Highlights
What are the main findings?
- The first integration of PPP, leveling, and InSAR into a unified framework achieves millimeter-scale accuracy for monitoring and assessing the safety of remote reclaimed islands.
- Integrated data reveal maximum displacements of 2 mm/yr at PPP points, 5 mm in leveling elevation, and InSAR deformation rates averaging −0.34 mm/yr with a peak of 18.60 mm/yr.
What are the implications of the main findings?
- The proposed framework successfully captured slow deformation and generated full-coverage settlement maps across point, linear, and areal scales, ultimately demonstrating the overall stability of the reclaimed island during the monitoring period.
- Our findings demonstrate the framework’s capability to delineate detailed defor-mation patterns and long-term trends, which is critical for predicting island stability and ensuring safety.
Abstract
To address the urgent need for safety maintenance of remote reclaimed islands, we propose a novel monitoring framework integrating PPP, leveling, and InSAR technologies to comprehensively capture slow surface deformations across point, line, and area dimensions. This study also details the data interpretation methods and critical processing workflow, using Shandong Haiyang Junzi-Lianli island as a case study. The monitoring results revealed maximum annual displacements of 2 mm for PPP reference points, 5 mm elevation variations for leveling benchmarks, and an average InSAR deformation rate of −0.34 mm/yr with peak deformation reaching 18.60 mm/yr. Meanwhile, cross-validation was performed on the results obtained from these three different techniques. The discrepancy between the benchmark PPP observation and the InSAR measurement was 3.81 mm. For the common monitoring points, the differences between leveling and InSAR ranged from 0.57 mm to 5.41 mm. The deformation trends observed in PPP reference points, leveling benchmarks, and corresponding InSAR time-series data demonstrated good consistency, indicating overall stability of the reclamation island. The proposed methodology accurately identifies minute surface deformations at different spatial scales (point, linear, and areal) of the artificial island, overcoming the limitations of single-technique approaches, thus proving to be an effective means for subsidence assessment of offshore artificial island structures. This study advances the technical framework for reclaimed island stability monitoring, offering data and solutions to identify subsidence risks and enhance disaster prevention.
1. Introduction
With the increasingly prominent contradiction between the rapid economic development of coastal regions and the growing demand for ecological environment resources [1,2], maritime expansion activities have gradually increased. Various coastal engineering projects have flourished, and land reclamation for artificial islands has emerged as an important method of urban spatial expansion. Reclaimed islands are a form of marine spatial resource development and utilization, effectively alleviating land use and ecological environmental pressures [3,4]. They generate significant economic and social value and have increasingly become an important means of safeguarding maritime rights and interests and exploiting marine resources, drawing widespread attention from coastal nations worldwide. Most coastal countries or regions around the world have undertaken land reclamation projects of varying scales. Notable examples include the United States, the Netherlands, Japan, Singapore, and Gulf countries such as the United Arab Emirates [5,6,7,8]. These nations have continuously expanded their living and development space by reclaiming land from the sea.
The construction of artificial islands involves the intersection of multiple disciplines. Reclaimed artificial islands are prone to creep deformation under long-term constant loads, which can lead to ground residual settlement [5,9,10]. This directly impacts critical real-world issues such as human life and property, making the stability of these islands a major concern for both authorities and residents. Reclaimed islands exist within a comprehensive and complex marine system, inevitably influenced by the combined effects of marine topography, geomorphology, geology, hydrodynamic conditions, and atmospheric factors. These influences inevitably jeopardize the safety and stability of the island’s foundation. Moreover, the interactions among these factors are uncertain-they both affect and constrain one another, making it highly challenging to predict the resulting engineering hazards. Current monitoring standards and regulations have yet to fully address these risks. On the other hand, marine engineering construction can alter shallow-sea environments, directly modifying hydrodynamic conditions. This leads to changes in sediment transport pathways and volumes, as well as transformations in tidal flat substrate structures. Consequently, reclaimed islands are exposed to a new and unstable environment. Compared to land-based structures, reclaimed islands face a higher risk of damage. The process of land subsidence is often irreversible—once it occurs, restoration becomes extremely difficult [11]. Given that artificial islands typically involve high construction costs, safety hazards such as subsidence can directly threaten buildings and infrastructure on the island, leading to significant economic losses [12] and even endangering human lives. Therefore, continuous stability monitoring of reclaimed islands must be conducted to promptly identify potential risks of island subsidence.
Monitoring and assessment of island subsidence serve as effective preventive measures against progressive geological hazards. Commonly used surface deformation monitoring methods primarily include conventional leveling surveys, GNSS monitoring, distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS), airborne LiDAR, and InSAR techniques [13,14,15,16]. Leveling surveying, with its long history of application, remains an important technical means for ground subsidence monitoring. However, it is susceptible to terrain and weather conditions, requires extended work cycles, and can only capture deformation measurements at discrete points. GNSS technology conducts continuous observation of fixed monitoring points on the ground, reflecting overall surface deformation through modeling. As the most widely used deformation monitoring method, its limitation lies in the susceptibility to signal obstruction and multipath effects. DFOS is an innovative measurement technology that uses light as the carrier and optical fibers as the medium to detect and transmit external signals [17,18,19]. This method is particularly suitable for distributed, high-resolution multi-parameter monitoring of localized ground subsidence. All the aforementioned monitoring methods are limited to point-based or linear measurements of surface deformation, suffering from low observation-point density and an inability to achieve full-area coverage. The advancement of remote sensing technologies has enabled the transition from point-to-area observations. Airborne LiDAR technology can rapidly, continuously, and comprehensively acquire 3D surface deformation data, making it particularly suitable for small-scale deformation monitoring. However, its accuracy is compromised under adverse weather conditions such as clouds and rain, and it struggles to detect minor pre-failure deformations of hazard bodies [20]. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) technology has become a widely utilized tool across multiple research fields over the past decades, owing to its prominent advantages of all-weather capability, strong penetration, high precision, and high-resolution acquisition of continuously covered surface elevation data [21,22,23,24,25,26]. It has emerged as an advanced, cutting-edge technology for surface deformation monitoring, capable of characterizing gradual surface change processes and potential risk events. This technology enables refined expression and characterization of deformation monitoring targets, paving a new path for monitoring land subsidence in reclaimed islands. Subsequently, scholars have utilized advanced InSAR technology to monitor ground subsidence and surface deformation in land reclamation areas [8,27,28,29,30,31]. When integrated with field investigations, these efforts have partially elucidated the underlying causes of settlement, yielding a series of successful cases and substantial research achievements.
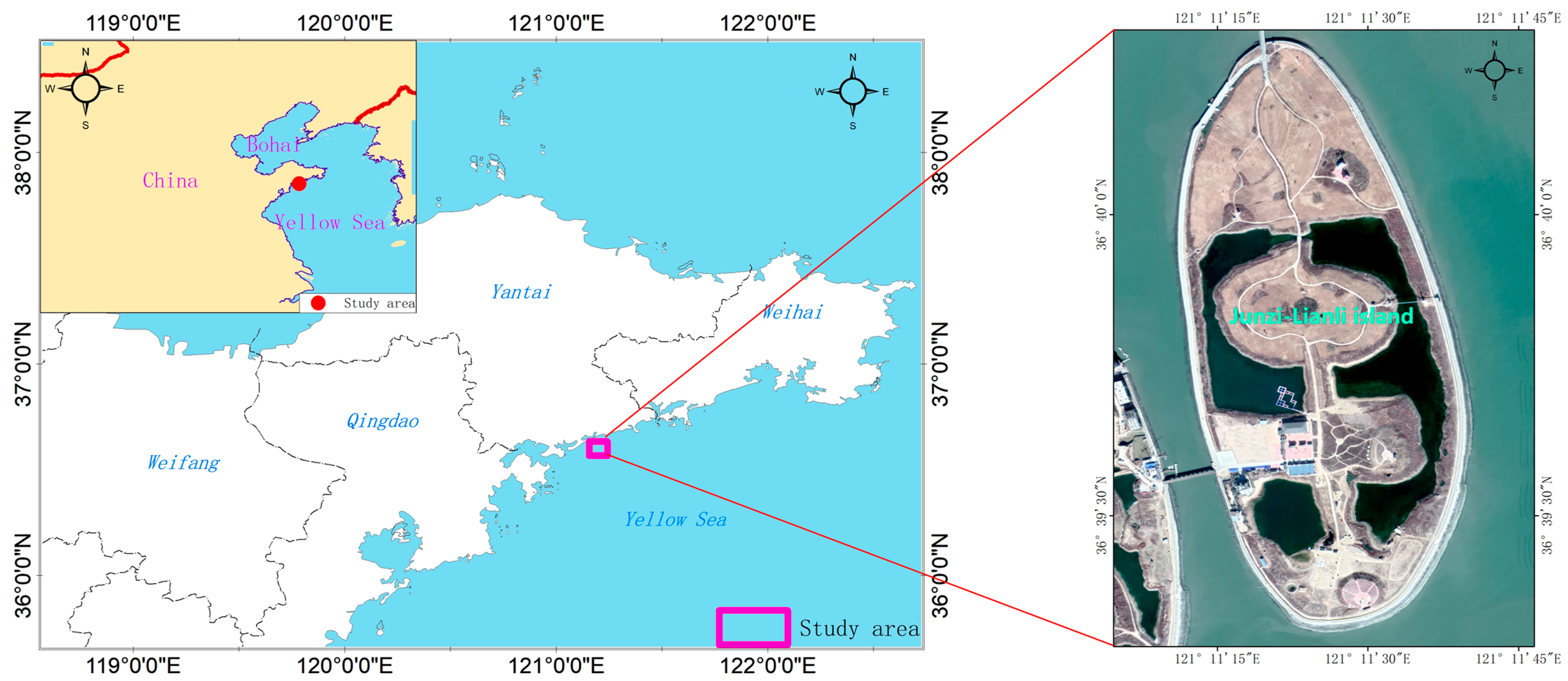
Current individual monitoring technologies all exhibit certain limitations to varying degrees. Some are limited to point-based deformation measurements, failing to comprehensively reflect the overall subsidence status of artificial islands. Even area-monitoring technologies like LiDAR face constraints such as weather susceptibility or low efficiency in large-scale monitoring. InSAR technology, however, can compensate for these shortcomings of existing methods, though its monitoring results still require validation with external data. For small, isolated areas such as offshore reclaimed islands, significant challenges exist, including severe decorrelation noise caused by lush vegetation, extreme weather conditions, variations in sensor attitude, and fluctuations in radar wave transmission ratios [15]. Additionally, reclaimed islands are typically located far from the mainland, making it necessary to establish a reference datum for comprehensive subsidence monitoring. GNSS Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technology can effectively address this requirement. Furthermore, the monitoring points connected by leveling surveys can be used to cross-validate InSAR monitoring results. Integrating data from different sources can help overcome these issues and derive properties of the phenomenon that would otherwise remain unknown. Surprisingly, only few attempts at such have been presented in the recent literature. Therefore, this study proposes an innovative approach integrating PPP, leveling, and InSAR technologies to establish a comprehensive artificial island subsidence assessment framework across three dimensions: point (GNSS), line (leveling), and area (InSAR). InSAR facilitates full-coverage subsidence monitoring of artificial islands, with PPP providing the geodetic datum and leveling data allowing for cross-validation of the InSAR accuracy. Finally, based on the interpreted deformation rates, a stability assessment model was utilized to classify the stability grade of the reclaimed island. Using Haiyang Junzi-Lianli Island in China as a case study (Figure 1), we analyze deformation trends and their driving mechanisms through multi-source, multi-temporal monitoring data, aiming to provide an effective model for high-precision operational deformation monitoring of reclaimed islands.
