Human Breast Milk NMR Metabolomic Profile across Specific Geographical Locations and Its Association with the Milk Microbiota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Breast Milk Sample Collection
2.2. Breast Milk Metabolite Profiling
2.3. Breast Milk DNA Extraction and Microbial 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
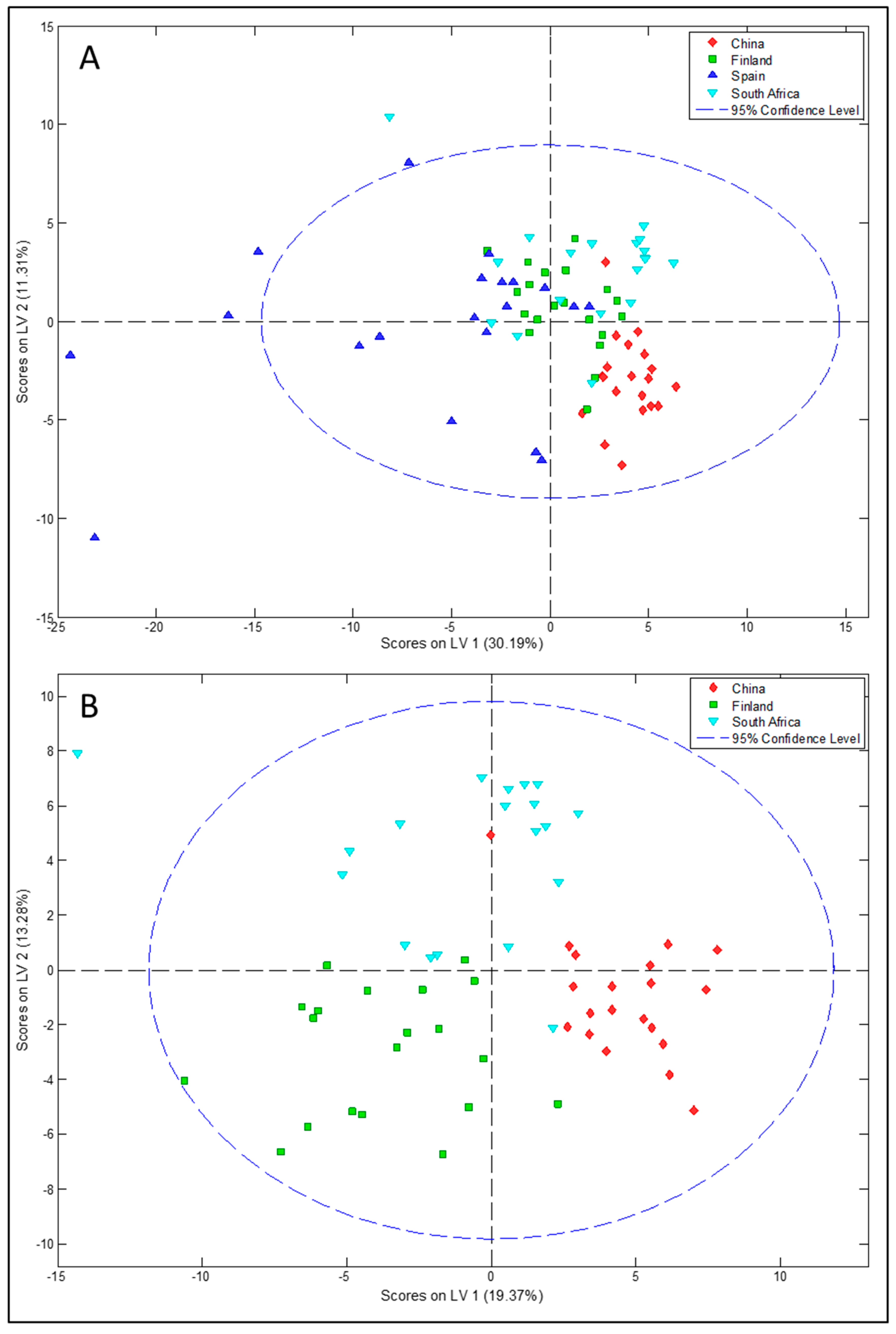
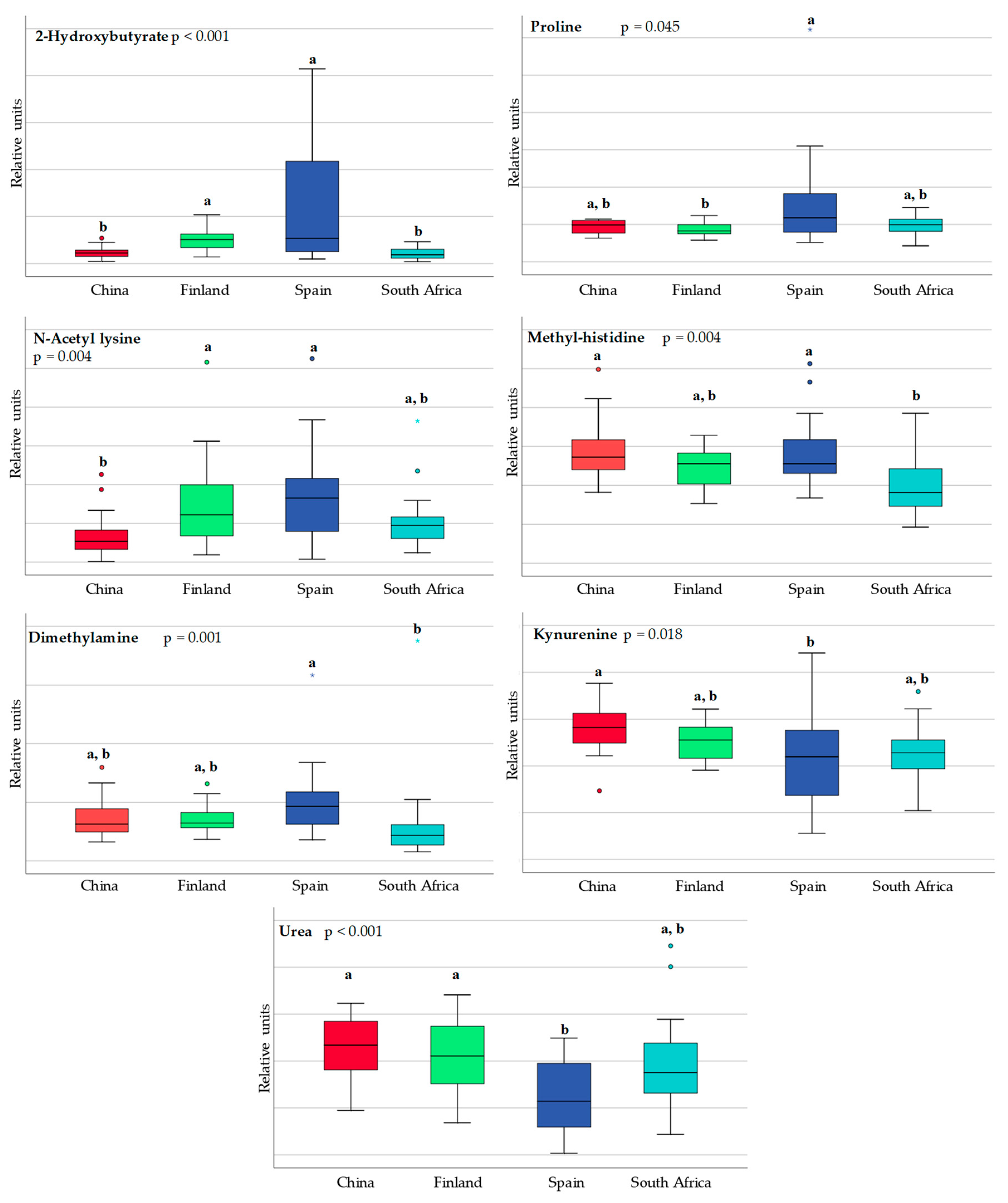
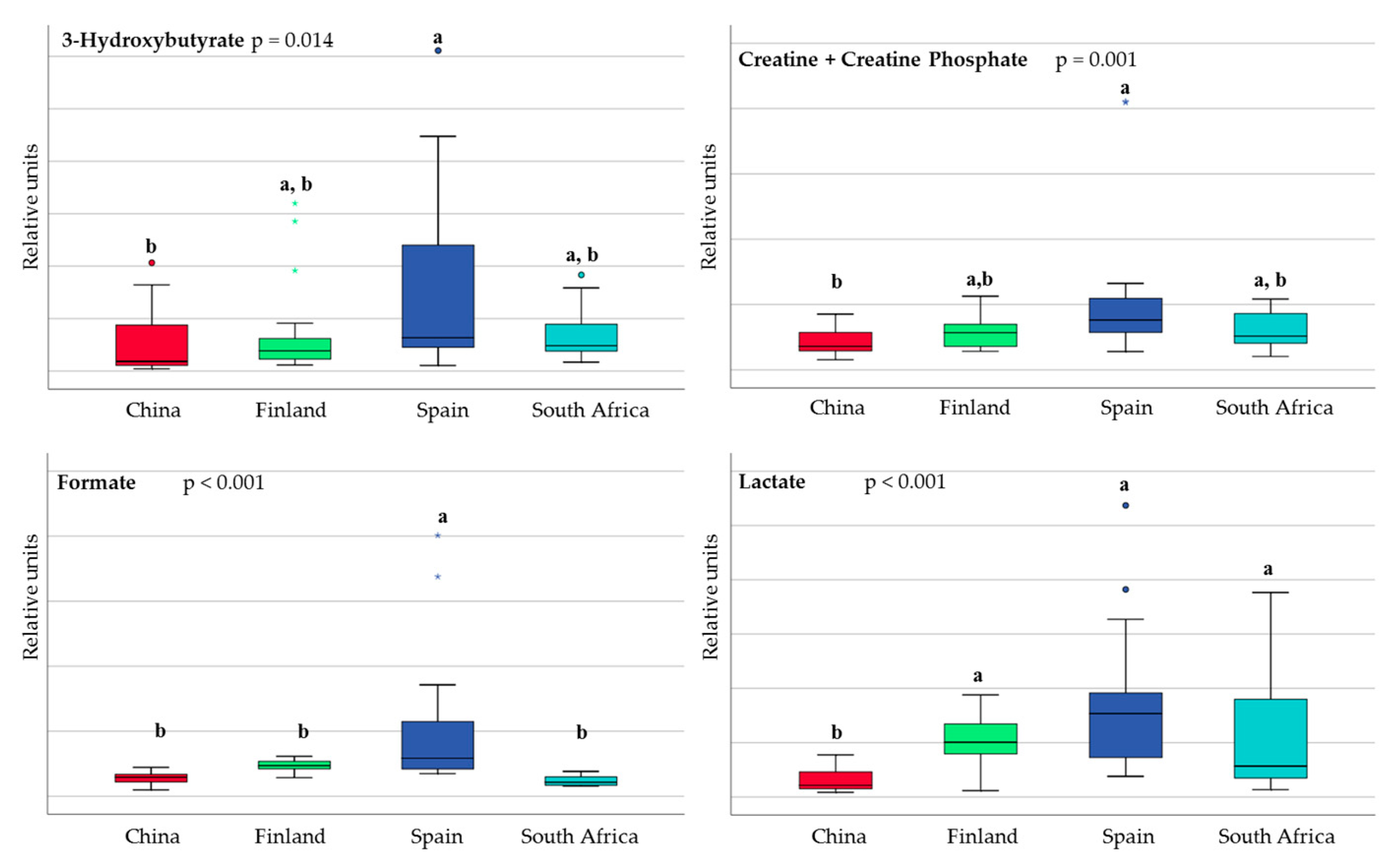
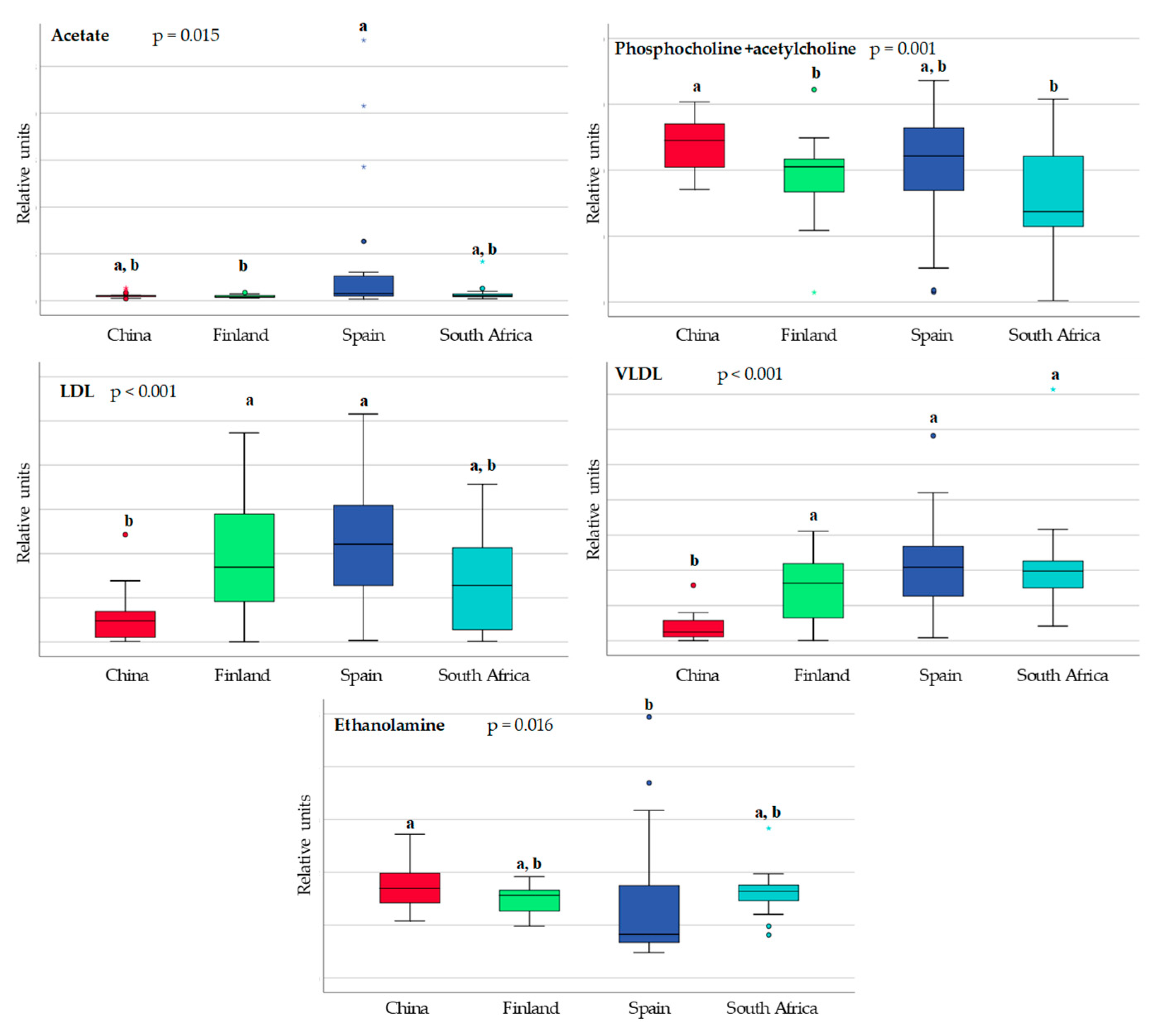
3.1. Differences in Milk Metabolites between Countries
3.2. Impact of Mode of Delivery on Human Milk Metabolites
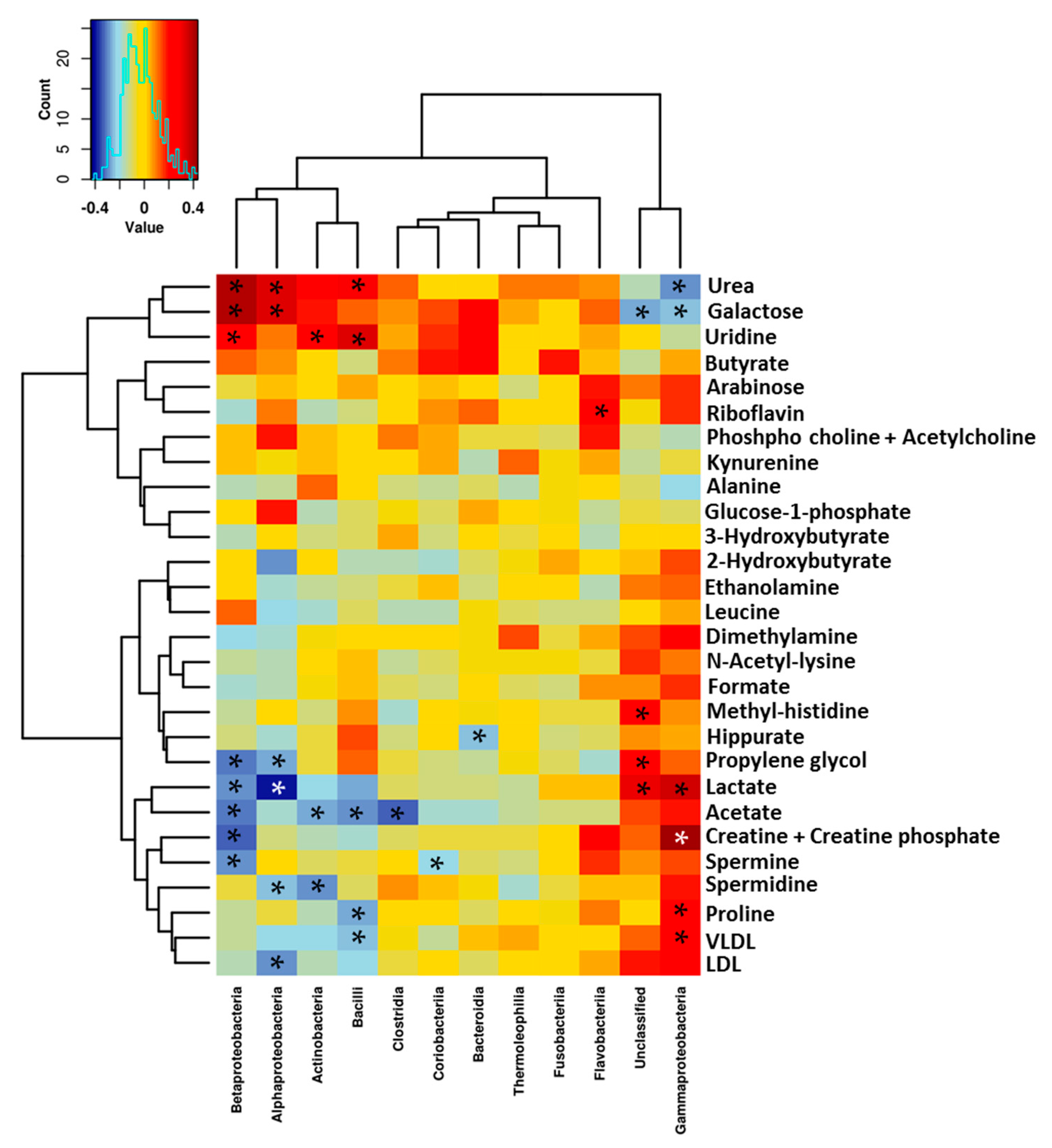
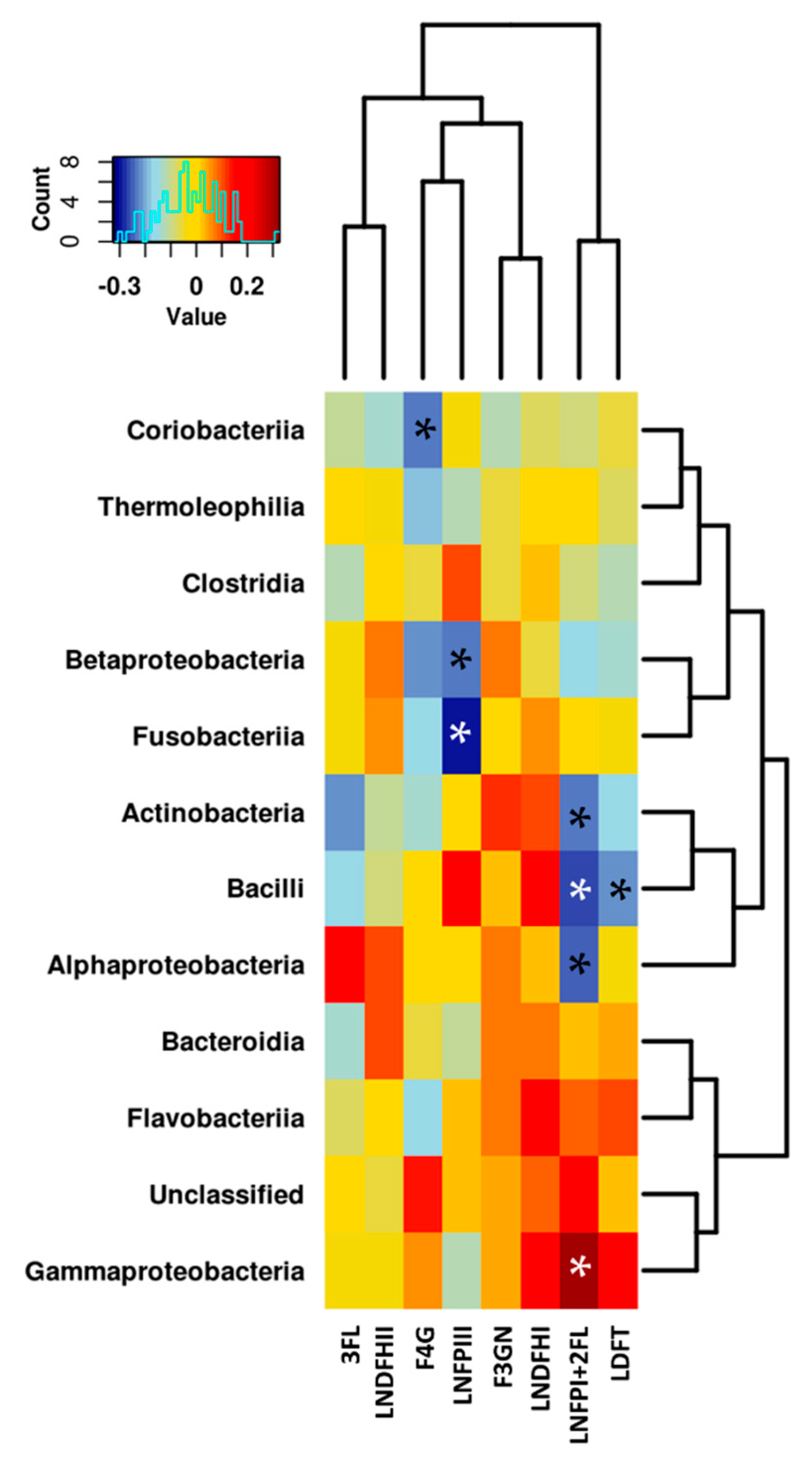
3.3. Relationship between the NMR Metabolomic Profile and Milk Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smilowitz, J.T.; O’Sullivan, A.; Barile, D.; German, J.B.; Lonnerdal, B.; Slupsky, C.M. The human milk metabolome reveals diverse oligosaccharide profiles. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuebe, A. The risks of not breastfeeding for mothers and infants. Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 2, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lodge, C.J.; Tan, D.J.; Lau, M.X.; Dai, X.; Tham, R.; Lowe, A.J.; Bowatte, G.; Allen, K.J.; Dharmage, S.C. Breastfeeding and asthma and allergies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luccioli, S.; Zhang, Y.; Verrill, L.; Ramos-Valle, M.; Kwegyir-Afful, E. Infant feeding practices and reported food allergies at 6 years of age. Pediatrics 2014, 134 (Suppl. 1), S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jwa, S.C.; Fujiwara, T.; Kondo, N. Latent protective effects of breastfeeding on late childhood overweight and obesity: A nationwide prospective study. Obesity 2014, 22, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marseglia, L.; Manti, S.; D’Angelo, G.; Cuppari, C.; Salpietro, V.; Filippelli, M.; Trovato, A.; Gitto, E.; Salpietro, C.; Arrigo, T. Obesity and breastfeeding: The strength of association. Women Birth 2015, 28, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longini, M.; Tataranno, M.L.; Proietti, F.; Tortoriello, M.; Belvisi, E.; Vivi, A.; Tassini, M.; Perrone, S.; Buonocore, G. A metabolomic study of preterm and term human and formula milk by proton MRS analysis: Preliminary results. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27 (Suppl. 2), 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.E.; Price, W.J.; Shafii, B.; Yahvah, K.M.; Bode, L.; McGuire, M.A.; McGuire, M.K. Relationships among microbial communities, maternal cells, oligosaccharides, and macronutrients in human milk. J. Hum. Lact. 2017, 33, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; du Toit, E.; Kulkarni, A.; Aakko, J.; Linderborg, K.M.; Yumei, Z.; Nicol, M.P.; Isolauri, E.; Yang, B.; Collado, M.C.; et al. Distinct patterns in human milk microbiota and fatty acid profiles across specific geographic locations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix-Amoros, A.; Collado, M.C.; Mira, A. Relationship between milk microbiota, bacterial load, macronutrients, and human cells during lactation. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munblit, D.; Boyle, R.J.; Warner, J.O. Factors affecting breast milk composition and potential consequences for development of the allergic phenotype. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.Y. Factors affecting human milk composition. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, O.; Morrow, A.L. Human milk composition nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 60, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuhas, R.; Pramuk, K.; Lien, E.L. Human milk fatty acid composition from nine countries varies most in DHA. Lipids 2006, 41, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gallego, C.; Kumar, H.; Garcia-Mantrana, I.; du Toit, E.; Suomela, J.P.; Linderborg, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Isolauri, E.; Yang, B.; Salminen, S.; et al. Breast milk polyamines and microbiota interactions: Impact of mode of delivery and geographical location. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, M.K.; Meehan, C.L.; McGuire, M.A.; Williams, J.E.; Foster, J.; Sellen, D.W.; Kamau-Mbuthia, E.W.; Kamundia, E.W.; Mbugua, S.; Moore, S.E.; et al. What’s normal? Oligosaccharide concentrations and profiles in milk produced by healthy women vary geographically. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.W.; Watanabe, K.; Hsu, C.C.; Chao, S.