High-Resolution Monitoring and Driving Factor Analysis of Long-Term Surface Deformation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin
Highlights
- High-resolution InSAR observations have finely characterized the spatial pattern of “overall stability and significant local deformation” in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin, and revealed that groundwater exploitation is its main driving factor.
- Results show that there is a strong coupling relationship between the ground deformation process and groundwater exploitation dynamics, and there is a significant symbiotic development feature between subsidence and ground fissure, with a disaster chain effect.
- Quantitatively revealing the dynamic coupling law between ground deformation and groundwater exploitation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin, providing scientific basis for elucidating the full chain feedback mechanism of “groundwater exploitation-ground deformation-geological hazards”.
- The main finding provides direct decision-making basis for effectively addressing geological risks such as ground subsidence, optimizing water resource management plans, and evaluating the effectiveness of groundwater overexploitation control.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
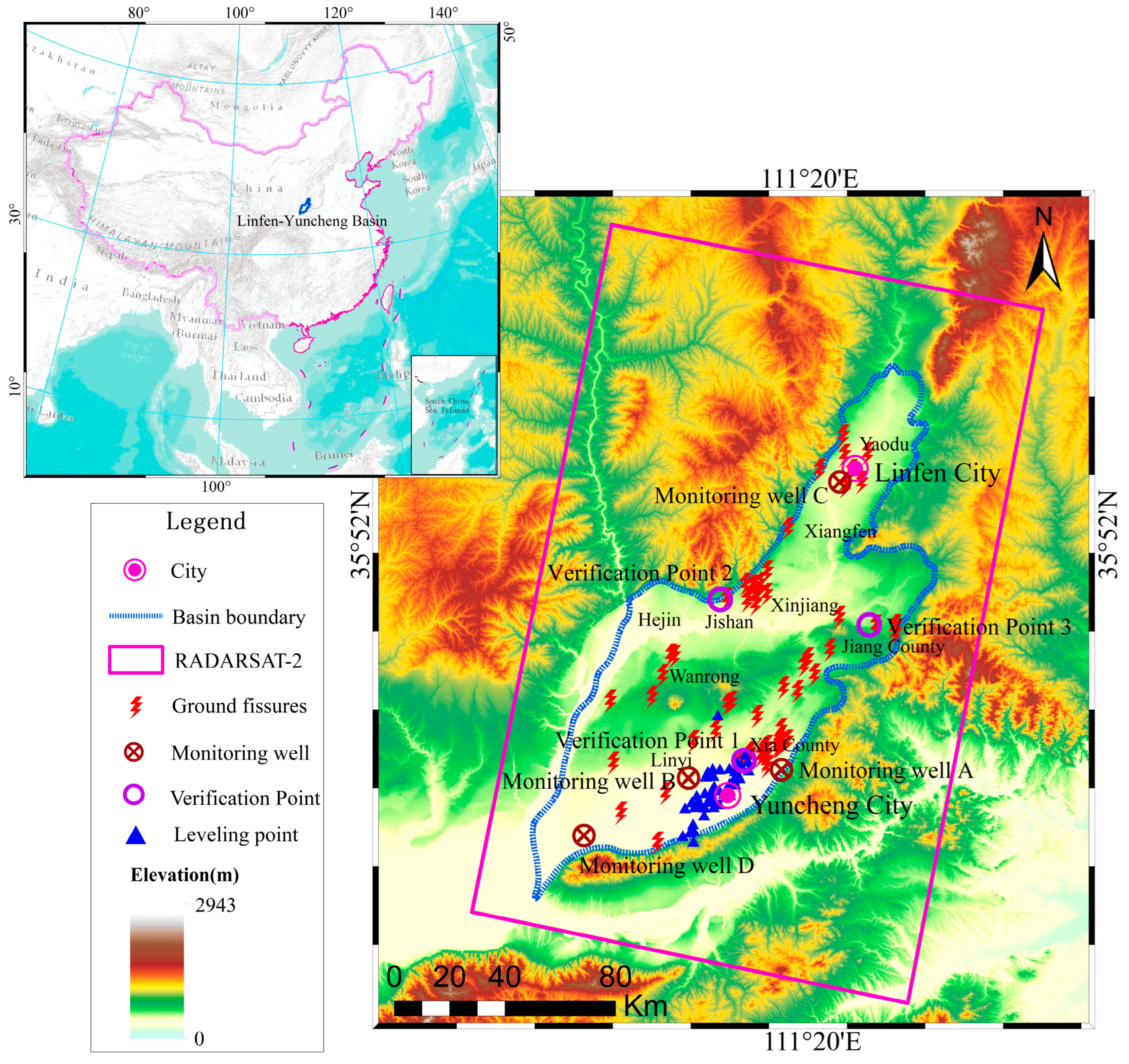
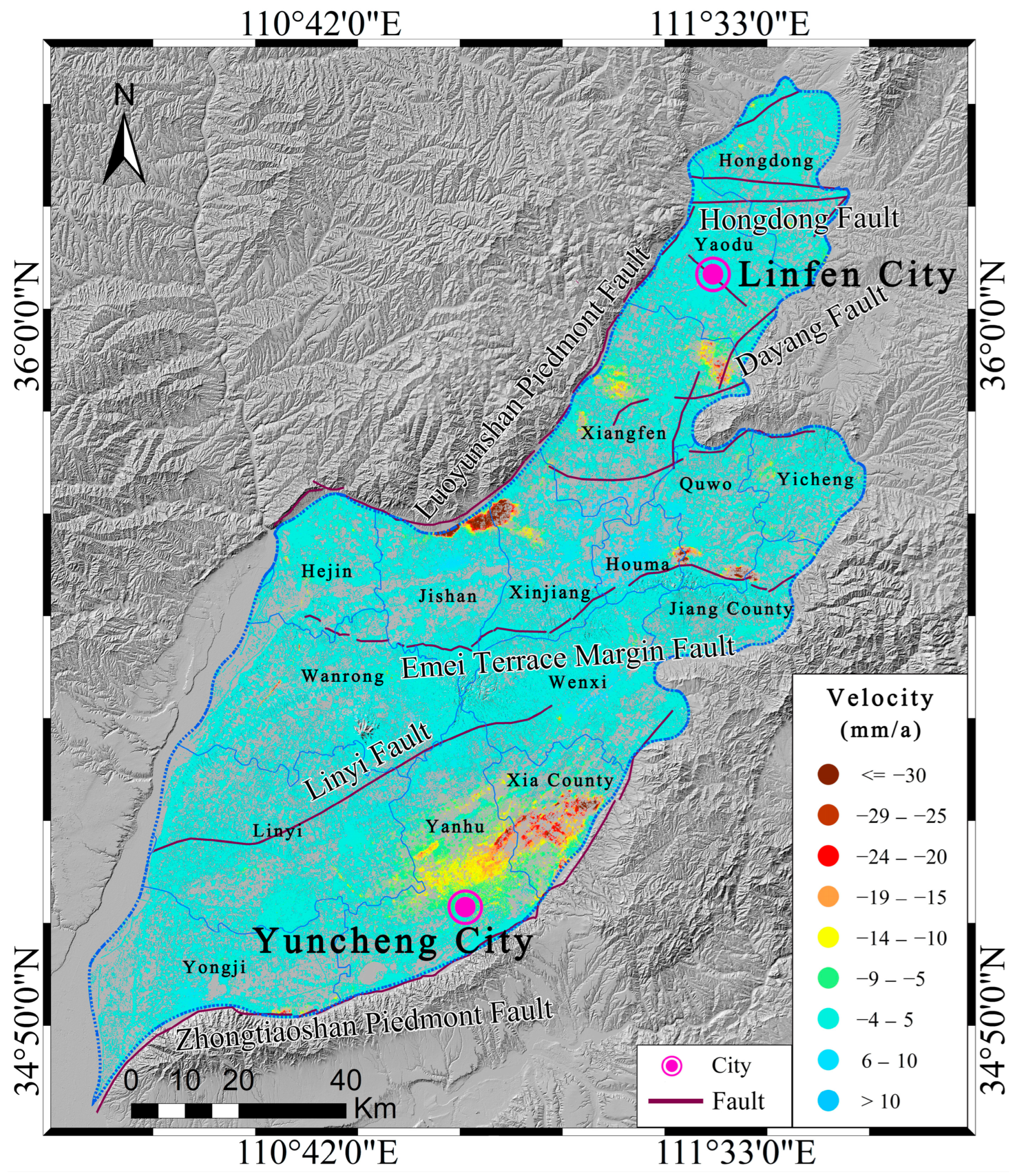
2.1. Study Area
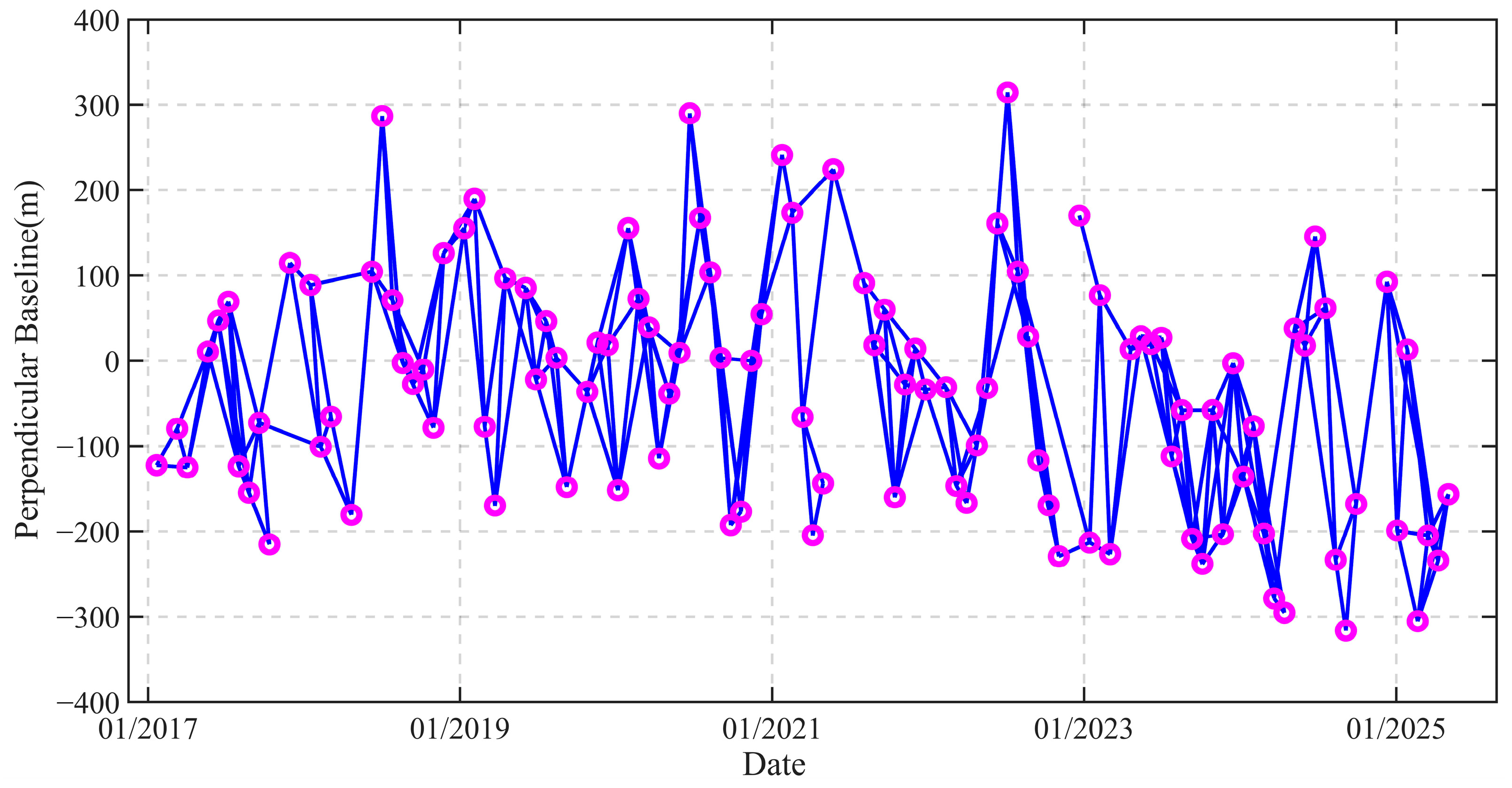
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Time Series InSAR Data Processing
2.3.1. SDFP-StaMPS
2.3.2. Processing Flow
3. Results
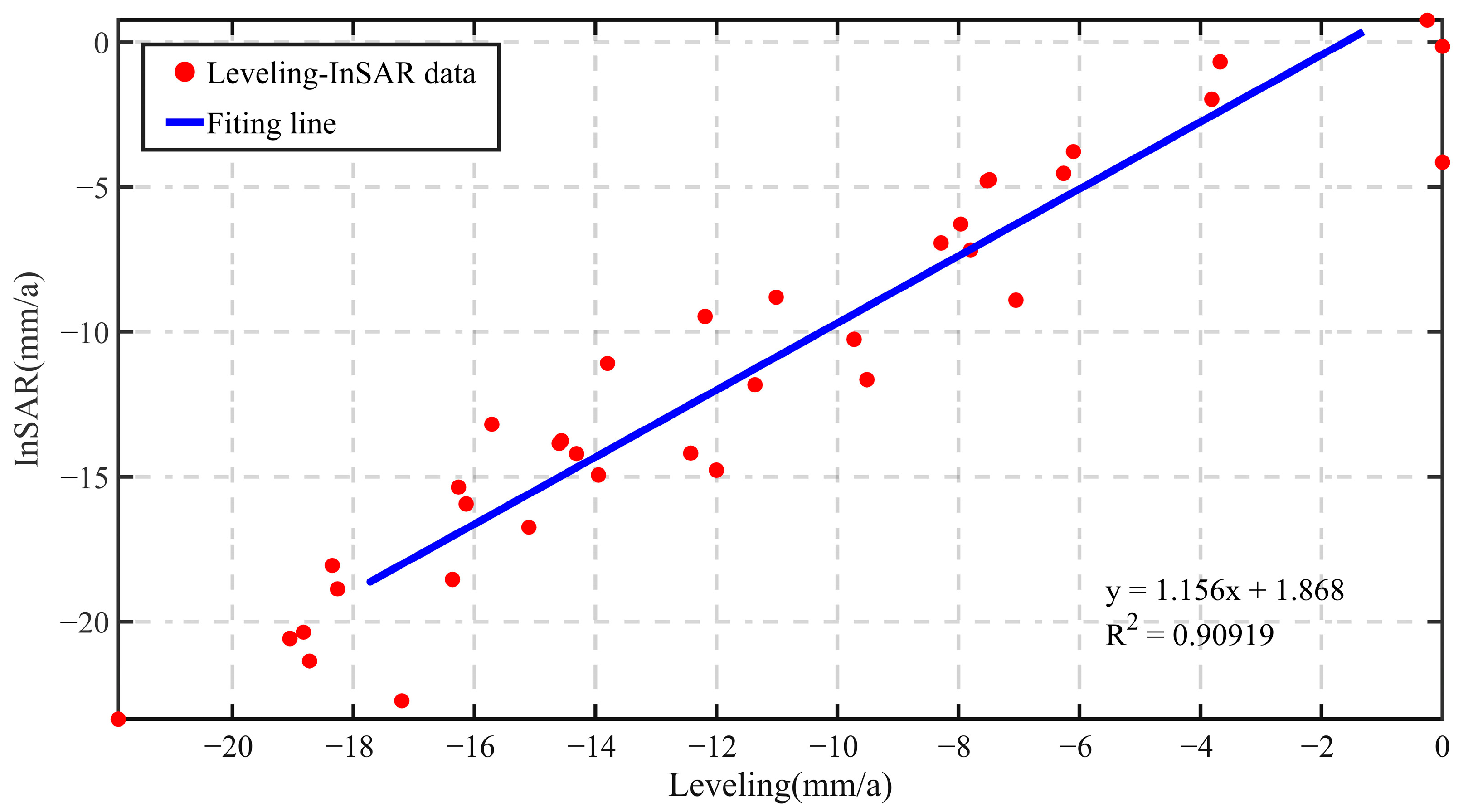
3.1. Precision Validation
3.2. Overall Surface Deformation Characteristics
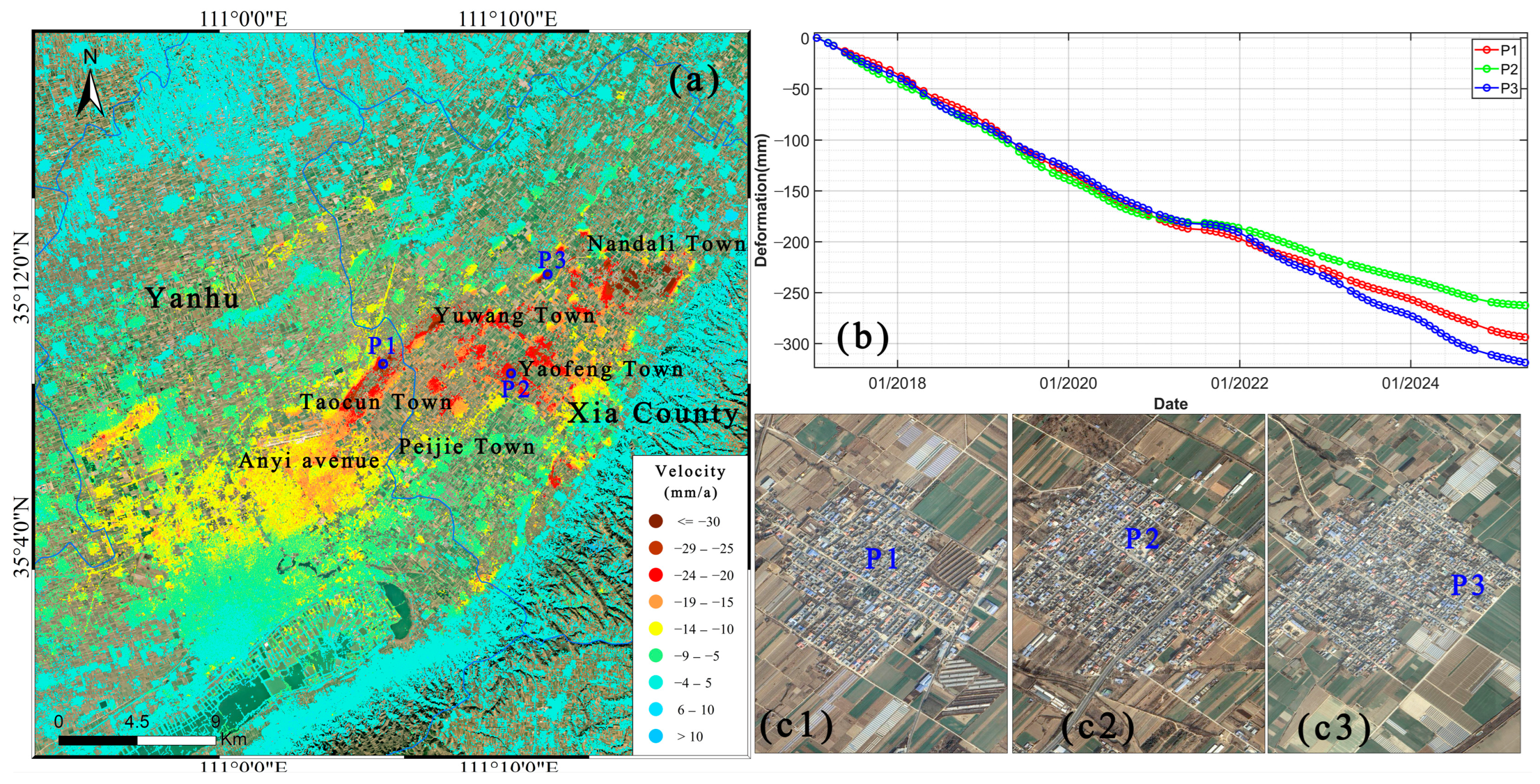
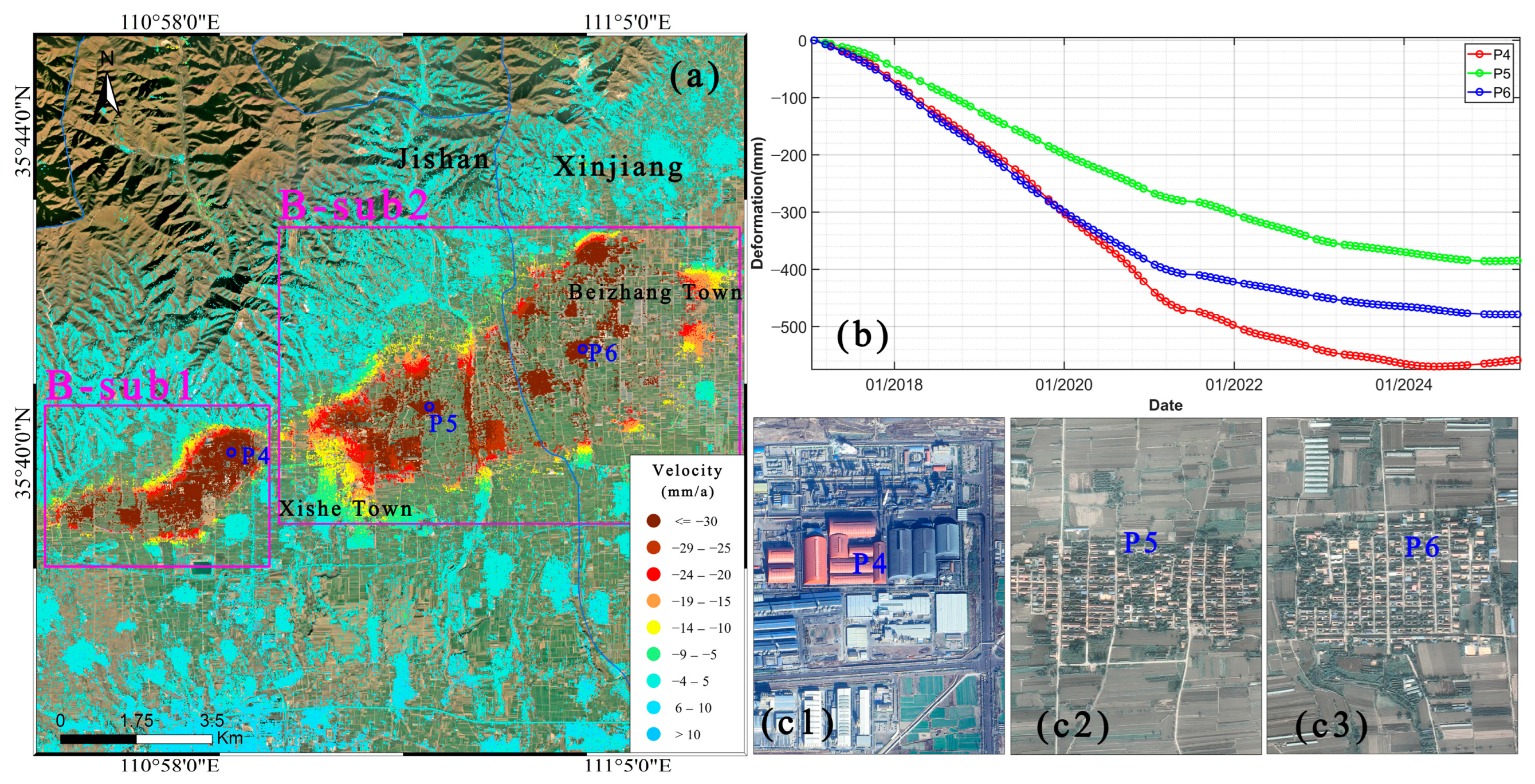
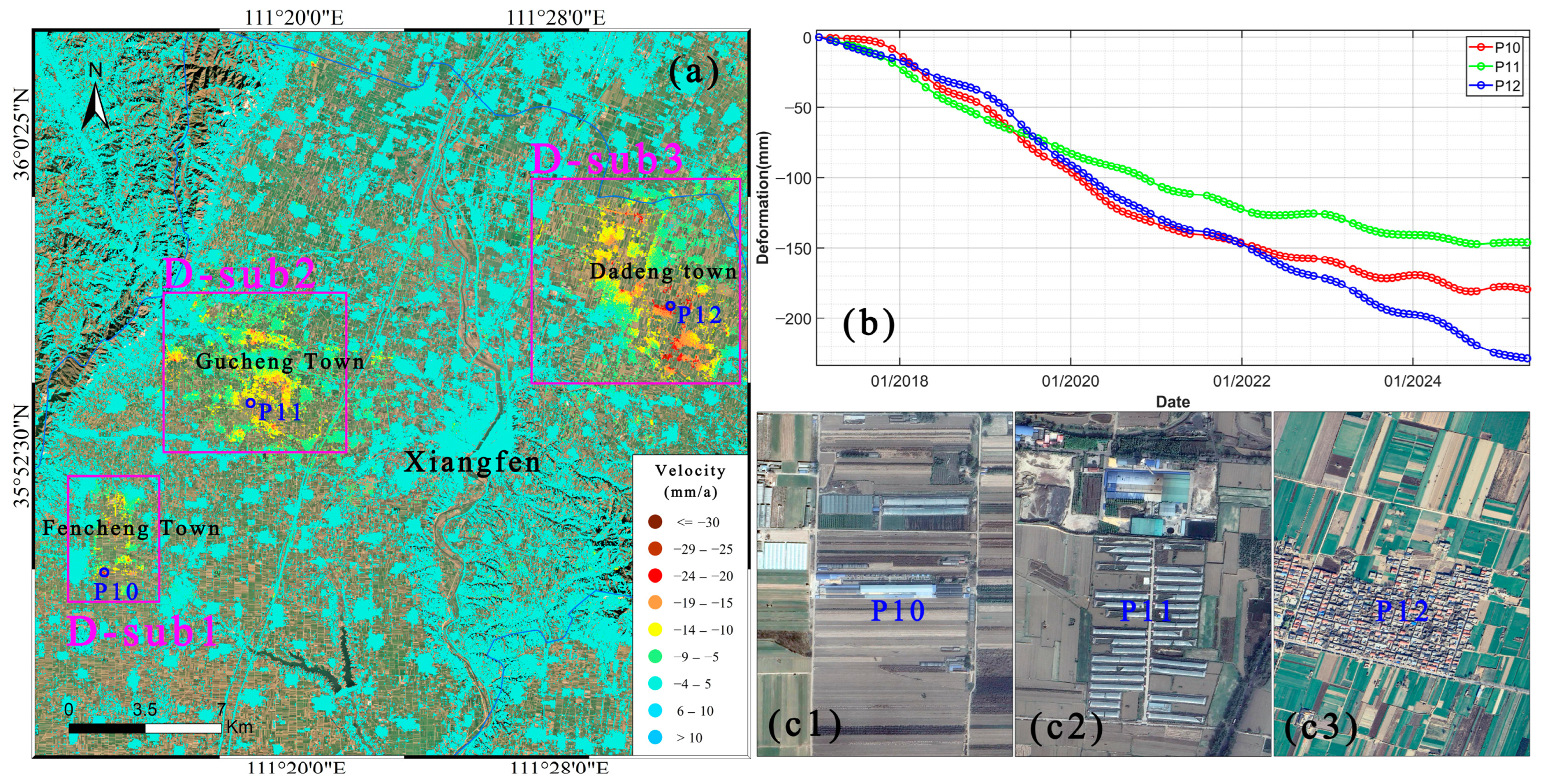