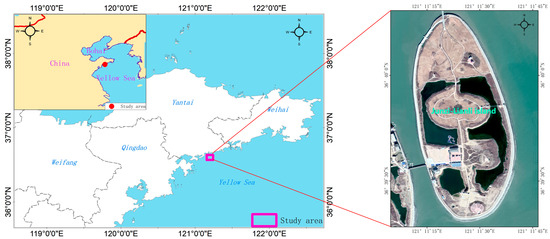
Figure 1.
Geographic location of the Junzi-Lianli island.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lianli island is situated at the southwestern tip of Haiyang National Tourist Resort, adjacent to China’s first national-level beach sports training base—Haiyang National Beach Sports Training Base. It forms a strategic “Golden Triangle” with Haiyang International Sand Sculpture Art Park and the Ten-Thousand-Meter Beach Bathing Resort, creating an east–west coastal corridor that spans both land and sea. It is the first offshore artificial island in northern China, formed through land reclamation with a total land area of 183 hectares. The water depth measures 2.5 m at the northernmost point and 4.9 m at the southernmost point. Its spatial layout features twin islands—east and west—connected to form a unity. The eastern island is named “Junzi-Lianli Island,” while the western island is called “Shunv-Lianli Island,” with the narrowest span between them being 98 m. The Lianli island bridge spans 1500 m in total length, creating dynamic connectivity between land and sea while linking the islands with the beachfront.
Lianli island is located in the northern temperate zone and falls within a continental oceanic monsoon climate region. It features four distinct seasons—winters without severe cold and summers without extreme heat [32]—along with abundant rainfall, receiving approximately 700 mm of annual precipitation. The study area experiences predominantly northerly winds in winter and southerly winds in summer. Spring and autumn serve as transitional seasons with alternating wind patterns: southerly winds prevail in spring, while northerly winds dominate in autumn [33]. In the study area’s coastal waters, the prevailing wave direction is SSE (South-Southeast) during spring, while the dominant storm wave direction shifts to SSW (South-Southwest) in autumn. The average wave height ranges between 0.5 and 0.8 m. The region experiences a regular semidiurnal tide with a mean tidal range of 2.39 m, characterized by strong reversing currents. The primary current direction follows a W-E (West-East) orientation [34,35,36].
2.2. Technical Workflow
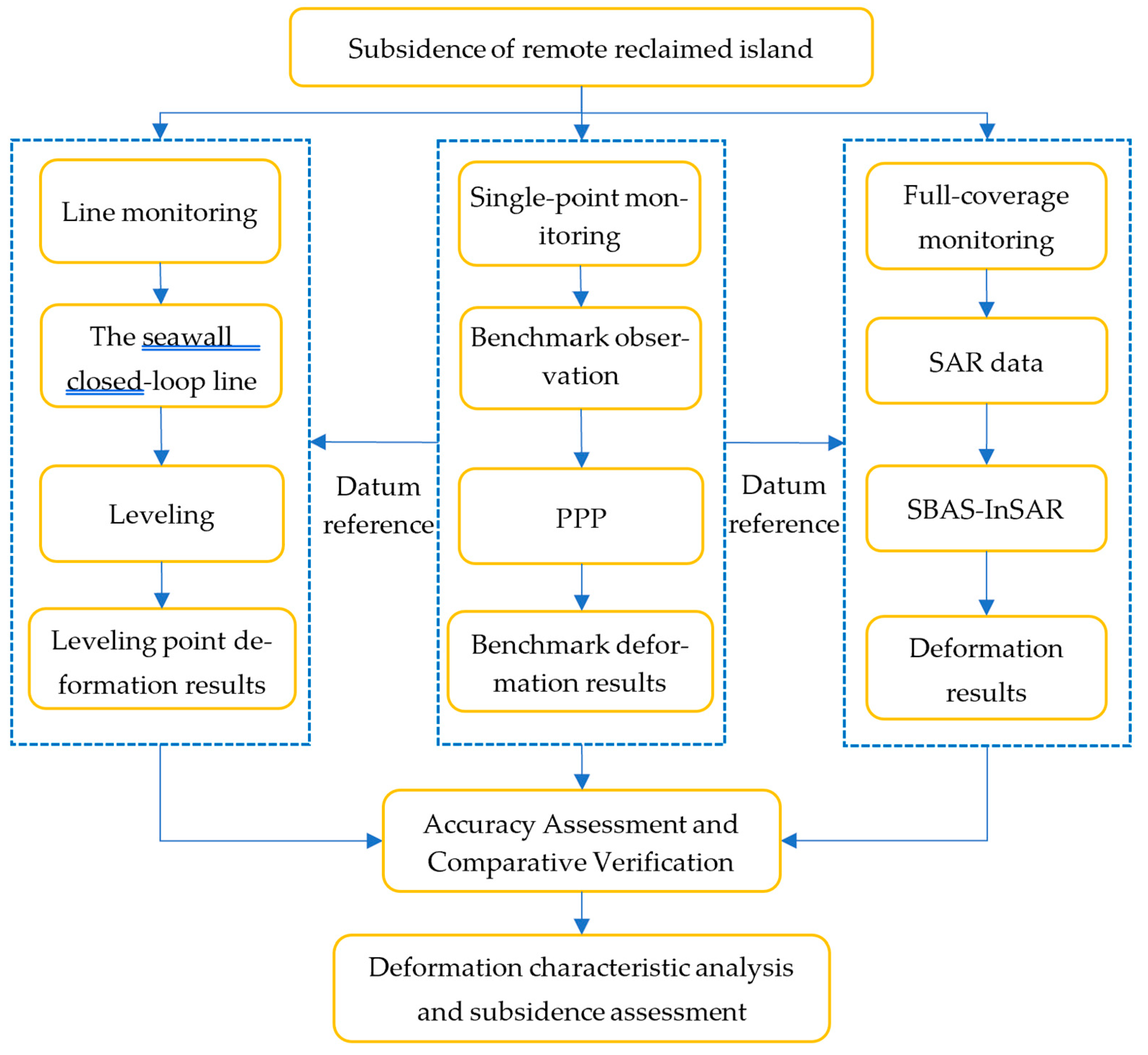
To address the challenge of stability diagnosis for remote reclaimed islands, we integrated PPP, leveling, and InSAR technologies, constructing a comprehensive subsidence monitoring and evaluation framework for reclaimed islands from point, line, and surface dimensions. First, PPP technology was employed to monitor benchmark points, establishing the initial geodetic datum reference for subsequent leveling surveys and InSAR monitoring. Subsequently, a closed-loop leveling network was established along the perimeter embankment, enabling comprehensive safety assessment of the entire island’s seawall through precise leveling measurements. Finally, InSAR technology was utilized to obtain complete-coverage surface deformation data, enabling comprehensive monitoring of ground subsidence across the entire artificial island. On this basis, cross-validation of measurement accuracy was conducted through mutual verification among these three techniques. Ultimately, the integrated monitoring enabled comprehensive identification of the reclaimed island’s deformation patterns, rigorous assessment of its stability status, and systematic analysis of the underlying causal mechanisms during the observation period (Figure 2).
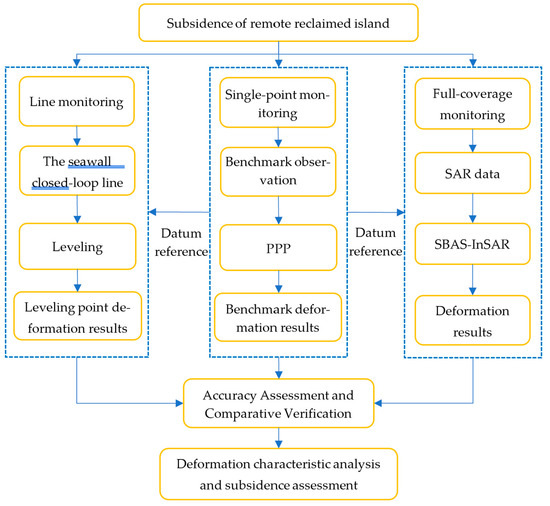
Figure 2.
Technical flowchart for monitoring and assessing subsidence of remote reclaimed islands by integrating PPP, Leveling, and InSAR.
2.3. PPP
PPP is a technique that utilizes carrier-phase and code pseudorange observations from Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), in conjunction with precise satellite orbit and clock correction products provided by third-party services, to achieve centimeter- to millimeter-level positioning accuracy with a single receiver. By leveraging high-precision satellite orbit and clock correction products provided by IGS or iGMAS, it mitigates or eliminates errors related to the satellite segment, signal propagation path, and receiver segment through model corrections or parameter estimation, thereby achieving high-precision positioning [37,38,39,40,41].
2.3.1. Observation Model
The primary GNSS observation data consists of ranging codes and carrier phase, with the fundamental observation equation [42] expressed as follows:
where and denote the receiver station and satellite indices, respectively; is the speed of light in vacuum; represents the geometric range between satellite and receiver ; (code pseudorange) and (carrier-phase pseudorange) are the raw observables; denotes the carrier phase measurement in cycles; and correspond to the receiver and satellite clock offsets, respectively; and signify the tropospheric and ionospheric propagation delays; is the integer phase ambiguity; and represent the measurement noise for code and phase observations, respectively.
PPP employs a dual-frequency ionosphere-free linear combination model to establish the geometric relationship between observations and unknown parameters. The combined observable [43] is expressed as:
where and represent the ionosphere-free combined phase and code pseudorange observables, respectively; denotes the signal frequency, with and corresponding to the frequencies of and carrier-phase observations; and are the raw pseudorange measurements at frequencies and ; and refer to the carrier-phase observations at frequencies and .
2.3.2. Error Correction
In addition to utilizing high-precision satellite orbit and clock products, PPP still contains various error sources such as atmospheric delay errors, receiver antenna phase center variations, and tidal effects, which must be mitigated or eliminated through appropriate methods to minimize their impact on positioning accuracy.
(1) Signal propagation-related errors
When GNSS signals propagate through the troposphere, they experience signal delay. The tropospheric delay effect can be calculated using the following equation:
where denotes the total tropospheric delay along the signal propagation path; , and represent the zenith hydrostatic (dry) and zenith wet (non-hydrostatic) delay components, respectively. Commonly used models such as the Saastamoinen and UNB models are employed to correct the hydrostatic (dry) tropospheric delay [44]. However, the wet delay component exhibits significant spatiotemporal variability due to its strong dependence on atmospheric water vapor distribution and cannot be precisely modeled. Therefore, in receiver position estimation, the wet delay is typically treated as an unknown parameter to be resolved in the positioning solution.
(2) Receiver Antenna Phase Center Variations
The variation in satellite signal strength, propagation direction, and elevation angle causes the actual Antenna Phase Center (APC) to deviate from its theoretical position [45], necessitating correction using an antenna correction model. Additionally, there is a discrepancy between the theoretical phase center of the antenna and the Antenna Reference Point (ARP), which can be corrected through geometric methods.
(3) Tidal Correction
Under the gravitational influence of celestial bodies, the Earth experiences periodic deformations, including solid Earth tides and ocean tide loading effects, which lead to variations in station positions. Therefore, it is necessary to correct the impact of such errors. The influence of solid Earth tides requires correction using precise models [46,47]. Ocean tide loading effects [48] are approximately one order of magnitude smaller than solid Earth tides in magnitude and can be corrected using models such as FES2004.
2.4. Leveling
Based on the second-class technical requirements in the “Specifications for the first and second order leveling” (GB/T 12897-2006) [49], the national second-class leveling measurement is adopted in China. The double-run (forward and backward observations) leveling method is employed, with the survey route forming a closed loop. After quality inspection and verification of the observed data, adjustment processing and analysis are performed. The leveling database consists of repeatedly measured height differences along leveling lines. The resulting network of leveling lines depends on the country-specific characteristics of the respective height system. The elevations of all leveling points are transformed to the PPP-derived reference benchmark elevation as the datum, yielding the final elevations for each leveling point.
