Mapping the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China over the Past Four Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
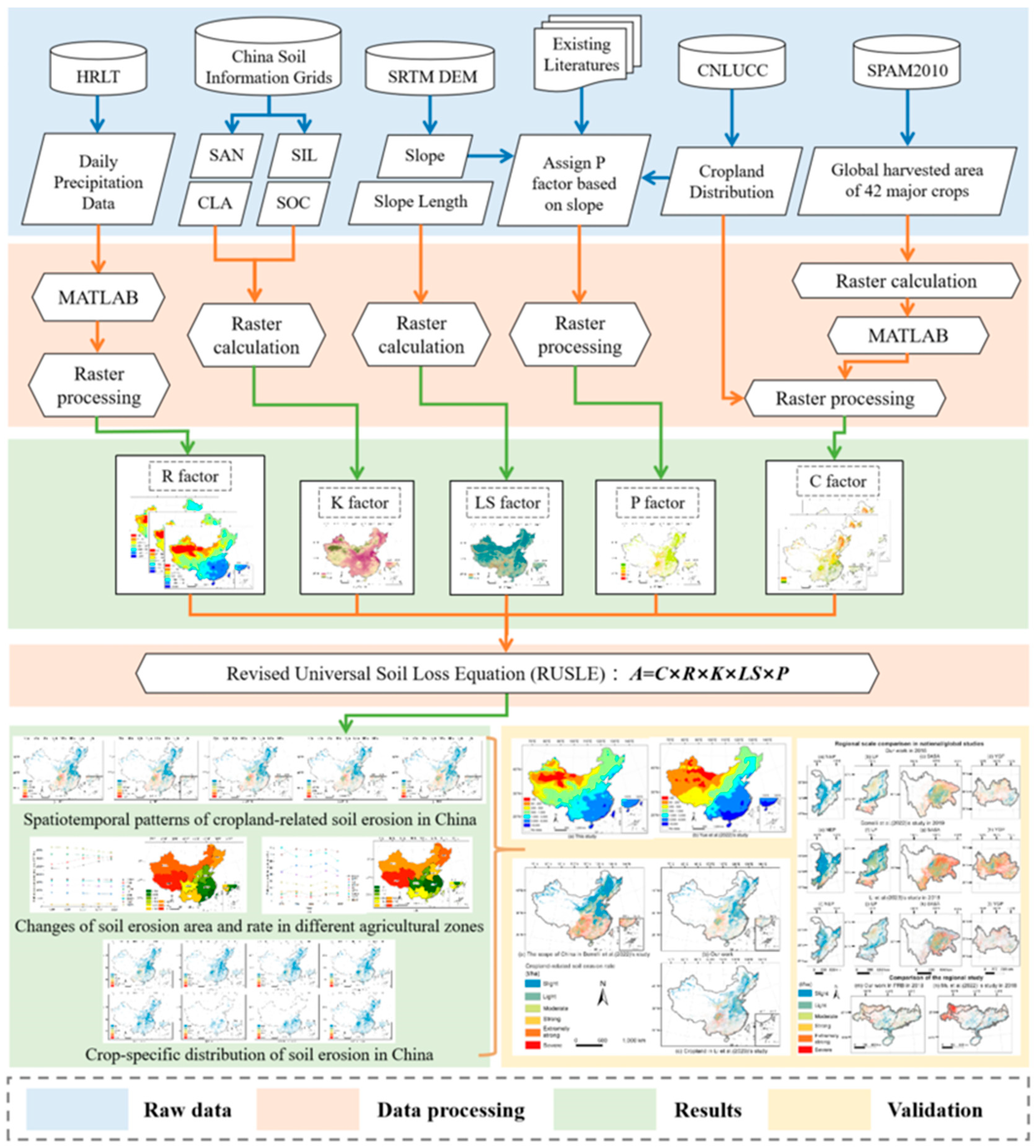
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Erosion Estimation
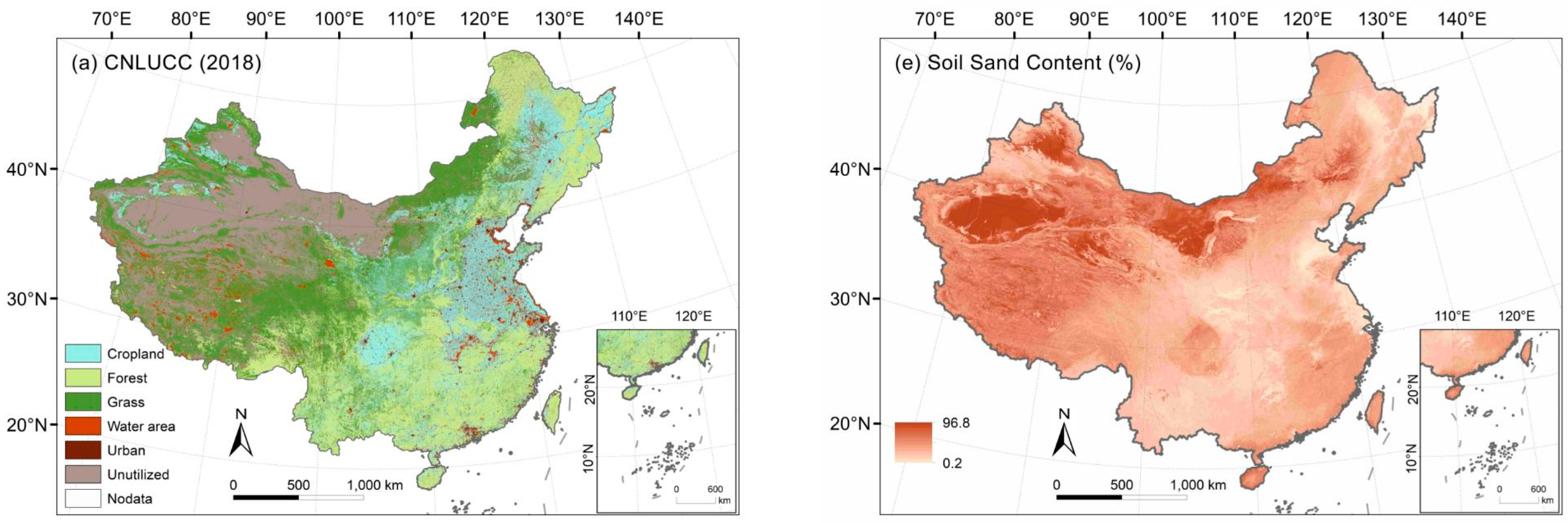
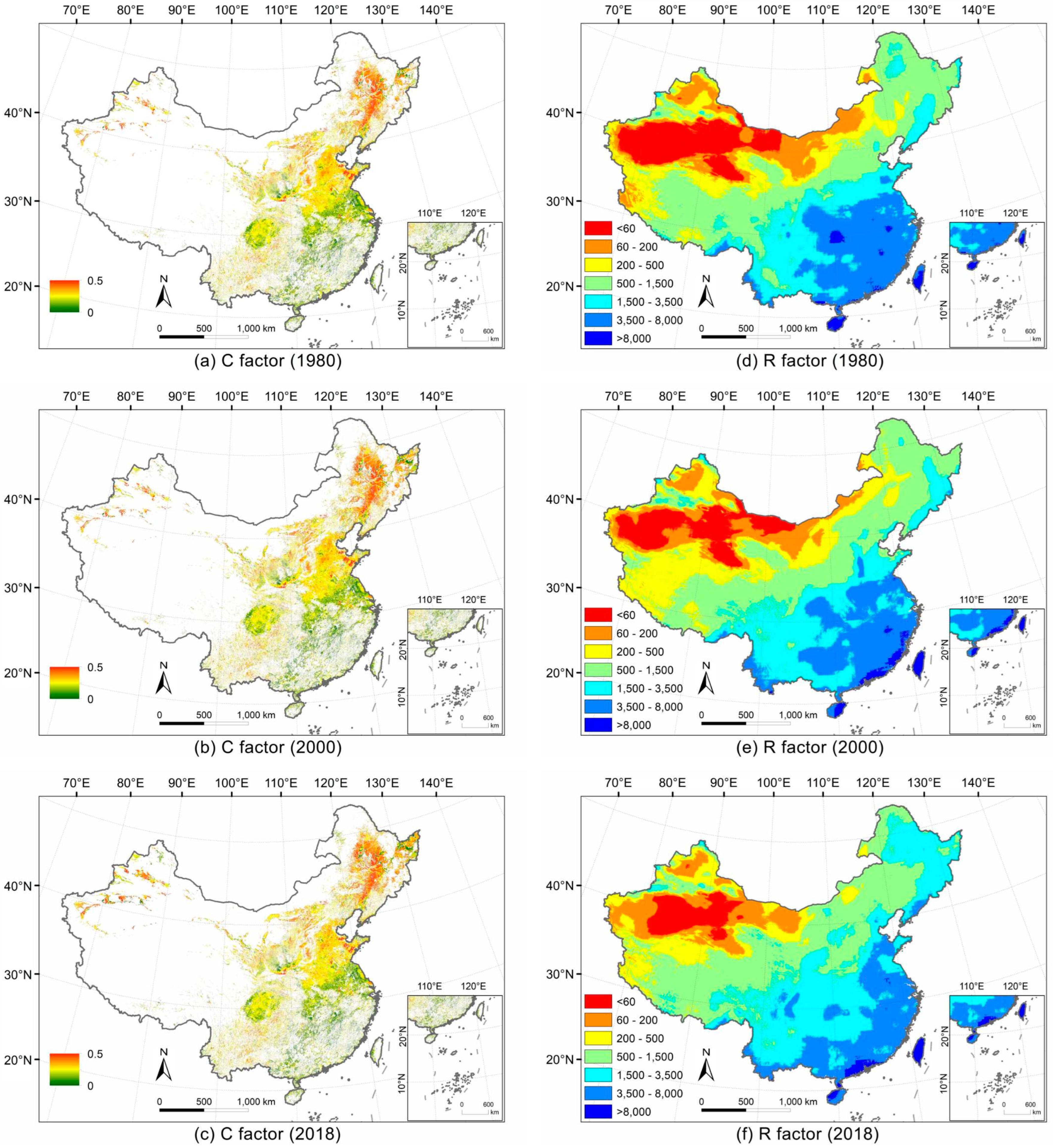
2.1.1. Land Cover and Management Factor for Cropland (C Factor)
2.1.2. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R Factor)
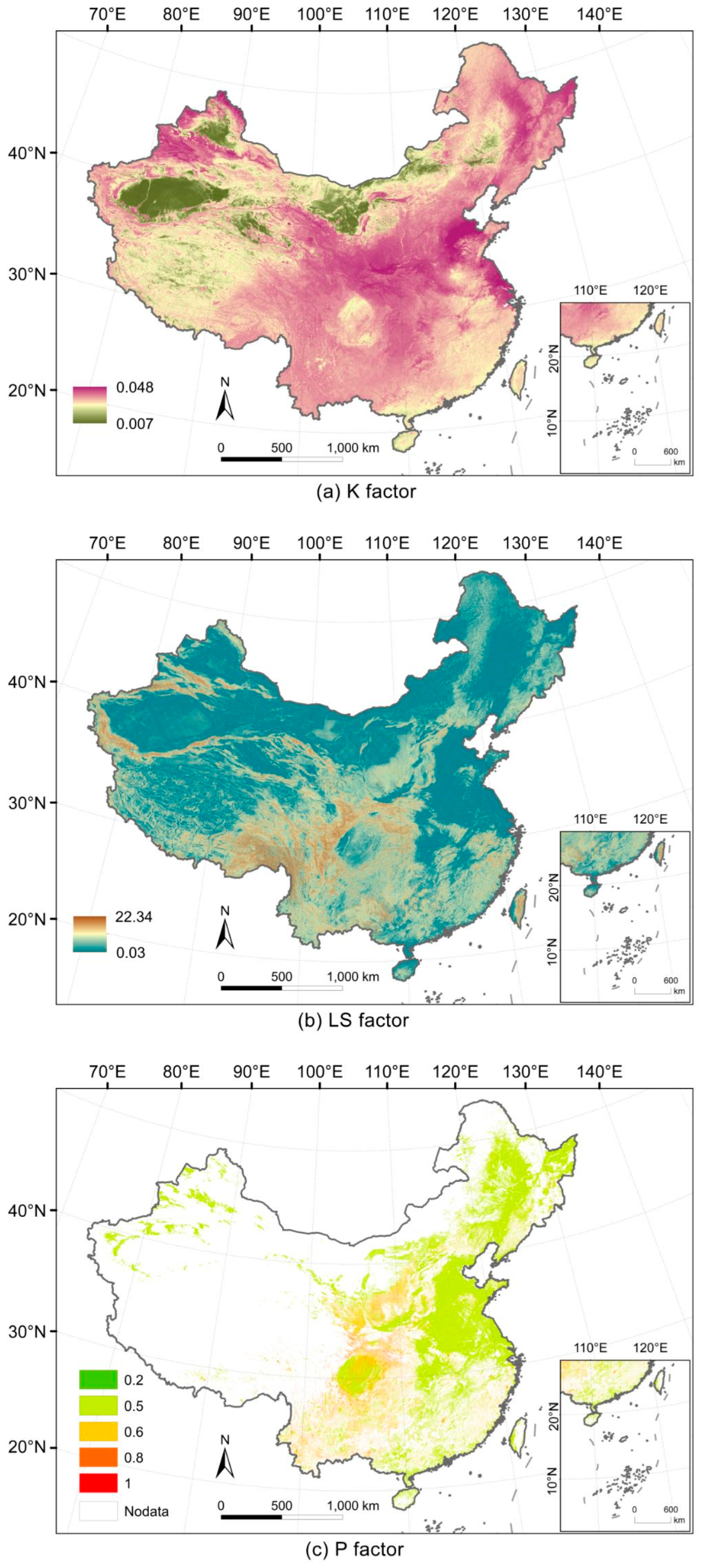
2.1.3. Soil Erodibility Factor (K Factor)
2.1.4. Topography Factor (LS Factor)
2.1.5. Support Practices Factor (P Factor)
3. Results
3.1. The Spatial Distribution of Physical Factors in the RUSLE Model
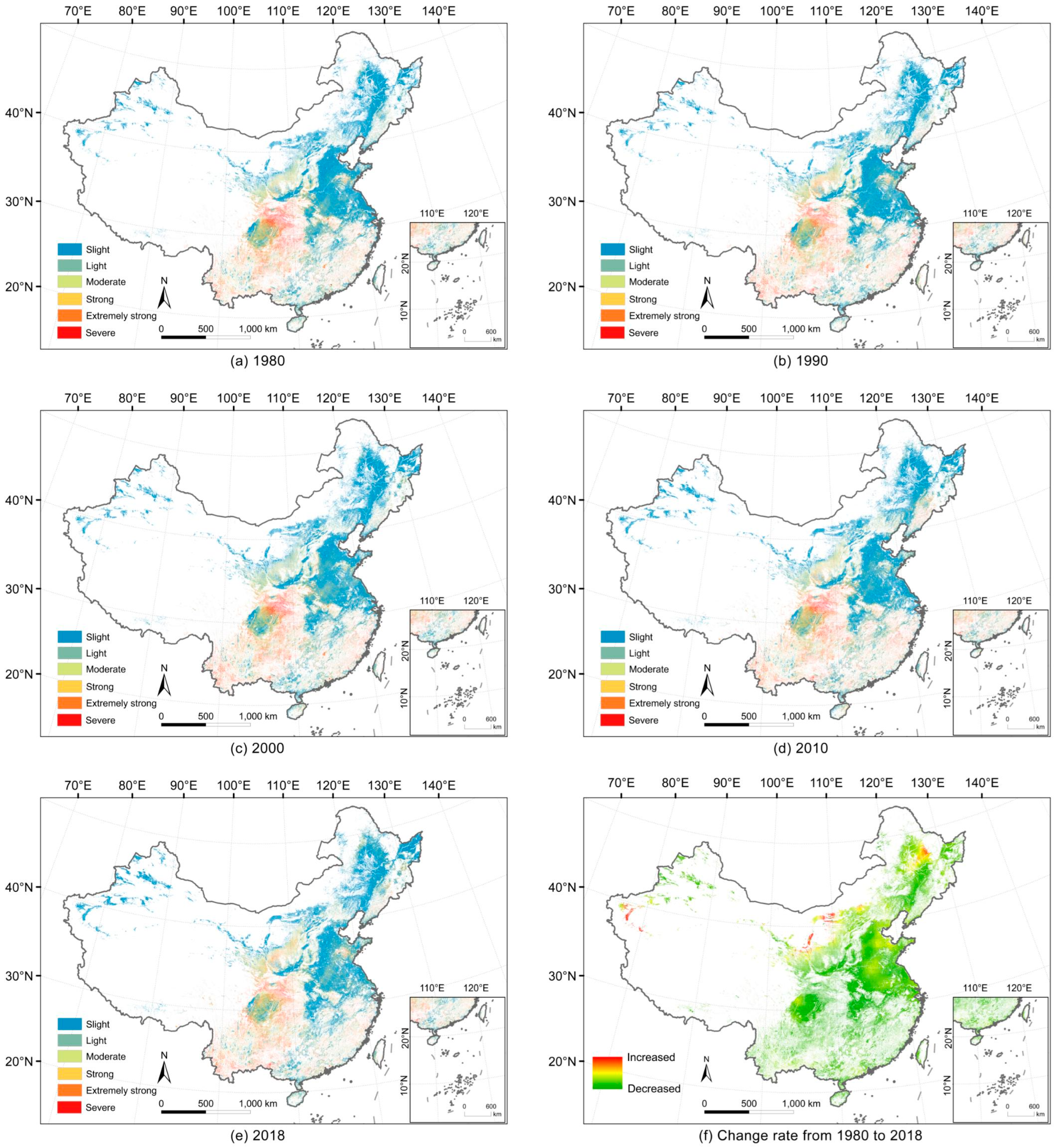
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China
3.2.1. Overview of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China
3.2.2. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Cropland Soil Erosion in Different Agricultural Zones
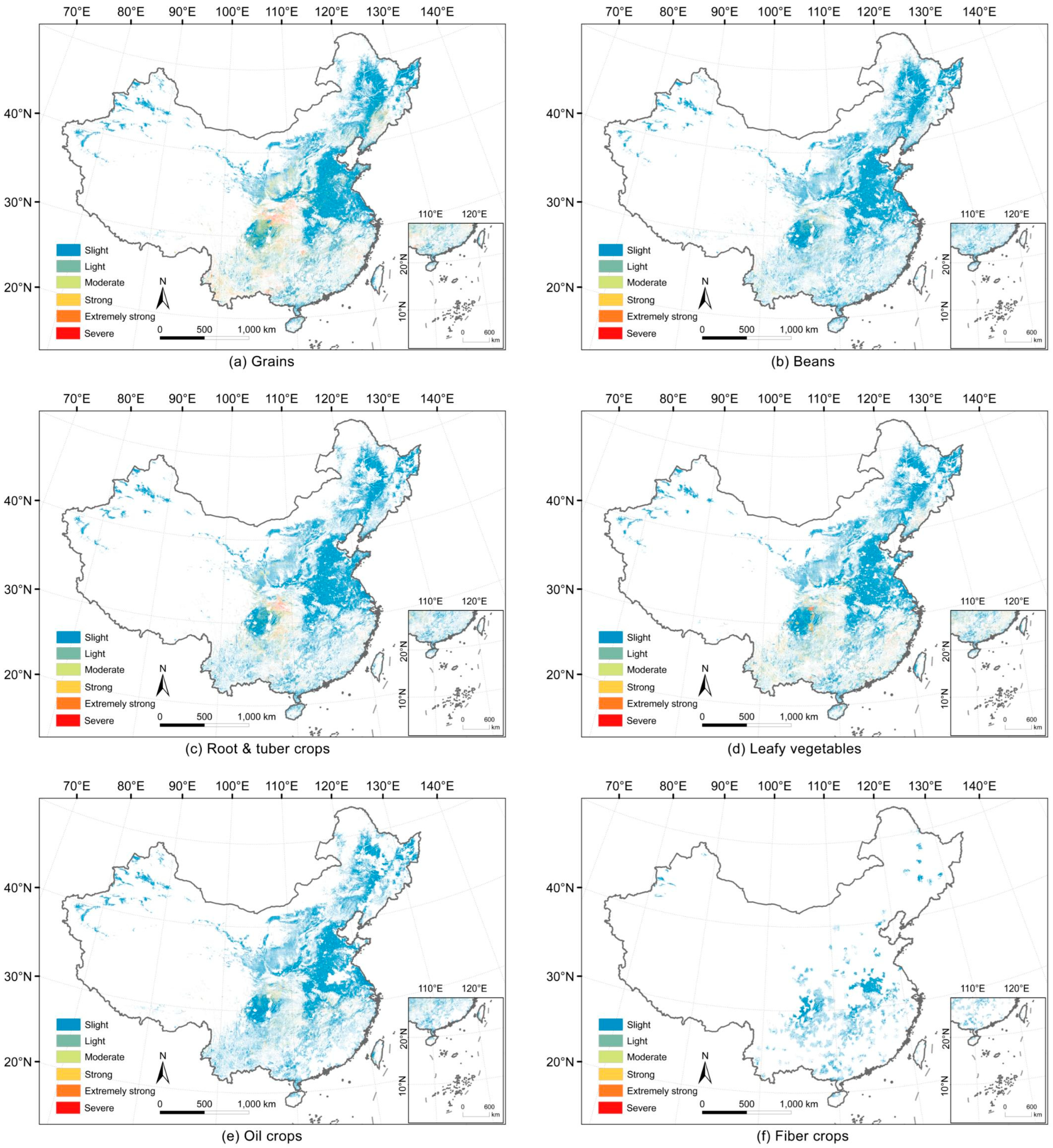
3.2.3. Crop-Specific Distribution of Soil Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Underlying Causes of Soil Erosion Changes
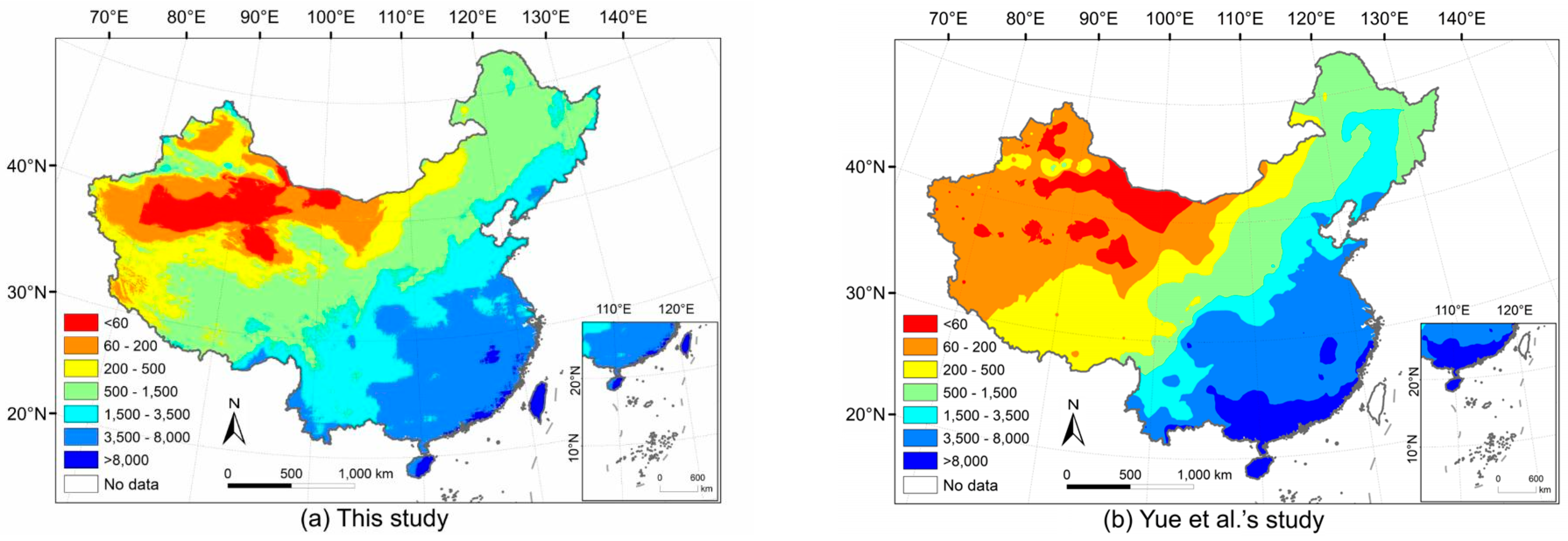
4.2. Comparison with Other Studies
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Policy Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Status of the World’s Soil Resources. 2015. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5199e.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Hou, L. Soil Degradation in China: Implications for Agricultural Sustainability, Food Security and the Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2005. Available online: https://api.mountainscholar.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/fd753e65-10ff-4164-907d-a284bff3bc8c/content (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Kan, S.; Chen, B.; Han, M.; Hayat, T.; Alsulami, H.; Chen, G. China’s forest land use change in the globalized world economy: Foreign trade and unequal household consumption. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Aulakh, M.S.; Yagi, K.; et al. World’s soils are under threat. Soil 2016, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wan, Y.; Huang, G.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X. Resilience analysis of global agricultural trade. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2024, 51, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, C.; Chen, B.