3.3. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Major Subsidence Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Relationship Between Surface Deformation and Ground Water Level Changes
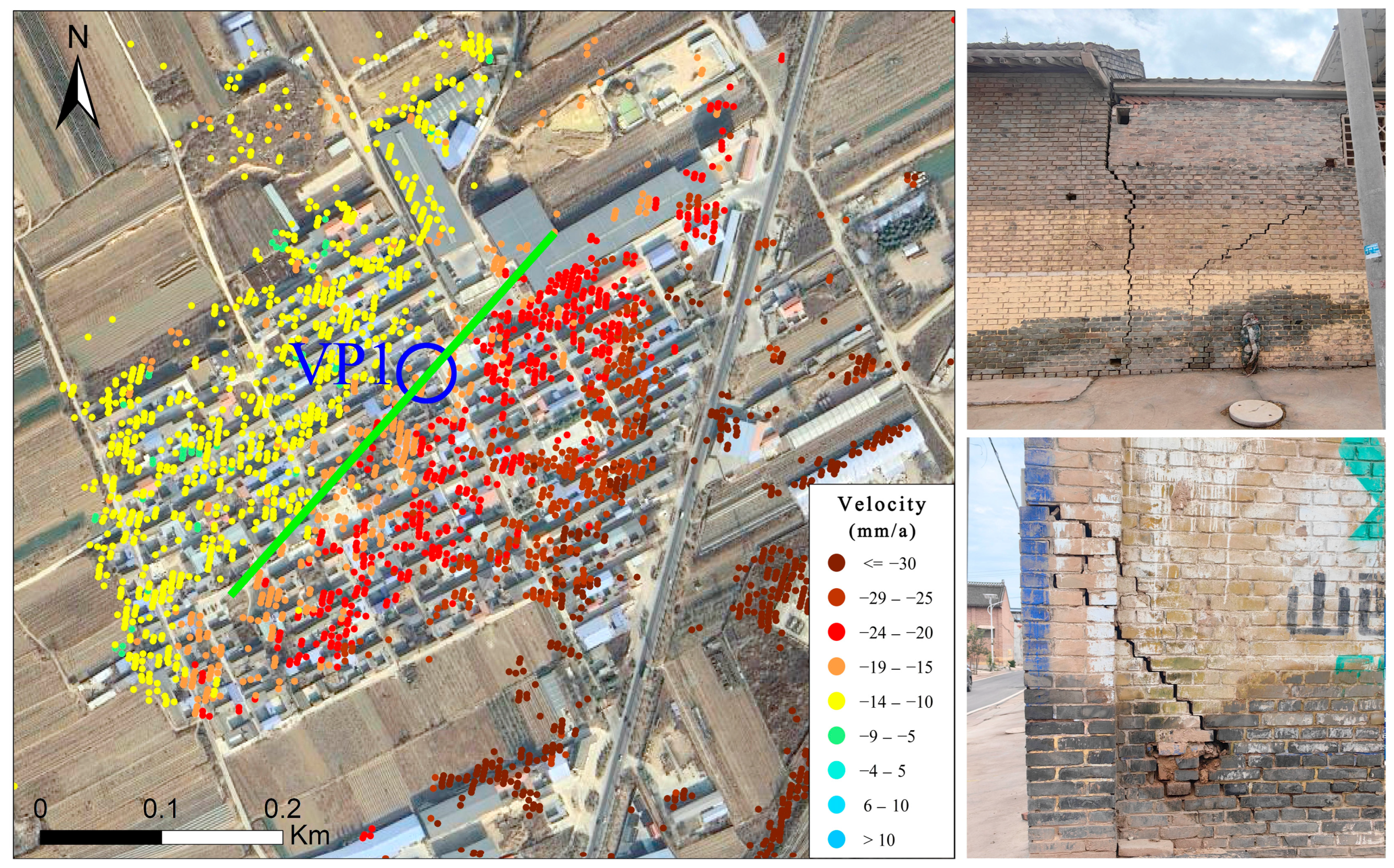
4.2. Analysis of the Relationship Between Surface Deformation and Ground Fissure Activity
4.3. Analysis of the Relationship Between Surface Deformation and Fault Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.L.; Li, D.M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.F.; Wei, K.Y. Segmentation Characteristics of Vertical Deformation of Main Faults in Shanxi Fault Depression Zone. Earthq. Res. China 2023, 39, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M. Division and Comprehensive Management Analysis of Groundwater Overexploitation Areas in Yuncheng City. Ground Water 2009, 31, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X. Current Situation and Protection Measures of Groundwater Overexploitation in Linfen City. Shanxi Hydrotech. 2008, 2, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Z.; Gao, J.X.; He, P.; Nie, Y.H.; Li, D.Q. Assessment on Water Eco-Environment in Mid-Eastern China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2005, 18, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Meng, R.F.; Bao, X.L.; Cao, W.G.; Li, Z.Y.; Xu, B.Y. Assessment of Water Level Threshold for Groundwater Restoration and Over-exploitation Remediation the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; UMUT, H.; Gou, X.H.; Luo, S.Z. Environmental Problems Caused by Excessive Exploitation of Groundwater at Chaiwopu Source in Xinjiang. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 15, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Cheng, W.C. A Review on Land Subsidence Caused by Groundwater Withdrawal in Xi’an, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 78, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, L. Discussion on Geological Hazards Caused by Exploitation of Deep Groundwater in North China. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharnagat, N.; Nema, A.K.; Mishra, P.K.; Patidar, N.; Kumar, R.; Suryawanshi, A.; Radha, L. State-of-the-Art Status of Google Earth Engine (GEE) Application in Land and Water Resource Management: A Scientometric Analysis. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2025, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sajith, V. Surface Displacement Studies Using Differential SAR Interferometry: An Overview. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2006, 6412, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.Q.; Mu, J.Q. D-InSAR Technique for Land Subsidence Monitoring. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Chatterjee, R.; Kumar, D.; Singh, K.; Sengar, V. Advanced Subsidence Monitoring Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry for Jharia Coal Field, Dhanbad, India. Proc. SPIE 2018, 10426, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.H.T.; Hanssen, R.; Rocca, F. Radar Interferometry: 20 Years of Development in Time Series Techniques and Future Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P.; Berardino, P.; Casu, F.; Euillades, P.; Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Zeni, G.; Lanari, R. Surface Deformation of Long Valley Caldera and Mono Basin, California, Investigated with the SBAS-InSAR Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xie, R. Coastal Subsidence Monitoring Associated with Land Reclamation Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, M. Wuhan Surface Subsidence Analysis in 2015-2016 Based on Sentinel-1A Data by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Hu, M.; Chen, S.; Yao, H.; Wang, L.; Xiong, X. Urban Land Subsidence Monitoring and Risk Assessment Using the Point Target Based SBAS-InSAR Method: A Case Study of Changsha City. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greif, V.; Vlcko, J. Monitoring of Post-failure Landslide Deformation by the PS-InSAR Technique at Lubietova in Central Slovakia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W. Monitoring Land Subsidence in the Southern Part of the Lower Liaohe Plain, China with a Multi-track PS-InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, G.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Zhou, C. Assessing Land Subsidence-Inducing Factors in the Shandong Province, China, by Using PS-InSAR Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, J.; Ma, P.F.; Lin, H. Identification and Analysis on Surface Deformation in the Urban Area of Nanchang Based on PS-InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, H.S.; Sun, Y.L.; Hou, J.G.; Liang, J. Long-Term Land Subsidence Monitoring of Beijing (China) Using the Small Baseline Subset (SBAS) Technique. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3648–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Ji, L.Y. Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technology Used in Datong Basin Ground Subsidence, Fissure and Fault Zone Monitoring. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2014, 39, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y. Deformation Monitoring of Ground Fissure with SAR Interferometry in Qingxu, Shanxi Province. J. Eng. Geology. 2011, 19, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, J. Land Subsidence and Ground Fissures in Xi’an, China 2005-2012 Revealed by Multi-band InSAR Time-Series Analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Qu, F.; Liu, Y. Different Scale Land Subsidence and Ground Fissure Monitoring with Multiple InSAR Techniques over Fenwei Basin, China. PIAHS 2015, 372, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Peng, J.B.; Ji, L.Y. Complex Deformation Monitoring over the