2.5. SBAS-InSAR
InSAR technology uses radar located at different spatial positions to observe the same target object, obtains two or more SAR images, and then performs interferometric processing to obtain elevation or deformation information on the target [50,51]. To overcome the influence of factors such as spatiotemporal decoherence and atmospheric delay on deformation monitoring results, researchers have proposed the small baseline subset InSAR (SBAS-InSAR) technology based on it to weaken the interference of factors [21,52], Thus obtaining higher precision deformation monitoring results. SBAS-InSAR is an InSAR time series analysis method that utilizes multiple main images and a short spatiotemporal baseline criterion. The SBAS-InSAR method has become a reliable method for monitoring slow ground displacement and has been widely used [53,54]. Its prominent feature is the comprehensive consideration of the correlation between temporal and spatial baselines to select multiple main images to enhance coherence and obtain more high-coherence points.
We used the phase information from SAR images to estimate the subtle deformations of island subsidence. The original N + 1 SAR images can produce M unwrapped interferograms under the SBAS baseline constraint. The phase in point of the i-th unwrapped interferogram (corresponding to the time and ) can be expressed as follows [55]:
where and indicate the LOS deformation at the time and . is the residual phase derived from DEM inaccuracy. The represents the error phase from the atmospheric delay, unwrapped error and thermal noise. is the phase of the unwrapping interferogram and can be expressed as
where the parameter to be solved are expressed as follows:
After removing the residual elevation phase and unwrapping error, the velocity phase is solved as follows:
where A is a matrix with dimensions of M × N, and then the SVD algorithm with minimum norm conditions is introduced to obtain the deformation rate.
2.6. Data Acquisition and Processing
The distribution of InSAR, leveling and GNSS data used for the estimation of surface displacements is shown in Figure 1 (pink rectangle). In the following, we will focus on introducing three technical methods for data acquisition and processing.
2.6.1. PPP Data
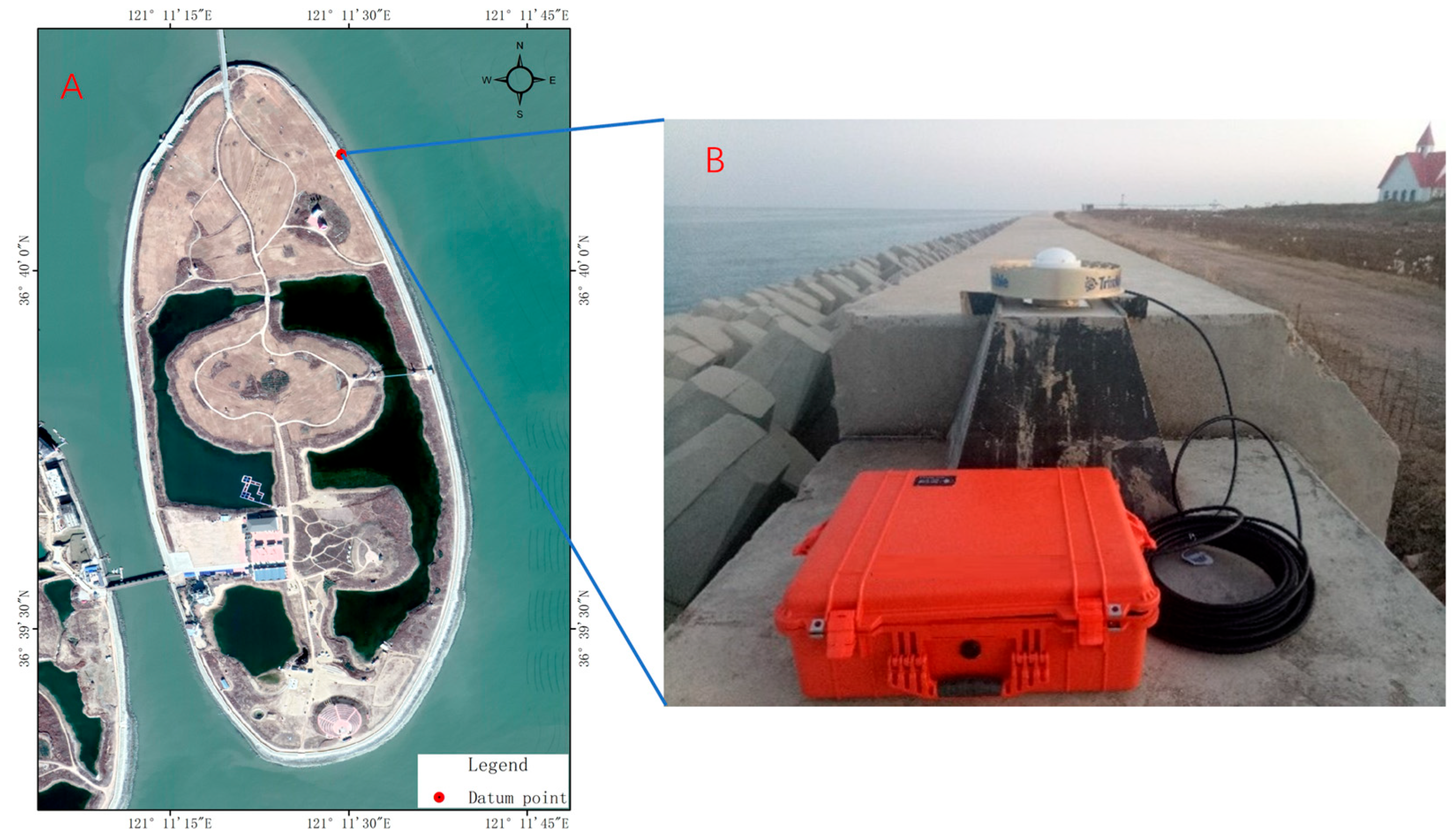
In order to obtain the precise coordinates of the datum points for island subsidence observation, three PPP static observations were conducted on Lianli Island on 14–15 November 2018, 22–23 October 2019, and 18–19 November 2020, respectively (Figure 3). The data was collected using a Trimble NetR9 receiver and a TRM59900.00 Choke Ring antenna (Trimble, California, USA), with each observation session lasting more than 24 h.
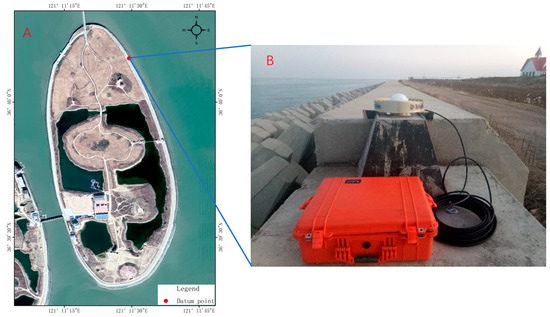
Figure 3.
Observing datum point using PPP. (A) Location of the datum point. (B) Field observation.
PPP data processing involves the following steps: First, the IGS precise ephemeris and satellite clock offsets are fitted into polynomials and linearly interpolated. Subsequently, data preprocessing—including cycle slip detection and repair, as well as phase smoothing of pseudorange—is conducted to obtain high-quality undifferenced phase and pseudorange observations. Next, error correction models are applied to mitigate or eliminate relevant errors before performing parameter estimation. Ultimately, high-precision 3D coordinates of the static observation points are derived.
2.6.2. Leveling Data
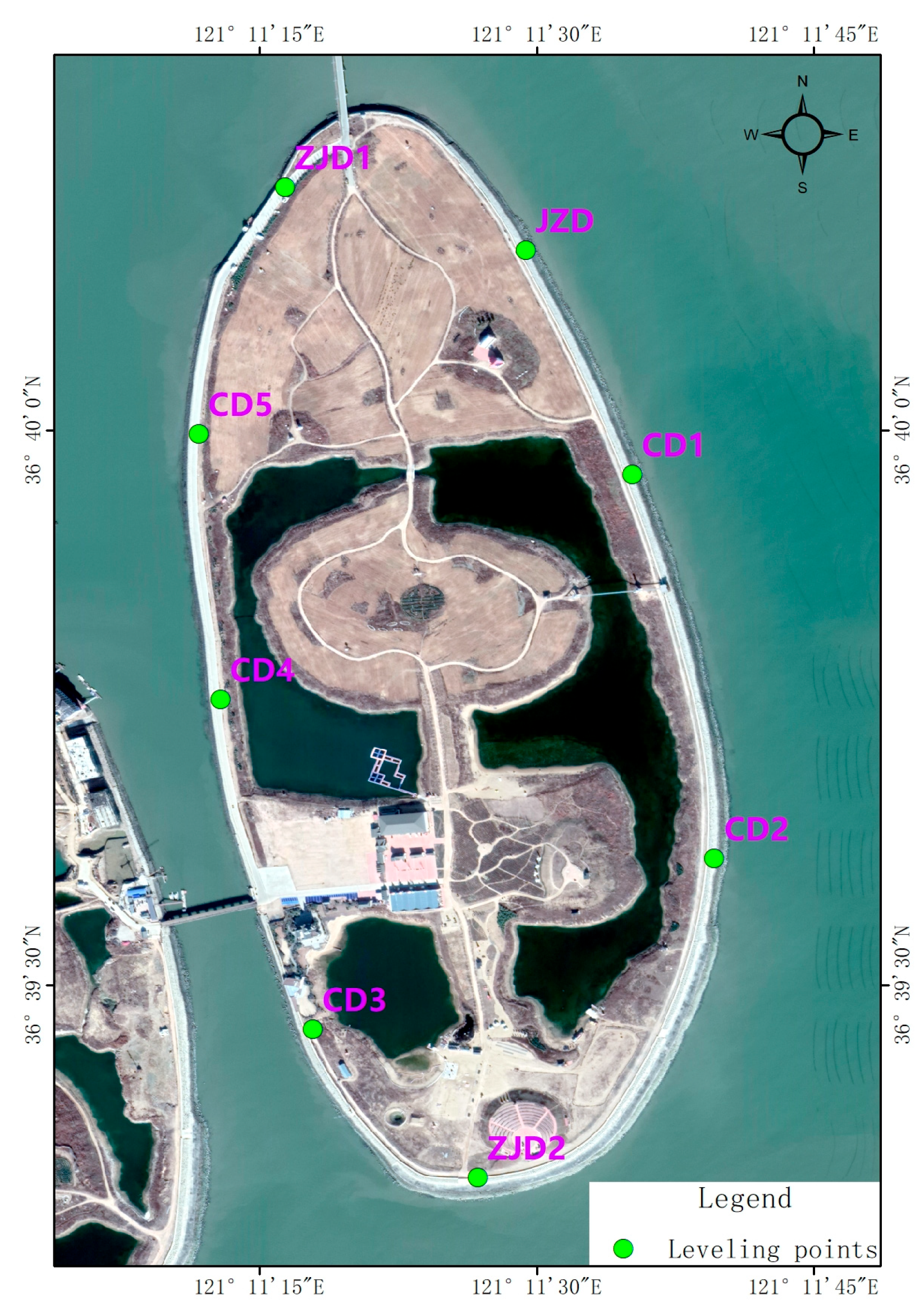
Leveling surveys were conducted synchronously with PPP observations in November 2018, October 2019, and November 2020, respectively. The leveling surveys were conducted in accordance with the Class II technical requirements specified in the “Specifications for the first and second order leveling” (GB/T 12897-2006) [49]. A second-order leveling approach was adopted, employing double-run measurements. Monitoring points were evenly distributed (Figure 4), and the survey routes formed closed loops to ensure accuracy and reliability.