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, C.C.; Cao, Y.M.; Huang, H.C.; Chang, C.H.; et al. Bacterial composition and diversity in breast milk samples from mothers living in Taiwan and mainland China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Downey, E.; O’Mahony, J.A.; O’Shea, C.A.; Ryan, C.A.; Kelly, A.L.; Bertram, H.C. The effect of gestational and lactational age on the human milk metabolome. Nutrients 2016, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spevacek, A.R.; Smilowitz, J.T.; Chin, E.L.; Underwood, M.A.; German, J.B.; Slupsky, C.M. Infant maturity at birth reveals minor differences in the maternal milk metabolome in the first month of lactation. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitoulas, L.R.; Kent, J.C.; Cox, D.B.; Owens, R.A.; Sherriff, J.L.; Hartmann, P.E. Variation in fat, lactose and protein in human milk over 24 h and throughout the first year of lactation. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.S.; Li, S.H.; Guo, Y.; Lu, J.H.; He, J.R.; Luo, B.J.; Jiang, F.J.; Shen, H.; Papasian, C.J.; Pang, H.; et al. Composition of gut microbiota in infants in china and global comparison. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallani, M.; Young, D.; Scott, J.; Norin, E.; Amarri, S.; Adam, R.; Aguilera, M.; Khanna, S.; Gil, A.; Edwards, C.A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota of 6-week-old infants across europe: Geographic influence beyond delivery mode, breast-feeding, and antibiotics. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Preter, V.; Vanhoutte, T.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; Rutgeerts, P.; Verbeke, K. Effect of lactulose and Saccharomyces boulardii administration on the colonic urea-nitrogen metabolism and the bifidobacteria concentration in healthy human subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, D.K.; Allen, L.H. Overview of nutrients in human milk. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 278s–294s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegou, M.; Gondret, F.; Lalande-Martin, J.; Tea, I.; Baeza, E.; Louveau, I. NMR-based metabolomics highlights differences in plasma metabolites in pigs exhibiting diet-induced differences in adiposity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Rios, A.