Linfen–Yuncheng Basin (China) with Time Series InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Yang, C.S. Deformation of Linfen–Yuncheng Basin (China) and Its Mechanisms Revealed by Π-RATE InSAR Technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F. InSAR Monitoring and Mechanism Analysis of Ground Fissure Activity in Yuncheng Basin. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Chang’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Q.H.; Zeng, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, Z.F.; He, P. Enrichment Elements and Reservoir Conditions of Helium Gas in Linfen Yuncheng Basin. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 56, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.H. New Structural Pattern and Seismic Activity in Linfen Basin. Earthq. Res. Shanxi. 1988, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G. Research on the Cenozoic Sedimentary Tectonic Evolution in Yuncheng Basin. Shanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Chang’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.L. Oil and Gas Resources Status Investigation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin. Ground Water 2016, 2, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; He, X.Q. The Current Situation of Ground Subsidence and Fault Prevention in Shanxi Province. Shanxi Archit. 2013, 12, 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.B.; Sun, X.H.; Lu, Q.Z.; Meng, L.; Wang, F. Characteristics and Mechanisms for Origin of Earth Fissures in Fenwei Basin. China Eng. Geol. 2019, 266, 105445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.S. Correlation Analysis of Groundwater Exploitation and Land Subsidence in Yuncheng Basin. Shanxi Archit. 2017, 23, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S.; Zhuang, H.D.; Tang, D.Q.; Li, Z.C. Characteristic and Mechanism Analysis of Ground Fissures in Yuncheng Basin. J. Geol. Hazards Environ. Preserv. 