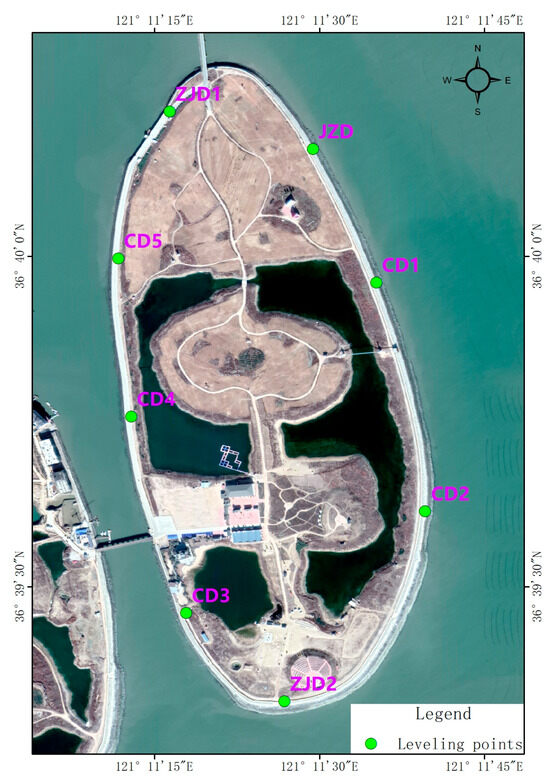

Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of leveling monitoring points.
2.6.3. InSAR Data
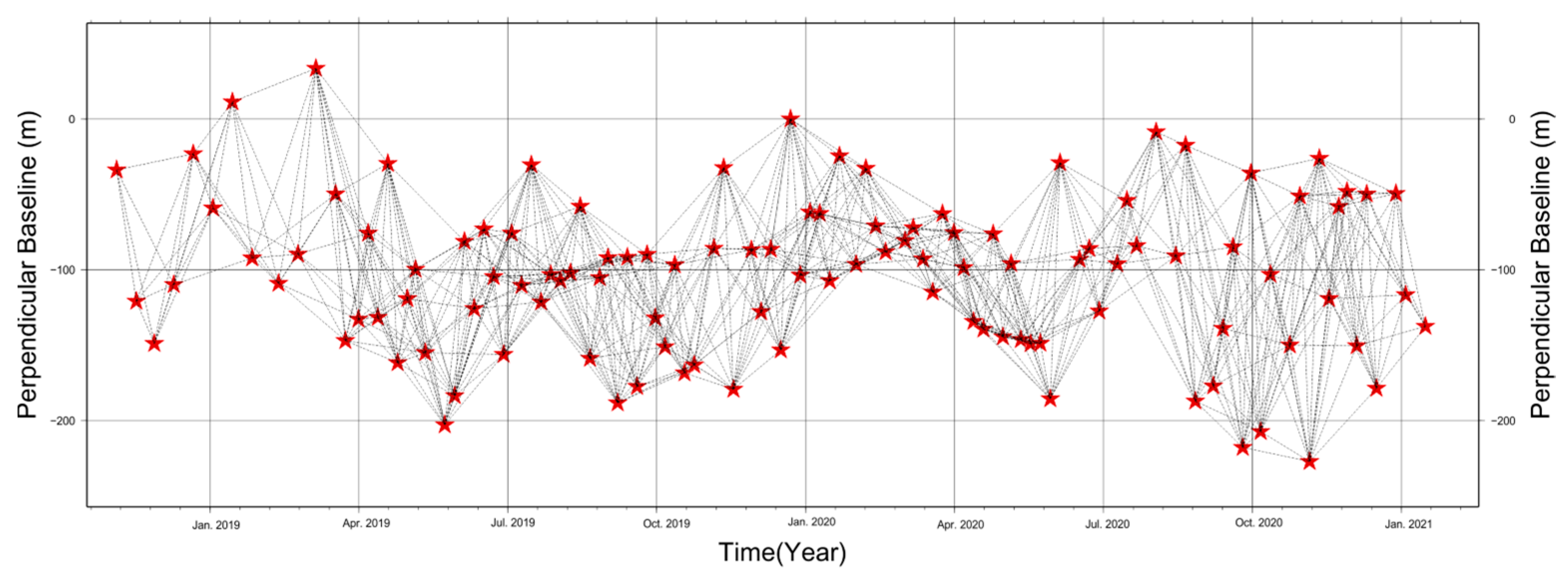
The surface deformation of Junzi-Lianli Island was monitored using Sentinel satellite data from the European Space Agency (ESA), with a total of 112 scenes acquired from January 2018 to December 2020. Using the Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) method, 747 interferograms were generated, as shown in Figure 5.
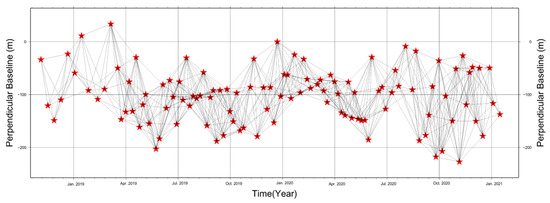
Figure 5.
SBAS-InSAR interferometric network datasets (the pentagram represents each SAR image).
This section presents the process of using SBAS-InSAR technology to determine the surface deformation of artificial islands.
Firstly, all SAR images are co-registered with the master SAR image and a small baseline set pair is established. Secondly, during the interference generation process, Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission Digital Elevation Model (SRTM DEM) is an external DEM that removes the flat and topographic effects [56]. And we used the Graphics processing unit (GPU)-assisted InSAR processing method [57,58] to improve the processing efficiency including geometric coregistration, resampling, and ESD correction. Thirdly, GACOS was utilized to generate atmospheric correction to all interferograms. Then, with high- and low-pass filters, the average deformation rate was calculated by employing the linear least squares (LS) method, and the time-series cumulative deformation was then obtained via the singular value decomposition (SVD) algorithm [21,52,59,60]. Finally, the deformation amount and deformation rate accumulated by time series in SAR coordinate system are converted to the WGS-84 coordinate system.
2.7. Stability Rating
For the stability assessment of the reclaimed island, we referred to the marine industry standard “Technical specification for stability monitoring of islands where the territorial sea base point is located” (HY/T 0487-2025) [61]. Following its settlement evaluation method (Table 1), we determined the stability grade of the island using either the average settlement rate or the cumulative settlement as the evaluation criterion.

Table 1.
Stability classification criteria for reclaimed islands.
3. Results
3.1. Observation Results of Benchmark Points Based on PPP
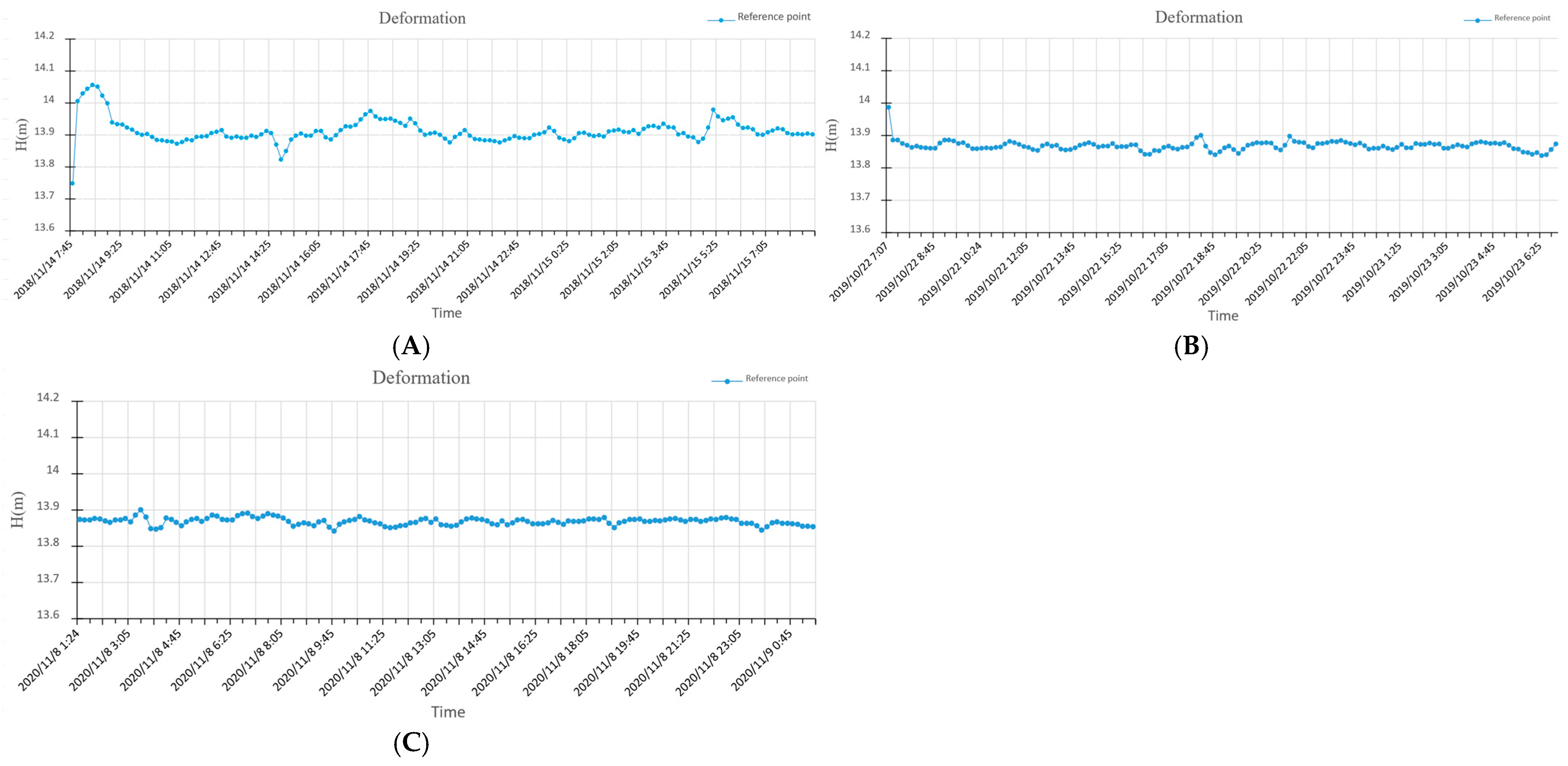
Using the precise orbits (15 min) and clock offsets (30 s) products from the COD analysis center to perform PPP solution for GNSS data from the GPS+GLONASS dual-system. In the PPP solution, the receiver antenna height is set to 0.000 m, and the positioning results are reduced to the Antenna Reference Point (ARP) of the receiver antenna. The variation curves during the three PPP static monitoring periods are shown in Figure 6. The elevation monitoring results of the reference datum point in November 2018, October 2019, and November 2020 were 13.866 m, 13.868 m, and 13.868 m, respectively, with an annual maximum deformation of 2 mm. According to the evaluation of PPP observation accuracy, an annual vertical variation in less than 6 mm [29] suggests that the observation station can be considered fixed. Therefore, the monitored reference point can be regarded as stable.
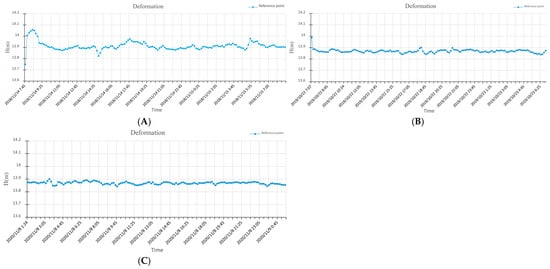
Figure 6.
PPP observation results of datum point in November 2018 (A), October 2019 (B), and November 2020 (C).
