Abstract
SAR ship detection is of great significance in marine safety, fisheries management, and maritime traffic. At present, many deep learning-based ship detection methods have improved the detection accuracy but also increased the complexity and computational cost. To address the issue, a lightweight prior feature fusion network (LPFFNet) is proposed to better improve the performance of SAR ship detection. A perception lightweight backbone network (PLBNet) is designed to reduce model complexity, and a multi-channel feature enhancement module (MFEM) is introduced to enhance the SAR ship localization capability. Moreover, a channel prior feature fusion network (CPFFNet) is designed to enhance the perception ability of ships of different sizes. Meanwhile, the residual channel focused attention module (RCFA) and the multi-kernel adaptive pooling local attention network (MKAP-LAN) are integrated to improve feature extraction capability. In addition, the enhanced ghost convolution (EGConv) is used to generate more reliable gradient information. And finally, the detection performance is improved by focusing on difficult samples through a smooth weighted focus loss function (SWF Loss). The experimental results have verified the effectiveness of the proposed model.
1. Introduction
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is an active imaging technology that can obtain high-resolution ground and ocean information. Compared with optical imaging systems, SAR has the advantage of all-weather and all-day observation, making it particularly valuable in maritime surveillance, search and rescue operations, and illegal vessel detection. It generates high-quality two-dimensional or three-dimensional images by emitting microwave signals and receiving echoes reflected by targets, which is widely used in remote sensing, environmental monitoring, and the national defense field. In ocean monitoring, SAR can provide high-resolution imaging even under extreme weather conditions such as heavy rain, fog, or strong winds. Therefore, SAR has become an important means for ship detection due to its ability to penetrate clouds and adverse weather conditions. SAR ship detection utilizes the intensity, shape, texture, and other features of radar echoes to distinguish and identify ships on the sea surface [1,2,3]. At present, the methods for SAR ship detection are mainly divided into two categories: one based on traditional methods and the other based on deep learning.
Traditional SAR ship detection methods [4,5,6] typically utilize threshold segmentation, constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection, and handcrafted feature extraction. They often rely on simple geometric and texture features, which make it difficult to cope with complex sea conditions, radar noise, and various interferences. These methods typically assume that ships exhibit distinct shapes and textures that can be effectively distinguished from the surrounding sea clutter. However, in real-world scenarios, factors such as varying sea states, strong ocean waves, and fluctuating weather conditions significantly affect the radar returns, leading to high false alarm rates. Additionally, different types of ships, including small vessels and low-reflectivity targets, may not be easily identified using conventional approaches. As a result, these limitations necessitate the development of more advanced detection techniques to enhance detection robustness and accuracy.
In recent years, the technology of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has made significant progress in various fields, such as object detection [7,8,9], speech signal processing [10,11], image segmentation [12,13], and object classification [14,15,16]. Deep learning-based SAR ship detection methods are gradually becoming mainstream, as they can fully utilize multi-level feature extraction capability and exhibit stronger robustness in complex sea conditions and noise environments. Unlike traditional feature-based approaches, CNN-based models automatically learn hierarchical representations from raw SAR images, obtaining both high-level semantic structures and low-level textures. This allows them to adapt more effectively to variations in ship size, orientation, and imaging conditions. Furthermore, with the integration of advanced architectures such as transformer-based networks and attention mechanisms, deep learning models can further enhance detection precision by focusing on key features while suppressing background clutter. These advancements make deep learning-based approaches a promising direction for next-generation SAR ship detection systems. Ai et al. [17] introduced a novel idea of a multi-scale rotation-invariant Haar-like feature integrated CNN to provide high-quality SAR ship detection. An effective arbitrary direction SAR ship detection network was designed by Sun et al. [18]. Bai et al. [19] designed a shallow feature reconstruction network to address the challenge of dense ship detection in a nearshore situation. Zou et al. [20] proposed a high-resolution detection method that incorporates an improved sample generation network to meet the application requirement of small sample high-resolution ship detection. Li et al. [21] utilized a multi-level pyramid structure to obtain deep-level features and employed decoupling modules to detect multi-scale and dense targets. Qin et al. [22] created a balanced cross-union loss by employing adaptive weights to enhance nearshore ship positioning performance. Tan et al. [23] considered that previous methods could not effectively combine the characteristics of the distance compression domain, and designed a detection network using gradients and geometric properties to improve the detection capability. Ju et al. [24] introduced a cascaded generative adversarial network that significantly improves the quality of SAR images and utilizes position and pixel value constraints to obtain images and position labels. Du et al. [25] designed a semi-supervised detection network based on scene feature learning. They constructed a background feature learning branch to improve the learning and representation capabilities of the network. Chen et al. [26] considered that many ship detection methods sacrifice detection accuracy to achieve real-time detection. They designed a hybrid detection framework and introduced object localization and classification modules to improve performance. Chen et al. [27] proposed an anchor-free ship detection method that utilizes ship grids to generate bounding boxes, effectively alleviating the problems of inaccurate feature localization and multi-scale variations. Mou et al. [28] proposed a feature-based ship detection scheme, which achieves ship detection while utilizing feature-based methods to detect ship wake, thus achieving the effect of assisting ship detection. Tian et al. [29] considered the problem of missed detection in small ships and introduced a fog simulation method to improve detection performance under extreme weather conditions. They also improved the module by introducing a lightweight detector and utilizing context converters to enhance localization capability. Zhou et al. [30] proposed a domain adaptive detection algorithm and designed an efficient distance metric function. They also introduced a dual branch feature extraction network to achieve better feature extraction.