2010, 2, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A New Method for Measuring Deformation on Volcanoes and Other Natural Terrains Using InSAR Persistent Scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 23, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.; Hooper, A.; Hanssen, R.; Bastos, L.; Ruiz, A. Persistent Scatterer InSAR: A Comparison of Methodologies Based on a Model of Temporal Deformation Vs. Spatial Correlation Selection Criteria. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Han, J.; Hao, T.; Li, R.; Qiao, G. Seasonal Deformation of Permafrost in Wudaoliang Basin in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Revealed by StaMPS-InSAR. Mar. Geod. 2019, 43, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar for Crustal Deformation Analysis, with Application to Volcán Alcedo, Galápagos. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2007, 112, B07407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gan, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Segoni, S.; Shi, X.; Motagh, M.; Singh, R. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment of the Wanzhou District: Merging Landslide Susceptibility Modelling (LSM) with InSAR-derived Ground Deformation Map. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, S.K.P.; Kim, D.J.; Jung, K. Monitoring the Vertical Land Motion of Tide Gauges and Its Impact on Relative Sea Level Changes in Korean Peninsula Using Sequential SBAS-InSAR Time-Series Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C. Nonlinear Subsidence Rate Estimation Using Permanent Scatterers in Differential SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Lu, Z.; Du, J.; Sun, Z.H.; Sun, G.T. Ground Deformation Monitoring Using Small Baseline DInSAR Technique: A Case Study in Taiyuan City from 2003 to 2009. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.Y.; Qu, F.F.; Zhang, J.Q. A Novel Method of Generating Deformation Time-Series Using Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar and Its Application in Mexico City. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, D.H.; Wang, Z. Several Opinions on Developing Agriculture through Groundwater Extraction in Northern China. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2007, 3, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.R. Evolution Characteristics and Mechanism of Flow Field in Groundwater Overexploitation Area in Yuncheng Basin. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Agricultural University, Shanxi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.S.; Li, W.Q.; Xu, Y.R.; Yan, X.B. Distribution Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of Mingtiaogang Fractures in Yuncheng Basin. Earthquake 2023, 43, 50–66. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.W.; Peng, J.B.; Deng, Y.H.; Wen, H.G.; Zang, M.D. The Study on Basic Characteristic of Earth Fissure in Linfen Basin. J. Eng. Geol. 2015, 23, 0856–0865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L. Thoughts on Water Resources Management in Linfen Area, Shanxi Province. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 9, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.P.; Li, Y.L.; Lv, S.H.; Wang, Y.R. Holocene slip rate and Paleoearthquake Records of the Salt Lake Segment of the Northern Zhongtiaoshan Fault, Shanxi Province. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Satellite/Mode | RADARSAT-2/Extra Fine |
|---|---|
| Band | 5.6 cm (C-band) |
| Flight direction | Descending |
| Resolution | 5 m |
| Incidence angle | 28.79° |
| Monitoring period | January 2017–May 2025 |
| Polarization | VV |
| Number of Images | 224 |
| NO. | Leveling | InSAR | NO. | Leveling | InSAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | −0.2 | 20 | −16.3 | −15.4 |
