Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An SAR ship detection framework via edge deformable convolution and point set representation is proposed, which can achieve the accurate detection of densely arranged multi-directional ships in port scenes.
- A feature extraction module based on edge deformable convolution is proposed, which explores the correlation between discontinuous target blocks in SAR images, suppressing speckle noise while learning the overall deformation features of ship targets.
- The RBF point set transformation function and the associated point set transformation penalty term are introduced, establishing efficient and accurate mapping between point set features and predicted rotation boxes. This approach enables the precise detection of ship target direction and position in complex scenes.
2. Related Work
2.1. Feature Extraction of Ship Targets in SAR Images
2.2. Ship Detection Method in SAR Images
3. Methodology
3.1. Method Overview
3.2. Feature Extraction Module via Edge Deformable Convolution
3.3. Multi-Directional Ship Detection Module via Point Set Transformation
- Classification quality assessmentWe measure the classification quality by utilizing the classification loss between the point set and the ground-truth . The specific formula is as follows:
- Localization quality assessmentThe localization quality is measured by the localization loss between the polygons generated from point sets and the ground-truth . The formula for localization quality is as follows:The location quality of a point set primarily focuses on the overlap extent between the polygon generated by the point set and the ground-truth while being insensitive to directional changes. This phenomenon is particularly evident in ship targets within remote sensing images.
