Phenology-Guided Wheat and Corn Identification in Xinjiang: An Improved U-Net Semantic Segmentation Model Using PCA and CBAM-ASPP
Highlights
- By analysing kNDVI/EVI time-series vegetation indices via GEE, this study identifies days 156–176 of the year as the optimal window for wheat and corn identification, effectively eliminating spectral similarity interference.
- An improved U-Net model integrated with ResNet50, CBAM, and a modified ASPP module achieves outstanding performance (mIoU of 83.03% and OA of 90.91%) on PCA-dimensionally reduced Sentinel-2 data, outperforming mainstream models like DeeplabV3+ and PSPnet.
- The PCA-constructed dataset supplements the spectral information that is missing in traditional RGB data, and when combined with the optimal time window and improved model, forms a complete “time series + data + model” technical path for accurate crop identification.
- The model exhibits strong generalization (error < 2% in Qitai County, Xinjiang) and can be extended to arid grain-producing areas for crop mapping, calculating area statistics, and yield estimation, providing practical support for national food security.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Determine the optimal identification window: Time-series vegetation indices were utilised to analyse the phenological characteristics of wheat and corn, thereby identifying the optimal window period for their accurate recognition.
- (2)
- Construct a high-efficiency dataset: PCA was applied to reduce the dimensionality of Sentinel-2 remote sensing data. Key principal components were extracted from the dimensionality-reduced data to build the input dataset for the model.
- (3)
- Improve the U-Net model: A Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and an improved Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) module were integrated into the U-Net model. This enhancement enables the model to extract crop feature information more accurately and efficiently.
- (4)
- Apply the model for crop extraction: Based on the improved model, wheat and corn were extracted from Sentinel-2 images covering Qitai County, Xinjiang, China.
2. Research Area and Materials
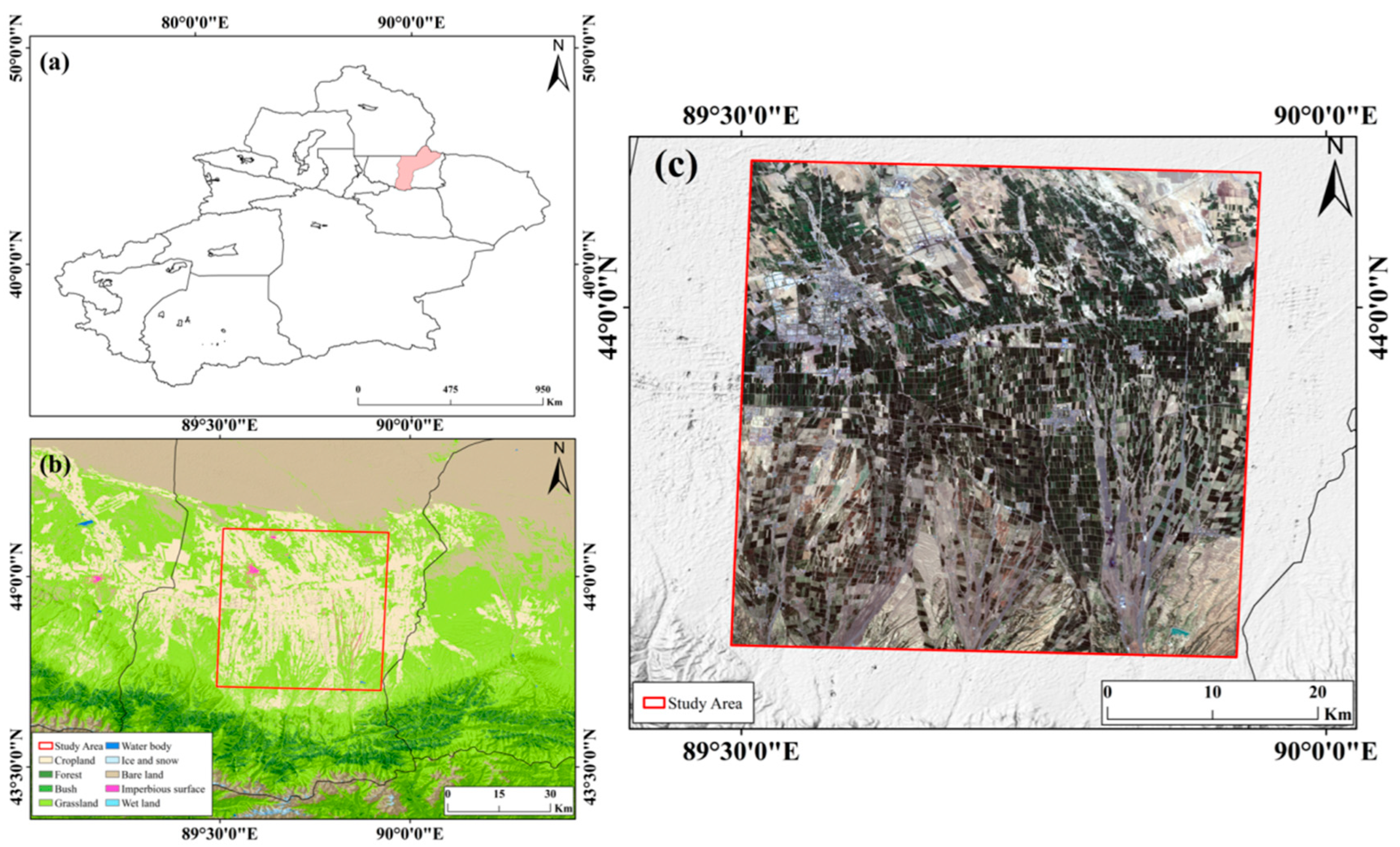
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Dataset Construction