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, B. Tracking embodied water uses and GHG emissions along Chinese supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, T. Farmland transition and its influences on grain production in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 70, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Kropp, J.P. Interplay between diets, health, and climate change. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, O.K.; Quine, T.A.; Govers, G.; De Gryze, S.; Six, J.; Harden, J.W.; Ritchie, J.C.; McCarty, G.W.; Heckrath, G.; Kosmas, C.; et al. The impact of agricultural soil Erosion on the global carbon cycle. Science 2007, 318, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panditharathne, D.L.D.; Abeysingha, N.S.; Nirmanee, K.G.S.; Mallawatantri, A. Application of Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Model to assess soil erosion in “Kalu Ganga” river basin in Sri Lanka. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 4037379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Annual Report 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/annual-report-2021 (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Wen, F.; Shi, Z. Factors affecting phase change in coupling coordination between population, crop yield, and soil erosion in China’s 281 cities. Land Use Policy 2023, 132, 106761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, G.K. RAPS-China: A Regional Analysis and Planning System; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis: Laxenburg, Austria, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z. Modelling and mapping soil erosion potential in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Suo, Y.; Zeng, X. Soil erosion in China based on the 2000 national remote sensing survey. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. The present situation, problems and countermeasures of cultivated land resources in China. J. Pet. Educ. Inst. Xinjiang 2002, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- General Office of the State Council of China. The Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Effectively Strengthening the Construction of High-Standard Farmland and Enhancing the National Food Security Guarantee Capability; General Office of the State Council of China: Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-11/21/content_5454258.htm (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Yin, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Z.; et al. The assessment of soil loss by water erosion in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M. The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: A review. Catena 2010, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Friedrich, T.; Shaxson, F.; Pretty, J. The spread of conservation agriculture: Justification, sustainability and uptake. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2009, 7, 292–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L.; Sun, R. A Chinese soil conservation dataset preventing soil water erosion from 1992 to 2019. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Blaschke, T.; Kazakopoulos, P.; Taubenböck, H.; Tiede, D. Is Spatial Resolution Critical in Urbanization Velocity Analysis? Investigations in the Pearl River Delta. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, C.; Wu, X. Mapping the spatial heterogeneity of global land use and land cover from 2020 to 2100 at a 1 km resolution. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sahu, A.P.; Sahoo, N.; Dash, S.S.; Raul, S.K.; Panigrahi, B. Global-scale application of the RUSLE model: A comprehensive review. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 806–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risse, L.M.; Nearing, M.A.; Laflen, J.M.; Nicks, A.D. Error assessment in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.A.A.; Baartman, J.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil erosion modelling: A global review and statistical analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.V.; Davies, J.; Silva, M.L.; Quinton, J.N. On the evaluation of soil erosion models: Are we doing enough? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golkarian, A.; Khosravi, K.; Panahi, M.; Clague, J.J. Spatial variability of soil water erosion: Comparing empirical and intelligent techniques. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xu, X. Sheet and Rill Erosion. In Watershed Erosion Processes. Geography of the Physical Environment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Science and Education Administration, United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Chuenchum, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, W. Predicted trends of soil erosion and sediment yield from future land use and climate change scenarios in the Lancang–Mekong River by using the modified RUSLE model. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. Assessing soil erosion using USLE model and MODIS data in the Guangdong, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 74, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Shen, Z.; Duan, X. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of soil erosion in Yunnan, Southwest China: RULSE assessments for recent 30 years and future predictions based on CMIP6. Catena 2023, 220, 106703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Peng, R.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Huhe, T. Spatio-temporal analysis and driving factors of soil water erosion in the three-river headwaters region, China. Water 2022, 14, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Dai, E.; Wu, C. Spatial and temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of soil conservation services on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2023, 221, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Huang, L. Spatial and temporal variability of soil erosion in Northeast China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Lin, H.; Ye, Y.; Ren, X. Changes in soil erosion in cropland in northeastern China over the past 300 years. Catena 2019, 176, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, R.; Sun, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of soil erosion in the ecotone between the Loess Plateau and Western Qinling Mountains based on RUSLE modeling, GIS, and remote sensing. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C.; Yang, J.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P. GloSEM: High-resolution global estimates of present and future soil displacement in croplands by water erosion. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xin, L.; Lu, Y. National scale assessment of the soil erosion and conservation function of terraces in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Dong, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, F. An assessment of soil loss by water erosion in no-tillage and mulching, China. Water 2023, 15, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, R.; Xiong, M.; Yang, G. Estimation of soil erosion based on the RUSLE model in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 3473–3485. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Weng, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J. Assessing Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Soil Erosion Caused by Water in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mccool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In Agriculture Handbook No. 703; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; You, L.; Wood-Sichra, U.; Ru, Y.; Joglekar, A.K.B.; Fritz, S.; Xiong, W.; Lu, M.; Wu, W.; Yang, P. A cultivated planet in 2010—Part 2: The global gridded agricultural-production maps. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3545–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Food Policy Research Institute. Global Spatially-Disaggregated Crop Production Statistics Data for 2010 Version 2.0. Harvard Dataverse, V4. 2019. Available online: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/PRFF8V (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Borrelli, P.; Hubacek, K.; Hu, Y.; Xu, B.; Fang, N.; et al. Human-altered soil loss dominates nearly half of water erosion in China but surges in agriculture-intensive areas. One Earth 2024, 7, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Impact of Agricultural Product Trade on Global Cropland Soil Erosion. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. China’s Multi-Period Land Use Land Cover Remote Sensing Monitoring Data Set (CNLUCC); Resource and Environment Data Cloud Platform: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Lai, C. Applicability of two satellite-based precipitation products for assessing rainfall erosivity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, F. HRLT: A high-resolution (1 d, 1 km) and long-term (1961–2019) gridded dataset for surface temperature and precipitation across China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4793–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xue, X.; Yue, T.; Xie, Y.; Gao, G. Spatiotemporal distribution and return period of rainfall erosivity in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Ma, Z.; Chappell, A.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Z.; Yu, W. Improving rainfall erosivity estimates using merged TRMM and gauge data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zheng, F.; Guan, Y. Improved USLE-K factor prediction: A case study on water erosion areas in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC-Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation: 1768; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, G. Basic Soil Property Dataset of High-Resolution China Soil Information Grids (2010–2018); Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles: Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised slope length factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASABE 1989, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.C.; Gobers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, K.; Yun, X. An empirical soil loss equation. In Proceedings of the 12th ISCO Conference, Beijing, China, 26–31 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. Effects of soil conservation techniques on water erosion control: A global analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. Global analysis of support practices in USLE-based soil erosion modeling. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2019, 43, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, R.; Liu, Y.; Kang, M.; Zhang, X. Regional differences in the soil and water conservation efficiency of conservation tillage in China. Catena 2019, 175, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of China. Soil Erosion Classification and Grading Standards. 2008. Available online: http://www.dgsbhj.com/UploadFiles/2015-12-07/14494781261644590.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Comprehensive agricultural zoning of China. Natl. Agric. Zoning Comm. China 1985, 6, 19. (In Chinese)
- Li, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, H.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Yu, S.; et al. Multiple perspective accountings of cropland soil erosion in China reveal its complex connection with socioeconomic activities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, J.; He, Y.; Chen, P. Evolution and ecological implications of land development and conservation patterns on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land 2022, 11, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Tao, F. Recent patterns of production for the main cereal grains: Implications for food security in China. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, N.; You, L.; Ke, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, M.; Waddington, S.R. Patterns of cereal yield growth across China from 1980 to 2010 and their implications for food production and food security. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Grain-for-green policy and its impacts on grain supply in West China. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, J.N.; Fiener, P. Soil erosion on arable land: An unresolved global environmental threat. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2024, 48, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Shaver, T.M.; Lindquist, J.L.; Shapiro, C.A.; Elmore, R.W.; Francis, C.A.; Hergert, G.W. Cover crops and ecosystem services: Insights from studies in temperate soils. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2449–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, S.; Goebes, P.; Puerta, V.L.; Pereira, E.I.P.; Wittwer, R.; Six, J.; van Der Heijden, M.G.; Scholten, T. Conservation tillage and organic farming reduce soil erosion. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 39, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, P.; Swoboda, D.; Blum, W.E.H. How effective is mulching and minimum tillage to control runoff and soil loss?—A literature review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on “25 Years Assessment of Erosion”, Ghent, Belgium, 22–26 September 2003; Volume 25, pp. 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Chatzichristaki, C.; Stefanidis, P. Assessing soil loss by water erosion in a typical Mediterranean ecosystem of northern Greece under current and future rainfall erosivity. Water 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, B. Rainfall erosivity mapping over mainland China based on high-density hourly rainfall records. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhorn, M.; Smets, B.; Bertels, L.; Roo, B.D.; Lesiv, M.; Tsendbazar, N.; Herold, M.; Fritz, S. Copernicus Global Land Service: Land Cover 100 m: Collection 3: Epoch 2019: Globe. Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Cai, S.; Niu, K.; Yang, X. Mapping soil erosion dynamics (1990–2020) in the Pearl River Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Holden, J.; Liu, B.; Chan, F.K.S.; Hu, J.; Wu, P.; Mu, X. Determining the drivers and rates of soil erosion on the Loess Plateau since 1901. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chang, J.; Huang, Y. Multiscale Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Soil Erosion and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Basin. Water 2022, 14, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Risse, L.M.; Nearing, M.A. Evaluation of WEPP and its comparison with USLE and RUSLE. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Event soil loss, runoff and the Universal Soil Loss Equation family of models: A review. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, N.B. A comparison of the RUSLE, EPIC and WEPP erosion models as calibrated to climate and soil of south-central Chile. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2005, 55, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Dataset Name | Spatial Resolution | Format | Dataset Production Methods | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China’s Multi-Period Land Use Land Cover Remote Sensing Monitoring Dataset (CNLUCC) | 30 m | TIFF | Remote sensing | https://doi.org/10.12078/2018070201 (accessed on 17 March 2023) |