| 2 | −14.0 | −14.9 | 21 | −13.8 | −11.1 |
| 3 | −12.2 | −9.5 | 22 | −11.4 | −11.8 |
| 4 | −14.3 | −14.2 | 23 | −11.0 | −8.8 |
| 5 | −19.1 | −20.6 | 24 | −9.7 | −10.3 |
| 6 | −21.9 | −23.4 | 25 | −9.5 | −11.6 |
| 7 | −14.6 | −13.9 | 26 | −3.8 | −2.0 |
| 8 | −12.4 | −14.2 | 27 | −7.5 | −4.8 |
| 9 | −16.4 | −18.5 | 28 | −8.0 | −6.3 |
| 10 | −18.3 | −18.9 | 29 | −8.3 | −6.9 |
| 11 | −18.4 | −18.1 | 30 | −7.8 | −7.2 |
| 12 | −14.6 | −13.8 | 31 | −7.1 | −8.9 |
| 13 | −18.8 | −20.4 | 32 | −7.5 | −4.7 |
| 14 | −17.2 | −22.7 | 33 | −6.3 | −4.5 |
| 15 | −16.1 | −15.9 | 34 | −6.1 | −3.8 |
| 16 | −18.7 | −21.4 | 35 | −0.3 | 0.8 |
| 17 | −15.7 | −13.2 | 36 | −3.7 | −0.7 |
| 18 | −15.1 | −16.7 | 37 | 0.0 | −4.2 |
| 19 | −12.0 | −14.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. High-Resolution Monitoring and Driving Factor Analysis of Long-Term Surface Deformation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213536
Wu Y, Chen L, Jiang T, Xu Y, Li Y, Jiang Z. High-Resolution Monitoring and Driving Factor Analysis of Long-Term Surface Deformation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(21):3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213536
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuting, Longyong Chen, Tao Jiang, Yihao Xu, Yan Li, and Zhe Jiang. 2025. "High-Resolution Monitoring and Driving Factor Analysis of Long-Term Surface Deformation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin" Remote Sensing 17, no. 21: 3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213536
APA StyleWu, Y., Chen, L., Jiang, T., Xu, Y., Li, Y., & Jiang, Z. (2025). High-Resolution Monitoring and Driving Factor Analysis of Long-Term Surface Deformation in the Linfen-Yuncheng Basin. Remote Sensing, 17(21), 3536. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17213536