- Oriented quality assessmentWe utilize the MinAeraRect point set transformation function to convert the predicted point set into oriented bounding boxes. Subsequently, we perform equidistant sampling along each edge of the oriented bounding boxes. Based on the sampled points, we compute the corner distance between the predicted box and the ground-truth box to determine the oriented quality of the point set. This process can be expressed as follows:where denotes the chamfer distance between two point sets.
4. Experiments
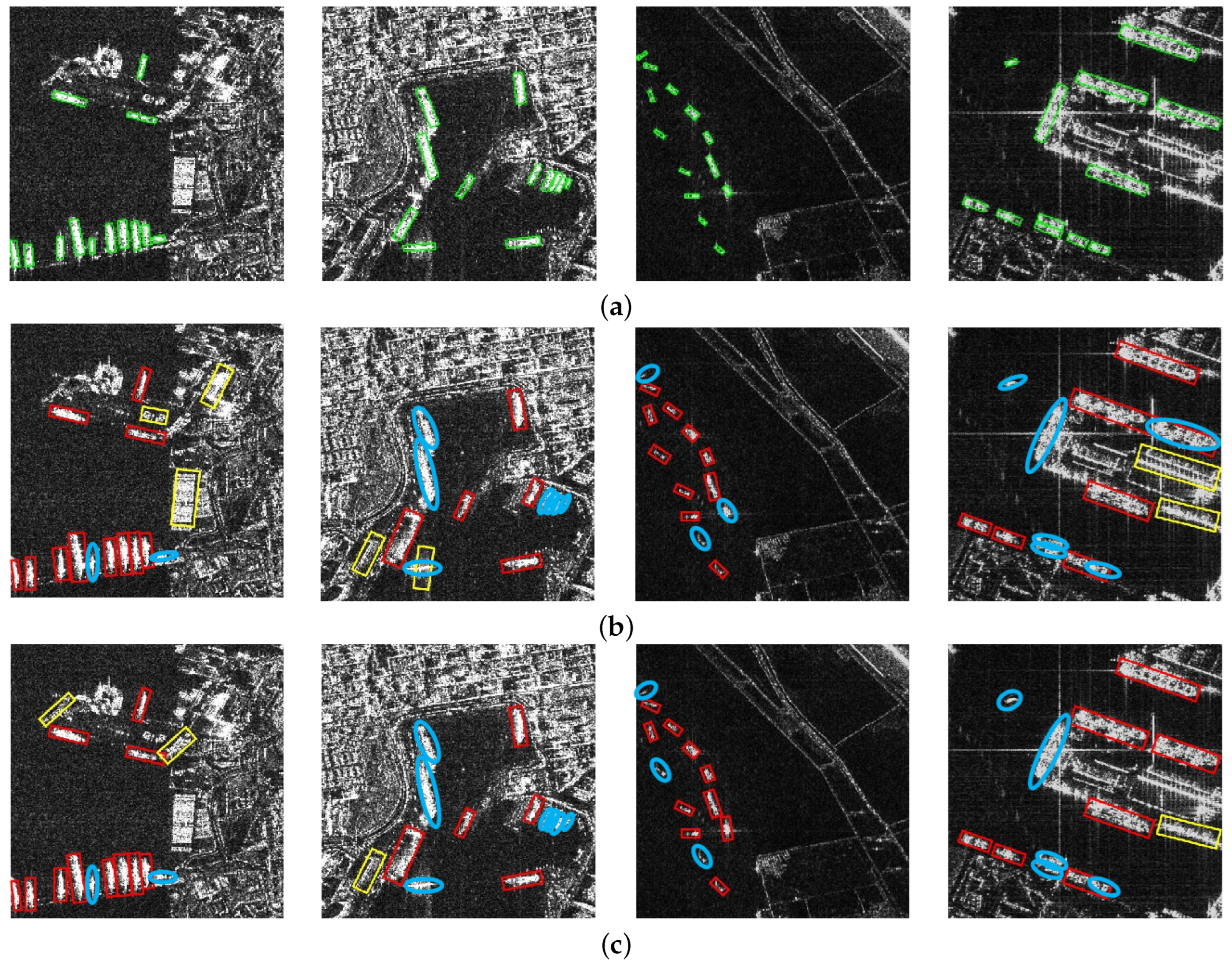
4.1. Datasets and Experimental Settings
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
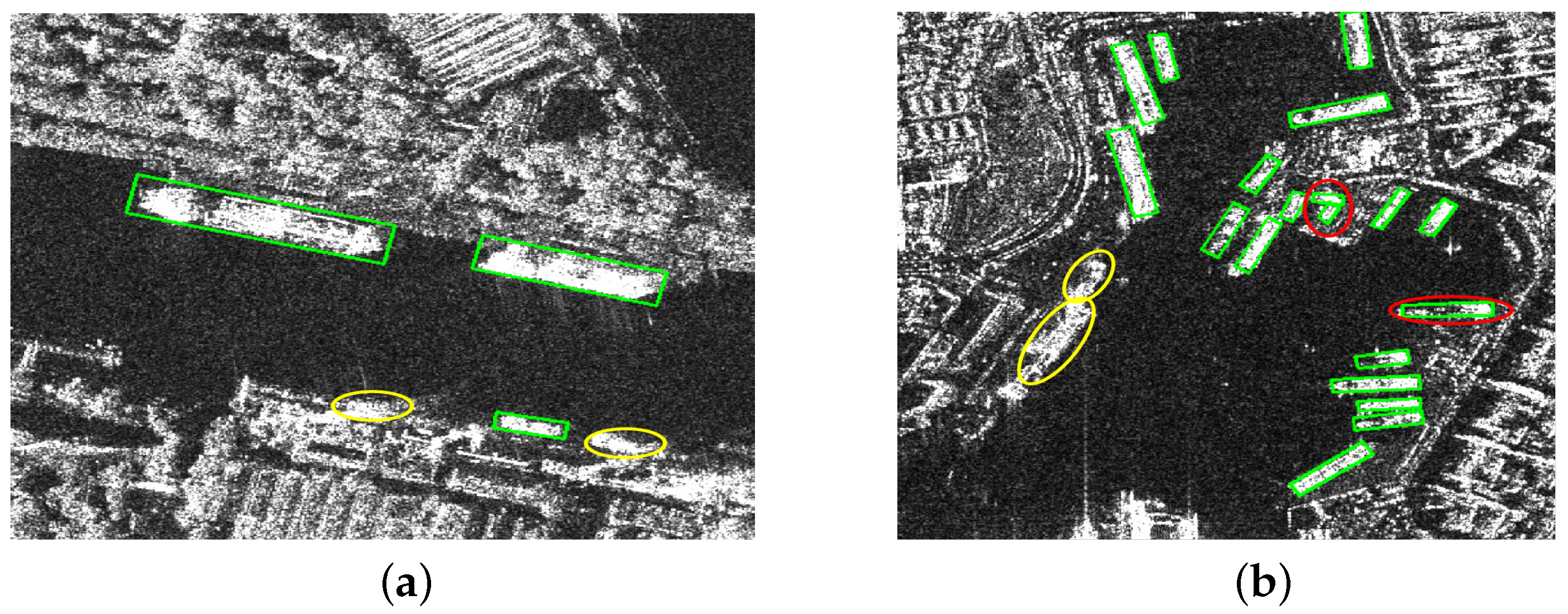
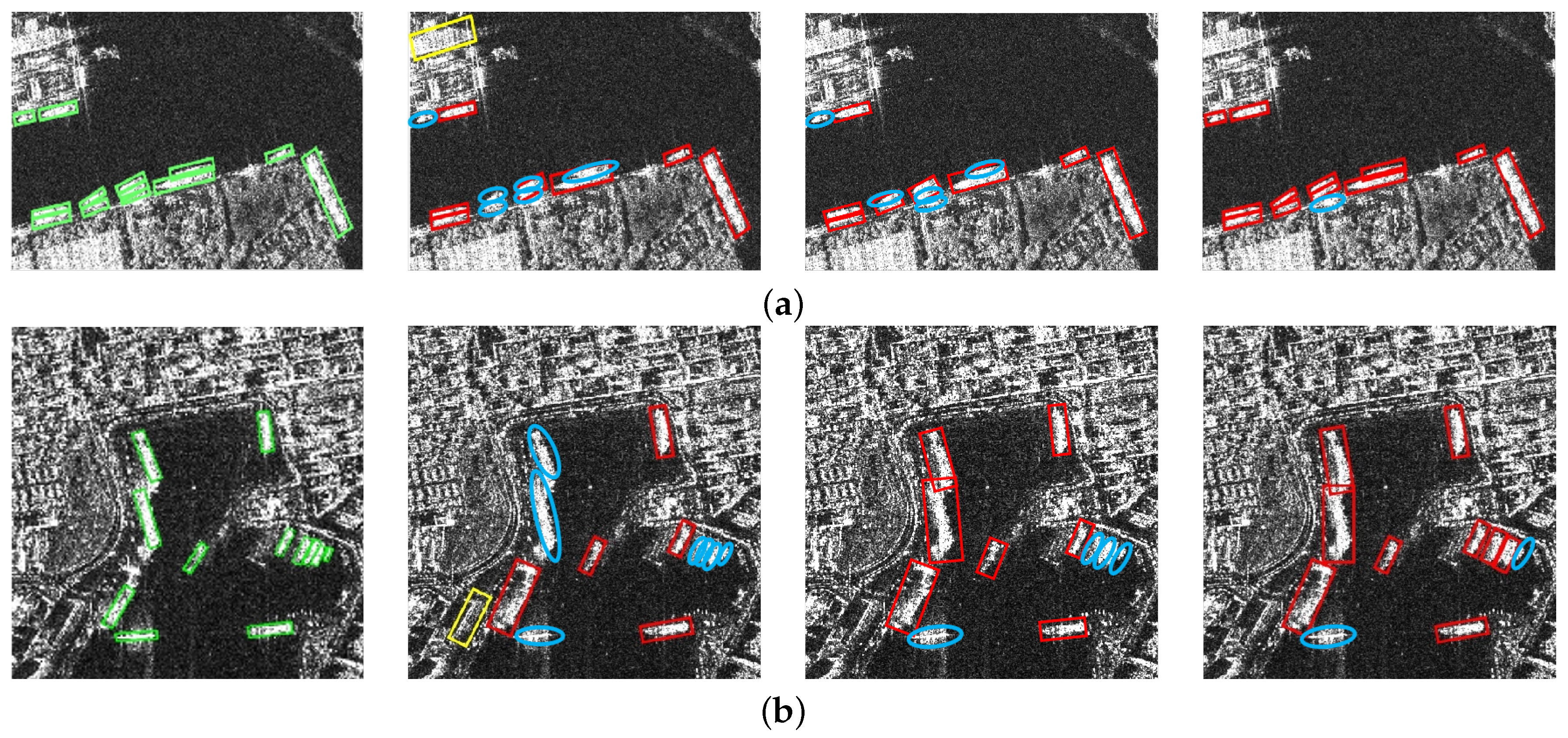
4.3. Ablation Experiments
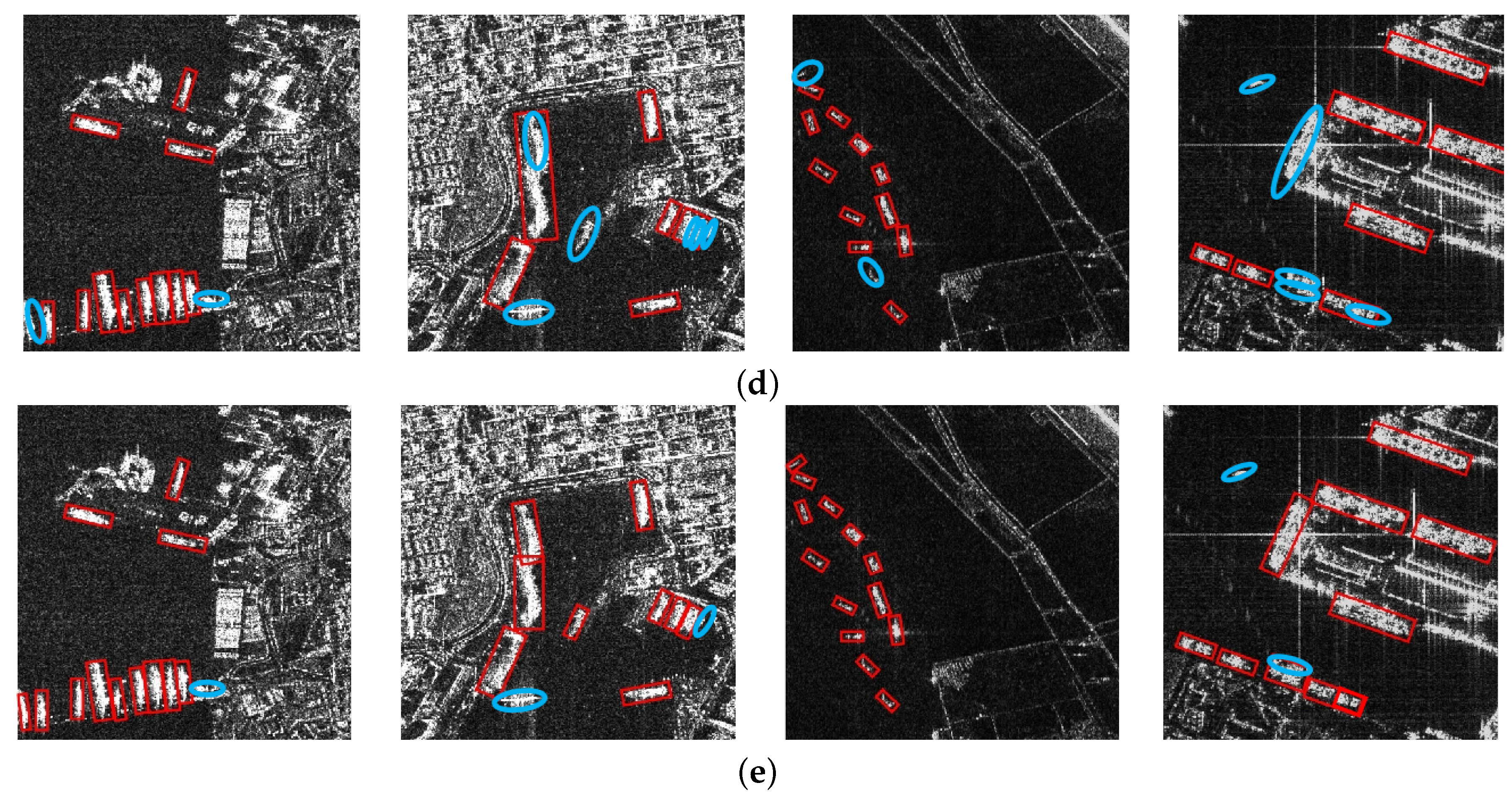
4.4. Comparison Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K. An advanced scheme for range ambiguity suppression of spaceborne SAR based on blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5230112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Qiu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, D. An advanced echo separation scheme for space-time waveform-encoding SAR based on digital beamforming and blind source separation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Yu, C. A Novel Spaceborne SAR Constellation Scheduling Algorithm for Sea Surface Moving Target Search Tasks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3715–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tang, S.; Chang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. A novel scheme for range ambiguity suppression of spaceborne SAR based on underdetermined blind source separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5207915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gens, R. Oceanographic applications of SAR remote sensing. GIScience Remote Sens. 2008, 45, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G. Statistical modeling of SAR images: A survey. Sensors 2010, 10, 775–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renga, A.; Graziano, M.D.; Moccia, A. Segmentation of marine SAR images by sublook analysis and application to sea traffic monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Deng, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Orbital Design Optimization for Large-Scale SAR Constellations: A Hybrid Framework Integrating Fuzzy Rules and Chaotic Sequences. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Ziyuan, Y.; Yanni, J.; Gui, G. Review of ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture imagery. J. Radar 2021, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Su, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, T. Deep learning for SAR ship detection: Past, present and future. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Cross-Sensor SAR Image Target Detection Based on Dynamic Feature Discrimination and Center-Aware Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5209417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Arbitrary-Direction SAR Ship Detection Method for Multiscale Imbalance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5208921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. SAR Small Ship Detection Based on Enhanced YOLO Network. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khesali, E.; Enayati, H.; Modiri, M.; Mohseni Aref, M. Automatic ship detection in Single-Pol SAR Images using texture features in artificial neural networks. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbay, K.; Özdemir, T.B. Ship Classification Based On Co-Occurrence Matrix and Support Vector Machines. Electrica 2024, 24, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, H. Ship target automatic detection based on hypercomplex flourier transform saliency model in high spatial resolution remote-sensing images. Sensors 2020, 20, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Hu, T.; Xia, Y.; Ma, B.; Sarwar, S.; Zhang, C. WDFA-YOLOX: A wavelet-driven and feature-enhanced attention YOLOX network for ship detection in SAR images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, D. An efficient and lightweight CNN model with soft quantification for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5230713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Liu, H.; Wan, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q. A-BFPN: An attention-guided balanced feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X. Quad-FPN: A novel quad feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, P.; Li, L.; Tian, T.; Tian, J. Two-stage cross-modality transfer learning method for military-civilian SAR ship recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4506405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Ji, K.; Yang, K.; Zou, H. A bilateral CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Shi, G. CFAR ship detection in nonhomogeneous sea clutter using polarimetric SAR data based on the notch filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4811–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pan, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, G. Adaptive CFAR method for SAR ship detection using intensity and texture feature fusion attention contrast mechanism. Sensors 2022, 22, 8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, C.; Shao, J. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 13–14 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, B.; Nie, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, X. Enhanced cascade R-CNN for multi-scale object detection in dense scenes from SAR images. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 20143–20153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; He, F.; Gui, C.; Dong, Z.; Xing, M. SAR target detection based on improved SSD with saliency map and residual network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A lightweight YOLO algorithm for multi-scale SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. A CenterNet++ model for ship detection in SAR images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yu, C.; Zhao, S.; Song, H. An anchor-free method based on transformers and adaptive features for arbitrarily oriented