3. Methods
3.1. Time Series Reconstruction of Vegetation Indices
3.2. Deep Learning Methods
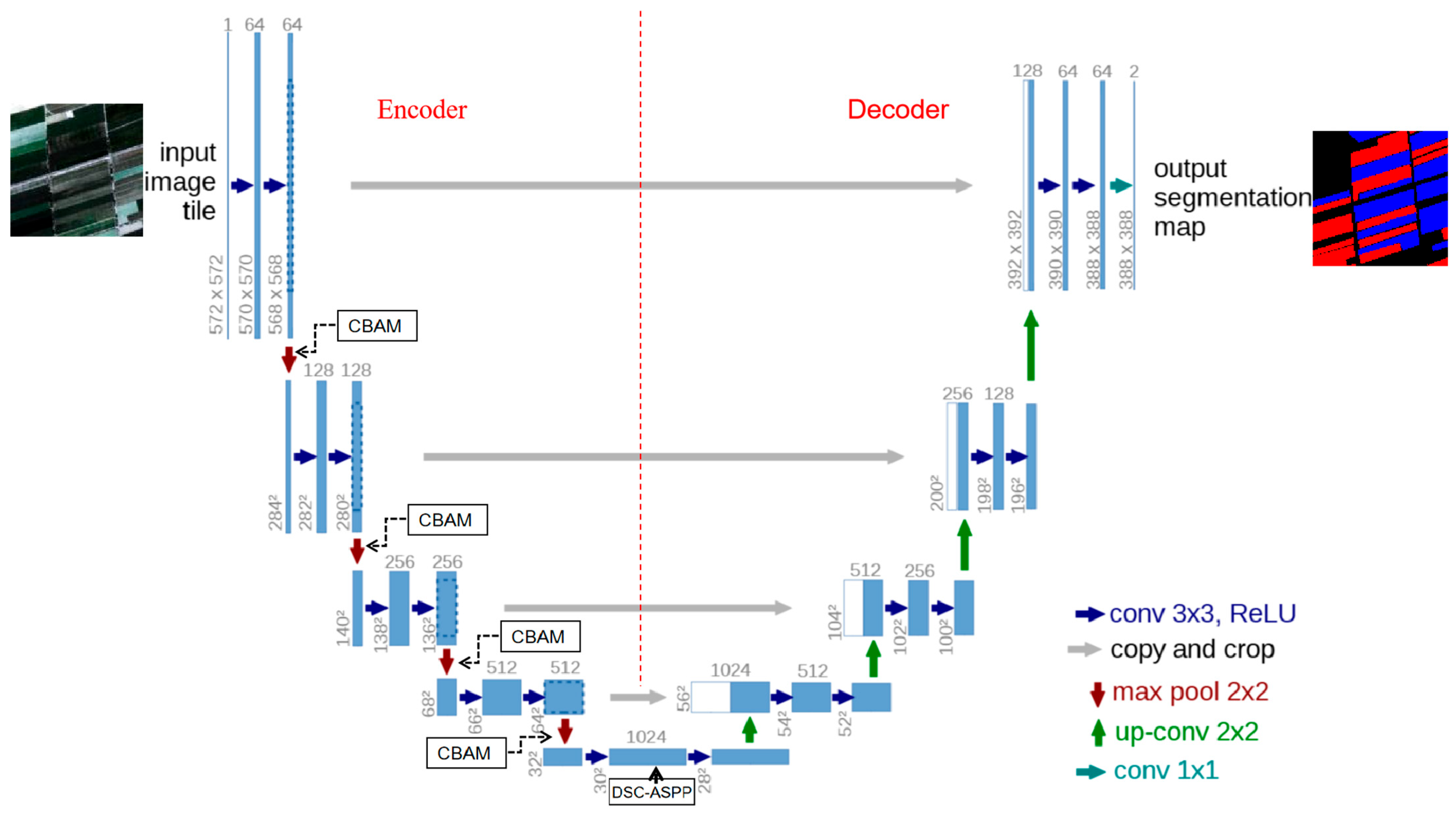
3.2.1. Improving the U-Net Model
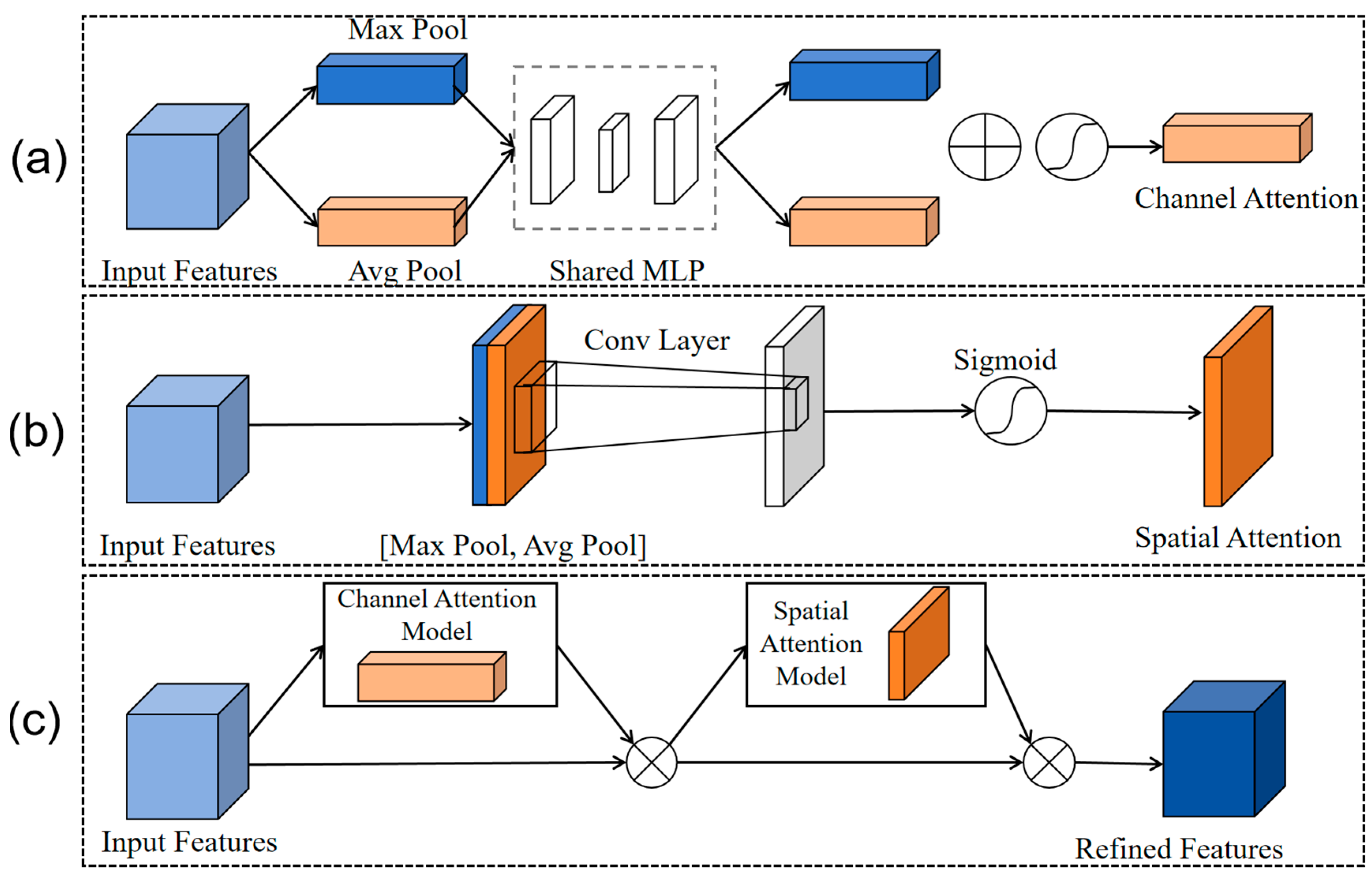
3.2.2. CBAM Attention Mechanism
3.2.3. ASPP Model Based on Deep Separable Convolutions
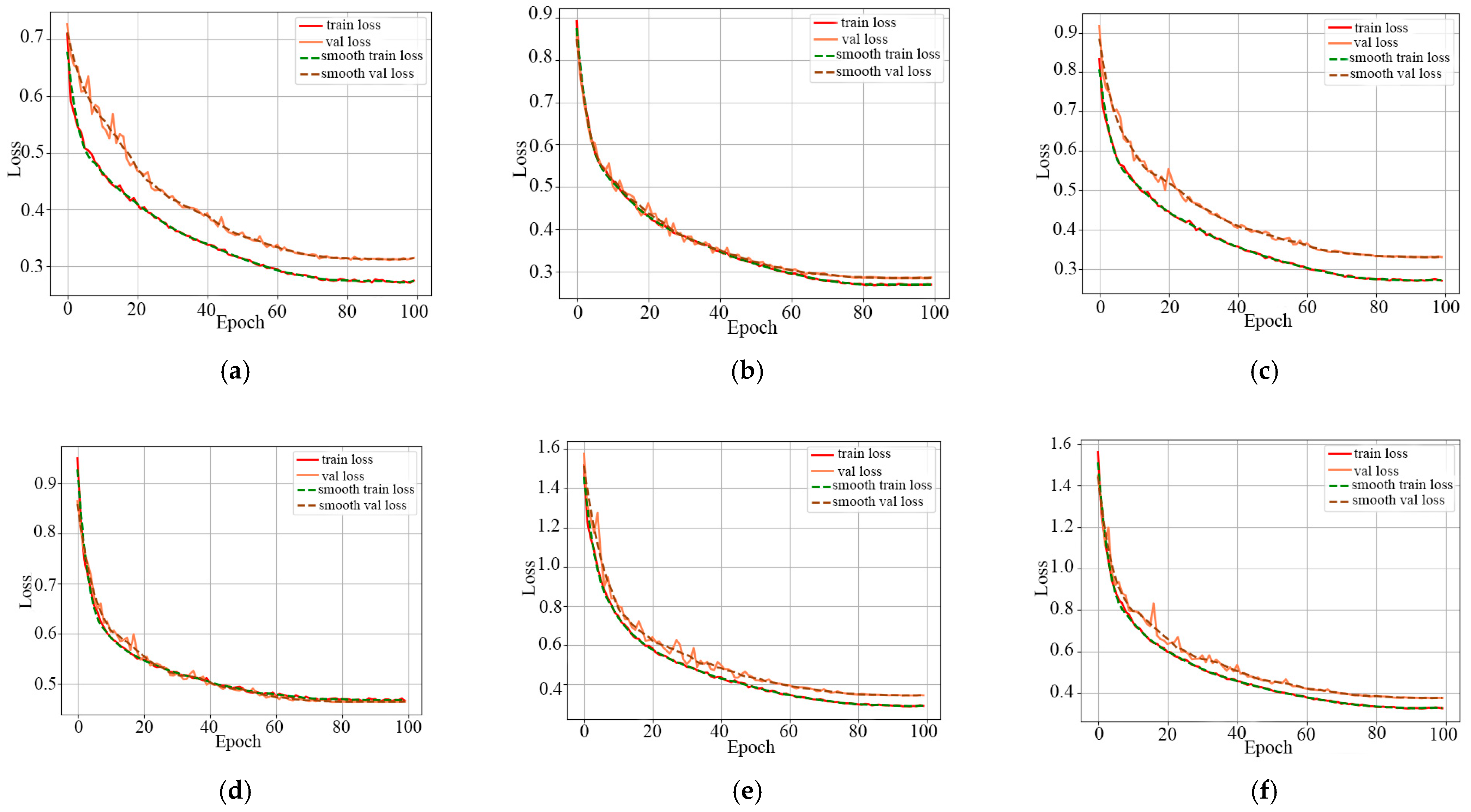
3.3. Training Experiment Parameter Settings
3.4. Accuracy Evaluation Method
4. Results and Analysis
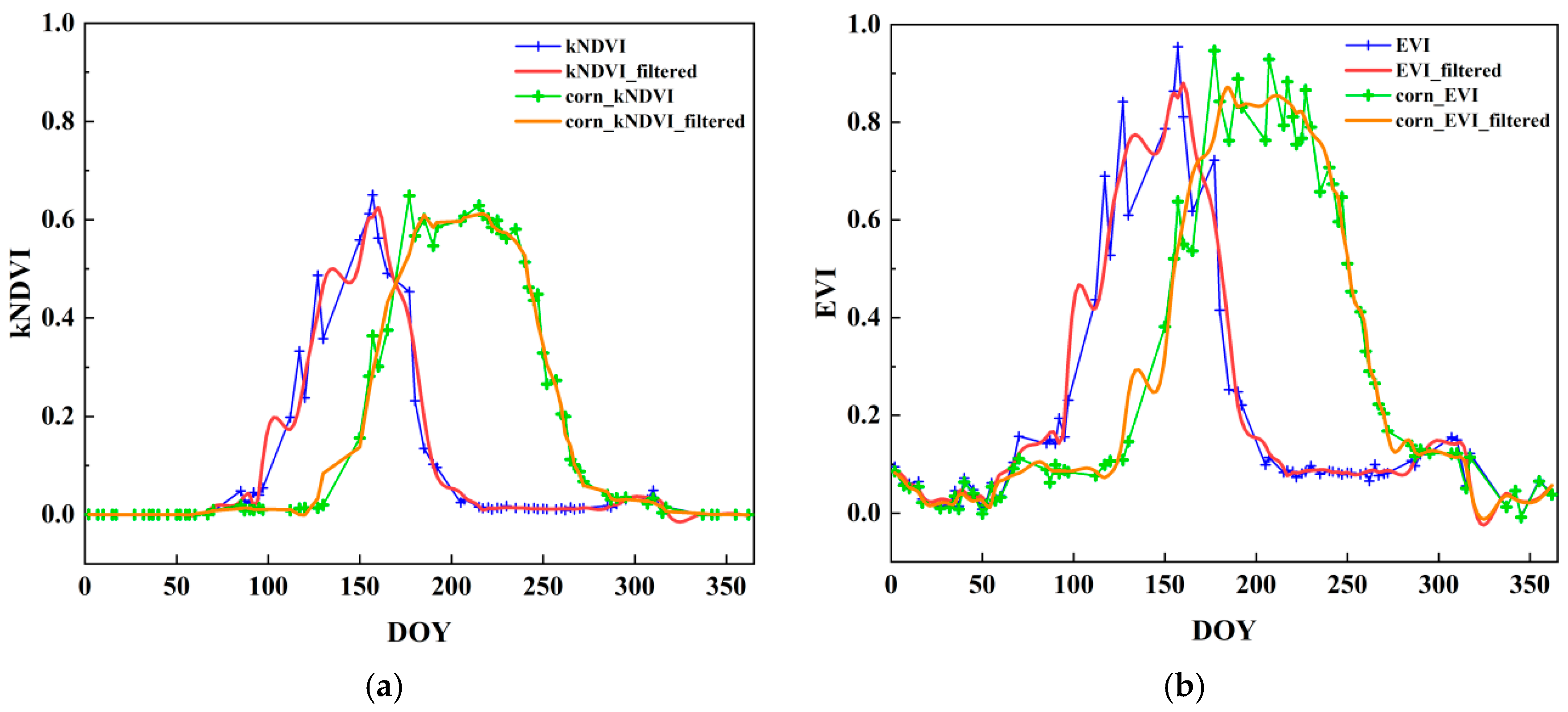
4.1. Time-Series Characteristics of Vegetation Indices for Wheat and Corn
4.2. Comparison and Analysis of Experimental Results from Different Datasets
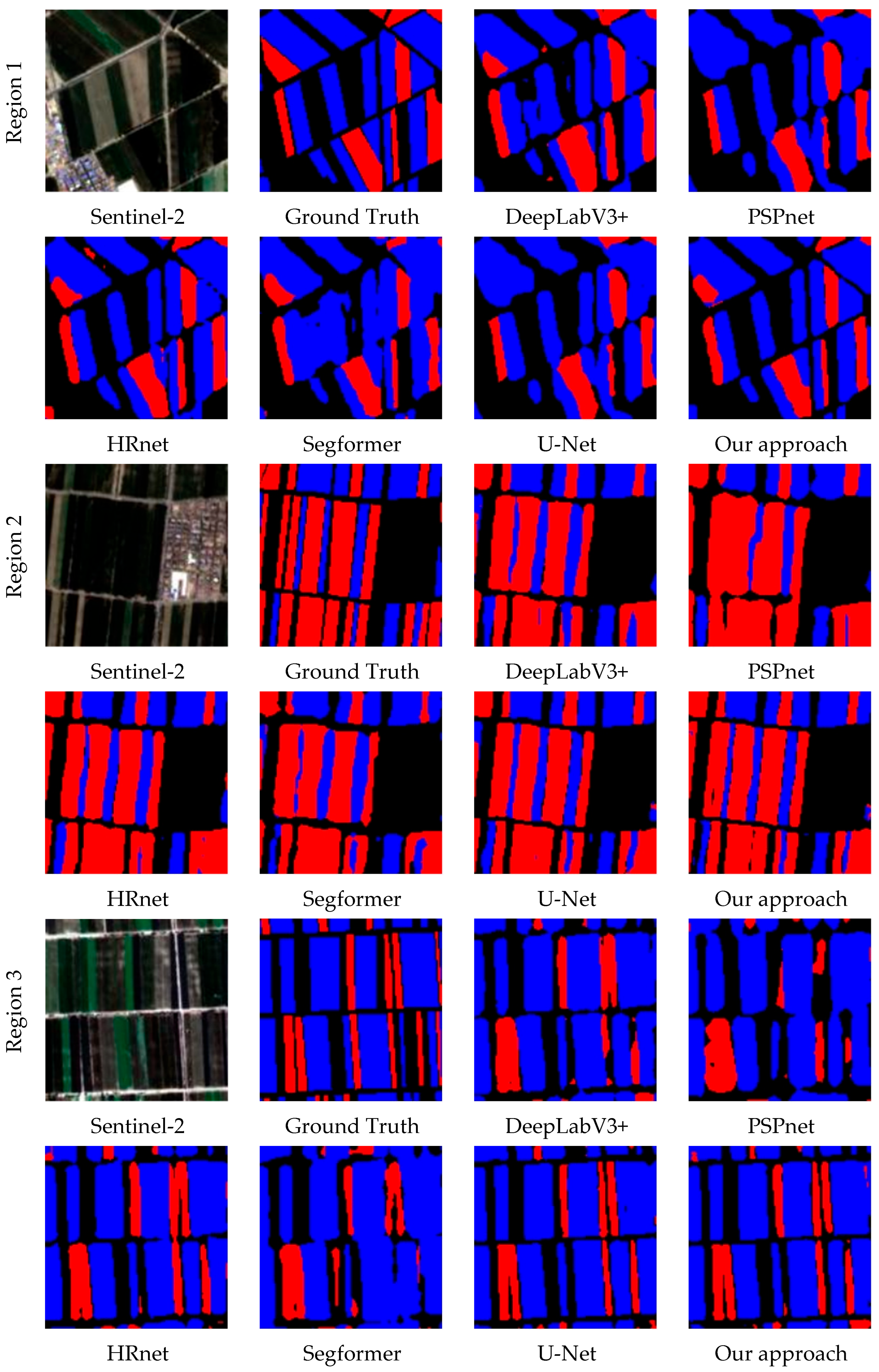
4.3. Comparison of Mapping Results from Different Algorithms
4.4. Ablation Experiment
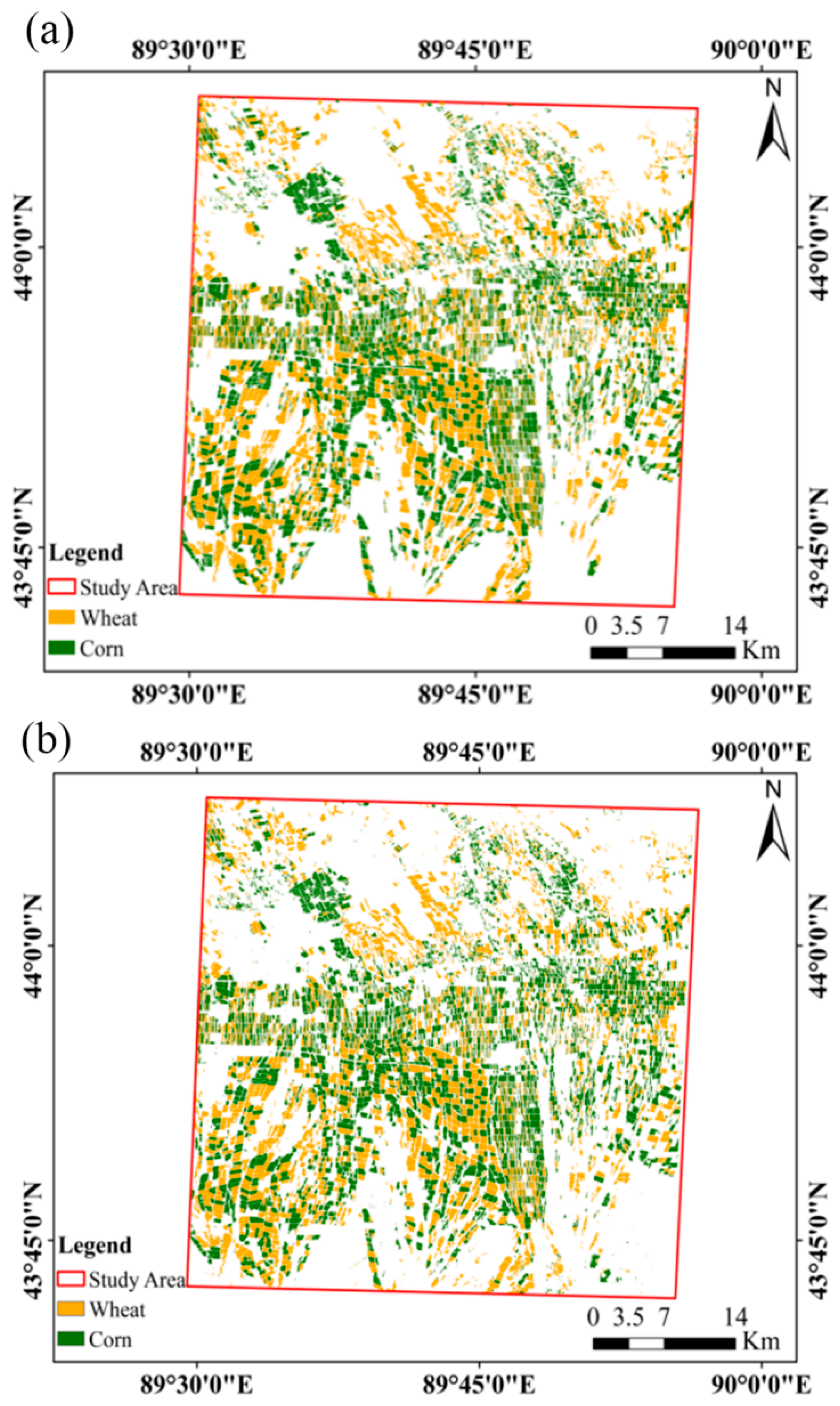
4.5. Model Generality Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. The Impact of Principal Component Analysis on the Results
5.2. Time Window for Vegetation Index
5.3. Algorithm Performance
5.4. Extraction Efficiency of Crop Types
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sishodia, R.; Ray, R.; Singh, S. Applications of Remote Sensing in Precision Agriculture: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote Sensing for Agricultural Applications: A Meta-Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Lu, D.; Tang, Z.; Song, D.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, N.; Huang, H.; Xu, W. Mapping Cropping Intensity Trends in China during 1982–2013. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J.; Huang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Yang, T.; Di, Y.; Xiao, X. The 10-m Crop Type Maps in Northeast China during 2017–2019. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, R.; Sankey, T.; Congalton, R.; Yadav, K.; Thenkabail, P.; Ozdogan, M.; Meador, A. MODIS Phenology-Derived, Multi-Year Distribution of Conterminous US Crop Types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, R.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Cai, W.; Chang, T.; Du, Y. Crop Aboveground Biomass Monitoring Model Based on UAV Spectral Index Reconstruction and Bayesian Model Averaging: A Case Study of Film-Mulched Wheat and Maize. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Dao, P.