In addition, unlike optical images, SAR images are susceptible to background noise interference. This affects the accuracy of SAR ship detection. Tang et al. [31] designed an attention module to address the impact of background noise and multi-scale ship targets on detection performance. They also introduced a feature-balancing module to alleviate the conflict between semantic and positional information. Zhou et al. [32] considered the impact of background noise and designed a feature refinement network to enhance the position and contour of ship targets and reduce the semantic loss of multi-scale ship targets. Ma et al. [33] reduced the effect of background noise for SAR ship detection by creating a center point distribution module. Zhang et al. [34] proposed a new deep learning neural network that can adaptively process frequency domain information and reduce ocean clutter in SAR images. Sun et al. [35] considered the interference of background information on SAR ship recognition and introduced a dual branch feature extraction architecture to improve performance. The above methods have improved the accuracy of SAR ship detection. However, they also increased the computational cost. To reduce the interference of image background on detection, Chen et al. [36] introduced a rotating decoupling head and a bidirectional feature network to improve detection efficiency, and utilized an attention mechanism to enhance feature extraction capability. To avoid confusion between complex backgrounds and ship targets, Min et al. [37] introduced a dual-path enhanced neck structure to extract contextual information, designed an enhanced feature module to enhance feature representation, and finally adjusted the receptive field through a context-enhanced detection head. Dong et al. [38] proposed a component-based SAR ship detection method that utilizes efficient aggregation networks to enhance feature representation and optimizes feature extraction structures through channel attention. Zhang et al. [39] proposed a new anchor-free detection method for SAR ship detection, which introduces a nested path aggregation module to fuse features and suppresses background interference information through an attention module to improve detection accuracy. Wang et al. [40] considered the impact of complex background interference and ship scale diversity on SAR ship detection, designed an SAR ship detection network based on multi-feature fusion and non-local channel attention mechanism. They employed the non-local channel attention block to enhance the nonlinear relationship between different channel features, and finally improved the performance of target detection by optimizing the loss function. Wang et al. [41] designed a scattering information fusion network for ship detection, introduced a semantic fusion module to enhance feature extraction, and used a scattering learning module to enhance the robustness of feature representation.
In order to meet the real requirements of SAR ship detection, some lightweight SAR ship detection networks have been designed. Yang et al. [42] proposed a lightweight SAR ship detection method to solve the difficult detection of small ships. It can reduce the number of parameters and achieve adaptive fusion of multi-scale features. Liu et al. [43] designed a lightweight detection network based on polar coordinate encoding. Liu et al. [44] considered the problems of large rotation angles and dense targets in remote sensing images, and introduced a multi-branch feature fusion module to improve feature extraction capabilities. Zhang et al. [45] introduced a ship detection method based on contextual information and an effective receiving field to address the imbalance between detection accuracy and computational efficiency. Man et al. [46] constructed the backbone network by using non-stride feature extraction modules, significantly reducing the number of parameters. Moreover, they designed a strip partial convolution module to improve global modeling capability with fewer parameters. Zhang et al. [47] designed a lightweight detection model to avoid missed and false detections while reducing model parameters. They introduced feature enhancement modules and lightweight attention modules to improve detection capability and localization accuracy, and improved the convergence speed by improving the loss function. Kong et al. [48] proposed a lightweight ship detection network considering complex backgrounds and differences in ship scales. They introduced a multi-scale feature extraction module to effectively extract global and local features, and designed a detection strategy based on adaptive thresholds to improve detection speed. Lv et al. [49] proposed an anchor-free detection method with significant representation and designed a lightweight backbone network to reduce model parameters, while utilizing a mixed domain attention mechanism to suppress background interference information. Meng et al. [50] introduced a lightweight backbone network based on contour guidance, and improved the fusion ability between feature layers through an adaptive feature pyramid network. Fang et al. [51] designed a lightweight feature-enhanced detection model to address the challenges in multi-scale ship detection tasks. The model utilizes feature convolution blocks and attention conversion modules to suppress speckle noise and capture global correlations. Although the above methods have made some progress in improving SAR ship detection performance, there are still shortcomings in balancing model accuracy and inference speed. To address this issue, a lightweight prior feature fusion network (LPFFNet) is proposed to improve the performance of SAR ship detection while reducing computational complexity. The main contributions of the proposed model are as follows:
- A perception lightweight backbone network (PLBNet) is designed to improve the feature extraction ability of the model while making the model lightweight. In addition, a multi-channel feature enhancement module (MFEM) is introduced to enhance the SAR ship localization capability and obtain more feature information.
- To more effectively address the scale diversity of SAR ship targets, a channel prior feature fusion network (CPFFNet) is proposed to enhance the perception ability of ships with different sizes by fusing multi-scale feature information. Meanwhile, the residual channel focused attention module (RCFA) and multi-kernel adaptive pooling local attention network (MKAP-LAN) are integrated to achieve more refined feature extraction and efficient feature fusion.
- To enhance the expression ability of deep features and avoid semantic information loss, the conventional convolution in the auxiliary reversible branch is replaced by enhanced ghost convolution (EGConv). This substitution can generate more reliable gradient information, allowing deep features to maintain key features while effectively reducing semantic loss during target task execution.