ship detection in SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 2012–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Momi, M.C.; Quan, S.; Ye, Z. ELLK-Net: An efficient lightweight large kernel network for SAR ship detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5221514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Han, B. A Lightweight Network for Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Edge Feature Aware and Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 99, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Yan, C. Scattering-Point-Guided Oriented RepPoints for Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhu, J. Oriented reppoints for aerial object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1829–1838. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Congan, X.; Hang, S.; Jianwei, L.; Yu, L.; Libo, Y.; Long, G.; Wenjun, Y.; Taoyang, W. RSDD-SAR: Rotated ship detection dataset in SAR images. J. Radars 2022, 11, 581–599. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhan, X.; Xu, Y.; Ke, X.; Zeng, T.; Su, H.; et al. SAR ship detection dataset (SSDD): Official release and comprehensive data analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3520–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Feng, Z.; He, T. R3det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3163–3171. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, C.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K. Rtmdet: An empirical study of designing real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.07784. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Qi, X.; Fan, H. LSR-Det: A Lightweight Detector for Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Oriented Bounding Box. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Dataset | SSDD | RSDD-SAR |
|---|---|---|
| Image number | 1160 | 7000 |
| Ship number | 2587 | 10,263 |
| Image size | 190–668 | |
| Number of sensors | 3 | 2 |
| Resolution (m) | 1–15 | 2–20 |