3.2. Leveling Measurement Monitoring Results
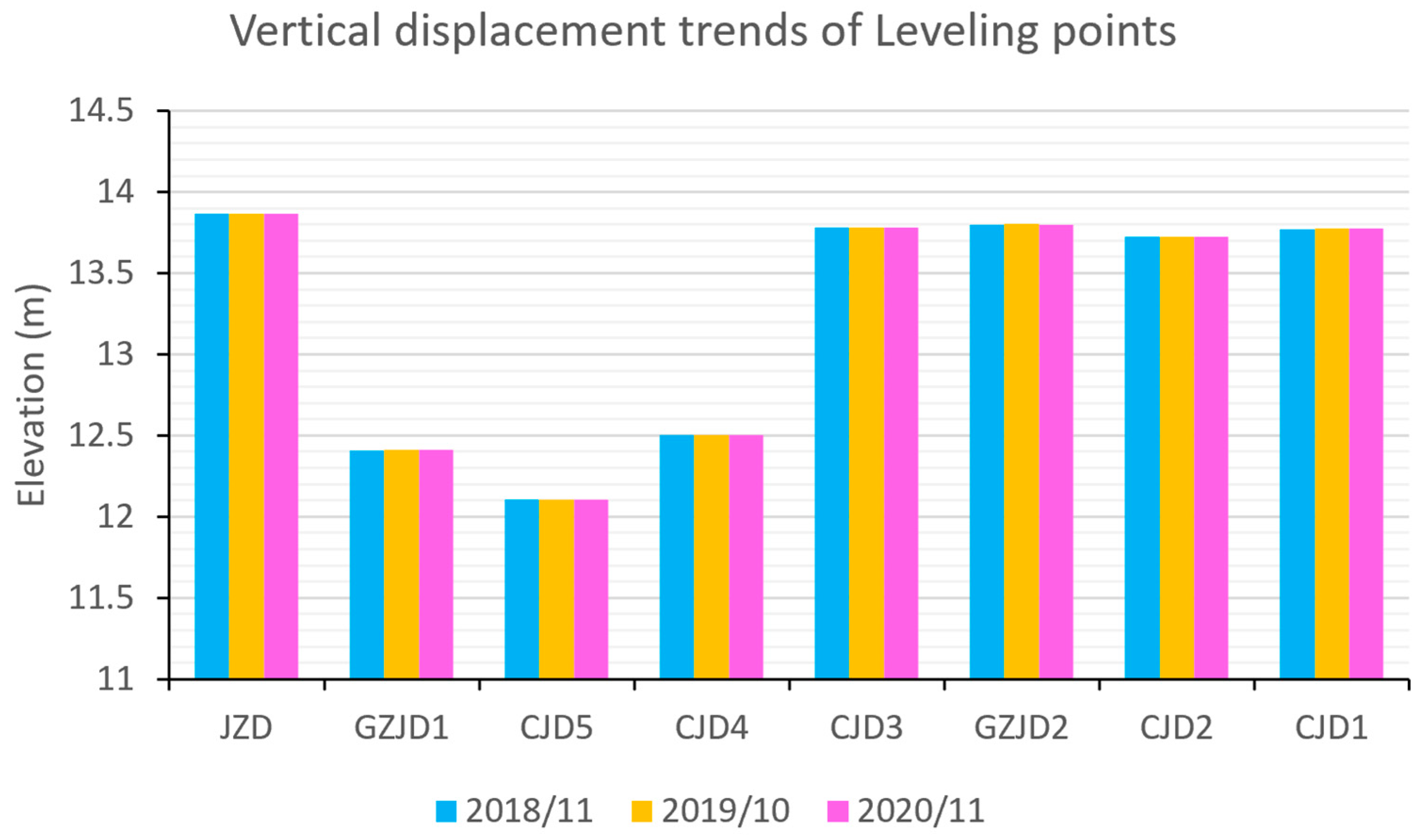
Three leveling surveys were conducted on the artificial island in November 2018, October 2019, and November 2020, respectively. Using the benchmark elevation obtained from each PPP monitoring session as the starting elevation for conversion, and after adjustment processing, the elevation changes in each leveling point are shown in Table 2 and Figure 7. During the three monitoring campaigns from November 2018 to November 2020, all leveling points exhibited maximum annual elevation changes of 5 mm, which we consider indicative of stable ground conditions.

Table 2.
Elevation difference variations in leveling points for 2018–2019 and 2019–2020.
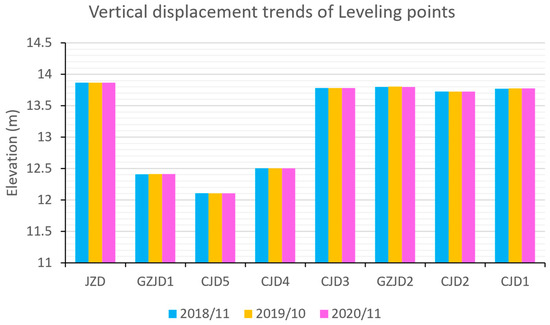
Figure 7.
Elevation changes in each leveling point over the three monitoring periods.
3.3. Deformation Monitoring Results Based on InSAR
(1) Land surface deformation and spatial distribution of reclaimed island
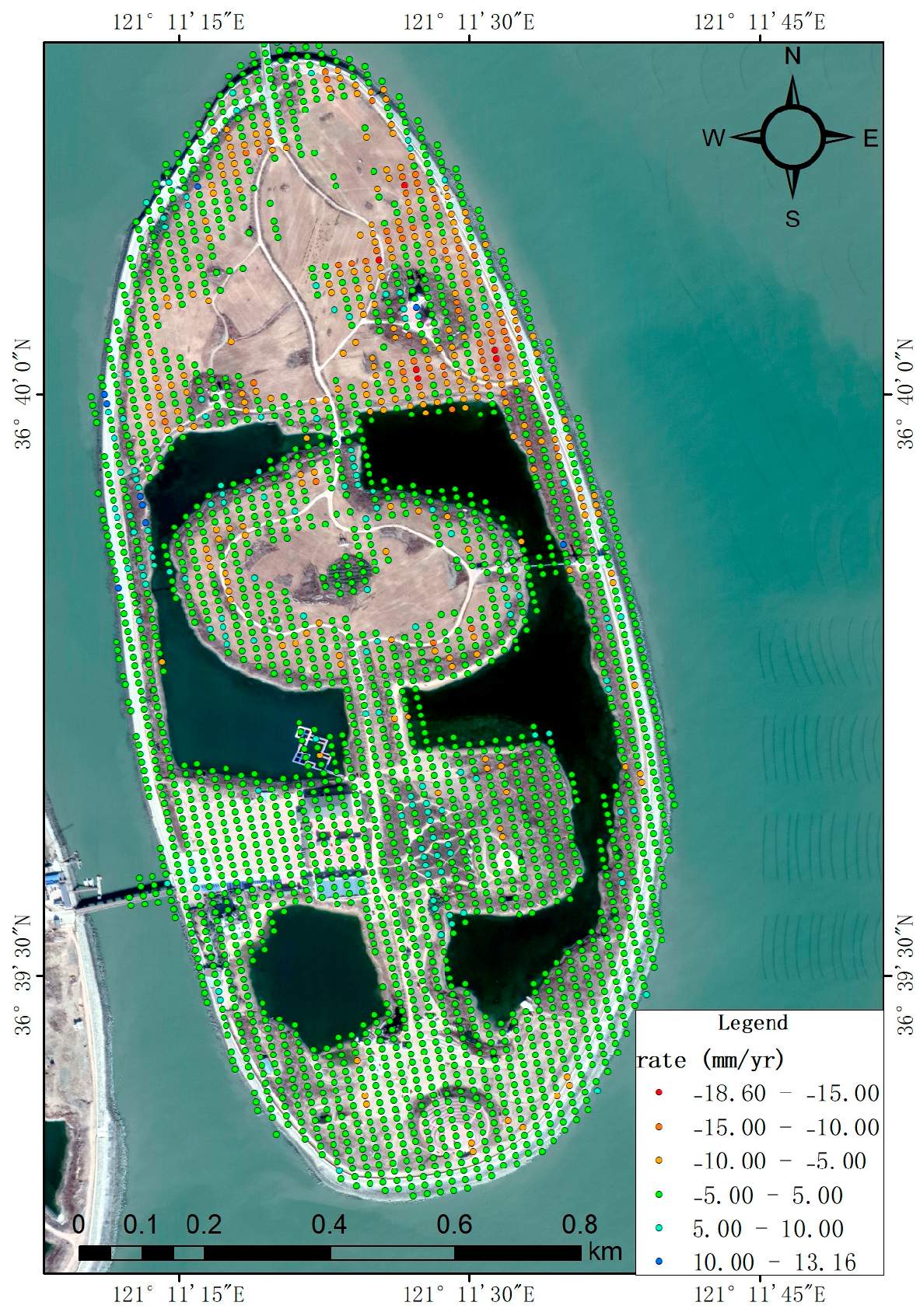
Using Sentinel-1A SAR data from January 2018 to December 2020, the average deformation rate of Junzi-Lianli island during this period was obtained through InSAR time-series analysis (Figure 8). Time-series monitoring revealed quasi-stable conditions across Junzi-Lianli island, though localized ground displacement was detected. Peak displacement velocities reached 13.16 mm/yr (uplift) and −18.60 mm/yr (subsidence), with a spatially averaged deformation rate of −0.34 mm/yr. The relatively significant deformation was primarily observed in the northern section of the reclaimed island. Field investigations revealed that this area had been temporarily utilized for crop cultivation.

Figure 8.
Annual mean deformation rate map of Lianli-Junzi island.