2. Materials and Methods
YOLOv9 [52] is a relatively new object detection model in the YOLO series. Compared to earlier versions, it introduces the concept of programmable gradient information (PGI), which generates gradient information through auxiliary reversible branches. This novel approach enhances feature propagation and mitigates vanishing gradient issues in deep networks, particularly in complex detection scenarios. By improving gradient flow, PGI helps the model maintain more detailed spatial and semantic information, leading to better localization accuracy and robustness in detecting small or occluded objects. Meanwhile, the architecture of PGI is built on the auxiliary branch, avoiding additional computational overhead. Unlike traditional gradient refinement techniques that often require extra computations or complex optimization strategies, PGI efficiently integrates with the network structure, ensuring real-time inference speed while enhancing feature representation. This makes YOLOv9 well-suited for applications that demand both high accuracy and efficiency, such as real-time SAR ship detection. The PGI mechanism mitigates information loss during data transmission in deep neural networks, enabling the model to transmit gradient information while maintaining input data integrity [53]. This advantage is particularly beneficial in SAR image processing, where preserving fine-grained details is crucial for distinguishing targets from background clutter. Additionally, the improved gradient transmission contributes to more stable training dynamics, reducing the risk of overfitting in scenarios with limited labeled data. Therefore, the YOLOv9 is selected as the baseline.
2.1. Overall Network Structure
The network structure of LPFFNet is shown in Figure 1. It can be seen that LPFFNet is mainly composed of the perception lightweight backbone network (PLBNet), the channel prior feature fusion network (CPFFNet), the auxiliary reversible branch, and the detection head. Among them, PLBNet introduces a multi-channel feature enhancement module (MFEM) for feature extraction, which reduces redundant information while improving the model’s understanding and representation ability of input data. CPFFNet introduces the residual channel focused attention module (RCFA) and multi-kernel adaptive pooling local attention network (MKAP-LAN). The RCFA module supports dynamic adjustment of weights. By using the different scales of deep-wise convolution operations, spatial relationships can be effectively extracted while preserving channel prior. The MKAP-LAN module can effectively capture local features through multi-core pooling, thereby improving model performance in fine-grained tasks. It can also dynamically adjust the pooling strategy based on input features, adapt the model to different input data, and enhance its understanding of complex scenarios. In addition, the introduction of an auxiliary reversible branch has greatly improved the overall performance. Auxiliary reversible branch can ensure the generation of gradients and continuous updating of network parameters, helping the backbone network retain more contextual information in the feature extraction process.
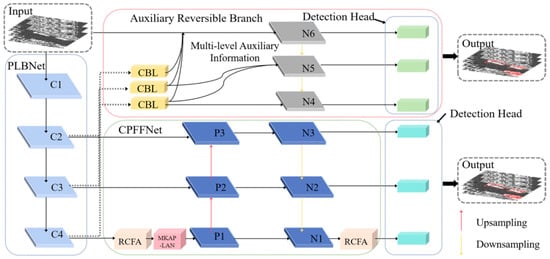
Figure 1.
The structure of LPFFNet.
2.2. The Structure of PLBNet
The network structure of PLBNet is shown in Figure 2. To achieve lightweight, PLBNet adopts deep-wise convolution to reduce computational complexity and implements parameter sharing to reduce storage overhead. Deep-wise convolutions substantially reduce both the number of trainable parameters and the computational burden, yet still preserve robust feature extraction capability. This helps avoid the computational cost associated with traditional convolutions while maintaining strong performance. Additionally, the application of parameter sharing enhances computational efficiency and reduces model redundancy, making it more suitable for SAR ship detection.
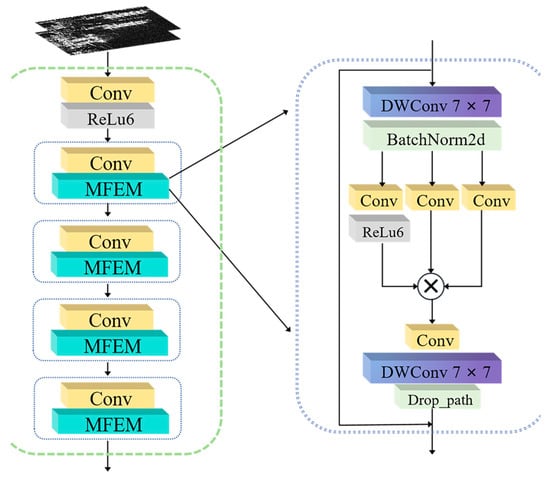
Figure 2.
The structure of PLBNet.
By continuously stacking MFEM modules in PLBNet, three feature layers of different sizes are generated and passed to CPFFNet. These multi-scale feature layers enable the network to capture both fine-grained details and global context, improving the robustness of object detection under varying imaging conditions. The hierarchical feature representation ensures that small targets, which are often challenging to detect in SAR imagery, receive sufficient attention at different processing stages.
The MFEM is a feature enhancement module in the backbone network. The input feature information X is first passed through the deep-wise convolution with a kernel size of 7 to extract initial features, and then standardized through a batch normalization operation. The use of a larger kernel size allows the network to capture more spatial context, improving feature representation for complex background suppression in SAR images. Next, three convolution channels are used to further extract features, and the output channel information is point-wise multiplied. The multi-branch design facilitates the learning of rich feature representations. It captures information from multiple receptive fields, which enhances the ability to distinguish ships from sea clutter. Subsequently, 1 × 1 convolution is used to perform dimensional transformation on the fused feature to restore the number of channels, and then the adjusted feature map is subjected to a deep convolution operation to capture deeper-level features. Furthermore, the drop path is introduced to prevent model overfitting, and the residual path is introduced to alleviate gradient vanishing. The drop path helps in regularizing the model by randomly skipping connections during training, which improves generalization, particularly in scenarios with limited labeled SAR data. Meanwhile, the residual connection ensures stable gradient flow, facilitating the effective training of deep networks and improving the learning of subtle object features in high-resolution SAR images. The output feature information Y of MFEM can be represented as follows:
where Dw(.) represents the deep-wise convolution operation, Bn(.) denotes the batch normalization operation, Conv(.) represents the conventional convolution operation, Rl(.) is the rectified linear unit operation, Pm(.) represents the point-wise multiplication operation, and Dp(.) denotes the drop path operation.