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Mata, P.; Fuentes, F.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Alonso, R.; Caballero, J.; Mata, N.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Ordovas, J.M. Polymorphism at the TRIB1 gene modulates plasma lipid levels: Insight from the Spanish familial hypercholesterolemia cohort study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith-Dennis, L.; Xu, G.; Goonatilleke, E.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Underwood, M.A.; Smilowitz, J.T. Composition and variation of macronutrients, immune proteins, and human milk oligosaccharides in human milk from nonprofit and commercial milk banks. J. Hum. Lact. 2018, 34, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Warren, C.D.; Altaye, M.; Morrow, A.L.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.; Pickering, L.K.; Newburg, D.S. Fucosylated human milk oligosaccharides vary between individuals and over the course of lactation. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunz, C.; Rudloff, S.; Baier, W.; Klein, N.; Strobel, S. Oligosaccharides in human milk: Structural, functional, and metabolic aspects. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2000, 20, 699–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.C.; Lewis, Z.T.; Krishnan, S.; Bernstein, R.M.; Moore, S.E.; Prentice, A.M.; Mills, D.A.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Zivkovic, A.M. Growth and morbidity of Gambian infants are influenced by maternal milk oligosaccharides and infant gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurl, S.; Munzert, M.; Boehm, G.; Matthews, C.; Stahl, B. Systematic review of the concentrations of oligosaccharides in human milk. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sprenger, N.; Lee, L.Y.; De Castro, C.A.; Steenhout, P.; Thakkar, S.K. Longitudinal change of selected human milk oligosaccharides and association to infants’ growth, an observatory, single center, longitudinal cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, L.; Kim, H.Y.; Hsiao, L.; Nissan, C.; Kankasa, C.; Mwiya, M.; Thea, D.M.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Bode, L. Oligosaccharide composition of breast milk influences survival of uninfected children born to HIV-infected mothers in Lusaka, Zambia. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aakko, J.; Kumar, H.; Rautava, S.; Wise, A.; Autran, C.; Bode, L.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Human milk oligosaccharide categories define the microbiota composition in human colostrum. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Goncalves, D.; Vinera, J.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Backhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 2014, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiminez, E.; Marin, M.L.; Xaus, J.; Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, J.M. Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, G.; de Los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G.; Fernandez, N.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M. Establishment and development of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria microbiota in breast-milk and the infant gut. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, M.A.; Maningat, P.; Sunehag, A.L.; Haymond, M.W. Precursors of hexoneogenesis within the human mammary gland. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E680–E687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belenguer, A.; Duncan, S.H.; Calder, A.G.; Holtrop, G.; Louis, P.; Lobley, G.E.; Flint, H.J. Two routes of metabolic cross-feeding between bifidobacterium adolescentis and butyrate-producing anaerobes from the human gut. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, C.; Ganzle, M. Lactic acid bacteria fermentation of human milk oligosaccharide components, human milk oligosaccharides and galactooligosaccharides. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 315, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewaschuk, J.B.; Naylor, J.M.; Zello, G.A. D-lactate in human and ruminant metabolism. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.; Toh, H.; Taylor, T.D.; Ohno, H.; Hattori, M. Acetate-producing bifidobacteria protect the host from enteropathogenic infection via carbohydrate transporters. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and their role as members of the human gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix-Amorós, A.; Martinez-Costa, C.; Querol, A.; Collado, M.C.; Mira, A. Multiple approaches detect the presence of fungi in human breastmilk samples from healthy mothers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guertin, K.A.; Moore, S.