(2) Time-series deformation analysis of characteristic points
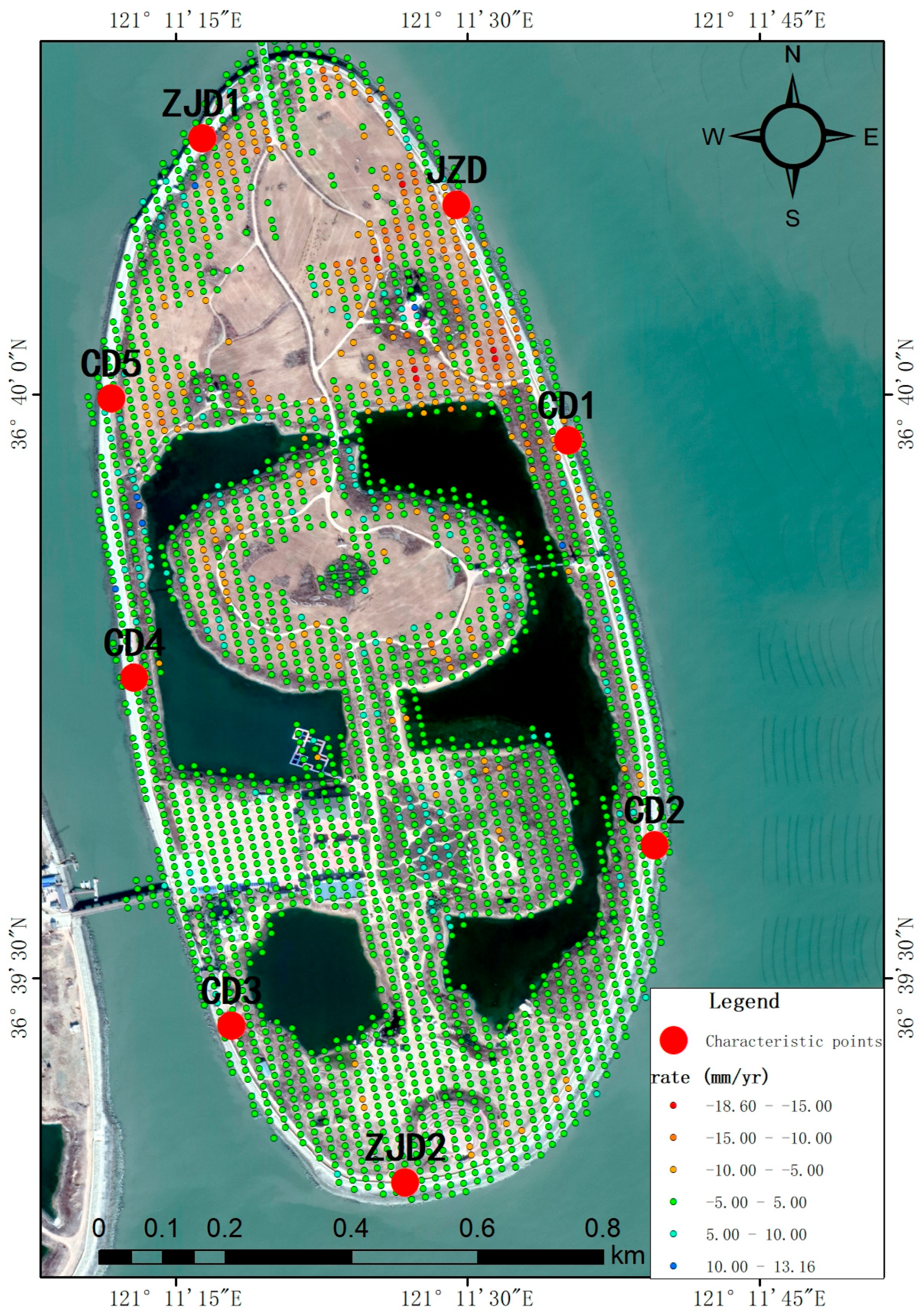
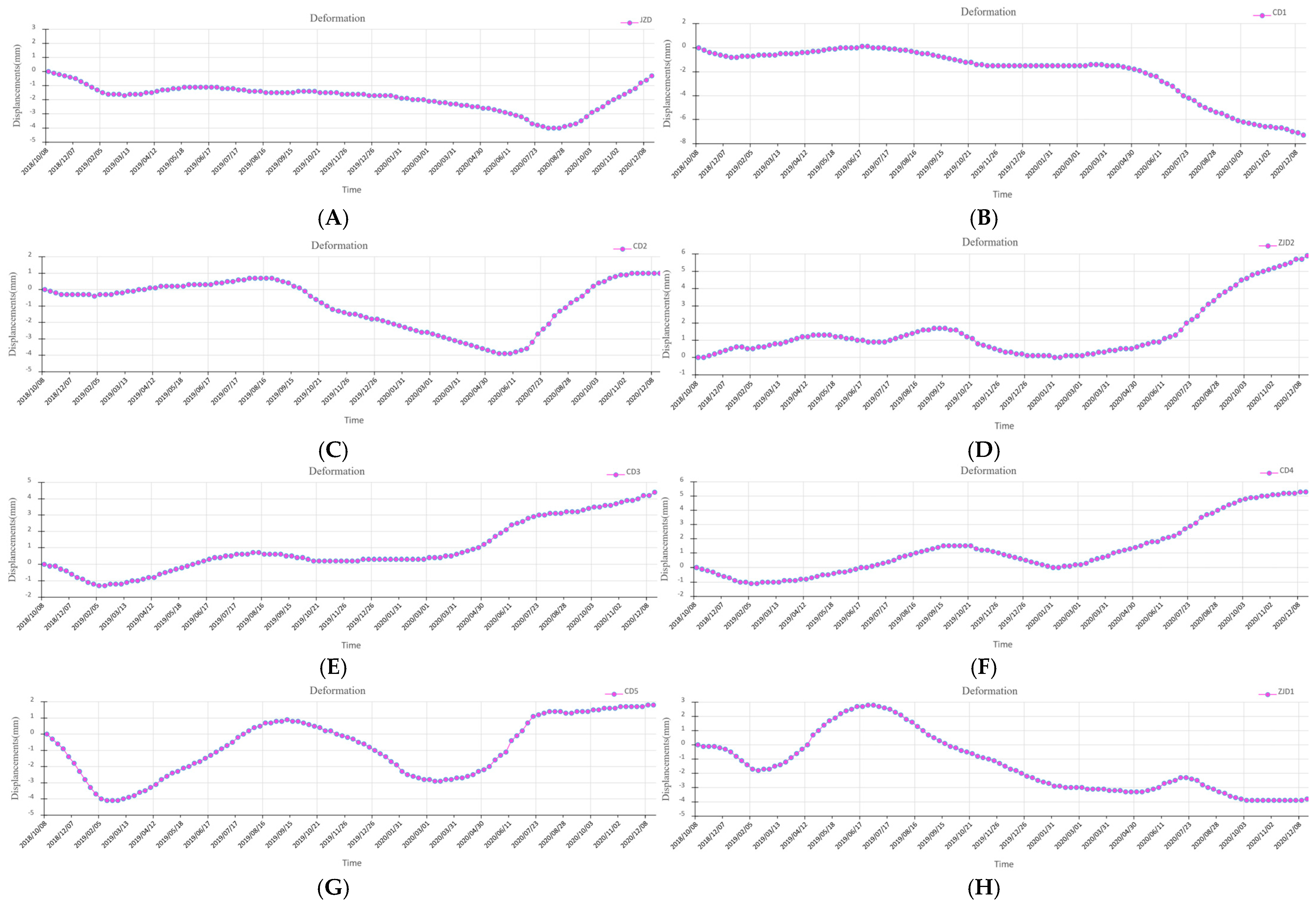
For a comprehensive assessment of reclaimed land subsidence dynamics, eight leveling monitoring points were strategically selected as feature points for high-resolution time-series displacement analysis (Figure 9). This configuration facilitates rigorous inter-comparison between leveling and InSAR monitoring methodologies. The deformation monitoring results for each individual point are presented in Figure 10. Given the location of the reclaimed island, which is far from the mainland, surrounded by sea, and subject to significant atmospheric noise due to high humidity, we conservatively estimate the accuracy of the InSAR-derived deformation rate to be within 10 mm/yr. This assessment supports the conclusion that this point is relatively stable. The derived deformation chronologies (Figure 10) demonstrate that characteristic point P1 along the Junzi-Lianli island embankment, which serves as a PPP monitoring station, exhibited a maximum displacement of ≤5 mm and remained essentially stable throughout the 2018–2020 monitoring period. The remaining characteristic points exhibited maximum deformations ≤ 8 mm during the monitoring period, with most displacements confined within 5 mm. We therefore conclude these points maintained overall geodetic stability. The composite breakwater structure, incorporating concrete and accropode armor units on the sloped revetment, demonstrates excellent wave energy dissipation, effectively ensuring embankment safety.
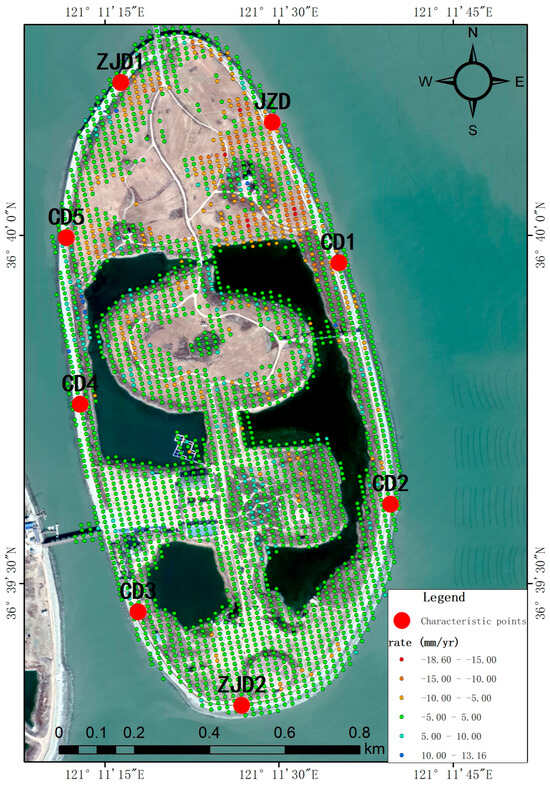

Figure 9.
Spatial distribution of characteristic points.
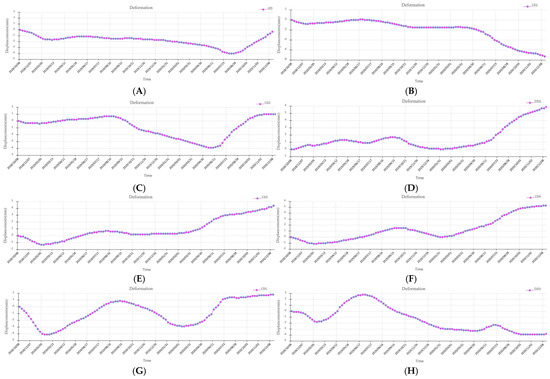
Figure 10.
Time-series deformation of the eight selected characteristic points during the 2018–2020. (A) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point JZD, (B) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point CD1, (C) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point CD2, (D) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point ZJD2, (E) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point CD3, (F) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point CD4, (G) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point CD5, (H) represents the time-series deformation of characteristic point ZJD1.
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy Verification
Since InSAR can only monitor the one-dimensional projection of surface deformation along the Line of Sight (LOS) direction—a vector in three-dimensional space—it is necessary to convert the LOS deformation results into the vertical deformation component for comparison with GNSS and leveling measurements. Based on field surveys, the surface deformation on Lianli Island is primarily vertical, with no appreciable horizontal displacement. Assuming negligible horizontal motion, the vertical deformation component is reasonably derived from Equation (10) using the SAR satellite data’s incidence angle of 39.16°.
where denotes the vertical deformation, represents the line-of-sight deformation, and is the radar incidence angle.
PPP observations revealed a 2 mm elevation change at the benchmark during November 2018 to October 2019, while InSAR monitoring showed an average deformation of −1.28 mm over the same period. These statistically consistent results confirm the stability of the benchmark and demonstrate mutual validation between the two monitoring techniques. During the period from October 2019 to November 2020, PPP observations showed no elevation change at the benchmark, while InSAR monitoring recorded an average deformation of −2.46 mm. We conclude that the benchmark remained stable, and the results from both techniques demonstrate consistent measurement precision.
A comparative analysis of leveling measurements and corresponding InSAR monitoring results is presented in Table 3. During the period from November 2018 to November 2020, the maximum elevation change observed via leveling was 3 mm, while InSAR detected a maximum displacement of 2.41 mm. The discrepancy between the two techniques at any given monitoring point did not exceed 6 mm, further confirming the stability of all benchmarks (i.e., no significant deformation occurred) and demonstrating the mutual reliability of both monitoring methods.

Table 3.
Cross-validation of leveling and InSAR monitoring results.
4.2. Scalability Analysis of the Method
The leveling or PPP is difficult to achieve entire surface deformation because of their sparse measurement points distributed on the reclamation island. Compared with the leveling and PPP, satellite InSAR has the advantages of all-weather operation, non-contact sensing, and wide-area imaging with spatial continuous coverage. Studies have indicated that space-borne InSAR can monitor large-scale surface deformation [62,63,64,65,66]. We also proved that this technology can also be used to monitor the subsidence of islands on a small scale. In addition, the abundant archived SAR data make it possible to retrospect the historical deformation, which can help interpret the deformation mechanism.
However, some limitations exist for satellite InSAR when monitoring the subsidence of reclamation island. Satellite InSAR has constant revisit time, which cannot be changed to adapt to the requirement. In addition, the InSAR technique can only measure deformation along the line-of-sight (LOS) direction. Alternatively, the commercial minor satellite constellation with high spatial resolutions and short revisiting time, e.g., ICEYE and Capella, can be employed to make up the deficiency of free Sentinel-1 for monitoring key reclamation island sections. Especially, UAV SAR is increasingly used in topographic mapping, disaster assessment, and environmental monitoring due to its lightweight, low-power, low-cost, high-resolution, and flexible operation [67,68,69]. However, the accuracy of inertial navigation systems is limited by UAV payload constraints. Moreover, the compact and lightweight nature of UAV SAR makes it vulnerable to airflow disturbances, necessitating motion error compensation [70,71,72]. Spaceborne SAR is more suitable for large-scale surface deformation surveys, while UAV SAR excels in localized high-precision detection. The organic integration of both can leverage their respective advantages of high spatiotemporal resolution and wide-area coverage to compensate for individual limitations.