2.3. The Structure of CPFFNet
The structure of CPFFNet is shown in Figure 3. The deep-level feature output by the backbone network is first passed through the residual channel focused attention module RCFA and the multi-kernel adaptive pooling local attention network MKAP-LAN. RCFA helps the model focus on important features and suppress irrelevant background noise. This is crucial in SAR image processing, where strong sea clutter can obscure targets. Meanwhile, MKAP-LAN aggregates multi-scale spatial information, enhancing the capability to detect objects of varying sizes. In CPFFNet, the RCFA and MKAP-LAN modules are utilized before feature fusion to improve the quality of input features. Then, to enhance the final feature expression, the features from different levels are fused. Multi-level feature fusion ensures that both fine-grained details and high-level semantic information contribute to detection, improving the model’s robustness to scale variations and environmental disturbances. This is particularly beneficial in SAR-based ship detection, where small and densely distributed targets can be challenging to distinguish. Finally, the RCFA module is introduced between the deep-level feature and the detection head. The main reason is that deep-level feature contains rich semantic information, which can effectively highlight relevant information by applying attention mechanisms to these features. Moreover, deep-level features can capture the global context, and the relationship between features can be better understood through attention mechanisms. By refining global feature relationships, RCFA strengthens the model’s ability to differentiate between ships and complex backgrounds, leading to more precise object localization. This operation significantly improves the model’s capability to interpret complex scenes, reducing false detection in challenging SAR environments.
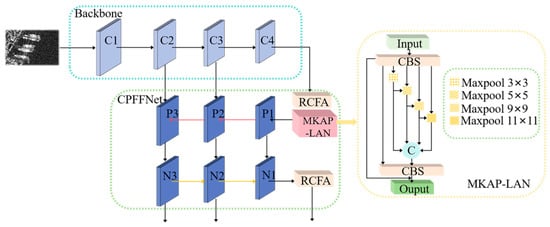
Figure 3.
The structure of CPFFNet.
Figure 4 presents the structure of the RCFA module. The RCFA module aims to enhance the representation capability of features and integrate spatial and channel information. This allows the module to capture complex dependencies between spatial and channel dimensions, improving the model’s ability to represent relevant features. Firstly, the input feature W is processed through pooling and convolution operations. Next, the weights of each channel are learned through the multi-layer perceptron and normalized using the sigmoid activation function to generate the channel map. The channel map WCP can be expressed by the following:
where W is the input information of RCFA, Avg(.) denotes the adaptive average pooling operation for output feature map with a width and height of 1, and Max(.) represents the adaptive max pooling operation with output feature map width and height of 1. Conv(.) denotes the conventional convolution operation, Mlp(.) represents the multi-layer perceptron operation, Sig(.) denotes the sigmoid operation, and Ad(.) represents the addition operation.
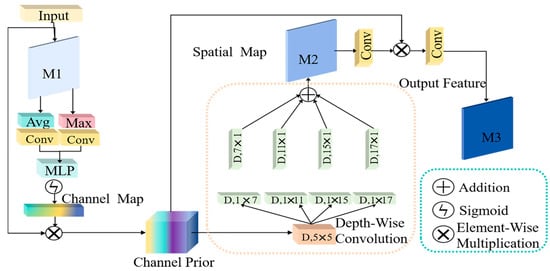
Figure 4.
The structure of RCFA.
Then, the input feature is introduced through the residual path and multiplied with the channel map to obtain the channel prior Wpm. To better capture contextual spatial dependency, the RCFA module employs deep-wise convolutions with different kernel sizes. These allow the network to adapt to various receptive fields and extract information from multiple spatial scales. Afterwards, different scales of deep-wise convolution operations are used to obtain the spatial map Wsm. The spatial map Wsm can be expressed by the following:
where Pm(.) represents the point-wise multiplication operation. Dconva×b represents the convolution with a kernel size of a × b. (a, b) = (7, 1), (11, 1), (15, 1), (17, 1).
The spatial map Wsm undergoes the convolution operation to achieve channel integration, and the result is multiplied element by element with the channel prior Wpm to obtain the fused feature Wf. Finally, a 1 × 1 convolution is performed to refine and integrate the fused feature. The output information Wout of RCFA can be represented as follows:
The MKAP-LAN module is a pooling network that could dynamically adjust the pooling strategy based on input features. This dynamic adjustment is achieved by evaluating the characteristics of the input features, such as their scale and context, and then selecting the most appropriate pooling parameters for each specific feature map. This approach enables the module to better adapt to different feature scales and contexts, improving its ability to capture relevant information. It can effectively capture local information through multi-core operation and integrate information from different layers. This multi-core operation also enables parallel processing, enhancing computational efficiency and facilitating the extraction of diverse local features from multiple perspectives. The structure of MKAP-LAN is shown in Figure 3.