| Frequency bands covered |
| Method | EDConv | Point Set Transformation | P (%) | R (%) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | × | × | 90.24 | 89.12 | 89.48 |
| ✓ | × | 92.10 | 90.09 | 90.23 | |
| × | ✓ | 93.22 | 90.23 | 90.74 | |
| Proposed | ✓ | ✓ | 94.91 | 91.35 | 91.62 |
| Method | EDConv | Point Set Transformation | P (%) | R (%) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | × | × | 92.25 | 88.33 | 88.40 |
| ✓ | × | 93.47 | 90.40 | 90.66 | |
| × | ✓ | 95.02 | 91.70 | 91.85 | |
| Proposed | ✓ | ✓ | 95.45 | 92.12 | 92.81 |
| Method | P (%) | R (%) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotated-RetinaNet | 89.77 | 84.30 | 85.22 |
| Oriented Faster R-CNN | 90.20 | 85.45 | 86.98 |
| S2A-Net | 89.82 | 86.45 | 88.37 |
| R3Det | 90.61 | 86.50 | 88.86 |
| Oriented Reppoints | 90.24 | 89.12 | 89.48 |
| Rotated-RTMDet-s | 91.60 | 88.50 | 90.16 |
| LSD-Det | 92.45 | 90.25 | 90.34 |
| Proposed | 94.91 | 92.35 | 91.62 |
| Method | P (%) | R (%) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotated-RetinaNet | 89.35 | 83.52 | 85.58 |
| Oriented Faster R-CNN | 90.53 | 86.79 | 87.36 |
| S2A-Net | 88.80 | 90.39 | 89.78 |
| R3Det | 90.76 | 88.46 | 89.62 |
| Oriented Reppoints | 92.25 | 88.33 | 88.40 |
| Rotated-RTMDet-s | 92.43 | 89.94 | 90.65 |
| LSD-Det | 93.86 | 91.02 | 91.45 |
| Proposed | 95.45 | 92.12 | 92.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Xue, F.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091612
Guan T, Chang S, Deng Y, Xue F, Wang C, Jia X. Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091612
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Tianyue, Sheng Chang, Yunkai Deng, Fengli Xue, Chunle Wang, and Xiaoxue Jia. 2025. "Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091612
APA StyleGuan, T., Chang, S., Deng, Y., Xue, F., Wang, C., & Jia, X. (2025). Oriented SAR Ship Detection Based on Edge Deformable Convolution and Point Set Representation. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091612