Therefore, at present, integrating multi-source SAR images with ground-based datasets such as PPP or leveling measurements remains essential for a comprehensive analysis of deformation mechanisms and their causative factors. This method has enabled us to overcome the limitations of single-technology approaches and achieved precise monitoring of complex scenarios in artificial island regions, demonstrating promising potential for wider application in complex coastal areas.
4.3. Strengths and Limitations of Monitoring Techniques
We obtained millimeter-scale deformation of the perimeter dam of the reclamation island using precise leveling techniques. This method offers high monitoring accuracy and excellent stability. However, leveling only provides discrete point-based or linear monitoring results, making it difficult to rapidly and accurately represent the regional land subsidence status. Additionally, measurements are challenging to conduct in specific restricted areas [73]. For large-area monitoring, the leveling method is inherently asynchronous, meaning that measurements from all monitoring points are not taken simultaneously. It is generally assumed that ground deformation during the survey period is negligible; however, this assumption becomes less valid in areas experiencing significant subsidence, where the deformation occurring within the measurement timeframe can introduce substantial errors. The longer the leveling route, the more the errors accumulate and the greater the time required for measurement [74,75]. Additionally, this technique demands substantial human and material resources, resulting in high monitoring costs.
Due to the island’s remote location from the mainland, conventional GNSS techniques like RTK or CORS were not feasible for monitoring. Therefore, the Precise Point Positioning (PPP) technique was employed to observe the reference points for real-time deformation. Post-processing of the PPP data also yielded millimeter-level accuracy [76,77]. For smaller areas, establishing a PPP monitoring network can achieve high-precision, real-time deformation detection. Compared to leveling, PPP requires less manpower during operation and enables long-term, automated monitoring. However, the monitoring points are relatively dispersed, making it difficult to form an areal coverage. Although PPP offers high precision in both planar and temporal dimensions, its performance is significantly influenced by environmental conditions [78], and the required equipment entails a substantial cost.
Utilizing InSAR technology, we rapidly acquired millimeter-scale stability status across the entire reclamation island. This technique shows great potential for ground observation, as it is unaffected by weather conditions and can quickly capture instantaneous, continuous, and areal data of the same moment. Furthermore, it provides long-time-series historical deformation data, which is unmatched by conventional surveying methods [79,80]. With the continuous launch of medium- and high-resolution radar satellites across different bands and the ongoing advancement of InSAR technology, its revisit period is shortening, and measurement accuracy is improving. Consequently, InSAR is poised to be widely applied in land subsidence monitoring and is expected to become a primary technique. However, InSAR still faces challenges, including decorrelation noise caused by dense vegetation, extreme weather, variations in sensor attitude, and radar wave penetration issues [15]. Another challenge of using InSAR for deformation measurement is that it can only capture one-dimensional displacement, namely, the projection of the true surface movement onto the Line-of-Sight (LOS) direction [81]. This one-dimensional measurement in the LOS can lead to an underestimation and misinterpretation of the actual surface deformation, which has become a bottleneck limiting the broader application and promotion of InSAR technology [82]. Consequently, how to effectively recover the true two-dimensional or even three-dimensional deformation fields remains a critical and urgent problem that InSAR technology needs to solve.
The above demonstrates that InSAR technology possesses a superior capability for areal stability monitoring of the reclamation island compared to leveling and PPP. Although precise leveling provides the most reliable accuracy, it was utilized in this study to calibrate the InSAR measurements, thereby further enhancing InSAR’s precision. In practical applications, an integrated InSAR and GNSS approach, known as GInSAR [83], can be employed. This integration expands the monitoring coverage, better reveals deformation patterns, improves the accuracy of GNSS monitoring, and increases the potential for near-real-time subsidence monitoring. InSAR acquires information from the entire observed area simultaneously. During repeat observations, the temporal sampling interval is equal and synchronous for all targets. In contrast, leveling is an asynchronous method for large-area monitoring, as measurements from individual points are not obtained at the same time. Consequently, this inherent discrepancy makes it fundamentally challenging to achieve truly simultaneous measurements over large areas using either InSAR or leveling alone—a critical premise for comparison that is often difficult to meet in reality, introducing uncertainty. In practice, completing a leveling line or network often requires an extended period. This process is subject to variable human factors and potential ground movement at benchmarks during the measurement campaign, introducing significant variability. However, in this study, the case study area—Junzi-Lianli Island—has a relatively small footprint. We established a closed leveling loop along the perimeter dam and completed double-run measurements within two days. Consequently, the dataset was considered quasi-synchronous, allowing for a synchronous comparison of the monitoring results.
The development trend of InSAR for monitoring reclamation island stability is mainly reflected in two aspects: first, further mitigating decorrelation to enhance the reliability of results; second, enabling the (near-) real-time processing of massive datasets to achieve dynamic updating of stability information. With the low cost of UAV platforms and the miniaturization of SAR equipment, integrated with high-precision differential GNSS for navigation and positioning, which provides an absolute reference and calibration, UAV SAR holds immense promise. Its mobility, rapid deployment, and high precision offer unparalleled advantages for monitoring coastal deformation and emergency surveying, making it a critical future direction.
4.4. Analysis of Factors Affecting Marine Reclamation Island Uneven Subsidence
Reclaimed islands, standing amid complex and dynamic ocean-atmosphere interactions, frequently suffer structural damage [12,84,85,86,87,88,89]. The forms of damage are diverse, ranging from breakwater failures, island inundation, or even complete island washout caused by extreme marine conditions (e.g., strong winds, storm surges, and high waves) [90,91,92,93], to island sliding or land subsidence induced by factors such as marine hydrodynamics, seabed topography changes, or the properties of reclaimed fill materials [8,9,94,95,96,97]. Reclaimed islands are surrounded by sea on all sides and may experience ground settlement due to numerous factors such as geology, geotechnics, hydrology, and meteorology. According to existing studies, in land reclamation areas, the underlying geological conditions are the primary factor leading to surface settlement [8,98], including variations in the thickness of fill and alluvial layers beneath the reclaimed area, as well as changes in soil geotechnical properties [99]. In addition to these geological factors, the height of reclamation and the construction sequence of reclamation projects also influence the magnitude of residual settlement. Additionally, studies have shown that the influence of fill loading on residual settlement is minimal within 5–10 years after reclamation completion [99]. However, under environmental factors such as tidal levels and rainfall [98], fluctuations in groundwater levels beneath the reclaimed area can occur [100,101]. The long-term soil consolidation process, driven by declining groundwater levels in confined aquifers of alluvial clay layers, may require an extended duration to complete—ranging from decades to several dozen years—depending on hydraulic conductivity and natural drainage conditions.
The Junzi-Lianli Island was constructed through a “reclamation before filling” approach, employing a slope-type revetment reinforced with concrete and accropode blocks [102] to dissipate wave energy. During construction, the “cofferdam-first” method was adopted, followed by the placement of rock fill and soft clay layers. According to deformation monitoring data from leveling points along the revetment, the maximum displacement recorded between 2018 and 2020 was 5 mm, with no significant settlement observed at any monitoring stations. This indicates overall structural stability, demonstrating that the revetment effectively mitigates wave scouring and that the current marine dynamic conditions have not adversely affected the artificial island’s stability. The InSAR results indicate no significant surface deformation across the entire artificial island. As the Junzi-Lianli Island was completed in 2012, its reclaimed fill materials have undergone over six years of consolidation and have now reached a stable state. The minor deformation detected in the northern section of the island was attributed to the temporary agricultural use of that area for crop cultivation, according to field investigations. This demonstrates that the properties of the reclaimed fill materials did not induce surface subsidence of the island during the monitoring period, indicating that the Junzi-Lianli Island remained in a relatively stable condition overall.
5. Conclusions
(1) In this study, addressing the stability assessment requirements for offshore reclaimed islands, we propose an integrated approach combining PPP, leveling, and InSAR time-series analysis to monitor and diagnose millimeter-scale ground subsidence. This multi-technique framework captures deformation characteristics of Junzi-Lianli island across point, linear, and areal dimensions throughout the monitoring period. The results demonstrate the high precision and reliability of this methodology. The research proves that synergistic use of geodetic and remote sensing techniques provides critical technical support for identifying subsidence risks, early warning, and mitigation strategies in reclaimed lands.
(2) The introduction of PPP technology into subsidence assessment of reclaimed islands provides a geodetic reference for leveling and InSAR measurements. PPP-monitored benchmarks demonstrated maximum annual changes of 2 mm, confirming their stability. Leveling results indicated equally stable conditions at all benchmarks along the perimeter embankment. InSAR full-coverage monitoring revealed generally stable ground conditions across the entire reclaimed land, with localized minor deformation (maximum subsidence rate: 18.60 mm/yr) in northern agricultural areas. The tri-technique approach enabled cross-validation, with all methods showing consistent stability assessments.
(3) Compared to leveling and PPP monitoring methods, InSAR technology is a non-contact measurement approach that can efficiently and accurately detect millimeter-scale minor settlement deformations in reclaimed islands. It not only provides single-point deformation data but also captures the overall continuous spatiotemporal changes in the monitored area, making it an effective tool for spatial deformation monitoring of offshore reclaimed island targets. The currently employed labor-consuming leveling or PPP can be efficiently complemented by satellite InSAR to achieve large-scale elaborative deformation monitoring.
(4) The inherent complexity of the natural geological conditions beneath reclaimed islands and the influence of anthropogenic construction sequences must be integrally considered, alongside geological, geotechnical, hydrological, and meteorological factors, to accurately decipher the stability mechanisms of reclaimed islands. In the near future, with the advent of low-cost UAV platforms and lightweight SAR equipment, UAV SAR systems equipped with high-precision differential GNSS for navigation and positioning—which provides both an absolute reference and a means for accuracy calibration—are poised to offer broad application prospects in monitoring surface deformation and supporting emergency mapping in coastal and island zones.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M. and Y.J.; Methodology, D.M. and Y.J.; Formal analysis, D.M., Y.J., B.C., Y.W. and M.L.; Investigation, D.M., B.C. and M.L.; Funding acquisition, D.M.; Project administration, D.M.; Writing—original draft, D.M. and Y.W.; Writing—review and editing, D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2023MD080), Fujian Key Laboratory of Island Monitoring and Ecological Development (Island Research Center, MNR) (No. 2023ZD08), the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201405028), and the Marine Industry Standards (No. 201810011-T).