2.4. The Structure of EGConv
The introduction of the auxiliary reversible branch can help the backbone network retain important information and promote the rapid convergence of the model. This auxiliary branch significantly improves the flow of information throughout the network. By allowing the model to retain key features through a separate path, it ensures that valuable information does not get lost during the forward pass. Moreover, the auxiliary reversible branch provides a stable gradient feedback path during backpropagation, which facilitates more effective feature learning and accelerates the convergence, especially in the early training stages. To avoid the loss of semantic information, the conventional convolution in the auxiliary reversible branch is replaced with EGConv. The EGConv improves feature representation by producing more feature maps with less computation. It keeps the computational cost low while ensuring efficient feature extraction. Compared to traditional convolution, it extracts deep features more effectively. This makes EGConv especially suitable for SAR image processing, where capturing key image features with limited resources is important. Figure 5 presents the structure of EGConv. Firstly, the input features P are extracted through the convolution operation with a kernel size of 1 to reduce computational complexity and obtain intermediate features. Then, the intermediate features are subjected to the deep-wise convolution operation with a kernel size of 5 to obtain deep features. And the above two convolution operations include a traditional convolution operation, a batch normalization operation, and a sigmoid linear unit operation. Then, the deep and intermediate features are concatenated to form a new feature and recover the number of channels. At the same time, the residual path is introduced to fuse information. Finally, batch normalization and sigmoid linear unit operations are used to stabilize the feature distribution and introduce nonlinearity to enhance the expressive power of the network.
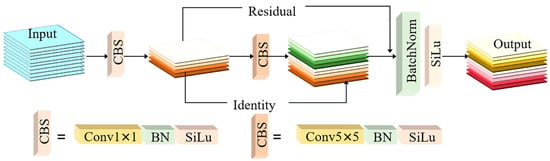
Figure 5.
The structure of EGConv.
2.5. SWF Loss Function
The slide loss function [54] is a commonly used loss function in image segmentation and object detection tasks. It is particularly effective in tasks that require precise delineation of object boundaries, as it can provide a more detailed and accurate representation of the object’s edges. By focusing on the boundaries and details of the target, the slide loss function can better process the edge information of the object, thereby improving the detection accuracy. Its smoothing property [55] helps alleviate instability during the training process and improves convergence speed. This smoothing property is particularly advantageous when training deep networks, as it helps to prevent gradient explosions and vanishing gradients, thus enabling more stable training. Therefore, the smooth weighted focus loss function (SWF Loss) based on the slide loss function is proposed here.
SWF Loss function improves the calculation of weights by introducing a square operation. It can avoid the discontinuity of the loss function and achieve a smooth weight change. In addition, focal loss is introduced to address the class imbalance issue, which is common in object detection tasks. Compared to traditional loss functions, focal loss gives more focus to difficult-to-detect samples, particularly those with low intersection over union (IoU), by assigning them higher weights. This helps the model to better handle the imbalance, ensuring that challenging samples are learned more effectively. This operation helps the model learn these difficult samples faster. By focusing on hard-to-detect samples, the model becomes more robust and capable of handling various challenging scenarios during training. The SWF Loss function is expressed by the following:
where β represents the average IoU value of all bounding boxes, with values greater than β being positive samples and values less than β being negative samples.
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
To validate the performance of LPFFNet, experiments were conducted on two commonly used SAR ship datasets, SSDD [56] and HRSID [57].
The SSDD is a publicly available dataset specifically designed for SAR ship detection. It contains SAR images with different sea conditions, varying resolutions, and multiple target scales. The primary targets in this dataset are ships, while the background includes the ocean, islands, and some nearshore areas. The dataset provides annotated bounding boxes for ship targets, making it suitable for object detection tasks. The HRSID is a high-resolution SAR ship detection dataset that includes more complex scenarios and densely distributed ship targets. The images in HRSID are collected from various sensors, covering a wide range of SAR imaging sources. Compared to SSDD, HRSID features a broader range of ship sizes and richer background information, such as coastlines, docks, and other maritime objects, which makes detection tasks more challenging. During the experiments, the datasets were partitioned into training, validation, and test sets with a ratio of 7:2:1. Furthermore, all experiments were conducted on PyTorch 1.11.0 + CUDA11.3 framework using a NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 12 GB graphics card. The code was implemented in Python 3.8. All the experiments were trained for 200 epochs with a batch size of 8.
In addition, the metrics of precision (P), recall (R), mAP@0.5, mAP@0.5:0.95, frames per second (FPS) and the number of parameters (Params) are used to evaluate the performance of LPFFNet, and mAP@0.5:0.95 is the evaluation metric that calculates mAP values within the IoU threshold range of 50–95%, and then averages them to more accurately evaluate the performance of the model at different IoU thresholds. The calculation formulas are as follows:
where NTP, NFP, and NFN represent the number of true positives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively. AP represents the average accuracy, j denotes the jth category, and N represents the total number of categories.
3.2. Experiments on Datasets
Firstly, the performance of LPFFNet is compared with other excellent detection models [58,59,60,61,62] on the SSDD dataset. The performance comparison results are given in Table 1. From Table 1, it can be clearly seen that LPFFNet has achieved the best performance metrics in P, R, mAP@0.5, and mAP@0.5:0.95. Compared to the suboptimal YOLOv9, P has increased by 1.09%, R has increased by 1.13%, mAP@0.5 has increased by 2.12%, mAP@0.5:0.95 has increased by 2.59%, parameters have decreased by 7.2 M, and FPS has increased by 8.3. Although LPFFNet has more parameters than RT-DETR, this is due to its auxiliary reversible branches. However, all other performance metrics are better than RT-DETR.

Table 1.
Comparison of different methods on SSDD dataset.
The visualization results on the SSDD dataset are presented in Figure 6. The green box indicates the real box, the red box indicates the predicted box, the blue box denotes the missed detection, and the yellow box represents the false detection. From Figure 6, it can be seen that both YOLOv9 and LPFFNet can accurately detect ship targets when there is no obstruction to the ships, as shown in the third set of images. However, when the distribution of small ships is dense, or there are ships at the edge of the image, YOLOv9 has missed detections, such as the first and second sets of images. However, our proposed LPFFNet can accurately detect all ships without false negatives. In addition, due to the complex background information of ports, it increases the difficulty of detecting ships near the coastline. For example, in the fourth set of images, YOLOv9 has false positives, mistakenly identifying the port background as a ship. However, our LPFFNet can accurately recognize all ships without false positives. The results indicate that our LPFFNet has successfully improved the performance of SAR ship detection.