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Huang, W.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Sinha, R.; Cross, A.J. Metabolomics in nutritional epidemiology: Identifying metabolites associated with diet and quantifying their potential to uncover diet-disease relations in populations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Playdon, M.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Cross, A.J.; Sinha, R.; Guertin, K.A.; Moy, K.A.; Rothman, N.; Irwin, M.L.; Mayne, S.T.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; et al. Comparing metabolite profiles of habitual diet in serum and urine. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.; Panasevich, M.R.; Alexander, D.; Vester Boler, B.M.; Rossoni Serao, M.C.; Faber, T.A.; Bauer, L.L.; Fahey, G.C. Fecal metabolomics of healthy breast-fed versus formula-fed infants before and during in vitro batch culture fermentation. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2534–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Metabolite | Origin |
|---|---|
| Amino acids and derivatives | |
| 2-Hydroxybutyrate (3.99) | endogenous |
| 2-Hydroxyisovalerate (0.95) | endogenous |
| Alanine (1.47) | endogenous |
| Anserine (8.91) | diet |
| Creatinine (3.03) | endogenous |
| Dimethylamine (2.72) | endogenous |
| Glutamate (2.34) | endogenous |
| Glutamine (2.47) | endogenous |
| Carnitine (3.21) | endogenous |
| Histidine (7.09) | endogenous |
| Isoleucine (0.99) | diet |
| Kynurenine (6.81) | endogenous |
| Leucine (0.94) | diet |
| Methionine (2.62) | diet |
| Methyl-histidine (7.88) | endogenous |
| N-Acetyl lysine (1.79) | endogenous |
| Phenylalanine (7.36) | endogenous |
| Proline (3.34) | endogenous |
| Taurine (3.25) | endogenous |
| Tryptophan (7.70) | diet |
| Tyrosine (3.06) | endogenous |
| Urea (5.77) | endogenous |
| Valine (0.98) | diet |
| Energy metabolites | |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate (1.17) | endogenous |
| Citrate (2.69) | endogenous |
| Creatine (3.01) | endogenous |
| Creatine-phosphate (3.02) | endogenous |
| Formate (8.44) | endogenous |
| Lactate (1.32) | endogenous |
| NADH (8.46) | endogenous |