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Shang, J. Recent Advances of Hyperspectral Imaging Technology and Applications in Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.; Macdonald, L.; Butler, G.; Chirino-Valle, I.; Condron, L. Biochar and Fertiliser Applications Influence Phosphorus Fractionation and Wheat Yield. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, J.; Bruzzone, L. Semantic Segmentation of Large-Size VHR Remote Sensing Images Using a Two-Stage Multiscale Training Architecture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5367–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Qiao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; et al. Identification of the Candidate Gene Controlling Tiller Angle in Common Wheat through Genome-Wide Association Study and Linkage Analysis. Crop J. 2023, 11, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Miao, R.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.; Yue, M. Research on SU-Net Winter Wheat Identification Method Based on GF-2. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Song, W.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y. Identifying Winter Wheat Using Landsat Data Based on Deep Learning Algorithms in the North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Chang, X.; Wang, D.; Tao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y. General Situation and Development of Wheat Production. Crops 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Zhou, G. The Climatic Suitability for Maize Cultivation in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Qian, X.; Shang, S.; Wan, H. Multi-Year Mapping of Cropping Systems in Regions with Smallholder Farms from Sentinel-2 Images in Google Earth Engine. Giscience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2309843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Ye, H.; Qiao, S.; Liu, R.; Nie, C.; Zhang, B.; Song, L.; Huang, S. Early Crop Mapping Based on Sentinel-2 Time-Series Data and the Random Forest Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Shakir, M. Feature Selection of Time Series MODIS Data for Early Crop Classification Using Random Forest: A Case Study in Kansas, USA. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5347–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Tao, H.; Li, Q.; Xie, H.; Xu, Y.; Mahemujiang, A.; Jiang, Y. Research on Machine Learning-Based Extraction and Classification of Crop Planting Information in Arid Irrigated Areas Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Time-Series Data. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Ghamisi, P.; Homayouni, S. Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, L.; Jiang, T.; Gao, F. MDE-U-Net: A Multitask Deformable U-Net Combined Enhancement Network for Farmland Boundary Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, W.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xue, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Yao, C. Super-Resolution Enhancement of Sentinel-2 Image for Retrieving LAI and Chlorophyll Content of Summer Corn. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 111, 125938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore, B. Mapping Paddy Rice Planting Area in Northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 Images, Phenology-Based Algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Zhou, J.; Liew, A.; Jia, X.; Chanussot, J.; Gao, Y. Conditional Random Field and Deep Feature Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ge, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Extracting Citrus-Growing Regions by Multiscale U-Net Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Zou, C.; Chen, J.; Han, W.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N. Crop Type Identification Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on an Improved DeepLabV3+ Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Li, L.; Jing, W. CACPU-Net: Channel Attention U-Net Constrained by Point Features for Crop Type Mapping. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1030595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, E. Enhancing the Digital Mapping Accuracy of Farmland Soil Organic Carbon in Arid Areas Using Agricultural Land Use History. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiong, C.; Bai, X. Value Transformation and Ecological Practice: The Path to Realizing the Value of Ecotourism Products in Heritage Sites-A Case Study of the Qitai Dry Farming System in Xinjiang. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, R.; Lewinski, S.; Rybicki, M.; Gromny, E.; Jenerowicz, M.; Krupinski, M.; Nowakowski, A.; Wojtkowski, C.; Krupinski, M.; Krätzschmar, E.; et al. Automated Production of a Land Cover/Use Map of Europe Based on Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M. Deep-Learning-Based Automatic Extraction of Aquatic Vegetation from Sentinel-2 Images-A Case Study of Lake Honghu. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps-Valls, G.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Moreno-Martínez, A.; Walther, S.; Duveiller, G.; Cescatti, A.; Mahecha, M.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; García-Haro, F.; Guanter, L.; et al. A Unified Vegetation Index for Quantifying the Terrestrial Biosphere. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Ya, Q.; Li, Z. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Climatic Driving Factors of Vegetation Coverage in the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2020 Based on kNDVI. Forests 2023, 14, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, X.; Ruan, W.; Zheng, M.; Gen, K.; Li, X.; Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Quantifying the Direct and Indirect Effects of Terrain, Climate and Human Activity on the Spatial Pattern of kNDVI-Based Vegetation Growth: A Case Study from the Minjiang River Basin, Southeast China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mao, J.; Chen, C.; Bi, Z. Research on the Remote Sensing Change Detection of Land Cover Types in Agricultural-Forestry Transition Zone Based on CNN-Transformer Hybrid Model. In Proceedings of the 2025 6th International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL), Ningbo, China, 23–25 May 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Lu, Y.; Qu, T.; Tian, H.; Su, J.; Luo, D.; Yang, Y. A Lightweight Winter Wheat Planting Area Extraction Model Based on Improved DeepLabv3+ and CBAM. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Monitoring Impervious Surface Area Dynamics in Urban Areas Using Sentinel-2 Data and Improved Deeplabv3+ Model: A Case Study of Jinan City, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fan, X.; Peng, M.; Guan, Q.; Tang, L. Semantic Segmentation for Remote Sensing Images Based on an AD-HRNet Model. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 2376–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Chang, L. A Study on the Dynamic Effects and Ecological Stress of Eco-Environment in the Headwaters of the Yangtze River Based on Improved DeepLab V3+ Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Han, H. EAR-Net: Efficient Atrous Residual Network for Semantic Segmentation of Street Scenes Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S. Accurate Wheat Lodging Extraction from Multi-Channel UAV Images Using a Lightweight Network Model. Sensors 2021, 21, 6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResU-Net-a: A Deep Learning Framework for Semantic Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wan, G.; Zhang, K.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Winter Wheat Lodging Area Extraction Using Deep Learning with GaoFen-2 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaria, A.; Kumar, U.; Jhanwwee, K.S.; Dasgupta, A.; Kaur, G.J. Classification and Identification of Crops Using Deep Learning with UAV Data. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International India Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (InGARSS), Ahmedabad, India, 6–10 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H. A Dual-Branch U-Net for Staple Crop Classification in Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Geng, Y.; Hou, J.; Du, Q. Learning Hyperspectral Images from RGB Images via a Coarse-to-Fine CNN. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 152102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhang, B.; Yan, J.; He, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J. Spatial-Spectral Attention-Enhanced Res-3D-OctConv for Corn and Weed Identification Utilizing Hyperspectral Imaging and Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Mapping the Main Phenological Spatiotemporal Changes of Summer Maize in the Huang-Huai-Hai Region Based on Multiple Remote Sensing Indices. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Li, T.; Shen, J.; Wei, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; et al. Winter Wheat Maturity Prediction via Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Qian, H.; Zhan, Y.; Lei, Y. Extraction of Winter-Wheat Planting Areas Using a Combination of U-Net and CBAM. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Han, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhai, X.; Huang, S.; Ma, W.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y. Multi-Year Crop Type Mapping Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Deep Semantic Segmentation Algorithm in the Hetao Irrigation District in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, J. Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation-Based Remote Sensing Identification Method for Winter Wheat Planting Area Extraction. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Guo, H.; Dai, D.; Yun, Y.; Li, L.; Hao, F.; Bai, J.; Ma, D. Identification of Maize Seed Varieties Using MobileNetV2 with Improved Attention Mechanism CBAM. Agriculture 2022, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J.; He, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, C. Maize Crop Row Recognition Algorithm Based on Improved U-Net Network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| April | May | June | July | August | September | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early | Mid | Late | Early | Mid | Late | Early | Mid | Late | Early | Mid | Late | Early | Mid | Late | Early | Mid | Late | |
| Wheat | Sowing | Emergence | Jointing | Tillering | Heading | Grain-filling | Milk stage | Maturity | ||||||||||
| Corn | Sowing | 3-leaf | 7-leaf | Jointing | Tillering | Milk stage | Maturity | |||||||||||
| Confusion Matrix | Prediction | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| True | False | ||
| Ground Truth | Positive | TP | FN |
| (True Positive) | (False Negative) | ||
| Negative | FP | TN | |
| (False Positive) | (True Negative) | ||
| Model | IoU | mIoU | PA | mPA | F1-Score | OA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Corn | Wheat | Corn | |||||
| Deeplabv3+ | 70.54 | 67.17 | 71.88 | 84.86 | 84.32 | 71.88 | 83.56 | 84.25 |
| PSPnet | 73.51 | 71.69 | 74.30 | 86.13 | 86.59 | 85.84 | 85.23 | 85.63 |
| HRnet | 77.03 | 74.58 | 77.80 | 88.46 | 87.93 | 88.03 | 87.48 | 87.94 |
| Segformer | 61.31 | 59.14 | 65.00 | 74.67 | 78.13 | 78.77 | 78.59 | 79.91 |
| U-Net | 76.60 | 73.57 | 77.30 | 88.92 | 89.08 | 88.03 | 87.16 | 87.61 |
| Our approach | 80.36 | 78.62 | 81.31 | 90.45 | 90.50 | 90.19 | 89.67 | 90.07 |