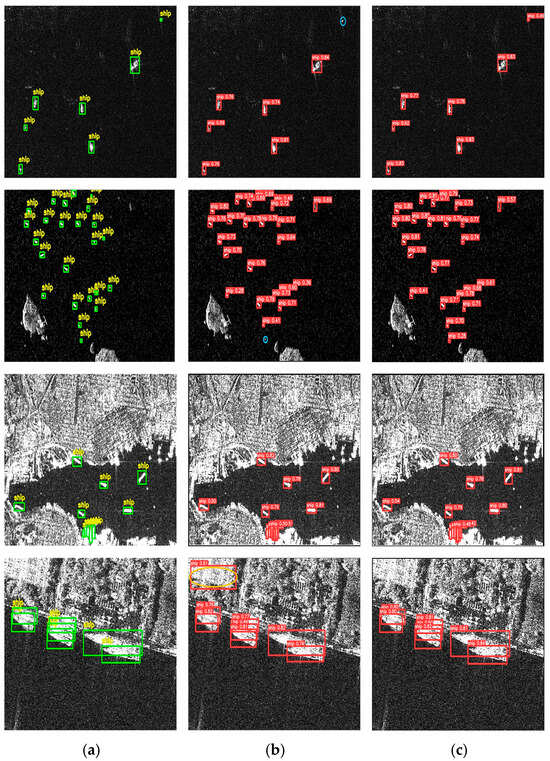
Figure 6.
Comparison of SAR ship detection results on SSDD dataset. (a) Ground truth, (b) detection results of YOLOv9, (c) detection results of LPFFNet.
Next, the comparative experiments are conducted on the HRSID dataset, and the performance comparison results are given in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, our LPFFNet achieved the best performance metrics in P, R, mAP@0.5, and mAP@0.5:0.95 compared to other models. Compared to YOLOv9, P has increased by 2.35%, R has increased by 3.43%, mAP@0.5 has increased by 1.29%, mAP@0.5:0.95 has increased by 4.31%, parameters have decreased by 7.2 M, and FPS has increased by 8.2.

Table 2.
Comparison of different methods on HRSID dataset.
The visualization results on the HRSID dataset are shown in Figure 7. When the sea surface background is complex, it could result in blurry ship information and increase the difficulty of detection. As in the last set of images, there is one missed detection of YOLOv9, while LPFFNet performs well and accurately detects all ships. In addition, there is a lot of background information in the port, which can easily lead to the missed detection of small ships near the port. For example, in the first set of images, YOLOv9 has one missed detection, but LPFFNet still accurately identifies all ships. When small ships are densely packed or concentrated around the coastline, the difficulty of detection greatly increases, which can lead to false negatives and false positives. For example, YOLOv9 has two false positives in the second set of images, but LPFFNet still performs well without any missed or false positives. Although LPFFNet shows two false negatives in the third set of images, it has a significant advantage in detection performance compared to YOLOv9. This is mainly because LPFFNet introduces MFEM to enhance the SAR ship localization capability, and introduces CPFFNet to enhance the perception capability of ships with different sizes by fusing multi-scale feature information. And the SWF Loss function is utilized to focus on difficult samples, thereby improving detection performance.
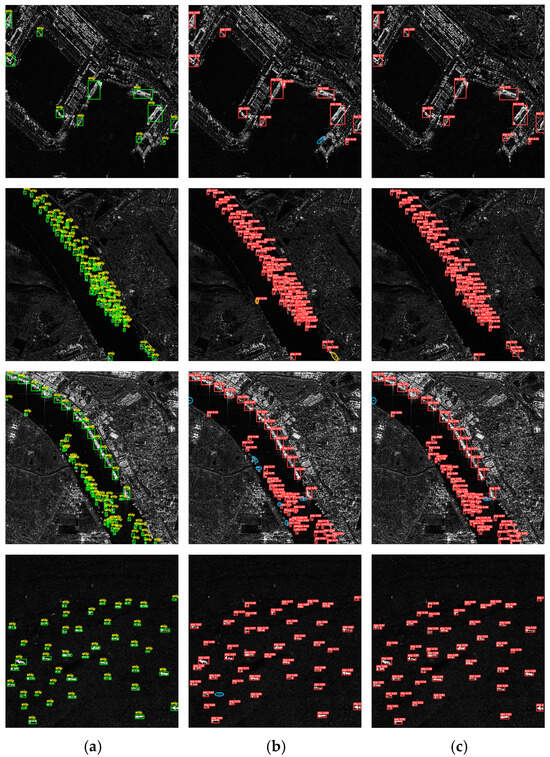
Figure 7.
Comparison of SAR ship detection results on HRSID dataset. (a) Ground truth, (b) detection results of YOLOv9, (c) detection results of LPFFNet.