| Neurotransmitters, growth factors and second messengers | |
| 4-Aminobutyrate (2.29) | endogenous |
| Putrescine (1.75) | microbial |
| Spermidine (2.61) | endogenous |
| Spermine (2.70) | endogenous |
| Fatty acids and associated metabolites | |
| 4-Aminohippurate (2.29) | endogenous |
| Acetate (1.91) | endogenous |
| Acetylcholine (3.21) | endogenous |
| Butyrate (2.16) | microbial |
| Choline (4.06) | diet |
| Ethanolamine (3.13) | endogenous |
| Glycero-3-phosphocholine (3.22) | endogenous |
| LDL * (1.29) | endogenous |
| Phosphocholine (3.2) | endogenous |
| VLDL * (1.27) | endogenous |
| Sugars and derivatives | |
| 1,6-anhydro-B-glucose (5.44) | diet |
| 2-fucosyllactose (5.31) | endogenous |
| 3-fucosyllactose (5.37) | endogenous |
| Arabinose (4.51) | microbial |
| Fucosyl-α-1,3-N-acetylglucosamine (5.14) | endogenous |
| Fucosyl-α-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine (5.01) | endogenous |
| Fucose (4.55) | endogenous |
| Galactose (4.57) | endogenous |
| Glucose (3.23) | endogenous |
| Glucose-1-phosphate (5.45) | endogenous |
| Lactose (3.75) | endogenous |
| Lactodifucotetraose (5.27) | endogenous |
| Lacto-N-difucohexaose I (5.18) | endogenous |
| Lacto-N-difucohexaose II (5.36) | endogenous |
| Lacto-N-fucopentaose I (5.31) | endogenous |
| Lacto-N-fucopentaose III (5.1) | endogenous |
| Myo-inositol (4.05) | endogenous |
| N-Acetylglucosamine (3.91) | endogenous |
| Vitamins and nucleosides | |
| Riboflavin (B2) (7.96) | diet |
| Uridine (5.92) | endogeonous |
| Others | |
| Ethanol (1.16) | diet |
| Hippurate (7.55) | microbial |
| Propylene glycol (1.14) | diet |
| Metabolite | China | Finland | Spain | South Africa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-fucosyllactose | 0.739 | 0.971 | 0.190 | ↑ 0.035 * |
| Alanine | 0.853 | 0.739 | 0.280 | ↑ 0.022 * |
| Butyrate | 0.579 | 0.579 | 0.436 | ↑ 0.006 * |
| Dimethylamine | 0.971 | 0.035 * | ↑ 0.035 * | 0.002 * |
| Ethanolamine | 0.631 | 0.579 | ↑ 0.000 * | 0.661 |
| Formate | ↑ 0.035 * | 0.684 | 0.796 | 0.006 * |
| Fucosyl-α-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine | 0.631 | 0.035 * | 0.247 | 0.002 * |
| Galactose | 0.579 | 0.579 | 0.481 | ↑ 0.002 * |
| Hippurate | 0.684 | 0.063 | ↑ 0.009 * | 0.022 * |
| Kynurenine | 0.143 | 0.075 | ↑ 0.011 * | 0.028 * |