| SPAM 2010 v2.0 Global Data | 10 km | TIFF | Data fusion | https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/PRFF8V (accessed on 3 July 2023) |
| HRLT: a high-resolution (1 d, 1 km) and long-term (1961–2019) gridded dataset for surface temperature and precipitation across China | 1 km | NetCDF | Data fusion | https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-4793-2022 (accessed on 5 April 2023) |
| Basic soil property dataset of high-resolution China Soil Information Grids (2010–2018) | 250 m | TIFF | Data fusion | https://doi.org/10.11666/00073.ver1.db (accessed on 23 June 2023) |
| SRTM DEM Data | 30 m | TIFF | Remote sensing | https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 16 June 2023) |
| China’s nine major agricultural regions data | / | SHP | Statistic analysis | https://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 2 May 2023) |
| N | Crop Types | Crop Classification | CCROPn |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grains | rice | 0.15 |
| maize | 0.38 | ||
| various | 0.20 | ||
| 2 | Beans | various | 0.32 |
| 3 | Root and tuber crops | various | 0.34 |
| 4 | Leafy vegetables | tobacco | 0.50 |
| various | 0.27 | ||
| 5 | Oil crops | cotton | 0.40 |
| various | 0.25 | ||
| 6 | Fiber crops | fiber crops | 0.28 |
| 7 | Shrubs, herbs, and spices | coffee | 0.20 |
| various | 0.15 | ||
| 8 | Other crops | various | 0.15 |
| Slope Values | P Factor |
|---|---|
| <10° | 0.5 |
| 10~25° | 0.6 |
| 25~45° | 0.8 |
| >45° | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Mapping the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China over the Past Four Decades. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091611
Xie Y, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Wu X. Mapping the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China over the Past Four Decades. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091611
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yitian, Tianyuan Zhang, Zhiqiang Zhang, and Xudong Wu. 2025. "Mapping the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China over the Past Four Decades" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091611
APA StyleXie, Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, Z., & Wu, X. (2025). Mapping the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Cropland-Related Soil Erosion in China over the Past Four Decades. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091611