| Model | IoU | mIoU | PA | mPA | F1-Score | OA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Corn | Wheat | Corn | |||||
| Deeplabv3+ | 71.32 | 70.83 | 73.13 | 86.61 | 86.74 | 85.46 | 84.45 | 84.94 |
| PSPnet | 74.87 | 74.57 | 75.66 | 87.89 | 88.49 | 86.90 | 86.13 | 86.36 |
| HRnet | 78.90 | 78.28 | 79.61 | 90.63 | 90.10 | 89.34 | 88.64 | 88.88 |
| Segformer | 66.29 | 65.23 | 68.45 | 81.01 | 81.66 | 81.73 | 81.21 | 81.92 |
| U-Net | 79.36 | 79.22 | 80.43 | 90.64 | 91.37 | 89.88 | 89.14 | 89.41 |
| Our approach | 82.37 | 82.16 | 83.03 | 92.07 | 92.68 | 91.34 | 90.73 | 90.91 |
| Baseline | CBAM | Improved ASPP | mIoU | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 80.43 | 89.14 | ||
| √ | √ | 82.83 | 90.61 | |
| √ | √ | 81.71 | 89.93 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 83.03 | 90.73 |
| Metric | Model A | Model B |
|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Parameters | 191,686,827 | 91,078,827 |
| GFLOPS (Computational load) | 15.97 G | 12.75 G |
| Estimated Memory Usage | 931.91 MB | 548.87 MB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Guo, X.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, F.; Li, R.; Li, X. Phenology-Guided Wheat and Corn Identification in Xinjiang: An Improved U-Net Semantic Segmentation Model Using PCA and CBAM-ASPP. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213563
Wei Y, Guo X, Lu Y, Hu H, Wang F, Li R, Li X. Phenology-Guided Wheat and Corn Identification in Xinjiang: An Improved U-Net Semantic Segmentation Model Using PCA and CBAM-ASPP. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(21):3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213563
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yang, Xian Guo, Yiling Lu, Hongjiang Hu, Fei Wang, Rongrong Li, and Xiaojing Li. 2025. "Phenology-Guided Wheat and Corn Identification in Xinjiang: An Improved U-Net Semantic Segmentation Model Using PCA and CBAM-ASPP" Remote Sensing 17, no. 21: 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213563
APA StyleWei, Y., Guo, X., Lu, Y., Hu, H., Wang, F., Li, R., & Li, X. (2025). Phenology-Guided Wheat and Corn Identification in Xinjiang: An Improved U-Net Semantic Segmentation Model Using PCA and CBAM-ASPP. Remote Sensing, 17(21), 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213563