| Lactodifucotetraose | 0.247 | ↑ 0.035 * | 0.247 | 0.447 |
| Leucine | 0.631 | ↑ 0.043 * | ↑ 0.009 * | 1.000 |
| Lacto-N-fucopentaose I and 2-fucosyllactose | 0.353 | 1.000 | 0.971 | 0.035 * |
| Lacto-N-fucopentaose III | 0.579 | 0.796 | 0.631 | 0.001 * |
| Methyl-histidine | 0.353 | 0.684 | ↑ 0.023 * | 0.043 * |
| Phosphocholine and acetylcholine | 0.393 | 0.796 | 1.000 | 0.002 * |
| Proline | 0.393 | 0.739 | ↑ 0.002 * | 1.000 |
| Propylene glycol | 0.912 | 0.089 | ↑ 0.023 * | 0.004 * |
| Riboflavin | 0.529 | 0.353 | ↑ 0.002 * | 0.400 |
| Spermidine | 0.579 | 0.353 | ↑ 0.000 * | 0.604 |
| Spermine | 0.143 | 0.315 | 0.853 | 0.003 * |
| Urea | 0.436 | 0.247 | 0.280 | 0.000 * |
| Uridine | 0.529 | 0.912 | 0.019 * | 0.243 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Gallego, C.; Morales, J.M.; Monleón, D.; Du Toit, E.; Kumar, H.; Linderborg, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S.; et al. Human Breast Milk NMR Metabolomic Profile across Specific Geographical Locations and Its Association with the Milk Microbiota. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101355
Gómez-Gallego C, Morales JM, Monleón D, Du Toit E, Kumar H, Linderborg KM, Zhang Y, Yang B, Isolauri E, Salminen S, et al. Human Breast Milk NMR Metabolomic Profile across Specific Geographical Locations and Its Association with the Milk Microbiota. Nutrients. 2018; 10(10):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101355
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Gallego, Carlos, Jose Manuel Morales, Daniel Monleón, Elloise Du Toit, Himanshu Kumar, Kaisa M. Linderborg, Yumei Zhang, Baoru Yang, Erika Isolauri, Seppo Salminen, and et al. 2018. "Human Breast Milk NMR Metabolomic Profile across Specific Geographical Locations and Its Association with the Milk Microbiota" Nutrients 10, no. 10: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101355
APA StyleGómez-Gallego, C., Morales, J. M., Monleón, D., Du Toit, E., Kumar, H., Linderborg, K. M., Zhang, Y., Yang, B., Isolauri, E., Salminen, S., & Collado, M. C. (2018). Human Breast Milk NMR Metabolomic Profile across Specific Geographical Locations and Its Association with the Milk Microbiota. Nutrients, 10(10), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101355