3.3. Ablation Experiments
To fully verify the effectiveness of our module, we conducted ablation experiments on the PLBNet, CPFNet, EGConv, and SWF Loss modules on the SSDD dataset. The purpose of these ablation experiments is to isolate the individual impact of each module and examine how each one contributes to the overall performance. Table 3 gives the experimental results. Except for CPFFNet, all performance metrics increase when the other three modules are used separately. Due to the introduction of the attention mechanism, the number of parameters in CPFFNet has slightly increased, but other performance metrics have been improved. Each of these modules serves a unique and complementary purpose. PLBNet specializes in global feature extraction, CPFFNet strengthens the contextual understanding of the image, EGConv enhances feature expression efficiency, and SWF Loss fine-tunes the weight distribution of the loss function. This clear division ensures that there is no redundancy between the modules, and they collectively improve overall performance. In addition, it could yield better performance by using the combination of modules than using them alone, indicating that these four modules can mutually promote each other to achieve optimal performance. This finding suggests that the combined use of these modules leads to a synergistic effect, where each module compensates for the limitations of others, ultimately achieving superior results. Figure 8 shows the loss function curves of the YOLOv9 model and the LPFFNet model proposed in this paper. By analyzing the loss function curves, it can be concluded that the loss functions of both models experience a sharp decline in the first 20 epochs, followed by a slow decline before stabilizing. The loss value of LPFFNet has always been below YOLOv9, with small fluctuations, indicating that the LPFFNet model has a faster learning speed and better optimization effect. Therefore, it can be concluded that LPFFNet is superior to YOLOv9 in both learning efficiency and generalization ability.

Table 3.
The ablation experiments on SSDD dataset.
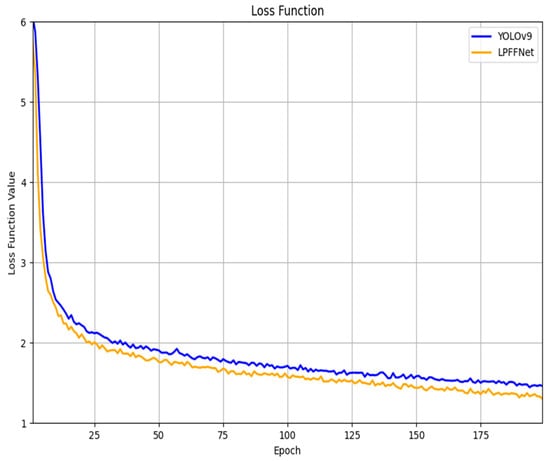
Figure 8.
Comparison of loss functions between YOLOv9 model and LPFFNet model.
4. Conclusions
To solve the difficulty of dense ship detection and the problem of missed detection of small ships, a lightweight prior feature fusion network LPFFNet, is proposed to improve the detection performance. The challenge of detecting small ships and dense ships in remote sensing images has been a longstanding issue, primarily due to the scale variation and overlapping of objects in such images. Specifically, the perception lightweight backbone network PLBNet is designed to obtain more feature information while improving computational efficiency. PLBNet effectively balances accuracy and computational complexity, making it suitable for real-time SAR ship detection. Moreover, MFEM is introduced to improve the target localization capability. In order to adapt to the scale diversity of ship targets, CPFFNet is designed to enhance the perception ability for ships of different scales. Moreover, EGConv is used to generate reliable gradient information. EGConv accelerates the gradient computation while maintaining the model’s ability to capture complex features, which is especially useful for learning difficult patterns in SAR images. In addition, a new loss function, SWF Loss, is proposed to enable the model to focus on difficult samples, thereby improving the detection performance. By giving more importance to challenging cases such as overlapping ships or small ships, SWF Loss enhances the model’s ability to detect these difficult instances. Experimental results confirm that the proposed method outperforms mainstream SAR ship detection methods in terms of detection performance.
Based on the contributions and experimental results, the LPFFNet model demonstrates significant improvements in detecting small and dense ships in remote sensing images. However, there are still some potential limitations that need to be considered. First, although the model effectively balances accuracy and computational complexity, its performance may still be affected by the quality and resolution of input SAR images. In cases where the image quality is poor or ships are heavily obscured by sea clutter, the model’s ability to detect small or overlapping ships may be limited. In addition, the model is primarily designed for SAR ship detection, and if applied to other remote sensing tasks or datasets, further adjustments may be required.
Future work will focus on addressing some of the current limitations of the model and further improving its performance. First, we plan to enhance the model’s ability to recognize small and dense targets in complex backgrounds by introducing more advanced feature extraction methods, such as multi-scale convolution and adaptive attention mechanisms. Additionally, considering the performance of the model on low-quality or noisy images, future research will focus on improving its robustness to low-resolution and noise-interfered images, possibly through data augmentation and more advanced noise removal techniques. Finally, we will also explore applying the LPFFNet model to other remote sensing tasks and perform transfer learning and adaptation for different task requirements to expand its application scope.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.R., P.Z. and P.L.; methodology, P.Z.; software, P.Z. and X.F.; validation, P.Z., X.F. and C.F.; formal analysis, P.Z. and X.F.; investigation, P.Z. and C.F.; resources, X.R. and P.L.; data curation, P.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, P.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.R., X.F., C.F. and P.L.; funding acquisition, X.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Project of Science and Technology Department of Henan Province under Grant 252102211029; Open Project of Institute for Complexity Science, Henan University of Technology under Grant CSKFJJ-2024-30; High-Performance Computing Platform of Henan University of Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, F.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, F. A sidelobe-aware small ship detection network for synthetic aperture radar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Fu, X.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Y. SAR ship detection algorithm based on deep dense sim attention mechanism network. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 16032–16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Dai, M.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. An anchor-free detection method for ship targets in high-resolution SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7799–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Du, L.; Guo, Y.; Du, Y. Unsupervised domain adaptation based on progressive transfer for ship detection: From optical to SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bi, F.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L. An intensity-space domain CFAR method for ship detection in HR SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.K.; Baumgartner, S.V.; da Silva, A.B.; Krieger, G. Range-Doppler based CFAR ship detection with automatic training data selection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Si, W.; Deng, Z. Research on modulation recognition method of multi-component radar signals based on deep convolution neural network. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2023, 17, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Deng, M.; Gao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D. AP-Net: A metallic surface defect detection approach with lightweight adaptive attention and enhanced feature pyramid. Clust. Comput.-J. Netw. Tools Appl. 2024, 27, 3837–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Cross-sensor SAR image target detection based on dynamic feature discrimination and center-aware calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5209417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, X.; Tao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zou, C. Convolutional-recurrent neural networks with multiple attention mechanisms for speech emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, Q.; Tao, H.; Zhu, C.; Xie, Y.; Guo, R. Cross-corpus speech emotion recognition based on causal emotion information representation. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2024, E107.D, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Soomro, N.; Han, G.; Liu, W. Content-sensitive superpixel segmentation via self-organization-map neural network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 63, 102572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Luo, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Deng, J.; Yu, L. Automatic lung segmentation in chest X-ray images using improved U-Net. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, T.; Gao, Z.; Li, H. Multiple instance learning-based two-stage metric learning network for whole slide image classification. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 5717–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ai, J.; Wu, L.; Guo, D.; Jia, W.; Hong, R. An active multi-target domain adaptation strategy: Progressive class prototype rectification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 27, 1874–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Geng, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, J.; Chen, C. Discriminative elastic-net broad learning systems for visual classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 155, 111445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Tian, R.; Luo, Q.; Jin, J.; Tang, B. Multi-scale rotation-invariant haar-like feature integrated CNN-based ship detection algorithm of multiple-target environment in SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10070–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Arbitrary-direction SAR ship detection method for multiscale imbalance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5208921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yao, C.; Ye, Z.; Xue, D.; Lin, X.; Hui, M. Feature enhancement pyramid and shallow feature reconstruction network for SAR ship detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, F.; Gu, F. MW-ACGAN: Generating multiscale high-resolution SAR images for ship detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Qi, R. Multilevel pyramid feature extraction and task decoupling network for SAR ship detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; He, Y. A semi-soft label-guided network with self-distillation for SAR inshore ship detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Leng, X.; Luo, R.; Sun, Z.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. YOLO-RC: SAR ship detection guided by characteristics of range-compressed domain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 18834–18851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J. SAR image generation method for oriented ship detection via generative adversarial networks. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Du, L.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Y. Semisupervised SAR ship detection network via scene characteristic learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xue, J.; Wen, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. EfficientShip: A hybrid deep learning framework for ship detection in the River. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 138, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Ship Grid: A novel anchor-free ship detection algorithm. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2024, 39, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, F.; Fan, Z.; Ge, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X. An efficient ship detection method based on YOLO and ship wakes using high-resolution optical Jilin1 satellite imagery. Sensors 2024, 24, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, J. LMSD-Net: A lightweight and high-performance ship detection network for optical remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. A domain adaptive few-shot SAR ship detection algorithm driven by the latent similarity between optical and SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5216318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhao, H.; Claramunt, C.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y. PPA-Net: Pyramid Pooling Attention Network for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Ren, H.; Hu, J.; Zou, L.; Wang, X. Multi-level feature-refinement anchor-free framework with consistent label-assignment mechanism for ship detection in SAR imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guan, D.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Wei, M. 3SD-Net: SAR small ship detection neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5221613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; He, Y. Frequency-adaptive learning for SAR ship detection in clutter scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Leng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. Ship recognition for complex SAR images via dual-branch transformer fusion network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4009905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Han, B.; Liu, W.; Montewka, J.; Liu, R.W. Orientation-aware ship detection via a rotation feature decoupling supported deep learning approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 125, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Dou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, D.; Li, L.; Wang, B. CM-YOLO: Context modulated representation learning for ship detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4202414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Hong, J.; Jing, M.; Wei, T. A large ship detection method based on component model in SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 4108–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y. NPA2Net: A nested path aggregation attention network for oriented SAR ship detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 9772–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.H.; Xu, N. SAR ship detection in complex background based on multi-feature fusion and non-local channel attention mechanism. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 7519–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, S. Scattering information fusion network for oriented ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4013105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, Y.; Zhou, Z. A super lightweight and efficient SAR image ship detector. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, J. Ellipse Polar Encoding for Oriented SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3502–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y. Rotating-YOLO: A novel YOLO model for remote sensing rotating object detection. Image Vis. Comput. 2025, 154, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Hu, R.; Yu, Y. ESarDet: An efficient SAR ship detection method based on context information and large effective receptive field. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Yu, W. ELSD-Net: A novel efficient and lightweight ship detection network for SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 4003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. YOLO-Ships: Lightweight ship object detection based on feature enhancement. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 101, 104170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, M.; Yasir, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, W. Lightweight algorithm for multi-scale ship detection based on high-resolution SAR images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 1390–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Wan, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, D.; Wu, B.; Sun, L. An anchor-free detection algorithm for SAR ship targets with deep saliency representation. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Qi, X.; Fan, H. LSR-Det: A lightweight detector for ship detection in SAR images based on oriented bounding box. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Gu, Y.; Peng, D. FEVT-SAR: Multi-category oriented SAR ship detection based on feature enhancement vision transformer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 2704–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2024, Proceeding of European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Başar, T. Gradient-tracking-based distributed optimization with guaranteed optimality under noisy information sharing. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 4796–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Yolo-facev2: A scale and occlusion aware face detector. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Tanveer, M.; Arshad, M. RoBoSS: A robust, bounded, sparse, and smooth loss function for supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhan, X.; Xu, Y.; Ke, X.; Zeng, T.; Su, H.; et al. SAR ship detection dataset (SSDD): Official release and comprehensive data analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, Proceeding of 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Centernet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6569–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).