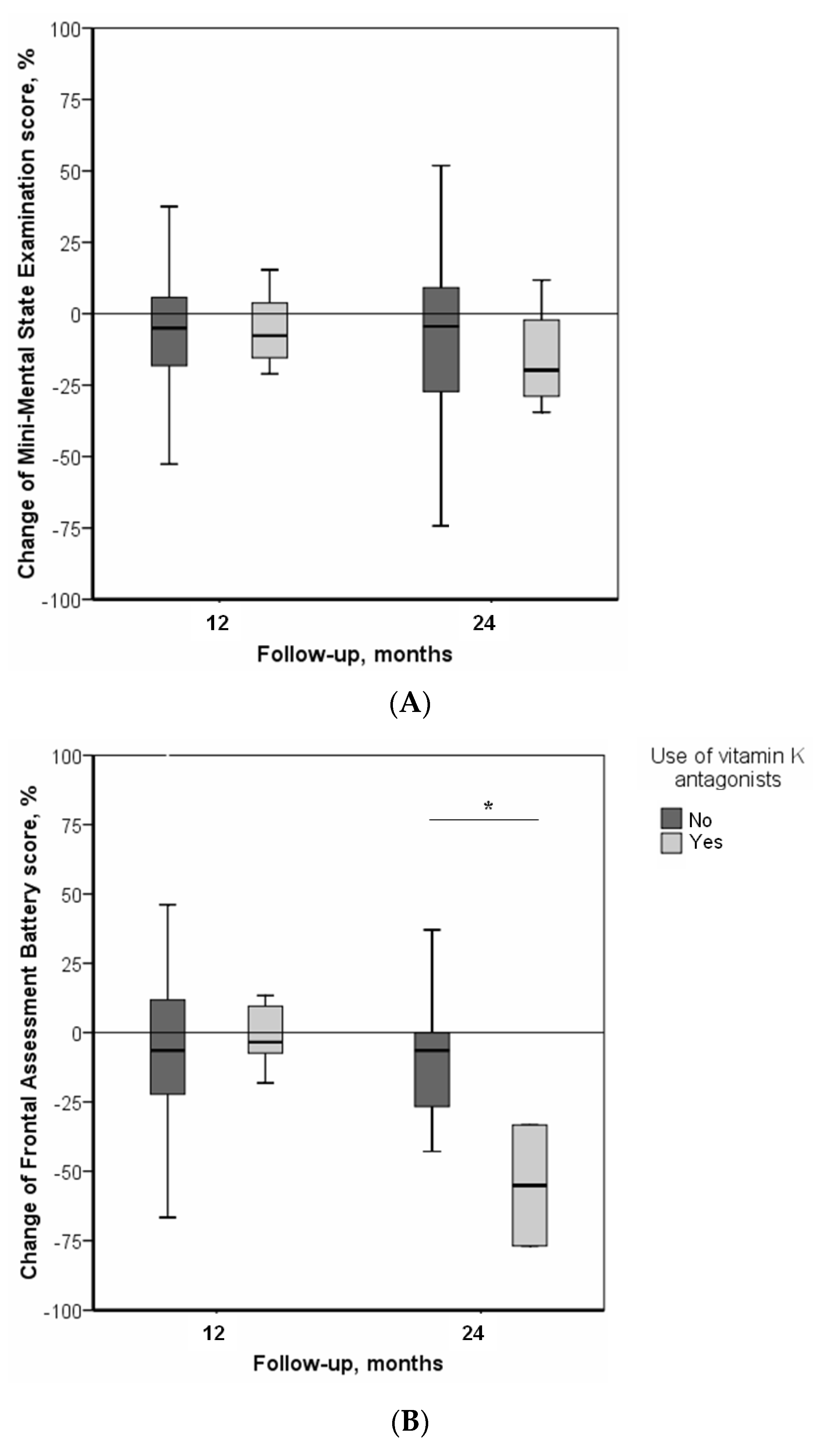
| Use Vitamin K Antagonists | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| β | [95% CI] | p-Value | |
| Change in MMSE score * | |||
| After 12 months of follow-up | −4.38 | [−21.08, 12.32] | 0.603 |
| After 24 months of follow-up | 45.21 | [−26.35, 116.78] | 0.201 |
| Change in FAB score † | |||
| After 12 months of follow-up | 14.35 | [−53.54, 82.24] | 0.659 |
| After 24 months of follow-up | −203.57 | [−246.14, −161.00] | 0.010 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brangier, A.; Ferland, G.; Rolland, Y.; Gautier, J.; Féart, C.; Annweiler, C. Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up. Nutrients 2018, 10, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060666
Brangier A, Ferland G, Rolland Y, Gautier J, Féart C, Annweiler C. Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up. Nutrients. 2018; 10(6):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060666
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrangier, Antoine, Guylaine Ferland, Yves Rolland, Jennifer Gautier, Catherine Féart, and Cedric Annweiler. 2018. "Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up" Nutrients 10, no. 6: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060666
APA StyleBrangier, A., Ferland, G., Rolland, Y., Gautier, J., Féart, C., & Annweiler, C. (2018). Vitamin K Antagonists and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: A 24-Month Follow-Up. Nutrients, 10(6), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10060666