Data Availability Statement
The data collected and analyzed supporting the current research are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Baoquan Cheng was employed by the company Qingjian Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Sang, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Hu, B. Monitoring and analysis of coastal reclamation from 1995–2015 in Tianjin Binhai New Area, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, N.; Li, Z.; Huang, C. Satellite derived coastal reclamation expansion in China since the 21st century. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 30, e01797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, H.; Sharples, S.; Assem, E. Impact of urban heat islands on the thermal comfort and cooling energy demand of artificial islands: A case study of AMWAJ Islands in Bahrain. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhout, C.; Andreasson, L.M. The legal framework for artificial energy islands in the northern seas. Int. J. Mar. Coast. Law 2023, 39, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, M.K. Practices and Problems of Land Reclamation in Western North America; University of North Dakota Press: Forks, ND, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, I.; Lawson, N. Airport construction: Materials use and geomorphic change. J. Air Trans. Manag. 2003, 9, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C. Response of the Geomorphic Dynamics to the Artificial Island Construction in Complicated Bathymetry—A Case Study for the Radial Sand Ridges Field. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.R.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, B.H.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, H.Y. Land subsidence monitoring and dynamic prediction of reclaimed islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou cities, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Qin, X.; Liao, M. Spatio-temporal characterization of a reclamation settlement in the Shanghai coastal area with time series analyses of X-, C-, and L-band SAR datasets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.F.; Li, B.; Qiu, W.; Xu, X.W. Research on settlement test and numerical calculation of west artificial island foundation of Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. Ships Offshore Struct. 2021, 16 (Suppl. S2), 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, K.J. Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control. 2005, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Bonano, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, H. The use of C-/X-band time-gapped SAR data and geotechnical models for the study of Shanghai’s ocean-reclaimed lands through the SBAS-DInSAR technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergason, K.C.; Rucker, M.L.; Panda, B.B. Methods for monitoring land subsidence and earth fissures in the Western USA. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Land Subsidence, Nagoya, Japan, 15–19 November 2015; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.F.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, R.Y.; Luo, H.B.; Jia, D.Z.; Zhang, Z.T. Application and prospect of the integration of InSAR and BDS/GNSS for land surface deformation monitoring. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Zhu, W.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, X.S.; Chen, B.; Du, J.T.; Song, C.; et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar for deformation mapping: Opportunities, Challenges and the outlook. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1485–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.M.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.S.; Li, Z.G. Land subsidence assessment of archipelago based on the InSAR time series analysis method. Water 2023, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.X.; Hu, Z.G.; Dai, K.Z. Applications and development of fiber optic sensors. J. Wuhan Inst. Chem. Technol. 2004, 26, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J. Distributed Optical Fiber Monitoring Technology on Deformation of Land Subsidence. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Y. Meticulously research on land subsidence in coastal area of Jiangsu at different scales. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.W.; Yang, C.S. Precision space observation technique for geological hazard monitoring and early warning. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline di_erential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, T.; Rott, H.; Kamelger, A. Analysis of Landslides in Alpine Areas by Means of SAR Interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Savio, G.; Barzaghi, R.; Borghi, A.; Musazzi, S.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Submillimeter accuracy of InSAR time series: Experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Perissin, D.; Liao, M.; Rocca, F. Deformation Monitoring by Long Term D-InSAR Analysis in Three Gorges Area, China. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, T. Time-Series InSAR Applications Over Urban Areas in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Gutiérrez, F.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Guerrero, J.; Notti, D.; Galve, J.P.; Fernández-Merodo, J.A.; Cooksley, G. Multi-sensor advanced DInSAR monitoring of very slow landslides: The Tena Valley case study(Central Spanish Pyrenees). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, G.; Cakır, Z.; Ergintav, S.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Analysis of secular ground motions in Istanbul from a long-term InSAR time-series (1992–2017). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Falabella, F.; Mastro, P.; Pepe, A. Generation of long-term InSAR ground displacement time-series through a novel multi-sensor data merging technique: The case study of the Shanghai coastal area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Characterizing and monitoring ground settlement of marine reclamation land of Xiamen New Airport, China with Sentinel-1 SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z. Two decades of settlement of Hong Kong International Airport measured with multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, C.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Wen, N.; Yin, Y.; Dong, X. Monitoring and Predicting the Subsidence of Dalian Jinzhou Bay International Airport, China by Integrating InSAR Observation and Terzaghi Consolidation Theory. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Q. Study on Community Diversity and Physical and Chemical Property of Soil of Interlace Zone of Sandy Coastal in Shandong. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H. Study on Impacts of the Haiyang Harbor’s Construction on the Sandy Coast. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, N.N. Impact Studies of the Man-Made Island Project to the Vicinity Area on the Sandy Coast. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Tian, Z.W.; Li, X.; Sun, H.F. Coastal erosion mechanism and its prevention in Haiyang. Mar. Sci. 2021, 45, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhang, X.D.; Hu, R.J.; Yin, Y.J.; Leng, X. Seasonal evolution of the typical sandy coast of southeastern Shangdong Peninsula and controlling factors-Take the 10000-meter beach in Haiyang as an example. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2022, 42, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Heroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in precise point positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Huisman, L.; Hu, C. Real-time precise point positioning in NAD83: Global and regional broadcast corrections compared. J. Surv. Eng. 2012, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P. Assessment of correct fixing rate for precise point positioning ambiguity resolution on a global scale. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.H. Research on Real-Time Precise Point Positioning Theory and Application. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.X. Rapid Ambiguity Resolution in GNSS Precise Point Positioning. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.B.; Hu, Y.F.; Yu, C. An improved global zenith tropospheric delay model. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.W.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.R.; Wang, L. Comparison and Analysis of Different Models of Antenna Phase Center Correction of BDS Satellites. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 35, 658–661. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.P.; Xu, H.Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.D.; Zhou, J.C.; Liu, M.; Gao, S. Study of Earth’s gravity tide and oceanic loading characteristics in Hong Kong area. Chin. J. Geophys. 2006, 49, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Qu, W.; Liu, Z. Analysis of ocean tide loading effect on GPS PPP of Hong Kong. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 36, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Ma, L.; Li, P. Determination of ocean tide loading displacements using kinematic PPP. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 631–638. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 12897—2006; Specifications for the First and Second Order Leveling. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Zebker, H.A.; Werner, C.L.; Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S. Accuracy of topographic maps derived from ERS-1 interferometric radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Springer: Dordrech, The Netherlands; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrech, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A quantitative assessment of the SBAS algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from DInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, S.P.; Meng, X.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Guo, X.S. Multi-scenario land use and carbon storage assessment in the Yellow River Delta under climate change and resource development. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-series algorithms, applications, and challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Balz, T.; Luo, H.; Liao, M.S.; Zhang, L. GPU accelerated interferometric SAR processing for Sentinel-1 TOPS data. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 129, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.Z.; Li, Y.S.; Li, B.Q.; Li, H. Fast InSAR time-series analysis method in a full-resolution SAR coordinate system: A case study of the Yellow River Delta. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.A.; Bürgmann, R. Time-dependent land uplift and subsidence in the Santa Clara Valley, California, from a large interferometric synthetic aperture radar data set. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2003, 108, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HY/T 0487-2025; Technical Specification for Stability Monitoring of Islands Where the Territorial Sea Base Point is Located. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2025.
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Soldato, M.; Confuorto, P.; Bianchini, S.; Sbarra, P.; Casagli, N. Review of Works Combining GNSS and InSAR in Europe. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizzi, A.; Brcic, R.; Zan, F.D. InSAR Performance for Large-Scale Deformation Measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.; Mohamed, A.; Esayas, G.; Dorina, M.; Michael, S. Land subsidence in the Texas coastal bend: Locations, rates, triggers, and consequences. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.A.; Chen, Z.; Shoaib, M.; Shah, S.U.; Khan, J.; Ying, Z. Land subsidence of coastal city of Pakistan using persistent scatterers In-SAR technique. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, M.A.; De Macedo, K.A.C.; Moreira, J.R. The first UAV-based P- and X-band interferometric SAR system. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, Z.J.; Xing, D.M.; Yang, L.; Bao, Z. A robust motion compensation approach for UAV SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3202–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Liu, C.; Zhan, X.L.; Han, S. Technology and applications of UAV synthetic aperture radar system. J. Radars 2016, 5, 333–349. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, S.; Sommer, R.; Janssen, D.; Tessmann, A.; Stilla, U. Airborne Circular W-Band SAR for Multiple Aspect Urban Site Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6996–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.J. An overview of Unmanned Airborne Miniature’s Development. Digit. Technol. Appl. 2019, 37, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, L.N.; Guo, L.; Ma, Y.H.; Shi, Y.P.; Liang, W.B. Review of circular SAR imaging by a small rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2025, 46, 303–316. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.; Yin, H.Q.; Su, G.L.; Tian, X.; Xu, Y.J. Spatial-temporal characteristics of land subsidence in Tianjin city based on leveling data. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.H.; Liu, S.W.; Guo, X.F.; Wang, Y. A study of surface deformation monitoring using differential SAR interferometry technique and analysis of its key problems. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2007, 4, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.M.; Chen, H.; Gan, W.J.; Wang, Z.H. Error analysis of the monitoring precision of the land surface small deformation on heavy rail with interferometry synthetic aperture radar. J. Transp. Eng. Inf. 2009, 7, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.X.; Huang, J.X.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.H.; Han, J.J.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, B. Review of PPP-RTK: Achievements, challenges, and opportunities. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, M.; Iqbal, U.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M. The implementation of precise point positioning (PPP): A comprehensive review. Sensors 2023, 23, 8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.L.; Shen, X.D.; Liu, J.J.; Qiao, T.R. Application of GPS technology in land subsidence monitoring. Geospat. Inf. 2020, 18, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, M.J.; Wu, H.A.; Liu, B.; Kang, Y.H.; He, Q. Ground subsidence monitoring over full territory of Jiangsu province with InSAR. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2019, 44, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.R. InSAR: Technological progress and its application to land subsidence monitoring. Shanghai Land Resour. 2013, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Li, Z.W.; Hu, J. Research progress and methods of InSAR for deformation monitoring. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wang, G.Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, K. Sentinel-1 InSAR and GPS-integrated long-term and seasonal subsidence monitoring in Houston, Texas, USA. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, G.; Sultan, N.; Savoye, B. The 1979 Nice harbour catastrophe revisited: Trigger mechanism inferred from geotechnical measurements and numerical modelling. Mar. Geol. 2007, 245, 40–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujima, K.; Shigihara, Y.; Tomita, T.; Honda, K.; Nobuoka, H.; Hanzawa, M.; Ohtani, H.; Orishimo, S.; Tatsumi, M. Survey results of the Indian Ocean tsunami in the Maldives. Coast. Eng. J. 2006, 48, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzrin, A.M.; Alonso, E.E.; Pinyol, N.M. Unexpected excessive settlements: Kansai International Airport, Japan. In Geomechanics of Failures; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mesri, G.; Funk, J.R. Settlement of the Kansai International Airport Island. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.X.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, D.R. The medium and long term settlement of reclamation airports. Prot. Eng. 2018, 40, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Study on Properties of Gravel Soil and Airport Settlement in Jinzhou Bay Reclamation area. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Oumeraci, H. Review and analysis of vertical breakwater failures-lessons leaned. Coast. Eng. 1994, 22, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L. Risk Analysis and Management of Breakwaters. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Jiang, X.L.; Liu, R. Discussion on the relationship between characteristics and the reasons of breakwater failures. Ocean. Eng. 2006, 24, 130–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.B.; Li, Y.H.; Lou, Y.; He, N. Automatic safety monitoring system and warning modes for artificial islands in coastal areas. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 34, 1712–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalié, O.; Sladen, A.; Kelner, M. Detailed quantification of delta subsidence, compaction and interaction with man-made structures: The case of the NCA airport, France. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 3, 3761–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, Y. Discussion of ‘Settlement of the Kansai International Airport Islands’ by G. Mesri J. R. Funk. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2016, 142, 07016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Settlement Prediction of Artificial Island Revetment Considering Creep. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.F.; Han, X.H.; Di, Y.P.; Guo, X.T. Practice of subsidence monitoring of artificial island based on levelling technology. Hydrogr. Surv. Charting 2021, 41, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Plant, G.W.; Covil, C.S. Site Preparation for the New Hong Kong International Airport-The Design, Construction and Performance of the Airport Platform; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.M.; Lin, H. Integrated analysis of SAR interferometric and geological data for investigating long-term reclamation settlement of Chek Lap Kok Airport, Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2010, 110, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Jiao, J. Changes of coastal groundwater systems in response to large-scale land reclamation. In New Topics in Water Resources Research and Management; Andreassen, H.M., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 79–136. [Google Scholar]
- Teatini, P.; Strozzi, T.; Tosi, L.; Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C.; Carbognin, L. Assessing short- and long-time displacements in the Venice coastland by synthetic aperture radar interferometric point target analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C. Research on Artificial Island Landscape Design Based on Haiyang Lianli Island. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).